Administrative Divisions Of Norway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A county municipality ( no, Fylkeskommune) is the public elected body that is responsible for certain public administrative and service tasks within a
A county municipality ( no, Fylkeskommune) is the public elected body that is responsible for certain public administrative and service tasks within a

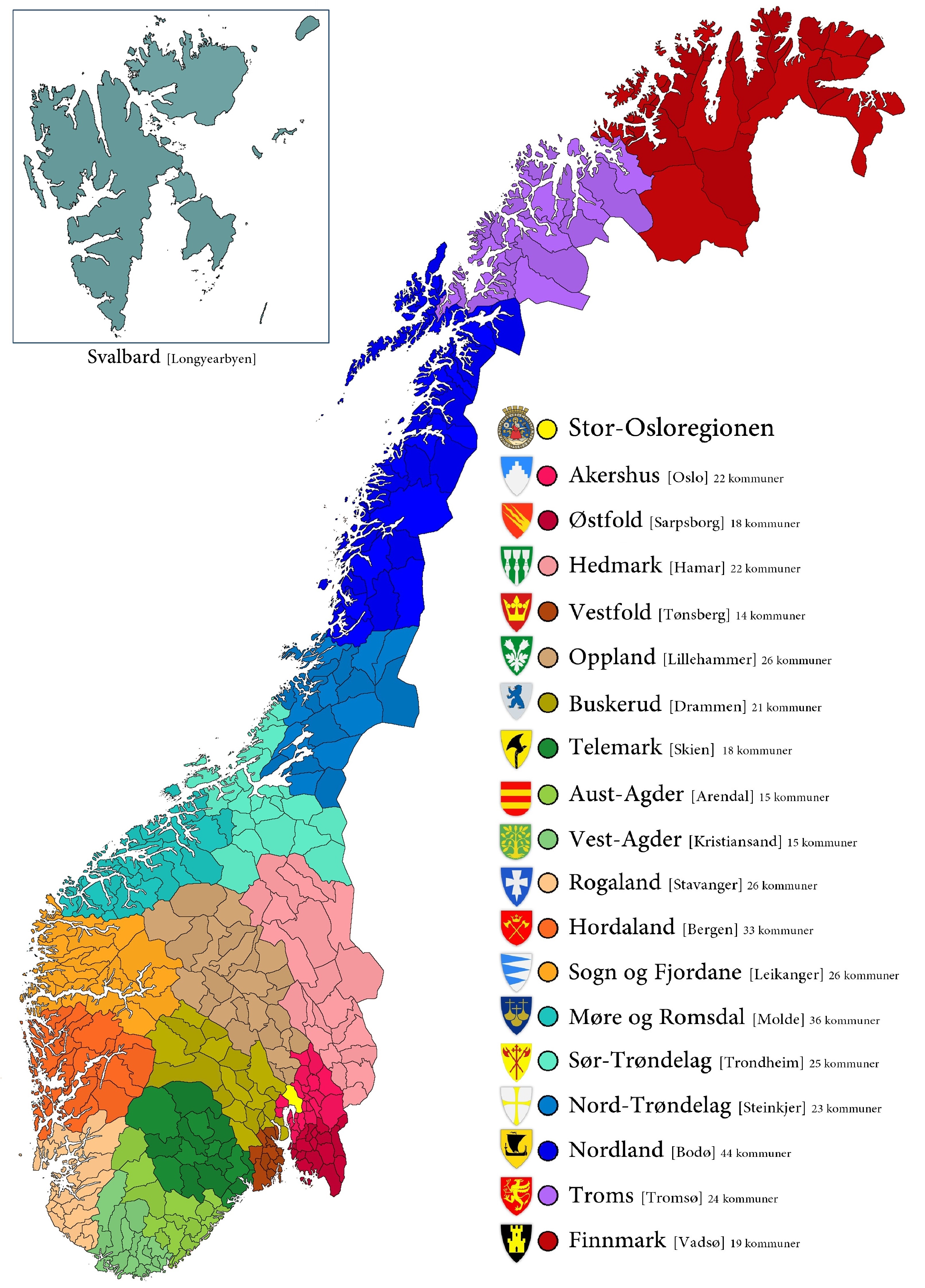 Municipal independence was established in 1838. The introduction of self-government in rural districts was a major political change. The
Municipal independence was established in 1838. The introduction of self-government in rural districts was a major political change. The
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
's elongated shape, its numerous internal geographical barriers, and the often widely dispersed and separated settlements are all factors that have strongly influenced the structure of the country's administrative subdivisions. This structure has varied over time and is subject to continuous review. In 2017 the government decided to abolish some of the counties and to merge them with other counties to form larger ones, reducing the number of counties from 19 to 11, which was implemented on 1 January 2020.
