Acute Pancreatitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden

 Regarding the need for computed tomography, practice guidelines state:
CT is an important common initial assessment tool for acute pancreatitis. Imaging is indicated during the initial presentation if:
*the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis is uncertain
*there is abdominal distension and tenderness, fever >102 F (38,9 C), or leukocytosis
*there is a Ranson score > 3 or APACHE score > 8
*there is no improvement after 72 hours of conservative medical therapy
*there has been an acute change in status: fever, pain, or shock
CT is recommended as a delayed assessment tool in the following situations:
*acute change in status
*to determine therapeutic response after surgery or interventional radiologic procedure
*before discharge in patients with severe acute pancreatitis
Abdominal CT should not be performed before the first 12 hours of onset of symptoms as early CT (<12 hours) may result in equivocal or normal findings.
CT findings can be classified into the following categories for easy recall:
*Intrapancreatic – diffuse or segmental enlargement, edema, gas bubbles, pancreatic pseudocysts and phlegmons/abscesses (which present 4 to 6 wks after initial onset)
*Peripancreatic / extrapancreatic – irregular pancreatic outline, obliterated peripancreatic fat, retroperitoneal edema, fluid in the lessar sac, fluid in the left anterior pararenal space
*Locoregional – Gerota's fascia sign (thickening of inflamed Gerota's fascia, which becomes visible), pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion (seen on basal cuts of the pleural cavity), adynamic ileus, etc.
The principal value of CT imaging to the treating clinician is the capacity to identify devitalised areas of the pancreas which have become necrotic due to ischaemia. Pancreatic necrosis can be reliably identified by intravenous contrast-enhanced CT imaging, and is of value if infection occurs and surgical or percutaneous debridement is indicated.
Regarding the need for computed tomography, practice guidelines state:
CT is an important common initial assessment tool for acute pancreatitis. Imaging is indicated during the initial presentation if:
*the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis is uncertain
*there is abdominal distension and tenderness, fever >102 F (38,9 C), or leukocytosis
*there is a Ranson score > 3 or APACHE score > 8
*there is no improvement after 72 hours of conservative medical therapy
*there has been an acute change in status: fever, pain, or shock
CT is recommended as a delayed assessment tool in the following situations:
*acute change in status
*to determine therapeutic response after surgery or interventional radiologic procedure
*before discharge in patients with severe acute pancreatitis
Abdominal CT should not be performed before the first 12 hours of onset of symptoms as early CT (<12 hours) may result in equivocal or normal findings.
CT findings can be classified into the following categories for easy recall:
*Intrapancreatic – diffuse or segmental enlargement, edema, gas bubbles, pancreatic pseudocysts and phlegmons/abscesses (which present 4 to 6 wks after initial onset)
*Peripancreatic / extrapancreatic – irregular pancreatic outline, obliterated peripancreatic fat, retroperitoneal edema, fluid in the lessar sac, fluid in the left anterior pararenal space
*Locoregional – Gerota's fascia sign (thickening of inflamed Gerota's fascia, which becomes visible), pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion (seen on basal cuts of the pleural cavity), adynamic ileus, etc.
The principal value of CT imaging to the treating clinician is the capacity to identify devitalised areas of the pancreas which have become necrotic due to ischaemia. Pancreatic necrosis can be reliably identified by intravenous contrast-enhanced CT imaging, and is of value if infection occurs and surgical or percutaneous debridement is indicated.
 On
On
www.sfar.org
Practice guidelines state: :2006: "The two tests that are most helpful at admission in distinguishing mild from severe acute pancreatitis are APACHE-II score and serum hematocrit. It is recommended that APACHE-II scores be generated during the first 3 days of hospitalization and thereafter as needed to help in this distinction. It is also recommended that serum hematocrit be obtained at admission, 12 h after admission, and 24 h after admission to help gauge adequacy of fluid resuscitation." :2005: "Immediate assessment should include clinical evaluation, particularly of any cardiovascular, respiratory, and renal compromise, body mass index, chest x ray, and APACHE II score"
online calculatorPathology Atlas
image. * Parikh RP, Upadhyay KJ. Cullen's sign for acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis. Indian J Med Res erial online2013 ited 2013 Jul 4137:1210 http://www.ijmr.org.in/text.asp?2013/137/6/1210/114397 {{DEFAULTSORT:Acute Pancreatitis Medical emergencies Pancreas disorders Inflammations Medical mnemonics de:Akute Pankreatitis
inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
of the pancreas. Causes in order of frequency include: 1) a gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of mi ...
impacted in the common bile duct
The common bile duct, sometimes abbreviated as CBD, is a duct in the gastrointestinal tract of organisms that have a gallbladder. It is formed by the confluence of the common hepatic duct and cystic duct and terminates by uniting with pancrea ...
beyond the point where the pancreatic duct
The pancreatic duct, or duct of Wirsung (also, the major pancreatic duct due to the existence of an accessory pancreatic duct), is a duct joining the pancreas to the common bile duct. This supplies it with pancreatic juice from the exocrine pancr ...
joins it; 2) heavy alcohol use; 3) systemic disease
A systemic disease is one that affects a number of organs and tissues, or affects the body as a whole.
