aftermath of the First World War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The aftermath of World War I saw drastic political, cultural, economic, and social change across Eurasia,
 Historians continue to argue about the impact the
Historians continue to argue about the impact the
 A
A
 The Soviet Union benefited from Germany's loss, as one of the first terms of the armistice was the abrogation of the
The Soviet Union benefited from Germany's loss, as one of the first terms of the armistice was the abrogation of the
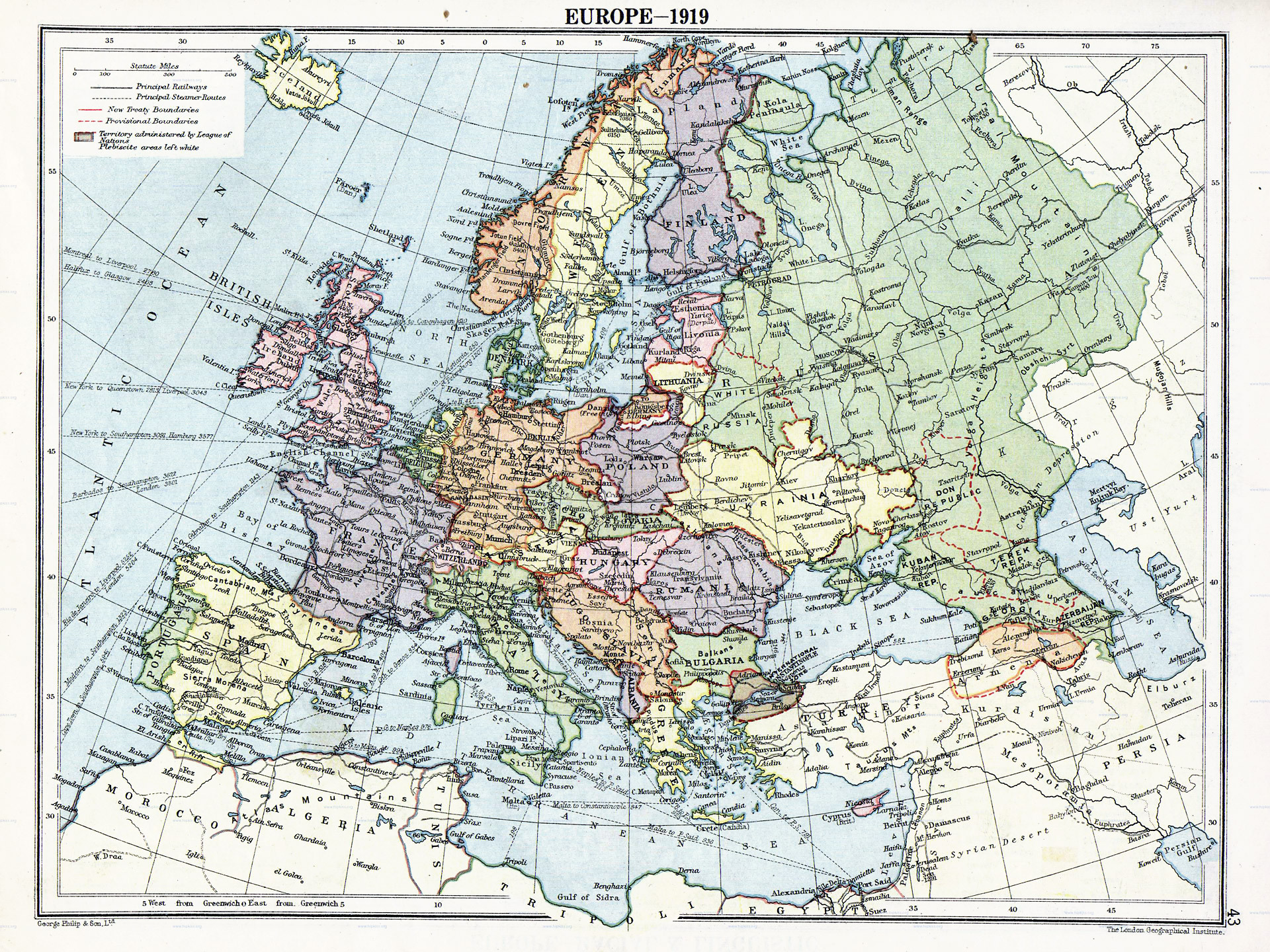
 The Western forces were officially supposed to occupy the old Empire, but rarely had enough troops to do so effectively. They had to deal with local authorities who had their own agenda to fulfill. At the peace conference in Paris the diplomats had to reconcile these authorities with the competing demands of the nationalists who had turned to them for help during the war, the strategic or political desires of the Western allies themselves, and other agendas such as a desire to implement the spirit of the Fourteen Points.
For example, in order to live up to the ideal of self-determination laid out in the Fourteen Points, Germans, whether Austrian or German, should be able to decide their own future and government. However, the French especially were concerned that an expanded Germany would be a huge security risk. Further complicating the situation, delegations such as the Czechs and Slovenians made strong claims on some German-speaking territories.
The result was treaties that compromised many ideals, offended many allies, and set up an entirely new order in the area. Many people hoped that the new nation states would allow for a new era of prosperity and peace in the region, free from the bitter quarrelling between nationalities that had marked the preceding fifty years. This hope proved far too optimistic. Changes in territorial configuration after World War I included:
* Establishment of the
The Western forces were officially supposed to occupy the old Empire, but rarely had enough troops to do so effectively. They had to deal with local authorities who had their own agenda to fulfill. At the peace conference in Paris the diplomats had to reconcile these authorities with the competing demands of the nationalists who had turned to them for help during the war, the strategic or political desires of the Western allies themselves, and other agendas such as a desire to implement the spirit of the Fourteen Points.
For example, in order to live up to the ideal of self-determination laid out in the Fourteen Points, Germans, whether Austrian or German, should be able to decide their own future and government. However, the French especially were concerned that an expanded Germany would be a huge security risk. Further complicating the situation, delegations such as the Czechs and Slovenians made strong claims on some German-speaking territories.
The result was treaties that compromised many ideals, offended many allies, and set up an entirely new order in the area. Many people hoped that the new nation states would allow for a new era of prosperity and peace in the region, free from the bitter quarrelling between nationalities that had marked the preceding fifty years. This hope proved far too optimistic. Changes in territorial configuration after World War I included:
* Establishment of the  *
*
 At the end of the war, the Allies occupied Constantinople ( Istanbul) and the Ottoman government collapsed. The Treaty of Sèvres, designed to repair damage caused by Ottomans during the war to the winning Allies, was signed by Ottoman Empire on 10 August 1920, but was never ratified by the Sultan.
The
At the end of the war, the Allies occupied Constantinople ( Istanbul) and the Ottoman government collapsed. The Treaty of Sèvres, designed to repair damage caused by Ottomans during the war to the winning Allies, was signed by Ottoman Empire on 10 August 1920, but was never ratified by the Sultan.
The
 In the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, funding the war had a severe economic cost. From being the world's largest overseas investor, it became one of its biggest debtors with interest payments forming around 40% of all government spending. Inflation more than doubled between 1914 and its peak in 1920, while the value of the Pound Sterling (consumer expenditure) fell by 61.2%. War reparations in the form of free German coal depressed local industry, precipitating the
In the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, funding the war had a severe economic cost. From being the world's largest overseas investor, it became one of its biggest debtors with interest payments forming around 40% of all government spending. Inflation more than doubled between 1914 and its peak in 1920, while the value of the Pound Sterling (consumer expenditure) fell by 61.2%. War reparations in the form of free German coal depressed local industry, precipitating the  In Ireland, the delaying of the
In Ireland, the delaying of the
 Alsace-Lorraine returned to France, the region which had been ceded to the Kingdom of Prussia in 1871 after the Franco-Prussian War. At the 1919 Peace Conference, Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau's aim was to ensure that Germany would not seek revenge in the following years. To this purpose, the chief commander of the Allied forces, Marshal Ferdinand Foch, had demanded that for the future protection of France the Rhine river should now form the border between France and Germany. Based on history, he was convinced that Germany would again become a threat, and, on hearing the terms of the Treaty of Versailles that had left Germany substantially intact, he observed that "This is not Peace. It is an Armistice for twenty years."
The destruction brought upon French territory was to be indemnified by the
Alsace-Lorraine returned to France, the region which had been ceded to the Kingdom of Prussia in 1871 after the Franco-Prussian War. At the 1919 Peace Conference, Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau's aim was to ensure that Germany would not seek revenge in the following years. To this purpose, the chief commander of the Allied forces, Marshal Ferdinand Foch, had demanded that for the future protection of France the Rhine river should now form the border between France and Germany. Based on history, he was convinced that Germany would again become a threat, and, on hearing the terms of the Treaty of Versailles that had left Germany substantially intact, he observed that "This is not Peace. It is an Armistice for twenty years."
