Ameloblastoma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ameloblastoma is a rare, benign or cancerous
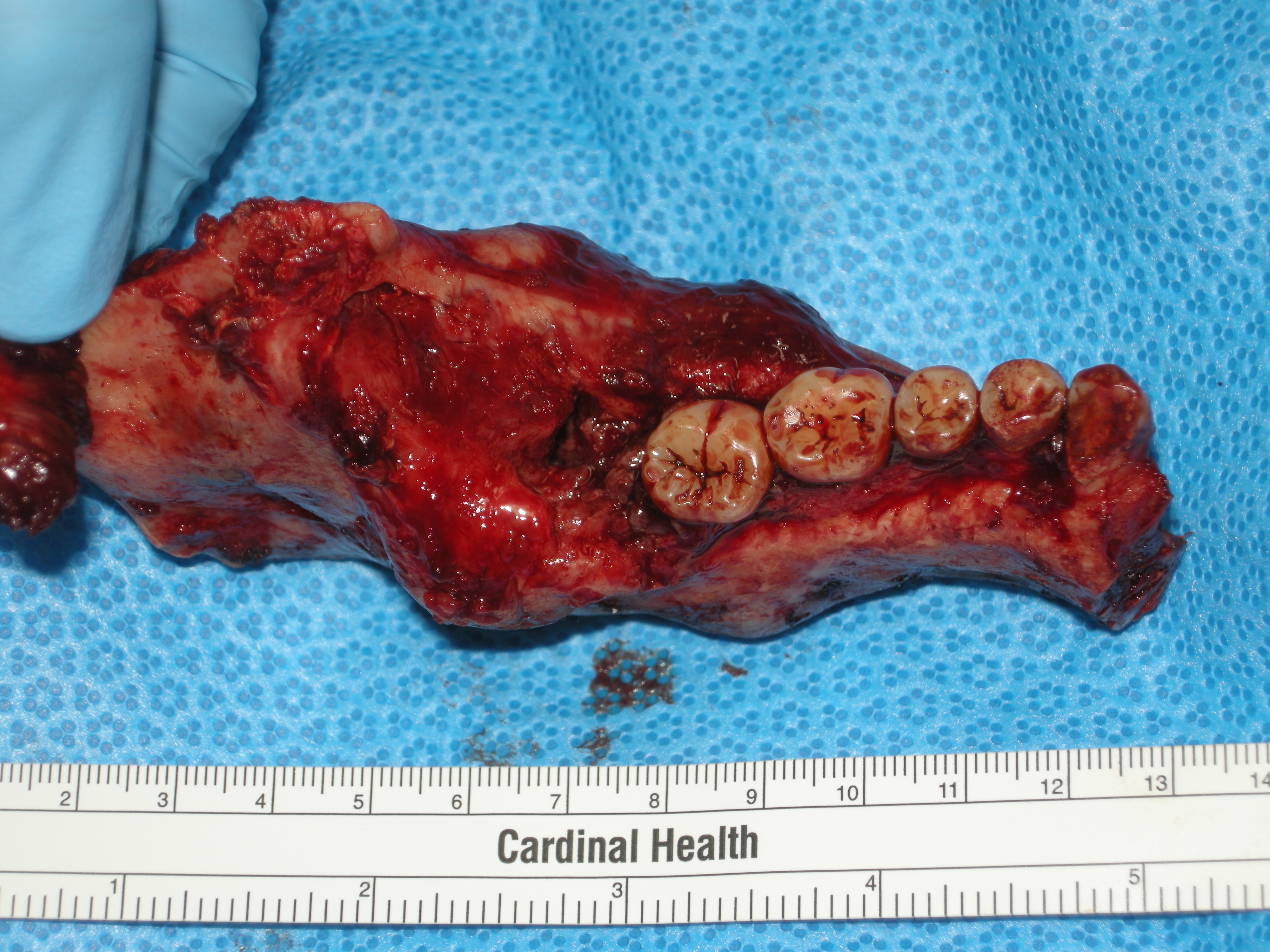 Conventional ameloblastomas have both
Conventional ameloblastomas have both

 While
While
tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
of odontogenic epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
( ameloblasts, or outside portion, of the teeth during development) much more commonly appearing in the lower jaw
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
than the upper jaw
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
. It was recognized in 1827 by Cusack. This type of odontogenic neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
was designated as an '' adamantinoma'' in 1885 by the French physician Louis-Charles Malassez
Louis-Charles Malassez (21 September 1842 – 22 December 1909) was a French anatomist and histologist born in Nevers, department of Nièvre.
