New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the
most populous city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the city proper, cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or th ...
in the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the
most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place
Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
. New York City lies at the southern tip of
New York State
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. stat ...
, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the
Northeast megalopolis
The Northeast megalopolis, also known as the Northeast Corridor, Acela Corridor, Boston–Washington corridor, or BosWash, is the world's largest megalopolis in terms of economic output and the second most populous megalopolis in the United St ...
and the
New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass, at , and one of the list of most populous metropolitan areas, most populous urban agg ...
, the largest
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
in the world by
urban landmass
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, t ...
. With over 20.1 million people in its
metropolitan statistical area
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally Incorporated town, incorporate ...
and 23.5 million in its
combined statistical area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and the territory of Puerto Ric ...
as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous
megacities
A megacity is a very large city, typically with a population of more than 10 million people. Precise definitions vary: the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs in its 2018 "World Urbanization Prospects" report counted urban ...
, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a
global
Global means of or referring to a globe and may also refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003
* ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007
* ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989
* ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015
* Bruno ...
cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human Society, societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, and habits of the ...
,
financial
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fina ...
,
entertainment
Entertainment is a form of activity that holds the attention and interest of an audience or gives pleasure and delight. It can be an idea or a task, but is more likely to be one of the activities or events that have developed over thousa ...
, and
media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass el ...
center with a significant influence on commerce,
health care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
and life sciences,
research, technology,
education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Va ...
,
politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies ...
,
tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
,
dining
A restaurant is a business that prepares and serves food and drinks to customers. Meals are generally served and eaten on the premises, but many restaurants also offer take-out and food delivery services. Restaurants vary greatly in appearanc ...
, art,
fashion
Fashion is a form of self-expression and autonomy at a particular period and place and in a specific context, of clothing, footwear, lifestyle, accessories, makeup, hairstyle, and body posture. The term implies a look defined by the fashion in ...
, and
sports
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, th ...
. Home to the
headquarters of the United Nations
zh, 联合国总部大楼french: Siège des Nations uniesrussian: Штаб-квартира Организации Объединённых Наций es, Sede de las Naciones Unidas
, image = Midtown Manhattan Skyline 004.jpg
, im ...
, New York is an important center for
international diplomacy
Diplomacy comprises spoken or written communication by representatives of states (such as leaders and diplomats) intended to influence events in the international system.Ronald Peter Barston, ''Modern diplomacy'', Pearson Education, 2006, p. 1 ...
, an established
safe haven
Safe haven may refer to:
* Sanctuary
Arts and entertainment
* ''Safe Haven'' (novel), a 2010 American novel by Nicholas Sparks
** ''Safe Haven'' (film), a 2013 American film adapted from the novel
* ''Safe Haven'' (short film), a 2009 American ...
for global investors,
and is sometimes
described as the
capital of the world.
Situated on
one of the world's largest natural harbors and extending into the
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, New York City comprises
five boroughs
5 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
5, five or number 5 may also refer to:
* AD 5, the fifth year of the AD era
* 5 BC, the fifth year before the AD era
Literature
* ''5'' (visual novel), a 2008 visual novel by Ram
* ''5'' (comics), an awar ...
, each of which is coextensive with a respective
county of the state of New York
There are 62 counties in the state of New York.
The first 12 were created immediately after the British took over the Dutch colony of New Amsterdam; two of these counties were later abolished, their land going to Massachusetts. The newest ...
. The five boroughs—
Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
(Kings County),
Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
(Queens County),
Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
(New York County),
the Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New Y ...
(Bronx County), and
Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey by the Arthur Kill and the Kill Van Kull an ...
(Richmond County)—were created when local governments were
consolidated into a single municipal entity in 1898. The city and its metropolitan area constitute the premier gateway for legal
immigration to the United States
Immigration has been a major source of population growth and Culture of the United States, cultural change throughout much of the history of the United States. In absolute numbers, the United States has a larger immigrant population than a ...
. As many as 800 languages are spoken in New York,
making it the most linguistically diverse city in the world. New York City is home to more than 3.2 million residents born outside the United States, the largest foreign-born population of any city in the world as of 2016.
, the New York metropolitan area is estimated to produce a
gross metropolitan product
Gross metropolitan product (GMP) is a monetary measure of the value of all final goods and services produced within a metropolitan statistical area during a specified period (''e.g.'', a quarter, a year). GMP estimates are commonly used to compare ...
of over $2.1 trillion, ranking it
first worldwide. If the New York metropolitan area were a
sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a polity, political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defin ...
, it would have the
eighth-largest economy in the world. , New York is home to the
highest number of billionaires and
millionaires
A millionaire is an individual whose net worth or wealth is equal to or exceeds one million units of currency. Depending on the currency, a certain level of prestige is associated with being a millionaire. In countries that use the short sc ...
of any city and, in 2017, was the
wealthiest city in the world.
New York City traces its origins to a trading post founded on the southern tip of Manhattan Island by
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
colonists in approximately 1624. The settlement was named
New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
( nl,
Nieuw Amsterdam, link=yes) in 1626 and was chartered as a city in 1653. The city came under English control in 1664 and was renamed New York after King
Charles II of England granted the lands to his brother, the
Duke of York
Duke of York is a title of nobility in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of English (later British) monarchs. The equivalent title in the Scottish peerage was Du ...
.
The city was regained by the Dutch in July 1673 and was renamed New Orange for one year and three months; the city has been continuously named New York since November 1674. New York City was the
capital of the United States
This is a list of capital cities of the United States, including places that serve or have served as federal, state, insular area, territorial, colonial and Native American capitals.
Washington has been the federal capital of the United States ...
from 1785 until 1790,
and has been the largest U.S. city since 1790. The
Statue of Liberty
The Statue of Liberty (''Liberty Enlightening the World''; French: ''La Liberté éclairant le monde'') is a List of colossal sculpture in situ, colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor in New York City, in the U ...
greeted millions of immigrants as they came to the U.S. by ship in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and is a symbol of the U.S. and its ideals of liberty and peace.
In the 21st century, New York City has emerged as a global node of creativity, entrepreneurship,
and environmental sustainability,
and as a symbol of freedom and cultural diversity. ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' has won the most
Pulitzer Prize
The Pulitzer Prize () is an award for achievements in newspaper, magazine, online journalism, literature, and musical composition within the United States. It was established in 1917 by provisions in the will of Joseph Pulitzer, who had made h ...
s for
journalism
Journalism is the production and distribution of reports on the interaction of events, facts, ideas, and people that are the "news of the day" and that informs society to at least some degree. The word, a noun, applies to the occupation (profes ...
and remains the U.S. media's "
newspaper of record
A newspaper of record is a major national newspaper with large circulation whose editorial and news-gathering functions are considered authoritative and independent; they are thus "newspapers of record by reputation" and include some of the o ...
".
[ In 2019, New York City was voted the greatest city in the world per a survey of over 30,000 people from 48 cities worldwide, citing its cultural diversity.]Times Square
Times Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment hub, and neighborhood in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It is formed by the junction of Broadway, Seventh Avenue, and 42nd Street. Together with adjacent ...
is the brightly illuminated hub of the Broadway Theater District
New York City's Theater District (sometimes spelled Theatre District, and officially zoned as the "Theater Subdistrict") is an area and neighborhood in Midtown Manhattan where most Broadway theaters are located, as well as many other theaters, ...
, one of the world's busiest pedestrian intersections,entertainment industry
Entertainment is a form of activity that holds the attention and Interest (emotion), interest of an audience or gives pleasure and delight. It can be an idea or a task, but is more likely to be one of the activities or events that have dev ...
. Many of the city's landmarks, skyscrapers
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ris ...
, and parks
A park is an area of natural, semi-natural or planted space set aside for human enjoyment and recreation or for the protection of wildlife or natural habitats. Urban parks are urban green space, green spaces set aside for recreation inside t ...
are known around the world, as is the city's fast pace, spawning the term '' New York minute''. The Empire State Building
The Empire State Building is a 102-story Art Deco skyscraper in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. The building was designed by Shreve, Lamb & Harmon and built from 1930 to 1931. Its name is derived from "Empire State", the nickname of the st ...
has become the global standard of reference to describe the height and length of other structures.[Multiple sources:
*
*
*]
The Stonewall Inn
The Stonewall Inn, often shortened to Stonewall, is a gay bar and recreational tavern in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of Lower Manhattan, New York City, and the site of the Stonewall riots of 1969, which is widely considered to be the s ...
in Greenwich Village
Greenwich Village ( , , ) is a neighborhood on the west side of Lower Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 14th Street to the north, Broadway to the east, Houston Street to the south, and the Hudson River to the west. Greenwich Village ...
, part of the Stonewall National Monument
Stonewall National Monument is a U.S. national monument in the West Village neighborhood of Greenwich Village in Lower Manhattan, New York City. The designated area includes the Stonewall Inn, the Christopher Park, and nearby streets including ...
, is considered the historic epicenter of LGBTQ+ culture and the birthplace
The place of birth (POB) or birthplace is the place where a person was born. This place is often used in legal documents, together with name and date of birth, to uniquely identify a person. Practice regarding whether this place should be a cou ...
of the modern gay rights movement
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) movements are social movements that advocate for LGBT people in society. Some focus on equal rights, such as the ongoing movement for same-sex marriage, while others focus on liberation, as in the ...
.nickname
A nickname is a substitute for the proper name of a familiar person, place or thing. Commonly used to express affection, a form of endearment, and sometimes amusement, it can also be used to express defamation of character. As a concept, it is ...
'' The City That Never Sleeps'', the New York City Subway
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system owned by the government of New York City and leased to the New York City Transit Authority, an affiliate agency of the state-run Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA). Opened on October 2 ...
is the largest single-operator rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be c ...
system worldwide, with passenger rail stations; and Penn Station Pennsylvania Station is a name applied by the Pennsylvania Railroad to several of its grand passenger terminals.
Pennsylvania Station or Penn Station may also refer to
Current train stations
* Baltimore Penn Station
* Pennsylvania Station (Cinci ...
in Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan and serves as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Buildin ...
is the busiest transportation hub in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, the term We ...
. The city has over 120 colleges and universities, including Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
, New York University
New York University (NYU) is a private research university in New York City. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded by a group of New Yorkers led by then-Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin.
In 1832, the ...
, and the City University of New York
The City University of New York ( CUNY; , ) is the Public university, public university system of Education in New York City, New York City. It is the largest urban university system in the United States, comprising 25 campuses: eleven Upper divis ...
system, which is the largest urban public university system in the United States. Anchored by Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for t ...
in the Financial District
A financial district is usually a central area in a city where financial services firms such as banks, insurance companies and other related finance corporations have their head offices. In major cities, financial districts are often home to s ...
of Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan (also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York) is the southernmost part of Manhattan, the central borough for business, culture, and government in New York City, which is the most populated city in the United States with ...
, New York City has been called both the world's leading financial center
A financial centre ( BE), financial center ( AE), or financial hub, is a location with a concentration of participants in banking, asset management, insurance or financial markets with venues and supporting services for these activities to t ...
[ and the most powerful city in the world,]market capitalization
Market capitalization, sometimes referred to as market cap, is the total value of a publicly traded company's outstanding common shares owned by stockholders.
Market capitalization is equal to the market price per common share multiplied by t ...
, the New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is by far the world's largest stock exchange by market capitalization of its listed c ...
and Nasdaq
The Nasdaq Stock Market () (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations Stock Market) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second ...
. New York City is the headquarters
Headquarters (commonly referred to as HQ) denotes the location where most, if not all, of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. In the United States, the corporate headquarters represents the entity at the center or the to ...
of the global art market, with numerous art galleries
An art gallery is a room or a building in which visual art is displayed. In Western cultures from the mid-15th century, a gallery was any long, narrow covered passage along a wall, first used in the sense of a place for art in the 1590s. The lon ...
and auction houses collectively hosting half of the world’s art auctions.
Etymology
In 1664, New York was named in honor of the Duke of York
Duke of York is a title of nobility in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of English (later British) monarchs. The equivalent title in the Scottish peerage was Du ...
, who would become King James II of England. James's elder brother, King Charles II, appointed the Duke proprietor
Ownership is the state or fact of legal possession and control over property, which may be any asset, tangible or intangible. Ownership can involve multiple rights, collectively referred to as title, which may be separated and held by different ...
of the former territory of New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the East Coast of the United States, east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territor ...
, including the city of New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
, when England seized it from Dutch control.
History
Early history
In the pre-Columbian era
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the Migration to the New World, original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization of the Americas, European colonization, w ...
, the area of present-day New York City was inhabited by Algonquian Native Americans, including the Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory includ ...
. Their homeland, known as Lenapehoking
Lenapehoking (Unami: ''Lënapehòkink'') is widely translated as ' homelands of the Lenape', which in the 16th and 17th centuries, ranged along the Eastern seaboard from western Connecticut to Delaware, and encompassed the territory adjacent to th ...
, included Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey by the Arthur Kill and the Kill Van Kull an ...
, Manhattan, the Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New Y ...
, the western portion of Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
(including the areas that would later become the boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle Ag ...
of Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
and Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
), and the Lower Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. The region stretches from the Capital District, New York, Capital Di ...
.
The first documented visit into New York Harbor
New York Harbor is at the mouth of the Hudson River where it empties into New York Bay near the East River tidal estuary, and then into the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of the United States. It is one of the largest natural harbors in t ...
by a European was in 1524 by Italian Giovanni da Verrazzano, an explorer from Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico an ...
in the service of the French crown
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the Kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I () as the firs ...
.New Angoulême
The written history of New York City began with the first European explorer, the Italian Giovanni da Verrazzano in 1524. European settlement began with the Dutch in 1608.
The "Sons of Liberty" campaigned against British authority in New York Ci ...
).Estêvão Gomes
Estêvão Gomes, also known by the Spanish version of his name, Esteban Gómez (c. 1483 – 1538), was a Portuguese cartographer and explorer. He sailed at the service of Castile (Spain) in the fleet of Ferdinand Magellan, but deserted the exp ...
sailing for Emperor Charles V, arrived in New York Harbor in January 1525 and charted the mouth of the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
, which he named ('Saint Anthony's River'). The Padrón Real
The Padrón Real (, ''Royal Register''), known after 2 August 1527 as the Padrón General (, ''General Register''), was the official and secret Spanish master map used as a template for the maps present on all Spanish ships during the 16th century ...
of 1527, the first scientific map to show the East Coast of North America continuously, was informed by Gomes' expedition and labeled the northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
as ''Tierra de Esteban Gómez'' in his honor.
In 1609, the English explorer Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 160 ...
rediscovered New York Harbor while searching for the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arct ...
to the Orient
The Orient is a term for the East in relation to Europe, traditionally comprising anything belonging to the Eastern world. It is the antonym of ''Occident'', the Western World. In English, it is largely a metonym for, and coterminous with, the c ...
for the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
.Maurice, Prince of Orange
Maurice of Orange ( nl, Maurits van Oranje; 14 November 1567 – 23 April 1625) was ''stadtholder'' of all the provinces of the Dutch Republic except for Friesland from 1585 at the earliest until his death in 1625. Before he became Prince o ...
. Hudson's first mate described the harbor as "a very good Harbour for all windes" and the river as "a mile broad" and "full of fish".capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, Department (country subdivision), department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city ...
of Albany, in the belief that it might be an oceanic tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage ...
before the river became too shallow to continue.Cape Cod
Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of mainland Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer mont ...
and Delaware Bay
Delaware Bay is the estuary outlet of the Delaware River on the northeast seaboard of the United States. It is approximately in area, the bay's freshwater mixes for many miles with the saltwater of the Atlantic Ocean.
The bay is bordered inlan ...
was claimed by the Netherlands and called ('New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the East Coast of the United States, east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territor ...
').
The first non–Native American inhabitant of what would eventually become New York City was Juan Rodriguez (transliterated
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one script to another that involves swapping letters (thus '' trans-'' + '' liter-'') in predictable ways, such as Greek → , Cyrillic → , Greek → the digraph , Armenian → or ...
to Dutch as ''Jan Rodrigues''), a merchant from Santo Domingo
, total_type = Total
, population_density_km2 = auto
, timezone = AST (UTC −4)
, area_code_type = Area codes
, area_code = 809, 829, 849
, postal_code_type = Postal codes
, postal_code = 10100–10699 (Distrito Nacional)
, websi ...
. Born in Santo Domingo of Portuguese and African descent, he arrived in Manhattan during the winter of 1613–14, trapping for pelts and trading with the local population as a representative of the Dutch. Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
, from 159th Street to 218th Street in Upper Manhattan
Upper Manhattan is the most northern region of the New York City borough of Manhattan. Its southern boundary has been variously defined, but some of the most common usages are 96th Street, the northern boundary of Central Park ( 110th Street), ...
, is named Juan Rodriguez Way in his honor.
Dutch rule
 A permanent European presence near
A permanent European presence near New York Harbor
New York Harbor is at the mouth of the Hudson River where it empties into New York Bay near the East River tidal estuary, and then into the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of the United States. It is one of the largest natural harbors in t ...
was established in 1624—making New York the 12th oldest continuously occupied European-established settlement in the continental United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
—with the founding of a Dutch fur trading
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most ...
settlement on Governors Island
Governors Island is a island in New York Harbor, within the New York City borough of Manhattan. It is located approximately south of Manhattan Island, and is separated from Brooklyn to the east by the Buttermilk Channel. The National Park ...
. In 1625, construction was started on a citadel
A citadel is the core fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of "city", meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
In ...
and Fort Amsterdam
Fort Amsterdam was a fort on the southern tip of Manhattan at the confluence of the Hudson and East rivers. It was the administrative headquarters for the Dutch and then English/British rule of the colony of New Netherland and subsequently the ...
, later called ''Nieuw Amsterdam'' (New Amsterdam), on present-day Manhattan Island
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
.[GovIsland Park-to-Tolerance: through Broad Awareness and Conscious Vigilance](_blank)
Tolerance Park. Retrieved February 9, 2017. See Legislative Resolutions Senate No. 5476 and Assembly No. 2708. The colony of New Amsterdam was centered on what would ultimately be known as Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan (also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York) is the southernmost part of Manhattan, the central borough for business, culture, and government in New York City, which is the most populated city in the United States with ...
. It extended from the southern tip of Manhattan to modern day Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for t ...
, where a 12-foot wooden stockade
A stockade is an enclosure of palisades and tall walls, made of logs placed side by side vertically, with the tops sharpened as a defensive wall.
Etymology
''Stockade'' is derived from the French word ''estocade''. The French word was derived ...
was built in 1653 to protect against Native American and British raids. In 1626, the Dutch colonial Director-General Peter Minuit
Peter Minuit (between 1580 and 1585 – August 5, 1638) was a Wallonian merchant from Tournai, in present-day Belgium. He was the 3rd Director of the Dutch North American colony of New Netherland from 1626 until 1631, and 3rd Governor of New N ...
, acting as charged by the Dutch West India Company
The Dutch West India Company ( nl, Geoctrooieerde Westindische Compagnie, ''WIC'' or ''GWC''; ; en, Chartered West India Company) was a chartered company of Dutch merchants as well as foreign investors. Among its founders was Willem Usselincx ( ...
, purchased the island of Manhattan from the ''Canarsie'', a small Lenape band, for "the value of 60 guilders
Guilder is the English translation of the Dutch and German ''gulden'', originally shortened from Middle High German ''guldin pfenninc'' "gold penny". This was the term that became current in the southern and western parts of the Holy Roman Empir ...
" (about $900 in 2018). A disproved legend claims that Manhattan was purchased for $24 worth of glass beads.
Following the purchase, New Amsterdam grew slowly.monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situati ...
in New Netherland, on authority granted by the Dutch States General
The States General of the Netherlands ( nl, Staten-Generaal ) is the supreme bicameral legislature of the Netherlands consisting of the Senate () and the House of Representatives (). Both chambers meet at the Binnenhof in The Hague.
The States G ...
. In 1639–1640, in an effort to bolster economic growth, the Dutch West India Company relinquished its monopoly over the fur trade, leading to growth in the production and trade of food, timber, tobacco, and slaves (particularly with the Dutch West Indies
The Dutch Caribbean (historically known as the Dutch West Indies) are the territories, colonies, and countries, former and current, of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean Sea. They are in the north and south-wes ...
).Peter Stuyvesant
Peter Stuyvesant (; in Dutch also ''Pieter'' and ''Petrus'' Stuyvesant, ; 1610 – August 1672)Mooney, James E. "Stuyvesant, Peter" in p.1256 was a Dutch colonial officer who served as the last Dutch director-general of the colony of New Net ...
began his tenure as the last Director-General
A director general or director-general (plural: ''directors general'', ''directors-general'', ''director generals'' or ''director-generals''
) or general director is a senior executive officer, often the chief executive officer, within a government ...
of New Netherland. During his tenure, the population of New Netherland grew from 2,000 to 8,000. Stuyvesant has been credited with improving law and order in the colony; however, he also earned a reputation as a despotic
Despotism ( el, Δεσποτισμός, ''despotismós'') is a form of government in which a single entity rules with absolute power. Normally, that entity is an individual, the despot; but (as in an autocracy) societies which limit respect an ...
leader. He instituted regulations on liquor sales, attempted to assert control over the Dutch Reformed Church
The Dutch Reformed Church (, abbreviated NHK) was the largest Christian denomination in the Netherlands from the onset of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century until 1930. It was the original denomination of the Dutch Royal Family and ...
, and blocked other religious groups (including Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abil ...
, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, and Lutherans
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
) from establishing houses of worship.
English rule
 In 1664, unable to summon any significant resistance, Stuyvesant surrendered New Amsterdam to English troops, led by Colonel
In 1664, unable to summon any significant resistance, Stuyvesant surrendered New Amsterdam to English troops, led by Colonel Richard Nicolls
Richard Nicolls (sometimes written as Nichols, 1624 – 28 May 1672) was the first English colonial governor of New York province.
Early life
Nicolls was born in 1624 in Ampthill in Bedfordshire, England. He was the son of Francis Nicolls (1 ...
, without bloodshed.Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War or the Second Dutch War (4 March 1665 – 31 July 1667; nl, Tweede Engelse Oorlog "Second English War") was a conflict between Kingdom of England, England and the Dutch Republic partly for control over the seas a ...
, the Dutch decided to keep the nascent plantation colony of what is now Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
(on the northern South American coast) they had gained from the English; and in return, the English kept New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
. The fledgling settlement was promptly renamed "New York" after the Duke of York
Duke of York is a title of nobility in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of English (later British) monarchs. The equivalent title in the Scottish peerage was Du ...
(the future King James II and VII), who would eventually be deposed in the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
. After the founding, the duke gave part of the colony to proprietors George Carteret
Vice Admiral Sir George Carteret, 1st Baronet ( – 14 January 1680 N.S.) was a royalist statesman in Jersey and England, who served in the Clarendon Ministry as Treasurer of the Navy. He was also one of the original lords proprietor of the ...
and John Berkeley. Fort Orange
Fort Orange ( nl, Fort Oranje) was the first permanent Dutch settlement in New Netherland; the present-day city of Albany, New York developed at this site. It was built in 1624 as a replacement for Fort Nassau, which had been built on nearb ...