Examples
* Mastocytosis, including mast cell activation syndrome and eosinophilic esophagitis
* Chronic fatigue syndrome
* Systemic vas ...
; 4) trauma; 5) and, in minors, mumps. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event; it may be recurrent; or it may progress to chronic pancreatitis.
Mild cases are usually successfully treated with conservative measures: hospitalization, pain control, nothing by mouth
Nothing by mouth is a medical instruction meaning to withhold food and fluids. It is also known as nil per os (npo or NPO), a Latin phrase that translates to English as "nothing through the mouth". Variants include nil by mouth (NBM), nihil/non/nu ...
, intravenous nutritional support, and intravenous fluid rehydration. Severe cases often require admission to an intensive care unit
220px, Intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensi ...
to monitor and manage complications of the disease. Complications are associated with a high mortality, even with optimal management.
Signs and symptoms
Common
*severeepigastric pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a more ...
(upper abdominal pain) radiating to the back in 50% of cases
* nausea
* vomiting
*loss of appetite
Anorexia is a medical term for a loss of appetite. While the term in non-scientific publications is often used interchangeably with anorexia nervosa, many possible causes exist for a loss of appetite, some of which may be harmless, while others i ...
*fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
* chills (shivering)
* hemodynamic instability, including shock
*tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ( ...
(rapid heartbeat)
* respiratory distress
*peritonitis
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part o ...
* hiccup
Although these are common symptoms, frequently they are not all present; and epigastric pain may be the only symptom.
Uncommon
The following are associated with severe disease: *Grey-Turner's sign
Grey Turner's sign refers to bruising of the flanks, the part of the body between the last rib and the top of the hip. The bruising appears as a blue discoloration, and is a sign of retroperitoneal hemorrhage, or bleeding behind the peritoneum, wh ...
(hemorrhagic discoloration of the flanks)
* Cullen's sign (hemorrhagic discoloration of the umbilicus)
*Pleural effusions (fluid in the bases of the pleural cavity)
* Grünwald sign (appearance of ecchymosis
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur close ...
, large bruise, around the umbilicus due to local toxic lesion of the vessels)
* Körte's sign (pain or resistance in the zone where the head of pancreas is located (in epigastrium, 6–7 cm above the umbilicus))
* Kamenchik's sign (pain with pressure under the xiphoid process
The xiphoid process , or xiphisternum or metasternum, is a small cartilaginous process (extension) of the inferior (lower) part of the sternum, which is usually ossified in the adult human. It may also be referred to as the ensiform process. Bo ...
)
* Mayo-Robson's sign (pain while pressing at the top of the angle lateral to the erector spinae muscles and below the left 12th rib (left costovertebral angle (CVA))
* Mayo-Robson's point – a point on border of inner 2/3 with the external 1/3 of the line that represents the bisection of the left upper abdominal quadrant, where tenderness on pressure exists in disease of the pancreas. At this point the tail of pancreas is projected on the abdominal wall.
Complications
Locoregional complications include pancreatic pseudocyst (most common, occurring in up to 25% of all cases, typically after 4–6 weeks) and phlegmon/abscess formation, splenic artery pseudoaneurysms, hemorrhage from erosions into splenic artery and vein, thrombosis of the splenic vein, superior mesenteric vein and portal veins (in descending order of frequency), duodenal obstruction, common bile duct obstruction, progression to chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion, sterile/infected pancreatic necrosis. Systemic complications include acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS),multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is altered organ function in an acutely ill patient requiring medical intervention to achieve homeostasis.
Although Irwin and Rippe cautioned in 2005 that the use of "multiple organ failure" or "multisy ...
, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia is a medical condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood serum. The normal range of blood calcium is typically between 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L) while levels less than 2.1 mm ...
(from fat saponification), hyperglycemia and insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (from pancreatic insulin-producing beta cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are a type of cell found in pancreatic islets that synthesize and secrete insulin and amylin. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type 1 diabetes, beta-cell mass and function are di ...
damage), malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a variety ...
due to exocrine failure
* Metabolic
**Hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia is a medical condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood serum. The normal range of blood calcium is typically between 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L) while levels less than 2.1 mm ...
, hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia
Hypertriglyceridemia is the presence of high amounts of triglycerides in the blood. Triglycerides are the most abundant fatty molecule in most organisms. Hypertriglyceridemia occurs in various physiologic conditions and in various diseases, and ...
* Respiratory
**Hypoxemia
Hypoxemia is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia has many causes, and often causes hypoxia as the blood is not supplying enough oxygen to the tissues of the bod ...
, atelectasis
Atelectasis is the collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct ...
, effusion, pneumonitis
Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue. Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest, exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris (e.g., animal dander), aspiration, herbicide ...
, acute respiratory distress syndrome
* Renal
** Renal artery or vein thrombosis
** Kidney failure
* Circulatory
** Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
** Hypovolemia and shock
** Myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
** Pericardial effusion
** Vascular thrombosis
* Gastrointestinal
** Gastrointestinal hemorrhage from stress ulceration
** Gastric varices (secondary to splenic vein thrombosis)
** Gastrointestinal obstruction
* Hepatobiliary
** Jaundice
** Portal vein thrombosis
* Neurologic
** Psychosis or encephalopathy
Encephalopathy (; from grc, ἐνκέφαλος "brain" + πάθος "suffering") means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but r ...
