æ on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Æ (

 In English, use of the ligature varies between different places and contexts, but it is fairly rare. In modern typography, if technological limitations make the use of ''æ'' difficult (such as in use of
In English, use of the ligature varies between different places and contexts, but it is fairly rare. In modern typography, if technological limitations make the use of ''æ'' difficult (such as in use of
 In Danish and Norwegian, ''æ'' is a separate letter of the alphabet that represents a
In Danish and Norwegian, ''æ'' is a separate letter of the alphabet that represents a
 Ossetian – which previously and later used a
Ossetian – which previously and later used a
lowercase
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally '' minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing system ...
: æ) is a character formed from the letters '' a'' and '' e'', originally a ligature Ligature may refer to:
Language
* Ligature (writing), a combination of two or more letters into a single symbol (typography and calligraphy)
* Ligature (grammar), a morpheme that links two words
Medicine
* Ligature (medicine), a piece of suture us ...
representing the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
diphthong
A diphthong ( ), also known as a gliding vowel or a vowel glide, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of ...
''ae''. It has been promoted to the status of a letter
Letter, letters, or literature may refer to:
Characters typeface
* Letter (alphabet), a character representing one or more of the sounds used in speech or none in the case of a silent letter; any of the symbols of an alphabet
* Letterform, the g ...
in some languages, including Danish, Norwegian, Icelandic, and Faroese. It was also used in both Old Swedish
Old Swedish ( Modern Swedish: ) is the name for two distinct stages of the Swedish language that were spoken in the Middle Ages: Early Old Swedish (), spoken from about 1225 until about 1375, and Late Old Swedish (), spoken from about 1375 unti ...
, before being replaced by ä, and Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
, where it was eventually dropped entirely in favour of a. The modern International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation ...
uses it to represent the near-open front unrounded vowel
The near-open front unrounded vowel, or near-low front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a lowercase of the ligature. Both the symbol and the sound ar ...
(the sound represented by the 'a' in English words like ''cat''). Diacritic
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacrit ...
variants include Ǣ/ǣ, Ǽ/ǽ, Æ̀/æ̀, Æ̂/æ̂ and Æ̃/æ̃.
As a letter of the Old English Latin alphabet
The Old English Latin alphabet generally consisted of about 24 letters, and was used for writing Old English from the 8th to the 12th centuries. Of these letters, most were directly adopted from the Latin alphabet, two were modified Latin letters ...
, it was called , "ash tree
''Fraxinus'' (), commonly called ash, is a genus of plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae, and comprises 45–65 species of usually medium-to-large trees, most of which are deciduous trees, although some subtropical species are evergr ...
", after the Anglo-Saxon futhorc
Anglo-Saxon runes or Anglo-Frisian runes are runes that were used by the Anglo-Saxons and Medieval Frisians (collectively called Anglo-Frisians) as an alphabet in their native writing system, recording both Old English and Old Frisian (, ᚱ� ...
rune ᚫ which it transliterated
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one writing system, script to another that involves swapping Letter (alphabet), letters (thus ''wikt:trans-#Prefix, trans-'' + ''wikt:littera#Latin, liter-'') in predictable ways, such as ...
; its traditional name in English is still ash, or æsh () if the ligature is included.


Languages
English
typewriter
A typewriter is a Machine, mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of Button (control), keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an i ...
s, telegraphs, or ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
), the digraph
Digraph, often misspelled as diagraph, may refer to:
* Digraph (orthography), a pair of characters used together to represent a single sound, such as "nq" in Hmong RPA
* Ligature (writing), the joining of two letters as a single glyph, such as " ...
'' ae'' is often used instead.
In Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
, ''æ'' represented a sound between ''a'' and ''e'' (), very much like the short ''a'' of ''cat'' in many dialects of Modern English. If long vowels are distinguished from short vowels, the long version is marked with a macron (''ǣ'') or, less commonly, an acute (''ǽ'').
In the United States, the issue of the ligature is sidestepped in many cases by use of a simplified spelling with "e", as happened with œ as well; thus, ''archeology'' is more commonly used than ''archaeology'' in American English. Usage of the ''ae'' diphthong, however, may vary. For example, ''medieval'' is now more common than ''mediaeval'' (and the now old-fashioned ''mediæval''), even in the United Kingdom.
French
In the modernFrench alphabet
French orthography encompasses the spelling and punctuation of the French language. It is based on a combination of phoneme, phonemic and historical principles. The spelling of words is largely based on the pronunciation of Old French –1200 AD, ...
, ''æ'' (called , 'e in the a') is used to spell Latin and Greek borrowings like '' curriculum vitæ'', '' et cætera'', '' ex æquo'', '' tænia'', and the first name Lætitia. It is mentioned in the name of Serge Gainsbourg
Serge Gainsbourg (; born Lucien Ginsburg; 2 April 1928 – 2 March 1991) was a French singer-songwriter, actor, composer, and director. Regarded as one of the most important figures in French pop, he was renowned for often provocative rel ...
