amphibious assault vehicle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Assault Amphibious Vehicle (AAV)—official designation AAVP-7A1 (formerly known as Landing Vehicle, Tracked, Personnel-7 abbr. LVTP-7)—is a fully tracked amphibious landing vehicle manufactured by U.S. Combat Systems (previously by
 The LVTP-7 was first introduced in 1972 as a replacement for the
The LVTP-7 was first introduced in 1972 as a replacement for the
- MarineCorpstimes.com, 29 January 2016Marines’ Upgraded AAVs Begin Delivering, Will Comprise One-Third of Lift Need In 2020s
- News.USNI.org, 23 March 2016 The AAV SU program was intended to upgrade 392 out of the some 1,000-vehicle fleet to keep them operational through 2035 as the ACV gradually entered service. However, in August 2018 the Marine Corps terminated the AAV upgrade program, instead opting for increased procurement of the ACV.
 Twenty U.S.-built LVTP-7s were used by
Twenty U.S.-built LVTP-7s were used by
''Defense News''. 19 June 2018.Marines Pick BAE to Build Amphibious Combat Vehicle; Contract Worth Up to $1.2B
. ''USNI News''. 19 June 2018.
 * LVTP-7: Original series introduced from 1972. Originally armed with a M85 12.7 mm (.50cal) machine gun.
* LVTP-7A1: 1982 upgraded. Renamed to AAVP-7A1 from 1984.
** AAVP-7A1 (Personnel): This is the most common AAV, as it carries a turret equipped with an M2HB 12.7 mm (.50 caliber) heavy machine gun, and a Mk19 40 mm automatic grenade launcher. It carries four crew radios as well as the AN/VIC-2 intercom system. It is capable of carrying 21 combat equipped Marines in addition to the crew of 4: driver, crew chief/vehicle commander, gunner, and rear crewman.
** AAVC-7A1 (Command): This vehicle does not have a turret, and much of the cargo space of the vehicle is occupied by communications equipment. This version only has two crew radios, and in addition to the VIC-2, it also carries two VRC-92s, a VRC-89, a PRC-103 UHF radio, a MRC-83 HF radio and the MSQ internetworking system used to control the various radios. This AAV has a crew of 3, and additionally carries 5 radio operators, 3 staff members, and 2 commanding officers. Recently, the C7 has been upgraded to use Harris Falcon II class radios, specifically the PRC-117 for VHF/UHF/SATCOM, and the PRC-150 for HF.
** AAVR-7A1 (Recovery): This vehicle also does not have a turret. The R7 is considered the "wrecker", as it has a crane as well as most tools and equipment needed for field repairs. It is by far the heaviest of the three, and sits considerably lower in the water. Crew of three, plus the repairmen.
Many P7s have been modified to carry the Mk 154 MCLC, or Mine Clearance Line Charge. The MCLC kit can fire three linear demolition charges to breach a lane through a minefield. MCLCs were used in the 1991
* LVTP-7: Original series introduced from 1972. Originally armed with a M85 12.7 mm (.50cal) machine gun.
* LVTP-7A1: 1982 upgraded. Renamed to AAVP-7A1 from 1984.
** AAVP-7A1 (Personnel): This is the most common AAV, as it carries a turret equipped with an M2HB 12.7 mm (.50 caliber) heavy machine gun, and a Mk19 40 mm automatic grenade launcher. It carries four crew radios as well as the AN/VIC-2 intercom system. It is capable of carrying 21 combat equipped Marines in addition to the crew of 4: driver, crew chief/vehicle commander, gunner, and rear crewman.
** AAVC-7A1 (Command): This vehicle does not have a turret, and much of the cargo space of the vehicle is occupied by communications equipment. This version only has two crew radios, and in addition to the VIC-2, it also carries two VRC-92s, a VRC-89, a PRC-103 UHF radio, a MRC-83 HF radio and the MSQ internetworking system used to control the various radios. This AAV has a crew of 3, and additionally carries 5 radio operators, 3 staff members, and 2 commanding officers. Recently, the C7 has been upgraded to use Harris Falcon II class radios, specifically the PRC-117 for VHF/UHF/SATCOM, and the PRC-150 for HF.
