
An airbag is a vehicle occupant-restraint system using a bag designed to inflate extremely quickly, then quickly deflate during a
collision. It consists of the airbag cushion, a flexible fabric bag, an inflation module, and an impact sensor. The purpose of the airbag is to provide a vehicle occupant with soft cushioning and restraint during a collision. It can reduce injuries between the flailing occupant and the interior of the vehicle.
The airbag provides an energy-absorbing surface between the vehicle's occupants and a steering wheel, instrument panel,
body pillar, headliner, and
windshield
The windshield (North American English) or windscreen (Commonwealth English) of an aircraft, car, bus, motorbike, truck, train, boat or streetcar is the front window, which provides visibility while protecting occupants from the elements. ...
. Modern
vehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), ...
s may contain up to 10 airbag modules in various configurations, including: driver, passenger, side-curtain, seat-mounted, door-mounted, B and C-pillar mounted side-impact, knee bolster, inflatable seat belt, and pedestrian airbag modules.
During a crash, the vehicle's crash sensors provide crucial information to the airbag electronic controller unit (ECU), including collision type, angle, and severity of impact. Using this information, the airbag ECU's crash algorithm determines if the crash event meets the criteria for deployment and triggers various firing circuits to deploy one or more airbag modules within the vehicle. Working as a supplemental restraint system to the vehicle's seat-belt systems, airbag module deployments are triggered through a
pyrotechnic process that is designed to be used once. Newer side-impact airbag modules consist of compressed-air cylinders that are triggered in the event of a side-on vehicle impact.
The first commercial designs were introduced in passenger automobiles during the 1970s, with limited success, and actually caused some fatalities. Broad commercial adoption of airbags occurred in many markets during the late 1980s and early 1990s. Many modern vehicles now include six or more units.
Active vs. passive safety
Airbags are considered "passive" restraints and act as a supplement to "active" restraints. Because no action by a vehicle occupant is required to activate or use the airbag, it is considered a "passive" device. This is in contrast to
seat belt
A seat belt (also known as a safety belt, or spelled seatbelt) is a vehicle safety device designed to secure the driver or a passenger of a vehicle against harmful movement that may result during a collision or a sudden stop. A seat belt red ...
s, which are considered "active" devices because the vehicle occupant must act to enable them.
This terminology is not related to
active and passive safety, which are, respectively, systems designed to prevent collisions in the first place, and systems designed to minimize the effects of collisions once they occur. In this use, a car
antilock braking system qualifies as an active-safety device, while both its seatbelts and airbags qualify as passive-safety devices. Further terminological confusion can arise from the fact that passive devices and systems—those requiring no input or action by the vehicle occupant—can operate independently in an active manner; an airbag is one such device. Vehicle safety professionals are generally careful in their use of language to avoid this sort of confusion, though
advertising
Advertising is the practice and techniques employed to bring attention to a product or service. Advertising aims to put a product or service in the spotlight in hopes of drawing it attention from consumers. It is typically used to promote a ...
principles sometimes prevent such
semantic
Semantics (from grc, σημαντικός ''sēmantikós'', "significant") is the study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy, linguistics and comput ...
caution in the consumer marketing of safety features. Further confusing the terminology, the
aviation safety community uses the terms "active" and "passive" in the ''opposite'' sense from the automotive industry.
History

Origins
The airbag "for the covering of aeroplane and other vehicle parts" traces its origins to a United States patent, submitted in 1919 by two dentists from
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
, Arthur Parrott & Harold Round
and approved in 1920. Air-filled bladders were in use as early as 1951. The airbag specifically for automobile use is credited independently to the American John W. Hetrick, who filed for an airbag patent on 5 August 1952, that was granted #2,649,311 by the United States Patent Office on 18 August 1953. German engineer Walter Linderer, who filed German patent #896,312 on 6 October 1951, was issued on 12 November 1953, approximately three months after American John Hetrick. Hetrick and Linderer's airbags were both based on a compressed air system, either released by spring, bumper contact, or by the driver. Later research during the 1960s showed that compressed air could not inflate the mechanical airbags fast enough to ensure maximum safety, leading to the current chemical and electrical airbags.
In patent applications, manufacturers sometimes use the term "inflatable occupant restraint systems".
Hetrick was an
industrial engineer and member of the
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
. His airbag design, however, only came about when he combined his experiences working with navy
torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, ...
es with his desire to protect his family on the road. Despite working with the major automobile manufacturers of his time, Hetrick was unable to attract investment. Although airbags are now required in every automobile sold in the United States, Hetrick's 1951 patent filing serves as an example of a "valuable" invention with little economic value to its inventor. Its first commercial use was not implemented until after the patent expired in 1971, at which point the airbag was installed in a few experimental
Ford cars.
In 1964, a Japanese automobile engineer,
Yasuzaburou Kobori (小堀保三郎), started developing an airbag "safety net" system. His design harnessed an explosive to inflate an airbag, for which he was later awarded patents in 14 countries. He died in 1975, before seeing widespread adoption of airbag systems.
In 1967, a breakthrough in the development of airbag crash
sensors came when Allen K. Breed invented a ball-in-tube mechanism for crash detection. Under his system, an
electromechanical sensor with a steel ball attached to a tube by a
magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nicke ...
would inflate an airbag in under 30 milliseconds. A small explosion of
sodium azide was used instead of compressed air during inflation for the first time.
Breed Corporation then marketed this innovation to
Chrysler
Stellantis North America (officially FCA US and formerly Chrysler ()) is one of the " Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. It is the American subsidiary of the multinational automotiv ...
. A similar "Auto-Ceptor" crash-restraint, developed by the
Eaton, Yale & Towne company for Ford, was soon also offered as an automatic safety system in the United States, while the Italian Eaton-Livia company offered a variant with localized air cushions.
In the early 1970s,
General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
began offering cars equipped with airbags, initially in government
fleet-purchased, 1973 Chevrolet Impala sedans. These cars came with a 1974-style Oldsmobile instrument panel and a special steering wheel that contained the driver-side air bag. Two of these cars were crash tested after 20 years and the airbags deployed perfectly. An early example of the air-bag cars survives as of 2009. GM's
Oldsmobile Toronado
The Oldsmobile Toronado is a personal luxury car manufactured and marketed by the Oldsmobile division of General Motors from 1966 to 1992 over four generations. The Toronado was noted for its transaxle version of GM's Turbo-Hydramatic transmiss ...
was the first domestic U.S. vehicle to include a passenger airbag. General Motors marketed its first airbag modules under the "Air Cushion Restraint System" name, or ACRS. The automaker discontinued the option for its 1977
model year, citing lack of consumer interest. Ford and GM then spent years
lobbying
In politics, lobbying, persuasion or interest representation is the act of lawfully attempting to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of government officials, most often legislators or members of regulatory agencies. Lobbying, whic ...
against air-bag requirements, claiming that the devices were unfeasible and inappropriate. Chrysler made driver-side airbags standard on 1988–1989 models, but airbags did not become widespread in American cars until the early 1990s.
As a substitute to seat belts
Airbags for passenger cars were introduced in the United States in the 1970s. When seat-belt usage rates in the country were quite low compared to modern-day, Ford built experimental cars with airbags in 1971.
Allstate operated a fleet of 200
Mercury Montereys and showed reliability of airbags as well as their operation in crash testing, which also was promoted by the insurance company in popular magazine advertisements. General Motors followed in 1973 using full-sized Chevrolet vehicles. The early fleet of experimental GM vehicles equipped with airbags experienced seven fatalities, one of which was later suspected to have been caused by the airbag.
In 1974, GM made its ACRS system (which consisted of a padded lower dashboard and a passenger-side air bag) available as a regular production option (RPO code AR3) in full-sized Cadillac, Buick and Oldsmobile models. The GM cars from the 1970s equipped with ACRS had a driver-side airbag, a driver-side knee restraint,.
