Anti-aliasing filter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An anti-aliasing filter (AAF) is a
 In the case of
In the case of
filter
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
used before a signal sampler to restrict the bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
of a signal
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing' ...
to satisfy the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem
The Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem is a theorem in the field of signal processing which serves as a fundamental bridge between continuous-time signals and discrete-time signals. It establishes a sufficient condition for a sample rate that per ...
over the band of interest. Since the theorem states that unambiguous reconstruction of the signal from its samples is possible when the power of frequencies above the Nyquist frequency
In signal processing, the Nyquist frequency (or folding frequency), named after Harry Nyquist, is a characteristic of a sampler, which converts a continuous function or signal into a discrete sequence. In units of cycles per second ( Hz), it ...
is zero, a brick wall filter
In signal processing, a sinc filter is an idealized filter that removes all frequency components above a given cutoff frequency, without affecting lower frequencies, and has linear phase response. The filter's impulse response is a sinc functi ...
is an idealized but impractical AAF. A practical AAF makes a trade off between reduced bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
and increased aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing is an effect that causes different signals to become indistinguishable (or ''aliases'' of one another) when sampled. It also often refers to the distortion or artifact that results when ...
. A practical anti-aliasing filter will typically permit some aliasing to occur or attenuate or otherwise distort some in-band frequencies close to the Nyquist limit. For this reason, many practical systems sample higher than would be theoretically required by a perfect AAF in order to ensure that all frequencies of interest can be reconstructed, a practice called oversampling
In signal processing, oversampling is the process of sampling a signal at a sampling frequency significantly higher than the Nyquist rate. Theoretically, a bandwidth-limited signal can be perfectly reconstructed if sampled at the Nyquist rate o ...
.
Optical applications
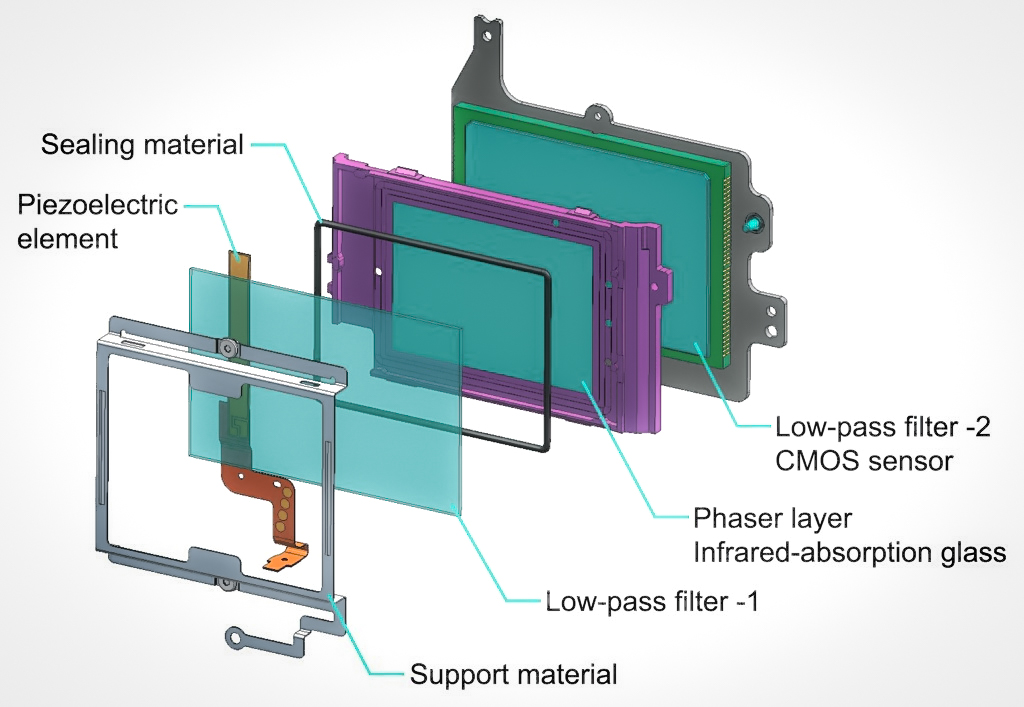
ThePentax K-3
The Pentax K-3 is a 24-megapixel Pentax
is a brand name used primarily by the Japanese multinational imaging and electronics company Ricoh for DSLR cameras, lenses, sport optics (including binoculars and rifle scopes), and CCTV optics. The P ...
from Ricoh introduced a unique sensor-based anti-aliasing filter. The filter works by micro vibrating the sensor element. The user can turn the vibration on or off, selecting anti-aliasing or no anti-aliasing.
 In the case of
In the case of optical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
image sampling, as by image sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of c ...
s in digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices ...
s, the anti-aliasing filter is also known as an optical low-pass filter (OLPF), blur filter, or AA filter. The mathematics of sampling in two spatial dimensions is similar to the mathematics of time-domain
Time domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental data, with respect to time. In the time domain, the signal or function's value is known for all real numbers, for the ca ...
sampling, but the filter implementation technologies are different.
The typical implementation in digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices ...
s is two layers of birefringent
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefring ...
material such as lithium niobate
Lithium niobate () is a non-naturally-occurring salt consisting of niobium, lithium, and oxygen. Its single crystals are an important material for optical waveguides, mobile phones, piezoelectric sensors, optical modulators and various other linea ...