, north on the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
, was renamed Albany after James's Scottish title. The transfer was confirmed in 1667 by the Treaty of Breda, which concluded the Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War or the Second Dutch War (4 March 1665 – 31 July 1667; nl, Tweede Engelse Oorlog "Second English War") was a conflict between Kingdom of England, England and the Dutch Republic partly for control over the seas a ...
.
On August 24, 1673, during the Third Anglo-Dutch War
The Third Anglo-Dutch War ( nl, Derde Engels-Nederlandse Oorlog), 27 March 1672 to 19 February 1674, was a naval conflict between the Dutch Republic and England, in alliance with France. It is considered a subsidiary of the wider 1672 to 1678 ...
, Dutch captain Anthony Colve
Anthony or Anthonij Colve ( fl. 1667-1695) was a Dutch naval captain and the Director-General of New Netherland during a brief restoration of Dutch rule in New Netherland (roughly present-day New York and New Jersey).
Career
Colve was likely inv ...
seized the colony of New York from the English at the behest of Cornelis Evertsen the Youngest and rechristened it "New Orange" after William III, the Prince of Orange
Prince of Orange (or Princess of Orange if the holder is female) is a title originally associated with the sovereign Principality of Orange, in what is now southern France and subsequently held by sovereigns in the Netherlands.
The title ...
.epidemic
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics ...
s brought on by contact with the Europeans caused sizeable population losses for the Lenape between the years 1660 and 1670. By 1700, the Lenape population had diminished to 200. New York experienced several yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. In ...
epidemics in the 18th century, losing ten percent of its population to the disease in 1702 alone.
Province of New York and slavery
 In the early 18th century, New York grew in importance as a trading port while as a part of the
In the early 18th century, New York grew in importance as a trading port while as a part of the colony of New York
The Province of New York (1664–1776) was a British proprietary colony and later royal colony on the northeast coast of North America. As one of the Middle Colonies, New York achieved independence and worked with the others to found the Unit ...
.slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, with 42% of households enslaving Africans by 1730, the highest percentage outside Charleston
Charleston most commonly refers to:
* Charleston, South Carolina
* Charleston, West Virginia, the state capital
* Charleston (dance)
Charleston may also refer to:
Places Australia
* Charleston, South Australia
Canada
* Charleston, Newfoundlan ...
, South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
. Most cases were that of domestic slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, as a New York household then commonly enslaved few or several people. Others were hired out to work at labor. Slavery became integrally tied to New York's economy through the labor of slaves throughout the port, and the banking and shipping industries trading with the American South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
. During construction in Foley Square
Foley Square, also called Federal Plaza, is a street intersection in the Civic Center neighborhood of Lower Manhattan, New York City, which contains a small triangular park named Thomas Paine Park. The space is bordered by Worth Street to the ...
in the 1990s, the African Burying Ground
African Burial Ground National Monument is a monument at Duane Street and African Burial Ground Way (Elk Street) in the Civic Center section of Lower Manhattan, New York City. Its main building is the Ted Weiss Federal Building at 290 Broadway. ...
was discovered; the cemetery included 10,000 to 20,000 of graves of colonial-era Africans, some enslaved and some free.John Peter Zenger
John Peter Zenger (October 26, 1697 – July 28, 1746) was a German printer and journalist in New York City. Zenger printed '' The New York Weekly Journal''. He was accused of libel in 1734 by William Cosby, the royal governor of New York, but ...
, who had been accused of seditious libel
Sedition and seditious libel were criminal offences under English common law, and are still criminal offences in Canada. Sedition is overt conduct, such as speech and organization, that is deemed by the legal authority to tend toward insurrection a ...
after criticizing colonial governor William Cosby
Brigadier-General William Cosby (1690–1736) was an Irish soldier who served as the British colonial governor of New York from 1732 to 1736. During his short term, Cosby was portrayed as one of the most oppressive governors in the Thirteen Co ...
, helped to establish the freedom of the press
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the fundamental principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic News media, media, especially publication, published materials, should be conside ...
in North America.Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
was founded under charter by King George II as King's College in Lower Manhattan.
American Revolution
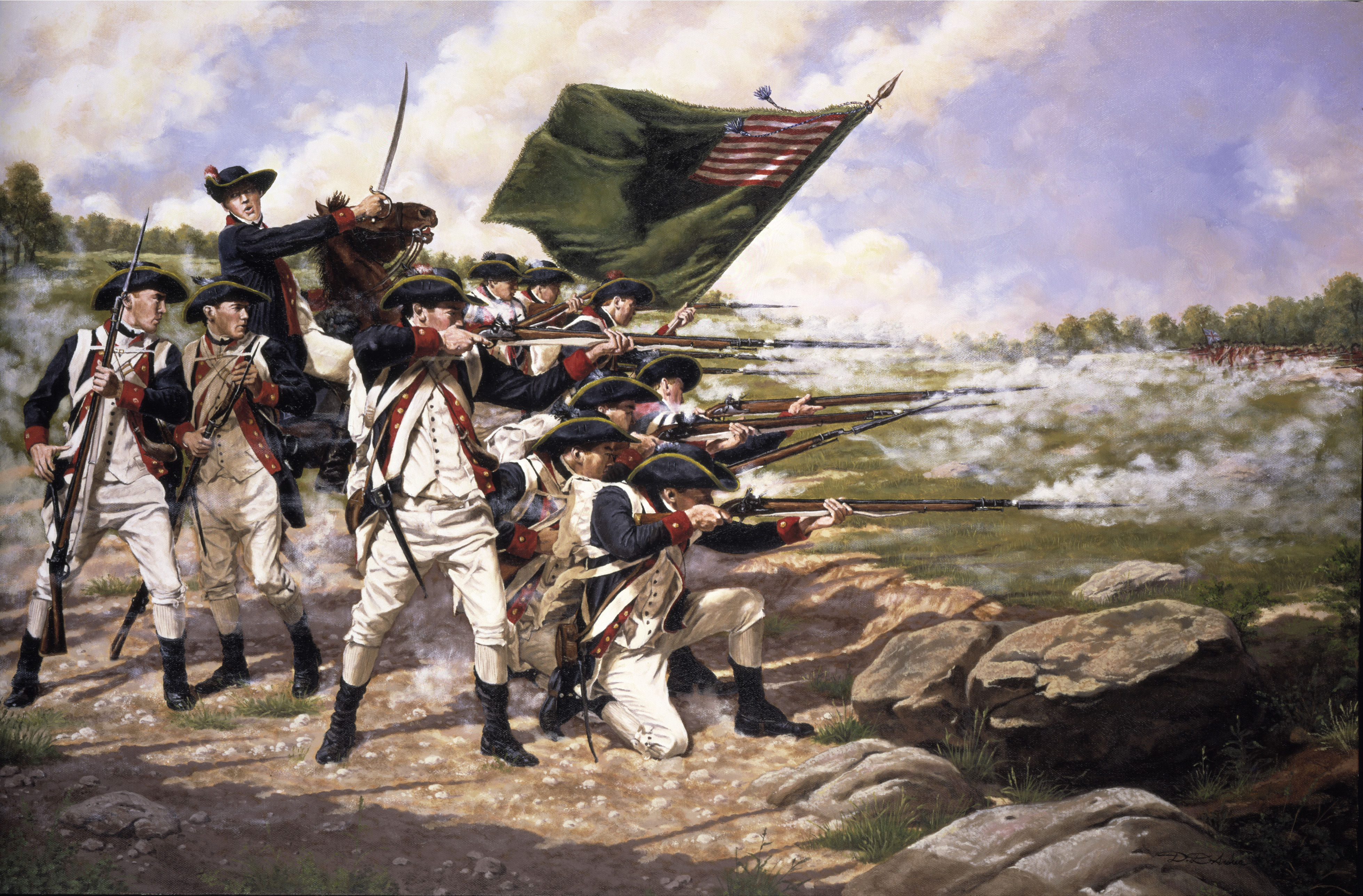 The
The Stamp Act Congress
The Stamp Act Congress (October 7 – 25, 1765), also known as the Continental Congress of 1765, was a meeting held in New York, New York, consisting of representatives from some of the British colonies in North America. It was the first gath ...
met in New York in October 1765, as the Sons of Liberty
The Sons of Liberty was a loosely organized, clandestine, sometimes violent, political organization active in the Thirteen American Colonies founded to advance the rights of the colonists and to fight taxation by the British government. It pl ...
, organized in the city, skirmished over the next ten years with British troops stationed there.Battle of Long Island
The Battle of Long Island, also known as the Battle of Brooklyn and the Battle of Brooklyn Heights, was an action of the American Revolutionary War fought on August 27, 1776, at the western edge of Long Island in present-day Brooklyn, New Yo ...
, the largest battle of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, was fought in August 1776 within the modern-day borough of Brooklyn.Loyalist
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cro ...
refugees and escaped slaves who joined the British lines for freedom newly promised by the Crown for all fighters. As many as 10,000 escaped slaves crowded into the city during the British occupation. When the British forces evacuated at the close of the war in 1783, they transported 3,000 freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), abolitionism, emancipation (gra ...
for resettlement in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
.freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), abolitionism, emancipation (gra ...
in England and the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
.
The only attempt at a peaceful solution to the war took place at the Conference House
Conference House (also known as Billop House) is a stone house in Tottenville, Staten Island, New York City built by Captain Christopher Billopp some time before 1680. It is located in Conference House Park near Ward's Point, the southernmost t ...
on Staten Island between American delegates, including Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
, and British general Lord Howe on September 11, 1776. Shortly after the British occupation began, the Great Fire of New York
The 1835 Great Fire of New York was one of three fires that rendered extensive damage to New York City in the 18th and 19th centuries. The fire occurred in the middle of an economic boom, covering 17 city blocks, killing two people, and destroyin ...
occurred, a large conflagration on the West Side
West Side or Westside may refer to:
Places Canada
* West Side, a neighbourhood of Windsor, Ontario
* West Side, a neighbourhood of Vancouver, British Columbia
United Kingdom
* West Side, Lewis, Outer Hebrides, Scotland
* Westside, Birmingham E ...
of Lower Manhattan, which destroyed about a quarter of the buildings in the city, including Trinity Church.
In 1785, the assembly of the Congress of the Confederation
The Congress of the Confederation, or the Confederation Congress, formally referred to as the United States in Congress Assembled, was the governing body of the United States of America during the Confederation period, March 1, 1781 – Mar ...
made New York City the national capital shortly after the war. New York was the last capital of the U.S. under the Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
and the first capital under the Constitution of the United States
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
. New York City as the U.S. capital hosted several events of national scope in 1789—the first President of the United States, George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
, was inaugurated; the first United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
and the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
each assembled for the first time; and the United States Bill of Rights
The United States Bill of Rights comprises the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. Proposed following the often bitter 1787–88 debate over the ratification of the Constitution and written to address the objections rais ...
was drafted, all at Federal Hall
Federal Hall is a historic building at 26 Wall Street in the Financial District of Manhattan in New York City. The current Greek Revival–style building, completed in 1842 as the Custom House, is operated by the National Park Service as a nati ...
on Wall Street. In 1790, New York surpassed Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
as the nation's largest city. At the end of that year, pursuant to the Residence Act
The Residence Act of 1790, officially titled An Act for establishing the temporary and permanent seat of the Government of the United States (), is a United States federal statute adopted during the second session of the First United States Co ...
, the national capital was moved to Philadelphia.
Nineteenth century
 Over the course of the nineteenth century, New York City's population grew from 60,000 to 3.43 million. Under New York State's
Over the course of the nineteenth century, New York City's population grew from 60,000 to 3.43 million. Under New York State's abolition
Abolition refers to the act of putting an end to something by law, and may refer to:
* Abolitionism, abolition of slavery
* Abolition of the death penalty, also called capital punishment
* Abolition of monarchy
*Abolition of nuclear weapons
*Abol ...
act of 1799, children of slave mothers were to be eventually liberated but to be held in indentured servitude
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract, called an "indenture", may be entered "voluntarily" for purported eventual compensation or debt repayment, ...
until their mid-to-late twenties. Together with slaves freed by their masters after the Revolutionary War and escaped slaves, a significant free-Black population gradually developed in Manhattan. Under such influential United States founders as Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
and John Jay
John Jay (December 12, 1745 – May 17, 1829) was an American statesman, patriot, diplomat, abolitionist, signatory of the Treaty of Paris, and a Founding Father of the United States. He served as the second governor of New York and the first ...
, the New York Manumission Society
The New-York Manumission Society was an American organization founded in 1785 by U.S. Founding Father John Jay, among others, to promote the gradual abolition of slavery and manumission of slaves of African descent within the state of New York. ...
worked for abolition and established the African Free School
The African Free School was a school for children of slaves and free people of color in New York City. It was founded by members of the New York Manumission Society, including Alexander Hamilton and John Jay, on November 2, 1787. Many of its alumni ...
to educate Black children.Commissioners' Plan of 1811
The Commissioners' Plan of 1811 was the original design for the streets of Manhattan above Houston Street and below 155th Street, which put in place the rectangular grid plan of streets and lots that has defined Manhattan on its march uptown u ...
, which expanded the city street grid
In urban planning, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogona ...
to encompass almost all of Manhattan. The 1825 completion of the Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing t ...
through central New York
Central New York is the central region of New York State, including the following counties and cities:
With a population of about 773,606 (2009) and an area of , the region includes the Syracuse metropolitan area.
Definitions
The New York ...
connected the Atlantic port to the agricultural markets and commodities of the North American interior via the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
and the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
. Local politics became dominated by Tammany Hall
Tammany Hall, also known as the Society of St. Tammany, the Sons of St. Tammany, or the Columbian Order, was a New York City political organization founded in 1786 and incorporated on May 12, 1789 as the Tammany Society. It became the main loc ...
, a political machine
In the politics of Representative democracy, representative democracies, a political machine is a party organization that recruits its members by the use of tangible incentives (such as money or political jobs) and that is characterized by a hig ...
supported by Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
and German immigrants.
 Several prominent American literary figures lived in New York during the 1830s and 1840s, including
Several prominent American literary figures lived in New York during the 1830s and 1840s, including William Cullen Bryant
William Cullen Bryant (November 3, 1794 – June 12, 1878) was an American romantic poet, journalist, and long-time editor of the ''New York Evening Post''. Born in Massachusetts, he started his career as a lawyer but showed an interest in poetry ...
, Washington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories "Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and " The Legen ...
, Herman Melville
Herman Melville (Name change, born Melvill; August 1, 1819 – September 28, 1891) was an American people, American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance (literature), American Renaissance period. Among his bes ...
, Rufus Wilmot Griswold
Rufus Wilmot Griswold (February 13, 1815 – August 27, 1857) was an American anthologist, editor, poet, and critic. Born in Vermont, Griswold left home when he was 15 years old. He worked as a journalist, editor, and critic in Philadelphia, New Y ...
, John Keese John Keese (24 November 1805 in New York City – 30 May 1856 in Brooklyn, New York) was a United States auctioneer, publisher and editor of books.
Biography
He received an academical education, and at the age of eighteen entered as clerk with a ...
, Nathaniel Parker Willis
Nathaniel Parker Willis (January 20, 1806 – January 20, 1867), also known as N. P. Willis,Baker, 3 was an American author, poet and editor who worked with several notable American writers including Edgar Allan Poe and Henry Wadsworth Longfello ...
, and Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wide ...
. Public-minded members of the contemporaneous business elite lobbied for the establishment of Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West Side, Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the List of New York City parks, fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban par ...
, which in 1857 became the first landscaped park in an American city.
The Great Irish Famine
The Great Famine ( ga, an Gorta Mór ), also known within Ireland as the Great Hunger or simply the Famine and outside Ireland as the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of starvation and disease in Ireland from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a ...
brought a large influx of Irish immigrants; more than 200,000 were living in New York by 1860, upwards of a quarter of the city's population. There was also extensive immigration from the German provinces, where revolutions had disrupted societies, and Germans comprised another 25% of New York's population by 1860.Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
candidates were consistently elected to local office, increasing the city's ties to the South and its dominant party. In 1861, Mayor Fernando Wood
Fernando Wood (February 14, 1812 – February 13, 1881) was an American Democratic Party politician, merchant, and real estate investor who served as the 73rd and 75th Mayor of New York City. He also represented the city for several terms in ...
called upon the aldermen
An alderman is a member of a municipal assembly or council in many jurisdictions founded upon English law. The term may be titular, denoting a high-ranking member of a borough or county council, a council member chosen by the elected members them ...
to declare independence from Albany and the United States after the South seceded, but his proposal was not acted on.military conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day und ...
laws during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
(1861–1865), which spared wealthier men who could afford to pay a $300 () commutation fee to hire a substitute, led to the Draft Riots of 1863
The New York City draft riots (July 13–16, 1863), sometimes referred to as the Manhattan draft riots and known at the time as Draft Week, were violent disturbances in Lower Manhattan, widely regarded as the culmination of white working-cla ...
, whose most visible participants were ethnic Irish working class.draft riots
The New York City draft riots (July 13–16, 1863), sometimes referred to as the Manhattan draft riots and known at the time as Draft Week, were violent disturbances in Lower Manhattan, widely regarded as the culmination of white working-cl ...
deteriorated into attacks on New York's elite, followed by attacks on Black New Yorkers and their property after fierce competition for a decade between Irish immigrants and Black people for work. Rioters burned the Colored Orphan Asylum to the ground, with more than 200 children escaping harm due to efforts of the New York Police Department
The New York City Police Department (NYPD), officially the City of New York Police Department, established on May 23, 1845, is the primary municipal law enforcement agency within the City of New York, the largest and one of the oldest in ...
, which was mainly made up of Irish immigrants.Williamsburg
Williamsburg may refer to:
Places
*Colonial Williamsburg, a living-history museum and private foundation in Virginia
*Williamsburg, Brooklyn, neighborhood in New York City
*Williamsburg, former name of Kernville (former town), California
*Williams ...
, Brooklyn, and New Jersey. The Black population in Manhattan fell below 10,000 by 1865, which it had last been in 1820. The White working class had established dominance.longshoremen
A stevedore (), also called a longshoreman, a docker or a dockworker, is a waterfront manual laborer who is involved in loading and unloading ships, trucks, trains or airplanes.
After the shipping container revolution of the 1960s, the number o ...
against Black men was especially fierce in the docks area.
Modern history
 In 1898, the modern City of New York was formed with the consolidation of Brooklyn (until then a separate city), the County of New York (which then included parts of the Bronx), the County of Richmond, and the western portion of the County of Queens. The opening of the subway in 1904, first built as separate private systems, helped bind the new city together.
In 1898, the modern City of New York was formed with the consolidation of Brooklyn (until then a separate city), the County of New York (which then included parts of the Bronx), the County of Richmond, and the western portion of the County of Queens. The opening of the subway in 1904, first built as separate private systems, helped bind the new city together.steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
''General Slocum
The PS ''General Slocum''"PS" stands for "Paddle Steamer" was a sidewheel passenger steamboat built in Brooklyn, New York, in 1891. During her service history, she was involved in a number of mishaps, including multiple groundings and collision ...
'' caught fire in the East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Queens ...
, killing 1,021 people on board.Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire
The Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, on Saturday, March 25, 1911, was the deadliest industrial disaster in the history of the city, and one of the deadliest in U.S. history. The ...
, the city's worst industrial disaster, took the lives of 146 garment workers and spurred the growth of the International Ladies' Garment Workers' Union
The International Ladies' Garment Workers' Union (ILGWU), whose members were employed in the women's clothing industry, was once one of the largest labor unions in the United States, one of the first U.S. unions to have a primarily female membe ...
and major improvements in factory safety standards.African diaspora
The African diaspora is the worldwide collection of communities descended from native Africans or people from Africa, predominantly in the Americas. The term most commonly refers to the descendants of the West and Central Africans who were e ...
in North America.Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the t ...
of literary and cultural life flourished during the era of Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic ...
.skyline
A skyline is the outline or shape viewed near the horizon. It can be created by a city’s overall structure, or by human intervention in a rural setting, or in nature that is formed where the sky meets buildings or the land.
City skylines ...
.
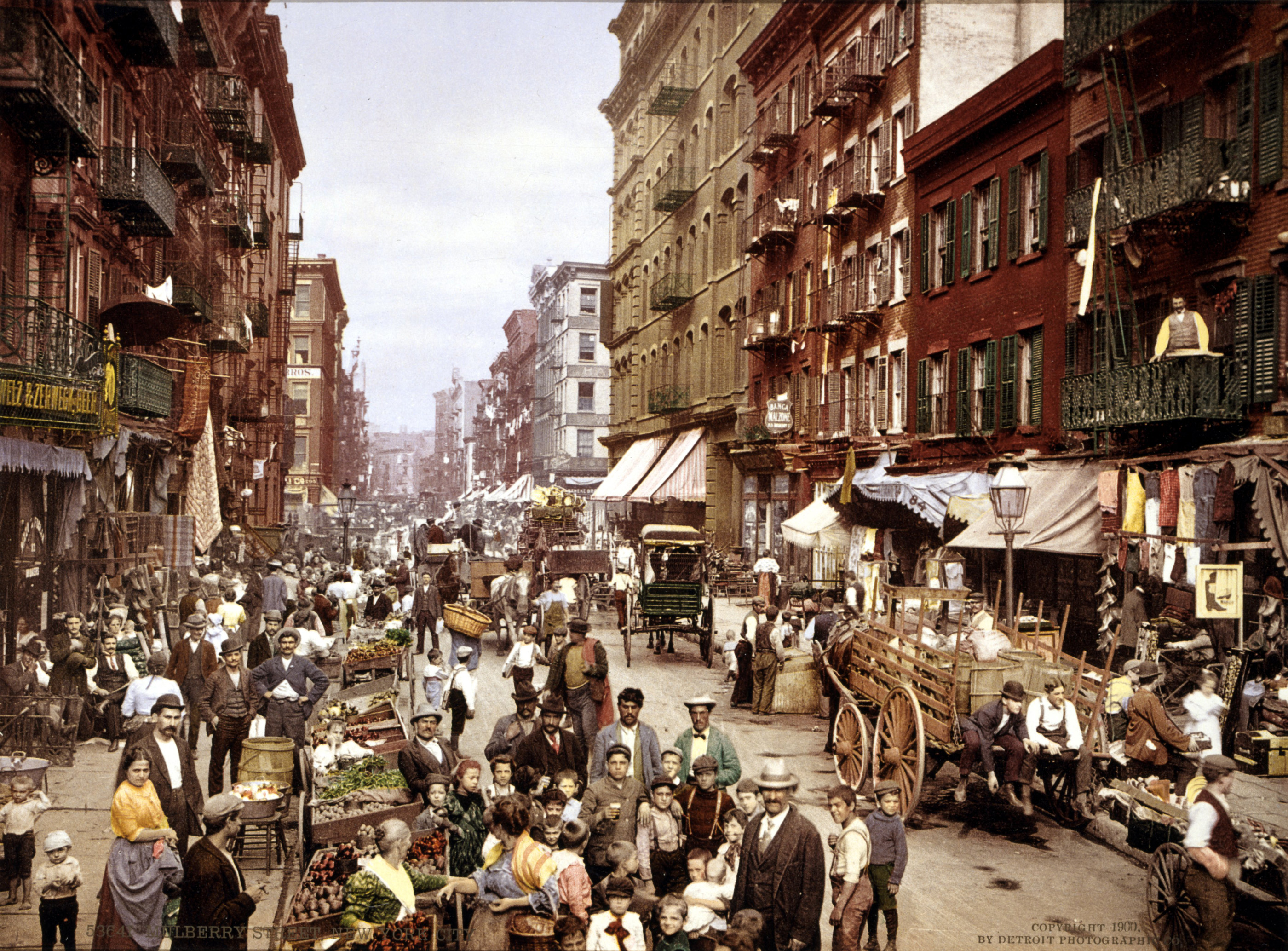 New York became the most populous
New York became the most populous urbanized area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, ...
in the world in the early 1920s, overtaking London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
. The metropolitan area surpassed the 10 million mark in the early 1930s, becoming the first megacity
A megacity is a very large city, typically with a population of more than 10 million people. Precise definitions vary: the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs in its 2018 "World Urbanization Prospects" report counted urban ...
in human history. The difficult years of the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
saw the election of reformer Fiorello La Guardia
Fiorello Henry LaGuardia (; born Fiorello Enrico LaGuardia, ; December 11, 1882September 20, 1947) was an American attorney and politician who represented New York in the House of Representatives and served as the 99th Mayor of New York City fro ...
as mayor and the fall of Tammany Hall
Tammany Hall, also known as the Society of St. Tammany, the Sons of St. Tammany, or the Columbian Order, was a New York City political organization founded in 1786 and incorporated on May 12, 1789 as the Tammany Society. It became the main loc ...
after eighty years of political dominance.