The destruction brought upon French territory was to be indemnified by the
 In 1882 Italy joined with the
In 1882 Italy joined with the

 Many towns in the participating countries have war memorials dedicated to local residents who lost their lives. Examples include:
* Australian War Memorial, Canberra, Australia
* Liberty Memorial, Kansas City, Missouri, United States
* Memorial for The Battle of Jutland, Thyborøn, Jutland, Denmark
* District of Columbia War Memorial, Washington, DC, United States
* Beaumont-Hamel Newfoundland Memorial
* Cenotaph#The Cenotaph, London, The Cenotaph, London, United Kingdom
* Menin Gate Memorial, Ypres, Belgium
* Thiepval Memorial
* Tyne Cot Cemetery, Tyne Cot Memorial to the Missing at Passendale, Passchendaele
* Verdun, Verdun Memorial Museum
* Vimy Memorial, Vimy Ridge Memorial, Vimy, France
* Gallipoli Memorial, Turkey
* Shrine of Remembrance, Melbourne, Australia
* Irish National War Memorial Gardens, Dublin, Ireland
* Island of Ireland Peace Park, Mesen, Messines, Belgium
* National War Memorial (Canada), National War Memorial, Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
* National War Memorial (Newfoundland), National War Memorial, St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, Newfoundland, Canada
* Kriegerdenkmal auf dem Neroberg, Wiesbaden, Hessen, Germany
* Fogliano Redipuglia#World War I memorial, Sacrario militare di Redipuglia, Fogliano Redipuglia, Italy
* Mausoleum of Mărășești, Romania
Many towns in the participating countries have war memorials dedicated to local residents who lost their lives. Examples include:
* Australian War Memorial, Canberra, Australia
* Liberty Memorial, Kansas City, Missouri, United States
* Memorial for The Battle of Jutland, Thyborøn, Jutland, Denmark
* District of Columbia War Memorial, Washington, DC, United States
* Beaumont-Hamel Newfoundland Memorial
* Cenotaph#The Cenotaph, London, The Cenotaph, London, United Kingdom
* Menin Gate Memorial, Ypres, Belgium
* Thiepval Memorial
* Tyne Cot Cemetery, Tyne Cot Memorial to the Missing at Passendale, Passchendaele
* Verdun, Verdun Memorial Museum
* Vimy Memorial, Vimy Ridge Memorial, Vimy, France
* Gallipoli Memorial, Turkey
* Shrine of Remembrance, Melbourne, Australia
* Irish National War Memorial Gardens, Dublin, Ireland
* Island of Ireland Peace Park, Mesen, Messines, Belgium
* National War Memorial (Canada), National War Memorial, Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
* National War Memorial (Newfoundland), National War Memorial, St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, Newfoundland, Canada
* Kriegerdenkmal auf dem Neroberg, Wiesbaden, Hessen, Germany
* Fogliano Redipuglia#World War I memorial, Sacrario militare di Redipuglia, Fogliano Redipuglia, Italy
* Mausoleum of Mărășești, Romania
free download
full coverage for major countries. * Gerwarth, Robert. "The central European counter-revolution: Paramilitary violence in Germany, Austria and Hungary after the great war." ''Past & Present'' 200.1 (2008): 175-209
online
*Margaret MacMillan, MacMillan, Margaret. ''Peacemakers: The Paris Peace Conference of 1919 and Its Attempt to End War'' (2001) * Kallis, Aristotle. "When fascism became mainstream: the challenge of extremism in times of crisis." ''Fascism'' 4.1 (2015): 1–24. * Mazower, Mark. ''Dark continent: Europe's twentieth century'' (2009). * Mowat, C.L. ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History, Vol. 12: The Shifting Balance of World Forces, 1898–1945'' (1968
online
25 chapters; 845pp *Overy, R. J. ''The Inter-War Crisis'' (2nd ed. 2016
excerpt
* Somervell, D.C. ''The Reign of King George V'' (1936
online
550pp; wide ranging political, social and economic coverage of Britain, 1910–35 * John Wheeler-Bennett ''The Wreck of Reparations, being the political background of the Lausanne Agreement, 1932'' New York, H. Fertig, 1972.
Post-war
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
*Kitchen, James E.
Colonial Empires after the War/Decolonization
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
*Bessel, Richard
Post-war Societies
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
*Rothermund, Dietmar
Post-war Economies
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
*Sharp, Alan
The Paris Peace Conference and its Consequences
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
FirstWorldWar.com
"A multimedia history of World War I"
The war to end all wars on BBC site
"The Heritage of the Great War"
The British Army in the Great War
{{authority control Aftermath of World War I, Interwar period, Aftermath
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, and even in areas outside those that were directly involved. Four empires collapsed due to the war, old countries were abolished, new ones were formed, boundaries were redrawn, international organizations were established, and many new and old ideologies took a firm hold in people's minds. World War I also had the effect of bringing political transformation to most of the principal parties involved in the conflict, transforming them into electoral democracies by bringing near- universal suffrage for the first time in history, as in Germany (1919 German federal election
Federal elections were held in Germany on 19 January 1919,Dieter Nohlen & Philip Stöver (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook'', p762 although members of the standing army in the east did not vote until 2 February. The elections were t ...
), Great Britain (1918 United Kingdom general election
The 1918 United Kingdom general election was called immediately after the Armistice with Germany which ended the First World War, and was held on Saturday, 14 December 1918. The governing coalition, under Prime Minister David Lloyd George, sent ...
), and Turkey (1923 Turkish general election
General elections were held in Turkey in 1923.Myron E. Weiner, Ergun Özbudun (1987) ''Competitive Elections in Developing Countries'', Duke University Press, p337 The Association for Defence of National Rights (later Republican People's Party) ...
).
Blockade of Germany
Through the period from theArmistice of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices ...
until the signing of the Treaty of Versailles with the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is al ...
on 28 June 1919, the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
maintained the naval blockade of Germany that had begun during the war. As the German economy
The economy of Germany is a highly developed social market economy. It has the largest national economy in Europe, the fourth-largest by nominal GDP in the world, and fifth by GDP (PPP). In 2017, the country accounted for 28% of the euro ...
was dependent on imports, it is estimated that 523,000 civilians had lost their lives. N. P. Howard, of the University of Sheffield
, mottoeng = To discover the causes of things
, established = – University of SheffieldPredecessor institutions:
– Sheffield Medical School – Firth College – Sheffield Technical School – University College of Sheffield
, type = P ...
, says that a further quarter of a million more died from disease or starvation in the eight-month period following the conclusion of the conflict. The continuation of the blockade after the fighting ended, as author Robert Leckie wrote in '' Delivered From Evil'', did much to "torment the Germans ... driving them with the fury of despair into the arms of the devil." The terms of the Armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from the L ...
did allow food to be shipped into Germany, but the Allies required that Germany provide the means (the shipping) to do so. The German government was required to use its gold reserves, being unable to secure a loan from the United States.
Historian Sally Marks claims that while "Allied warships remained in place against a possible resumption of hostilities, the Allies offered food and medicine after the armistice, but Germany refused to allow its ships to carry supplies". Further, Marks states that despite the problems facing the Allies, from the German government, "Allied food shipments arrived in Allied ships before the charge made at Versailles". This position is also supported by Elisabeth Gläser who notes that an Allied task force, to help feed the German population, was established in early 1919 and that by May 1919 " Germany adbecame the chief recipient of American and Allied food shipments". Gläser further claims that during the early months of 1919, while the main relief effort was being planned, France provided food shipments to Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
and the Rhineland. She further claims that the German government delayed the relief effort by refusing to surrender their merchant fleet to the Allies. Finally, she concludes that "the very success of the relief effort had in effect deprived the lliesof a credible threat to induce Germany to sign the Treaty of Versailles. However, it is also the case that for eight months following the end of hostilities, the blockade was continually in place, with some estimates that a further 100,000 casualties among German civilians due to starvation were caused, on top of the hundreds of thousands which already had occurred. Food shipments, furthermore, had been entirely dependent on Allied goodwill, causing at least in part the post-hostilities irregularity.
Paris Peace Conference
After the Paris Peace Conference of 1919, the signing of the Treaty of Versailles on 28 June 1919, between Germany on the one side and France, Italy, Britain and other minor allied powers on the other, officially ended war between those countries. Other treaties ended the relationships of the United States and the other Central Powers. Included in the 440 articles of the Treaty of Versailles were the demands that Germany officially accept responsibility "for causing all the loss and damage" of the war and pay economic reparations. The treaty drastically limited the German military machine: German troops were reduced to 100,000 and the country was prevented from possessing major military armaments such as tanks, warships, armored vehicles and submarines.Influenza epidemic
 Historians continue to argue about the impact the
Historians continue to argue about the impact the 1918 flu pandemic
The 1918–1920 influenza pandemic, commonly known by the misnomer Spanish flu or as the Great Influenza epidemic, was an exceptionally deadly global influenza pandemic caused by the H1N1 influenza A virus. The earliest documented case was ...
had on the outcome of the war. It has been posited that the Central Powers may have been exposed to the viral wave before the Allies. The resulting casualties having greater effect, having been incurred during the war, as opposed to the allies who suffered the brunt of the pandemic after the Armistice. When the extent of the epidemic was realized, the respective censorship programs of the Allies and Central Powers limited the public's knowledge regarding the true extent of the disease. Because Spain was neutral, their media was free to report on the Flu, giving the impression that it began there. This misunderstanding led to contemporary reports naming it the " Spanish flu." Investigative work by a British team led by virologist John Oxford of St Bartholomew's Hospital
St Bartholomew's Hospital, commonly known as Barts, is a teaching hospital located in the City of London. It was founded in 1123 and is currently run by Barts Health NHS Trust.
History
Early history
Barts was founded in 1123 by Rahere (died ...
and the Royal London Hospital, identified a major troop staging and hospital camp in Étaples, France as almost certainly being the center of the 1918 flu pandemic. A significant precursor virus was harbored in birds, and mutated to pigs that were kept near the front. The exact number of deaths is unknown but about 50 million people are estimated to have died from the influenza outbreak worldwide. In 2005, a study found that, "The 1918 virus strain developed in birds and was similar to the 'bird flu' that in the 21st century spurred fears of another worldwide pandemic, yet proved to be a normal treatable virus that did not produce a heavy impact on the world's health."