, which spreads each optical point into a cluster of four points. The choice of spot separation for such a filter involves a tradeoff among sharpness, aliasing, and fill factor (the ratio of the active refracting area of a microlens array
A microlens is a small lens, generally with a diameter less than a millimetre (mm) and often as small as 10 micrometres (µm). The small sizes of the lenses means that a simple design can give good optical quality but sometimes unwanted effects ...
to the total contiguous area occupied by the array). In a monochrome
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, monochrom ...
or three-CCD
A three-CCD (3CCD) camera is a camera whose imaging system uses three separate charge-coupled devices (CCDs), each one receiving filtered red, green, or blue color ranges. Light coming in from the lens is split by a beam-splitter prism into th ...
or Foveon X3
The Foveon X3 sensor is a digital camera image sensor designed by Foveon, Inc., (now part of Sigma Corporation) and manufactured by Dongbu Electronics.
It uses an array of photosites that consist of three vertically stacked photodiodes. Each o ...
camera, the microlens array alone, if near 100% effective, can provide a significant anti-aliasing function,
while in color filter array (e.g. Bayer filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digital cameras, cam ...
) cameras, an additional filter is generally needed to reduce aliasing to an acceptable level.
Audio applications
Anti-aliasing filters are used at the input of ananalog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide ...
. Similar filters are used as reconstruction filter
In a mixed-signal system ( analog and digital), a reconstruction filter, sometimes called an anti-imaging filter, is used to construct a smooth analog signal from a digital input, as in the case of a digital to analog converter ( DAC) or other samp ...
s at the output of a digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC, D/A, D2A, or D-to-A) is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
There are several DAC archit ...
. In the latter case, the filter prevents imaging, the reverse process of aliasing where in-band frequencies are mirrored out of band.
Oversampling
Withoversampling
In signal processing, oversampling is the process of sampling a signal at a sampling frequency significantly higher than the Nyquist rate. Theoretically, a bandwidth-limited signal can be perfectly reconstructed if sampled at the Nyquist rate o ...
, a higher intermediate digital sample rate is used, so that a nearly ideal digital filter
In signal processing, a digital filter is a system that performs mathematical operations on a sampled, discrete-time signal to reduce or enhance certain aspects of that signal. This is in contrast to the other major type of electronic filter, t ...
can sharply cut off aliasing near the original low Nyquist frequency
In signal processing, the Nyquist frequency (or folding frequency), named after Harry Nyquist, is a characteristic of a sampler, which converts a continuous function or signal into a discrete sequence. In units of cycles per second ( Hz), it ...
and give better phase response
In signal processing, phase response is the relationship between the phase of a sinusoidal input and the output signal passing through any device that accepts input and produces an output signal, such as an amplifier or a filter.
Amplifiers, f ...
, while a much simpler analog filter
Analogue filters are a basic building block of signal processing much used in electronics. Amongst their many applications are the separation of an audio signal before application to bass, mid-range, and tweeter loudspeakers; the combining and ...
can stop frequencies above the new higher Nyquist frequency. Because analog filters have relatively high cost and limited performance, relaxing the demands on the analog filter can greatly reduce both aliasing and cost. Furthermore, because some noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference aris ...
is averaged out, the higher sampling rate can moderately improve signal-to-noise ratio.
Alternatively, a signal may be intentionally sampled at a higher rate to reduce the requirements on the anti-alias filter. For example, CD audio typically extends up to 20 kHz, but is sampled with a 22.05 kHz Nyquist rate. By sampling at a rate 2.05 kHz higher than the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem
The Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem is a theorem in the field of signal processing which serves as a fundamental bridge between continuous-time signals and discrete-time signals. It establishes a sufficient condition for a sample rate that per ...
calls for, both aliasing and attenuation of higher audio frequencies can be prevented even with less than ideal filters.
Bandpass signals
Often, an anti-aliasing filter is alow-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
; this is not a requirement, however. Generalizations of the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem allow sampling of other band-limited passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter. For example, a radio receiver contains a bandpass filter to select the frequency of the desired radio signal out of all the radio waves picked up by its antenn ...
signals instead of baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable int ...
signals.
For signals that are bandwidth limited, but not centered at zero, a band-pass filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects (attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
Description
In electronics and signal processing, a filter is usually a two-port ...
can be used as an anti-aliasing filter. For example, this could be done with a single-sideband modulated or frequency modulated
Frequency modulation (FM) is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and computing.
In analog freq ...
signal. If one desired to sample an FM radio broadcast centered at 87.9 MHz and bandlimited to a 200 kHz band, then an appropriate anti-alias filter would be centered on 87.9 MHz with 200 kHz bandwidth (or passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter. For example, a radio receiver contains a bandpass filter to select the frequency of the desired radio signal out of all the radio waves picked up by its antenn ...
of 87.8 MHz to 88.0 MHz), and the sampling rate would be no less than 400 kHz, but should also satisfy other constraints to prevent aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing is an effect that causes different signals to become indistinguishable (or ''aliases'' of one another) when sampled. It also often refers to the distortion or artifact that results when ...
.
Signal overload
It is very important to avoid input signal overload when using an anti-aliasing filter. If the signal is strong enough, it can causeclipping
Clipping may refer to:
Words
* Clipping (morphology), the formation of a new word by shortening it, e.g. "ad" from "advertisement"
* Clipping (phonetics), shortening the articulation of a speech sound, usually a vowel
* Clipping (publications) ...
at the analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide ...
, even after filtering. When distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signa ...
due to clipping occurs after the anti-aliasing filter, it can create components outside the passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter. For example, a radio receiver contains a bandpass filter to select the frequency of the desired radio signal out of all the radio waves picked up by its antenn ...
of the anti-aliasing filter; these components can then alias, causing the reproduction of other non- harmonically related frequencies.
Notes
References
{{DSP Digital signal processing Linear filters Electronic filter applications Anti-aliasing