Returning World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
veterans created a post-war economic boom
An economic expansion is an increase in the level of economic activity, and of the goods and services available. It is a period of economic growth as measured by a rise in real GDP. The explanation of fluctuations in aggregate economic activity ...
and the development of large housing tract
Tract housing is a type of housing development in which multiple similar houses are built on a tract (area) of land that is subdivided into smaller lots. Tract housing developments are found in suburb developments that were modeled on the "Levitt ...
s in eastern Queens and Nassau County as well as similar suburban areas in New Jersey. New York emerged from the war unscathed as the leading city of the world, with Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for t ...
leading America's place as the world's dominant economic power. The United Nations Headquarters
The United Nations is headquartered in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, United States, and the complex has served as the official headquarters of the United Nations since its completion in 1951. It is in the Turtle Bay, Manhattan, Turtle Bay neig ...
was completed in 1952, solidifying New York's global geopolitical
Geopolitics (from Greek γῆ ''gê'' "earth, land" and πολιτική ''politikḗ'' "politics") is the study of the effects of Earth's geography (human and physical) on politics and international relations. While geopolitics usually refers to ...
influence, and the rise of abstract expressionism
Abstract expressionism is a post–World War II art movement in American painting, developed in New York City in the 1940s. It was the first specifically American movement to achieve international influence and put New York at the center of the ...
in the city precipitated New York's displacement of Paris as the center of the art world.
 The Stonewall riots were a series of spontaneous, violent protests by members of the LGBT community, gay community against a police raid that took place in the early morning hours of June 28, 1969, at the
The Stonewall riots were a series of spontaneous, violent protests by members of the LGBT community, gay community against a police raid that took place in the early morning hours of June 28, 1969, at the Stonewall Inn
The Stonewall Inn, often shortened to Stonewall, is a gay bar and recreational tavern in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of Lower Manhattan, New York City, and the site of the Stonewall riots of 1969, which is widely considered to be the s ...
in the Greenwich Village
Greenwich Village ( , , ) is a neighborhood on the west side of Lower Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 14th Street to the north, Broadway to the east, Houston Street to the south, and the Hudson River to the west. Greenwich Village ...
neighborhood of Lower Manhattan. New York City suffered the bulk of the economic damage and largest loss of human life in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks, September 11, 2001, attacks.
New York City suffered the bulk of the economic damage and largest loss of human life in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks, September 11, 2001, attacks.Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, the term We ...
, prompting New York Governor Kathy Hochul and New York City Mayor Eric Adams declared corresponding public health emergency (United States), public health emergencies in the state and city, respectively, in July 2022.
Geography
 During the Wisconsin glaciation, 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, the New York City area was situated at the edge of a large ice sheet over in depth.
During the Wisconsin glaciation, 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, the New York City area was situated at the edge of a large ice sheet over in depth.Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
and Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey by the Arthur Kill and the Kill Van Kull an ...
. That action also left bedrock at a relatively shallow depth, providing a solid Foundation (engineering), foundation for most of Manhattan's skyscrapers.
New York City is situated in the northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
, in southeastern New York State, approximately halfway between Washington, D.C. and Boston. The location at the mouth of the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
, which feeds into a naturally sheltered harbor and then into the Atlantic Ocean, has helped the city grow in significance as a trading port. Most of New York City is built on the three islands of Long Island, Manhattan, and Staten Island.
The Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
flows through the Hudson Valley into New York Bay. Between New York City and Troy, New York, the river is an estuary. The Hudson River separates the city from the U.S. state of New Jersey. The East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Queens ...
—a tidal strait—flows from Long Island Sound and separates the Bronx and Manhattan from Long Island. The Harlem River, another tidal strait between the East and Hudson rivers, separates most of Manhattan from the Bronx. The Bronx River, which flows through the Bronx and Westchester County, is the only entirely fresh water, freshwater river in the city.Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan (also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York) is the southernmost part of Manhattan, the central borough for business, culture, and government in New York City, which is the most populated city in the United States with ...
, with developments such as Battery Park City in the 1970s and 1980s.[New York State Gazetteer from 2010 United States Census](_blank)
United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 9, 2017.
Boroughs
 is sometimes referred to collectively as the ''Five Boroughs''. Each borough is coextensive with a respective Administrative divisions of New York (state)#County, county of
is sometimes referred to collectively as the ''Five Boroughs''. Each borough is coextensive with a respective Administrative divisions of New York (state)#County, county of New York State
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. stat ...
, making New York City one of the List of U.S. municipalities in multiple counties, U.S. municipalities in multiple counties. There are :Neighborhoods in New York City, hundreds of distinct neighborhoods throughout the boroughs, many with a definable history and character.
If the boroughs were each independent cities, four of the boroughs (Brooklyn, Queens, Manhattan, and the Bronx) would be among the ten most populous cities in the United States (Staten Island would be ranked 37th as of 2020); these same boroughs are coterminous with the four most densely populated counties in the United States: New York (Manhattan), Kings (Brooklyn), Bronx, and Queens.
Manhattan
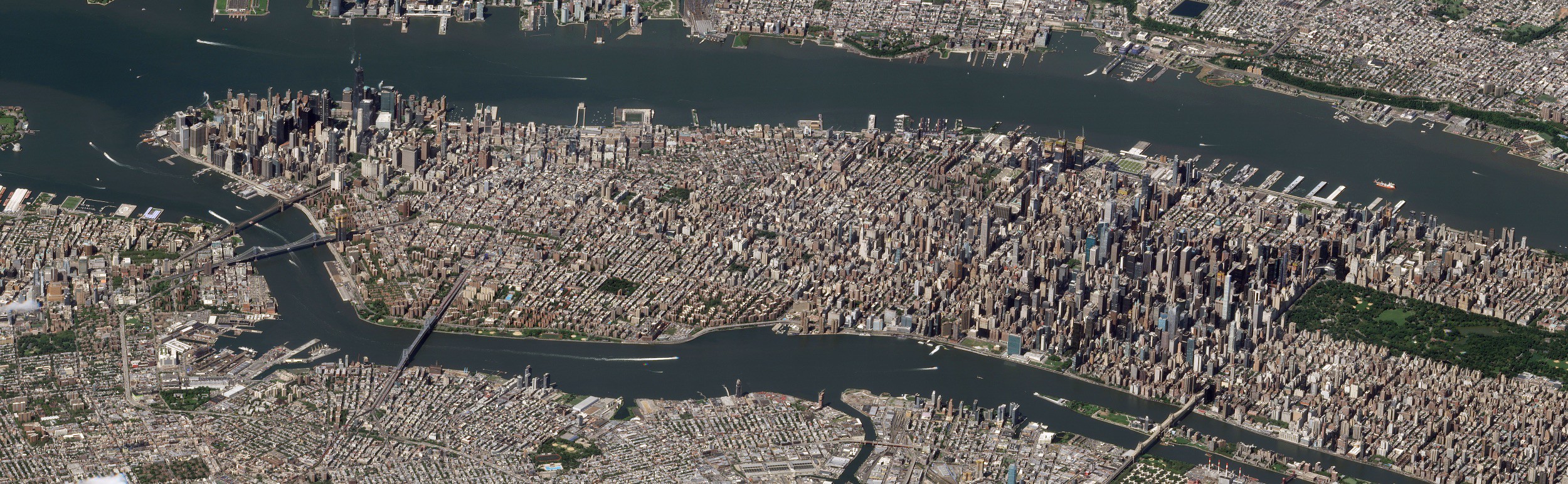

Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
(New York County) is the geographically smallest and most densely populated borough. It is home to Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West Side, Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the List of New York City parks, fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban par ...
and most of the city's skyscrapers, and is sometimes locally known as ''The City''.headquarters
Headquarters (commonly referred to as HQ) denotes the location where most, if not all, of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. In the United States, the corporate headquarters represents the entity at the center or the to ...
of many major multinational corporations, the Headquarters of the United Nations, United Nations Headquarters, Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for t ...
, and a number of important universities. The borough of Manhattan is often described as the financial and cultural center of the world.
Most of the borough is situated on Manhattan Island, at the mouth of the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
and the East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Queens ...
, and its southern tip, at the confluence of the two rivers, represents the birthplace of New York City itself. Several small islands also compose part of the borough of Manhattan, including Randall's Island, Wards Island, and Roosevelt Island in the East River, and Governors Island
Governors Island is a island in New York Harbor, within the New York City borough of Manhattan. It is located approximately south of Manhattan Island, and is separated from Brooklyn to the east by the Buttermilk Channel. The National Park ...
and Liberty Island to the south in New York Harbor
New York Harbor is at the mouth of the Hudson River where it empties into New York Bay near the East River tidal estuary, and then into the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of the United States. It is one of the largest natural harbors in t ...
.
Manhattan Island is loosely divided into the Lower Manhattan, Lower, Midtown Manhattan, Midtown, and Upper Manhattan, Uptown regions. Uptown Manhattan is divided by Central Park into the Upper East Side and the Upper West Side, and above the park is Harlem, bordering the Bronx (Bronx County).
Harlem was predominantly occupied by Jewish and Italian Americans in the 19th century until the Great Migration. It was the center of the Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the t ...
.
The borough of Manhattan also includes a small neighborhood on the mainland, called Marble Hill, Manhattan, Marble Hill, which is contiguous with the Bronx. New York City's remaining four boroughs are collectively referred to as the ''Outer Boroughs''.
Brooklyn
Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
(Kings County), on the western tip of Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
, is the city's most populous borough. Brooklyn is known for its cultural, social, and ethnic diversity, an independent art scene, List of Brooklyn neighborhoods, distinct neighborhoods, and a distinctive architectural heritage. Downtown Brooklyn is the largest central core neighborhood in the Outer Boroughs. The borough has a long beachfront shoreline including Coney Island, established in the 1870s as one of the earliest amusement grounds in the U.S. Marine Park (Brooklyn park), Marine Park and Prospect Park (Brooklyn), Prospect Park are the two largest parks in Brooklyn. Since 2010, Brooklyn has evolved into a thriving hub of entrepreneurship and high tech, high-technology Startup company, startup firms,
Queens
Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
(Queens County), on Long Island north and east of Brooklyn, is geographically the largest borough, the most Ethnic diversity, ethnically diverse county in the United States,
The Bronx
The Bronx (Bronx County) is both New York City's northernmost borough, and the only one that is mostly on the mainland. It is the location of Yankee Stadium, the baseball park of the New York Yankees, and home to the largest Housing cooperative, cooperatively-owned housing complex in the United States, Co-op City, Bronx, Co-op City. It is also home to the Bronx Zoo, the world's largest metropolitan zoo,
Staten Island
Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey by the Arthur Kill and the Kill Van Kull an ...
(Richmond County) is the most suburban in character of the five boroughs. Staten Island is connected to Brooklyn by the Verrazano-Narrows Bridge, and to Manhattan by way of the free Staten Island Ferry, a daily commuter ferry that provides unobstructed views of the Statue of Liberty
The Statue of Liberty (''Liberty Enlightening the World''; French: ''La Liberté éclairant le monde'') is a List of colossal sculpture in situ, colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor in New York City, in the U ...
, Ellis Island, and Lower Manhattan. In central Staten Island, the Staten Island Greenbelt spans approximately , including of walking trails and one of the last undisturbed forests in the city. Designated in 1984 to protect the island's natural lands, the Greenbelt comprises seven city parks.
File:Long Island City from One World Observatory 2017.jpg, The growing skyline of Long Island City, Queens, Long Island City, Queens (background), facing the East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Queens ...
and Manhattan in May 2017
File:1650 Grand Concourse.jpg, The Grand Concourse (Bronx), Grand Concourse in the Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New Y ...
, foreground, with Manhattan in the background in February 2018
File:St. George from Staten Island Ferry (7231533884).jpg, St. George, Staten Island as seen from the Staten Island Ferry, the world's busiest passenger-only ferry system, shuttling passengers between Manhattan and Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey by the Arthur Kill and the Kill Van Kull an ...
Architecture
New York has architecturally noteworthy buildings in a wide range of styles and from distinct time periods, from the Dutch Colonial Wyckoff House, Pieter Claesen Wyckoff House in Brooklyn, the oldest section of which dates to 1656, to the modern One World Trade Center, the skyscraper at World Trade Center site, Ground Zero in Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan (also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York) is the southernmost part of Manhattan, the central borough for business, culture, and government in New York City, which is the most populated city in the United States with ...
and the List of most expensive buildings in the world, most expensive office tower in the world by construction cost.
Manhattan's skyline
A skyline is the outline or shape viewed near the horizon. It can be created by a city’s overall structure, or by human intervention in a rural setting, or in nature that is formed where the sky meets buildings or the land.
City skylines ...
, with its many skyscrapers, is universally recognized, and the city has been home to several of the Skyscraper#History of the tallest skyscrapers, tallest buildings in the world. , New York City had 6,455 high-rise buildings, the third most in the world after Hong Kong and Seoul. Of these, , 550 completed structures were at least high, with more than fifty completed List of tallest buildings in New York City, skyscrapers taller than . These include the Woolworth Building, an early example of Gothic Revival architecture in skyscraper design, built with massively scaled Gothic detailing; completed in 1913, for 17 years it was the world's tallest building.
The 1916 Zoning Resolution required Setback (architecture), setbacks in new buildings and restricted towers to a percentage of the Land lot, lot size, to allow sunlight to reach the streets below. The Art Deco style of the Chrysler Building (1930) and Empire State Building
The Empire State Building is a 102-story Art Deco skyscraper in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. The building was designed by Shreve, Lamb & Harmon and built from 1930 to 1931. Its name is derived from "Empire State", the nickname of the st ...
(1931), with their tapered tops and steel spires, reflected the zoning requirements. The buildings have distinctive ornamentation, such as the eagles at the corners of the 61st floor on the Chrysler Building, and are considered some of the finest examples of the Art Deco style. A highly influential example of the International style (architecture), international style in the United States is the Seagram Building (1957), distinctive for its façade using visible bronze-toned I-beams to evoke the building's structure. The Condé Nast Building (2000) is a prominent example of Sustainable design, green design in American skyscrapers[Lankevich (1998), pp. 82–83; ] A distinctive feature of many of the city's buildings is the roof-mounted wooden water tower. In the 1800s, the city required their installation on buildings higher than six stories to prevent the need for excessively high water pressures at lower elevations, which could break municipal water pipes. Garden city movement, Garden apartments became popular during the 1920s in outlying areas, such as Jackson Heights, Queens, Jackson Heights.
According to the United States Geological Survey, an updated analysis of seismic hazard in July 2014 revealed a "slightly lower hazard for tall buildings" in New York City than previously assessed. Scientists estimated this lessened risk based upon a lower likelihood than previously thought of slow shaking near the city, which would be more likely to cause damage to taller structures from an earthquake in the vicinity of the city. Manhattan contained over 500 million square feet of office space as of 2022; the Covid-19 pandemic and remote work, hybrid work model have prompted consideration of commercial-to-residential conversion within Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan and serves as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Buildin ...
.
Climate
Under the Köppen climate classification, using the isotherm, New York City features a humid subtropical climate (Cfa), and is thus the northernmost major city on the North American continent with this categorization. The suburbs to the immediate north and west lie in the transitional zone between humid subtropical and humid continental climates (Dfa). Winters are chilly and damp, and prevailing wind patterns that blow sea breezes offshore temper the moderating effects of the Atlantic Ocean; yet the Atlantic and the partial shielding from colder air by the Appalachian Mountains keep the city warmer in the winter than inland North American cities at similar or lesser latitudes such as Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, and Indianapolis. The daily mean temperature in January, the area's coldest month, is .
Winters are chilly and damp, and prevailing wind patterns that blow sea breezes offshore temper the moderating effects of the Atlantic Ocean; yet the Atlantic and the partial shielding from colder air by the Appalachian Mountains keep the city warmer in the winter than inland North American cities at similar or lesser latitudes such as Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, and Indianapolis. The daily mean temperature in January, the area's coldest month, is .
Parks
 The city of New York has a complex park system, with various lands operated by the National Park Service, the New York State Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation, and the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation. In its 2018 ParkScore ranking, The Trust for Public Land reported that the park system in New York City was the ninth-best park system among the fifty most populous U.S. cities. ParkScore ranks urban park systems by a formula that analyzes median park size, park acres as percent of city area, the percent of city residents within a half-mile of a park, spending of park services per resident, and the number of playgrounds per 10,000 residents. In 2021, the New York City Council banned the use of synthetic pesticides by city agencies and instead required organic lawn management. The effort was started by teacher Paula Rogovin's kindergarten class at P.S. 290.
The city of New York has a complex park system, with various lands operated by the National Park Service, the New York State Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation, and the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation. In its 2018 ParkScore ranking, The Trust for Public Land reported that the park system in New York City was the ninth-best park system among the fifty most populous U.S. cities. ParkScore ranks urban park systems by a formula that analyzes median park size, park acres as percent of city area, the percent of city residents within a half-mile of a park, spending of park services per resident, and the number of playgrounds per 10,000 residents. In 2021, the New York City Council banned the use of synthetic pesticides by city agencies and instead required organic lawn management. The effort was started by teacher Paula Rogovin's kindergarten class at P.S. 290.
National parks
 Gateway National Recreation Area contains over , most of it in New York City. In Brooklyn and Queens, the park contains over of salt marsh, wetlands, islands, and water, including most of Jamaica Bay and the Jamaica Bay Wildlife Refuge. Also in Queens, the park includes a significant portion of the western Rockaway Peninsula, most notably Jacob Riis Park and Fort Tilden. In Staten Island, it includes Fort Wadsworth, with historic pre-Civil War era Battery Weed and Fort Tompkins Quadrangle, Fort Tompkins, and Great Kills Park, with beaches, trails, and a marina.
The Statue of Liberty National Monument and Ellis Island Immigration Museum are managed by the National Park Service and are in both New York and New Jersey. They are joined in the harbor by Governors Island National Monument. Historic sites under federal management on Manhattan Island include
Gateway National Recreation Area contains over , most of it in New York City. In Brooklyn and Queens, the park contains over of salt marsh, wetlands, islands, and water, including most of Jamaica Bay and the Jamaica Bay Wildlife Refuge. Also in Queens, the park includes a significant portion of the western Rockaway Peninsula, most notably Jacob Riis Park and Fort Tilden. In Staten Island, it includes Fort Wadsworth, with historic pre-Civil War era Battery Weed and Fort Tompkins Quadrangle, Fort Tompkins, and Great Kills Park, with beaches, trails, and a marina.
The Statue of Liberty National Monument and Ellis Island Immigration Museum are managed by the National Park Service and are in both New York and New Jersey. They are joined in the harbor by Governors Island National Monument. Historic sites under federal management on Manhattan Island include Stonewall National Monument
Stonewall National Monument is a U.S. national monument in the West Village neighborhood of Greenwich Village in Lower Manhattan, New York City. The designated area includes the Stonewall Inn, the Christopher Park, and nearby streets including ...
; Castle Clinton National Monument; Federal Hall National Memorial; Theodore Roosevelt Birthplace National Historic Site; General Grant National Memorial (Grant's Tomb); African Burial Ground National Monument; and Hamilton Grange National Memorial. List of National Historic Landmarks in New York City, Hundreds of properties are listed on the National Register of Historic Places or as a National Historic Landmark.
State parks
There are seven state parks within the confines of New York City. Some of them include:
*The Clay Pit Ponds State Park Preserve is a natural area that includes extensive Trail riding, riding trails.
*Riverbank State Park is a facility that rises over the Hudson River.
*East River State Park, Marsha P. Johnson State Park is a state park in Brooklyn and Manhattan that borders the East River that was renamed in honor of Marsha P. Johnson.
City parks
 New York City has over of Urban park, municipal parkland and of public beaches. The largest municipal park in the city is Pelham Bay Park in the Bronx, with .
New York City has over of Urban park, municipal parkland and of public beaches. The largest municipal park in the city is Pelham Bay Park in the Bronx, with .Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West Side, Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the List of New York City parks, fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban par ...
, an Greenwich Village
Greenwich Village ( , , ) is a neighborhood on the west side of Lower Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 14th Street to the north, Broadway to the east, Houston Street to the south, and the Hudson River to the west. Greenwich Village ...
neighborhood of Lower Manhattan. The Washington Square Arch at the northern gateway to the park is an iconic symbol of both New York University
New York University (NYU) is a private research university in New York City. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded by a group of New Yorkers led by then-Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin.
In 1832, the ...
and Greenwich Village.
* Prospect Park (Brooklyn), Prospect Park in Brooklyn has a meadow, a lake, and extensive woodlands. Within the park is the historic Battle Pass, prominent in the Battle of Long Island.
* Flushing Meadows–Corona Park in Queens, with its making it the city's fourth largest park, was the setting for the 1939 New York World's Fair, 1939 World's Fair and the 1964 New York World's Fair, 1964 World's Fair and is host to the USTA Billie Jean King National Tennis Center and the annual US Open (tennis), U.S. Open Tennis Championships tournament.
* Over a fifth of the Bronx's area, , is dedicated to open space and parks, including Pelham Bay Park, Van Cortlandt Park, the Bronx Zoo, and the New York Botanical Gardens.
* In Staten Island, the Conference House Park contains the historic Conference House
Conference House (also known as Billop House) is a stone house in Tottenville, Staten Island, New York City built by Captain Christopher Billopp some time before 1680. It is located in Conference House Park near Ward's Point, the southernmost t ...