's song ''Elaeudanla Téïtéïa'', a reading of the French spelling of the name Lætitia: "L, A, E dans l'A, T, I, T, I, A."
Latin
InClassical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a Literary language, literary standard language, standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It formed parallel to Vulgar Latin around 75 BC out of Old Latin ...
, the combination ''AE'' denotes the diphthong
A diphthong ( ), also known as a gliding vowel or a vowel glide, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of ...
, which had a value similar to the long ''i'' in ''fine'' as pronounced in most dialects of Modern English. Both classical and present practice is to write the letters separately, but the ligature was used in medieval and early modern writings, in part because ''æ'' was reduced to the simple vowel during the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. In some medieval scripts, the ligature was simplified to ''ę'', an ''e'' with ogonek
The tail or ( ; Polish: , "little tail", diminutive of ) is a diacritic hook placed under the lower right corner of a vowel in the Latin alphabet used in several European languages, and directly under a vowel in several Native American langu ...
, called the ''e caudata
file:Sacrecon.png, 270px, Part of a Latin book published in Rome in 1632. ''E caudata'' is used in the words Sacrę, propagandę, prædictę, and grammaticę. The spelling grammaticæ, with ''æ'', is also used.
The e caudata (, Latin for "tailed e ...
'' (Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
for "tailed e"). That was further simplified into a plain ''e'', which may have influenced or been influenced by the pronunciation change. However, the ligature is still relatively common in liturgical book
A liturgical book, or service book, is a book published by the authority of a church body that contains the text and directions for the liturgy of its official Church service, religious services.
Christianity Roman Rite
In the Roman Rite of ...
s and musical scores.
Other Germanic languages
Old Norse InOld Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
, ''æ'' represents the long vowel . The short version of the same vowel, , if it is distinguished from , is written as ''ę''.
Icelandic
In Icelandic, ''æ'' represents the diphthong
A diphthong ( ), also known as a gliding vowel or a vowel glide, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of ...
, which can be long or short.
Faroese
In most varieties of Faroese, ''æ'' is pronounced as follows:
* when simultaneously stressed and occurring either word-finally, before a vowel letter, before a single consonant letter, or before the consonant-letter groups ''kl'', ''kr'', ''pl'', ''pr'', ''tr'', ''kj'', ''tj'', ''sj'', and those consisting of ''ð'' and one other consonant letter, except for ''ðr'' when pronounced like ''gr'' (except as below)
*a rather open when directly followed by the sound , as in (silent ''ð'') and (silent ''g'')
* in all other cases
One of its etymological origins is Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
é (the other is Old Norse æ), which is particularly evident in the dialects of Suðuroy
Suðuroy (pronounced: �suːwʊrɔior �suːri ‘South Island’, ) is the southernmost of the Faroe Islands. The island covers 163.7 square kilometres (63.2 sq mi). In 2018 the population was 4,601. Suðuroy region ( sýsla) comprise ...
, where Æ is or :
* (eider
The eiders () are large seaducks in the genus ''Somateria''. The three extant species all breed in the cooler latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere.
The down feathers of eider ducks and some other ducks and geese are used to fill pillows and qu ...
): Southern , Northern Faroese
* (family, direction): Southern , Northern Faroese
German and Swedish
The equivalent letter in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
and Swedish is , but it is not located at the same place within the alphabet. In German, it is not a separate letter from "A" but in Swedish, it is the second-to-last letter (between å and ö).
In the normalized spelling of Middle High German
Middle High German (MHG; or ; , shortened as ''Mhdt.'' or ''Mhd.'') is the term for the form of High German, High German language, German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High ...
, represents a long vowel . The actual spelling in the manuscripts varies, however.
Danish and Norwegian
 In Danish and Norwegian, ''æ'' is a separate letter of the alphabet that represents a
In Danish and Norwegian, ''æ'' is a separate letter of the alphabet that represents a monophthong
A monophthong ( ) is a pure vowel sound, or one whose articulation at beginning and end is relatively fixed, with the tongue moving neither up nor down and neither forward nor backward towards a new position of articulation. A monophthong can be ...
. It follows '' z'' and precedes '' ø'' and '' å''. In Norwegian, there are four ways of pronouncing the letter:
* as in (the name of the letter), , , , , , , , , , , , , ("trees")
* as in , , , , , , , , (where is pronounced as a diphthong )
* as in , , , , , , , , , , ("thread(s)" erb
* as in , , , , , ,
In many northern, western, and southwestern Norwegian dialects such as Trøndersk
__NOTOC__
Trøndersk (), also known as ''trøndermål'' () or ''trøndsk'' (), is a Norwegian dialect, or rather a group of several sub-dialects. As is the case with all Norwegian dialects, it has no standardised orthography, and its users writ ...
and in the western Danish dialects of and Southern Jutland
Southern Jutland (; ) is the region south of the Kongeå in Jutland, Denmark and north of the Eider (river) in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The region north of the Kongeå is called . Both territories had their own ting assemblies in the Mi ...