** AAVR-7A1 (Recovery): This vehicle also does not have a turret. The R7 is considered the "wrecker", as it has a crane as well as most tools and equipment needed for field repairs. It is by far the heaviest of the three, and sits considerably lower in the water. Crew of three, plus the repairmen.
Many P7s have been modified to carry the Mk 154 MCLC, or Mine Clearance Line Charge. The MCLC kit can fire three linear demolition charges to breach a lane through a minefield. MCLCs were used in the 1991
File:Early prototype of the AAV Turret Trainer.jpg, Early pre-production prototype of the AAV TT
File:AAVs preparing to debark USS Gunston Hall (LSD 44).jpg,
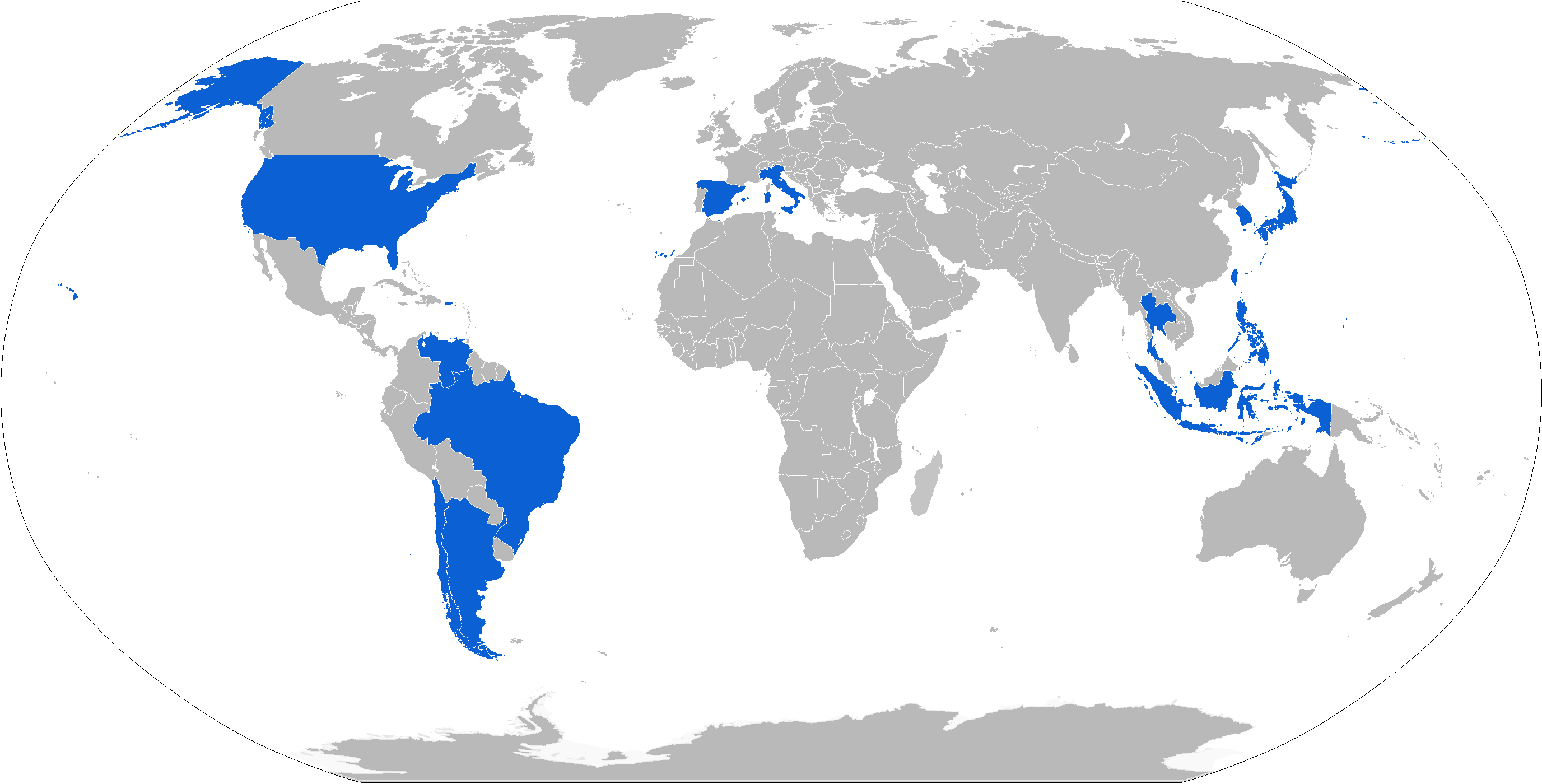
 * : Naval Infantry Command originally received 21 vehicles (19 LVTP-7, 1 LVTP-7 and 1 LVTR-7), 11 of them (9 LVTP-7, 1 LVTC-7 and 1 LVTR-7) were upgraded locally by MECATROL with Caterpillar C7 diesel engines and minor changes to running gear and other components
* : Brazilian Marine Corps has 49
* : 76 will be procured for use with the Hellenic Marine Corps of the Hellenic Navy
* : 15 in service with the
* : Naval Infantry Command originally received 21 vehicles (19 LVTP-7, 1 LVTP-7 and 1 LVTR-7), 11 of them (9 LVTP-7, 1 LVTC-7 and 1 LVTR-7) were upgraded locally by MECATROL with Caterpillar C7 diesel engines and minor changes to running gear and other components