The passenger-side airbag protected both front passengers,
and unlike most modern systems, integrated a knee and torso cushion while also having a dual-stage deployment dictated by force of the impact. The cars equipped with ACRS had lap belts for all seating positions, but lacked shoulder belts. Shoulder belts were already mandatory in the United States on closed cars without airbags for the driver and outer front passenger, but GM chose to market its airbags as a substitute for shoulder belts. Prices for this option on Cadillac models were US$225 in 1974, $300 in 1975, and $340 in 1976 (US$ in dollars ).
The early development of airbags coincided with international interest in automobile safety legislation. Some safety experts advocated a
performance-based occupant-protection standard rather than one mandating a particular technical solution (which could rapidly become outdated and prove to not be a
cost-effective approach). Less emphasis was placed on other designs as countries successfully mandated seatbelt restrictions, however.
[
]
As a supplemental restraint system
Frontal airbag
The auto industry and research and regulatory communities have moved away from their initial view of the airbag as a seat-belt replacement, and the bags are now nominally designated as supplemental restraint systems (SRS) or supplemental inflatable restraints.
In 1981, Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz (), commonly referred to as Mercedes and sometimes as Benz, is a German luxury and commercial vehicle automotive brand established in 1926. Mercedes-Benz AG (a Mercedes-Benz Group subsidiary established in 2019) is headquarte ...
introduced the airbag in West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 ...
as an option on its flagship saloon model, S-Class (W126). In the Mercedes system, the sensors automatically tensioned the seat belts to reduce occupants' motion on impact and then deployed the airbag on impact. This integrated the seat belts and airbag into a restraint system, rather than the airbag being considered an alternative to the seat belt.
In 1987, the Porsche 944 Turbo became the first car to have driver and passenger airbags as standard equipment. The Porsche 944 and 944S had this as an available option. The same year also had the first airbag in a Japanese car, the Honda Legend.
In 1988, Chrysler
Stellantis North America (officially FCA US and formerly Chrysler ()) is one of the " Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. It is the American subsidiary of the multinational automotiv ...
became the first United States automaker to fit a driver-side airbag as standard equipment, which was offered in six different models.Chrysler minivans
The Chrysler minivans are a series of minivans that have been produced and marketed by the American automaker Chrysler since the 1984 model year. Currently in its sixth generation, the model line is marketed worldwide, primarily in North Ameri ...
came with airbags starting for the 1991 model year.Chrysler Concorde
The Chrysler Concorde is a full-size, front wheel drive four-door sedan that was produced by Chrysler from 1992 to 2004. It assumed the C-body Chrysler New Yorker Salon's position as the entry-level full-size sedan in the Chrysler brand lin ...
sedans ahead of any safety regulations. Early 1993 saw the 4-millionth airbag-equipped Chrysler vehicle roll off the assembly line. In October 1993, the Dodge Ram became the first pickup truck
A pickup truck or pickup is a light-duty truck that has an enclosed cabin, and a back end made up of a cargo bed that is enclosed by three low walls with no roof (this cargo bed back end sometimes consists of a tailgate and removable covering) ...
with a standard driver-side airbag.
The first known collision between two airbag-equipped automobiles took place on 12 March 1990 in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
, USA. A 1989 Chrysler LeBaron crossed the center line and hit another 1989 Chrysler LeBaron in a head-on collision
A head-on collision is a traffic collision where the front ends of two vehicles such as cars, trains, ships or planes hit each other when travelling in opposite directions, as opposed to a side collision or rear-end collision.
Rail transpor ...
, causing both driver airbags to deploy. The drivers suffered only minor injuries despite extensive damage to the vehicles.
The United States Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991 required passenger cars and light trucks built after 1 September 1998 to have airbags for the driver and the front passenger.Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, airbags were almost unheard of until the early 1990s. By 1991, four manufacturers – BMW, Honda
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a producti ...
, Mercedes-Benz, and Volvo
The Volvo Group ( sv, Volvokoncernen; legally Aktiebolaget Volvo, shortened to AB Volvo, stylized as VOLVO) is a Swedish multinational manufacturing corporation headquartered in Gothenburg. While its core activity is the production, distributio ...
– offered the airbag on some of their higher-end models, but shortly afterward, airbags became a common feature on more mainstream cars, with Ford and Vauxhall
Vauxhall ( ) is a district in South West London, part of the London Borough of Lambeth, England. Vauxhall was part of Surrey until 1889 when the County of London was created. Named after a medieval manor, "Fox Hall", it became well known for ...
/Opel
Opel Automobile GmbH (), usually shortened to Opel, is a German automobile manufacturer which has been a subsidiary of Stellantis since 16 January 2021. It was owned by the American automaker General Motors from 1929 until 2017 and the PSA Grou ...
among the manufacturers to introduce the airbag to its model ranges in 1992. Citroën
Citroën () is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded in March 1919 by André Citroën. Citroën is owned by Stellantis since 2021 and previously was part of the PSA Group after Peugeot acquired 8 ...
, Fiat
Fiat Automobiles S.p.A. (, , ; originally FIAT, it, Fabbrica Italiana Automobili di Torino, lit=Italian Automobiles Factory of Turin) is an Italian automobile manufacturer, formerly part of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, and since 2021 a subsidiar ...
, Nissan
, trading as Nissan Motor Corporation and often shortened to Nissan, is a Japanese multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Nishi-ku, Yokohama, Japan. The company sells its vehicles under the Nissan, Infiniti, and Datsun bra ...
, Hyundai Hyundai is a South Korean industrial conglomerate (" chaebol"), which was restructured into the following groups:
* Hyundai Group, parts of the former conglomerate which have not been divested
** Hyundai Mobis, Korean car parts company
** Hyundai A ...
, Peugeot
Peugeot (, , ) is a French brand of automobiles owned by Stellantis.
The family business that preceded the current Peugeot companies was founded in 1810, with a steel foundry that soon started making hand tools and kitchen equipment, and then ...
, Renault
Groupe Renault ( , , , also known as the Renault Group in English; legally Renault S.A.) is a French multinational automobile manufacturer established in 1899. The company produces a range of cars and vans, and in the past has manufactured ...
, and Volkswagen
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German Automotive industry, motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a ...
followed shortly afterwards.
By 1999, finding a new mass market car without an airbag at least as optional equipment was difficult, and some late 1990s products, such as the Volkswagen Golf Mk4, also featured side airbags. The Peugeot 306 is one example of the European automotive mass-market evolution: starting in early 1993, most of these models did not even offer a driver's airbag as an option, but by 1999, even side airbags were available on several variants. Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
...
was late to offer airbag systems on a broader scale, since even in the 1994 model year, its popular models did not offer airbags. Instead, the German automaker until then relied solely on its proprietary cable-based procon-ten
procon-ten (lower case initial ''"p"'') (an acronym for ''Programmed Contraction-Tension'') is a proprietary ''Safety Restraint System'' (SRS), used by German car manufacturer Audi from 1986 until the mid-1990s.
Audi was one of the last German ...
restraint system.
Variable force-deployment front airbags were developed to help minimize injury from the airbag itself.
The emergence of the airbag has contributed to a sharp decline in the number of deaths and serious injuries on the roads of Europe since 1990, and by 2010, the number of cars on European roads lacking an airbag represented a very small percentage of cars, mostly the remaining cars dating from the mid-1990s or earlier.
Many new cars in Latin America, including the Kia Picanto, Kia Rio, Hyundai Accent, and Suzuki Alto, are still regularly sold without airbags, as neither airbags nor automatic braking systems in new cars are compulsory in Latin America.