(confusion, delusion and coma)
** Cerebral Embolism
** Blindness
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment� ...
(angiopathic retinopathy with hemorrhage)
* Hematologic
** Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
** Disseminated intravascular coagulation
** Leucocytosis
*Dermatologic
** Painful subcutaneous fat necrosis
*Miscellaneous
** Subcutaneous fat necrosis
** Arthalgia
Causes
Most common
* Biliary pancreatitis due to gallstones or constriction of ampulla of Vater in 40% of cases * Alcohol in 30% of cases * Idiopathic in 15-25% of cases * Metabolic disorders: hereditary pancreatitis, hypercalcemia, elevated triglycerides, malnutrition * Post- endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography * Abdominal trauma * Penetrating ulcers * Carcinoma of thehead of pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocri ...
, and other cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
* Drugs: diuretics
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics i ...
(e.g., thiazides
Thiazide () refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of diuretics based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine. The thiazide drug class was discovered and developed at Merck and Co. in the 1950s. The first ...
, furosemide), gliptins (e.g., vildagliptin
Vildagliptin, sold under the brand name Galvus and others, is an oral anti-hyperglycemic agent (anti-diabetic drug) of the DPP-4 inhibitors, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class of drugs. Vildagliptin inhibits the inactivation of Glucag ...
, sitagliptin, saxagliptin
Saxagliptin, sold under the brand name Onglyza, is an oral hypoglycemic ( anti-diabetic drug) of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class. Early development was solely by Bristol-Myers Squibb; in 2007 AstraZeneca joined with Bristol-My ...
, linagliptin
Linagliptin, sold under the brand name Tradjenta among others, is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes (but not type 1) in conjunction with exercise and diet. It is generally less preferred than metformin and sulfonylureas as an initial tr ...
), tetracycline, sulfonamides, estrogens
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal acti ...
, azathioprine
Azathioprine (AZA), sold under the brand name Imuran, among others, is an immunosuppressive medication. It is used in rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and systemic lupus erythematosus, ...
and mercaptopurine
Mercaptopurine (6-MP), sold under the brand name Purinethol among others, is a medication used for cancer and autoimmune diseases. Specifically it is used to treat acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), Crohn's dis ...
, pentamidine, salicylates, steroids, Depakote
* Infections: mumps, viral hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is liver inflammation due to a viral infection. It may present in acute form as a recent infection with relatively rapid onset, or in chronic form.
The most common causes of viral hepatitis are the five unrelated hepatotropic vi ...
, coxsackie B virus
Coxsackie B is a group of six serotypes of coxsackievirus (CVB1-CVB6), a pathogenic enterovirus, that trigger illness ranging from gastrointestinal distress to full-fledged pericarditis and myocarditis (coxsackievirus-induced cardiomyopathy).
Th ...
, cytomegalovirus, ''Mycoplasma pneumoniae
''Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' is a very small bacterium in the class Mollicutes. It is a human pathogen that causes the disease mycoplasma pneumonia, a form of atypical bacterial pneumonia related to cold agglutinin disease. ''M. pneumoniae'' is c ...
'', '' Ascaris''
*Structural abnormalities: choledochocele, pancreas divisum
* Radiotherapy
* Autoimmune pancreatitis
Autoimmune Pancreatitis (AIP) is an increasingly recognized type of chronic pancreatitis that can be difficult to distinguish from pancreatic carcinoma but which responds to treatment with corticosteroids, particularly prednisone. Although autoi ...
* Severe hypertriglyceridemia
Hypertriglyceridemia is the presence of high amounts of triglycerides in the blood. Triglycerides are the most abundant fatty molecule in most organisms. Hypertriglyceridemia occurs in various physiologic conditions and in various diseases, and ...
Less common
* Scorpion venom * Chinese liver fluke * Ischemia frombypass surgery
Bypass surgery refers to a class of surgery involving rerouting a tubular body part.
Types include:
* Vascular bypass surgery such as coronary artery bypass surgery, a heart operation
* Cardiopulmonary bypass, a technique used in coronary artery ...
* Heart valve surgery
* Fat necrosis
Fat necrosis is a form of necrosis characterized by the action upon fat by digestive enzymes.
In fat necrosis the enzyme lipase releases fatty acids from triglycerides. The fatty acids then complex with calcium to form soaps. These soaps appea ...
* Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
* Infections other than mumps, including varicella zoster
* Hyperparathyroidism
* Valproic acid
Valproate (VPA) and its valproic acid, sodium valproate, and valproate semisodium forms are medications primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and prevent migraine headaches. They are useful for the prevention of seizures in those ...
* Cystic fibrosis
* Anorexia
Anorexia nervosa, often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by low weight, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. ''Anorexia'' is a term of Gre ...
or bulimia
Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging or fasting, and excessive concern with body shape and weight. The aim of this activity is to expel the body of calories eaten ...