* : Brazilian Marine Corps has 49
* : 76 will be procured for use with the Hellenic Marine Corps of the Hellenic Navy
* : 15 in service with the
FAS AAV article
AAV Fact File at the official USMC website
Paper regarding high energy lasers and the MTU
AAV 7A1 on Armour.ws
USMC Amtrac Association Website
{{Authority control Tracked amphibious vehicles Vehicles introduced in 1972 Armoured personnel carriers of South Korea Armoured personnel carriers of Japan Armored personnel carriers of the United States Amphibious armoured personnel carriers FMC Corporation Military vehicles introduced in the 1970s
United Defense
United Defense Industries (UDI) was an American defense contractor which became part of BAE Systems Land & Armaments after being acquired by BAE Systems in 2005. The company produced combat vehicles, artillery, naval guns, missile launchers an ...
, a former division of FMC Corporation
FMC Corporation is an American chemical manufacturing company headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, which originated as an insecticide producer in 1883 and later diversified into other industries. In 1941 at the beginning of US involvemen ...
).
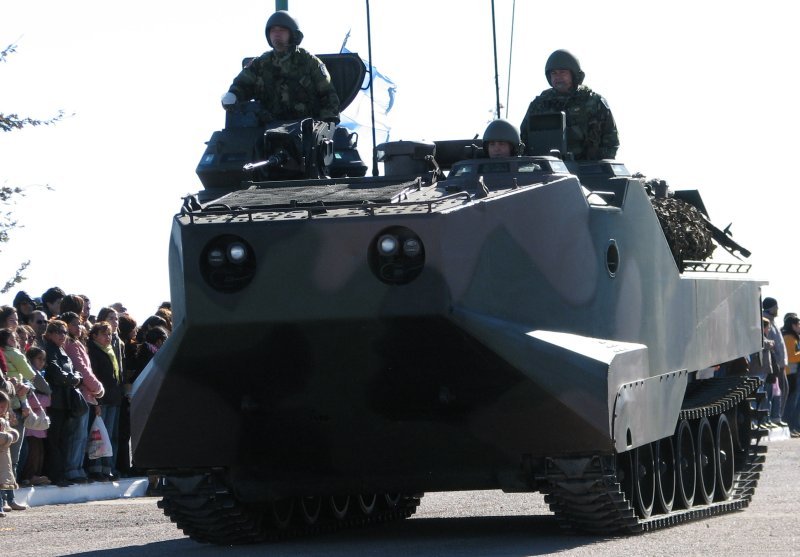
The AAV-P7/A1 is the current amphibious troop transport of the United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combi ...