Ethnic minorities
The dissolution of the German, Russian, Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman empires created a number of new countries inCentral and Eastern Europe
Central and Eastern Europe is a term encompassing the countries in the Baltics, Central Europe, Eastern Europe and Southeast Europe (mostly the Balkans), usually meaning former communist states from the Eastern Bloc and Warsaw Pact in Europe ...
and the Middle East. Some of them, such as Czechoslovakia and Poland, had substantial ethnic minorities who were sometimes not fully satisfied with the new boundaries that cut them off from fellow ethnics. For example, Czechoslovakia had Germans, Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Cen ...
, Ruthenians and Ukrainians, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 mi ...
and Hungarians. The League of Nations sponsored various Minority Treaties in an attempt to deal with the problem, but with the decline of the League in the 1930s, these treaties became increasingly unenforceable. One consequence of the massive redrawing of borders and the political changes in the aftermath of the war was the large number of European refugees. These and the refugees of the Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East th ...
led to the creation of the Nansen passport
Nansen passports, originally and officially stateless persons passports, were internationally recognized refugee travel documents from 1922 to 1938, first issued by the League of Nations's Office of the High Commissioner for Refugees to stateles ...
.
Ethnic minorities made the location of the frontiers generally unstable. Where the frontiers have remained unchanged since 1918, there has often been the expulsion of an ethnic group, such as the Sudeten Germans. Economic and military cooperation amongst these small states was minimal, ensuring that the defeated powers of Germany and the Soviet Union retained a latent capacity to dominate the region. In the immediate aftermath of the war, defeat drove cooperation between Germany and the Soviet Union but ultimately these two powers would compete to dominate eastern Europe.
Approximately 1.5 million Armenians, native inhabitants of the Armenian Highland, were exterminated in Turkey as a consequence of the Genocide of Armenians committed by the Young Turk Government.
Political upheavals
New nations break free
German and Austrian forces in 1918 defeated the Russian armies, and the new communist government in Moscow signed theTreaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
in March 1918. In that treaty, Russia renounced all claims to Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Ukraine, and the territory of Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It w ...
, and it was left to Germany and Austria-Hungary "to determine the future status of these territories in agreement with their population." Later on, Vladimir Lenin's government also renounced the Partition of Poland treaty, making it possible for Poland to claim its 1772 borders. However, the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was rendered obsolete when Germany was defeated later in 1918, leaving the status of much of eastern Europe in an uncertain position.
Revolutions
 A
A far-left
Far-left politics, also known as the radical left or the extreme left, are politics further to the left on the left–right political spectrum than the standard political left. The term does not have a single definition. Some scholars conside ...
and often explicitly Communist revolutionary wave
A revolutionary wave or revolutionary decade is one series of revolutions occurring in various locations within a similar time-span. In many cases, past revolutions and revolutionary waves have inspired current ones, or an initial revolution has ...
occurred in several European countries in 1917–1920, notably in Germany and Hungary. The single most important event precipitated by the privations of World War I was the Russian Revolution of 1917.
Germany
In Germany, there was a socialist revolution which led to the brief establishment of a number of communist political systems in (mainly urban) parts of the country, the abdication of Kaiser Wilhelm II, and the creation of theWeimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is al ...
.
On 28 June 1919 the Weimar Republic was forced, under threat of continued Allied advance, to sign the Treaty of Versailles. Germany viewed the one-sided treaty as a humiliation and as blaming it for the entire war. While the intent of the treaty was to assign guilt to Germany to justify financial reparations, the notion of blame took root as a political issue in German society and was never accepted by nationalists, although it was argued by some, such as German historian Fritz Fischer. The German government disseminated propaganda to further promote this idea, and funded the Centre for the Study of the Causes of the War
The Centre for the Study of the Causes of the War (in German: Zentralstelle zur Erforschung der Kriegsursachen) was a think tank based in Berlin, funded by the German government, whose sole purpose was to disseminate the official government positio ...
to this end.
132 billion gold marks ($31.5 billion, 6.6 billion pounds) were demanded from Germany in reparations, of which only 50 billion had to be paid. In order to finance the purchases of foreign currency required to pay off the reparations, the new German republic printed tremendous amounts of money – to disastrous effect. Hyperinflation plagued Germany between 1921 and 1923. In this period the worth of fiat Papiermarks with respect to the earlier commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
The price of a co ...
Goldmarks was reduced to one trillionth (one million millionth) of its value. In December 1922 the Reparations Commission declared Germany in default, and on 11 January 1923 French and Belgian troops occupied the Ruhr until 1925.
The treaty required Germany to permanently reduce the size of its army to 100,000 men, and destroy their tanks, air force, and U-boat fleet (her capital ships, moored at Scapa Flow, were scuttled by their crews to prevent them from falling into Allied hands).
Germany saw relatively small amounts of territory transferred to Denmark, Czechoslovakia, and Belgium, a larger amount to France (including the temporary French occupation of the Rhineland) and the greatest portion as part of a reestablished Poland. Germany's overseas colonies were divided between a number of Allied countries, most notably the United Kingdom in Africa, but it was the loss of the territory that composed the newly independent Polish state, including the German city of Danzig and the separation of East Prussia from the rest of Germany, that caused the greatest outrage. Nazi propaganda would feed on a general German view that the treaty was unfair – many Germans never accepted the treaty as legitimate, and lent their political support to Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and then ...
.
Russian Empire
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
. At the time of the armistice Russia was in the grips of a civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policie ...
which left more than seven million people dead and large areas of the country devastated. The nation as a whole suffered socially and economically.
Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia gained independence. They were occupied again by the Soviet Union in 1940.
Finland gained a lasting independence, though she repeatedly had to fight the Soviet Union for her borders in the Winter War.
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
were established as independent states in the Caucasus region
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historical ...
. However, after the withdrawal of the Russian Army
The Russian Ground Forces (russian: Сухопутные войска �ВSukhoputnyye voyska V}), also known as the Russian Army (, ), are the land forces of the Russian Armed Forces.
The primary responsibilities of the Russian Ground Forces ...
in 1917 and during 1920 Turkish invasion of Armenia, Turkey captured the Armenian territory around Artvin
Artvin ( Laz and ; hy, Արտուին, translit=Artuin) is a city in northeastern Turkey about inland from the Black Sea.
It is located on a hill overlooking the Çoruh River near the Deriner Dam. It is a former bishopric and (vacant) Arme ...
, Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of K ...
, and Iğdır
Iğdır ( Turkish ; ku, Îdir or ; hy, Իգդիր, Igdir, also ) is the capital of Iğdır Province in the Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey.
History
Iğdır went by the Armenian name of Tsolakert during the Middle Ages. s.v. "Igdir," Armenia ...
, and these territorial losses became permanent. As consequence of invasions of Turkey and Russian Red Army all three Transcaucasian countries were proclaimed as Soviet Republics
The Republics of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics or the Union Republics ( rus, Сою́зные Респу́блики, r=Soyúznye Respúbliki) were national-based administrative units of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ( ...
in 1920 and in 1922 were absorbed into the Soviet Union as the Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic
, conventional_long_name = Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic
, common_name = Transcaucasian SFSR
, p1 = Armenian Soviet Socialist RepublicArmenian SSR
, flag_p1 = Flag of SSRA ...
.
Romania gained Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds o ...
from Russia.
The Russian concession of Tianjin
The Russian concession of Tianjin (Chinese: 天津俄租界, pinyin: ''Tiānjīn é zūjiè'', Russian: Российская концессия Тяньцзиня) was a territory ( concession) in the Chinese city of Tientsin occupied colonially by ...
was occupied by the Chinese Beiyang government
The Beiyang government (), officially the Republic of China (), sometimes spelled Peiyang Government, refers to the government of the Republic of China which sat in its capital Peking (Beijing) between 1912 and 1928. It was internationally ...
in 1920; in 1924 the Soviet Union renounced its claims to the district.
Austria-Hungary
With the war having turned decisively against theCentral Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
, the people of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1 ...
