Laniakea Supercluster on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Laniakea Supercluster (; Hawaiian for "open skies" or "immense heaven") is the
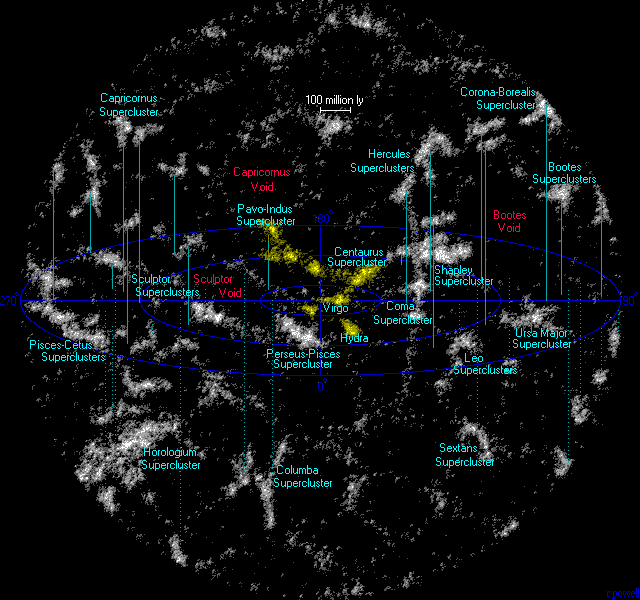 The neighboring superclusters to the Laniakea Supercluster are the
The neighboring superclusters to the Laniakea Supercluster are the
Meet Laniakea, Our Home Supercluster
"Laniakea Supercluster"
Daniel Pomarède, 4 September 2014—video representation of the findings of the discovery paper * YouTube
"Laniakea: Our Home Supercluster"
Nature Video, 3 September 2014—Redrawing the boundaries of the cosmic map, they redefine our home supercluster and name it Laniakea. {{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Solar System, Science 201409?? Galaxy superclusters
galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. ...
supercluster
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn ...
that is home to the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
and approximately 100,000 other nearby galaxies.
It was defined in September 2014, when a group of astronomers including R. Brent Tully
Richard Brent Tully (born March 9, 1943) is a Canadian-born American astronomer at the Institute for Astronomy in Honolulu, Hawaii.
Born in Toronto, Ontario, and raised in Vancouver, British Columbia, Tully's specialty is the astrophysics of gal ...
of the University of Hawaiʻi
The University of Hawaiʻi System, formally the University of Hawaiʻi and popularly known as UH, is a public college and university system that confers associate, bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees through three universities, seven com ...
, Hélène Courtois
Hélène (Di Nella) Courtois (born 1970) is a French astrophysicist specialising in cosmography. She is a professor at the University of Lyon 1 and has been a chevalier of the Ordre des Palmes Académiques since 2015.
As the director of a resea ...
of the University of Lyon, Yehuda Hoffman of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI; he, הַאוּנִיבֶרְסִיטָה הַעִבְרִית בִּירוּשָׁלַיִם) is a public research university based in Jerusalem, Israel. Co-founded by Albert Einstein and Dr. Chaim Weiz ...
, and Daniel Pomarède of CEA Université Paris-Saclay
Paris-Saclay University (french: Université Paris-Saclay) is a public research university based in Paris, France. It is one of the 13 prestigious universities that emerged from the division of the University of Paris, also known as the Sorbonne. ...
published a new way of defining superclusters according to the relative velocities of galaxies. The new definition of the local supercluster subsumes the prior defined local supercluster, the Virgo Supercluster, as an appendage.
Follow-up studies suggest that the Laniakea Supercluster is not gravitationally bound. It will disperse rather than continue to maintain itself as an overdensity relative to surrounding areas.
Name
The name () means 'immense heaven' in Hawaiian, . The name was suggested by Nawaʻa Napoleon, an associate professor of Hawaiian language at Kapiolani Community College. The name honorsPolynesian navigators
Polynesian is the adjectival form of Polynesia. It may refer to:
* Polynesians, an ethnic group
* Polynesian culture, the culture of the indigenous peoples of Polynesia
* Polynesian mythology, the oral traditions of the people of Polynesia
* Poly ...
, who used knowledge of the heavens to navigate the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
.
Characteristics
The Laniakea Supercluster encompasses approximately 100,000 galaxies stretched out over . It has the approximate mass of 1017 solar masses, or 100,000 times that of our galaxy, which is almost the same as that of the Horologium Supercluster. It consists of four subparts, which were known previously as separate superclusters: * Virgo Supercluster, the part in which the Milky Way resides. * Hydra–Centaurus Supercluster ** the Great Attractor, Laniakea's central gravitational point near Norma ** Antlia Wall, known as Hydra Supercluster ** Centaurus Supercluster *Pavo–Indus Supercluster
The Pavo-Indus Supercluster is a neighboring supercluster located about away in the constellations of Pavo, Indus, and Telescopium. The supercluster contains three main clusters, Abell 3656, Abell 3698, and Abell 3742.