He studied medicine in Paris, where he worked as an ''interne'' from 1867. He served with the 5th Am ...
. It was finally renamed to the modern name ''ameloblastoma'' in 1930 by Ivey and Churchill.
While these tumors are rarely malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
or metastatic
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
(that is, they rarely spread to other parts of the body), and progress slowly, the resulting lesions
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classifi ...
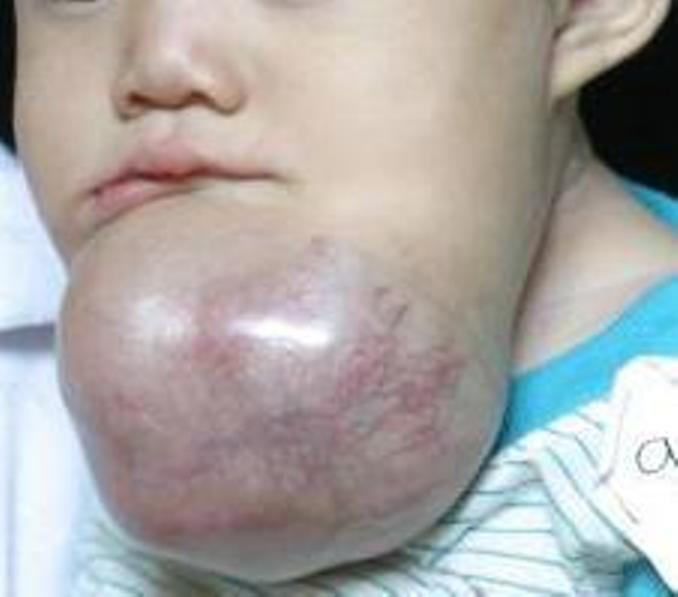
can cause severe abnormalities of the face
The face is the front of an animal's head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may aff ...
and jaw leading to severe disfiguration. Additionally, as abnormal cell growth easily infiltrates and destroys surrounding bony tissues, wide surgical excision is required to treat this disorder. If an aggressive tumor is left untreated, it can obstruct the nasal and oral airways making it impossible to breathe without oropharyngeal
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
intervention. The term "ameloblastoma" is from the early English word ''amel'', meaning enamel and the Greek word , meaning germ.
Types
Four types of ameloblastoma have been described by the WHO 2017 classification: * Conventional (solid/multicystic) type ameloblastoma * Unicystic ameloblastoma * Peripheral/extraosseous ameloblastoma * Metastasising ameloblastomaConventional ameloblastoma
Previously known as solid/multicystic ameloblastoma. Usually presents with multiple large cystic areas.Unicystic ameloblastoma
Ameloblastoma with a single cyst cavity account for around 10% of ameloblastomas. Present in younger patients in their second and third decades of life, often in relation to unerupted third molar.Metastasising ameloblastoma
Histologically atypical ameloblastoma can, rarely, lead tometastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, the ...
, usually in the lung. 'Metastasis' look histologically identical to the primary tumour and are benign in nature.
Peripheral ameloblastoma
The peripheral subtype composes 2% of all ameloblastomas.Presentation
Ameloblastomas can be found both in the maxilla and mandible. Although, 80% are situated in the mandible with the posterior ramus area being the most frequent site. The neoplasms are often associated with the presence of uneruptedteeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, ...
, displacement of adjacent teeth and resorption of roots.
Symptoms include a slow-growing, painless swelling leading to facial deformity. As the swelling gets progressively larger it can impinge on other structures resulting in loose teeth and malocclusion
In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855-19 ...
. Bone can also be perforated leading to soft tissue involvement.
The lesion has a tendency to expand the bony cortices because the slow growth rate of the lesion allows time for the periosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones.
Structu ...
to develop a thin shell of bone ahead of the expanding lesion. This shell of bone cracks when palpated. This phenomenon is referred to as "Egg Shell Cracking" or crepitus
Crepitus is "a grating sound or sensation produced by friction between bone and cartilage or the fractured parts of a bone".
Various types of crepitus that can be heard in joint pathologies are:
*Bone crepitus: This can be heard when two fragme ...
, an important diagnostic feature.
Maxillary ameloblastomas can be dangerous and even lethal. Due to thin bone and weak barriers, the neoplasm can extend into the sinonasal passages, pterygomaxillary fossa and eventually into the cranium and brain. Rare orbital invasion of the neoplasm has also been reported.
Histopathology
 Conventional ameloblastomas have both
Conventional ameloblastomas have both cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble) ...
ic and solid neoplastic
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
structures.