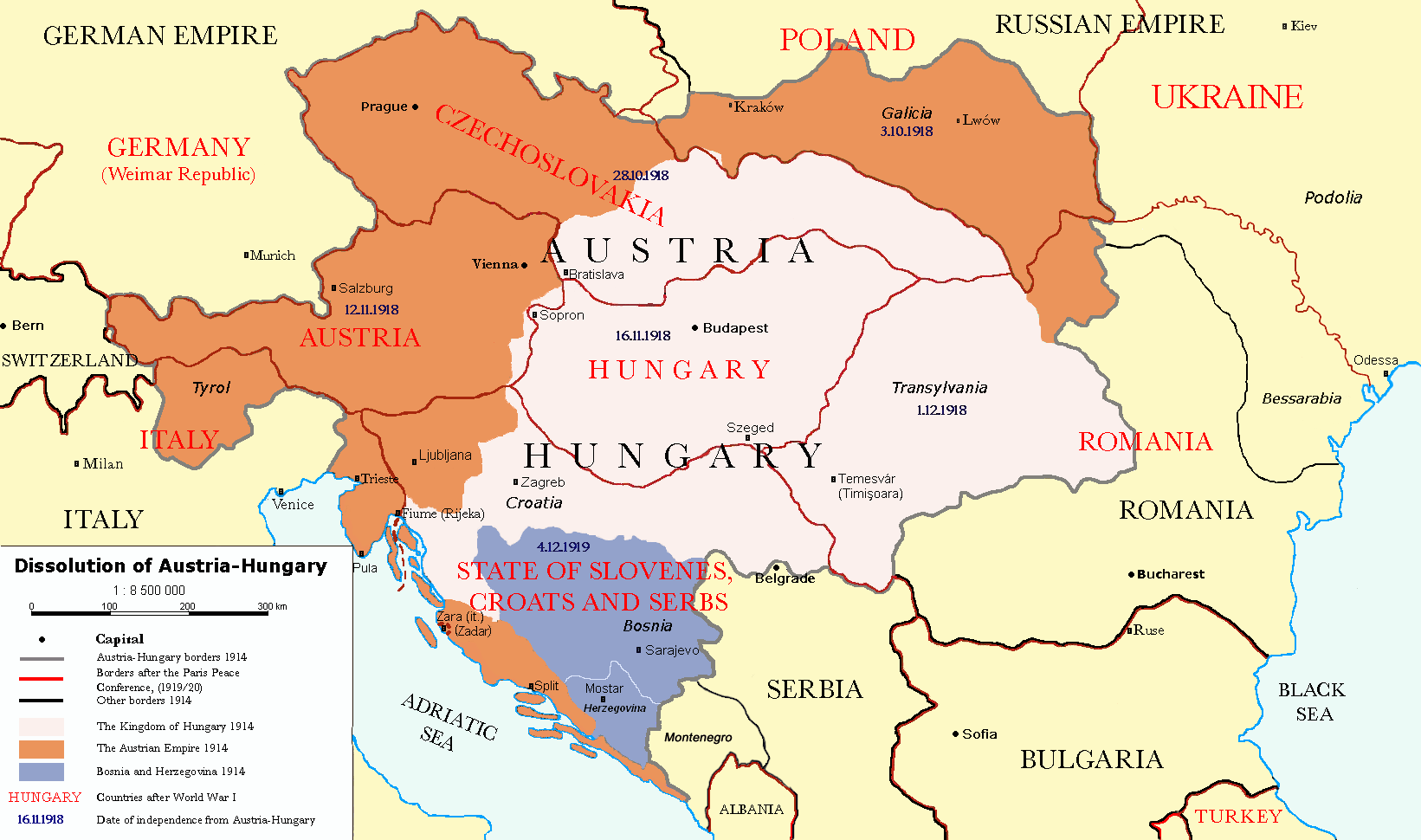
lost faith in their allied countries, and even before the armistice in November, radical nationalism had already led to several declarations of independence in south-central Europe after November 1918. As the central government had ceased to operate in vast areas, these regions found themselves without a government and many new groups attempted to fill the void. During this same period, the population was facing food shortages and was, for the most part, demoralized by the losses incurred during the war. Various political parties, ranging from ardent nationalists, to social democrats, to communists attempted to set up governments in the names of the different nationalities. In other areas, existing nation states such as Romania engaged regions that they considered to be theirs. These moves created de facto governments that complicated life for diplomats, idealists, and the Western allies.
 The Western forces were officially supposed to occupy the old Empire, but rarely had enough troops to do so effectively. They had to deal with local authorities who had their own agenda to fulfill. At the peace conference in Paris the diplomats had to reconcile these authorities with the competing demands of the nationalists who had turned to them for help during the war, the strategic or political desires of the Western allies themselves, and other agendas such as a desire to implement the spirit of the Fourteen Points.
For example, in order to live up to the ideal of self-determination laid out in the Fourteen Points, Germans, whether Austrian or German, should be able to decide their own future and government. However, the French especially were concerned that an expanded Germany would be a huge security risk. Further complicating the situation, delegations such as the Czechs and Slovenians made strong claims on some German-speaking territories.
The result was treaties that compromised many ideals, offended many allies, and set up an entirely new order in the area. Many people hoped that the new nation states would allow for a new era of prosperity and peace in the region, free from the bitter quarrelling between nationalities that had marked the preceding fifty years. This hope proved far too optimistic. Changes in territorial configuration after World War I included:
* Establishment of the
The Western forces were officially supposed to occupy the old Empire, but rarely had enough troops to do so effectively. They had to deal with local authorities who had their own agenda to fulfill. At the peace conference in Paris the diplomats had to reconcile these authorities with the competing demands of the nationalists who had turned to them for help during the war, the strategic or political desires of the Western allies themselves, and other agendas such as a desire to implement the spirit of the Fourteen Points.
For example, in order to live up to the ideal of self-determination laid out in the Fourteen Points, Germans, whether Austrian or German, should be able to decide their own future and government. However, the French especially were concerned that an expanded Germany would be a huge security risk. Further complicating the situation, delegations such as the Czechs and Slovenians made strong claims on some German-speaking territories.
The result was treaties that compromised many ideals, offended many allies, and set up an entirely new order in the area. Many people hoped that the new nation states would allow for a new era of prosperity and peace in the region, free from the bitter quarrelling between nationalities that had marked the preceding fifty years. This hope proved far too optimistic. Changes in territorial configuration after World War I included:
* Establishment of the Republic of German Austria
The Republic of German-Austria (german: Republik Deutschösterreich or ) was an unrecognised state that was created following World War I as an initial rump state for areas with a predominantly German-speaking and ethnic German population w ...
and the Hungarian Democratic Republic
The First Hungarian Republic ( hu, Első Magyar Köztársaság), until 21 March 1919 the Hungarian People's Republic (), was a short-lived unrecognized country, which quickly transformed into a small rump state due to the foreign and military p ...
, disavowing any continuity with the empire and exiling the Habsburg family in perpetuity.
* Eventually, after 1920, the new borders of Hungary did not include approx. two-thirds of the lands of the former Kingdom of Hungary, including areas where the ethnic Magyars were in a majority. The new republic of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous c ...
maintained control over most of the predominantly German-controlled areas, but lost various other German majority lands in what was the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
.
 *
* Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohe ...
, Moravia, Opava Silesia and the western part of the Duchy of Cieszyn
The Duchy of Teschen (german: Herzogtum Teschen), also Duchy of Cieszyn ( pl, Księstwo Cieszyńskie) or Duchy of Těšín ( cs, Těšínské knížectví), was one of the Duchies of Silesia centered on Cieszyn () in Upper Silesia. It was split o ...
, large part of Upper Hungary and Carpathian Ruthenia formed the new Czechoslovakia.
* Galicia, the eastern part of the Duchy of Cieszyn
The Duchy of Teschen (german: Herzogtum Teschen), also Duchy of Cieszyn ( pl, Księstwo Cieszyńskie) or Duchy of Těšín ( cs, Těšínské knížectví), was one of the Duchies of Silesia centered on Cieszyn () in Upper Silesia. It was split o ...
, northern Árva County
Árva County ( hu, Árva vármegye, la, Comitatus Arvensis, sk, Oravská stolica/župa, german: Komitat Arwa, pl, Komitat Orawa) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary since the 14th century until 1920. Its territor ...
and northern Szepes County
Szepes ( sk, Spiš; la, Scepusium, pl, Spisz, german: link=no, Zips) was an administrative county of the Kingdom of Hungary, called Scepusium before the late 19th century. Its territory today lies in northeastern Slovakia, with a very small are ...
were transferred to Poland.
* the Southern half of the County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised ...
and Trieste were granted to Italy.
* Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
, Croatia-Slavonia
The Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia ( hr, Kraljevina Hrvatska i Slavonija; hu, Horvát-Szlavónország or ; de-AT, Königreich Kroatien und Slawonien) was a nominally autonomous kingdom and constitutionally defined separate political nation with ...
, Međimurje, Dalmatia, Slovenia, Syrmia, parts of Bács-Bodrog, Baranya, Torontál and Temes Counties were joined with Serbia to form the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
, later Yugoslavia.
* Transylvania, parts of Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of ...
, Crișana
Crișana ( hu, Körösvidék, german: Kreischgebiet) is a geographical and historical region in north-western Romania, named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Ro ...
, and Maramureș and Bukovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter Berge ...
became part of Romania.
* The Austro-Hungarian concession in Tianjin was ceded to the Republic of China.
These changes were recognized in, but not caused by, the Treaty of Versailles. They were subsequently further elaborated in the Treaty of Saint-Germain and the Treaty of Trianon.
The 1919 treaties generally included guarantees of minority rights, but there was no enforcement mechanism. The new states of eastern Europe mostly all had large ethnic minorities. Millions of Germans found themselves in the newly created countries as minorities. More than two million ethnic Hungarians found themselves living outside of Hungary in Czechoslovakia, Romania and the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. Many of these national minorities found themselves in hostile situations because the modern governments were intent on defining the national character of the countries, often at the expense of the other nationalities. The interwar years
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relative ...
were hard for religious minorities in the new states built around ethnic nationalism. The Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
s were especially distrusted because of their minority religion and distinct subculture. This was a dramatic come-down from the days of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Although antisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
had been widespread during Habsburg rule, Jews faced no official discrimination because they were, for the most part, ardent supporters of the multi-national state and the monarchy.
The economic disruption of the war and the end of the Austro-Hungarian customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set up ...
created great hardship in many areas. Although many states were set up as democracies after the war, one by one, with the exception of Czechoslovakia, they reverted to some form of authoritarian rule. Many quarreled amongst themselves but were too weak to compete effectively. Later, when Germany rearmed, the nation states of south-central Europe were unable to resist its attacks, and fell under German domination to a much greater extent than had ever existed in Austria-Hungary.