= Shape of airbags
=
The Citroën C4 provided the first "shaped" driver airbag, made possible by this car's unusual fixed-hub steering wheel.
In 2019, Honda announced it would introduce a new front passenger airbag technology. Developed by Autoliv
Autoliv Inc. is a Swedish-American
automotive safety supplier with sales to all leading car manufacturers worldwide. Together with its joint ventures, Autoliv has over 68,000 employees in 27 countries, of whom 5700 are involved in research, dev ...
and Honda R&D in Ohio, United States, this new airbag design features three inflatable chambers connected across the front by a "noninflatable sail panel." The two outer chambers are larger than the middle chamber. When the airbag deploys, the sail panel cushions the occupant's head from the impact of hitting the airbag, and the three chambers hold the occupant's head in place, like a catcher's mitt. The goal of the tri-chamber airbag is to help "arrest high-speed movement" of the head, thereby reducing the likelihood of concussion injuries in a collision. The first vehicle to come with the tri-chamber airbag installed from the factory was in 2020 (for the 2021 model year) for the Acura TLX. Honda hopes that the new technology will soon make its way to all vehicles.
= Rear airbag
=
Mercedes began offering rear passengers protection in frontal collisions in September 2020 (for the 2021 model year) for the Mercedes-Benz S-Class (W223).
Side airbag

 Essentially, two types of side airbags are commonly used today - the side-torso airbag and the side-curtain airbag. More recently, center airbags are becoming more common in the European market.
Most vehicles equipped with side-curtain airbags also include side-torso airbags. However, some, such as the Chevrolet Cobalt, 2007–09 model Chevrolet Silverado/GMC Sierra, and 2009–12 Dodge Ram do not feature the side-torso airbag.
From around 2000, side-impact airbags became commonplace on even low- to mid-range vehicles, such as the smaller-engined versions of the Ford Fiesta and Peugeot 206, and curtain airbags were also becoming regular features on mass-market cars. The Toyota Avensis, launched in 2003, was the first mass-market car to be sold in Europe with nine airbags.
Essentially, two types of side airbags are commonly used today - the side-torso airbag and the side-curtain airbag. More recently, center airbags are becoming more common in the European market.
Most vehicles equipped with side-curtain airbags also include side-torso airbags. However, some, such as the Chevrolet Cobalt, 2007–09 model Chevrolet Silverado/GMC Sierra, and 2009–12 Dodge Ram do not feature the side-torso airbag.
From around 2000, side-impact airbags became commonplace on even low- to mid-range vehicles, such as the smaller-engined versions of the Ford Fiesta and Peugeot 206, and curtain airbags were also becoming regular features on mass-market cars. The Toyota Avensis, launched in 2003, was the first mass-market car to be sold in Europe with nine airbags.
= Side torso airbag
=
Side-impact airbags or side-torso airbags are a category of airbags usually located in the seat or door panel, and inflate between the seat occupant and the door. These airbags are designed to reduce the risk of injury to the pelvic and lower abdomen regions. Most vehicles are now being equipped with different types of designs, to help reduce injury and ejection from the vehicle in rollover crashes. More recent side-airbag designs include a two chamber system; a firmer lower chamber for the pelvic region and softer upper chamber for the ribcage.
Swedish company Autoliv AB was granted a patent on side-impact airbags, and they were first offered as an option in 1994
= Side tubular or curtain airbag
=
In 1997, the BMW 7 Series and 5 Series were fitted with tubular-shaped head side airbags (inflatable tubular structure), the "Head Protection System (HPS)" as standard equipment. This airbag was designed to offer head protection in side impact collisions and also maintained inflation for up to seven seconds for rollover protection. However, this tubular-shaped airbag design has been quickly replaced by an inflatable 'curtain' airbag.
In May 1998, Toyota began offering a side-curtain airbag deploying from the roof on the Progrés. In 1998, the Volvo S80 was given roof-mounted curtain airbags to protect both front and rear passengers. Curtain airbags were then made standard equipment on all new Volvo cars from 2000 except for the first-generation C70, which received an enlarged side-torso airbag that also protects the head of front-seat occupants.
Roll-sensing curtain airbag (RSCA)
Roll-sensing curtain airbags are designed to stay inflated for a longer duration of time, cover a larger proportion of the window, and be deployed in a roll-over crash. They offer protection to occupants' heads and help to prevent ejection. SUVs and pickups are more likely to be equipped with RSCAs due to their higher probability of rolling over and often a switch can disable the feature in case the driver wants to take the vehicle off-road.
= Center airbag
=
 In 2009, Toyota developed the first production rear-seat center airbag designed to reduce the severity of secondary injuries to rear passengers in a side collision. This system deploys from the rear center seat first appearing in on the Crown Majesta. In late 2012, General Motors with supplier Takata introduced a front center airbag; it deploys from the driver's seat.
In 2009, Toyota developed the first production rear-seat center airbag designed to reduce the severity of secondary injuries to rear passengers in a side collision. This system deploys from the rear center seat first appearing in on the Crown Majesta. In late 2012, General Motors with supplier Takata introduced a front center airbag; it deploys from the driver's seat.
Hyundai Motor Group
The Hyundai Motor Group (HMG; ; ; stylized as HYUΠDAI) is a South Korean '' chaebol'' (loosely similar to a multinational conglomerate but without a central holding company or ownership structure) headquartered in Seoul, South Korea.
The H ...
announced its development of center side airbag on September 18, 2019 installed inside the driver’s seat.
Some Volkswagen
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German Automotive industry, motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a ...
vehicles in 2022 equipped with center airbags include the ID.3 and the Golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standardized playing area, and coping wi ...
.
The Polestar 2 also includes a center airbag.
With EuroNCAP updating its testing guidelines in 2020, European and Australian market vehicles increasingly use front center airbags, rear torso airbags and rear seatbelt pretensioners.
Knee airbag
The second driver-side and separate knee airbag was used in the Kia Sportage
The Kia Sportage is a lineup of sport utility vehicles manufactured by the South Korean manufacturer Kia since 1993. Since 2004, the Sportage has been categorized as a compact crossover SUV, while previously it occupied the compact SUV class. It ...
SUV and has been standard equipment since then. The airbag is located beneath the steering wheel.
 The Toyota Caldina introduced the first driver-side SRS knee airbag on the Japanese market in 2002. Toyota Avensis became the first vehicle sold in Europe equipped with a driver's knee airbag. The
The Toyota Caldina introduced the first driver-side SRS knee airbag on the Japanese market in 2002. Toyota Avensis became the first vehicle sold in Europe equipped with a driver's knee airbag. The EuroNCAP
The European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) is a European voluntary car safety performance assessment programme (i.e. a New Car Assessment Program) based in Leuven (Belgium) formed in 1996, with the first results released in Februa ...
reported on the 2003 Avensis, "There has been much effort to protect the driver's knees and legs and a knee airbag worked well." Since then certain models have also included front-passenger knee airbags, which deploy near or over the glove compartment in a crash. Knee airbags are designed to reduce leg injury. The knee airbag has become increasingly common from 2000.
Rear curtain airbag
In 2008, the new Toyota iQ microcar featured the first production rear-curtain shield airbag to protect the rear occupants' heads in the event of a rear-end impact.
Seat cushion airbag
Another feature of the Toyota iQ was a seat-cushion airbag in the passenger seat to prevent the pelvis from diving below the lap belt during a frontal impact or submarining. Later Toyota models such as the Yaris added the feature to the driver's seat, as well.
Seat-belt airbag
The seat-belt airbag is designed to better distribute the forces experienced by a buckled person in a crash by means of an increased seat belt area. This is done to reduce possible injuries to the rib cage or chest of the belt wearer.