Solid structure
Solid areas containfibrous tissue
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
islands or epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
that interconnect through strands and sheets. The epithelial cells tend to move the nucleus away from the basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium an ...
to the opposite pole of the cell. This process is called ''reverse polarization''. Two main histological patterns most often occur: ''follicular'' and ''plexiform''. Other less common histological variants include ''acanthomatous'', ''basal cell'', and ''granular cell'' patterns.
Follicular
The most common follicular type has an outer arrangement of columnar or palisaded ameloblasts-like cells and inner zone of triangular shaped cells resemblingstellate reticulum
The stellate reticulum is a group of cells located in the center of the enamel organ of a developing tooth. These cells are star-shaped and synthesize glycosaminoglycans. As glycosaminoglycans are produced, water
Water (chemical formula ...
from the bell stage of tooth development.
Plexiform
The plexiform type has epithelium that proliferates in a "Fish Net Pattern". The plexiform ameloblastoma shows epithelium proliferating in a 'cord like fashion', hence the name 'plexiform'. There are layers of cells in between the proliferating epithelium with well-formed desmosomal junctions, simulating spindle cell layers. The ameloblasts cells can be less prominent.Cystic structure
Large cysts up to a few centimetres in diameter can be found. In follicular type, cysts develop in the stellate reticulum and in the plexiform type, cysts are caused by degeneration of connective tissue stroma.Desmoplastic ameloblastoma
A distinctive histological variant of conventional ameloblastoma. Found in near equal frequencies in both maxilla and mandible. Resemble a fibro-osseous lesion with no obvious ameloblasts whilst dominated by dense collagenous tissue (desmoplastic). In one center, desmoplastic ameloblastomas represented about 9% of all ameloblastomas encountered. A systematic review showed a predilection for males and predominance in fourth and fifth decades in life. 52% desmoplastic ameloblastomas showed mandibular involvement, with a tendency to anterior region. Majority of tumours were found to have ill-defined margins radiographically.Diagnosis
Ameloblastoma is tentatively diagnosed throughradiograph
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeut ...
ic examination and must be confirmed by histological examination through biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
.
Radiographically, the tumour area appears as a rounded and well-defined lucency in the bone with varying size and features. Numerous cyst-like radiolucent areas can be seen in larger tumours (multi-locular) giving a characteristic "soap bubble" appearance. A single radiolucent area can be seen in smaller tumours (unilocular). The radiodensity
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypod ...
of an ameloblastoma is about 30 Hounsfield units, which is about the same as keratocystic odontogenic tumours. However, ameloblastomas show more bone expansion and seldom show high density areas.
Lingual plate expansion is helpful in diagnosing ameloblastoma as cysts rarely do this. Resorption of roots of involved teeth can be seen in some cases, but is not unique to ameloblastoma.
Differential diagnosis
* Keratocystic odontogenic tumour *Central giant-cell granuloma
Central giant-cell granuloma (CGCG) is a localised benign condition of the jaws. It is twice as common in females and is more likely to occur before age 30. Central giant-cell granulomas are more common in the anterior mandible, often crossing th ...
* Odontogenic myxoma
The odontogenic myxoma is an uncommon benign odontogenic tumor arising from embryonic connective tissue associated with tooth formation.Sapp, J. Philip., Lewis R. Eversole, and George P. Wysocki. Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. 2nd ...
Treatment
 While
While chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemother ...
, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Rad ...
, curettage
Curettage ( or ), in medical procedures, is the use of a curette (French, meaning scoopMosby's Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary, Fourth Edition, Mosby-Year Book 1994, p. 422) to remove tissue by scraping or scooping.
Curettages are ...
and liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen—LN2—is nitrogen in a liquid state at low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, low viscosity liquid that is wid ...
have been rarely effective in cases of ameloblastoma, surgical resection or enucleation remains the most definitive treatment for this condition. However, in a detailed study of 345 patients, chemotherapy and radiation therapy was contraindicated for the treatment of ameloblastomas. Thus, surgery is the most common treatment of this neoplasm. A case of giant ameloblastoma was recently reported and managed with total mandibulectomy and pectoralis major myocutaneous flap reconstruction. A systematic review found that 79% of desmoplastic ameloblastoma cases were treated by resection. Conservative treatment requires very careful case selection.
Surgical resection
The aim of treatment and surgery is to remove the entire tumour with a margin of surrounding tissue (block resection) for a good prognosis. Preferable removal includes 10mm of normal bone around the neoplasm. Larger ameloblastomas can require partial resection of the jaw bone followed bybone grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured wit ...
. There is evidence that the treatment of conventional ameloblastoma is best done by bone resection. A systematic review found that 79% of desmoplastic ameloblastoma cases were treated by resection.