Ottoman Empire
occupation of Smyrna
The city of Smyrna (modern-day İzmir) and surrounding areas were under Greek military occupation from 15 May 1919 until 9 September 1922. The Allied Powers authorized the occupation and creation of the Zone of Smyrna ( el, Ζώνη Σμύρ� ...
by Greece on 18 May 1919 triggered a nationalist movement
The Nationalist Movement is a Mississippi-founded white nationalist organization with headquarters in Georgia that advocates what it calls a "pro-majority" position. It has been called white supremacist by the Associated Press and Anti-Defamati ...
to rescind the terms of the treaty. Turkish revolutionaries
The Turkish National Movement ( tr, Türk Ulusal Hareketi) encompasses the political and military activities of the Turkish revolutionaries that resulted in the creation and shaping of the modern Republic of Turkey, as a consequence of the def ...
led by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, a successful Ottoman commander, rejected the terms enforced at Sèvres and under the guise of General Inspector of the Ottoman Army, left Istanbul for Samsun
Samsun, historically known as Sampsounta ( gr, Σαμψούντα) and Amisos ( Ancient Greek: Αμισός), is a city on the north coast of Turkey and is a major Black Sea port. In 2021, Samsun recorded a population of 710,000 people. The ci ...
to organize the remaining Ottoman forces to resist the terms of the treaty. On the eastern front, after the invasion of Armenia in 1920 and signing of the Treaty of Kars
The Treaty of Kars ( tr, Kars Antlaşması, rus, Карсский договор, Karskii dogovor, ka, ყარსის ხელშეკრულება, hy, Կարսի պայմանագիր, az, Qars müqaviləsi) was a treaty that est ...
with the Russian S.F.S.R. Turkey took over territory lost to Armenia and post-Imperial Russia.
On the western front, the growing strength of the Turkish National Movement forces led the Kingdom of Greece, with the backing of Britain, to invade deep into Anatolia in an attempt to deal a blow to the revolutionaries. At the Battle of Dumlupınar
The Battle of Dumlupınar ( el, Μάχη του Τουμλού Μπουνάρ, translit=Máchi tou Toumloú Bounár, tr, Dumlupınar (Meydan) Muharebesi, lit=Dumlupınar (Field) Battle), or known as Field Battle of the Commander-in-Chief ( t ...
, the Greek army was defeated and forced into retreat, leading to the burning of Smyrna and the withdrawal of Greece from Asia Minor. With the nationalists empowered, the army marched on to reclaim Istanbul, resulting in the Chanak Crisis
The Chanak Crisis ( tr, Çanakkale Krizi), also called the Chanak Affair and the Chanak Incident, was a war scare in September 1922 between the United Kingdom and the Government of the Grand National Assembly in Turkey. ''Chanak'' refers to Ça ...
in which the British Prime Minister, David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor, (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. He was a Liberal Party politician from Wales, known for leading the United Kingdom during ...
, was forced to resign. After Turkish resistance gained control over Anatolia and Istanbul, the Sèvres treaty was superseded by the Treaty of Lausanne
The Treaty of Lausanne (french: Traité de Lausanne) was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. The treaty officially settled the confl ...
which formally ended all hostilities and led to the creation of the modern Turkish Republic. As a result, Turkey became the only power of World War I to overturn the terms of its defeat, and negotiate with the Allies as an equal.
Lausanne Treaty formally acknowledged the new League of Nations mandates in the Middle East, the cession of their territories on the Arabian Peninsula, and British sovereignty over Cyprus. The League of Nations granted ''Class A'' mandates for the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (french: Mandat pour la Syrie et le Liban; ar, الانتداب الفرنسي على سوريا ولبنان, al-intidāb al-fransi 'ala suriya wa-lubnān) (1923−1946) was a League of Nations mandate foun ...
and British Mandate of Mesopotamia
The Mandate for Mesopotamia ( ar, الانتداب البريطاني على العراق) was a proposed League of Nations mandate to cover Ottoman Iraq (Mesopotamia). It would have been entrusted to the United Kingdom but was superseded by th ...
and Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East J ...
, the latter comprising two autonomous regions: Mandate Palestine and the Emirate of Transjordan
The Emirate of Transjordan ( ar, إمارة شرق الأردن, Imārat Sharq al-Urdun, Emirate of East Jordan), officially known as the Amirate of Trans-Jordan, was a British protectorate established on 11 April 1921,
. Parts of the Ottoman Empire on the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
became part of what is today Saudi Arabia and Yemen. The dissolution of the Ottoman Empire became a pivotal milestone in the creation of the modern Middle East, the result of which bore witness to the creation of new conflicts and hostilities in the region.
United Kingdom
 In the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, funding the war had a severe economic cost. From being the world's largest overseas investor, it became one of its biggest debtors with interest payments forming around 40% of all government spending. Inflation more than doubled between 1914 and its peak in 1920, while the value of the Pound Sterling (consumer expenditure) fell by 61.2%. War reparations in the form of free German coal depressed local industry, precipitating the
In the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, funding the war had a severe economic cost. From being the world's largest overseas investor, it became one of its biggest debtors with interest payments forming around 40% of all government spending. Inflation more than doubled between 1914 and its peak in 1920, while the value of the Pound Sterling (consumer expenditure) fell by 61.2%. War reparations in the form of free German coal depressed local industry, precipitating the 1926 United Kingdom general strike
The 1926 general strike in the United Kingdom was a general strike that lasted nine days, from 4 to 12 May 1926. It was called by the General Council of the Trades Union Congress (TUC) in an unsuccessful attempt to force the Government of the ...
.
British private investments abroad were sold, raising £550 million. However, £250 million in new investment also took place during the war. The net financial loss was therefore approximately £300 million; less than two years investment compared to the pre-war average rate and more than replaced by 1928. Material loss was "slight": the most significant being 40% of the British Merchant Navy
The Merchant Navy is the maritime register of the United Kingdom and comprises the seagoing commercial interests of UK-registered ships and their crews. Merchant Navy vessels fly the Red Ensign and are regulated by the Maritime and Coastguard ...
sunk by German U-boats. Most of this was replaced in 1918 and all immediately after the war. The military historian Correlli Barnett
Correlli Douglas Barnett CBE FRHistS FRSL FRSA (28 June 1927 – 10 July 2022) was an English military historian, who also wrote works of economic history, particularly on the United Kingdom's post-war " industrial decline".
Early life
Barnett ...
has argued that "in objective truth the Great War in no way inflicted crippling economic damage on Britain" but that the war "crippled the British ''psychologically'' but in no other way".
Less concrete changes include the growing assertiveness of Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
nations. Battles such as Gallipoli
The Gallipoli peninsula (; tr, Gelibolu Yarımadası; grc, Χερσόνησος της Καλλίπολης, ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the European part of Turkey, with the Aegean Sea to the west and the Dardanelles s ...
for Australia and New Zealand, and Vimy Ridge
The Battle of Vimy Ridge was part of the Battle of Arras, in the Pas-de-Calais department of France, during the First World War. The main combatants were the four divisions of the Canadian Corps in the First Army, against three divisions of ...
for Canada led to increased national pride and a greater reluctance to remain subordinate to Britain, leading to the growth of diplomatic autonomy in the 1920s. These battles were often decorated in propaganda in these nations as symbolic of their power during the war. Overseas possessions such as British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
and Nigeria also became increasingly assertive, because of their participation in the war. The populations in these countries became increasingly aware of their own power and Britain's fragility.
 In Ireland, the delaying of the
In Ireland, the delaying of the Government of Ireland Act 1914
The Government of Ireland Act 1914 (4 & 5 Geo. 5 c. 90), also known as the Home Rule Act, and before enactment as the Third Home Rule Bill, was an Act passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom intended to provide home rule (self-govern ...
, which was enacted to resolve the Home Rule issue, later exacerbated by the Government's severe response to the 1916 Easter Rising and its failed attempt to introduce conscription in Ireland in 1918, led to an increased support for separatist radicals. This led indirectly to the outbreak of the Irish War of Independence in 1919. The creation of the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between the ...
that followed this conflict in effect represented a territorial loss for the United Kingdom that was all but equal to the loss sustained by Germany, and furthermore, compared to Germany, a much greater loss in terms of its ratio to the country's prewar territory. However, the new Irish Free State remained a dominion within the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
.
World War I also caused a major realignment in British parliamentary politics by leading to the rise of the democratic socialist
Democratic socialism is a left-wing political philosophy that supports political democracy and some form of a socially owned economy, with a particular emphasis on economic democracy, workplace democracy, and workers' self-management within ...
Labour Party and to the break-up and decline of the social liberal Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world. The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left.
__TOC__ Active liberal parties
This is a li ...
. Liberal Prime Minister H. H. Asquith
Herbert Henry Asquith, 1st Earl of Oxford and Asquith, (12 September 1852 – 15 February 1928), generally known as H. H. Asquith, was a British statesman and Liberal Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom ...
ran into disagreements with not only the Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
opposition but members of his own party led by David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor, (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. He was a Liberal Party politician from Wales, known for leading the United Kingdom during ...
who disagreed with his handling of the war. Although Asquith agreed to form a coalition government, the disputes continued and eventually Lloyd George led a faction of the Liberals to form a new coalition government
A coalition government is a form of government in which political parties cooperate to form a government. The usual reason for such an arrangement is that no single party has achieved an absolute majority after an election, an atypical outcome in ...
with the cooperation of the Conservatives. During the 1918 "coupon" election Conservatives and Liberals endorsed by the Coalition won a landslide majority in the British Parliament. However, the split between Lloyd George's National Liberals and Asquith's Independent Liberals fatally weakened the party. On the other hand, the Labour Party remained unified despite tensions between pacifist and pro-war leaders, used the war to expand the British trade union movement, and benefitted from the establishment of universal suffrage under the Representation of the People Act 1918. As a result both Liberal factions performed poorly in the 1922 general election while Labour became the Official Opposition for the first time. The Liberals reluctantly collaborated with Labour to help it form a brief minority government
A minority government, minority cabinet, minority administration, or a minority parliament is a government and cabinet formed in a parliamentary system when a political party or coalition of parties does not have a majority of overall seats in ...
under Ramsay MacDonald. The Liberals would not fully reunify until Asquith's death in 1928, and thereafter primarily expressed influence through confidence and supply
In a parliamentary democracy based on the Westminster system, confidence and supply are required for a ruling cabinet to retain power in the lower house.
