Vidarbha on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vidarbha (Pronunciation: id̪Éɾb汃 is a geographical region in the west Indian state of
 According to the Hindu epic '' Mahabharata'' and other '' Puranic'' scriptures, princess Rukmini considered to be an incarnation of the goddess Lakshmi and the wife of lord Krishna, was born to Bhishmaka, the king of the Vidarbha kingdom. Vidarbha was part of the Satavahana Empire during 1st to 2nd century CE), ascertained by the Satavahana coins found in
According to the Hindu epic '' Mahabharata'' and other '' Puranic'' scriptures, princess Rukmini considered to be an incarnation of the goddess Lakshmi and the wife of lord Krishna, was born to Bhishmaka, the king of the Vidarbha kingdom. Vidarbha was part of the Satavahana Empire during 1st to 2nd century CE), ascertained by the Satavahana coins found in  The coins and inscriptions from the period of
The coins and inscriptions from the period of
 Vidarbha lies in
Vidarbha lies in
 The GDP of the region is estimated to be 2021-22. The region also holds considerable mineral resources and forest cover. The region is economically under developed compared to the rest of Maharashtra with considerable
The GDP of the region is estimated to be 2021-22. The region also holds considerable mineral resources and forest cover. The region is economically under developed compared to the rest of Maharashtra with considerable
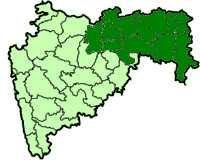 The
The
Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
. Forming the eastern part of the state, it comprises Amravati (earlier Berar) and Nagpur divisions. As per the 2011 Census, the region had a population of 23,003,179. The region occupies 31.6% of the total area and is home to 21.3% of the total population of Maharashtra. Situated in central India, it borders the state of Madhya Pradesh to the north, Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states â Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prade ...
to the east, Telangana to the south and Marathwada and Uttar Maharashtra regions of Maharashtra to the west.
According to the Hindu epic '' Mahabharata'', Rukmini, the wife of lord Krishna, was born to Bhishmaka, the king of the Vidarbha kingdom. Vidarbha was part of the Satavahana Empire during 1st to 2nd century CE). The coins and inscriptions from the period of Paramara
The Paramara dynasty (IAST: ParamÄra) was an Indian dynasty that ruled Malwa and surrounding areas in west-central India between 9th and 14th centuries. They belonged to the Parmara clan of the Rajputs.
The dynasty was established in either th ...
king Jagadeva, the son of the Udayaditya (reigned c. 1060â1086) have been found in the northern parts the region. According to the ''Ain-i-Akbari
The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' ( fa, ) or the "Administration of Akbar", is a 16th-century detailed document recording the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl in the Persian language. It for ...
'', the region was part of Berar Subah, in the Medieval period. In 1680, the region was captured by Sambhaji, the son of Shivaji, who was the founder of Maratha empire. In 1724, Asaf Jah, who later became the Nizam of Hyderabad
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (NiáºÄm ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
, declared independence and brought most of the region under his nominal rule. The administration and right of collecting taxes were held by the Marathas. In 1803, following the defeat of the Marathas, the region came under the rule of British East India Company. Later, the British Empire took control of the region from the British East India Company in 1857. After Indian Independence in 1947, the region was part of the Bombay State
Bombay State was a large Indian state created at the time of India's Independence, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Presidency (roughly equating to the present-day Indian state of Maharashtra, excluding Sou ...
. After the Re-organization of Indian states, majority of the region became part of Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
in 1960.
The GDP of the region is estimated to be 2022-23. The economy of the region is largely dependent on agriculture with oranges and cotton being the major crops. The region also holds considerable mineral resources and forest cover. The region is economically under developed compared to the rest of Maharashtra with considerable poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
and malnutrition. Agriculture is largely dependent on seasonal monsoons and the region receives very less rainfall due to its location in the rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
region of the Western Ghats. Droughts and famines
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompani ...
are common with more than 1.4 lakh farmer suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
s in the period 1997 to 2006.
The largest and major city in the region is Nagpur and other major towns include Amravati, Akola, Chandrapur and Gondia. Varhadi and Zadi dialects of Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
is widely spoken. There have been demands for a separate state of Vidarbha, due to perceived neglect from the Government of Maharashtra
The Government of Maharashtra is the state governing authority for the state of Maharashtra, India. It is a democratically elected government with 288 MLAs elected to the Vidhan Sabha for a five-year term.
Maharashtra has a Maharashtra Legisla ...
. While the demand is supported by major political parties BJP and Congress, it is opposed by Shiv Sena
Shiv Sena ( IAST: ''Åiva SÄnÄ'') () was a right-wing to far-right Marathi regionalist and Hindu ultranationalist political party in India founded in 1966 by cartoonist Bal Thackeray. Originally emerging from nativist movements in Bom ...