Enucleation
Smaller mandibular neoplasms have been enucleated where the cavity of the tumour is curetted, allowing preservation of the bone cortex and the lower border of the mandible. Although, recurrence rate for this type of treatment is higher. Unicystic ameloblastomas—called ''intraluminal unicystic'' or ''plexiform unicystic'' ameloblastomas can be enucleated, as the epithelium is only limited to the inner cyst wall and lumen.Radiation and chemotherapy
Radiation is ineffective in many cases of ameloblastoma. There have also been reports ofsarcoma
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal ( connective tissue) origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sar ...
being induced as the result of using radiation to treat ameloblastoma. Chemotherapy is also often ineffective. However, there is some controversy regarding this and some indication that some ameloblastomas might be more responsive to radiation that previously thought.
Follow-up and recurrence
Persistent follow-up examination including radiographs is essential for managing ameloblastoma. Follow-up should occur at regular intervals for at least 10 years. Follow up is important, because 50% of all recurrences occur within 5 years postoperatively. Recurrence is common, although the recurrence rates for block resection followed by bone graft are lower than those of enucleation and curettage. Follicular variants appear to recur more than plexiform variants. Unicystic lesions recur less frequently than "non-unicystic" lesions. A low recurrence rate of around 10% can be seen in unicystic ameloblastomas. Recurrence within a bone graft (following resection of the original tumor) does occur, but is less common. Seeding to the bone graft is suspected as a cause of recurrence. The recurrences in these cases seem to stem from the soft tissues, especially the adjacentperiosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones.
Structu ...
. Recurrence has been reported to occur as many as 36 years after treatment. To reduce the likelihood of recurrence within grafted bone, meticulous surgery with attention to the adjacent soft tissues is required.
Molecular biology
'' BRAF'' V600E gene and '' SMO'' gene mutations have been found in ameloblastomas. V600E mutation is also seen in other malignant and benign neoplasms, which activate the MAP kinase pathway required for cell division and differentiation but is the most commonly seen mutation in ameloblastoma. 72% of ''BRAF'' mutations are found in the mandible. A recent study discovered a high frequency of ''BRAF''V600E V600E is a mutation of the BRAF gene in which valine (V) is substituted by glutamic acid (E) at amino acid 600. It is a driver mutation in a proportion of certain diagnoses, including melanoma, hairy cell leukemia, papillary thyroid carcinoma, col ...
mutations (15 of 24 samples, 63%) in conventional ameloblastoma. These data suggests drugs targeting mutant ''BRAF'' as potential novel therapies for ameloblastoma.
SMO mutations lead to the activation of the hedgehog pathway
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is a signaling pathway that transmits information to embryonic cells required for proper cell differentiation. Different parts of the embryo have different concentrations of hedgehog signaling proteins. The pathway ...
giving similar results as V600E but is less frequently seen. 55% of SMO mutations are found in the maxilla.
Evidence shows that suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 may inhibit the local invasiveness of ameloblastoma, however, this was only demonstrated ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology a ...
''. There is also some research suggesting that α5β1 integrin may participate in the local invasiveness of ameloblastomas.
Epidemiology
People with African heritage have been shown to have a higher incidence compared to Caucasians, with the site often being in the midline of the mandible. The annual incidence rates per million for ameloblastomas are 1.96, 1.20, 0.18 and 0.44 for black males, black females, white males and white females respectively. Ameloblastomas account for about one percent of all oral tumors and about 18% of odontogenic tumors. Men and women are equally affected, though women average four years younger than men when tumors first occur, and tumors run larger in females.See also
*Ameloblastic fibroma An ameloblastic fibroma is a fibroma of the ameloblastic tissue, that is, an odontogenic tumor arising from the enamel organ or dental lamina. It may be either truly neoplastic or merely hamartomatous (an odontoma). In neoplastic cases, it may be la ...
*Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma The ameloblastic fibro-odontoma (AFO) is essentially a benign tumor with the features characteristic of ameloblastic fibroma along with enamel and dentin (hard tissues). Though it is generally regarded as benign, there have been cases of its malig ...
*Bone grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured wit ...
*Epithelial cell rests of Malassez
In dentistry, the epithelial cell rests of Malassez (ERM) or epithelial rests of Malassez (''pax epithelialis pediodontii'') are part of the periodontal ligament cells around a tooth. They are discrete clusters of residual cells from Hertwig's ep ...
*List of cutaneous conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier agai ...
* Matrix Metalloproteinase-2
*Tooth development
Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate st ...
and Odontogenesis
References
External links
{{Odontogenic tumors Odontogenic tumors