A confidence-and-supply agreement is one whereby a party or independent members of parl ...
arrangements and coalitions
A coalition is a group formed when two or more people or groups temporarily work together to achieve a common goal. The term is most frequently used to denote a formation of power in political or economical spaces.
Formation
According to ''A Gui ...
in the event of a hung parliament.
United States
While disillusioned by the war, it having not achieved the high ideals promised by PresidentWoodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
, American commercial interests did finance Europe's rebuilding and reparation efforts in Germany, at least until the onset of the Great Depression. American opinion on the propriety of providing aid to Germans and Austrians was split, as evidenced by an exchange of correspondence between Edgar Gott, an executive with The Boeing Company
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product ...
and Charles Osner, chairman of the Committee for the Relief of Destitute Women and Children in Germany and Austria. Gott argued that relief should first go to citizens of countries that had suffered at the hands of the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
, while Osner made an appeal for a more universal application of humanitarian ideals. The American economic influence allowed the Great Depression to start a domino effect, pulling Europe in as well.
France
 Alsace-Lorraine returned to France, the region which had been ceded to the Kingdom of Prussia in 1871 after the Franco-Prussian War. At the 1919 Peace Conference, Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau's aim was to ensure that Germany would not seek revenge in the following years. To this purpose, the chief commander of the Allied forces, Marshal Ferdinand Foch, had demanded that for the future protection of France the Rhine river should now form the border between France and Germany. Based on history, he was convinced that Germany would again become a threat, and, on hearing the terms of the Treaty of Versailles that had left Germany substantially intact, he observed that "This is not Peace. It is an Armistice for twenty years."
The destruction brought upon French territory was to be indemnified by the
Alsace-Lorraine returned to France, the region which had been ceded to the Kingdom of Prussia in 1871 after the Franco-Prussian War. At the 1919 Peace Conference, Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau's aim was to ensure that Germany would not seek revenge in the following years. To this purpose, the chief commander of the Allied forces, Marshal Ferdinand Foch, had demanded that for the future protection of France the Rhine river should now form the border between France and Germany. Based on history, he was convinced that Germany would again become a threat, and, on hearing the terms of the Treaty of Versailles that had left Germany substantially intact, he observed that "This is not Peace. It is an Armistice for twenty years."
The destruction brought upon French territory was to be indemnified by the reparations
Reparation(s) may refer to:
Christianity
* Restitution (theology), the Christian doctrine calling for reparation
* Acts of reparation, prayers for repairing the damages of sin
History
*War reparations
**World War I reparations, made from ...
negotiated at Versailles. This financial imperative dominated France's foreign policy throughout the 1920s, leading to the 1923 Occupation of the Ruhr
The Occupation of the Ruhr (german: link=no, Ruhrbesetzung) was a period of military occupation of the Ruhr region of Germany by France and Belgium between 11 January 1923 and 25 August 1925.
France and Belgium occupied the heavily industrial ...
in order to force Germany to pay. However, Germany was unable to pay, and obtained support from the United States. Thus, the Dawes Plan
The Dawes Plan (as proposed by the Dawes Committee, chaired by Charles G. Dawes) was a plan in 1924 that successfully resolved the issue of World War I reparations that Germany had to pay. It ended a crisis in European diplomacy following W ...
was negotiated after Prime Minister Raymond Poincaré
Raymond Nicolas Landry Poincaré (, ; 20 August 1860 – 15 October 1934) was a French statesman who served as President of France from 1913 to 1920, and three times as Prime Minister of France.
Trained in law, Poincaré was elected deputy in 1 ...
's occupation of the Ruhr, and then the Young Plan
The Young Plan was a program for settling Germany's World War I reparations. It was written in August 1929 and formally adopted in 1930. It was presented by the committee headed (1929–30) by American industrialist Owen D. Young, founder and fo ...
in 1929.
Also extremely important in the War was the participation of French colonial troops
The ''Troupes coloniales'' ("Colonial Troops") or ''Armée coloniale'' ("Colonial Army"), commonly called ''La Coloniale'', were the military forces of the French colonial empire from 1900 until 1961. From 1822 to 1900 these troops were de ...
(who amounted for around 10% of the total number of troops deployed by France across the war), including the Senegalese '' tirailleurs'', and troops from Indochina, North Africa, and Madagascar. When these soldiers returned to their homelands and continued to be treated as second class citizens, many became the nuclei of pro-independence groups.
Furthermore, under the state of war declared during the hostilities, the French economy
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
had been somewhat centralized in order to be able to shift into a " war economy", leading to a first breach with classical liberalism.
Finally, the socialists' support of the National Union government (including Alexandre Millerand
Alexandre Millerand (; – ) was a French politician. He was Prime Minister of France from 20 January to 23 September 1920 and President of France from 23 September 1920 to 11 June 1924. His participation in Waldeck-Rousseau's cabinet at the st ...
's nomination as Minister of War) marked a shift towards the French Section of the Workers' International's (SFIO) turn towards social democracy and participation in "bourgeois governments", although Léon Blum maintained a socialist rhetoric.
Women in France
“But with its faceless state machinery and unremitting mechanized slaughter, the war instead collapsed these old ideals” (Roberts 2). When the war was over and the men returned home, the world was a vastly different place than it had been before the war. Many ideals and beliefs were shattered with the war. Those returning from the front lines, and even those who were on the Homefront, were left to pick up the pieces of what was left of those ideals and beliefs, and try to rebuild them. Before the Great War, many thought this war would be a quick war, like many before had been. With new technology and weapons though, the war was at a stalemate for a large part of it, dragging what many thought would be a quick war out into a long, grueling war. With so much death and destruction done to France, it is not surprising when looking back that the way of life for French citizens was forever changed. Many citizens saw the change in culture and blamed the war for taking away the rose tinted glasses that society had viewed things through. Many scholars and writers, such as Drieu la Rochelle, found many ways to describe this new view on reality such as stripping away clothes (Roberts 2). This comparison of the new reality and clothing being stripped away also ties into the fact that gender roles changed greatly after the war. During the war many jobs had been left to women because many men were fighting on the front lines. This gave women a new sense of freedom that they had not been able to experience ever before. Not many women wanted to go back to how things were before the war, when they expected to stay at home and take care of the house. When the war was over many of the older generations and men wanted women to return to their previous roles. At a time where gender roles were so heavily defined and intertwined with the culture of many places, for French citizens viewing how many women went against said roles after World War 1, or the Great War as it was called at the time, it was ghastly. While gender roles had slowly been changing over time since the Industrial Revolution gave more work options outside of the home in factories, it had never been such a quick and drastic change as it was after World War 1. During the war many men went off to fight, leaving behind factory jobs that were usually seen as a man's job only. These jobs had to be filled and without men there to fill the jobs, it was women who stepped up to fill the hole instead. France suffered a great loss of life during World War 1, leaving many jobs unable to be refilled even after the war. Debates and discussions concerning gender identity and gender roles in relation to society became one of the main ways to discuss the war and people's stances on it (Roberts 5). The war left people struggling to grasp the new reality. There were mixed reactions to the new way of life after World War 1 and how it affected both men and women. Some people were willing to completely embrace the new standards that were emerging following the war, while others harshly rejected the changes, seeing the changes as summarizing all the horrors they experienced during the war. Others looked for ways to compromise between the new and old way of life, tried to combine the ideals and beliefs from before and after the war to find a healthy middle ground. Discussions pertaining to women during post-war debates often split the view of women into three categories—the “modern woman,” the “mother,” and the “single woman” (Roberts 9). These categories broke up the view of women by the roles they took on, the jobs they did, the way they acted, or by the beliefs they might hold. These categories also came to encompass the views of gender roles in relation to before and after the war. The “mother” category relates back to the role of women before the Great War, the woman who stayed at home and took care of the household while the husband was off at work. The “modern woman” relates to how many women were after the war, working jobs meant for men, engaging in sexual pleasures, and often doing things at a fast pace. The “single woman” was the middle ground between the other two that were very different from one another. The “single woman” came to represent the women who would never be able to marry because there were not enough men for every woman to marry (Roberts 10). One thing that sparked much debate in regards to the postwar woman is fashion. During the war things like cloth material were rationed, with people being encouraged to not use as much fabric, so that there would be enough for the military. In response to these rations, women wore shorter dresses and skirts, usually about knee length, or pants. This change in apparel was something that many women continued to wear even after the war ended. It was such a drastic change to the clothing norms for women before the war. This change led to some “modern women” to be described in harsh lights, as if wearing dresses and skirts that short showed that those women were promiscuous. Those coming back from the war, from the fighting, were very traumatized and had wanted to come back to a home that was not very changed in order to give themselves a sense of normalcy. When these men came back to a home that had changed a lot they did not know what to make of it. Gone were the times of very defined gender roles that most of society conformed to. It was often hard for these traumatized men to accept these new changes, especially the changes in how women behaved.Italy
 In 1882 Italy joined with the
In 1882 Italy joined with the German Empire
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditar ...
and the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise o ...
to form the Triple Alliance. However, even if relations with Berlin became very friendly, the alliance with Vienna remained purely formal, as the Italians were keen to acquire Trentino and Trieste, parts of the Austro-Hungarian empire populated by Italians.