. It is used by U.S. Marine Corps Amphibious Assault Battalions to land the surface assault elements of the landing force and their equipment in a single lift from assault shipping during amphibious operations to inland objectives and to conduct mechanized operations and related combat support in subsequent mechanized operations ashore. It is also operated by other forces. Marines call them "amtracs", a shortening of their original designation, "amphibious tractor".
In June 2018, the Marine Corps announced they had selected the BAE Systems/ Iveco wheeled SuperAV for the Amphibious Combat Vehicle
The Amphibious Combat Vehicle (ACV) is a program initiated by Marine Corps Systems Command to procure an amphibious assault vehicle for the United States Marine Corps to supplement and ultimately replace the aging Assault Amphibious Vehicle (AA ...
(ACV) program to supplement and ultimately replace the AAV.
History
Development
 The LVTP-7 was first introduced in 1972 as a replacement for the
The LVTP-7 was first introduced in 1972 as a replacement for the LVTP-5
The LVTP-5 (landing vehicle, tracked, personnel 5) is a family of amphibious armored fighting vehicles used by the Philippine Marine Corps and, formerly, the United States Marine Corps. It was designed by the BorgWarner company and built by FMC ( ...
. In 1982, FMC was contracted to conduct the LVTP-7 Service Life Extension Program (SLEP), which converted the LVT-7 vehicles to the improved AAV-7A1 vehicle by adding an improved engine, transmission, and weapons system and improving the overall maintainability of the vehicle. The Cummins VT400 diesel engine replaced the GM 8V53T, and this was driven through FMC's HS-400-3A1 transmission. The hydraulic traverse and elevation of the weapon station was replaced by electric motors, which eliminated the danger from hydraulic fluid fires. The suspension and shock absorbers were strengthened as well. The fuel tank was made safer, and a fuel-burning smoke generator system was added. Eight smoke grenade launchers were also placed around the armament station. The headlight clusters were housed in a square recess instead of the earlier round type. The driver was provided with an improved instrument panel and a night vision device, and a new ventilation system was installed. These upgraded vehicles were originally called LVT-7A1, but the Marine Corps renamed the LVTP-7A1 to AAV-7A1 in 1984.
Another improvement was added starting in 1987 in the form of a Cadillac Gage weapon station or Up-Gunned Weapon Station (UGWS) which was armed with both a .50 cal (12.7 mm) M2HB machine gun and a Mk-19 40 mm grenade launcher.
Enhanced Applique Armor Kits (EAAK) were developed for the AAV-7A1 in 1989 and fitted by 1993, and the added weight of the new armor necessitated the addition of a bow plane kit when operating afloat.
The Assault Amphibious Vehicle Reliability, Availability, Maintainability/Rebuild to Standard (AAV RAM/RS) Program was approved in 1997. It encompassed all AAV systems and components to return the AAV to the original vehicle's performance specifications and ensure acceptable readiness until the EFV should become operational. The program replaced both the AAV engine and suspension with US Army M2 Bradley
The M2 Bradley, or Bradley IFV, is an American infantry fighting vehicle that is a member of the Bradley Fighting Vehicle family. It is manufactured by BAE Systems Land & Armaments, which was formerly United Defense.
The Bradley is designed ...
Fighting Vehicle (BFV) components modified for the AAV. Ground clearance returned to and the horsepower to ton ratio increased from 13 to 1 to its original 17 to 1. The introduction of the BFV components and the rebuild to standard effort was expected to reduce maintenance costs for the expected remaining life of the AAV through the year 2013.