, the word "I" (Standard Danish: , Bokmål
Bokmål () (, ; ) is one of the official written standards for the Norwegian language, alongside Nynorsk. Bokmål is by far the most used written form of Norwegian today, as it is adopted by 85% to 90% of the population in Norway. There is no cou ...
Norwegian: , Nynorsk
Nynorsk (; ) is one of the two official written standards of the Norwegian language, the other being Bokmål. From 12 May 1885, it became the state-sanctioned version of Ivar Aasen's standard Norwegian language (''Landsmål''), parallel to the Da ...
Norwegian: ) is pronounced . Thus, when this word is written as it is pronounced in these dialects (rather than the standard), it is often spelled with the letter "æ".
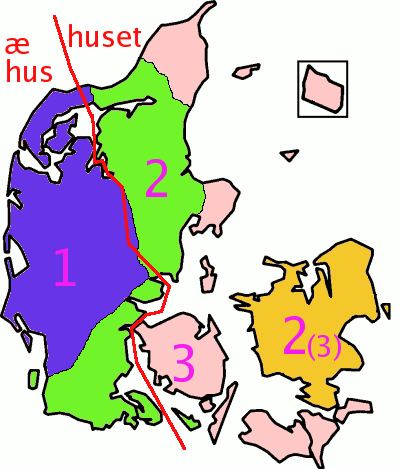
In western and southern Jutish dialects of Danish, is also the proclitic
In morphology and syntax, a clitic ( , backformed from Greek "leaning" or "enclitic"Crystal, David. ''A First Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics''. Boulder, CO: Westview, 1980. Print.) is a morpheme that has syntactic characteristics of a w ...
definite article
In grammar, an article is any member of a class of dedicated words that are used with noun phrases to mark the identifiability of the referents of the noun phrases. The category of articles constitutes a part of speech.
In English, both "the" ...
: (the house), as opposed to Standard Danish and all other Nordic varieties which have enclitic
In morphology and syntax, a clitic ( , backformed from Greek "leaning" or "enclitic"Crystal, David. ''A First Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics''. Boulder, CO: Westview, 1980. Print.) is a morpheme that has syntactic characteristics of a ...
definite articles (Danish, Swedish, Norwegian: ; Icelandic, Faroese: he house.
Ossetian
 Ossetian – which previously and later used a
Ossetian – which previously and later used a Cyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Easte ...
with an identical-looking letter ( Ӕ and ӕ) – was written using the Latin script from 1923 to 1938, and included this character. It is pronounced as a near-open central vowel
The near-open central vowel, or near-low central vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a rotated lowercase double-story a.
In English ...
.
South American languages
The letter ''Æ'' is used in the official orthography ofKawésqar
The Kawésqar, also known as the Kaweskar, Alacaluf, Alacalufe or Halakwulup, are an Indigenous people who live in Chilean Patagonia, specifically in the Brunswick Peninsula, and Wellington, Santa Inés, and Desolación islands northwest of t ...
spoken in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
and also in that of the Fuegian language Yaghan
Yaghan, Yagán or Yahgan may refer to:
* Yahgan people, an ethnic group of Argentina and Chile
* Yahgan language
Yahgan or Yagán (also spelled Yaghan, Jagan, Iakan, and also known as Yámana, Háusi Kúta, or Yágankuta) is an extinct language ...
.
International Phonetic Alphabet
The symbol is also used in theInternational Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation ...
(IPA) to denote a near-open front unrounded vowel
The near-open front unrounded vowel, or near-low front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a lowercase of the ligature. Both the symbol and the sound ar ...
like in the word ''cat'' in many dialects of Modern English, which is the sound that was most likely represented by the Old English letter. In the IPA, it is always in lowercase
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally '' minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing system ...
. is a superscript IPA letter.
Uralic Phonetic Alphabet
The Uralic Phonetic Alphabet
Finno-Ugric transcription (FUT) or the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet (UPA) is a phonetic transcription or notational system used predominantly for the transcription and reconstruction of Uralic languages. It was first published in 1901 by Eemil Nesto ...
(UPA) uses four additional æ-related symbols, see Unicode table below.
Unicode
See also
Footnotes
Notes
References
Further reading
*Robert Bringhurst
Robert Bringhurst Appointments to the Order of Canada (2013). (born 1946) is a CanadianWong (1999). poet, typographer and author. He has translated substantial works from Haida and Navajo and from classical Greek and Arabic. He wrote ''The El ...
(2002). ''The Elements of Typographic Style
''The Elements of Typographic Style'' is a book on typography and style by Canadian typographer, poet and translator Robert Bringhurst. Originally published in 1992 by Hartley & Marks Publishers, it was revised in 1996, 2001 (v2.4), 2002 (v2. ...
''. Vancouver: Hartley & Marks. . p. 271.
External links
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Ae E E E Latin-script letters Latin-script ligatures E Old English E Phonetic transcription symbols Vowel letters