, site of the only attempt of a peaceful resolution to the American Revolution which was conducted in September 1775, attended by Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
representing the Americans and Lord Howe representing the British Crown. The historic Burial Ridge, the largest Native American burial ground within New York City, is within the park.
Military installations
Brooklyn is home to Fort Hamilton, the United States Armed Forces, U.S. military's only active duty installation within New York City, aside from U.S. Coast Guard, Coast Guard operations. The facility was established in 1825 on the site of a small artillery battery, battery used during the American Revolution, and it is one of America's longest serving military forts. Today, Fort Hamilton serves as the headquarters of the North Atlantic Division of the United States Army Corps of Engineers and for the New York City Recruiting Battalion. It also houses the 1179th Transportation Brigade, the 722nd Aeromedical Staging Squadron, and a military entrance processing station. Other formerly active military reservations still used for United States National Guard, National Guard and military training or reserve operations in the city include Fort Wadsworth in Staten Island and Fort Totten (New York), Fort Totten in Queens.
Demographics
New York City is the most populous city in the United States,Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
, the second-most populous U.S. city;New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass, at , and one of the list of most populous metropolitan areas, most populous urban agg ...
.Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
, in Brooklyn, or in Queens.
Population density
 In 2020, the city had an estimated population density of , rendering it the nation's most densely populated of all larger municipalities (those with more than 100,000 residents), with several small cities (of fewer than 100,000) in adjacent Hudson County, New Jersey having List of United States cities by population density, greater density, as per the 2010 census. Geographically co-extensive with New York County, the borough of Manhattan's 2017 population density of makes it the County statistics of the United States#Population density, highest of any county in the United States and List of United States cities by population density#New York City boroughs, higher than the density of any individual American city. The next three densest counties in the United States, placing second through fourth, are also New York boroughs: Brooklyn, the Bronx, and Queens respectively.
In 2020, the city had an estimated population density of , rendering it the nation's most densely populated of all larger municipalities (those with more than 100,000 residents), with several small cities (of fewer than 100,000) in adjacent Hudson County, New Jersey having List of United States cities by population density, greater density, as per the 2010 census. Geographically co-extensive with New York County, the borough of Manhattan's 2017 population density of makes it the County statistics of the United States#Population density, highest of any county in the United States and List of United States cities by population density#New York City boroughs, higher than the density of any individual American city. The next three densest counties in the United States, placing second through fourth, are also New York boroughs: Brooklyn, the Bronx, and Queens respectively.
Race and ethnicity
 The city's population in 2020 was 30.9% White Americans, White (non-Hispanic), 28.7% Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic or Latino, 20.2% African Americans, Black or African American (non-Hispanic), 15.6% Asian Americans in New York City, Asian, and 0.2% Native Americans in the United States, Native American (non-Hispanic). A total of 3.4% of the non-Hispanic population identified with Multiracial Americans, more than one race. Throughout its history, New York has been a major port of entry for immigrants into the United States. More than 12 million European American, European immigrants were received at Ellis Island between 1892 and 1924. The term "melting pot" was first coined to describe densely populated immigrant neighborhoods on the Lower East Side, Manhattan, Lower East Side. By 1900, German American, Germans constituted the largest immigrant group, followed by the Irish American, Irish, Ashkenazi Jews, Jews, and Italian American, Italians. In 1940, Whites represented 92% of the city's population.
The city's population in 2020 was 30.9% White Americans, White (non-Hispanic), 28.7% Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic or Latino, 20.2% African Americans, Black or African American (non-Hispanic), 15.6% Asian Americans in New York City, Asian, and 0.2% Native Americans in the United States, Native American (non-Hispanic). A total of 3.4% of the non-Hispanic population identified with Multiracial Americans, more than one race. Throughout its history, New York has been a major port of entry for immigrants into the United States. More than 12 million European American, European immigrants were received at Ellis Island between 1892 and 1924. The term "melting pot" was first coined to describe densely populated immigrant neighborhoods on the Lower East Side, Manhattan, Lower East Side. By 1900, German American, Germans constituted the largest immigrant group, followed by the Irish American, Irish, Ashkenazi Jews, Jews, and Italian American, Italians. In 1940, Whites represented 92% of the city's population.[''The Newest New Yorkers: 2013''](_blank)
New York City Department of City Planning, December 2013. Retrieved February 9, 2017. "The immigrant share of the population has also doubled since 1965, to 37 percent. With foreign-born mothers accounting for 51 percent of all births, approximately 6-in-10 New Yorkers are either immigrants or the children of immigrants." In New York, no single country or region of origin dominates.Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
. New York contains the highest total Asian population of any U.S. city proper. The New York City borough of Queens is home to the state's largest Asian American population and the largest Andes, Andean (Colombian American, Colombian, Ecuadorian American, Ecuadorian, Peruvian American, Peruvian, and Bolivian American, Bolivian) populations in the United States, and is also the most ethnically diverse urban area in the world.[*
*
*
*
* ] as well as in Chinatown, Brooklyn, Brooklyn, and around Chinatown, Flushing, Flushing, Queens, are thriving as traditionally urban enclaves—while also expanding rapidly eastward into suburban Nassau County on Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
, as the New York metropolitan region and New York State have become the top destinations for new Chinese immigrants, respectively, and large-scale Chinese emigration, Chinese immigration continues into New York City and surrounding areas, People of Norwegian American, Norwegian and Swedish American, Swedish descent both stood at about 20,000 each, while people of Czech American, Czech, Lithuanian American, Lithuanian, Portuguese American, Portuguese, Scotch-Irish American, Scotch-Irish, and Welsh American, Welsh descent all numbered between 12,000 and 14,000. Arab Americans number over 160,000 in New York City, with the highest concentration in Brooklyn. Demographics of Central Asia, Central Asians, primarily Uzbek Americans, are a rapidly growing segment of the city's non-Hispanic White population, enumerating over 30,000, and including more than half of all Central Asian immigrants to the United States, most settling in Queens or Brooklyn. Albanian Americans are most highly concentrated in the Bronx, while Astoria, Queens is the epicenter of American Greek culture as well as the Greek Cypriots, Cypriot community.
The wider New York City metropolitan statistical area, with more than twenty million people, about fifty percent more than second-place Los Angeles metropolitan area, Los Angeles,
People of Norwegian American, Norwegian and Swedish American, Swedish descent both stood at about 20,000 each, while people of Czech American, Czech, Lithuanian American, Lithuanian, Portuguese American, Portuguese, Scotch-Irish American, Scotch-Irish, and Welsh American, Welsh descent all numbered between 12,000 and 14,000. Arab Americans number over 160,000 in New York City, with the highest concentration in Brooklyn. Demographics of Central Asia, Central Asians, primarily Uzbek Americans, are a rapidly growing segment of the city's non-Hispanic White population, enumerating over 30,000, and including more than half of all Central Asian immigrants to the United States, most settling in Queens or Brooklyn. Albanian Americans are most highly concentrated in the Bronx, while Astoria, Queens is the epicenter of American Greek culture as well as the Greek Cypriots, Cypriot community.
The wider New York City metropolitan statistical area, with more than twenty million people, about fifty percent more than second-place Los Angeles metropolitan area, Los Angeles, Ecuador, Colombia, Guyana, Peru, Brazil, and Venezuela are the top source countries from South America for immigrants to the New York City region; the Dominican Republic, Jamaica, Haiti, and Trinidad and Tobago in the Caribbeans in New York City, Caribbean; Nigeria, Egypt, Ghana, Tanzania, Kenya, and South Africa from Africa; and El Salvador, Honduras, and Guatemala in Central America. Amidst a resurgence of Puerto Rican migration to New York City, this population had increased to approximately 1.3 million in the metropolitan area . In 2022, New York City began receiving thousands of Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino immigrants bused from the state of Texas, mostly originating from Venezuela, Ecuador, Columbia, and Honduras.
Since 2010, Little Australia has emerged and is growing rapidly, representing the Australasian presence in Nolita, Manhattan.
Ecuador, Colombia, Guyana, Peru, Brazil, and Venezuela are the top source countries from South America for immigrants to the New York City region; the Dominican Republic, Jamaica, Haiti, and Trinidad and Tobago in the Caribbeans in New York City, Caribbean; Nigeria, Egypt, Ghana, Tanzania, Kenya, and South Africa from Africa; and El Salvador, Honduras, and Guatemala in Central America. Amidst a resurgence of Puerto Rican migration to New York City, this population had increased to approximately 1.3 million in the metropolitan area . In 2022, New York City began receiving thousands of Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino immigrants bused from the state of Texas, mostly originating from Venezuela, Ecuador, Columbia, and Honduras.
Since 2010, Little Australia has emerged and is growing rapidly, representing the Australasian presence in Nolita, Manhattan.
Sexual orientation and gender identity
The New York metropolitan area is home to about 570,000 self-identifying Gays in New York City, gay and Bisexuality, bisexual people, LGBT demographics of the United States#By metropolitan area, the largest in the United States and one of the world's largest and the most prominent. Same-sex sexual activity between consenting adults has been legal in New York since the ''New York v. Onofre'' case in 1980 which invalidated the state's Sodomy laws in the United States#State and territorial laws prior to Lawrence v. Texas, sodomy law. Same-sex marriage in New York, Same-sex marriages in New York were legalized on June 24, 2011, and were authorized to take place on July 23, 2011. Brian Silverman, the author of ''Frommer's New York City from $90 a Day,'' wrote the city has "one of the world's largest, loudest, and most powerful LGBT communities", and "Gay and lesbian culture is as much a part of New York's basic identity as yellow cabs, high-rise buildings, and Broadway theatre". LGBT culture in New York City, LGBT LGBT travel, travel guide ''Queer in the World'' states, "The fabulosity of Gay New York is unrivaled on Earth, and LGBT culture, queer culture seeps into every corner of its five boroughs". LGBT activism, LGBT advocate and entertainer Madonna as a gay icon, Madonna stated metaphorically, "Anyways, not only is New York City the best place in the world because of the queer people here. Let me tell you something, if you can make it here, then you must be queer."
The annual New York City Pride March (or New York City LGBT Pride March, gay Pride march, pride parade) proceeds southward down Fifth Avenue and ends at Greenwich Village, Manhattan, Greenwich Village in Lower Manhattan; the parade is the list of largest LGBT events, largest pride parade in the world, attracting tens of thousands of participants and millions of sidewalk spectators each June.
Religion
Christianity
 Largely as a result of Western European missionary work and colonialism, Christianity is the largest religion in New York City,
Largely as a result of Western European missionary work and colonialism, Christianity is the largest religion in New York City,[ Catholic Church, Roman Catholicism is the largest Christian denomination (33%), followed by Protestantism (23%), and List of Christian denominations, other Christians (3%). The Roman Catholic population are primarily served by the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New York and Roman Catholic Diocese of Brooklyn, Diocese of Brooklyn. Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholics are divided into numerous jurisdictions throughout the city. Evangelicalism, Evangelical Protestantism is the largest branch of Protestantism in the city (9%), followed by Mainline Protestantism (8%), while the converse is usually true for other cities and metropolitan areas.]
Judaism
 American Jews, Judaism, the Jews in New York City, second-largest religion practiced in New York City, with approximately 1.6 million adherents as of 2022, represents Jewish population by city, the largest Jewish community of any city in the world, greater than the combined totals of Tel Aviv and Jerusalem.
American Jews, Judaism, the Jews in New York City, second-largest religion practiced in New York City, with approximately 1.6 million adherents as of 2022, represents Jewish population by city, the largest Jewish community of any city in the world, greater than the combined totals of Tel Aviv and Jerusalem.Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
.
Islam
 Islam ranks as the third largest religion in New York City, following Christianity and Judaism, with estimates ranging between 600,000 and 1,000,000 observers of Islam, including 10% of the city's public school children. Given both the size and scale of the city, as well as its relative proxinity and accessibility by aviation, air transportation to the Middle East, North Africa, Central Asia, and South Asia, 22.3% of Islam in the United States, American Muslims live in New York City, with 1.5 million Muslims in the greater
Islam ranks as the third largest religion in New York City, following Christianity and Judaism, with estimates ranging between 600,000 and 1,000,000 observers of Islam, including 10% of the city's public school children. Given both the size and scale of the city, as well as its relative proxinity and accessibility by aviation, air transportation to the Middle East, North Africa, Central Asia, and South Asia, 22.3% of Islam in the United States, American Muslims live in New York City, with 1.5 million Muslims in the greater New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass, at , and one of the list of most populous metropolitan areas, most populous urban agg ...
, representing the largest metropolitan Muslim population in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, the term We ...
—and the most ethnically diverse Muslim population of any city in the world.
Hinduism and other religious affiliations
Following these three largest religious groups in New York City are Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism, Zoroastrianism, and a variety of other religions, as well as atheism. In 2014, 24% of New Yorkers identified with no organized religious affiliation; a little over 3% of New Yorkers were Atheism, atheist.
Wealth and income disparity
New York City, like other large cities, has a high degree of income disparity, as indicated by its Gini Coefficient, Gini coefficient of 0.55 as of 2017. In the first quarter of 2014, the average weekly wage in New York County (Manhattan) was $2,749, representing the highest total among large counties in the United States. As of 2017, New York City was home to the highest number of billionaires of any city in the world at 103,
Economy
New York City is a Global city, global hub of business and commerce and an established safe haven
Safe haven may refer to:
* Sanctuary
Arts and entertainment
* ''Safe Haven'' (novel), a 2010 American novel by Nicholas Sparks
** ''Safe Haven'' (film), a 2013 American film adapted from the novel
* ''Safe Haven'' (short film), a 2009 American ...
for global investors,
Ashkan Zandieh. Accessed June 1, 2022.[ medical technology and research, retailing, world trade, transportation, tourism, real estate, new media, traditional media, advertising, legal services, accountancy, insurance, both musical theater, musical and straight play, prose Broadway theatre, theater, fashion, and the arts in the United States; while Silicon Alley, metonymous for New York's broad-spectrum high technology sphere, continues to expand. The Port of New York and New Jersey is a major economic engine, handling a maritime transport, maritime cargo volume in the ten months through October 2022 of over 8.2 million Twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEUs, benefitting Panamax, post-Panamax from the expansion of the Panama Canal, and accelerating ahead of California seaports in monthly cargo volumes.
Many Fortune 500 corporations are headquartered in New York City, as are a large number of multinational corporations. One out of ten private sector jobs in the city is with a foreign company. New York City has been ranked first among cities across the globe in attracting Capital (economics), capital, business, and tourists. New York City's role as the top global center for the Advertising, advertising industry is metonymously reflected as ''Madison Avenue#Advertising industry, Madison Avenue''.]Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
, and an unofficial chocolate district in Brooklyn is home to several chocolate makers and retailers.
Wall Street
 New York City's most important economic sector lies in its role as the headquarters for the Financial center, U.S. financial industry, metonymously known as ''Wall Street''. The city's Security (finance), securities industry continues to form the largest segment of the city's financial sector and is an important economic engine. Many large financial companies are headquartered in New York City, and the city is also home to a burgeoning number of financial Startup company, startup companies.
New York City's most important economic sector lies in its role as the headquarters for the Financial center, U.S. financial industry, metonymously known as ''Wall Street''. The city's Security (finance), securities industry continues to form the largest segment of the city's financial sector and is an important economic engine. Many large financial companies are headquartered in New York City, and the city is also home to a burgeoning number of financial Startup company, startup companies.
Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan (also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York) is the southernmost part of Manhattan, the central borough for business, culture, and government in New York City, which is the most populated city in the United States with ...
is home to the New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is by far the world's largest stock exchange by market capitalization of its listed c ...
, at New York Stock Exchange Building, 11 Wall Street, and the Nasdaq
The Nasdaq Stock Market () (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations Stock Market) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second ...
, at One Liberty Plaza, 165 Broadway, representing the world's largest and second largest stock exchanges, respectively, when measured both by overall average daily trading volume and by total market capitalization
Market capitalization, sometimes referred to as market cap, is the total value of a publicly traded company's outstanding common shares owned by stockholders.
Market capitalization is equal to the market price per common share multiplied by t ...
of their listed companies in 2013.Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan and serves as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Buildin ...
, with 400 million square feet (37.2 million m2) in 2018,
Tech and biotech
Silicon Alley, centered in New York, has evolved into a metonymy, metonym for the sphere encompassing the metropolitan region's high technology industries involving the internet, new media, financial technology (''fintech'') and cryptocurrency, telecommunications, digital media, software development, biotechnology, game design, and other fields within information technology that are supported by its entrepreneurship ecosystem and venture capital investments.
High technology startup companies and employment are growing in New York City and the region. The technology sector has been claiming a greater share of New York City's economy since 2010.
Real estate
 Real estate is a major force in the city's economy, as the total value of all New York City property was assessed at US$1.072 trillion for the 2017 fiscal year, an increase of 10.6% from the previous year, with 89% of the increase coming from market effects.
Real estate is a major force in the city's economy, as the total value of all New York City property was assessed at US$1.072 trillion for the 2017 fiscal year, an increase of 10.6% from the previous year, with 89% of the increase coming from market effects.Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West Side, Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the List of New York City parks, fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban par ...
. In 2022, one-bedroom apartments in Manhattan rented at a median monthly price of US$3,600.00, one of the world's highest.
Tourism
 Tourism is a vital industry for New York City, and NYC & Company represents the city's official bureau of tourism. New York has witnessed a growing combined volume of international and domestic tourists, reflecting over 60 million visitors to the city per year, the world's busiest tourist destination.
Tourism is a vital industry for New York City, and NYC & Company represents the city's official bureau of tourism. New York has witnessed a growing combined volume of international and domestic tourists, reflecting over 60 million visitors to the city per year, the world's busiest tourist destination.[ Approximately 12 million visitors to New York City have been from outside the United States, with the highest numbers from the United Kingdom, Canada, Brazil, and China. Multiple sources have called New York the most photographed city in the world.] ''I Love New York'' (stylized I ❤ NY) is both a logo and a song that are the basis of an advertising campaign and have been used since 1977 to promote tourism in New York City, and later to promote New York State as well. The trademarked logo, owned by Empire State Development Corporation, New York State Empire State Development, appears in souvenir shops and brochures throughout the city and state, some licensed, many not. The song is the List of U.S. state songs, state song of New York.
The majority of the most high-profile tourist destinations to the city are situated in Manhattan. These include
''I Love New York'' (stylized I ❤ NY) is both a logo and a song that are the basis of an advertising campaign and have been used since 1977 to promote tourism in New York City, and later to promote New York State as well. The trademarked logo, owned by Empire State Development Corporation, New York State Empire State Development, appears in souvenir shops and brochures throughout the city and state, some licensed, many not. The song is the List of U.S. state songs, state song of New York.
The majority of the most high-profile tourist destinations to the city are situated in Manhattan. These include Times Square
Times Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment hub, and neighborhood in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It is formed by the junction of Broadway, Seventh Avenue, and 42nd Street. Together with adjacent ...
; Broadway theatre, Broadway theater productions; the Empire State Building
The Empire State Building is a 102-story Art Deco skyscraper in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. The building was designed by Shreve, Lamb & Harmon and built from 1930 to 1931. Its name is derived from "Empire State", the nickname of the st ...
; the Statue of Liberty
The Statue of Liberty (''Liberty Enlightening the World''; French: ''La Liberté éclairant le monde'') is a List of colossal sculpture in situ, colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor in New York City, in the U ...
; Ellis Island; the United Nations Headquarters
The United Nations is headquartered in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, United States, and the complex has served as the official headquarters of the United Nations since its completion in 1951. It is in the Turtle Bay, Manhattan, Turtle Bay neig ...
; the World Trade Center (2001–present), World Trade Center (including the National September 11 Museum and One World Trade Center); the art museums along Fifth Avenue#Museum Mile, Museum Mile; green spaces such as Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West Side, Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the List of New York City parks, fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban par ...
, Washington Square Park, the High Line, and the medieval gardens of The Cloisters; the Stonewall Inn
The Stonewall Inn, often shortened to Stonewall, is a gay bar and recreational tavern in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of Lower Manhattan, New York City, and the site of the Stonewall riots of 1969, which is widely considered to be the s ...
; Rockefeller Center; ethnic enclaves including the Manhattan Chinatown, Koreatown, Manhattan, Koreatown, Curry Hill, Harlem, Spanish Harlem, Little Italy, and Little Australia, Manhattan, Little Australia; Luxury goods, luxury shopping along Fifth Avenue, Fifth and Madison Avenues; and events such as the New York's Village Halloween Parade, Halloween Parade in Greenwich Village
Greenwich Village ( , , ) is a neighborhood on the west side of Lower Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 14th Street to the north, Broadway to the east, Houston Street to the south, and the Hudson River to the west. Greenwich Village ...
; the Brooklyn Bridge (shared with Brooklyn); the Macy's Thanksgiving Day Parade; the lighting of the Rockefeller Center Christmas Tree; the New York City St. Patrick's Day Parade, St. Patrick's Day Parade; seasonal activities such as ice skating in Central Park in the wintertime; the Tribeca Film Festival; and free performances in Central Park at SummerStage.
Points of interest have also developed in the city outside Manhattan and have made the outer boroughs tourist destinations in their own right. These include numerous ethnic enclaves; the Unisphere, Flushing Meadows-Corona Park, and Downtown Flushing in Queens; Downtown Brooklyn, Coney Island, Williamsburg
Williamsburg may refer to:
Places
*Colonial Williamsburg, a living-history museum and private foundation in Virginia
*Williamsburg, Brooklyn, neighborhood in New York City
*Williamsburg, former name of Kernville (former town), California
*Williams ...
, Park Slope, Brooklyn, Park Slope, and Prospect Park (Brooklyn), Prospect Park in Brooklyn; the Bronx Zoo, the New York Botanical Garden, and the Grand Concourse (Bronx), Grand Concourse in the Bronx; and the Staten Island Ferry shuttling passengers between Staten Island and the South Ferry Terminal bordering Battery Park in Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan (also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York) is the southernmost part of Manhattan, the central borough for business, culture, and government in New York City, which is the most populated city in the United States with ...
, at the historical birthplace of New York City.
Media and entertainment
 New York City has been described as the show business, entertainment
New York City has been described as the show business, entertainmententertainment industry
Entertainment is a form of activity that holds the attention and Interest (emotion), interest of an audience or gives pleasure and delight. It can be an idea or a task, but is more likely to be one of the activities or events that have dev ...
, with many films, television series, books, and other media being set there. , New York City was the second-largest center for filmmaking and television production in the United States, producing about 200 feature films annually, employing 130,000 individuals. The filmed entertainment industry has been growing in New York, contributing nearly $9 billion to the New York City economy alone as of 2015. By volume, New York is the world leader in independent film production—one-third of all American independent films are produced there. More than 200 newspapers and 350 consumer magazines have an office in the city,
More than 200 newspapers and 350 consumer magazines have an office in the city,The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' (NYT). Nicknamed "the Grey Lady", the NYT has won the most Pulitzer Prize
The Pulitzer Prize () is an award for achievements in newspaper, magazine, online journalism, literature, and musical composition within the United States. It was established in 1917 by provisions in the will of Joseph Pulitzer, who had made h ...
s for journalism
Journalism is the production and distribution of reports on the interaction of events, facts, ideas, and people that are the "news of the day" and that informs society to at least some degree. The word, a noun, applies to the occupation (profes ...
and is considered the U.S. media's "newspaper of record".Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
. The city also has a comprehensive ethnic press, with 270 newspapers and magazines published in more than 40 languages. ''El Diario La Prensa'' is New York's largest Spanish language, Spanish-language daily and the oldest in the nation. ''New York Amsterdam News, The New York Amsterdam News'', published in Harlem, is a prominent African American newspaper. ''The Village Voice'', historically the largest alternative newspaper in the United States, announced in 2017 that it would cease publication of its print edition and convert to a fully digital venture.