* Codeine phosphate reaction
Pathology
Pathogenesis
Acute pancreatitis occurs when there is abnormal activation of digestive enzymes within the pancreas. This occurs through inappropriate activation of inactive enzyme precursors calledzymogens
In biochemistry, a zymogen (), also called a proenzyme (), is an inactive precursor of an enzyme. A zymogen requires a biochemical change (such as a hydrolysis reaction revealing the active site, or changing the configuration to reveal the active ...
(or proenzymes) inside the pancreas, most notably trypsinogen Trypsinogen () is the precursor form (or zymogen) of trypsin, a digestive enzyme. It is produced by the pancreas and found in pancreatic juice, along with amylase, lipase, and chymotrypsinogen. It is cleaved to its active form, trypsin, by ent ...
. Normally, trypsinogen is converted to its active form ( trypsin) in the first part of the small intestine ( duodenum), where the enzyme assists in the digestion of proteins. During an episode of acute pancreatitis, trypsinogen comes into contact with lysosomal enzymes (specifically cathepsin
Cathepsins (Ancient Greek ''kata-'' "down" and ''hepsein'' "boil"; abbreviated CTS) are proteases (enzymes that degrade proteins) found in all animals as well as other organisms. There are approximately a dozen members of this family, which are di ...
), which activate trypsinogen to trypsin. The active form trypsin then leads to further activation of other molecules of trypsinogen. The activation of these digestive enzymes lead to inflammation, edema, vascular injury, and even cellular death. The death of pancreatic cells occurs via two main mechanisms: necrosis, which is less organized and more damaging, or apoptosis, which is more controlled. The balance between these two mechanisms of cellular death is mediated by caspases which regulate apoptosis and have important anti-necrosis functions during pancreatitis: preventing trypsinogen activation, preventing ATP depletion through inhibiting polyADP-ribose polymerase, and by inhibiting the inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs). If, however, the caspases are depleted due to either chronic ethanol exposure or through a severe insult then necrosis can predominate.
Pathophysiology
The two types of acute pancreatitis are mild and severe, which are defined based on whether the predominant response to cell injury is inflammation (mild) or necrosis (severe). In mild pancreatitis, there is inflammation and edema of the pancreas. In severe pancreatitis, there is necrosis of the pancreas, and nearby organs may become injured. As part of the initial injury there is an extensive inflammatory response due to pancreatic cells synthesizing and secreting inflammatory mediators: primarilyTNF-alpha
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
and IL-1. A hallmark of acute pancreatitis is a manifestation of the inflammatory response, namely the recruitment of neutrophils to the pancreas. The inflammatory response leads to the secondary manifestations of pancreatitis: hypovolemia from capillary permeability, acute respiratory distress syndrome, disseminated intravascular coagulations, renal failure, cardiovascular failure, and gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
Histopathology
The acute pancreatitis (acute hemorrhagic pancreatic necrosis) is characterized by acute inflammation and necrosis of pancreas parenchyma, focal enzymic necrosis of pancreatic fat and vessel necrosis ( hemorrhage). These are produced by intrapancreatic activation of pancreatic enzymes. Lipase activation produces the necrosis of fat tissue in pancreatic interstitium and peripancreatic spaces as well as vessel damage. Necrotic fat cells appear as shadows, contours of cells, lacking the nucleus, pink, finely granular cytoplasm. It is possible to find calcium precipitates (). Digestion of vascular walls results in thrombosis and hemorrhage. Inflammatory infiltrate is rich in neutrophils. Due to the pancreas lacking a capsule, the inflammation and necrosis can extend to include fascial layers in the immediate vicinity of the pancreas.Diagnosis
Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed using clinical history andphysical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the pati ...
, based on the presence of at least 2 of 3 criteria: abdominal pain, elevated serum lipase or amylase, and abdominal imaging findings consistent with acute pancreatitis. Additional blood studies are used to identify organ failure, offer prognostic information, and determine if fluid resuscitation is adequate and whether endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is necessary.
* Blood investigations – complete blood count, kidney function tests, liver function, serum calcium, serum amylase and lipase
* Imaging – A triple phase abdominal CT and abdominal ultrasound are together considered the gold standard for the evaluation of acute pancreatitis. Other modalities including the abdominal x-ray lack sensitivity and are not recommended. An important caveat is that imaging during the first 12 hours may be falsely reassuring as the inflammatory and necrotic process usually requires 48 hours to fully manifest.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis includes: * Perforatedpeptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines ...
* Biliary colic
Biliary colic, also known as symptomatic cholelithiasis, a gallbladder attack or gallstone attack, is when a colic (sudden pain) occurs due to a gallstone temporarily blocking the cystic duct. Typically, the pain is in the right upper part of th ...
* Acute cholecystitis
* Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
* Pleuritic
Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other sym ...
pain
* Myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
Biochemical
* Elevated serumamylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of ...
and lipase levels, in combination with severe abdominal pain, often trigger the initial diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. However, they have no role in assessing disease severity.
* Serum lipase rises 4 to 8 hours from the onset of symptoms and normalizes within 7 to 14 days after treatment.
* Serum amylase may be normal (in 10% of cases) for cases of acute or chronic pancreatitis (depleted acinar cell mass) and hypertriglyceridemia.
* Reasons for false positive elevated serum amylase include salivary gland disease (elevated salivary amylase), bowel obstruction, infarction, cholecystitis, and a perforated ulcer.