*2010: Ford ExplorerFord Flex
The Ford Flex is a full-size crossover SUV or wagon that was manufactured by the Ford Motor Company; a single generation was produced from the 2009 to 2019 model years. Introduced as the successor to the Ford Taurus X, the model line also fu ...
: optional rear seat belt airbags; standard on the 2013 Lincoln MKT
The Lincoln MKT is a full-size 3-row luxury crossover SUV that was marketed by the Lincoln division of Ford Motor Company; a single generation was produced from the 2010 to the 2019 model years. Slotted between the Lincoln MKX (renamed the Lin ...
*2010: Lexus LFA
The is a two-seat sports car manufactured by Lexus, the luxury car division of Toyota. It is the second model in the F marque line of performance vehicles from Lexus, following the IS F, and also the first standalone Lexus F model. Three c ...
had seat belt airbags for driver and passenger
*2013: Mercedes-Benz S-Class (W222) has rear seat ''beltbags''
*2014: Ford Mondeo Mk IV has optional rear seat belt airbags for the two outer seats
Cessna Aircraft also introduced seat belt airbags.[ They are as of 2003]
Pedestrian airbag
Airbag(s) mounted to the exterior of vehicles, so called ''pedestrian airbags'', are designed to reduce injuries in the event of a vehicle to pedestrian collision. When a collision is detected the airbag will deploy and cover hard areas, such as a-pillars
Manufacturers
SRS airbag suppliers include Autoliv
Autoliv Inc. is a Swedish-American
automotive safety supplier with sales to all leading car manufacturers worldwide. Together with its joint ventures, Autoliv has over 68,000 employees in 27 countries, of whom 5700 are involved in research, dev ...
, Daicel, TRW and JSS (which now owns Breed, Key Safety Systems and Takata). The majority of impact sensors of airbags are manufactured by the Lanka Harness Company.
Operation
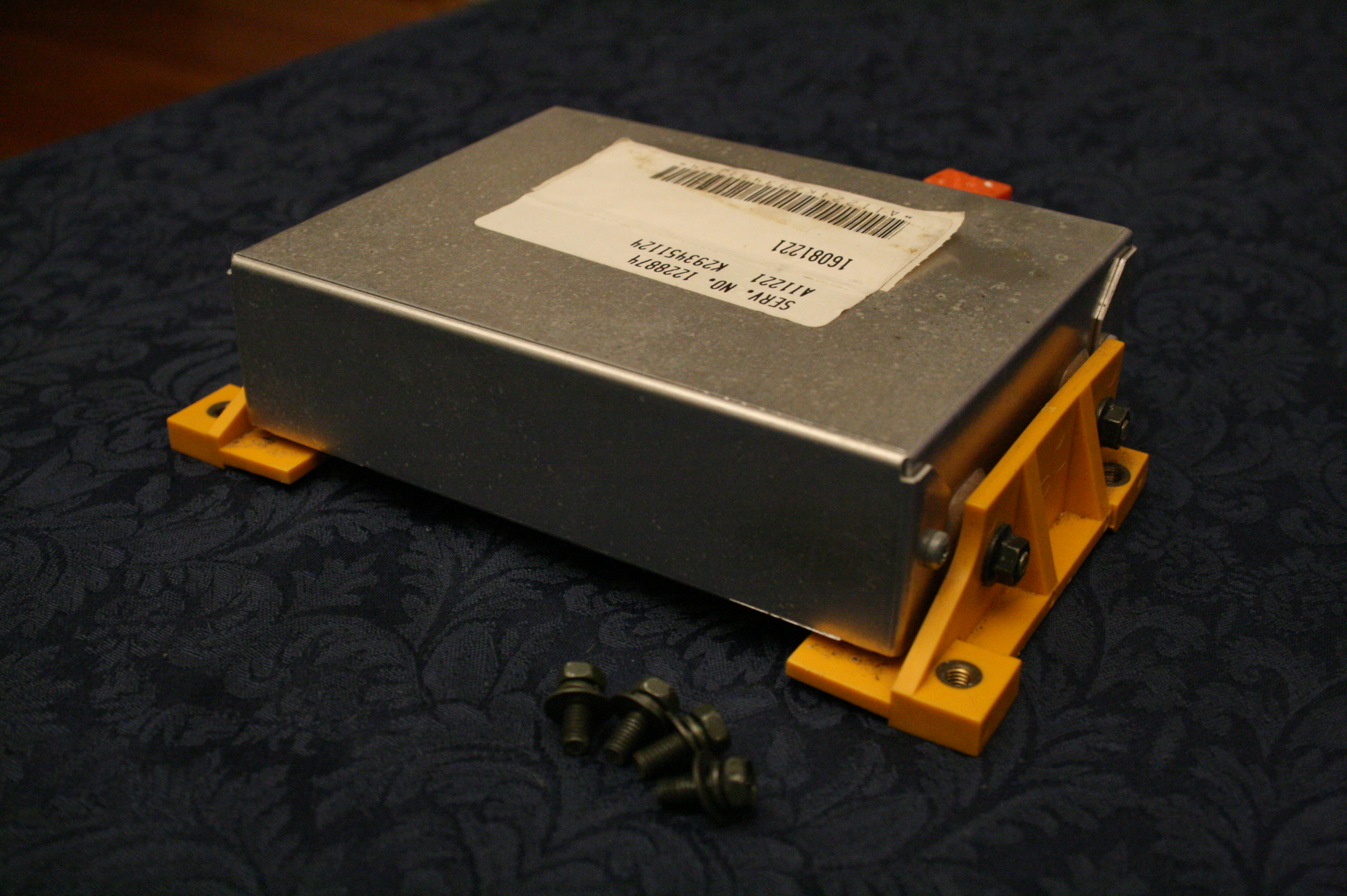 The airbags in the vehicle are controlled by a central airbag control unit (ACU), a specific type of ECU. The ACU monitors a number of related sensors within the vehicle, including accelerometers, impact sensors, side (door) pressure sensors, wheel speed sensors,
The airbags in the vehicle are controlled by a central airbag control unit (ACU), a specific type of ECU. The ACU monitors a number of related sensors within the vehicle, including accelerometers, impact sensors, side (door) pressure sensors, wheel speed sensors, gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rot ...
s, brake pressure sensors, and seat occupancy sensors. Oftentimes, ACUs log this—and other—sensor data in a circular buffer and record it to onboard non-volatile memory, in order to provide a snapshot of the crash event for investigators. As such, an ACU frequently functions as the vehicle's event data recorder
An event data recorder (EDR), more specifically motor vehicle event data recorder (MVEDR), similar to an accident data recorder (ADR) sometimes referred to informally as an automotive black box (by analogy with the common nickname for flight re ...
; not all EDRs are ACUs, and not all ACUs include EDR features. An ACU typically includes capacitors within its circuitry, so that the module remains powered and able to deploy the airbags in the event that the vehicle's battery connection to the ACU is severed during a crash.
The bag itself and its inflation mechanism is concealed within the steering wheel boss (for the driver), or the dashboard (for the front passenger), behind plastic flaps or doors which are designed to tear open under the force of the bag inflating. Once the requisite threshold has been reached or exceeded, the airbag control unit will trigger the ignition of a gas generator
A gas generator is a device for generating gas. A gas generator may create gas by a chemical reaction or from a solid or liquid source, when storing a pressurized gas is undesirable or impractical.
The term often refers to a device that uses a ...
propellant to rapidly inflate a fabric bag. As the vehicle occupant collides with and squeezes the bag, the gas escapes in a controlled manner through small vent holes. The airbag's volume and the size of the vents in the bag are tailored to each vehicle type, to spread out the deceleration of (and thus force experienced by) the occupant over time and over the occupant's body, compared to a seat belt alone.