Formal subdivisions
There are three levels of political administration in Norway: * The Kingdom, covering all of Metropolitan Norway, including its integral overseas areas ofSvalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group rang ...
and Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger ...
. Whereas Svalbard is subject to an international treaty with some limits to Norwegian sovereignty, Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger ...
shares county governor (''fylkesmann'') with Nordland
Nordland (; smj, Nordlánnda, sma, Nordlaante, sme, Nordlánda, en, Northland) is a county in Norway in the Northern Norway region, the least populous of all 11 counties, bordering Troms og Finnmark in the north, Trøndelag in the south, ...
county.
* The Counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
, known in Norwegian as ''fylker'' (singular ''fylke''), of which there are 11. These derive in part from divisions that preceded Norway's constitution in 1814 and independence in 1905. The counties also function as constituencies
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other polity ...
in elections for Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
.
* The Municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the ...
, known in Norwegian as ''kommuner'' (singular ''kommune'') of which there are 422. In addition the Longyearbyen
Longyearbyen (, locally �lɔ̀ŋjɑrˌbyːən "The Longyear Town") is the world's northernmost settlement with a population greater than 1,000 and the largest inhabited area of Svalbard, Norway. It stretches along the foot of the left bank ...
local authority has some similarities to a municipality.
* External dependencies
As the infrastructure for travel and communication has improved over the years, so the benefits of further consolidation have remained under review. The number of municipalities has decreased from 744 in the early 1960s to today's 442, and more mergers are planned. Similarly, the political responsibilities of the counties have decreased, and there was talk earlier of combining them into 5–9 regions by 2010. Although those specific plans did not come to fruition, a similar scheme is again under consideration in 2018.
Within the government administration, there are a few exceptions to the county subdivisions:
* The Norwegian court system is divided into six appellate districts.
* The state Church of Norway
The Church of Norway ( nb, Den norske kirke, nn, Den norske kyrkja, se, Norgga girku, sma, Nöörjen gærhkoe) is an evangelical Lutheran denomination of Protestant Christianity and by far the largest Christian church in Norway. The church ...
is divided into eleven dioceses.
* The 13 constituencies for elections to the Sámi Parliament of Norway
sje, Sámedigge sju, Sámiediggie sma, Saemiedigkie sms, Sääʹmteʹǧǧ no, Sametinget
, legislature = 9th Sámi Parliament
, coa_pic = Nordsamisk_farge_symmetrisk_stor-01.svg
, house_type = Unicameral
, foundation ...
, which is a part of the Norwegian state apparatus, do not follow the county borders – sometimes encompassing several counties. They do, however, follow municipality borders.
County
County municipality
county
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
. Each county is governed as a county municipality, with the exception of Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
, which is both a municipality and a county municipality. The main responsibility of the county municipalities are upper secondary schools, dental care, public transport
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typi ...
, county roads
A county highway (also county road or county route; usually abbreviated CH or CR) is a road in the United States and in the Canadian province of Ontario that is designated and/or maintained by the county highway department. Route numbering can ...
, culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
, cultural heritage management
Cultural heritage management (CHM) is the vocation and practice of managing cultural heritage. It is a branch of cultural resources management (CRM), although it also draws on the practices of cultural conservation, restoration, museology, arc ...
, land use planning
Land use planning is the process of regulating the use of land by a central authority. Usually, this is done to promote more desirable social and environmental outcomes as well as a more efficient use of resources. More specifically, the goals ...
and business development.
The main body of each county municipality is the county council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
Ireland
The county councils created under British rule in 1899 continue to exist in Irela ...
(''fylkesting''), elected by direct election by all legal residents every fourth year. The county councils typically have 30-50 members and meet about six times a year. They are divided into standing committees and an executive board (''fylkesutvalg''), that meet considerably more often. Both the council and executive board are led by the Chairman of the County Council
The chairperson, also chairman, chairwoman or chair, is the presiding officer of an organized group such as a board, committee, or deliberative assembly. The person holding the office, who is typically elected or appointed by members of the grou ...
or County Mayor (''fylkesordfører'').
The national government, formally the King, is represented in each county by a county governor ( no, Fylkesmann
The county governor ( nb, statsforvalteren; nn, statsforvaltaren, lit. ''state administrator'' in English) is a Norwegian government agency that represents the central government administration in every county in Norway. Responsible for a num ...
). This office mainly functions as a supervising authority over the county and municipality administrations, and their decisions can be appealed to him.
Municipality
Municipalities are the atomic unit of local government and are responsible for primary education (through 10th grade), outpatient health services, senior citizen services, some social services, zoning, economic development, and municipal roads. Law enforcement andchurch services
A church service (or a service of worship) is a formalized period of Christian communal worship, often held in a church building. It often but not exclusively occurs on Sunday, or Saturday in the case of those churches practicing seventh-day Sa ...
are provided at a national level in Norway. The main body of each municipality is the municipality council (''kommunestyre''), elected by direct election by all legal residents every fourth year.