Education
New York City has the largest educational system of any city in the world.[ The city’s educational infrastructure spans primary education, secondary education, higher education, and research.
]
Primary and secondary education
The New York City Public Schools system, managed by the New York City Department of Education, is the largest public school system in the United States, serving about 1.1 million students in more than 1,700 separate primary and secondary schools. The city's public school system includes nine Specialized high schools in New York City, specialized high schools to serve academically and artistically gifted students. The city government pays the Pelham Public Schools to educate a very small, detached section of the Bronx.
Higher education and research

 More than a million students, the highest number of any city in the United States, are enrolled in New York City's more than 120 higher education institutions, with more than half a million in the
More than a million students, the highest number of any city in the United States, are enrolled in New York City's more than 120 higher education institutions, with more than half a million in the City University of New York
The City University of New York ( CUNY; , ) is the Public university, public university system of Education in New York City, New York City. It is the largest urban university system in the United States, comprising 25 campuses: eleven Upper divis ...
(CUNY) system alone , including both degree and professional programs. According to Academic Ranking of World Universities, New York City has, on average, the best higher education institutions of any global city.
The public CUNY system is one of the largest universities in the nation, comprising 25 institutions across all five boroughs: senior colleges, community colleges, and other graduate/professional schools. The public State University of New York (SUNY) system includes campuses in New York City, including SUNY Downstate College of Medicine, Downstate Health Sciences University, Fashion Institute of Technology, SUNY Maritime College, Maritime College, and the SUNY College of Optometry, College of Optometry.
New York City is home to such notable private universities as Barnard College, Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
, Cooper Union, Fordham University, New York University
New York University (NYU) is a private research university in New York City. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded by a group of New Yorkers led by then-Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin.
In 1832, the ...
, New York Institute of Technology, Rockefeller University, and Yeshiva University; several of these universities are ranked among the top universities in the world,New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass, at , and one of the list of most populous metropolitan areas, most populous urban agg ...
.
The city also hosts other smaller private colleges and universities, including many religious and special-purpose institutions, such as Pace University, St. John's University (Jamaica, NY), St. John's University, Juilliard School, The Juilliard School, Manhattan College, Adelphi University - Manhattan, Mercy College (New York), College of Mount Saint Vincent, The College of Mount Saint Vincent, Parsons School of Design, The New School, Pratt Institute, New York Film Academy, School of Visual Arts, The School of Visual Arts, The King's College (New York City), The King's College, Marymount Manhattan College, and Wagner College.
Much of the scientific research in the city is done in medicine and the life sciences. In 2019, the New York metropolitan area ranked first on the list of cities and metropolitan areas by share of published articles in life sciences. New York City has the most postgraduate life sciences degrees awarded annually in the United States, and in 2012, 43,523 licensed physicians were practicing in New York City. There are 127 Nobel laureates with roots in local institutions .
Human resources
Public health
 The New York City Health and Hospitals Corporation (HHC) operates the Public hospital#United States, public hospitals and outpatient care, outpatient clinics in New York City. A New York state public-benefit corporations, public benefit corporation with , HHC is the largest municipal healthcare system in the United States with $10.9 billion in annual revenues, HHC is the largest municipal healthcare system in the United States serving 1.4 million patients, including more than 475,000 uninsured city residents.
The New York City Health and Hospitals Corporation (HHC) operates the Public hospital#United States, public hospitals and outpatient care, outpatient clinics in New York City. A New York state public-benefit corporations, public benefit corporation with , HHC is the largest municipal healthcare system in the United States with $10.9 billion in annual revenues, HHC is the largest municipal healthcare system in the United States serving 1.4 million patients, including more than 475,000 uninsured city residents.
Public safety
Police and law enforcement
 The
The New York Police Department
The New York City Police Department (NYPD), officially the City of New York Police Department, established on May 23, 1845, is the primary municipal law enforcement agency within the City of New York, the largest and one of the oldest in ...
(NYPD) has been the largest police force in the United States by a significant margin, with more than 35,000 sworn officers. Members of the NYPD are frequently referred to by politicians, the media, and their own police cars by the nickname, ''New York's Finest''.
Crime overall has trended downward in New York City since the 1990s. In 2012, the NYPD came under scrutiny for its use of a New York City stop-and-frisk program, stop-and-frisk program, which has undergone several policy revisions since then. In 2014, New York City had the third-lowest murder rate among the largest U.S. cities, having become significantly safer after a spike in crime in the 1970s through 1990s. Sociologists and criminologists have not reached consensus on the explanation for the dramatic long-term decrease in the city's crime rate. Some attribute the phenomenon to new tactics used by the NYPD, including its use of CompStat and the broken windows theory. Others cite the end of the crack epidemic and demographic changes, including from immigration. Another theory is that widespread exposure to lead pollution from automobile exhaust, which can lower intelligence and increase aggression levels, incited the initial crime wave in the mid-20th century, most acutely affecting heavily trafficked cities like New York. A strong correlation was found demonstrating that violent crime rates in New York and other big cities began to fall after lead was removed from American gasoline in the 1970s. Another theory cited to explain New York City's falling homicide rate is the inverse correlation between the number of murders and the increasingly wet climate in the city.
Organized crime has long been associated with New York City, beginning with the Forty Thieves (New York gang), Forty Thieves and the Roach Guards in the Five Points, Manhattan, Five Points neighborhood in the 1820s, followed by the Tong (organization), Tongs in the same neighborhood, which ultimately evolved into Chinatown, Manhattan. The 20th century saw a rise in the American Mafia, Mafia, dominated by the Five Families, as well as in gangs, including the Black Spades. The Mafia and gang presence has declined in the city in the 21st century.
Sociologists and criminologists have not reached consensus on the explanation for the dramatic long-term decrease in the city's crime rate. Some attribute the phenomenon to new tactics used by the NYPD, including its use of CompStat and the broken windows theory. Others cite the end of the crack epidemic and demographic changes, including from immigration. Another theory is that widespread exposure to lead pollution from automobile exhaust, which can lower intelligence and increase aggression levels, incited the initial crime wave in the mid-20th century, most acutely affecting heavily trafficked cities like New York. A strong correlation was found demonstrating that violent crime rates in New York and other big cities began to fall after lead was removed from American gasoline in the 1970s. Another theory cited to explain New York City's falling homicide rate is the inverse correlation between the number of murders and the increasingly wet climate in the city.
Organized crime has long been associated with New York City, beginning with the Forty Thieves (New York gang), Forty Thieves and the Roach Guards in the Five Points, Manhattan, Five Points neighborhood in the 1820s, followed by the Tong (organization), Tongs in the same neighborhood, which ultimately evolved into Chinatown, Manhattan. The 20th century saw a rise in the American Mafia, Mafia, dominated by the Five Families, as well as in gangs, including the Black Spades. The Mafia and gang presence has declined in the city in the 21st century.
Firefighting
 The New York City Fire Department, Fire Department of New York (FDNY) provides fire protection, technical rescue, primary response to biological, chemical, and radioactive hazards, and emergency medical services for the five boroughs of New York City. The FDNY is the largest municipal fire department in the United States and the second largest in the world after the Tokyo Fire Department. The FDNY employs approximately 11,080 uniformed firefighters and more than 3,300 uniformed Emergency medical technician, EMTs and paramedics. The FDNY's motto is ''New York's Bravest''.
The fire department faces multifaceted firefighting challenges in many ways unique to New York. In addition to responding to List of building types, building types that range from wood-frame single family homes to High-rise, high-rise structures, the FDNY also responds to fires that occur in the
The New York City Fire Department, Fire Department of New York (FDNY) provides fire protection, technical rescue, primary response to biological, chemical, and radioactive hazards, and emergency medical services for the five boroughs of New York City. The FDNY is the largest municipal fire department in the United States and the second largest in the world after the Tokyo Fire Department. The FDNY employs approximately 11,080 uniformed firefighters and more than 3,300 uniformed Emergency medical technician, EMTs and paramedics. The FDNY's motto is ''New York's Bravest''.
The fire department faces multifaceted firefighting challenges in many ways unique to New York. In addition to responding to List of building types, building types that range from wood-frame single family homes to High-rise, high-rise structures, the FDNY also responds to fires that occur in the New York City Subway
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system owned by the government of New York City and leased to the New York City Transit Authority, an affiliate agency of the state-run Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA). Opened on October 2 ...
. Secluded bridges and tunnels, as well as large parks and wooded areas that can give rise to brush fires, also present challenges.
The FDNY is headquartered at 9 MetroTech Center in Downtown Brooklyn, and the FDNY Fire Academy is on the Randalls and Wards Islands, Randalls Island. There are three Bureau of Fire Communications alarm offices which receive and dispatch alarms to appropriate units. One office, at 11 Metrotech Center in Brooklyn, houses Manhattan/Citywide, Brooklyn, and Staten Island Fire Communications; the Bronx and Queens offices are in separate buildings.
Public library system
 The New York Public Library (NYPL), which has the largest collection of any public library system in the United States, serves Manhattan, the Bronx, and Staten Island.
The New York Public Library (NYPL), which has the largest collection of any public library system in the United States, serves Manhattan, the Bronx, and Staten Island.
Culture and contemporary life
New York City has been described as the cultural capital of the world by Manhattan's Baruch College.Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the t ...
, which established the African-American literary canon in the United States. The city became the center of stand-up comedy in the early 20th century, jazzabstract expressionism
Abstract expressionism is a post–World War II art movement in American painting, developed in New York City in the 1940s. It was the first specifically American movement to achieve international influence and put New York at the center of the ...
in the 1950s, and the birthplace of Hip hop culture, hip-hop in the 1970s.Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the t ...
in literature and visual art; abstract expressionism
Abstract expressionism is a post–World War II art movement in American painting, developed in New York City in the 1940s. It was the first specifically American movement to achieve international influence and put New York at the center of the ...
(also known as the New York School (art), New York School) in painting; and Hip hop music, hip-hop,Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
) disco in music. New York City has been considered the dance capital of the world. The city is also frequently the setting for novels, movies (see List of films set in New York City), and television programs. New York Fashion Week is one of the world's preeminent fashion events and is afforded extensive coverage by the media. New York has also frequently been ranked the top fashion capital of the world on the annual list compiled by the Global Language Monitor.
Pace
 One of the most common traits attributed to New York City is its fast pace,
One of the most common traits attributed to New York City is its fast pace,
Arts
New York City has more than 2,000 arts and cultural organizations and more than 500 Art gallery, art galleries.Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
and along 42nd Street began featuring a new stage form that became known as the Musical theatre, Broadway musical. Strongly influenced by the city's immigrants, productions such as those of Edward Harrigan, Harrigan and Hart, George M. Cohan, and others used song in narratives that often reflected themes of hope and ambition. New York City itself is the List of plays and musicals set in New York City, subject or background of many plays and musicals.
Performing arts
 Broadway theatre is one of the premier forms of English-language theatre in the world, named after
Broadway theatre is one of the premier forms of English-language theatre in the world, named after Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
, the major thoroughfare that crosses Times Square
Times Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment hub, and neighborhood in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It is formed by the junction of Broadway, Seventh Avenue, and 42nd Street. Together with adjacent ...
, also sometimes referred to as "The Great White Way". List of Broadway theaters, Forty-one venues in Midtown Manhattan's Theatre District, Manhattan, Theatre District, each with at least 500 seats, are classified as Broadway theatres. According to The Broadway League, Broadway shows sold approximately $1.27 billion worth of tickets in the 2013–2014 season, an 11.4% increase from $1.139 billion in the 2012–2013 season. Attendance in 2013–2014 stood at 12.21 million, representing a 5.5% increase from the 2012–2013 season's 11.57 million.
Visual arts
New York City is home to hundreds of cultural institutions and historic sites. Fifth Avenue, Museum Mile is the name for a section of Fifth Avenue running from 82nd to 105th streets on the Upper East Side of Manhattan,
Cuisine
 New York City's food culture includes an array of international cuisines influenced by the city's immigrant history. Central Europe, Central and Eastern European immigrants, especially Jewish Americans, Jewish immigrants from those regions, brought bagels, Cheesecake#North America, cheesecake, hot dogs, knishes, and delicatessens (or delis) to the city. Italian diaspora, Italian immigrants brought New York-style pizza and Italian cuisine into the city, while Jewish immigrants and
New York City's food culture includes an array of international cuisines influenced by the city's immigrant history. Central Europe, Central and Eastern European immigrants, especially Jewish Americans, Jewish immigrants from those regions, brought bagels, Cheesecake#North America, cheesecake, hot dogs, knishes, and delicatessens (or delis) to the city. Italian diaspora, Italian immigrants brought New York-style pizza and Italian cuisine into the city, while Jewish immigrants and Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
immigrants brought pastrami and corned beef, respectively. Chinese restaurant, Chinese and other Asian restaurants, sandwich joints, trattorias, diners, and coffeehouses are ubiquitous throughout the city. Some 4,000 mobile food vendors licensed by the city, many immigrant-owned, have made Middle Eastern foods such as falafel and kebabs examples of modern New York street food. The city is home to "nearly one thousand of the finest and most diverse haute cuisine restaurants in the world", according to Michelin. The New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene assigns letter grades to the city's restaurants based upon their inspection results. As of 2019, there were 27,043 restaurants in the city, up from 24,865 in 2017. The Queens Night Market in Flushing Meadows–Corona Park attracts more than ten thousand people nightly to sample food from more than 85 countries.
Parades
New York City is well known for its street parades, which celebrate a broad array of themes, including holidays, nationalities, human rights, and major league sports team championship victories. The majority of parades are held in Manhattan. The primary orientation of the annual street parades is typically from north to south, marching along major avenues. The annual Macy's Thanksgiving Day Parade is the world's largest parade,Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West Side, Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the List of New York City parks, fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban par ...
and processing southward to the flagship Macy's Herald Square store; the parade is viewed on telecasts worldwide and draws millions of spectators in person.Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
from Bowling Green (New York City), Bowling Green to City Hall Park in Lower Manhattan.
Accent and dialect
The New York area is home to a distinctive regional accent and speech pattern called the New York City English, New York dialect, alternatively known as ''Brooklynese'' or ''New Yorkese''. It has generally been considered one of the most recognizable accents within American English.
The traditional New York area speech pattern is known for its rapid delivery, and its accent is characterized as Rhoticity in English, non-rhotic so that the sound does not appear at the end of a syllable or immediately before a consonant; therefore the pronunciation of the city name as "New Yawk."
Sports
New York City is home to the headquarters of the National Football League, Major League Baseball, the National Basketball Association, the National Hockey League, and Major League Soccer. The New York metropolitan area hosts the List of American and Canadian cities by number of major professional sports franchises, most sports teams in the first four major North American professional sports leagues with nine, one more than Los Angeles, and has 11 top-level professional sports teams if Major League Soccer is included, also one more than Los Angeles. Participation in professional sports in the city predates all professional leagues.
The city has played host to more than forty major professional teams in the five sports and their respective competing leagues. Four of the ten most expensive stadiums ever built worldwide (MetLife Stadium, the new Yankee Stadium, Madison Square Garden, and Citi Field) are in the New York metropolitan area. Madison Square Garden, Madison Square Garden (1925), its predecessor, Yankee Stadium (1923), the original Yankee Stadium and Ebbets Field, are sporting venues in New York City, the latter two having been commemorated on Postage stamps and postal history of the United States, U.S. postage stamps. New York was the first of eight American cities to have won titles in all four major leagues (MLB, NHL, NFL and NBA), having done so following the Knicks' 1970 NBA Finals, 1970 title. In 1972, it became the first city to win titles in five sports when the Cosmos won the NASL Final 1972, NASL final.
New York has been described as the "Capital of Baseball". There have been 35 Major League Baseball World Series and 73 Pennant (sports)#Pennants as trophies, pennants won by New York teams. It is one of only five metro areas (Los Angeles metropolitan area, Los Angeles, Chicago metropolitan area, Chicago, Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area, Baltimore–Washington, and the San Francisco Bay Area being the others) to have two baseball teams. Additionally, there have been 14 World Series in which two New York City teams played each other, known as a Subway Series and occurring most recently in . No other metropolitan area has had this happen more than once (Chicago in , St. Louis in , and the San Francisco Bay Area in ).
The city's two Major League Baseball teams are the New York Mets, who play at Citi Field in Queens, and the New York Yankees, who play at Yankee Stadium in the Bronx. These teams compete in six games of interleague play every regular season that has also come to be called the Subway Series. The Yankees have won a record 27 championships, while the Mets have won the World Series twice. The city also was once home to the Brooklyn Dodgers (now the Los Angeles Dodgers), who won the World Series once, and the New York Giants (NL), New York Giants (now the San Francisco Giants), who won the World Series five times. Both teams moved to California in 1958. There is also one Minor League Baseball team in the city, the Mets-affiliated Brooklyn Cyclones, and the city will gain a club in the independent Atlantic League of Professional Baseball, Atlantic League when the Staten Island FerryHawks begin play in 2022.
The city is represented in the National Football League by the New York Giants and the New York Jets, although both teams play their home games at MetLife Stadium in nearby East Rutherford, New Jersey, which hosted Super Bowl XLVIII in 2014.
The metropolitan area is home to three National Hockey League teams. The New York Rangers, the traditional representative of the city itself and one of the league's Original Six, play at Madison Square Garden in Manhattan. The New York Islanders, traditionally representing Nassau County, New York, Nassau and Suffolk County, New York, Suffolk Counties of Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
, play in UBS Arena in Elmont, New York, and played in Brooklyn's Barclays Center from 2015 to 2020. The New Jersey Devils play at Prudential Center in nearby Newark, New Jersey and traditionally represent the counties of neighboring New Jersey which are coextensive with the boundaries of the New York metropolitan area and media market.
The city's National Basketball Association teams are the Brooklyn Nets (previously known as the New York Nets and New Jersey Nets as they moved around the metropolitan area) and the New York Knicks, while the New York Liberty is the city's Women's National Basketball Association team. The first national college-level basketball championship, the National Invitation Tournament, was held in New York in 1938 and remains in the city. The city is well known for its links to basketball, which is played in nearly every park in the city by local youth, many of whom have gone on to play for major college programs and in the NBA.
In soccer, New York City is represented by New York City FC of Major League Soccer, who play their home games at Yankee Stadium and the New York Red Bulls, who play their home games at Red Bull Arena (Harrison), Red Bull Arena in nearby Harrison, New Jersey. NJ/NY Gotham FC also plays their home games in Red Bull Arena, representing the metropolitan area in the National Women's Soccer League. Historically, the city is known for the New York Cosmos (1970–85), New York Cosmos, the highly successful former professional soccer team which was the American home of Pelé. A new version of the New York Cosmos (2010), New York Cosmos was formed in 2010, and most recently played in the third-division National Independent Soccer Association before going on hiatus in January 2021. New York will be one of eleven US host cities for the 2026 FIFA World Cup.
The annual US Open (tennis), United States Open Tennis Championships is one of the world's four Grand Slam (tennis), Grand Slam tennis tournaments and is held at the USTA National Tennis Center, National Tennis Center in Flushing Meadows-Corona Park, Queens. The New York City Marathon, which courses through all five boroughs, is the world's largest running marathon,
Environment
 Environmental issues in New York City are affected by the city's size, density, Transportation in New York City, abundant public transportation infrastructure, and location at the mouth of the
Environmental issues in New York City are affected by the city's size, density, Transportation in New York City, abundant public transportation infrastructure, and location at the mouth of the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
. For example, it is both one of the country's biggest sources of pollution, and has the lowest per-capita greenhouse gas emissions rate and electricity usage. Governors Island
Governors Island is a island in New York Harbor, within the New York City borough of Manhattan. It is located approximately south of Manhattan Island, and is separated from Brooklyn to the east by the Buttermilk Channel. The National Park ...
is planned to host a US$1 billion research and education center with the intention of making New York City the global leader in addressing the climate change, climate crisis.
Environmental impact reduction
New York City has focused on reducing its Human impact on the environment, environmental impact and carbon footprint.
Water purity and availability
The New York City drinking water supply is extracted from the protected Catskill Mountains Drainage basin, watershed. As a result of the watershed's integrity and undisturbed natural water filtration system, New York is one of only four major cities in the United States the majority of whose drinking water is pure enough not to require purification through water treatment plants. The city's municipal water system is the largest in the United States, moving over one billion gallons of water per day;Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
.Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
and the Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New Y ...
completed, and with segments serving Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
and Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
planned for construction in 2020. In 2018, New York City announced a $1 billion investment to protect the integrity of its water system and to maintain the purity of its unfiltered water supply.
Air quality
According to the 2016 World Health Organization Global Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database, the annual average concentration in New York City's air of particulate matter measuring 2.5micrometers or less (PM2.5) was 7.0micrograms per cubic meter, or 3.0micrograms within the recommended limit of the WHO Air Quality Guidelines for the annual mean PM2.5. The New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene, in partnership with Queens College, City University of New York, Queens College, conducts the New York Community Air Survey to measure pollutants at about 150 locations.
Environmental revitalization
Newtown Creek, a a long estuary that forms part of the border between the boroughs of Brooklyn and Queens, has been designated a Superfund site for environmental clean-up and remediation of the waterway's recreational and economic resources for many communities. One of the most heavily used bodies of water in the Port of New York and New Jersey, it had been one of the most contaminated industrial sites in the country,
Government and politics
Government
 New York City has been a metropolitan municipality with a Strong Mayor, Strong mayor–council form of government since its consolidation in 1898. In New York City, the city government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services.
The Mayor of New York City, mayor and council members are elected to four-year terms. The New York City Council, City Council is a unicameral body consisting of 51 council members whose districts are defined by geographic population boundaries. Each term for the mayor and council members lasts four years and has a two Term limit, consecutive-term limit, which is reset after a four-year break. The ''New York City Administrative Code'', the ''New York City Rules'', and the ''The City Record, City Record'' are the code of local laws, compilation of regulations, and official journal, respectively.
New York City has been a metropolitan municipality with a Strong Mayor, Strong mayor–council form of government since its consolidation in 1898. In New York City, the city government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services.
The Mayor of New York City, mayor and council members are elected to four-year terms. The New York City Council, City Council is a unicameral body consisting of 51 council members whose districts are defined by geographic population boundaries. Each term for the mayor and council members lasts four years and has a two Term limit, consecutive-term limit, which is reset after a four-year break. The ''New York City Administrative Code'', the ''New York City Rules'', and the ''The City Record, City Record'' are the code of local laws, compilation of regulations, and official journal, respectively.