, one of the major regional political parties in the state.
History
 According to the Hindu epic '' Mahabharata'' and other '' Puranic'' scriptures, princess Rukmini considered to be an incarnation of the goddess Lakshmi and the wife of lord Krishna, was born to Bhishmaka, the king of the Vidarbha kingdom. Vidarbha was part of the Satavahana Empire during 1st to 2nd century CE), ascertained by the Satavahana coins found in
According to the Hindu epic '' Mahabharata'' and other '' Puranic'' scriptures, princess Rukmini considered to be an incarnation of the goddess Lakshmi and the wife of lord Krishna, was born to Bhishmaka, the king of the Vidarbha kingdom. Vidarbha was part of the Satavahana Empire during 1st to 2nd century CE), ascertained by the Satavahana coins found in Pauni
Pauni is a town and a Municipal Council in Bhandara district in the Indian state of Maharashtra.
Now it has National Highway NH-247. Pauni is also known as Kashi of Vidarbha due to its wide swath of temples.
Geography
Pauni is located at . It h ...
.
 The coins and inscriptions from the period of
The coins and inscriptions from the period of Paramara
The Paramara dynasty (IAST: ParamÄra) was an Indian dynasty that ruled Malwa and surrounding areas in west-central India between 9th and 14th centuries. They belonged to the Parmara clan of the Rajputs.
The dynasty was established in either th ...
king Jagadeva have been found in the northern parts the region. An inscription discovered at Jainad names Jagadeva as the son of the Paramara king Udayaditya (reigned c. 1060â1086). Scholar M. H. Krishna argued that the Chalukya king Someshvara Someshwara or its variant spellings ''Someshwar'', ''Someshvara'' and ''Someshvar'' may refer to:
* Soma (deity), a Vedic Hindu deity
* Shiva, a Hindu deity
People
* Someshvara I, 11th century Indian king from the Western Chalukya dynasty
* Somes ...
was known by the title "Jagadeva" ("Lord of the world") in the northern part of his kingdom, and it was he who issued these coins. However, all the known Chalukya coins featured Kannada script
The Kannada script (IAST: ''Kannaá¸a lipi''; obsolete: Kanarese or Canarese script in English) is an abugida of the Brahmic family, used to write Kannada, one of the Dravidian languages of South India especially in the state of Karnataka. Ka ...
, while the coins of Jagadeva featured the Nagari script used by the Paramaras.
According to the ''Ain-i-Akbari
The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' ( fa, ) or the "Administration of Akbar", is a 16th-century detailed document recording the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl in the Persian language. It for ...
'', the region was part of Berar Subah, known as the Gulshan-e-Berar in the Medieval period. In 1680, the region was captured by Sambhaji, the son of Shivaji who was the founder of Maratha empire. In 1724, following a battle at Buldana
Buldhana is the district headquarters and a Municipal Council in the Buldhana District of Amravati division in the Indian State of Maharashtra.
Climate
Demographics
As of the 2011 India census, Buldhana had a population of 67,431. Males con ...
, Asaf Jah defeated the Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
governor and declared independence. Most of the region came under the nominal rule of Jah, who later became the Nizam of Hyderabad
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (NiáºÄm ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
, though the administration and right of collecting chauth were held by the Marathas. In 1803, following the defeat of the Marathas, the region came under the rule of British East India Company.
Later, the British Empire took control of the region from the British East India Company in 1857. After Indian Independence in 1947, the region was part of the Bombay State
Bombay State was a large Indian state created at the time of India's Independence, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Presidency (roughly equating to the present-day Indian state of Maharashtra, excluding Sou ...
. After the States Reorganisation Act
The States Reorganisation act, 1956 was a major reform of the boundaries of India's States and territories of India, states and territories, organising them along linguistic lines.
Although additional changes to India's state boundaries have b ...
, which re-organized state boundaries, majority of the region became part of Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
.
Geography
 Vidarbha lies in
Vidarbha lies in Central India
Central India is a loosely defined geographical region of India. There is no clear official definition and various ones may be used. One common definition consists of the states of Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh, which are included in alm ...
on the northern part of the Deccan Plateau. It borders the state of Madhya Pradesh to the north, Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states â Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prade ...
to the east, Telangana to the south and Marathwada and Uttar Maharashtra regions of Maharashtra to the west. It lies in the rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
region of the Western Ghats and the terrain is largely flat. The Satpura Range lies to the north of Vidarbha region with Melghat in Amravati district forming part of the southern offshoot of the Satpura Range. Large basaltic rock formations exists throughout the region, part of the 66-million-year-old volcanic Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India (17â24°N, 73â74°E). It is one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. It consists of numerous layers of solidified flood ...