In March 2015, SAIC was awarded a contract to perform an AAV Survivability Upgrade (SU). Marine Corps and SAIC officials unveiled the AAV SU prototype in January 2016, with survivability enhancements including replacing the angled EAAK with 49 advanced buoyant ceramic armor panels, a bonded spall liner, armor-protected external fuel tanks, an aluminum armor underbelly providing Mine Resistant Ambush Protected (MRAP
Mine-Resistant Ambush Protected (MRAP; ) is a term for United States Armed Forces, United States military light tactical vehicles produced as part of the MRAP program that are designed specifically to withstand improvised explosive device (IE ...
)-equivalent blast protection, and blast mitigating seats as well as a more powerful engine, new suspension system, and increased reserve buoyancy.Marines' aging amphibious vehicle fleet to get better armor, more power- MarineCorpstimes.com, 29 January 2016Marines’ Upgraded AAVs Begin Delivering, Will Comprise One-Third of Lift Need In 2020s
- News.USNI.org, 23 March 2016 The AAV SU program was intended to upgrade 392 out of the some 1,000-vehicle fleet to keep them operational through 2035 as the ACV gradually entered service. However, in August 2018 the Marine Corps terminated the AAV upgrade program, instead opting for increased procurement of the ACV.
Combat history
 Twenty U.S.-built LVTP-7s were used by
Twenty U.S.-built LVTP-7s were used by Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
during the 1982 invasion of the Falkland Islands
The Invasion of the Falkland Islands ( es, Invasión de las Islas Malvinas), code-named Operation Rosario (), was a military operation launched by Argentine forces on 2 April 1982, to capture the Falkland Islands, and served as a catalyst for ...
with most returning to the Argentine mainland before the war ended.
From 1982 to 1984, LVTP-7s were deployed with U.S. Marines as part of the multi-national peacekeeping force in Beirut, Lebanon. As Marines became increasingly involved in hostilities, several vehicles sustained minor damage from shrapnel and small arms fire.
On October 25, 1983 U.S. Marine LVTP-7s conducted a highly successful amphibious landing on the island of Grenada as part of Operation Urgent Fury.
It was heavily used in the 1991 Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a Coalition of the Gulf War, 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Ba'athist Iraq, ...
and Operation Restore Hope
The Unified Task Force (UNITAF) was a United States-led, United Nations-sanctioned multinational force which operated in Somalia from 5 December 1992 until 4 May 1993. A United States initiative (code-named Operation Restore Hope), U ...
.
After the 2003 invasion of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq was a United States-led invasion of the Republic of Iraq and the first stage of the Iraq War. The invasion phase began on 19 March 2003 (air) and 20 March 2003 (ground) and lasted just over one month, including 26 ...
, AAV-7A1s were criticized for providing poor protection for the crew and passengers compared with other vehicles, such as the M2 Bradley
The M2 Bradley, or Bradley IFV, is an American infantry fighting vehicle that is a member of the Bradley Fighting Vehicle family. It is manufactured by BAE Systems Land & Armaments, which was formerly United Defense.
The Bradley is designed ...
. Eight were disabled or destroyed during the Battle of Nasiriyah, where they faced RPG, mortar, tank and artillery fire. At least one vehicle was destroyed by fire from friendly A-10 Warthog
The Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II is a single-seat, twin-turbofan, straight-wing, subsonic attack aircraft developed by Fairchild Republic for the United States Air Force (USAF). In service since 1976, it is named for the Republic ...
aircraft.
On 3 August 2005, 14 U.S. Marines and their Iraqi interpreter were killed when their AAV struck a roadside bomb in the city of Haditha in the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
river valley in western Iraq.
Eight U.S. Marines and one U.S. Navy sailor died on 30 July 2020, when their AAV sank in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Clemente Island, California, during a training exercise, ahead of an upcoming deployment. As a result of the incident, on 15 December 2021 the U.S. Marine Corps announced that it has banned its fleet of amphibious armored personnel carriers from maritime operations except in emergencies.