* If the lipase level is about 2.5 to 3 times that of amylase, it is an indication of pancreatitis due to alcohol.
**Decreased serum calcium
**Glycosuria
Regarding selection on these tests, two practice guidelines state:
: "It is usually not necessary to measure both serum amylase and lipase. Serum lipase may be preferable because it remains normal in some nonpancreatic conditions that increase serum amylase including macroamylasemia, parotitis, and some carcinomas. In general, serum lipase is thought to be more sensitive and specific than serum amylase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis"
: "Although amylase is widely available and provides acceptable accuracy of diagnosis, where lipase is available it is preferred for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis (recommendation grade A)"
Most, but not all individual studies support the superiority of the lipase. In one large study, there were no patients with pancreatitis who had an elevated amylase with a normal lipase. Another study found that the amylase could add diagnostic value to the lipase, but only if the results of the two tests were combined with a discriminant function equation.
While often quoted lipase levels of 3 or more times the upper-limit of normal is diagnostic of pancreatitis, there are also other differential diagnosis to be considered relating to this rise.
Computed tomography
 Regarding the need for computed tomography, practice guidelines state:
CT is an important common initial assessment tool for acute pancreatitis. Imaging is indicated during the initial presentation if:
*the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis is uncertain
*there is abdominal distension and tenderness, fever >102 F (38,9 C), or leukocytosis
*there is a Ranson score > 3 or APACHE score > 8
*there is no improvement after 72 hours of conservative medical therapy
*there has been an acute change in status: fever, pain, or shock
CT is recommended as a delayed assessment tool in the following situations:
*acute change in status
*to determine therapeutic response after surgery or interventional radiologic procedure
*before discharge in patients with severe acute pancreatitis
Abdominal CT should not be performed before the first 12 hours of onset of symptoms as early CT (<12 hours) may result in equivocal or normal findings.
CT findings can be classified into the following categories for easy recall:
*Intrapancreatic – diffuse or segmental enlargement, edema, gas bubbles, pancreatic pseudocysts and phlegmons/abscesses (which present 4 to 6 wks after initial onset)
*Peripancreatic / extrapancreatic – irregular pancreatic outline, obliterated peripancreatic fat, retroperitoneal edema, fluid in the lessar sac, fluid in the left anterior pararenal space
*Locoregional – Gerota's fascia sign (thickening of inflamed Gerota's fascia, which becomes visible), pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion (seen on basal cuts of the pleural cavity), adynamic ileus, etc.
The principal value of CT imaging to the treating clinician is the capacity to identify devitalised areas of the pancreas which have become necrotic due to ischaemia. Pancreatic necrosis can be reliably identified by intravenous contrast-enhanced CT imaging, and is of value if infection occurs and surgical or percutaneous debridement is indicated.
Regarding the need for computed tomography, practice guidelines state:
CT is an important common initial assessment tool for acute pancreatitis. Imaging is indicated during the initial presentation if:
*the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis is uncertain
*there is abdominal distension and tenderness, fever >102 F (38,9 C), or leukocytosis
*there is a Ranson score > 3 or APACHE score > 8
*there is no improvement after 72 hours of conservative medical therapy
*there has been an acute change in status: fever, pain, or shock
CT is recommended as a delayed assessment tool in the following situations:
*acute change in status
*to determine therapeutic response after surgery or interventional radiologic procedure
*before discharge in patients with severe acute pancreatitis
Abdominal CT should not be performed before the first 12 hours of onset of symptoms as early CT (<12 hours) may result in equivocal or normal findings.
CT findings can be classified into the following categories for easy recall:
*Intrapancreatic – diffuse or segmental enlargement, edema, gas bubbles, pancreatic pseudocysts and phlegmons/abscesses (which present 4 to 6 wks after initial onset)
*Peripancreatic / extrapancreatic – irregular pancreatic outline, obliterated peripancreatic fat, retroperitoneal edema, fluid in the lessar sac, fluid in the left anterior pararenal space
*Locoregional – Gerota's fascia sign (thickening of inflamed Gerota's fascia, which becomes visible), pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion (seen on basal cuts of the pleural cavity), adynamic ileus, etc.
The principal value of CT imaging to the treating clinician is the capacity to identify devitalised areas of the pancreas which have become necrotic due to ischaemia. Pancreatic necrosis can be reliably identified by intravenous contrast-enhanced CT imaging, and is of value if infection occurs and surgical or percutaneous debridement is indicated.
Magnetic resonance imaging
While computed tomography is considered the gold standard in diagnostic imaging for acute pancreatitis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has become increasingly valuable as a tool for the visualization of the pancreas, particularly of pancreatic fluid collections and necrotized debris. Additional utility of MRI includes its indication for imaging of patients with an allergy to CT's contrast material, and an overall greater sensitivity to hemorrhage, vascular complications, pseudoaneurysms, and venous thrombosis. Another advantage of MRI is its utilization ofmagnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a medical imaging technique. It uses magnetic resonance imaging to visualize the biliary and pancreatic ducts non-invasively. This procedure can be used to determine whether gallstones are ...