The signals from the various sensors are fed into the airbag control unit, which determines from them the angle of impact, the severity, or the force of the crash, along with other variables. Depending on the result of these calculations, the ACU may also deploy various additional restraint devices, such as seat belt
A seat belt (also known as a safety belt, or spelled seatbelt) is a vehicle safety device designed to secure the driver or a passenger of a vehicle against harmful movement that may result during a collision or a sudden stop. A seat belt red ...
pre-tensioners, and/or airbags (including frontal bags for driver and front passenger, along with seat-mounted side bags, and "curtain" airbags which cover the side glass). Each restraint device is typically activated with one or more pyrotechnic devices, commonly called an initiator or electric match. The electric match, which consists of an electrical conductor wrapped in a combustible material, activates with a current pulse between 1 and 3 amperes in less than 2 milliseconds. When the conductor becomes hot enough, it ignites the combustible material, which initiates the gas generator. In a seat belt pre-tensioner, this hot gas is used to drive a piston that pulls the slack out of the seat belt. In an airbag, the initiator is used to ignite solid propellant inside the airbag inflator. The burning propellant generates inert gas which rapidly inflates the airbag in approximately 20 to 30 milliseconds. An airbag must inflate quickly in order to be fully inflated by the time the forward-traveling occupant reaches its outer surface. Typically, the decision to deploy an airbag in a frontal crash is made within 15 to 30 milliseconds after the onset of the crash, and both the driver and passenger airbags are fully inflated within approximately 60–80 milliseconds after the first moment of vehicle contact. If an airbag deploys too late or too slowly, the risk of occupant injury from contact with the inflating airbag may increase. Since more distance typically exists between the passenger and the instrument panel, the passenger airbag is larger and requires more gas to fill it.
Older airbag systems contained a mixture of sodium azide (NaN3), KNO3, and SiO2. A typical driver-side airbag contains approximately 50–80 g of NaN3, with the larger passenger-side airbag containing about 250 g. Within about 40 milliseconds of impact, all these components react in three separate reactions that produce nitrogen gas. The reactions, in order, are as follows.
# 2 NaN3 → 2 Na + 3 N2 (g)
# 10 Na + 2 KNO3 → K2O + 5 Na2O + N2 (g)
# K2O + Na2O + 2 SiO2 → K2SiO3 + Na2SiO3
The first two reactions create 4 molar equivalents of nitrogen gas, and the third converts the remaining reactants to relatively inert potassium silicate and sodium silicate
Sodium silicate is a generic name for chemical compounds with the formula or ·, such as sodium metasilicate , sodium orthosilicate , and sodium pyrosilicate . The anions are often polymeric. These compounds are generally colorless transparent ...
. The reason that KNO3 is used rather than something like NaNO3 is because it is less hygroscopic. It is very important that the materials used in this reaction are not hygroscopic because absorbed moisture can de-sensitize the system and cause the reaction to fail.
The particle size of the initial reactants is important to reliable operation. The NaN3 and KNO3 must be between 10 and 20 µm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Uni ...
, while the SiO2 must be between 5 and 10 µm.
There are ongoing efforts to find alternative compounds that can be used in airbags which have less toxic reactants. In a journal article by Akiyoshi et al., it was found that for the reaction of the Sr complex nitrate, (Sr(NH2NHCONHNH2)∙(NO3)2) of carbohydrazide (SrCDH) with various oxidizing agents resulted in the evolution of N2 and CO2 gases. Using KBrO3 as the oxidizing agent resulted in the most vigorous reaction as well as the lowest initial temperature of the reaction. The N2 and CO2 gases evolved made up 99% of all gases evolved. Nearly all the starting materials won't decompose until reaching temperatures of 500 °C or higher so this could be a viable option as an airbag gas generator.
In a patent containing another plausible alternative to NaN3 driven airbags, the gas generating materials involved the use of guanidine nitrate
Guanidine nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula (NH2)3O3. It is a colorless, water-soluble salt. It is produced on a large scale and finds use as precursor for nitroguanidine, fuel in pyrotechnics and gas generators. Its correct ...
, 5-aminotetrazole, bitetrazole dihydrate, nitroimidazole
5-Nitroimidazole is an organic compound with the formula O2NC3H2N2H. The nitro group at position 5 on the imidazole ring is the most common positional isomer. The term nitroimidazole also refers to a class of antibiotics that share similar ch ...
, and basic copper nitrate
Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu( NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common ...
. It was found that these non-azide reagents allowed for a less toxic, lower combustion temperature reaction, and more easily disposable airbag inflation system.
Front airbags normally do not protect the occupants during side, rear, or rollover collisions. Since airbags deploy only once and deflate quickly after the initial impact, they will not be beneficial during a subsequent collision. Safety belts help reduce the risk of injury in many types of crashes. They help to properly position occupants to maximize the airbag's benefits and they help restrain occupants during the initial and any following collisions.
In vehicles equipped with a rollover sensing system, accelerometers and gyroscopes are used to sense the onset of a rollover event. If a rollover event is determined to be imminent, side-curtain airbags are deployed to help protect the occupant from contact with the side of the vehicle interior, and also to help prevent occupant ejection as the vehicle rolls over.
Triggering conditions
 Airbags are designed to deploy in frontal and near-frontal collisions more severe than a threshold defined by the regulations governing vehicle construction in whatever particular market the vehicle is intended for: United States regulations require deployment in crashes at least equivalent in deceleration to a 23 km/h (14 mph) barrier collision, or similarly, striking a parked car of similar size across the full front of each vehicle at about twice the speed. International regulations are performance-based, rather than technology-based, so airbag deployment threshold is a function of overall vehicle design.
Unlike crash tests into barriers, real-world crashes typically occur at angles other than directly into the front of the vehicle, and the crash forces usually are not evenly distributed across the front of the vehicle. Consequently, the relative speed between a striking and struck vehicle required to deploy the airbag in a real-world crash can be much higher than an equivalent barrier crash. Because airbag sensors measure deceleration, the vehicle speed is not a good indicator of whether an airbag should have deployed. Airbags can deploy due to the vehicle's undercarriage striking a low object protruding above the roadway due to the resulting deceleration.
The airbag sensor is a
Airbags are designed to deploy in frontal and near-frontal collisions more severe than a threshold defined by the regulations governing vehicle construction in whatever particular market the vehicle is intended for: United States regulations require deployment in crashes at least equivalent in deceleration to a 23 km/h (14 mph) barrier collision, or similarly, striking a parked car of similar size across the full front of each vehicle at about twice the speed. International regulations are performance-based, rather than technology-based, so airbag deployment threshold is a function of overall vehicle design.
Unlike crash tests into barriers, real-world crashes typically occur at angles other than directly into the front of the vehicle, and the crash forces usually are not evenly distributed across the front of the vehicle. Consequently, the relative speed between a striking and struck vehicle required to deploy the airbag in a real-world crash can be much higher than an equivalent barrier crash. Because airbag sensors measure deceleration, the vehicle speed is not a good indicator of whether an airbag should have deployed. Airbags can deploy due to the vehicle's undercarriage striking a low object protruding above the roadway due to the resulting deceleration.
The airbag sensor is a MEMS
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), also written as micro-electro-mechanical systems (or microelectronic and microelectromechanical systems) and the related micromechatronics and microsystems constitute the technology of microscopic devices, ...
accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acce ...
, which is a small integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
with integrated micro mechanical elements. The microscopic mechanical element moves in response to rapid deceleration, and this motion causes a change in capacitance, which is detected by the electronics on the chip that then sends a signal to fire the airbag. The most common MEMS accelerometer in use is the ADXL-50 by Analog Devices
Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI), also known simply as Analog, is an American multinational semiconductor company specializing in data conversion, signal processing and power management technology, headquartered in Wilmington, Massachusetts.
The ...
, but there are other MEMS manufacturers as well.