During World War I Italy aligned with the Allies, instead of joining Germany and Austria. This could happen since the alliance formally had merely defensive prerogatives, while the Central Empires were the ones who started the offensive. With the Treaty of London, Britain secretly offered Italy Trentino and Tyrol as far as Brenner, Trieste and Istria, all the Dalmatian coast except Fiume
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Prim ...
, full ownership of Albanian Valona and a protectorate over Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares la ...
, Antalya in Turkey and a share of the Partitioning of the Ottoman Empire, Turkish and German colonial empire#Confiscation, German colonial empire, in exchange for Italy siding against the Central Empires.
After the victory, Vittorio Orlando, Italy's President of the Council of Ministers of Italy, President of the Council of Ministers, and Sidney Sonnino, its Foreign Minister of Italy, Foreign Minister, were sent as the Italian representatives to Paris Peace Conference, 1919, Paris with the aim of gaining the promised territories and as much other land as possible. In particular, there was an especially strong opinion about the status of Fiume
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Prim ...
, which they believed was rightly Italian due to Italian population, in agreement with Woodrow Wilson, Wilson's Fourteen Points, the ninth of which read:
''"A readjustment of the frontiers of Italy should be effected along clearly recognizable lines of nationality''".
Nevertheless, by the end of the war the Allies realized they had made contradictory agreements with other Nations, especially regarding Central Europe and the Middle-East. In the meetings of the "Big Four", in which Orlando's powers of diplomacy were inhibited by his lack of English, the Great powers were only willing to offer Trentino to the Brenner, the Dalmatian port of Zadar, Zara, the island of Lastovo, Lagosta and a couple of small German colonies. All other territories were promised to other nations and the great powers were worried about Italy's imperial ambitions; Wilson, in particular, was a staunch supporter of Yugoslav rights on Dalmatia against Italy and despite the Treaty of London which he did not recognize. As a result of this, Orlando left the conference in a rage. This simply favored Britain and France, which divided among themselves the former Ottoman and German territories in Africa.
In Italy, the discontent was relevant: irredentists, Irredentism (see: ''Italian irredentism, irredentismo'') claimed Fiume and Dalmatia as Italian lands; many felt the Country had taken part in a meaningless war without getting any serious benefits. This idea of a "mutilated victory" (''Mutilated victory, vittoria mutilata'') was the reason which led to the ''Italian Regency of Carnaro#Impresa di Fiume, Impresa di Fiume'' ("''Fiume Exploit''"). On September 12, 1919, the nationalist poet Gabriele d'Annunzio led around 2,600 troops from the Royal Italian Army (the Granatieri di Sardegna Mechanized Brigade, Granatieri di Sardegna), nationalists and irredentists, into a seizure of the city, forcing the withdrawal of the inter-Allied (American, British and French) occupying forces.
The "mutilated victory" (''Mutilated victory, vittoria mutilata'') became an important part of Italian Fascist propaganda.
China
The Republic of China (1912-49), Republic of China had been one of the Allies; during the war, they had sent Chinese Labour Corps, thousands of labourers to France. At the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, Paris Peace Conference in 1919, the Chinese delegation called for an end to Western imperialistic institutions in China, but was rebuffed. China requested at least the formal restoration of its territory of Jiaozhou Bay, under German colonial control as the Kiautschou Bay Leased Territory since 1898. But the western Allies rejected China's request, instead granting transfer to Japan of all of Germany's pre-war territory and rights in China. Subsequently, China did not sign the Treaty of Versailles, instead signing a separate peace treaty with Germany in 1921. The Austro-Hungarian and German concessions in Tianjin were placed under the administration of the Chinese government; in 1920 they occupied the Russian area as well. The western Allies' substantial accession to Japan's territorial ambitions at China's expense led to the May Fourth Movement in China, a social and political movement that had profound influence over subsequent Chinese history. The May Fourth Movement is often cited as the birth of Chinese nationalism, and both the Kuomintang and Chinese Communist Party consider the Movement to be an important period in their own histories.Japan
Because of the treaty that Japan had signed with Great Britain in 1902, Japan was one of the Allies during the war. With British assistance, Japanese forces attacked Germany's territories in Shandong, Shandong, China, including the East Asian coaling base of the Imperial German Navy. The German forces were defeated and surrendered to Japan in November 1914. The Japanese navy also succeeded in seizing several of Germany's island possessions in the Western Pacific: the Marianas, Caroline Islands, Carolines, and Marshall Islands. At the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, Paris Peace Conference in 1919, Japan was granted all of Germany's pre-war rights in Shandong, Shandong province in China (despite China also being one of the Allies during the war): outright possession of the territory of Jiaozhou Bay, and favorable commercial rights throughout the rest of the province, as well as the South Seas Mandate over the German Pacific island possessions that the Imperial Japanese Navy had taken. Also, Japan was granted a permanent seat on the Council of the League of Nations. Nevertheless, the Western powers refused Japan's request for the inclusion of a Racial Equality Proposal, 1919, "racial equality" clause as part of the Treaty of Versailles. Shandong reverted to Chinese control in 1922 after mediation by the United States during the Washington Naval Conference. Weihai followed in 1930.Territorial gains and losses
Countries that gained or regained territory or independence after World War I
* : independence from Russian Empire * : gained control of German New Guinea, the Bismarck Archipelago and Nauru * : gained territories (Burgenland, Őrvidék) from Hungary * : independence from Russian Empire * : gained control of Eupen-Malmedy and theAfrica
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n territories of Ruanda-Urundi from the German Empire
* : gained control of several cities from the Russian Empire
* : gained territories from the Cisleithania, Austrian Empire (Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohe ...
, Moravia, and part of Austrian Silesia, Silesia) and Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary (mostly Upper Hungary and Carpathian Ruthenia)
* : Free City of Danzig, semi-autonomous free city with independence from the German Empire
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditar ...
* : gained Nordschleswig after the 1920 Schleswig plebiscites from the German Empire
* : independence from the Russian Empire
* : independence from the Russian Empire
* : gained Alsace-Lorraine as well as various Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n colonies from the German Empire, and Middle East territories from the Ottoman Empire. The African and Middle East gains were officially League of Nations Mandates.
* : independence from the Russian Empire
* : gained Western Thrace from Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgaria
* : Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between the ...
(approximately five-sixths of Ireland (island), the island) gained independence from the United Kingdom (but still part of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
as a Dominion)
* : gained South Tyrol, Trieste, Istria, and Zadar from the Austro-Hungarian Empire
* : gained Jiaozhou Bay and most of the Shandong Peninsula from China and the South Seas Mandate (both controlled by German Empire before the war)
* : independence from the Russian Empire
* : independence from the Russian Empire
* : gained control of German Samoa
* : recreated and gained parts of the Cisleithania, Austrian Empire, German Empire
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditar ...
, Russian Empire and Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary (small northern parts of the former Árva County, Árva and Szepes County, Szepes counties)
* : gained control of the port of Kionga
* : gained Transylvania, parts of Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of ...
, Crișana
Crișana ( hu, Körösvidék, german: Kreischgebiet) is a geographical and historical region in north-western Romania, named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Ro ...
, and Maramureș from the Kingdom of Hungary, Bukovina from the Austrian Empire, regained Dobruja from Bulgaria, and Bessarabia from the Russian Empire
* : gained control of South West Africa
* : gained control of part of the Armenian Highlands from the Russian Empire in the Treaty of Kars
The Treaty of Kars ( tr, Kars Antlaşması, rus, Карсский договор, Karskii dogovor, ka, ყარსის ხელშეკრულება, hy, Կարսի պայմանագիր, az, Qars müqaviləsi) was a treaty that est ...
, while losing territory overall
* : gained independence from the Russian Empire and recognized by Soviet Russia in the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
* : gained League of Nations Mandates in Africa and the Middle East
* : created from the Kingdom of Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
, Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia and gained parts from Cisleithania, Austrian Empire (part of Duchy of Carniola, Kingdom of Dalmatia) and Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary (Međimurje (region), Muraköz, Prekmurje, Muravidék, parts of Baranya (region), Baranya, Bačka, Bácska and Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of ...
)
Nations that lost territory or independence after World War I
* : as the successor state of Cisleithania in the Austro-Hungarian Empire * : lost Western Thrace to Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece, also lost a part of Pirin Macedonia and Western Outlands to Serbia (Yugoslavia) * : temporarily lost Jiaozhou Bay and most of Shandong to the Empire of Japan * : as the successor state of theGerman Empire
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditar ...
* : as the successor state of Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen, Transleithania in the Austro-Hungarian Empire
* : declared union with Serbia and subsequently became incorporated into Kingdom of Yugoslavia, Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
* , as the successor state of the Russian Empire
* : as the successor state of the Ottoman Empire (although it did simultaneously gain some territory from the Russian Empire in the Treaty of Kars
The Treaty of Kars ( tr, Kars Antlaşması, rus, Карсский договор, Karskii dogovor, ka, ყარსის ხელშეკრულება, hy, Կարսի պայմանագիր, az, Qars müqaviləsi) was a treaty that est ...
and reverse some territorial losses in Anatolia with the Turkish War of Independence)
* : lost most of Ireland as the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between the ...