Replacement attempts
Cancelled: Expeditionary Fighting Vehicle
Renamed from the Advanced Assault Amphibious Vehicle in late 2003, theExpeditionary Fighting Vehicle
The Expeditionary Fighting Vehicle (EFV) (formerly known as the Advanced Amphibious Assault Vehicle (AAAV)) was an amphibious assault vehicle developed by General Dynamics during the 1990s and 2000s for use by the U.S. Marine Corps. It would ...
(EFV) was designed to replace the aging AAV. Able to transport a full Marine rifle squad to shore from an amphibious assault ship beyond the horizon with three times the speed in water and about twice the armor of the AAV, and superior firepower as well it was the Marine Corps' number one priority ground weapon system acquisition. The EFV was intended for deployment in 2015. However, in January 2011, United States Defense Secretary Robert Gates
Robert Michael Gates (born September 25, 1943) is an American intelligence analyst and university president who served as the 22nd United States secretary of defense from 2006 to 2011. He was originally appointed by president George W. Bush a ...
announced plans to cancel the Expeditionary Fighting Vehicle. In 2012, the USMC dropped the EFV and cancelled the program.
Replacement: Amphibious Combat Vehicle
In June 2018, the Marine Corps announced they had selected the BAE Systems/ Iveco wheeled SuperAV for theAmphibious Combat Vehicle
The Amphibious Combat Vehicle (ACV) is a program initiated by Marine Corps Systems Command to procure an amphibious assault vehicle for the United States Marine Corps to supplement and ultimately replace the aging Assault Amphibious Vehicle (AA ...
(ACV) program to supplement and ultimately replace the AAV.BAE wins Marine Corps contract to build new amphibious combat vehicle''Defense News''. 19 June 2018.Marines Pick BAE to Build Amphibious Combat Vehicle; Contract Worth Up to $1.2B
. ''USNI News''. 19 June 2018.
Variants
 * LVTP-7: Original series introduced from 1972. Originally armed with a M85 12.7 mm (.50cal) machine gun.
* LVTP-7A1: 1982 upgraded. Renamed to AAVP-7A1 from 1984.
** AAVP-7A1 (Personnel): This is the most common AAV, as it carries a turret equipped with an M2HB 12.7 mm (.50 caliber) heavy machine gun, and a Mk19 40 mm automatic grenade launcher. It carries four crew radios as well as the AN/VIC-2 intercom system. It is capable of carrying 21 combat equipped Marines in addition to the crew of 4: driver, crew chief/vehicle commander, gunner, and rear crewman.
** AAVC-7A1 (Command): This vehicle does not have a turret, and much of the cargo space of the vehicle is occupied by communications equipment. This version only has two crew radios, and in addition to the VIC-2, it also carries two VRC-92s, a VRC-89, a PRC-103 UHF radio, a MRC-83 HF radio and the MSQ internetworking system used to control the various radios. This AAV has a crew of 3, and additionally carries 5 radio operators, 3 staff members, and 2 commanding officers. Recently, the C7 has been upgraded to use Harris Falcon II class radios, specifically the PRC-117 for VHF/UHF/SATCOM, and the PRC-150 for HF.
** AAVR-7A1 (Recovery): This vehicle also does not have a turret. The R7 is considered the "wrecker", as it has a crane as well as most tools and equipment needed for field repairs. It is by far the heaviest of the three, and sits considerably lower in the water. Crew of three, plus the repairmen.
Many P7s have been modified to carry the Mk 154 MCLC, or Mine Clearance Line Charge. The MCLC kit can fire three linear demolition charges to breach a lane through a minefield. MCLCs were used in the 1991
* LVTP-7: Original series introduced from 1972. Originally armed with a M85 12.7 mm (.50cal) machine gun.
* LVTP-7A1: 1982 upgraded. Renamed to AAVP-7A1 from 1984.