 Each borough is coextensive with a judicial district of the state New York State Unified Court System, Unified Court System, of which the New York City Criminal Court, Criminal Court and the New York City Civil Court, Civil Court are the local courts, while the New York Supreme Court conducts major trials and appeals. Manhattan hosts the First Department of the New York Supreme Court, Appellate Division, Supreme Court, Appellate Division while Brooklyn hosts the Second Department. There are also several extrajudicial administrative courts, which are executive agencies and not part of the state Unified Court System.
Uniquely among major American cities, New York is divided between, and is host to the main branches of, two different U.S. district courts: the District Court for the Southern District of New York, whose main courthouse is on
Each borough is coextensive with a judicial district of the state New York State Unified Court System, Unified Court System, of which the New York City Criminal Court, Criminal Court and the New York City Civil Court, Civil Court are the local courts, while the New York Supreme Court conducts major trials and appeals. Manhattan hosts the First Department of the New York Supreme Court, Appellate Division, Supreme Court, Appellate Division while Brooklyn hosts the Second Department. There are also several extrajudicial administrative courts, which are executive agencies and not part of the state Unified Court System.
Uniquely among major American cities, New York is divided between, and is host to the main branches of, two different U.S. district courts: the District Court for the Southern District of New York, whose main courthouse is on Foley Square
Foley Square, also called Federal Plaza, is a street intersection in the Civic Center neighborhood of Lower Manhattan, New York City, which contains a small triangular park named Thomas Paine Park. The space is bordered by Worth Street to the ...
near City Hall in Manhattan and whose jurisdiction includes Manhattan and the Bronx; and the District Court for the Eastern District of New York, whose main courthouse is in Brooklyn and whose jurisdiction includes Brooklyn, Queens, and Staten Island. The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit and U.S. Court of International Trade are also based in New York, also on Foley Square in Manhattan.
Politics
 The present mayor is Eric Adams. He was elected in 2021 New York City mayoral election, 2021 with 67% of the vote, and assumed office on January 1, 2022.
The Democratic Party holds the majority of public offices. As of April 2016, 69% of registered voters in the city are Democrats and 10% are Republican Party (United States), Republicans. New York City has not been carried by a Republican presidential election since President Calvin Coolidge won the five boroughs in United States presidential election in New York, 1924, 1924. A Republican candidate for statewide office has not won all five boroughs of New York City since the city’s incorporation in 1898. In United States presidential election in New York, 2012, 2012, Democrat Barack Obama became the first presidential candidate of any party to receive more than 80% of the overall vote in New York City, sweeping all five boroughs. Party platforms center on affordable housing, education, and economic development, and labor politics are of importance in the city. Thirteen out of 27 U.S. congressional districts in the state of New York include portions of New York City.
New York is one of the most important sources of political fundraising in the United States. At least four of the top five ZIP Codes in the nation for political contributions were in Manhattan for the 2004 United States elections, 2004, 2006 United States elections, 2006, and 2008 United States elections, 2008 elections. The top ZIP Code, 10021 on the Upper East Side, generated the most money for the 2004 presidential campaigns of George W. Bush and John Kerry. The city has a strong imbalance of payments with the national and state governments. It receives 83 cents in services for every $1 it sends to the federal government in Taxation in the United States, taxes (or annually sends $11.4 billion more than it receives back). City residents and businesses also sent an additional $4.1 billion in the 2009–2010 fiscal year to the state of New York than the city received in return.
The present mayor is Eric Adams. He was elected in 2021 New York City mayoral election, 2021 with 67% of the vote, and assumed office on January 1, 2022.
The Democratic Party holds the majority of public offices. As of April 2016, 69% of registered voters in the city are Democrats and 10% are Republican Party (United States), Republicans. New York City has not been carried by a Republican presidential election since President Calvin Coolidge won the five boroughs in United States presidential election in New York, 1924, 1924. A Republican candidate for statewide office has not won all five boroughs of New York City since the city’s incorporation in 1898. In United States presidential election in New York, 2012, 2012, Democrat Barack Obama became the first presidential candidate of any party to receive more than 80% of the overall vote in New York City, sweeping all five boroughs. Party platforms center on affordable housing, education, and economic development, and labor politics are of importance in the city. Thirteen out of 27 U.S. congressional districts in the state of New York include portions of New York City.
New York is one of the most important sources of political fundraising in the United States. At least four of the top five ZIP Codes in the nation for political contributions were in Manhattan for the 2004 United States elections, 2004, 2006 United States elections, 2006, and 2008 United States elections, 2008 elections. The top ZIP Code, 10021 on the Upper East Side, generated the most money for the 2004 presidential campaigns of George W. Bush and John Kerry. The city has a strong imbalance of payments with the national and state governments. It receives 83 cents in services for every $1 it sends to the federal government in Taxation in the United States, taxes (or annually sends $11.4 billion more than it receives back). City residents and businesses also sent an additional $4.1 billion in the 2009–2010 fiscal year to the state of New York than the city received in return.
Transportation
 New York City's comprehensive transportation system is both complex and extensive.
New York City's comprehensive transportation system is both complex and extensive.
Rapid transit
Mass transit in New York City, most of which runs 24 hours a day, accounts for one in every three users of mass transit in the United States, and two-thirds of the nation's rail riders live in the New York City metropolitan area.
Rail
The iconic New York City Subway
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system owned by the government of New York City and leased to the New York City Transit Authority, an affiliate agency of the state-run Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA). Opened on October 2 ...
system is the largest rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be c ...
system in the world when measured by stations in operation, with , and by length of routes. Nearly all of New York's subway system is open 24 hours a day, in contrast to the overnight shutdown common to systems in most cities, including MTR, Hong Kong, London Underground, London, Paris Métro, Paris, Seoul Metropolitan Subway, Seoul, and Tokyo Subway, Tokyo. The New York City Subway is also Metro systems by annual passenger rides, the busiest metropolitan rail transit system in the Western Hemisphere, with 1.76 billion passenger rides in 2015, while Grand Central Terminal, also referred to as "Grand Central Station", is the world's largest Train station, railway station by number of train platforms.
 Public transport is essential in New York City. 54.6% of New Yorkers commuted to work in 2005 using mass transit. This is in contrast to the rest of the United States, where 91% of commuters travel in automobiles to their workplace.
Public transport is essential in New York City. 54.6% of New Yorkers commuted to work in 2005 using mass transit. This is in contrast to the rest of the United States, where 91% of commuters travel in automobiles to their workplace.West Side
West Side or Westside may refer to:
Places Canada
* West Side, a neighbourhood of Windsor, Ontario
* West Side, a neighbourhood of Vancouver, British Columbia
United Kingdom
* West Side, Lewis, Outer Hebrides, Scotland
* Westside, Birmingham E ...
of Manhattan, from which Amtrak provides connections to Boston, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, and Washington, D.C. along the Northeast Corridor, and long-distance train service to other North American cities.
The Staten Island Railway rapid transit system solely serves Staten Island, operating 24 hours a day. The Port Authority Trans-Hudson (PATH train) links Midtown and Lower Manhattan to northeastern New Jersey, primarily Hoboken, New Jersey, Hoboken, Jersey City, New Jersey, Jersey City, and Newark, New Jersey, Newark. Like the New York City Subway, the PATH operates 24 hours a day; meaning three of the six rapid transit systems in the world which operate on 24-hour schedules are wholly or partly in New York (the others are a portion of the Chicago 'L', the PATCO Speedline serving Philadelphia, and the Copenhagen Metro).
Multibillion-dollar heavy rail transit projects under construction in New York City include the Second Avenue Subway, and the East Side Access project.
Buses
 New York City's public MTA Regional Bus Operations, bus fleet runs 24/7 and is the largest in North America. The Port Authority Bus Terminal, the main intercity bus terminal of the city, serves 7,000 buses and 200,000 commuters daily, making it the busiest bus station in the world.
New York City's public MTA Regional Bus Operations, bus fleet runs 24/7 and is the largest in North America. The Port Authority Bus Terminal, the main intercity bus terminal of the city, serves 7,000 buses and 200,000 commuters daily, making it the busiest bus station in the world.
Air
Aviation in the New York metropolitan area, New York's airspace is the busiest in the United States and one of the world's busiest air transportation corridors. The three busiest airports in the New York metropolitan area include John F. Kennedy International Airport, Newark Liberty International Airport, and LaGuardia Airport; 130.5 million travelers used these three airports in 2016. JFK and Newark Liberty were the List of the busiest airports in the United States#10 busiest US airports by international passenger traffic (2012), busiest and fourth busiest U.S. gateways for international air passengers, respectively, in 2012; , JFK was the World's busiest airports by international passenger traffic, busiest airport for international passengers in North America.
 Plans have advanced to expand passenger volume at a fourth airport, Stewart International Airport near Newburgh, New York, by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey. Plans were announced in July 2015 to entirely rebuild LaGuardia Airport in a multibillion-dollar project to replace its aging facilities. Other commercial airports in or serving the
Plans have advanced to expand passenger volume at a fourth airport, Stewart International Airport near Newburgh, New York, by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey. Plans were announced in July 2015 to entirely rebuild LaGuardia Airport in a multibillion-dollar project to replace its aging facilities. Other commercial airports in or serving the New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass, at , and one of the list of most populous metropolitan areas, most populous urban agg ...
include Long Island MacArthur Airport, Trenton–Mercer Airport and Westchester County Airport. The primary general aviation airport serving the area is Teterboro Airport.
Ferries
 The Staten Island Ferry is the world's busiest Ferry, ferry route, carrying more than 23 million passengers from July 2015 through June 2016 on the route between Staten Island and Lower Manhattan and running 24 hours a day. Other ferry systems shuttle commuters between Manhattan and other locales within the city and the metropolitan area.
NYC Ferry, a New York City Economic Development Corporation, NYCEDC initiative with routes planned to travel to all five boroughs, was launched in 2017, with second graders choosing the names of the ferries. Meanwhile, Seastreak ferry announced construction of a 600-passenger high-speed luxury ferry in September 2016, to shuttle riders between the Jersey Shore and Manhattan, anticipated to start service in 2017; this would be the largest vessel in its class.
The Staten Island Ferry is the world's busiest Ferry, ferry route, carrying more than 23 million passengers from July 2015 through June 2016 on the route between Staten Island and Lower Manhattan and running 24 hours a day. Other ferry systems shuttle commuters between Manhattan and other locales within the city and the metropolitan area.
NYC Ferry, a New York City Economic Development Corporation, NYCEDC initiative with routes planned to travel to all five boroughs, was launched in 2017, with second graders choosing the names of the ferries. Meanwhile, Seastreak ferry announced construction of a 600-passenger high-speed luxury ferry in September 2016, to shuttle riders between the Jersey Shore and Manhattan, anticipated to start service in 2017; this would be the largest vessel in its class.
Taxis, vehicles for hire, and trams
 Other features of the city's transportation infrastructure encompass 13,587 Taxicabs of New York City, yellow taxicabs; other vehicle for hire companies; and the Roosevelt Island Tramway, an aerial tramway that transports commuters between Roosevelt Island and Manhattan Island.
Other features of the city's transportation infrastructure encompass 13,587 Taxicabs of New York City, yellow taxicabs; other vehicle for hire companies; and the Roosevelt Island Tramway, an aerial tramway that transports commuters between Roosevelt Island and Manhattan Island.
Streets and highways
 Despite New York's heavy reliance on its vast public transit system, streets are a defining feature of the city. The
Despite New York's heavy reliance on its vast public transit system, streets are a defining feature of the city. The Commissioners' Plan of 1811
The Commissioners' Plan of 1811 was the original design for the streets of Manhattan above Houston Street and below 155th Street, which put in place the rectangular grid plan of streets and lots that has defined Manhattan on its march uptown u ...
greatly influenced the city's physical development. Several of the city's streets and avenues, including Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
, Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for t ...
, Madison Avenue (Manhattan), Madison Avenue,Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
, and southwestern Connecticut through various Bridges and tunnels in New York City, bridges and tunnels. Because these highways serve millions of outer borough and suburban residents who Commuting, commute into Manhattan, it is quite common for motorists to be stranded for hours in traffic congestion that are a daily occurrence, particularly during rush hour. Congestion pricing in New York City will go into effect in 2022 at the earliest.
New York City is also known for its rules regarding turning at red lights. Unlike the rest of the United States, New York State prohibits right or left turns on red in cities with a population greater than one million, to reduce traffic collisions and increase pedestrian safety. In New York City, therefore, all turns at red lights are illegal unless a sign permitting such maneuvers is present.
River crossings
 New York City is located on one of the world's largest natural harbors, and the boroughs of Manhattan and Staten Island are primarily coterminous with islands of the same names, while Queens and Brooklyn are at the west end of the larger Long Island, and the Bronx is on New York State's mainland. This situation of boroughs separated by water led to the development of an extensive infrastructure of bridges and tunnels.
The George Washington Bridge is the world's busiest motor vehicle bridge,
New York City is located on one of the world's largest natural harbors, and the boroughs of Manhattan and Staten Island are primarily coterminous with islands of the same names, while Queens and Brooklyn are at the west end of the larger Long Island, and the Bronx is on New York State's mainland. This situation of boroughs separated by water led to the development of an extensive infrastructure of bridges and tunnels.
The George Washington Bridge is the world's busiest motor vehicle bridge,Financial District
A financial district is usually a central area in a city where financial services firms such as banks, insurance companies and other related finance corporations have their head offices. In major cities, financial districts are often home to s ...
at the southern tip of Manhattan to Red Hook, Brooklyn, Red Hook in Brooklyn.
Cycling network
Cycling in New York City is associated with mixed cycling conditions that include urban density, relatively flat terrain, congested roadways with stop-and-go traffic, and many pedestrians. The city's large cycling population includes Utility cycling, utility cyclists, such as delivery and messenger services; cycling clubs for recreational cyclists; and an increasing number of Bicycle commuting, commuters. Cycling is increasingly popular in New York City; in 2017 there were approximately 450,000 daily bike trips, compared with 170,000 daily bike trips in 2005.
People
Global outreach
In 2006, the ''Twin towns and sister cities, Sister City Program of the City of New York, Inc.''
See also
* Outline of New York City
Notes
References
Further reading
* From Google Books.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
*
NYC Go
official tourism website
*
*
Collections
145,000 NYC photographs at the Museum of the City of New York
*
{{#related:New York
New York City,
1624 establishments in North America
1624 establishments in the Dutch Empire
1898 establishments in New York (state)
1898 establishments in New York City
Cities in New York (state)
Cities in the New York metropolitan area
Establishments in New Netherland
Former capitals of the United States
Former state capitals in the United States
Populated coastal places in New York (state)
Populated places established by the Dutch West India Company
Populated places established in 1624
Populated places established in 1898
New York (state) populated places on the Hudson River
Port cities and towns of the United States Atlantic coast
Articles with accessibility problems
 A permanent European presence near
A permanent European presence near  In 1664, unable to summon any significant resistance, Stuyvesant surrendered New Amsterdam to English troops, led by Colonel
In 1664, unable to summon any significant resistance, Stuyvesant surrendered New Amsterdam to English troops, led by Colonel  In the early 18th century, New York grew in importance as a trading port while as a part of the
In the early 18th century, New York grew in importance as a trading port while as a part of the  The
The  Over the course of the nineteenth century, New York City's population grew from 60,000 to 3.43 million. Under New York State's
Over the course of the nineteenth century, New York City's population grew from 60,000 to 3.43 million. Under New York State's  Several prominent American literary figures lived in New York during the 1830s and 1840s, including
Several prominent American literary figures lived in New York during the 1830s and 1840s, including  In 1898, the modern City of New York was formed with the consolidation of Brooklyn (until then a separate city), the County of New York (which then included parts of the Bronx), the County of Richmond, and the western portion of the County of Queens. The opening of the subway in 1904, first built as separate private systems, helped bind the new city together. Throughout the first half of the 20th century, the city became a world center for industry, commerce, and communication.
In 1904, the
In 1898, the modern City of New York was formed with the consolidation of Brooklyn (until then a separate city), the County of New York (which then included parts of the Bronx), the County of Richmond, and the western portion of the County of Queens. The opening of the subway in 1904, first built as separate private systems, helped bind the new city together. Throughout the first half of the 20th century, the city became a world center for industry, commerce, and communication.
In 1904, the  New York became the most populous
New York became the most populous  The Stonewall riots were a series of spontaneous, violent protests by members of the LGBT community, gay community against a police raid that took place in the early morning hours of June 28, 1969, at the
The Stonewall riots were a series of spontaneous, violent protests by members of the LGBT community, gay community against a police raid that took place in the early morning hours of June 28, 1969, at the  New York City suffered the bulk of the economic damage and largest loss of human life in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks, September 11, 2001, attacks. Two of the four airliners hijacked that day were flown into the twin towers of the World Trade Center, destroying the towers and killing 2,192 civilians, 343 firefighters, and 71 law enforcement officers. The North Tower became the tallest building ever to be destroyed anywhere then or subsequently.
World Trade Center site#Planning for the new World Trade Center, The area was rebuilt with a new One World Trade Center, a National September 11 Memorial & Museum, 9/11 memorial and museum, and other new buildings and infrastructure. The World Trade Center (PATH station), World Trade Center PATH station, which had opened on July 19, 1909, as the Hudson Terminal, was also destroyed in the attacks. A temporary station was built and opened on November 23, 2003. An permanent rail station designed by Santiago Calatrava, the World Trade Center Transportation Hub, the city's third-largest hub, was completed in 2016. The new One World Trade Center is the tallest skyscraper in the Western Hemisphere and the List of tallest buildings in the world, seventh-tallest building in the world by pinnacle height, with its spire reaching a symbolic in reference to the year of United States Declaration of Independence, U.S. independence.
The Occupy Wall Street protests in Zuccotti Park in the Financial District (Manhattan), Financial District of Lower Manhattan began on September 17, 2011, receiving global attention and popularizing the Occupy movement against Social inequality, social and economic inequality worldwide.
In March 2020, the first case of Coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19 in the city was confirmed in Manhattan. The city rapidly replaced Wuhan, China to become the global epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic, pandemic during the early phase, before the infection became widespread across the world and the rest of the nation. As of March 2021, New York City had recorded COVID-19 pandemic in New York City, over 30,000 deaths from COVID-19-related complications. In 2022, the LGBT culture in New York City, LGBT community in New York City became the epicenter of the monkeypox outbreak in the
New York City suffered the bulk of the economic damage and largest loss of human life in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks, September 11, 2001, attacks. Two of the four airliners hijacked that day were flown into the twin towers of the World Trade Center, destroying the towers and killing 2,192 civilians, 343 firefighters, and 71 law enforcement officers. The North Tower became the tallest building ever to be destroyed anywhere then or subsequently.
World Trade Center site#Planning for the new World Trade Center, The area was rebuilt with a new One World Trade Center, a National September 11 Memorial & Museum, 9/11 memorial and museum, and other new buildings and infrastructure. The World Trade Center (PATH station), World Trade Center PATH station, which had opened on July 19, 1909, as the Hudson Terminal, was also destroyed in the attacks. A temporary station was built and opened on November 23, 2003. An permanent rail station designed by Santiago Calatrava, the World Trade Center Transportation Hub, the city's third-largest hub, was completed in 2016. The new One World Trade Center is the tallest skyscraper in the Western Hemisphere and the List of tallest buildings in the world, seventh-tallest building in the world by pinnacle height, with its spire reaching a symbolic in reference to the year of United States Declaration of Independence, U.S. independence.
The Occupy Wall Street protests in Zuccotti Park in the Financial District (Manhattan), Financial District of Lower Manhattan began on September 17, 2011, receiving global attention and popularizing the Occupy movement against Social inequality, social and economic inequality worldwide.
In March 2020, the first case of Coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19 in the city was confirmed in Manhattan. The city rapidly replaced Wuhan, China to become the global epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic, pandemic during the early phase, before the infection became widespread across the world and the rest of the nation. As of March 2021, New York City had recorded COVID-19 pandemic in New York City, over 30,000 deaths from COVID-19-related complications. In 2022, the LGBT culture in New York City, LGBT community in New York City became the epicenter of the monkeypox outbreak in the  During the Wisconsin glaciation, 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, the New York City area was situated at the edge of a large ice sheet over in depth. The erosive forward movement of the ice (and its subsequent retreat) contributed to the separation of what is now
During the Wisconsin glaciation, 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, the New York City area was situated at the edge of a large ice sheet over in depth. The erosive forward movement of the ice (and its subsequent retreat) contributed to the separation of what is now 
 Winters are chilly and damp, and prevailing wind patterns that blow sea breezes offshore temper the moderating effects of the Atlantic Ocean; yet the Atlantic and the partial shielding from colder air by the Appalachian Mountains keep the city warmer in the winter than inland North American cities at similar or lesser latitudes such as Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, and Indianapolis. The daily mean temperature in January, the area's coldest month, is . Temperatures usually drop to several times per winter, yet can also reach for several days even in the coldest winter month. Spring and autumn are unpredictable and can range from cool to warm, although they are usually mild with low humidity. Summers are typically hot and humid, with a daily mean temperature of in July.
Nighttime temperatures are often enhanced due to the urban heat island effect. Daytime temperatures exceed on average of 17 days each summer and in some years exceed , although this is a rare achievement, last occurring on July 18, 2012. Similarly, readings of are also extremely rare, last occurring on February 14, 2016. Extreme temperatures have ranged from , recorded on February 9, 1934, up to on July 9, 1936; the coldest recorded wind chill was on the same day as the all-time record low. The record cold daily maximum was on December 30, 1917, while, conversely, the record warm daily minimum was , on July 2, 1903. The average water temperature of the nearby Atlantic Ocean ranges from in February to in August.
The city receives of precipitation annually, which is relatively evenly spread throughout the year. Average winter snowfall between 1991 and 2020 has been ; this varies considerably between years. Hurricanes and tropical storms are rare in the New York area. Hurricane Sandy brought a destructive storm surge to New York City on the evening of October 29, 2012, flooding numerous streets, tunnels, and subway lines in Lower Manhattan and other areas of the city and cutting off electricity in many parts of the city and its suburbs. The storm and its profound impacts have prompted the discussion of constructing seawalls and other coastal barriers around the shorelines of the city and the metropolitan area to minimize the risk of destructive consequences from another such event in the future.
The coldest month on record is January 1857, with a mean temperature of whereas the warmest months on record are July 1825 and July 1999, both with a mean temperature of . The warmest years on record are 2012 and 2020, both with mean temperatures of . The coldest year is 1836, with a mean temperature of . The driest month on record is June 1949, with of rainfall. The wettest month was August 2011, with of rainfall. The driest year on record is 1965, with of rainfall. The wettest year was 1983, with of rainfall. The snowiest month on record is February 2010, with of snowfall. The snowiest season ''(Jul–Jun)'' on record is 1995–1996, with of snowfall. The least snowy season was 1972–1973, with of snowfall. The earliest seasonal trace of snowfall occurred on October 10, in both 1979 and 1925. The latest seasonal trace of snowfall occurred on May 9, in both 2020 and 1977.