Initial attempts using mercury switches did not work well. Before MEMS, the primary system used to deploy airbags was called a "rolamite
Rolamite is a technology for very low friction bearings developed by Sandia National Laboratories in the 1960s. It is the only elementary machine discovered in the twentieth century and can be used in various ways such as a component in switches, ...
". A rolamite is a mechanical device, consisting of a roller suspended within a tensioned band. As a result of the particular geometry and material properties used, the roller is free to translate with little friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of ...
or hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of ...
. This device was developed at Sandia National Laboratories. The rolamite, and similar macro-mechanical devices were used in airbags until the mid-1990s when they were universally replaced with MEMS.
Nearly all airbags are designed to automatically deploy in the event of a vehicle fire when temperatures reach 150–200 °C (300–400 °F). This safety feature, often termed auto-ignition, helps to ensure that such temperatures do not cause an explosion of the entire airbag module.
Today, airbag triggering algorithms
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
are becoming much more complex. They try to reduce unnecessary deployments and adapt the deployment speed to the crash conditions. The algorithms are considered valuable intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
. Experimental algorithms may take into account such factors as the weight of the occupant, the seat location, seatbelt use, and even attempt to determine if a baby seat is present.
Inflation
When the frontal airbags are to deploy, a signal is sent to the inflator unit within the airbag control unit. An igniter starts a rapid chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking ...
generating primarily nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
gas (N2) to fill the airbag making it deploy through the module cover. Some airbag technologies use compressed nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
or argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice a ...
gas with a pyrotechnic operated valve ("hybrid gas generator"), while other technologies use various energetic propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the ...
s. Although propellants containing the highly toxic sodium azide (NaN3) were common in early inflator designs, little to no toxic sodium azide has been found on used airbags.
The azide-containing pyrotechnic gas generators contain a substantial amount of the propellant. The driver-side airbag would contain a canister containing about 50 grams of sodium azide. The passenger side container holds about 200 grams of sodium azide.
The alternative propellants may incorporate, for example, a combination of nitroguanidine
Nitroguanidine - sometimes abbreviated NGu - is a colorless, crystalline solid that melts at 257 °C and decomposes at 254 °C. Nitroguanidine is an extremely insensitive but powerful high explosive. Wetting it with > 20 wt.-% water effe ...
, phase-stabilized ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) or other nonmetallic oxidizer, and a nitrogen-rich fuel different from azide (e.g. tetrazoles, triazoles, and their salts). The burn rate modifiers in the mixture may be an alkaline metal nitrate (NO3-) or nitrite
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also ...
(NO2-), dicyanamide or its salts, sodium borohydride (NaBH4), etc. The coolants and slag formers may be e.g. clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay pa ...
, silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
, alumina, glass, etc. Other alternatives are e.g. nitrocellulose
Nitrocellulose (also known as cellulose nitrate, flash paper, flash cotton, guncotton, pyroxylin and flash string, depending on form) is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to a mixture of nitric acid and ...
based propellants (which have high gas yield but bad storage stability, and their oxygen balance requires secondary oxidation of the reaction products to avoid buildup of carbon monoxide), or high-oxygen nitrogen-free organic compounds with inorganic oxidizers (e.g., di or tricarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxyli ...
s with chlorates (ClO3-) or perchlorate
A perchlorate is a chemical compound containing the perchlorate ion, . The majority of perchlorates are commercially produced salts. They are mainly used as oxidizers for pyrotechnic devices and to control static electricity in food packaging. ...
s (ClO4-) and eventually metallic oxides; the nitrogen-free formulation avoids formation of toxic nitrogen oxide Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
*Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
* Nitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide
* Nitrogen trioxide (), or ...
s).
From the onset of the crash, the entire deployment and inflation process is about 0.04 seconds. Because vehicles change speed so quickly in a crash, airbags must inflate rapidly to reduce the risk of the occupant hitting the vehicle's interior.
Variable-force deployment
Advanced airbag technologies are being developed to tailor airbag deployment to the severity of the crash, the size, and posture of the vehicle occupant, belt usage, and how close that person is to the actual airbag. Many of these systems use multi-stage inflators that deploy less forcefully in stages in moderate crashes than in very severe crashes. Occupant sensing devices let the airbag control unit know if someone is occupying a seat adjacent to an airbag, the mass/weight of the person, whether a seat belt or child restraint is being used, and whether the person is forward in the seat and close to the airbag. Based on this information and crash severity information, the airbag is deployed at either a high force level, a less forceful level, or not at all.
Adaptive airbag systems may utilize multi-stage airbags to adjust the pressure within the airbag. The greater the pressure within the airbag, the more force the airbag will exert on the occupants as they come in contact with it. These adjustments allow the system to deploy the airbag with a moderate force for most collisions; reserving the maximum force airbag only for the severest of collisions. Additional sensors to determine the location, weight or relative size of the occupants may also be used. Information regarding the occupants and the severity of the crash are used by the airbag control unit, to determine whether airbags should be suppressed or deployed, and if so, at various output levels.

Post-deployment
A chemical reaction produces a burst of nitrogen to inflate the bag. Once an airbag deploys, deflation begins immediately as the gas escapes through vent(s) in the fabric (or, as it is sometimes called, the cushion) and cools. Deployment is frequently accompanied by the release of dust-like particles, and gases in the vehicle's interior (called effluent). Most of this dust consists of cornstarch
Corn starch, maize starch, or cornflour (British English) is the starch derived from corn (maize) grain. The starch is obtained from the endosperm of the kernel. Corn starch is a common food ingredient, often used to thicken sauces or sou ...
, french chalk, or talcum powder, which are used to lubricate the airbag during deployment.
Newer designs produce effluent primarily consisting of harmless talcum powder/cornstarch and nitrogen gas. In older designs using an azide-based propellant (usually NaN3), varying amounts of sodium hydroxide nearly always are initially present. In small amounts this chemical can cause minor irritation to the eyes and/or open wounds; however, with exposure to air, it quickly turns into sodium bicarbonate (baking soda). However, this transformation is not 100% complete, and invariably leaves residual amounts of hydroxide ion from NaOH. Depending on the type of airbag system, potassium chloride may also be present.
For most people, the only effect the dust may produce is some minor irritation of the throat and eyes. Generally, minor irritations only occur when the occupant remains in the vehicle for many minutes with the windows closed and no ventilation. However, some people with asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
may develop a potentially lethal asthmatic attack from inhaling the dust.
Because of the airbag exit flap design of the steering wheel boss and dashboard panel, these items are not designed to be recoverable if an airbag deploys, meaning that they have to be replaced if the vehicle has not been written off
A write-off is a reduction of the recognized value of something. In accounting, this is a recognition of the reduced or zero value of an asset. In income tax statements, this is a reduction of taxable income, as a recognition of certain expenses ...
in a collision. Moreover, the dust-like particles and gases can cause irreparable cosmetic damage to the dashboard and upholstery, meaning that minor collisions which result in the deployment of airbags can be costly, even if there are no injuries and there is only minor damage to the vehicle structure.
Regulatory specifications
United States
On 11 July 1984, the United States government amended Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 208 Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 208 (FMVSS 208) regulates automotive occupant crash protection in the United States. Like all other Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, FMVSS 208 is administered by the United States Department of Transpo ...
(FMVSS 208) to require cars produced after 1 April 1989 to be equipped with a passive restraint for the driver. An airbag or an automatic seat belt
A seat belt (also known as a safety belt, or spelled seatbelt) is a vehicle safety device designed to secure the driver or a passenger of a vehicle against harmful movement that may result during a collision or a sudden stop. A seat belt reduc ...
would meet the requirements of the standard. Airbag introduction was stimulated by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA ) is an agency of the U.S. federal government, part of the Department of Transportation. It describes its mission as "Save lives, prevent injuries, reduce vehicle-related crashes" relat ...