** AAVP-7A1 (Personnel): This is the most common AAV, as it carries a turret equipped with an M2HB 12.7 mm (.50 caliber) heavy machine gun, and a Mk19 40 mm automatic grenade launcher. It carries four crew radios as well as the AN/VIC-2 intercom system. It is capable of carrying 21 combat equipped Marines in addition to the crew of 4: driver, crew chief/vehicle commander, gunner, and rear crewman.
** AAVC-7A1 (Command): This vehicle does not have a turret, and much of the cargo space of the vehicle is occupied by communications equipment. This version only has two crew radios, and in addition to the VIC-2, it also carries two VRC-92s, a VRC-89, a PRC-103 UHF radio, a MRC-83 HF radio and the MSQ internetworking system used to control the various radios. This AAV has a crew of 3, and additionally carries 5 radio operators, 3 staff members, and 2 commanding officers. Recently, the C7 has been upgraded to use Harris Falcon II class radios, specifically the PRC-117 for VHF/UHF/SATCOM, and the PRC-150 for HF.
** AAVR-7A1 (Recovery): This vehicle also does not have a turret. The R7 is considered the "wrecker", as it has a crane as well as most tools and equipment needed for field repairs. It is by far the heaviest of the three, and sits considerably lower in the water. Crew of three, plus the repairmen.
Many P7s have been modified to carry the Mk 154 MCLC, or Mine Clearance Line Charge. The MCLC kit can fire three linear demolition charges to breach a lane through a minefield. MCLCs were used in the 1991 Persian Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a Coalition of the Gulf War, 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Ba'athist Iraq, ...
and again in Operation Iraqi Freedom in 2003.
In the 1970s, the U.S. Army used an LVTP-7 as the basis for their Mobile Test Unit (MTU), a ground-based high-energy anti-aircraft laser. After several successful test firings at Redstone Army Arsenal, the laser was reportedly transferred to NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
.
* KAAV7A1: KAAV7A1 amphibious vehicle series based on AAV-7A1 by Samsung Techwin
Hanwha Techwin (), founded as Samsung Techwin, is a video surveillance company. It is a subsidiary of Hanwha Group. The company employs 1,822 people and is headquartered in South Korea. Its total sales in 2020 were 529.8 billion South Korean won ...
(now Hanwha Defense) and BAE systems developed and manufactured in South Korea by Samsung Techwin.
Training systems
The Office of Naval Research (ONR) under the Virtual Training and Environments (VIRTE) program, led by then LCDR Dylan Schmorrow, developed a prototype training system called the AAV Turret Trainer. The system consists of an actual surplus turret mounted with ISMT (Indoor Simulated Marksmanship Trainer) weapons firing on a projected screen displaying the VIRTE Virtual Environment. A total of 15 systems were produced for the USMC and one system for Taiwan.Well deck
In traditional nautical use, well decks were decks lower than decks fore and aft, usually at the main deck level, so that breaks appear in the main deck profile, as opposed to a flush deck profile. The term goes back to the days of sail. Late-20 ...
with AAVs
File:AAV-Nsry.jpg, A USMC AAV destroyed near Nasiriyah in 2003
File:AAV-7 en Santander2.JPG, Spanish marines
The Spanish Naval Infantry ( es, Infantería de Marina) is the Marines, naval infantry unit of the Spanish Navy () responsible for conducting amphibious warfare by utilizing naval platforms and resources. The Marine Corps is fully integrated in ...