. Bhandara and Gondia district are entirely occupied by metamorphic rock and alluvium, making their geology unique in Maharashtra. The Poorna river basin lies in Western Vidarbha and comprises Akola, Amaravati and Buldhana districts. The region has extremely high innate soil and water salinity.
Administration
Vidarbha has 11 districts divided into two divisions: Amravati (earlier Berar) and Nagpur divisions. Each district has a collector's office which is responsible for day-to-day administration. The District Collector is a Central Indian Government IAS appointee who is in charge of the governance of a district in a state.Demographics
Vidarbha has a total population of according to the 2011 India census. The region occupies 31.6% of the total area and is home to 21.3% of the total population of Maharashtra. According to the 2011 census, Hinduism was the principal religion in the state at 76.91% of the total population, whileBuddhists
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
constituted 13.08 of the total population. Vidarbha accounts for 45.91% of total Buddhists in Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
.
The largest city in the region is Nagpur and other major towns include Amravati, Akola, Chandrapur and Gondia.
Language and culture
As per the 2011 census, 73.72% of the population speaksMarathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
, 8.30% Hindi, 6.23% Urdu, 2.58% Lambadi, 1.83% Gondi, 1.10% Korku and 1.02% Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
as their first language. Varhadi and Zadi dialects of Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
is widely spoken.
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35â37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
festivals like Holi, Diwali
Diwali (), Dewali, Divali, or Deepavali ( IAST: ''dÄ«pÄvalÄ«''), also known as the Festival of Lights, related to Jain Diwali, Bandi Chhor Divas, Tihar, Swanti, Sohrai, and Bandna, is a religious celebration in Indian religions. It is ...
and Dasara are celebrated throughout the region.
The Nagpur Central Museum
The Nagpur Central Museum, popularly known as Ajab Bangla, is located in Nagpur, Maharashtra, India. Established in 1863, Nagpur Central Museum is one of the oldest museums in India and Maharashtra. It holds important artifacts such as dinosaur ...
( 1863) maintains collections from the region.
Economy
 The GDP of the region is estimated to be 2021-22. The region also holds considerable mineral resources and forest cover. The region is economically under developed compared to the rest of Maharashtra with considerable
The GDP of the region is estimated to be 2021-22. The region also holds considerable mineral resources and forest cover. The region is economically under developed compared to the rest of Maharashtra with considerable poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
and malnutrition.
The economy of the region is largely dependent on agriculture with oranges and cotton being the major crops. Agriculture is largely dependent on seasonal monsoons and the region receives very less rainfall. Droughts and famines
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompani ...
are common with more than 1.4 lakh farmer suicides
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, raising living organisms for food or raw materials. The term usually applies to people who do some combination of raising field crops, orchards, vineyards, poultry, or other livestock. A farmer mig ...
in the period 1997 to 2006. Though Government of India has provided relief packages aimed at the region, with corruption rampant in the region. Columnist and journalist P Sainath
Palagummi Sainath (born 1957) is an Indian columnist and author of the acclaimed book ''Everybody Loves a Good Drought''. He has extensively written on rural India, his notable interests are poverty, structural inequities, caste discriminat ...
opined that the relief packages were destined to fail as corruption in the government meant that little impact happened on the ground.
Nagpur is a major hub for business and healthcare. MIHAN
The Multi-modal International Cargo Hub and Airport at Nagpur (MIHAN) is an airport project for Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar International Airport, Nagpur. It is the biggest economical development project currently underway in India in terms of invest ...
is the major cargo hub in the region, operational out of Nagpur Airport.
Nagpur also hosts Information Technology Special Economic Zone (IT SEZ). for information-technology companies. Amravati and Yavatmal are known for cotton production. Chandrapur has a thermal power station, which is one of the biggest in India. There are other heavy industries and mines in the region.
The region has mineral resources with coal and manganese, the major minerals. Iron ore and limestone have also been identified as potential mining resources. Chandrapur district contributes 29% of all mineral output of Maharashtra.
Education
Sports and recreation
Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
is the most popular sport in the region. Nagpur's Vidarbha Cricket Association Ground (VCA) hosted international cricket matches. In 2008, the new Vidarbha Cricket Association Stadium
The Vidarbha Cricket Association Stadium , also known as New VCA Stadium, is a cricket ground in Nagpur, Maharashtra, India. It is the largest cricket stadium in India in terms of field area.
The ground, located at Jamtha on the southern out ...
was built in Jamtha.
The eastern part of Vidarbha consists of Maharashtra's oldest National Park
A national park is a nature park, natural park in use for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state dec ...