Borough
Three municipalities, Oslo,Bergen
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Vestland county on the Western Norway, west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the list of towns and cities in Norway, secon ...
and Stavanger
Stavanger (, , American English, US usually , ) is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Norway. It is the fourth largest city and third largest metropolitan area in Norway (through conurbation with neighboring Sandnes) and the a ...
, are divided into boroughs. In Oslo and Stavanger, they elect their own political council. They are part of the municipal organization, but have a certain amount of influence in issues regarding health, education and naming.
Integral territories
BothSvalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group rang ...
and Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger ...
are "part of the Kingdom of Norway", although they are not allocated to a particular county and have not been declared as dependencies. Svalbard and Jan Mayen is administered outside of the ''fylker'' system.
Dependencies
Norway has threedependent territories
A dependent territory, dependent area, or dependency (sometimes referred as an external territory) is a territory that does not possess full political independence or sovereignty as a sovereign state, yet remains politically outside the controlli ...
( no, biland), all uninhabited and located in the Southern Hemisphere. Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island ( ; or ''Bouvetøyen'') is an island claimed by Norway, and declared an uninhabited protected nature reserve. It is a subantarctic volcanic island, situated in the South Atlantic Ocean at the southern end of the Mid-Atlantic R ...
is a Subantarctic
The sub-Antarctic zone is a region in the Southern Hemisphere, located immediately north of the Antarctic region. This translates roughly to a latitude of between 46° and 60° south of the Equator. The subantarctic region includes many islands ...
island in the South Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
. ''Queen Maud Land
Queen Maud Land ( no, Dronning Maud Land) is a roughly region of Antarctica claimed by Norway as a dependent territory. It borders the claimed British Antarctic Territory 20° west and the Australian Antarctic Territory 45° east. In addi ...
'' is a sector of Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
which spans between 20° west and 45° east. ''Peter I Island
Peter I Island ( no, Peter I Øy) is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Bellingshausen Sea, from continental Antarctica. It is claimed as a dependency of Norway and, along with Bouvet Island and Queen Maud Land, composes one of the three ...
'' is a volcanic island located off the coast of Ellsworth Land
Ellsworth Land is a portion of the Antarctic continent bounded on the west by Marie Byrd Land, on the north by Bellingshausen Sea, on the northeast by the base of Antarctic Peninsula, and on the east by the western margin of the Filchner–Ronne ...
of continental Antarctica. Both Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land are south of 60°S and are thus part of the Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico
, name = Antarctic Treaty System
, image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder
, image_width = 180px
, caption ...
. While the treaty states that the claims are not affected by the treaty, only the other countries with claims recognize Norwegian sovereignty on the island. The dependencies are administration by the Polar Affairs Department of the Ministry of Justice and the Police in Oslo. Norwegian criminal law
Criminal law is the body of law that relates to crime. It prescribes conduct perceived as threatening, harmful, or otherwise endangering to the property, health, safety, and moral welfare of people inclusive of one's self. Most criminal law ...
, private law
Private law is that part of a civil law legal system which is part of the '' jus commune'' that involves relationships between individuals, such as the law of contracts and torts (as it is called in the common law), and the law of obligations ...
and procedural law
Procedural law, adjective law, in some jurisdictions referred to as remedial law, or rules of court, comprises the rules by which a court hears and determines what happens in civil, lawsuit, criminal or administrative proceedings. The rules a ...
applies to the dependencies, in addition to other laws that explicitly state they are valid on the island.
Informal subdivisions
Regions
Norway is generally divided into five regions ( no, landsdel), which largely represent areas with a common language and culture:Northern Norway
Northern Norway ( nb, Nord-Norge, , nn, Nord-Noreg; se, Davvi-Norga) is a geographical region of Norway, consisting of the two northernmost counties Nordland and Troms og Finnmark, in total about 35% of the Norwegian mainland. Some of the lar ...
, Trøndelag
Trøndelag (; sma, Trööndelage) is a county in the central part of Norway. It was created in 1687, then named Trondhjem County ( no, Trondhjems Amt); in 1804 the county was split into Nord-Trøndelag and Sør-Trøndelag by the King of Denma ...
, Western Norway
Western Norway ( nb, Vestlandet, Vest-Norge; nn, Vest-Noreg) is the region along the Atlantic coast of southern Norway. It consists of the counties Rogaland, Vestland, and Møre og Romsdal. The region has no official or political-administrativ ...