Winters are chilly and damp, and prevailing wind patterns that blow sea breezes offshore temper the moderating effects of the Atlantic Ocean; yet the Atlantic and the partial shielding from colder air by the Appalachian Mountains keep the city warmer in the winter than inland North American cities at similar or lesser latitudes such as Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, and Indianapolis. The daily mean temperature in January, the area's coldest month, is . Temperatures usually drop to several times per winter, yet can also reach for several days even in the coldest winter month. Spring and autumn are unpredictable and can range from cool to warm, although they are usually mild with low humidity. Summers are typically hot and humid, with a daily mean temperature of in July.
Nighttime temperatures are often enhanced due to the urban heat island effect. Daytime temperatures exceed on average of 17 days each summer and in some years exceed , although this is a rare achievement, last occurring on July 18, 2012. Similarly, readings of are also extremely rare, last occurring on February 14, 2016. Extreme temperatures have ranged from , recorded on February 9, 1934, up to on July 9, 1936; the coldest recorded wind chill was on the same day as the all-time record low. The record cold daily maximum was on December 30, 1917, while, conversely, the record warm daily minimum was , on July 2, 1903. The average water temperature of the nearby Atlantic Ocean ranges from in February to in August.
The city receives of precipitation annually, which is relatively evenly spread throughout the year. Average winter snowfall between 1991 and 2020 has been ; this varies considerably between years. Hurricanes and tropical storms are rare in the New York area. Hurricane Sandy brought a destructive storm surge to New York City on the evening of October 29, 2012, flooding numerous streets, tunnels, and subway lines in Lower Manhattan and other areas of the city and cutting off electricity in many parts of the city and its suburbs. The storm and its profound impacts have prompted the discussion of constructing seawalls and other coastal barriers around the shorelines of the city and the metropolitan area to minimize the risk of destructive consequences from another such event in the future.
The coldest month on record is January 1857, with a mean temperature of whereas the warmest months on record are July 1825 and July 1999, both with a mean temperature of . The warmest years on record are 2012 and 2020, both with mean temperatures of . The coldest year is 1836, with a mean temperature of . The driest month on record is June 1949, with of rainfall. The wettest month was August 2011, with of rainfall. The driest year on record is 1965, with of rainfall. The wettest year was 1983, with of rainfall. The snowiest month on record is February 2010, with of snowfall. The snowiest season ''(Jul–Jun)'' on record is 1995–1996, with of snowfall. The least snowy season was 1972–1973, with of snowfall. The earliest seasonal trace of snowfall occurred on October 10, in both 1979 and 1925. The latest seasonal trace of snowfall occurred on May 9, in both 2020 and 1977.
 The city of New York has a complex park system, with various lands operated by the National Park Service, the New York State Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation, and the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation. In its 2018 ParkScore ranking, The Trust for Public Land reported that the park system in New York City was the ninth-best park system among the fifty most populous U.S. cities. ParkScore ranks urban park systems by a formula that analyzes median park size, park acres as percent of city area, the percent of city residents within a half-mile of a park, spending of park services per resident, and the number of playgrounds per 10,000 residents. In 2021, the New York City Council banned the use of synthetic pesticides by city agencies and instead required organic lawn management. The effort was started by teacher Paula Rogovin's kindergarten class at P.S. 290.
The city of New York has a complex park system, with various lands operated by the National Park Service, the New York State Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation, and the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation. In its 2018 ParkScore ranking, The Trust for Public Land reported that the park system in New York City was the ninth-best park system among the fifty most populous U.S. cities. ParkScore ranks urban park systems by a formula that analyzes median park size, park acres as percent of city area, the percent of city residents within a half-mile of a park, spending of park services per resident, and the number of playgrounds per 10,000 residents. In 2021, the New York City Council banned the use of synthetic pesticides by city agencies and instead required organic lawn management. The effort was started by teacher Paula Rogovin's kindergarten class at P.S. 290.
 Gateway National Recreation Area contains over , most of it in New York City. In Brooklyn and Queens, the park contains over of salt marsh, wetlands, islands, and water, including most of Jamaica Bay and the Jamaica Bay Wildlife Refuge. Also in Queens, the park includes a significant portion of the western Rockaway Peninsula, most notably Jacob Riis Park and Fort Tilden. In Staten Island, it includes Fort Wadsworth, with historic pre-Civil War era Battery Weed and Fort Tompkins Quadrangle, Fort Tompkins, and Great Kills Park, with beaches, trails, and a marina.
The Statue of Liberty National Monument and Ellis Island Immigration Museum are managed by the National Park Service and are in both New York and New Jersey. They are joined in the harbor by Governors Island National Monument. Historic sites under federal management on Manhattan Island include
Gateway National Recreation Area contains over , most of it in New York City. In Brooklyn and Queens, the park contains over of salt marsh, wetlands, islands, and water, including most of Jamaica Bay and the Jamaica Bay Wildlife Refuge. Also in Queens, the park includes a significant portion of the western Rockaway Peninsula, most notably Jacob Riis Park and Fort Tilden. In Staten Island, it includes Fort Wadsworth, with historic pre-Civil War era Battery Weed and Fort Tompkins Quadrangle, Fort Tompkins, and Great Kills Park, with beaches, trails, and a marina.
The Statue of Liberty National Monument and Ellis Island Immigration Museum are managed by the National Park Service and are in both New York and New Jersey. They are joined in the harbor by Governors Island National Monument. Historic sites under federal management on Manhattan Island include  New York City has over of Urban park, municipal parkland and of public beaches. The largest municipal park in the city is Pelham Bay Park in the Bronx, with .
*
New York City has over of Urban park, municipal parkland and of public beaches. The largest municipal park in the city is Pelham Bay Park in the Bronx, with .
*  In 2020, the city had an estimated population density of , rendering it the nation's most densely populated of all larger municipalities (those with more than 100,000 residents), with several small cities (of fewer than 100,000) in adjacent Hudson County, New Jersey having List of United States cities by population density, greater density, as per the 2010 census. Geographically co-extensive with New York County, the borough of Manhattan's 2017 population density of makes it the County statistics of the United States#Population density, highest of any county in the United States and List of United States cities by population density#New York City boroughs, higher than the density of any individual American city. The next three densest counties in the United States, placing second through fourth, are also New York boroughs: Brooklyn, the Bronx, and Queens respectively.
In 2020, the city had an estimated population density of , rendering it the nation's most densely populated of all larger municipalities (those with more than 100,000 residents), with several small cities (of fewer than 100,000) in adjacent Hudson County, New Jersey having List of United States cities by population density, greater density, as per the 2010 census. Geographically co-extensive with New York County, the borough of Manhattan's 2017 population density of makes it the County statistics of the United States#Population density, highest of any county in the United States and List of United States cities by population density#New York City boroughs, higher than the density of any individual American city. The next three densest counties in the United States, placing second through fourth, are also New York boroughs: Brooklyn, the Bronx, and Queens respectively.
 The city's population in 2020 was 30.9% White Americans, White (non-Hispanic), 28.7% Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic or Latino, 20.2% African Americans, Black or African American (non-Hispanic), 15.6% Asian Americans in New York City, Asian, and 0.2% Native Americans in the United States, Native American (non-Hispanic). A total of 3.4% of the non-Hispanic population identified with Multiracial Americans, more than one race. Throughout its history, New York has been a major port of entry for immigrants into the United States. More than 12 million European American, European immigrants were received at Ellis Island between 1892 and 1924. The term "melting pot" was first coined to describe densely populated immigrant neighborhoods on the Lower East Side, Manhattan, Lower East Side. By 1900, German American, Germans constituted the largest immigrant group, followed by the Irish American, Irish, Ashkenazi Jews, Jews, and Italian American, Italians. In 1940, Whites represented 92% of the city's population.
Approximately 37% of the city's population is foreign born, and more than half of all children are born to mothers who are immigrants as of 2013.''The Newest New Yorkers: 2013''
The city's population in 2020 was 30.9% White Americans, White (non-Hispanic), 28.7% Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic or Latino, 20.2% African Americans, Black or African American (non-Hispanic), 15.6% Asian Americans in New York City, Asian, and 0.2% Native Americans in the United States, Native American (non-Hispanic). A total of 3.4% of the non-Hispanic population identified with Multiracial Americans, more than one race. Throughout its history, New York has been a major port of entry for immigrants into the United States. More than 12 million European American, European immigrants were received at Ellis Island between 1892 and 1924. The term "melting pot" was first coined to describe densely populated immigrant neighborhoods on the Lower East Side, Manhattan, Lower East Side. By 1900, German American, Germans constituted the largest immigrant group, followed by the Irish American, Irish, Ashkenazi Jews, Jews, and Italian American, Italians. In 1940, Whites represented 92% of the city's population.
Approximately 37% of the city's population is foreign born, and more than half of all children are born to mothers who are immigrants as of 2013.''The Newest New Yorkers: 2013'' People of Norwegian American, Norwegian and Swedish American, Swedish descent both stood at about 20,000 each, while people of Czech American, Czech, Lithuanian American, Lithuanian, Portuguese American, Portuguese, Scotch-Irish American, Scotch-Irish, and Welsh American, Welsh descent all numbered between 12,000 and 14,000. Arab Americans number over 160,000 in New York City, with the highest concentration in Brooklyn. Demographics of Central Asia, Central Asians, primarily Uzbek Americans, are a rapidly growing segment of the city's non-Hispanic White population, enumerating over 30,000, and including more than half of all Central Asian immigrants to the United States, most settling in Queens or Brooklyn. Albanian Americans are most highly concentrated in the Bronx, while Astoria, Queens is the epicenter of American Greek culture as well as the Greek Cypriots, Cypriot community.
The wider New York City metropolitan statistical area, with more than twenty million people, about fifty percent more than second-place Los Angeles metropolitan area, Los Angeles, is also Ethnic diversity, ethnically diverse, with the largest Foreign born#Metropolitan regions with largest foreign born populations, foreign-born population of any metropolitan region in the world. The New York region continues to be by far the leading metropolitan gateway for legal immigrants admitted into the United States, substantially exceeding the combined totals of Los Angeles and Miami metropolitan area, Miami. It is home to the largest Jews in New York City, Jewish and Israeli American, Israeli communities outside Israel, with the Jewish population in the region numbering over 1.5 million in 2012 and including many diverse Jewish sects, predominantly from around the Middle East and Eastern Europe, and including a rapidly growing Orthodox Jewish population, also the largest outside Israel.
The metropolitan area is also home to 20% of the nation's Indians in the New York City metropolitan region, Indian Americans and at least 20 Little India (location), Little India enclaves, and 15% of all Korean Americans in New York City, Korean Americans and four Koreatown, Manhattan, Koreatowns; the largest Asian Indian population in the Western Hemisphere; the largest Russian American, Italian American, and African American populations; the largest Dominican American, Puerto Rican migration to New York City, Puerto Rican American, and South American and second-largest overall Hispanic and Latino American, Hispanic population in the United States, numbering 4.8 million; and includes multiple established Chinatowns within New York City alone.
People of Norwegian American, Norwegian and Swedish American, Swedish descent both stood at about 20,000 each, while people of Czech American, Czech, Lithuanian American, Lithuanian, Portuguese American, Portuguese, Scotch-Irish American, Scotch-Irish, and Welsh American, Welsh descent all numbered between 12,000 and 14,000. Arab Americans number over 160,000 in New York City, with the highest concentration in Brooklyn. Demographics of Central Asia, Central Asians, primarily Uzbek Americans, are a rapidly growing segment of the city's non-Hispanic White population, enumerating over 30,000, and including more than half of all Central Asian immigrants to the United States, most settling in Queens or Brooklyn. Albanian Americans are most highly concentrated in the Bronx, while Astoria, Queens is the epicenter of American Greek culture as well as the Greek Cypriots, Cypriot community.
The wider New York City metropolitan statistical area, with more than twenty million people, about fifty percent more than second-place Los Angeles metropolitan area, Los Angeles, is also Ethnic diversity, ethnically diverse, with the largest Foreign born#Metropolitan regions with largest foreign born populations, foreign-born population of any metropolitan region in the world. The New York region continues to be by far the leading metropolitan gateway for legal immigrants admitted into the United States, substantially exceeding the combined totals of Los Angeles and Miami metropolitan area, Miami. It is home to the largest Jews in New York City, Jewish and Israeli American, Israeli communities outside Israel, with the Jewish population in the region numbering over 1.5 million in 2012 and including many diverse Jewish sects, predominantly from around the Middle East and Eastern Europe, and including a rapidly growing Orthodox Jewish population, also the largest outside Israel.
The metropolitan area is also home to 20% of the nation's Indians in the New York City metropolitan region, Indian Americans and at least 20 Little India (location), Little India enclaves, and 15% of all Korean Americans in New York City, Korean Americans and four Koreatown, Manhattan, Koreatowns; the largest Asian Indian population in the Western Hemisphere; the largest Russian American, Italian American, and African American populations; the largest Dominican American, Puerto Rican migration to New York City, Puerto Rican American, and South American and second-largest overall Hispanic and Latino American, Hispanic population in the United States, numbering 4.8 million; and includes multiple established Chinatowns within New York City alone.
 Ecuador, Colombia, Guyana, Peru, Brazil, and Venezuela are the top source countries from South America for immigrants to the New York City region; the Dominican Republic, Jamaica, Haiti, and Trinidad and Tobago in the Caribbeans in New York City, Caribbean; Nigeria, Egypt, Ghana, Tanzania, Kenya, and South Africa from Africa; and El Salvador, Honduras, and Guatemala in Central America. Amidst a resurgence of Puerto Rican migration to New York City, this population had increased to approximately 1.3 million in the metropolitan area . In 2022, New York City began receiving thousands of Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino immigrants bused from the state of Texas, mostly originating from Venezuela, Ecuador, Columbia, and Honduras.
Since 2010, Little Australia has emerged and is growing rapidly, representing the Australasian presence in Nolita, Manhattan. In 2011, there were an estimated 20,000 Australian residents of New York City, nearly quadruple the 5,537 in 2005. Qantas Airways of Australia and Air New Zealand have been planning for long-haul flights from New York to Sydney and Auckland, which would both rank among the longest non-stop flights in the world. A Little Sri Lanka has developed in the Tompkinsville, Staten Island, Tompkinsville neighborhood of Staten Island. Le Petit Sénégal, or Little Senegal, is based in Harlem. Richmond Hill, Queens is often thought of as "Little Guyana" for its large Guyana, Guyanese community, as well as Punjab Avenue, Punjab Avenue (ਪੰਜਾਬ ਐਵੇਨਿਊ), or Punjab, Little Punjab, for its high concentration of Punjabi people. Little Poland, Brooklyn, Little Poland is expanding rapidly in Greenpoint, Brooklyn.
Ecuador, Colombia, Guyana, Peru, Brazil, and Venezuela are the top source countries from South America for immigrants to the New York City region; the Dominican Republic, Jamaica, Haiti, and Trinidad and Tobago in the Caribbeans in New York City, Caribbean; Nigeria, Egypt, Ghana, Tanzania, Kenya, and South Africa from Africa; and El Salvador, Honduras, and Guatemala in Central America. Amidst a resurgence of Puerto Rican migration to New York City, this population had increased to approximately 1.3 million in the metropolitan area . In 2022, New York City began receiving thousands of Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino immigrants bused from the state of Texas, mostly originating from Venezuela, Ecuador, Columbia, and Honduras.
Since 2010, Little Australia has emerged and is growing rapidly, representing the Australasian presence in Nolita, Manhattan. In 2011, there were an estimated 20,000 Australian residents of New York City, nearly quadruple the 5,537 in 2005. Qantas Airways of Australia and Air New Zealand have been planning for long-haul flights from New York to Sydney and Auckland, which would both rank among the longest non-stop flights in the world. A Little Sri Lanka has developed in the Tompkinsville, Staten Island, Tompkinsville neighborhood of Staten Island. Le Petit Sénégal, or Little Senegal, is based in Harlem. Richmond Hill, Queens is often thought of as "Little Guyana" for its large Guyana, Guyanese community, as well as Punjab Avenue, Punjab Avenue (ਪੰਜਾਬ ਐਵੇਨਿਊ), or Punjab, Little Punjab, for its high concentration of Punjabi people. Little Poland, Brooklyn, Little Poland is expanding rapidly in Greenpoint, Brooklyn.
 Largely as a result of Western European missionary work and colonialism, Christianity is the largest religion in New York City, which is home to the highest number of church (building), churches of any city in the world. Catholic Church, Roman Catholicism is the largest Christian denomination (33%), followed by Protestantism (23%), and List of Christian denominations, other Christians (3%). The Roman Catholic population are primarily served by the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New York and Roman Catholic Diocese of Brooklyn, Diocese of Brooklyn. Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholics are divided into numerous jurisdictions throughout the city. Evangelicalism, Evangelical Protestantism is the largest branch of Protestantism in the city (9%), followed by Mainline Protestantism (8%), while the converse is usually true for other cities and metropolitan areas. In Evangelicalism, Baptists are the largest group; in Mainline Protestantism, Calvinism, Reformed Protestants compose the largest subset. The majority of historically Black church, African American churches are affiliated with the National Baptist Convention, USA, Inc., National Baptist Convention (USA) and Progressive National Baptist Convention. The Church of God in Christ is one of the largest predominantly Black Pentecostalism, Pentecostal denominations in the area. Approximately 1% of the population is Mormon. The Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of America and other Orthodox Christians (mainstream and independent) were the largest Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian groups. The American Orthodox Catholic Church (initially led by Aftimios Ofiesh) was founded in New York City in 1927.
Largely as a result of Western European missionary work and colonialism, Christianity is the largest religion in New York City, which is home to the highest number of church (building), churches of any city in the world. Catholic Church, Roman Catholicism is the largest Christian denomination (33%), followed by Protestantism (23%), and List of Christian denominations, other Christians (3%). The Roman Catholic population are primarily served by the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New York and Roman Catholic Diocese of Brooklyn, Diocese of Brooklyn. Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholics are divided into numerous jurisdictions throughout the city. Evangelicalism, Evangelical Protestantism is the largest branch of Protestantism in the city (9%), followed by Mainline Protestantism (8%), while the converse is usually true for other cities and metropolitan areas. In Evangelicalism, Baptists are the largest group; in Mainline Protestantism, Calvinism, Reformed Protestants compose the largest subset. The majority of historically Black church, African American churches are affiliated with the National Baptist Convention, USA, Inc., National Baptist Convention (USA) and Progressive National Baptist Convention. The Church of God in Christ is one of the largest predominantly Black Pentecostalism, Pentecostal denominations in the area. Approximately 1% of the population is Mormon. The Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of America and other Orthodox Christians (mainstream and independent) were the largest Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian groups. The American Orthodox Catholic Church (initially led by Aftimios Ofiesh) was founded in New York City in 1927.
 American Jews, Judaism, the Jews in New York City, second-largest religion practiced in New York City, with approximately 1.6 million adherents as of 2022, represents Jewish population by city, the largest Jewish community of any city in the world, greater than the combined totals of Tel Aviv and Jerusalem. Nearly half of the city’s Jews live in
American Jews, Judaism, the Jews in New York City, second-largest religion practiced in New York City, with approximately 1.6 million adherents as of 2022, represents Jewish population by city, the largest Jewish community of any city in the world, greater than the combined totals of Tel Aviv and Jerusalem. Nearly half of the city’s Jews live in  New York City's most important economic sector lies in its role as the headquarters for the Financial center, U.S. financial industry, metonymously known as ''Wall Street''. The city's Security (finance), securities industry continues to form the largest segment of the city's financial sector and is an important economic engine. Many large financial companies are headquartered in New York City, and the city is also home to a burgeoning number of financial Startup company, startup companies.
New York City's most important economic sector lies in its role as the headquarters for the Financial center, U.S. financial industry, metonymously known as ''Wall Street''. The city's Security (finance), securities industry continues to form the largest segment of the city's financial sector and is an important economic engine. Many large financial companies are headquartered in New York City, and the city is also home to a burgeoning number of financial Startup company, startup companies.
 Tourism is a vital industry for New York City, and NYC & Company represents the city's official bureau of tourism. New York has witnessed a growing combined volume of international and domestic tourists, reflecting over 60 million visitors to the city per year, the world's busiest tourist destination. Approximately 12 million visitors to New York City have been from outside the United States, with the highest numbers from the United Kingdom, Canada, Brazil, and China. Multiple sources have called New York the most photographed city in the world.
Tourism is a vital industry for New York City, and NYC & Company represents the city's official bureau of tourism. New York has witnessed a growing combined volume of international and domestic tourists, reflecting over 60 million visitors to the city per year, the world's busiest tourist destination. Approximately 12 million visitors to New York City have been from outside the United States, with the highest numbers from the United Kingdom, Canada, Brazil, and China. Multiple sources have called New York the most photographed city in the world. New York City has been described as the show business, entertainment and digital media capital of the world. The city is a prominent location for the American
New York City has been described as the show business, entertainment and digital media capital of the world. The city is a prominent location for the American  More than 200 newspapers and 350 consumer magazines have an office in the city, and the publishing industry employs about 25,000 people. Two of the three national daily newspapers with the largest Circulation (newspaper), circulations in the United States are published in New York: ''The Wall Street Journal'' and ''
More than 200 newspapers and 350 consumer magazines have an office in the city, and the publishing industry employs about 25,000 people. Two of the three national daily newspapers with the largest Circulation (newspaper), circulations in the United States are published in New York: ''The Wall Street Journal'' and ''
 More than a million students, the highest number of any city in the United States, are enrolled in New York City's more than 120 higher education institutions, with more than half a million in the
More than a million students, the highest number of any city in the United States, are enrolled in New York City's more than 120 higher education institutions, with more than half a million in the  The New York City Health and Hospitals Corporation (HHC) operates the Public hospital#United States, public hospitals and outpatient care, outpatient clinics in New York City. A New York state public-benefit corporations, public benefit corporation with , HHC is the largest municipal healthcare system in the United States with $10.9 billion in annual revenues, HHC is the largest municipal healthcare system in the United States serving 1.4 million patients, including more than 475,000 uninsured city residents. HHC was created in 1969 by the New York State Legislature as a public benefit corporation (Chapter 1016 of the Laws 1969). HHC operates 11 acute care hospitals, five nursing homes, six diagnostic and treatment centers, and more than 70 community-based primary care sites, serving primarily the poor and working class. HHC's MetroPlus Health Plan is one of the New York area's largest providers of government-sponsored health insurance and is the plan of choice for nearly half a million New Yorkers.
HHC's facilities annually provide millions of New Yorkers services interpreted in more than 190 languages. The most well-known hospital in the HHC system is Bellevue Hospital, the oldest public hospital in the United States. Bellevue is the designated hospital for treatment of the President of the United States and other List of current heads of state and government, world leaders if they become sick or injured while in New York City. The president of HHC is Ramanathan Raju, MD, a surgeon and former CEO of the Cook County health system in Illinois. In August 2017, Mayor Bill de Blasio signed legislation outlawing pharmacies from selling cigarettes once their existing licenses to do so expired, beginning in 2018.