deploying from an AAV-7 during an exhibition in 2009
File:US Navy 090425-N-4879G-393 A group of multinational amphibious assault vehicles from the amphibious dock landing ship USS Ashland (LSD 48) deploy smoke to cover their landing during a simulated amphibious landing demonstration.jpg, Landing force demonstration
File:Exercise TRIDENT JUNCTURE (22525166631).jpg, Italian Lagunari on an exercise in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
Operators

 * : Naval Infantry Command originally received 21 vehicles (19 LVTP-7, 1 LVTP-7 and 1 LVTR-7), 11 of them (9 LVTP-7, 1 LVTC-7 and 1 LVTR-7) were upgraded locally by MECATROL with Caterpillar C7 diesel engines and minor changes to running gear and other components
* : Brazilian Marine Corps has 49
* : 76 will be procured for use with the Hellenic Marine Corps of the Hellenic Navy
* : 15 in service with the
* : Naval Infantry Command originally received 21 vehicles (19 LVTP-7, 1 LVTP-7 and 1 LVTR-7), 11 of them (9 LVTP-7, 1 LVTC-7 and 1 LVTR-7) were upgraded locally by MECATROL with Caterpillar C7 diesel engines and minor changes to running gear and other components
* : Brazilian Marine Corps has 49
* : 76 will be procured for use with the Hellenic Marine Corps of the Hellenic Navy
* : 15 in service with the Indonesian Marine Corps
'' ("Glorious on the Land and Sea")
, colors =
, colors_label = Beret color
, march = Mars Korps Marinir
, mascot =
, equipment =
...
; donated by South Korea.Data Ranratfib Korps Marinir, 2020
* : Due to be replaced by the Italian Marines.
* : Amphibious Rapid Deployment Brigade has 58 (46 personnel, 6 command and 6 recovery) After a period of testing 6 AAVP-7A1s, Japan on 7 April 2016 announced it would purchase 30 systems. Vehicles are AAV7A1 Reliability, Availability, and Maintainability/Rebuild to Standard (RAM/RS) versions, with a more powerful engine and drive train and an upgraded suspension system, providing improved mobility, command, control and repair capabilities. Deliveries to take place in mid to late 2017.
* : Philippine Marine Corps
The Philippine Marine Corps (PMC) ( fil, Hukbong Kawal Pandagat ng Pilipinas) is the marine corps of the Philippines, a naval infantry force under the command of the Philippine Navy. The PMC conducts amphibious, expeditionary, and special op ...
All 8 AAV units has been delivered as of 2019 and currently operated by the Philippine Marine Corps, plans to order at least 16.
* : Republic of China Marine Corps
The Republic of China Marine Corps (ROCMC; ), also known colloquially as the Taiwan Marine Corps, is the amphibious arm of the Republic of China Navy (ROCN) responsible for amphibious combat, counter-landing and reinforcement of the areas under th ...
has 90(78 personnel, 8 command and 4 recovery) and 1 AAV Turret Trainer. Thirty-six currently on order for $375 million USD.
* : Spanish Navy Marines have 19 (16 personnel, 2 command and 1 recovery)
* : Republic of Korea Marine Corps
The Republic of Korea Marine Corps (ROKMC; ko, 대한민국 해병대, Daehanminguk Haebyeongdae), also known as the ROK Marine Corps or ROK Marines, is the marine corps of South Korea. The ROKMC is a branch of the Republic of Korea Navy respo ...
has approximately 168 KAAV variants
* : Royal Thai Marine Corps
The Royal Thai Marine Corps or RTMC ( th, ราชนาวิกโยธินแห่งราชอาณาจักรไทย) are the marines of the Royal Thai Navy. The Royal Thai Marine Corps was founded in 1932, when the first batt ...
has 36, AAVP-7A1, AAVC-7A1, AAVR-7A1. Upgraded locally by Chaiseri to match with the BAE Systems's AAV7A1 RAM/RS standard. On March 10, 2022, it's reported that Chaiseri will create a local version, known as the AAVP1A1.
* : United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combi ...
possesses 1,311 of them
See also
* 3rd Assault Amphibian Battalion * WWII/Korea LVT Museum *Notes
External links
FAS AAV article
AAV Fact File at the official USMC website
Paper regarding high energy lasers and the MTU
AAV 7A1 on Armour.ws
USMC Amtrac Association Website
{{Authority control Tracked amphibious vehicles Vehicles introduced in 1972 Armoured personnel carriers of South Korea Armoured personnel carriers of Japan Armored personnel carriers of the United States Amphibious armoured personnel carriers FMC Corporation Military vehicles introduced in the 1970s