(MRCP) sequences. MRCP provides useful information regarding the etiology of acute pancreatitis, i.e., the presence of tiny biliary stones (choledocholithiasis
Common bile duct stone, also known as choledocholithiasis, is the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct (CBD) (thus '' choledocho-'' + ''lithiasis''). This condition can cause jaundice and liver cell damage. Treatments include choledocholi ...
or cholelithiasis) and duct anomalies. Clinical trials indicate that MRCP can be as effective a diagnostic tool for acute pancreatitis with biliary etiology as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems. It is primarily performed by highly skille ...
, but with the benefits of being less invasive and causing fewer complications.
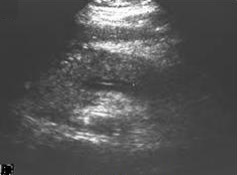
Ultrasound
 On
On abdominal ultrasonography
Abdominal ultrasonography (also called abdominal ultrasound imaging or abdominal sonography) is a form of medical ultrasonography (medical application of ultrasound technology) to visualise abdominal anatomical structures. It uses transmission a ...
, the finding of a hypoechoic and bulky pancreas is regarded as diagnostic of acute pancreatitis.
Treatment
Initial management of a patient with acute pancreatitis consists of supportive care with fluid resuscitation, pain control, nothing by mouth, and nutritional support.Fluid replacement
Aggressive hydration at a rate of 5 to 10 mL/kg per hour of isotonic crystalloid solution (e.g., normal saline or lactated Ringer's solution) to all patients with acute pancreatitis, unless cardiovascular, renal, or other related comorbid factors preclude aggressive fluid replacement. In patients with severe volume depletion that manifests as hypotension and tachycardia, more rapid repletion with 20 mL/kg of intravenous fluid given over 30 minutes followed by 3 mL/kg/hour for 8 to 12 hours. Fluid requirements should be reassessed at frequent intervals in the first six hours of admission and for the next 24 to 48 hours. The rate of fluid resuscitation should be adjusted based on clinical assessment, hematocrit and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) values. In the initial stages (within the first 12 to 24 hours) of acute pancreatitis, fluid replacement has been associated with a reduction in morbidity and mortality.Pain control
Abdominal pain is often the predominant symptom in patients with acute pancreatitis and should be treated with analgesics. Opioids are safe and effective at providing pain control in patients with acute pancreatitis. Adequate pain control requires the use of intravenous opiates, usually in the form of a patient-controlled analgesia pump.Hydromorphone
Hydromorphone, also known as dihydromorphinone, and sold under the brand name Dilaudid among others, is an opioid used to treat moderate to severe pain. Typically, long-term use is only recommended for pain due to cancer. It may be used by mou ...
or fentanyl (intravenous) may be used for pain relief in acute pancreatitis. Fentanyl is being increasingly used due to its better safety profile, especially in renal impairment. As with other opiates, fentanyl can depress respiratory function. It can be given both as a bolus as well as constant infusion.
Meperidine
Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisl ...
has been historically favored over morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
because of the belief that morphine caused an increase in sphincter of Oddi pressure. However, no clinical studies suggest that morphine can aggravate or cause pancreatitis or cholecystitis. In addition, meperidine has a short half-life and repeated doses can lead to accumulation of the metabolite normeperidine, which causes neuromuscular side effects and, rarely, seizures.
Bowel rest
In the management of acute pancreatitis, the treatment is to stop feeding the patient, giving them nothing by mouth, giving intravenous fluids to preventdehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mil ...
, and sufficient pain control. As the pancreas is stimulated to secrete enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s by the presence of food in the stomach, having no food pass through the system allows the pancreas to rest. Approximately 20% of patients have a relapse of pain during acute pancreatitis. Approximately 75% of relapses occur within 48 hours of oral refeeding.
The incidence of relapse after oral refeeding may be reduced by post-pyloric enteral
Enteral administration is food or drug administration via the human gastrointestinal tract. This contrasts with parenteral nutrition or drug administration (Greek ''para'', "besides" + ''enteros''), which occurs from routes outside the GI tract, ...
rather than parenteral feeding prior to oral refeeding. IMRIE scoring is also useful.
Nutritional support
Recently, there has been a shift in the management paradigm fromtotal parenteral nutrition
Parenteral nutrition (PN) is the feeding of nutritional products to a person intravenously, bypassing the usual process of eating and digestion. The products are made by pharmaceutical compounding companies. The person receives a nutritional mix ...
(TPN) to early, post-pyloric enteral feeding (in which a feeding tube is endoscopically or radiographically introduced to the third portion of the duodenum). The advantage of enteral feeding is that it is more physiological, prevents gut mucosal atrophy, and is free from the side effects of TPN (such as fungemia). The additional advantages of post-pyloric feeding are the inverse relationship of pancreatic exocrine secretions and distance of nutrient delivery from the pylorus, as well as reduced risk of aspiration.
Disadvantages of a naso-enteric feeding tube include increased risk of sinusitis (especially if the tube remains in place greater than two weeks) and a still-present risk of accidentally intubating the trachea even in intubated patients (contrary to popular belief, the endotracheal tube cuff alone is not always sufficient to prevent NG tube entry into the trachea).