, Kingdom of Egypt, Egypt in 1922 and Emirate of Afghanistan, Afghanistan in 1919
Social trauma
The experiences of the war in the west are commonly assumed to have led to a sort of collective national trauma afterward for all of the participating countries. The optimism of Exposition Universelle (1900), 1900 was entirely gone and those who fought became what is known as "the Lost Generation" because they never fully recovered from their suffering. For the next few years, much of Europe mourned privately and publicly; memorials were erected in thousands of villages and towns. So many British men of marriageable age died or were injured that the students of one girls' school were warned that only 10% would marry. The 1921 United Kingdom census found 19,803,022 women and 18,082,220 men in England and Wales, a difference of 1.72 million which newspapers called the "Surplus Two Million". In the 1921 census there were 1,209 single women aged 25 to 29 for every 1,000 men. In 1931 50% were still single, and 35% of them did not marry while still able to bear children. As early as 1923, Stanley Baldwin recognized a new strategic reality that faced Britain in a disarmament speech. Chemical weapon, Poison gas and the aerial bombing of civilians were new developments of the First World War. The British civilian population, for many centuries, had not had any serious reason to fear invasion. So the new threat of poison gas dropped from enemy Bomber, bomber aircraft excited a grossly exaggerated view of the civilian deaths that would occur on the outbreak of any future war. Baldwin expressed this in his statement that "The bomber will always get through." The traditional British policy of a balance of power in Europe no longer safeguarded the British home population. One gruesome reminder of the sacrifices of the generation was the fact that this was one of the first times in international conflict whereby more men died in battle than from disease, which was the main cause of deaths in most previous wars. This social trauma made itself manifest in many different ways. Some people were revolted by nationalism and what they believed it had caused, so they began to work toward a more internationalism (politics), internationalist world through organizations such as the League of Nations. Pacifism became increasingly popular. Others had the opposite reaction, feeling that only military strength could be relied upon for protection in a chaotic and inhumane world that did not respect hypothetical notions of civilization. Certainly a sense of disillusionment and Cynicism (contemporary), cynicism became pronounced. Nihilism grew in popularity. Many people believed that the war heralded the end of the world as they had known it, including the collapse of capitalism and imperialism. Communist and socialist movements around the world drew strength from this theory, enjoying a level of popularity they had never known before. These feelings were most pronounced in areas directly or particularly harshly affected by the war, such as central Europe, Russia and France. Artists such as Otto Dix, George Grosz, Ernst Barlach, and Käthe Kollwitz represented their experiences, or those of their society, in blunt paintings and sculpture. Similarly, authors such as Erich Maria Remarque wrote grim novels detailing their experiences. These works had a strong impact on society, causing a great deal of controversy and highlighting conflicting interpretations of the war. In Germany, German nationalism, German nationalists including the Nazism, Nazis believed that much of this work was Degenerate art, degenerate and undermined the cohesion of society as well as dishonoring the dead.Remains of ammunition
Throughout the areas where trenches and fighting lines were located, such as the Champagne, France, Champagne region of France, quantities of unexploded ordnance have remained, some of which remain dangerous, continuing to cause injuries and occasional fatalities in the 21st century. Some are found by farmers ploughing their fields and have been called the iron harvest. Some of this ammunition contains Chemical weapons in World War I, toxic chemical products such as mustard gas. Cleanup of major battlefields is a continuing task with no end in sight for decades to come. Squads remove, defuse or destroy hundreds of tons of unexploded ammunition from both World Wars every year in Belgium, France, and Germany.Memorials
War memorials
 Many towns in the participating countries have war memorials dedicated to local residents who lost their lives. Examples include:
* Australian War Memorial, Canberra, Australia
* Liberty Memorial, Kansas City, Missouri, United States
* Memorial for The Battle of Jutland, Thyborøn, Jutland, Denmark
* District of Columbia War Memorial, Washington, DC, United States
* Beaumont-Hamel Newfoundland Memorial
* Cenotaph#The Cenotaph, London, The Cenotaph, London, United Kingdom
* Menin Gate Memorial, Ypres, Belgium
* Thiepval Memorial
* Tyne Cot Cemetery, Tyne Cot Memorial to the Missing at Passendale, Passchendaele
* Verdun, Verdun Memorial Museum
* Vimy Memorial, Vimy Ridge Memorial, Vimy, France
* Gallipoli Memorial, Turkey
* Shrine of Remembrance, Melbourne, Australia
* Irish National War Memorial Gardens, Dublin, Ireland
* Island of Ireland Peace Park, Mesen, Messines, Belgium
* National War Memorial (Canada), National War Memorial, Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
* National War Memorial (Newfoundland), National War Memorial, St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, Newfoundland, Canada
* Kriegerdenkmal auf dem Neroberg, Wiesbaden, Hessen, Germany
* Fogliano Redipuglia#World War I memorial, Sacrario militare di Redipuglia, Fogliano Redipuglia, Italy
* Mausoleum of Mărășești, Romania
Many towns in the participating countries have war memorials dedicated to local residents who lost their lives. Examples include:
* Australian War Memorial, Canberra, Australia
* Liberty Memorial, Kansas City, Missouri, United States
* Memorial for The Battle of Jutland, Thyborøn, Jutland, Denmark
* District of Columbia War Memorial, Washington, DC, United States
* Beaumont-Hamel Newfoundland Memorial
* Cenotaph#The Cenotaph, London, The Cenotaph, London, United Kingdom
* Menin Gate Memorial, Ypres, Belgium
* Thiepval Memorial
* Tyne Cot Cemetery, Tyne Cot Memorial to the Missing at Passendale, Passchendaele
* Verdun, Verdun Memorial Museum
* Vimy Memorial, Vimy Ridge Memorial, Vimy, France
* Gallipoli Memorial, Turkey
* Shrine of Remembrance, Melbourne, Australia
* Irish National War Memorial Gardens, Dublin, Ireland
* Island of Ireland Peace Park, Mesen, Messines, Belgium
* National War Memorial (Canada), National War Memorial, Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
* National War Memorial (Newfoundland), National War Memorial, St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, Newfoundland, Canada
* Kriegerdenkmal auf dem Neroberg, Wiesbaden, Hessen, Germany
* Fogliano Redipuglia#World War I memorial, Sacrario militare di Redipuglia, Fogliano Redipuglia, Italy
* Mausoleum of Mărășești, Romania
Tombs of unknown soldiers
* Monument to the Unknown Hero, Belgrade, Serbia * India Gate, Amar Jawan Jyoti, New Delhi, India * Canadian Tomb of the Unknown Soldier, Tomb of the Unknown Soldier, Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada * Arc de Triomphe, Paris, France * The Unknown Warrior, The Tomb of the Unknown Warrior in Westminster Abbey, London, United Kingdom * Tomb of the Unknowns, Arlington National Cemetery, Virginia, United States * Monument of Vittorio Emanuele II, Tomba del milite ignoto, Rome, Italy * Australian War Memorial, Canberra, Australia * New Zealand Tomb of the Unknown Warrior, Wellington, New Zealand * Tomb of the Unknown Soldier (Athens), Tomb of the Unknown Soldier, Syntagma Square, Athens, Greece * Tomb of the Unknown Soldier in Bucharest, Tomb of the Unknown Soldier, Bucharest, Romania * Tomb of the Unknown Soldier (Portugal), Tomb of the Unknown Soldier in Batalha Monastery, Batalha, Portugal, Batalha, Portugal * Tomb of the Unknown Soldier, Warsaw, PolandSee also
* International relations (1919–1939) * Revolutions of 1917–1923 * Interwar period * Political history of the worldNotes
*Further reading
* Aldcroft, Derek Howard. ''Europe's third world: the European periphery in the interwar years'' (2006). * Blom, Philipp. ''Fracture: Life and Culture in the West, 1918–1938'' (2015). * Cornelissen, Christoph, and Arndt Weinrich, eds. ''Writing the Great War - The Historiography of World War I from 1918 to the Present'' (2020free download
full coverage for major countries. * Gerwarth, Robert. "The central European counter-revolution: Paramilitary violence in Germany, Austria and Hungary after the great war." ''Past & Present'' 200.1 (2008): 175-209
online
*Margaret MacMillan, MacMillan, Margaret. ''Peacemakers: The Paris Peace Conference of 1919 and Its Attempt to End War'' (2001) * Kallis, Aristotle. "When fascism became mainstream: the challenge of extremism in times of crisis." ''Fascism'' 4.1 (2015): 1–24. * Mazower, Mark. ''Dark continent: Europe's twentieth century'' (2009). * Mowat, C.L. ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History, Vol. 12: The Shifting Balance of World Forces, 1898–1945'' (1968
online
25 chapters; 845pp *Overy, R. J. ''The Inter-War Crisis'' (2nd ed. 2016
excerpt
* Somervell, D.C. ''The Reign of King George V'' (1936
online
550pp; wide ranging political, social and economic coverage of Britain, 1910–35 * John Wheeler-Bennett ''The Wreck of Reparations, being the political background of the Lausanne Agreement, 1932'' New York, H. Fertig, 1972.
External links
Post-war
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
*Kitchen, James E.
Colonial Empires after the War/Decolonization
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
*Bessel, Richard
Post-war Societies
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
*Rothermund, Dietmar
Post-war Economies
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
*Sharp, Alan
The Paris Peace Conference and its Consequences
in
1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
FirstWorldWar.com
"A multimedia history of World War I"
The war to end all wars on BBC site
"The Heritage of the Great War"
The British Army in the Great War
{{authority control Aftermath of World War I, Interwar period, Aftermath