The New York City Health and Hospitals Corporation (HHC) operates the Public hospital#United States, public hospitals and outpatient care, outpatient clinics in New York City. A New York state public-benefit corporations, public benefit corporation with , HHC is the largest municipal healthcare system in the United States with $10.9 billion in annual revenues, HHC is the largest municipal healthcare system in the United States serving 1.4 million patients, including more than 475,000 uninsured city residents. HHC was created in 1969 by the New York State Legislature as a public benefit corporation (Chapter 1016 of the Laws 1969). HHC operates 11 acute care hospitals, five nursing homes, six diagnostic and treatment centers, and more than 70 community-based primary care sites, serving primarily the poor and working class. HHC's MetroPlus Health Plan is one of the New York area's largest providers of government-sponsored health insurance and is the plan of choice for nearly half a million New Yorkers.
HHC's facilities annually provide millions of New Yorkers services interpreted in more than 190 languages. The most well-known hospital in the HHC system is Bellevue Hospital, the oldest public hospital in the United States. Bellevue is the designated hospital for treatment of the President of the United States and other List of current heads of state and government, world leaders if they become sick or injured while in New York City. The president of HHC is Ramanathan Raju, MD, a surgeon and former CEO of the Cook County health system in Illinois. In August 2017, Mayor Bill de Blasio signed legislation outlawing pharmacies from selling cigarettes once their existing licenses to do so expired, beginning in 2018.
 The
The  Sociologists and criminologists have not reached consensus on the explanation for the dramatic long-term decrease in the city's crime rate. Some attribute the phenomenon to new tactics used by the NYPD, including its use of CompStat and the broken windows theory. Others cite the end of the crack epidemic and demographic changes, including from immigration. Another theory is that widespread exposure to lead pollution from automobile exhaust, which can lower intelligence and increase aggression levels, incited the initial crime wave in the mid-20th century, most acutely affecting heavily trafficked cities like New York. A strong correlation was found demonstrating that violent crime rates in New York and other big cities began to fall after lead was removed from American gasoline in the 1970s. Another theory cited to explain New York City's falling homicide rate is the inverse correlation between the number of murders and the increasingly wet climate in the city.
Organized crime has long been associated with New York City, beginning with the Forty Thieves (New York gang), Forty Thieves and the Roach Guards in the Five Points, Manhattan, Five Points neighborhood in the 1820s, followed by the Tong (organization), Tongs in the same neighborhood, which ultimately evolved into Chinatown, Manhattan. The 20th century saw a rise in the American Mafia, Mafia, dominated by the Five Families, as well as in gangs, including the Black Spades. The Mafia and gang presence has declined in the city in the 21st century.
Sociologists and criminologists have not reached consensus on the explanation for the dramatic long-term decrease in the city's crime rate. Some attribute the phenomenon to new tactics used by the NYPD, including its use of CompStat and the broken windows theory. Others cite the end of the crack epidemic and demographic changes, including from immigration. Another theory is that widespread exposure to lead pollution from automobile exhaust, which can lower intelligence and increase aggression levels, incited the initial crime wave in the mid-20th century, most acutely affecting heavily trafficked cities like New York. A strong correlation was found demonstrating that violent crime rates in New York and other big cities began to fall after lead was removed from American gasoline in the 1970s. Another theory cited to explain New York City's falling homicide rate is the inverse correlation between the number of murders and the increasingly wet climate in the city.
Organized crime has long been associated with New York City, beginning with the Forty Thieves (New York gang), Forty Thieves and the Roach Guards in the Five Points, Manhattan, Five Points neighborhood in the 1820s, followed by the Tong (organization), Tongs in the same neighborhood, which ultimately evolved into Chinatown, Manhattan. The 20th century saw a rise in the American Mafia, Mafia, dominated by the Five Families, as well as in gangs, including the Black Spades. The Mafia and gang presence has declined in the city in the 21st century.
 The New York City Fire Department, Fire Department of New York (FDNY) provides fire protection, technical rescue, primary response to biological, chemical, and radioactive hazards, and emergency medical services for the five boroughs of New York City. The FDNY is the largest municipal fire department in the United States and the second largest in the world after the Tokyo Fire Department. The FDNY employs approximately 11,080 uniformed firefighters and more than 3,300 uniformed Emergency medical technician, EMTs and paramedics. The FDNY's motto is ''New York's Bravest''.
The fire department faces multifaceted firefighting challenges in many ways unique to New York. In addition to responding to List of building types, building types that range from wood-frame single family homes to High-rise, high-rise structures, the FDNY also responds to fires that occur in the
The New York City Fire Department, Fire Department of New York (FDNY) provides fire protection, technical rescue, primary response to biological, chemical, and radioactive hazards, and emergency medical services for the five boroughs of New York City. The FDNY is the largest municipal fire department in the United States and the second largest in the world after the Tokyo Fire Department. The FDNY employs approximately 11,080 uniformed firefighters and more than 3,300 uniformed Emergency medical technician, EMTs and paramedics. The FDNY's motto is ''New York's Bravest''.
The fire department faces multifaceted firefighting challenges in many ways unique to New York. In addition to responding to List of building types, building types that range from wood-frame single family homes to High-rise, high-rise structures, the FDNY also responds to fires that occur in the  The New York Public Library (NYPL), which has the largest collection of any public library system in the United States, serves Manhattan, the Bronx, and Staten Island. Queens is served by the Queens Borough Public Library (QPL), the nation's second-largest public library system, while the Brooklyn Public Library (BPL) serves Brooklyn.
In 2013, the New York Public Library and the Brooklyn Public Library announced that they would merge their technical services departments into a new department called BookOps. This proposed merger anticipated a savings of $2 million for the Brooklyn Public Library and $1.5 million for the New York Public Library. Although not currently part of the merger, it is expected that the Queens Public Library will eventually share some resources with the other city libraries.
The New York Public Library (NYPL), which has the largest collection of any public library system in the United States, serves Manhattan, the Bronx, and Staten Island. Queens is served by the Queens Borough Public Library (QPL), the nation's second-largest public library system, while the Brooklyn Public Library (BPL) serves Brooklyn.
In 2013, the New York Public Library and the Brooklyn Public Library announced that they would merge their technical services departments into a new department called BookOps. This proposed merger anticipated a savings of $2 million for the Brooklyn Public Library and $1.5 million for the New York Public Library. Although not currently part of the merger, it is expected that the Queens Public Library will eventually share some resources with the other city libraries.
 One of the most common traits attributed to New York City is its fast pace, which spawned the term ''wiktionary:New York minute, New York minute''. Journalist Walt Whitman characterized New York's streets as being traversed by "hurrying, feverish, electric crowds".
One of the most common traits attributed to New York City is its fast pace, which spawned the term ''wiktionary:New York minute, New York minute''. Journalist Walt Whitman characterized New York's streets as being traversed by "hurrying, feverish, electric crowds".
 Broadway theatre is one of the premier forms of English-language theatre in the world, named after
Broadway theatre is one of the premier forms of English-language theatre in the world, named after 
 New York City's food culture includes an array of international cuisines influenced by the city's immigrant history. Central Europe, Central and Eastern European immigrants, especially Jewish Americans, Jewish immigrants from those regions, brought bagels, Cheesecake#North America, cheesecake, hot dogs, knishes, and delicatessens (or delis) to the city. Italian diaspora, Italian immigrants brought New York-style pizza and Italian cuisine into the city, while Jewish immigrants and
New York City's food culture includes an array of international cuisines influenced by the city's immigrant history. Central Europe, Central and Eastern European immigrants, especially Jewish Americans, Jewish immigrants from those regions, brought bagels, Cheesecake#North America, cheesecake, hot dogs, knishes, and delicatessens (or delis) to the city. Italian diaspora, Italian immigrants brought New York-style pizza and Italian cuisine into the city, while Jewish immigrants and  New York City has been a metropolitan municipality with a Strong Mayor, Strong mayor–council form of government since its consolidation in 1898. In New York City, the city government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services.
The Mayor of New York City, mayor and council members are elected to four-year terms. The New York City Council, City Council is a unicameral body consisting of 51 council members whose districts are defined by geographic population boundaries. Each term for the mayor and council members lasts four years and has a two Term limit, consecutive-term limit, which is reset after a four-year break. The ''New York City Administrative Code'', the ''New York City Rules'', and the ''The City Record, City Record'' are the code of local laws, compilation of regulations, and official journal, respectively.
New York City has been a metropolitan municipality with a Strong Mayor, Strong mayor–council form of government since its consolidation in 1898. In New York City, the city government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services.
The Mayor of New York City, mayor and council members are elected to four-year terms. The New York City Council, City Council is a unicameral body consisting of 51 council members whose districts are defined by geographic population boundaries. Each term for the mayor and council members lasts four years and has a two Term limit, consecutive-term limit, which is reset after a four-year break. The ''New York City Administrative Code'', the ''New York City Rules'', and the ''The City Record, City Record'' are the code of local laws, compilation of regulations, and official journal, respectively.
 Each borough is coextensive with a judicial district of the state New York State Unified Court System, Unified Court System, of which the New York City Criminal Court, Criminal Court and the New York City Civil Court, Civil Court are the local courts, while the New York Supreme Court conducts major trials and appeals. Manhattan hosts the First Department of the New York Supreme Court, Appellate Division, Supreme Court, Appellate Division while Brooklyn hosts the Second Department. There are also several extrajudicial administrative courts, which are executive agencies and not part of the state Unified Court System.
Uniquely among major American cities, New York is divided between, and is host to the main branches of, two different U.S. district courts: the District Court for the Southern District of New York, whose main courthouse is on
Each borough is coextensive with a judicial district of the state New York State Unified Court System, Unified Court System, of which the New York City Criminal Court, Criminal Court and the New York City Civil Court, Civil Court are the local courts, while the New York Supreme Court conducts major trials and appeals. Manhattan hosts the First Department of the New York Supreme Court, Appellate Division, Supreme Court, Appellate Division while Brooklyn hosts the Second Department. There are also several extrajudicial administrative courts, which are executive agencies and not part of the state Unified Court System.
Uniquely among major American cities, New York is divided between, and is host to the main branches of, two different U.S. district courts: the District Court for the Southern District of New York, whose main courthouse is on  The present mayor is Eric Adams. He was elected in 2021 New York City mayoral election, 2021 with 67% of the vote, and assumed office on January 1, 2022.
The Democratic Party holds the majority of public offices. As of April 2016, 69% of registered voters in the city are Democrats and 10% are Republican Party (United States), Republicans. New York City has not been carried by a Republican presidential election since President Calvin Coolidge won the five boroughs in United States presidential election in New York, 1924, 1924. A Republican candidate for statewide office has not won all five boroughs of New York City since the city’s incorporation in 1898. In United States presidential election in New York, 2012, 2012, Democrat Barack Obama became the first presidential candidate of any party to receive more than 80% of the overall vote in New York City, sweeping all five boroughs. Party platforms center on affordable housing, education, and economic development, and labor politics are of importance in the city. Thirteen out of 27 U.S. congressional districts in the state of New York include portions of New York City.
New York is one of the most important sources of political fundraising in the United States. At least four of the top five ZIP Codes in the nation for political contributions were in Manhattan for the 2004 United States elections, 2004, 2006 United States elections, 2006, and 2008 United States elections, 2008 elections. The top ZIP Code, 10021 on the Upper East Side, generated the most money for the 2004 presidential campaigns of George W. Bush and John Kerry. The city has a strong imbalance of payments with the national and state governments. It receives 83 cents in services for every $1 it sends to the federal government in Taxation in the United States, taxes (or annually sends $11.4 billion more than it receives back). City residents and businesses also sent an additional $4.1 billion in the 2009–2010 fiscal year to the state of New York than the city received in return.
The present mayor is Eric Adams. He was elected in 2021 New York City mayoral election, 2021 with 67% of the vote, and assumed office on January 1, 2022.
The Democratic Party holds the majority of public offices. As of April 2016, 69% of registered voters in the city are Democrats and 10% are Republican Party (United States), Republicans. New York City has not been carried by a Republican presidential election since President Calvin Coolidge won the five boroughs in United States presidential election in New York, 1924, 1924. A Republican candidate for statewide office has not won all five boroughs of New York City since the city’s incorporation in 1898. In United States presidential election in New York, 2012, 2012, Democrat Barack Obama became the first presidential candidate of any party to receive more than 80% of the overall vote in New York City, sweeping all five boroughs. Party platforms center on affordable housing, education, and economic development, and labor politics are of importance in the city. Thirteen out of 27 U.S. congressional districts in the state of New York include portions of New York City.
New York is one of the most important sources of political fundraising in the United States. At least four of the top five ZIP Codes in the nation for political contributions were in Manhattan for the 2004 United States elections, 2004, 2006 United States elections, 2006, and 2008 United States elections, 2008 elections. The top ZIP Code, 10021 on the Upper East Side, generated the most money for the 2004 presidential campaigns of George W. Bush and John Kerry. The city has a strong imbalance of payments with the national and state governments. It receives 83 cents in services for every $1 it sends to the federal government in Taxation in the United States, taxes (or annually sends $11.4 billion more than it receives back). City residents and businesses also sent an additional $4.1 billion in the 2009–2010 fiscal year to the state of New York than the city received in return.
 New York City's comprehensive transportation system is both complex and extensive.
New York City's comprehensive transportation system is both complex and extensive.
 Public transport is essential in New York City. 54.6% of New Yorkers commuted to work in 2005 using mass transit. This is in contrast to the rest of the United States, where 91% of commuters travel in automobiles to their workplace. According to the New York City Comptroller, workers in the New York City area spend an average of 6hours and 18 minutes getting to work each week, the longest commute time in the nation among large cities. New York is the only U.S. city in which a majority (52%) of households do not have a car; only 22% of Manhattanites own a car. Due to their List of U.S. cities with high transit ridership, high usage of mass transit, New Yorkers spend less of their household income on transportation than the national average, saving $19 billion annually on transportation compared to other urban Americans.
New York City's commuter rail network is the largest in North America. The rail network, connecting New York City to its suburbs, consists of the Long Island Rail Road, Metro-North Railroad, and New Jersey Transit rail operations, New Jersey Transit. The combined systems converge at Grand Central Terminal and Pennsylvania Station (New York City), Pennsylvania Station and contain more than 250 stations and 20 rail lines. In Queens, the elevated AirTrain JFK, AirTrain people mover system connects 24 hours a day JFK International Airport to the New York City Subway and the Long Island Rail Road; a separate AirTrain system is planned alongside the Grand Central Parkway to connect LaGuardia Airport to these transit systems. For intercity rail, New York City is served by Amtrak, whose busiest station by a significant margin is Pennsylvania Station on the
Public transport is essential in New York City. 54.6% of New Yorkers commuted to work in 2005 using mass transit. This is in contrast to the rest of the United States, where 91% of commuters travel in automobiles to their workplace. According to the New York City Comptroller, workers in the New York City area spend an average of 6hours and 18 minutes getting to work each week, the longest commute time in the nation among large cities. New York is the only U.S. city in which a majority (52%) of households do not have a car; only 22% of Manhattanites own a car. Due to their List of U.S. cities with high transit ridership, high usage of mass transit, New Yorkers spend less of their household income on transportation than the national average, saving $19 billion annually on transportation compared to other urban Americans.
New York City's commuter rail network is the largest in North America. The rail network, connecting New York City to its suburbs, consists of the Long Island Rail Road, Metro-North Railroad, and New Jersey Transit rail operations, New Jersey Transit. The combined systems converge at Grand Central Terminal and Pennsylvania Station (New York City), Pennsylvania Station and contain more than 250 stations and 20 rail lines. In Queens, the elevated AirTrain JFK, AirTrain people mover system connects 24 hours a day JFK International Airport to the New York City Subway and the Long Island Rail Road; a separate AirTrain system is planned alongside the Grand Central Parkway to connect LaGuardia Airport to these transit systems. For intercity rail, New York City is served by Amtrak, whose busiest station by a significant margin is Pennsylvania Station on the  New York City's public MTA Regional Bus Operations, bus fleet runs 24/7 and is the largest in North America. The Port Authority Bus Terminal, the main intercity bus terminal of the city, serves 7,000 buses and 200,000 commuters daily, making it the busiest bus station in the world.
New York City's public MTA Regional Bus Operations, bus fleet runs 24/7 and is the largest in North America. The Port Authority Bus Terminal, the main intercity bus terminal of the city, serves 7,000 buses and 200,000 commuters daily, making it the busiest bus station in the world.
 Plans have advanced to expand passenger volume at a fourth airport, Stewart International Airport near Newburgh, New York, by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey. Plans were announced in July 2015 to entirely rebuild LaGuardia Airport in a multibillion-dollar project to replace its aging facilities. Other commercial airports in or serving the
Plans have advanced to expand passenger volume at a fourth airport, Stewart International Airport near Newburgh, New York, by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey. Plans were announced in July 2015 to entirely rebuild LaGuardia Airport in a multibillion-dollar project to replace its aging facilities. Other commercial airports in or serving the  The Staten Island Ferry is the world's busiest Ferry, ferry route, carrying more than 23 million passengers from July 2015 through June 2016 on the route between Staten Island and Lower Manhattan and running 24 hours a day. Other ferry systems shuttle commuters between Manhattan and other locales within the city and the metropolitan area.
NYC Ferry, a New York City Economic Development Corporation, NYCEDC initiative with routes planned to travel to all five boroughs, was launched in 2017, with second graders choosing the names of the ferries. Meanwhile, Seastreak ferry announced construction of a 600-passenger high-speed luxury ferry in September 2016, to shuttle riders between the Jersey Shore and Manhattan, anticipated to start service in 2017; this would be the largest vessel in its class.
The Staten Island Ferry is the world's busiest Ferry, ferry route, carrying more than 23 million passengers from July 2015 through June 2016 on the route between Staten Island and Lower Manhattan and running 24 hours a day. Other ferry systems shuttle commuters between Manhattan and other locales within the city and the metropolitan area.
NYC Ferry, a New York City Economic Development Corporation, NYCEDC initiative with routes planned to travel to all five boroughs, was launched in 2017, with second graders choosing the names of the ferries. Meanwhile, Seastreak ferry announced construction of a 600-passenger high-speed luxury ferry in September 2016, to shuttle riders between the Jersey Shore and Manhattan, anticipated to start service in 2017; this would be the largest vessel in its class.
 Other features of the city's transportation infrastructure encompass 13,587 Taxicabs of New York City, yellow taxicabs; other vehicle for hire companies; and the Roosevelt Island Tramway, an aerial tramway that transports commuters between Roosevelt Island and Manhattan Island.
Other features of the city's transportation infrastructure encompass 13,587 Taxicabs of New York City, yellow taxicabs; other vehicle for hire companies; and the Roosevelt Island Tramway, an aerial tramway that transports commuters between Roosevelt Island and Manhattan Island.
 Despite New York's heavy reliance on its vast public transit system, streets are a defining feature of the city. The
Despite New York's heavy reliance on its vast public transit system, streets are a defining feature of the city. The  New York City is located on one of the world's largest natural harbors, and the boroughs of Manhattan and Staten Island are primarily coterminous with islands of the same names, while Queens and Brooklyn are at the west end of the larger Long Island, and the Bronx is on New York State's mainland. This situation of boroughs separated by water led to the development of an extensive infrastructure of bridges and tunnels.
The George Washington Bridge is the world's busiest motor vehicle bridge, connecting Manhattan to Bergen County, New Jersey. The Verrazano-Narrows Bridge is the longest suspension bridge in the Americas and one of the world's longest. The Brooklyn Bridge is an icon of the city itself. The towers of the Brooklyn Bridge are built of limestone, granite, and Rosendale cement, and their architectural style is neo-Gothic, with characteristic pointed arches above the passageways through the stone towers. This bridge was also the longest suspension bridge in the world from its opening until 1903, and is the first steel-wire suspension bridge. The Queensboro Bridge is an important piece of Cantilever bridge, cantilever architecture. The Manhattan Bridge, opened in 1909, is considered to be the forerunner of modern suspension bridges, and its design served as the model for many of the long-span suspension bridges around the world; the Manhattan Bridge, Throgs Neck Bridge, Triborough Bridge, and Verrazano-Narrows Bridge are all examples of structural expressionism.
Manhattan Island is linked to New York City's outer boroughs and New Jersey by several tunnels as well. The Lincoln Tunnel, which carries 120,000 vehicles a day under the Hudson River between New Jersey and Midtown Manhattan, is the busiest vehicular tunnel in the world. The tunnel was built instead of a bridge to allow unfettered passage of large passenger and cargo ships that sailed through New York Harbor and up the Hudson River to Manhattan's piers. The Holland Tunnel, connecting Lower Manhattan to Jersey City, New Jersey, was the world's first mechanically ventilated vehicular tunnel when it opened in 1927. The Queens-Midtown Tunnel, built to relieve congestion on the bridges connecting Manhattan with Queens and Brooklyn, was the largest non-federal project in its time when it was completed in 1940. President Franklin D. Roosevelt was the first person to drive through it. The Brooklyn-Battery Tunnel (officially known as the Hugh L. Carey Tunnel) runs underneath Battery Park and connects the
New York City is located on one of the world's largest natural harbors, and the boroughs of Manhattan and Staten Island are primarily coterminous with islands of the same names, while Queens and Brooklyn are at the west end of the larger Long Island, and the Bronx is on New York State's mainland. This situation of boroughs separated by water led to the development of an extensive infrastructure of bridges and tunnels.
The George Washington Bridge is the world's busiest motor vehicle bridge, connecting Manhattan to Bergen County, New Jersey. The Verrazano-Narrows Bridge is the longest suspension bridge in the Americas and one of the world's longest. The Brooklyn Bridge is an icon of the city itself. The towers of the Brooklyn Bridge are built of limestone, granite, and Rosendale cement, and their architectural style is neo-Gothic, with characteristic pointed arches above the passageways through the stone towers. This bridge was also the longest suspension bridge in the world from its opening until 1903, and is the first steel-wire suspension bridge. The Queensboro Bridge is an important piece of Cantilever bridge, cantilever architecture. The Manhattan Bridge, opened in 1909, is considered to be the forerunner of modern suspension bridges, and its design served as the model for many of the long-span suspension bridges around the world; the Manhattan Bridge, Throgs Neck Bridge, Triborough Bridge, and Verrazano-Narrows Bridge are all examples of structural expressionism.
Manhattan Island is linked to New York City's outer boroughs and New Jersey by several tunnels as well. The Lincoln Tunnel, which carries 120,000 vehicles a day under the Hudson River between New Jersey and Midtown Manhattan, is the busiest vehicular tunnel in the world. The tunnel was built instead of a bridge to allow unfettered passage of large passenger and cargo ships that sailed through New York Harbor and up the Hudson River to Manhattan's piers. The Holland Tunnel, connecting Lower Manhattan to Jersey City, New Jersey, was the world's first mechanically ventilated vehicular tunnel when it opened in 1927. The Queens-Midtown Tunnel, built to relieve congestion on the bridges connecting Manhattan with Queens and Brooklyn, was the largest non-federal project in its time when it was completed in 1940. President Franklin D. Roosevelt was the first person to drive through it. The Brooklyn-Battery Tunnel (officially known as the Hugh L. Carey Tunnel) runs underneath Battery Park and connects the