, the Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve
The Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve is a wildlife sanctuary in Chandrapur district of Maharashtra state in India. It is Maharashtra's oldest and largest national park. Created in 1955, the reserve includes the Tadoba National Park and the Andhari W ...
, one of the Project Tiger Reserves. Shegaon is a place of pilgrimage with temples attributed to the Hindu saint Gajanan Maharaj who lived there. Chikhaldara
Chikhaldara is a hill station and a municipal council in Amravati district in the Indian state of Maharashtra.
Chikaldhara, literally translates from Marathi to mud stream/falls (''chikal'' + ''dhara''). Hindus claim that this place was featu ...
in Amravati district is a hill station
A hill station is a town located at a higher elevation than the nearby plain or valley. The term was used mostly in colonial Asia (particularly in India), but also in Africa (albeit rarely), for towns founded by European colonialists as refuges ...
and popular tourist destination.
Politics
Vidarbha has ten Lok Sabha constituencies. Nagpur district has two seats Nagpur and Ramtek, while Gadchiroli-Chimur Lok Sabha constituency is spread across districts of Chandrapur, Gadchiroli and Gondia. Yavatmal andWashim district
Washim district (Marathi pronunciation: aËÊim is a district in Maharashtra, India. The headquarters is at Washim. The area of the district is .
Demography and Geography
The district had a population of 1,020,216 of which 17.49% were urban ...
s form part of YavatmalâWashim Lok Sabha constituency
YavatmalâWashim Lok Sabha constituency is one of the 48 Lok Sabha (lower house of the Indian parliament) constituencies of Maharashtra state in western India. This constituency was created on 19 February 2008 as a part of the implementation of ...
. Other seats include Akola, Amravati, Bhandara, Buldhana, Gondia, and Wardha. Amravati and Ramtek seats are reserved for Scheduled Caste
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people and among the most disadvantaged socio-economic groups in India. The terms are recognized in the Constitution of India and the groups are designa ...
candidates, while Gadchiroli-Chimur is reserved for Scheduled Tribes
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people and among the most disadvantaged socio-economic groups in India. The terms are recognized in the Constitution of India and the groups are designa ...
. In the Maharashtra Legislative Assembly, the region is represented by 62 Vidhan Sabha seats.
Demand for statehood
 The
The Vidarbha movement
The Vidarbha movement includes political activities organised by various individuals, organizations and political parties, for creation of a separate state of Vidarbha, within the republic of India, with Nagpur as the capital. The proposed stat ...
started in the 1930s demanding a separate state of Vidarbha. The demand has been raised at times due to perceived neglect of the region by the Government of Maharashtra
The Government of Maharashtra is the state governing authority for the state of Maharashtra, India. It is a democratically elected government with 288 MLAs elected to the Vidhan Sabha for a five-year term.
Maharashtra has a Maharashtra Legisla ...
. While the demand is supported by major political parties BJP and Congress, it is opposed by Shiv Sena
Shiv Sena ( IAST: ''Åiva SÄnÄ'') () was a right-wing to far-right Marathi regionalist and Hindu ultranationalist political party in India founded in 1966 by cartoonist Bal Thackeray. Originally emerging from nativist movements in Bom ...
, one of the major regional political parties in the state. Political economist Shrikant Jichkar
Shrikant Jichkar (Marathi : शà¥à¤°à¥à¤à¤¾à¤à¤¤ à¤à¤¿à¤à¤à¤¾à¤°) (14 September 1954 â 2 June 2004) was an Indian central civil servant and politician. He obtained 20 university degrees, and was elected the youngest MLA in the count ...
opposed the separation of the region from Maharashtra, stating that it was not sustainable. He noted that income from available natural resources would not be able to balance the subsidies given by the government, whose cooperation would be vital to any development and that the division introduces societal risks due to dividing of the Marathi-speaking state.
See also
*Dehani lift irrigation scheme
The Dehani lift irrigation scheme is a technologically sophisticated project to irrigate Vidarbha, a large, semi-arid region of India.
Background
Vidharba is a semi-arid region that has an ailing agricultural community which has huge amounts of ...
* List of cities in Vidarbha
Vidarbha is an easternmost region of Indian state of Maharashtra comprising Nagpur Division and Amravati Division. It occupies 31.6% of total area and holds 21.3% of total population of Maharashtra.
Nagpur is the largest city of Vidarbha as ...
* List of Maratha dynasties and states
* Manav Vikas Mission
* Proposed states and territories of India
Proposal(s) or The Proposal may refer to:
* Proposal (business)
* Research proposal
* Proposal (marriage)
* Proposition, a proposal in logic and philosophy
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''The Proposal'' (album)
Films
* ''The Proposal'' ...
References
External links
{{Proposed states and territories of India Regions of India Regions of Maharashtra Proposed states and union territories of India