. However, airbags were not mandatory on light trucks until 1997.
In 1998, FMVSS 208 was amended to require dual front airbags, and reduced-power, second-generation airbags were also mandated. This was due to the injuries caused by first-generation airbags, though FMVSS 208 continues to require that bags be engineered and calibrated to be able to "save" the life of an ''unbelted'' 50th-percentile size and weight "male" crash test dummy. The technical performance and validation requirements for the inflator assembly used in airbag modules are specified in SAE
SAE or Sae may refer to:
Science and technology
:
* Selective area epitaxy, local growth of epitaxial layer through a patterned dielectric mask deposited on a semiconductor substrate
* Serious adverse event, in a clinical trial
* Simultaneous Aut ...
USCAR 24–2.
Outside the United States
Some countries outside North America adhere to internationalized European ECE vehicle and equipment regulations rather than the United States Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. ECE airbags are generally smaller and inflate less forcefully than United States airbags because the ECE specifications are based on ''belted'' crash test dummies.
The Euro NCAP vehicle safety rating encourages manufacturers to take a comprehensive approach to occupant safety; a good rating can only be achieved by combining airbags with other safety features.[Frontal impact test description]
Euro NCAP website Almost every new car sold in Europe is equipped with front and side airbags, but in the European Union in 2020 and in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, and most other developed countries there is no direct legal requirement for new cars to feature airbags.
Ecuador requires dual front airbags in new car models since 2013.
Since January 2014, with the exception of micro vehicles, all new cars made or imported in Argentina must have front airbags.
Since 1 January 2014, all new cars sold in Brazil must have dual front airbags.
Since July 2014, all new cars sold in Uruguay must have dual front airbags.
Since December 2016, all new cars sold in Chile must have dual front airbags.
Since 1 January 2017, all cars made or imported in Colombia must have dual front airbags.
Since 1 January 2020, all new cars sold in Mexico must have dual front airbags.
On 5 March 2021, the Indian Ministry of Road Transport and Highways mandated that all new vehicle models introduced in India after 1 April 2021 have dual front airbags; the regulation also requires that all existing models be equipped with dual front airbags by 31 August 2021.
India also mandated that all passenger vehicles sold after October 2023 must have a minimum of 6 airbags.
Maintenance
Inadvertent airbag deployment while the vehicle is being serviced can result in severe injury, and an improperly installed or defective airbag unit may not operate or perform as intended. Those servicing a vehicle, as well as first responders, must exercise extreme awareness, as many airbag control systems may remain powered for roughly 30 minutes after disconnecting the vehicle's battery. Some countries impose restrictions on the sale, transport, handling, and service of airbags and system components. In Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, airbags are regulated as harmful explosives; only mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to objec ...
with special training are allowed to service airbag systems.
Some automakers (such as Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz (), commonly referred to as Mercedes and sometimes as Benz, is a German luxury and commercial vehicle automotive brand established in 1926. Mercedes-Benz AG (a Mercedes-Benz Group subsidiary established in 2019) is headquarte ...
) call for the replacement of undeployed airbags after a certain period of time to ensure their reliability in a collision. One example is the 1992 S500, which has an expiry date sticker attached to the door pillar. Some Škoda vehicles indicate an expiry date of 14 years from the date of manufacture. In this case, replacement would be uneconomic as the car would have negligible value at 14 years old, far less than the cost of fitting new airbags. Volvo
The Volvo Group ( sv, Volvokoncernen; legally Aktiebolaget Volvo, shortened to AB Volvo, stylized as VOLVO) is a Swedish multinational manufacturing corporation headquartered in Gothenburg. While its core activity is the production, distributio ...
has stated that "airbags do not require replacement during the lifetime of the vehicle," though this cannot be taken as a guarantee on the device.
Limitations
 Although the millions of installed airbags in use have an excellent safety record, some limitations on their ability to protect car occupants exist. The original implementation of front airbags did little to protect against side collisions, which can be more dangerous than frontal collisions because the protective crumple zone in front of the passenger compartment is completely bypassed. Side airbags and protective airbag curtains are increasingly being required in modern vehicles to protect against this very common category of collisions.
Airbags are designed to deploy once only, so are ineffective if any further collisions occur after an initial impact. Multiple impacts may occur during certain rollover or other incidents involving multiple collisions, such as many multivehicle collisions.
Although the millions of installed airbags in use have an excellent safety record, some limitations on their ability to protect car occupants exist. The original implementation of front airbags did little to protect against side collisions, which can be more dangerous than frontal collisions because the protective crumple zone in front of the passenger compartment is completely bypassed. Side airbags and protective airbag curtains are increasingly being required in modern vehicles to protect against this very common category of collisions.
Airbags are designed to deploy once only, so are ineffective if any further collisions occur after an initial impact. Multiple impacts may occur during certain rollover or other incidents involving multiple collisions, such as many multivehicle collisions.windshield
The windshield (North American English) or windscreen (Commonwealth English) of an aircraft, car, bus, motorbike, truck, train, boat or streetcar is the front window, which provides visibility while protecting occupants from the elements. ...
. In an underride collision, the car's crush zone
Crumple zones, crush zones, or crash zones are a structural safety feature used in vehicles, mainly in automobiles, to increase the time over which a change in velocity (and consequently momentum) occurs from the impact during a collision by a ...
s designed to absorb collision energy are completely bypassed, and the airbags may not deploy in time because the car does not decelerate appreciably until the windshield and roof pillars have already impacted the trailer bed.power steering
A power steering is a mechanical device equipped on a motor vehicle that helps drivers steer the vehicle by reducing steering effort needed to turn the steering wheel, making it easier for the vehicle to turn or maneuver at lower speeds.
Hydra ...
, and power brakes, and may be the direct cause of a collision. If a violent collision occurs, the disabled airbags will not deploy to protect vehicle occupants. In 2014, General Motors admitted to concealing information about fatal collisions caused by defective ignition switches that would abruptly shut down a car (including its airbags). Between 13 and 74 deaths have been directly attributed to this defect, depending on how the fatalities are classified.
Injuries and fatalities
 Under some rare conditions, airbags can injure and in some very rare instances kill vehicle occupants. To provide crash protection for occupants not wearing seat belts, United States airbag designs trigger much more forcefully than airbags designed to the international ECE standards used in most other countries. Recent "smart" airbag controllers can recognize if a seatbelt is used, and alter the airbag cushion deployment parameters accordingly.
In 1990, the first automotive fatality attributed to an airbag was reported.
Under some rare conditions, airbags can injure and in some very rare instances kill vehicle occupants. To provide crash protection for occupants not wearing seat belts, United States airbag designs trigger much more forcefully than airbags designed to the international ECE standards used in most other countries. Recent "smart" airbag controllers can recognize if a seatbelt is used, and alter the airbag cushion deployment parameters accordingly.
In 1990, the first automotive fatality attributed to an airbag was reported.National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA ) is an agency of the U.S. federal government, part of the Department of Transportation. It describes its mission as "Save lives, prevent injuries, reduce vehicle-related crashes" relat ...
(NHTSA) recalled over 33 million vehicles in May 2015, and fined Takata $70 million in November 2015. Toyota, Mazda, and Honda have said that they will not use ammonium-nitrate inflators.
Airbag fatality statistics
From 1990 to 2000, the United States NHTSA identified 175 fatalities caused by air bags. Most of these (104) have been children. About 3.3 million air-bag deployments have occurred during that interval, and the agency estimates more than 6,377 lives were saved and countless injuries were prevented.[The statement "they've saved some 26,000 lives, according to estimates from the ... (NHTSA)" has been published. ]
A rear-facing infant restraint put in the front seat of a vehicle places an infant's head close to the airbag, which can cause severe head injuries
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
or death if the airbag deploys. Some modern cars include a switch to disable the front-passenger airbag, in case a child-supporting seat is used there (although not in Australia, where rear-facing child seats are prohibited in the front where an airbag is fitted).