Oxygen
Oxygen may be provided in some patients (about 30%) if Pao2 levels fall below 70mm of Hg.Antibiotics
Up to 20 percent of people with acute pancreatitis develop an infection outside the pancreas such as bloodstream infections, pneumonia, or urinary tract infections. These infections are associated with an increase in mortality. When an infection is suspected, antibiotics should be started while the source of the infection is being determined. However, if cultures are negative and no source of infection is identified, antibiotics should be discontinued. Preventative antibiotics are not recommended in people with acute pancreatitis, regardless of the type (interstitial or necrotizing) or disease severity (mild, moderately severe, or severe)Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
In 30% of those with acute pancreatitis, no cause is identified.Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems. It is primarily performed by highly skille ...
(ERCP) with empirical biliary sphincterotomy has an equal chance of causing complications and treating the underlying cause, therefore, is not recommended for treating acute pancreatitis. If a gallstone is detected, ERCP, performed within 24 to 72 hours of presentation with successful removal of the stone, is known to reduce morbidity and mortality. The indications for early ERCP are:
* Clinical deterioration or lack of improvement after 24 hours
* Detection of common bile duct stones or dilated intrahepatic or extrahepatic ducts on abdominal CT
The risks of ERCP are that it may worsen pancreatitis, it may introduce an infection to otherwise sterile pancreatitis, and bleeding.
Surgery
Surgery is indicated for (i) infected pancreatic necrosis and (ii) diagnostic uncertainty and (iii) complications. The most common cause of death in acute pancreatitis is secondary infection. Infection is diagnosed based on 2 criteria *Gas bubbles on CT scan (present in 20 to 50% of infected necrosis) *Positive bacterial culture on FNA (fine needle aspiration, usually CT or US guided) of the pancreas. Surgical options for infected necrosis include: *Minimally invasive management – necrosectomy through small incision in skin (left flank) or abdomen *Conventional management – necrosectomy with simple drainage *Closed management – necrosectomy with closed continuous postoperative lavage *Open management – necrosectomy with planned staged reoperations at definite intervals (up to 20+ reoperations in some cases)Other measures
*Pancreatic enzyme inhibitors are proven not to work. *The use of octreotide has been shown not to improve outcomes.Classification by severity: prognostic scoring systems
Acute pancreatitis patients recover in majority of cases. Some may develop abscess, pseudocyst or duodenal obstruction. In 5 percent cases, it may result in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), disseminated intravascular coagulation DIC. Acute pancreatitis can be further divided into mild and severe pancreatitis. Mostly the Ranson Criteria are used to determine severity of acute pancreatitis. In severe pancreatitis serious amounts of necrosis determine the further clinical outcome. About 20% of the acute pancreatitis are severe with a mortality of about 20%. This is an important classification as severe pancreatitis will need intensive care therapy whereas mild pancreatitis can be treated on the common ward. Necrosis will be followed by asystemic inflammatory response syndrome
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is an inflammatory state affecting the whole body. It is the body's response to an infectious or noninfectious insult. Although the definition of SIRS refers to it as an "inflammatory" response, i ...
(SIRS) and will determine the immediate clinical course. The further clinical course is then determined by bacterial infection. SIRS is the cause of bacterial (Gram negative) translocation from the patients colon.
There are several ways to help distinguish between these two forms. One is the above-mentioned Ranson Score.
In predicting the prognosis, there are several scoring indices that have been used as predictors of survival. Two such scoring systems are the Ranson criteria and APACHE II (Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation) indices. Most, but not all (comment=this study used an Apache cutoff of >=10) studies report that the Apache score may be more accurate. In the negative study of the APACHE-II, the APACHE-II 24-hour score was used rather than the 48-hour score. In addition, all patients in the study received an ultrasound twice which may have influenced allocation of co-interventions. Regardless, only the APACHE-II can be fully calculated upon admission. As the APACHE-II is more cumbersome to calculate, presumably patients whose only laboratory abnormality is an elevated lipase or amylase do not need assessment with the APACHE-II; however, this approach is not studied. The APACHE-II score can be calculated awww.sfar.org
Practice guidelines state: :2006: "The two tests that are most helpful at admission in distinguishing mild from severe acute pancreatitis are APACHE-II score and serum hematocrit. It is recommended that APACHE-II scores be generated during the first 3 days of hospitalization and thereafter as needed to help in this distinction. It is also recommended that serum hematocrit be obtained at admission, 12 h after admission, and 24 h after admission to help gauge adequacy of fluid resuscitation." :2005: "Immediate assessment should include clinical evaluation, particularly of any cardiovascular, respiratory, and renal compromise, body mass index, chest x ray, and APACHE II score"
Ranson score
The Ranson score is used to predict the severity of acute pancreatitis. They were introduced in 1974.At admission
* age in years > 55 years * white blood cell count > 16000 cells/mm3 * blood glucose > 11.1 mmol/L (> 200 mg/dL) * serum AST > 250 IU/L * serum LDH > 350 IU/LAt 48 hours
* Calcium (serum calcium < 2.0 mmol/L (< 8.0 mg/dL) * Hematocrit fall >10% * Oxygen (hypoxemia PO2 < 60 mmHg) * BUN increased by 1.8 or more mmol/L (5 or more mg/dL) after IV fluid hydration * Base deficit (negative base excess) > 4 mEq/L * Sequestration of fluids > 6 L The criteria for point assignment is that a certain breakpoint be met at any time during that 48 hour period, so that in some situations it can be calculated shortly after admission. It is applicable to both gallstone and alcoholic pancreatitis. Alternatively, pancreatitis can be diagnosed by meeting any of the following:Alternative Ranson score
Ranson's score of ≥ 8 Organ failure Substantial pancreatic necrosis (at least 30% glandular necrosis according to contrast-enhanced CT) Interpretation If the score ≥ 3, severe pancreatitis likely. If the score < 3, severe pancreatitis is unlikely Or Score 0 to 2 : 2% mortality Score 3 to 4 : 15% mortality Score 5 to 6 : 40% mortality Score 7 to 8 : 100% mortalityAPACHE II score
"Acute Physiology And Chronic Health Evaluation" ( APACHE II) score > 8 points predicts 11% to 18% mortality *Hemorrhagic peritoneal fluid *Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
*Indicators of organ failure
*Hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
(SBP <90 mmHG) or tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ( ...