, Southern Norway
Southern Norway ( no, Sørlandet; lit. "The Southland") is the geographical region (''landsdel'') along the Skagerrak coast of southern Norway. The region is an informal description since it does not have any governmental function. It rough ...
and Eastern Norway
Eastern Norway ( nb, Østlandet, nn, Austlandet) is the geographical region of the south-eastern part of Norway. It consists of the counties Vestfold og Telemark, Viken, Oslo and Innlandet.
Eastern Norway is by far the most populous region ...
. Regions hold no official status in the government, but is used for organizing some public organizations, including the Norwegian Public Roads Administration
The Norwegian Public Roads Administration ( no, Statens vegvesen) is a Norwegian government agency responsible for national and county public roads in Norway. This includes planning, construction and operation of the national and county road netw ...
and the regional health authorities. Central Norway
Central Norway ( nb, Midt-Norge, nn, Midt-Noreg) is an informal region of Norway that is not clearly defined. The term ''Central Norway'' may in its most limited usage refer only to Trøndelag county, but may also be understood to include all or ...
is a region which consists of Trøndelag
Trøndelag (; sma, Trööndelage) is a county in the central part of Norway. It was created in 1687, then named Trondhjem County ( no, Trondhjems Amt); in 1804 the county was split into Nord-Trøndelag and Sør-Trøndelag by the King of Denma ...
and Møre og Romsdal
Møre og Romsdal (; en, Møre and Romsdal) is a county in the northernmost part of Western Norway. It borders the counties of Trøndelag, Innlandet, and Vestland. The county administration is located in the town of Molde, while Ålesund is t ...
. Trøndelag and Northern Norway is collectively known as Nordenfjells Nordenfjells or Nordafjells ("North of the Mountains") is currently a name for the area of Norway north of mountain range of Dovrefjell. The term is largely used when referring collectively to Central Norway and Northern Norway. Until around 1800 th ...
. Sápmi
(, smj, Sábme / Sámeednam, sma, Saepmie, sju, Sábmie, , , sjd, Са̄мь е̄ммьне, Saam' jiemm'n'e) is the cultural region traditionally inhabited by the Sámi people. Sápmi is in Northern and Eastern Europe and includes the ...
is an area which spans into Sweden, Finland and Russia and is defined as the "homeland" of the Sami
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise ...
. The Norwegian Meteorological Institute
The Norwegian Meteorological Institute ( no, Meteorologisk institutt), also known internationally as MET Norway, is Norway's national meteorological institute. It provides weather forecasts for civilian and military uses and conducts research in m ...
uses different regions, corresponding to the weather patterns.
Districts
Districts ( no, distrikt) represent an unofficial area organized by common language, culture or geographical barriers. Their boundaries are subjective and some areas may be regarded as belonging to multiple districts. Districts are larger than municipalities and smaller than counties, although some districts may span across county borders. Some districts form a hierarchy where a district can be subdivided into multiple lesser districts.Settlements and rural areas
Statistics Norway
Statistics Norway ( no, Statistisk sentralbyrå, abbreviated to ''SSB'') is the Norwegian statistics bureau. It was established in 1876.
Relying on a staff of about 1,000, Statistics Norway publish about 1,000 new statistical releases every ye ...
uses the term "settlement" for any collection of at least 200 people who live close together. Outside of these there may be rural areas which have an unofficial border. Sometimes these are defined by school districts. Cities are often divided into boroughs, which may or may not have
History
 Municipal independence was established in 1838. The introduction of self-government in rural districts was a major political change. The
Municipal independence was established in 1838. The introduction of self-government in rural districts was a major political change. The Norwegian farm culture
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
*Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
*Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including the ...
(''bondekultur'') that emerged came to serve as a symbol of national resistance to the forced union with Sweden. The legislation of 1837 gave both the towns and the rural areas the same institutions: a minor change for the town, but a major advance for the rural communities.
The composition and number of municipalities, their functions, and the existence and functions of the counties are being continuously debated. However, there are currently no plans for reform.
See also
* ISO 3166-2 codes of Norway * FIPS region codes of Norway (standard withdrawn in 2008) *NUTS of Norway
As a member of EFTA, Norway (NO) is not included in the Classification of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS), but in a similar classification used for coding statistical regions of countries that are not part of the EU but are candidate co ...
* Subdivisions of the Nordic countries
The subdivisions of the Nordic countries are similar given the countries' shared culture and history.
Denmark
*Denmark proper
**5 regions ()
**98 municipalities ()
*2 autonomous insular overseas dependencies
**Faroe Islands
***6 regions
***3 ...
* List of possessions of Norway
This is a list of current and former territorial possessions of the Kingdom of Norway.
Current overseas territories
Integral areas of Norway which are unincorporated:
* Svalbard (including Bear Island), in the Arctic, a part of Norway since ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Administrative Divisions Of Norway