In vehicles with side airbags, it is dangerous for occupants to lean against the windows, doors, and pillars, or to place objects between themselves and the side of the vehicle. Articles hung from a vehicle's clothes hanger hooks can be hazardous if the vehicle's side-curtain airbags deploy. A seat-mounted airbag may also cause internal injury if the occupant leans against the door.
Aerospace and military applications
The aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and ast ...
industry and the United States government have applied airbag technologies for many years. NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
and United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national sec ...
have incorporated airbag systems in various aircraft and spacecraft applications as early as the 1960s.
Spacecraft airbag landing systems
The first use of airbags for landing were Luna 9 and Luna 13
Luna 13 (E-6M series) was an unmanned space mission of the Luna program.
Overview
The Luna 13 spacecraft was launched toward the Moon from an Earth-orbiting platform and accomplished a soft landing on 24 December 1966, in the region of Oceanus P ...
, which landed on the Moon in 1966 and returned panoramic images. As with later missions, these would use the airbags to bounce along the surface, absorbing landing energy. The Mars Pathfinder
''Mars Pathfinder'' (''MESUR Pathfinder'') is an American robotic spacecraft that landed a base station with a roving probe on Mars in 1997. It consisted of a lander, renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station, and a lightweight, wheeled robot ...
lander employed an innovative airbag landing system, supplemented with aerobraking, parachute
A parachute is a device used to slow the motion of an object through an atmosphere by creating drag or, in a ram-air parachute, aerodynamic lift. A major application is to support people, for recreation or as a safety device for aviators, w ...
, and solid rocket
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants ( fuel/ oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder; they were used in warfare by the Arabs, Chinese, ...
landing thrusters. This prototype successfully tested the concept, and the two Mars Exploration Rover Mission landers employed similar landing systems. The Beagle 2
The ''Beagle 2'' is an inoperative British Mars lander that was transported by the European Space Agency's 2003 ''Mars Express'' mission. It was intended to conduct an astrobiology mission that would have looked for evidence of past life on Mar ...
Mars lander also tried to use airbags for landing; the landing was successful, and the lander touched down safely, but several of the spacecraft's solar panels failed to deploy, thereby disabling the spacecraft.
Aircraft airbag landing systems
Airbags have also been used on military fixed-wing aircraft, such as the escape crew capsule of the F-111 Aardvark
The General Dynamics F-111 Aardvark is a retired supersonic, medium-range, multirole combat aircraft. Production variants of the F-111 had roles that included ground attack (e.g. interdiction), strategic bombing (including nuclear weapons ca ...
.
Occupant protection
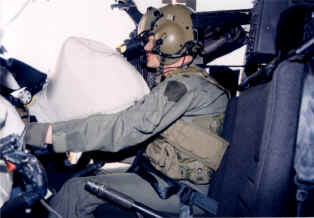 The
The United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, ...
has incorporated airbags in its UH-60A/L Black Hawk and OH-58D Kiowa Warrior helicopter fleets. The Cockpit Air Bag System (CABS) consists of forward and lateral airbags, and an inflatable tubular structure (on the OH-58D only) with an Electronic Crash Sensor Unit (ECSU). The CABS system was developed by the United States Army Aviation Applied Technology Directorate
The United States Army Aviation Applied Technology Directorate (AATD) is a tenant activity located at Fort Eustis, Virginia. It is a directorate of the Aviation Development Directorate under the Aviation and Missile Research, Development, and En ...
, through a contract with Simula Safety Systems (now BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh-largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenue ...
). It is the first conventional airbag system for occupant injury prevention (worldwide) designed and developed and placed in service for an aircraft, and the first specifically for helicopter applications.
Motorcycle airbag systems
 In the mid-1970s, the UK Transport Research Laboratory tested several types of motorcycle airbags. In 2006
In the mid-1970s, the UK Transport Research Laboratory tested several types of motorcycle airbags. In 2006 Honda
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a producti ...
introduced the first production motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle Steering, steered by a Motorcycle handlebar, handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: Long-distance ...
airbag safety system on its Gold Wing motorcycle. Honda claims that sensors in the front forks can detect a severe frontal collision and decide when to deploy the airbag, absorbing some of the forward energy of the rider and reducing the velocity at which the rider may be thrown from the motorcycle.
More commonly, air bag vests – either integrated into the motorcyclist's jacket or worn over it – have started to become used by regular riders on the street. MotoGP
Grand Prix motorcycle racing is the premier class of motorcycle road racing events held on road circuits sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de Motocyclisme (FIM). Independent motorcycle racing events have been held since the start ...
has made it compulsory since 2018 for riders to wear suits with integrated airbags.
See also
* Airbag dermatitis
* Airplane airbags
* Precrash system
* Safety standards
References
External links
Chemistry behind airbags
Pictures and details about the 1970s GM Air Cushion Restraint System
* History of air bags and how the technology gave rise to today's "smart cars".
{{Authority control
1973 introductions
20th-century inventions
Aircraft emergency systems
American inventions
Bags
Vehicle parts
Vehicle safety technologies
 An airbag is a vehicle occupant-restraint system using a bag designed to inflate extremely quickly, then quickly deflate during a collision. It consists of the airbag cushion, a flexible fabric bag, an inflation module, and an impact sensor. The purpose of the airbag is to provide a vehicle occupant with soft cushioning and restraint during a collision. It can reduce injuries between the flailing occupant and the interior of the vehicle.
The airbag provides an energy-absorbing surface between the vehicle's occupants and a steering wheel, instrument panel, body pillar, headliner, and
An airbag is a vehicle occupant-restraint system using a bag designed to inflate extremely quickly, then quickly deflate during a collision. It consists of the airbag cushion, a flexible fabric bag, an inflation module, and an impact sensor. The purpose of the airbag is to provide a vehicle occupant with soft cushioning and restraint during a collision. It can reduce injuries between the flailing occupant and the interior of the vehicle.
The airbag provides an energy-absorbing surface between the vehicle's occupants and a steering wheel, instrument panel, body pillar, headliner, and 

 In 2009, Toyota developed the first production rear-seat center airbag designed to reduce the severity of secondary injuries to rear passengers in a side collision. This system deploys from the rear center seat first appearing in on the Crown Majesta. In late 2012, General Motors with supplier Takata introduced a front center airbag; it deploys from the driver's seat.
In 2009, Toyota developed the first production rear-seat center airbag designed to reduce the severity of secondary injuries to rear passengers in a side collision. This system deploys from the rear center seat first appearing in on the Crown Majesta. In late 2012, General Motors with supplier Takata introduced a front center airbag; it deploys from the driver's seat.
 The Toyota Caldina introduced the first driver-side SRS knee airbag on the Japanese market in 2002. Toyota Avensis became the first vehicle sold in Europe equipped with a driver's knee airbag. The
The Toyota Caldina introduced the first driver-side SRS knee airbag on the Japanese market in 2002. Toyota Avensis became the first vehicle sold in Europe equipped with a driver's knee airbag. The  The airbags in the vehicle are controlled by a central airbag control unit (ACU), a specific type of ECU. The ACU monitors a number of related sensors within the vehicle, including accelerometers, impact sensors, side (door) pressure sensors, wheel speed sensors,
The airbags in the vehicle are controlled by a central airbag control unit (ACU), a specific type of ECU. The ACU monitors a number of related sensors within the vehicle, including accelerometers, impact sensors, side (door) pressure sensors, wheel speed sensors, 
 The
The