> 130 beat/min
*PO2 <60 mmHg
* Oliguria (<50 mL/h) or increasing BUN
A bun is a type of bread roll, typically filled with savory fillings (for example hamburger). A bun may also refer to a sweet cake in certain parts of the world. Though they come in many shapes and sizes, buns are most commonly round, and are g ...
and creatinine
Creatinine (; ) is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass).
Biological relevance
Serum creatinine (a blood measurement) is an importa ...
*Serum calcium < 1.90 mmol/L (<8.0 mg/dL) or serum albumin <33 g/L (<3.2.g/dL)>
Balthazar score
Developed in the early 1990s by Emil J. Balthazar ''et al.'', the Computed Tomography Severity Index (CTSI) is a grading system used to determine the severity of acute pancreatitis. The numerical CTSI has a maximum of ten points, and is the sum of the Balthazar grade points and pancreatic necrosis grade points: Balthazar grade Necrosis score CTSI's staging of acute pancreatitis severity has been shown by a number of studies to provide more accurate assessment than APACHE II, Ranson, andC-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin- ...
(CRP) level. However, a few studies indicate that CTSI is not significantly associated with the prognosis of hospitalization in patients with pancreatic necrosis, nor is it an accurate predictor of AP severity.
Glasgow score
The Glasgow score is valid for both gallstone and alcohol induced pancreatitis, whereas the Ranson score is only for alcohol induced pancreatitis. If a patient scores 3 or more it indicates severe pancreatitis and the patient should be considered for transfer to ITU. It is scored through the mnemonic, PANCREAS: *P - PaO2 <8kPa *A - Age >55-years-old *N - Neutrophilia: WCC >15x10(9)/L *C - Calcium <2 mmol/L *R - Renal function: Urea >16 mmol/L *E - Enzymes: LDH >600iu/L; AST >200iu/L *A - Albumin <32g/L (serum) *S - Sugar: blood glucose >10 mmol/LBISAP score
Predicts mortality risk in pancreatitis with fewer variables than Ranson's criteria. Data should be taken from the first 24 hours of the patient's evaluation. *BUN >25 mg/dL (8.9 mmol/L) *Abnormal mental status with a Glasgow coma score <15 *Evidence of SIRS (systemic inflammatory response syndrome) *Patient age >60 years old *Imaging study reveals pleural effusion Patients with a score of zero had a mortality of less than one percent, whereas patients with a score of five had a mortality rate of 22 percent. In the validation cohort, the BISAP score had similar test performance characteristics for predicting mortality as the APACHE II score. As is a problem with many of the other scoring systems, the BISAP has not been validated for predicting outcomes such as length of hospital stay, need for ICU care, or need for intervention.Epidemiology
In the United States, the annual incidence is 18 cases of acute pancreatitis per 100,000 population, and it accounts for 220,000 hospitalizations in the US. In a European cross-sectional study, incidence of acute pancreatitis increased from 12.4 to 15.9 per 100,000 annually from 1985 to 1995; however, mortality remained stable as a result of better outcomes. Another study showed a lower incidence of 9.8 per 100,000 but a similar worsening trend (increasing from 4.9 in 1963–74) over time. In Western countries, the most common cause is alcohol, accounting for 65 percent of acute pancreatitis cases in the US, 20 percent of cases in Sweden, and 5 percent of those in the United Kingdom. In Eastern countries,gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of mi ...
s are the most common cause of acute pancreatitis. The causes of acute pancreatitis also varies across age groups, with trauma and systemic disease (such as infection) being more common in children. Mumps is a more common cause in adolescents and young adults than in other age groups.
See also
* Canine pancreatitis * Chronic pancreatitisReferences
External links
* Banks et al. Modified Marshall scoring systeonline calculator
image. * Parikh RP, Upadhyay KJ. Cullen's sign for acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis. Indian J Med Res erial online2013 ited 2013 Jul 4137:1210 http://www.ijmr.org.in/text.asp?2013/137/6/1210/114397 {{DEFAULTSORT:Acute Pancreatitis Medical emergencies Pancreas disorders Inflammations Medical mnemonics de:Akute Pankreatitis