Other groups and clust ...
* Southern Supercluster
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
, including Fornax Cluster (S373), Dorado and Eridanus clouds.
The most massive galaxy clusters of the Laniakea Supercluster are Virgo, Hydra
Hydra generally refers to:
* Lernaean Hydra, a many-headed serpent in Greek mythology
* ''Hydra'' (genus), a genus of simple freshwater animals belonging to the phylum Cnidaria
Hydra or The Hydra may also refer to:
Astronomy
* Hydra (constel ...
, Centaurus, Abell 3565, Abell 3574, Abell 3521, Fornax, Eridanus, and Norma. The entire supercluster consists of approximately 300 to 500 known galaxy clusters and groups. The real number may be much larger because some of these are traversing the Zone of Avoidance
The Zone of Avoidance (ZOA, ZoA), or Zone of Galactic Obscuration (ZGO), is the area of the sky that is obscured by the Milky Way.
The Zone of Avoidance was originally called the Zone of Few Nebulae in an 1878 paper by English astronomer Richard ...
, an area of the sky that is partially obscured by gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
and dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in homes ...
from the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
galaxy, making them essentially undetectable.
Superclusters are some of the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. Acc ...
's largest structures and have boundaries that are difficult to define, especially from the inside. Within a given supercluster, most galaxy motions will be directed inward, toward the center of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force may ...
. In the case of Laniakea, this gravitational focal point is called the Great Attractor, and influences the motions of the Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way.
It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of .
It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form ...
of galaxies, where the Milky Way galaxy resides, and all others throughout the supercluster. Unlike its constituent clusters, Laniakea is not gravitationally bound and is projected to be torn apart by dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univer ...
.
Although the confirmation of the existence of the Laniakea Supercluster emerged in 2014, early studies in the 1980s already suggested that several of the superclusters then known might be connected. For example, South African astronomer Tony Fairall stated in 1988 that redshifts suggested that the Virgo and Hydra–Centaurus superclusters may be connected.
Location
 The neighboring superclusters to the Laniakea Supercluster are the
The neighboring superclusters to the Laniakea Supercluster are the Shapley Supercluster
The Shapley Supercluster or Shapley Concentration (SCl 124) is the largest concentration of galaxies in our nearby universe that forms a gravitationally interacting unit, thereby pulling itself together instead of expanding with the universe. It a ...
, Hercules Supercluster, Coma Supercluster, and Perseus–Pisces Supercluster
The Perseus–Pisces Supercluster (SCl 40) is one of the largest known structures in the universe. Even at a distance of 250 million light-years, this chain of galaxy clusters extends more than 40° across the northern winter sky. The Perseus-Pis ...
. The edges of the superclusters and Laniakea were not clearly known at the time of Laniakea's definition. Since then, the study of the edges of the supercluster and of structures beyond them has substantially improved.
Laniakea is itself a constituent part of the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex
The Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex is a galaxy filament. It includes the Laniakea Supercluster which contains the Virgo Supercluster lobe which in turn contains the Local Group, the galaxy cluster that includes the Milky Way.
This filament ...
, a galaxy filament
In cosmology, galaxy filaments (subtypes: supercluster complexes, galaxy walls, and galaxy sheets) Boris V. Komberg, Andrey V. Kravtsov, Vladimir N. Lukash; "The search and investigation of the Large Groups of Quasars" ; ;R.G. Clowes; "Large Qu ...
.
See also
*Dipole repeller
The dipole repeller is a center of effective repulsion in the large-scale flow of galaxies in the neighborhood of the Milky Way, first detected in 2017.
It is thought to represent a large supervoid, the ''Dipole Repeller Void''.
The dipole ...
* Galaxy cluster
* Galaxy filament
In cosmology, galaxy filaments (subtypes: supercluster complexes, galaxy walls, and galaxy sheets) Boris V. Komberg, Andrey V. Kravtsov, Vladimir N. Lukash; "The search and investigation of the Large Groups of Quasars" ; ;R.G. Clowes; "Large Qu ...
* Illustris project
The Illustris project was a series of astrophysical simulations run by an international collaboration of scientists. The aim was to study the processes of galaxy formation and evolution in the universe with a comprehensive physical model. Early r ...
* Local Void
The Local Void is a vast, empty region of space, lying adjacent to the Local Group. Discovered by Brent Tully and Rick Fisher in 1987, the Local Void is now known to be composed of three separate sectors, separated by bridges of "wispy fil ...
– nearest neighboring void
* Supercluster
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn ...
* Void (astronomy)
Cosmic voids (also known as dark space) are vast spaces between filaments (the largest-scale structures in the universe), which contain very few or no galaxies. The cosmological evolution of the void regions differs drastically from the evolut ...
* List of Abell clusters
References
Further reading
*Meet Laniakea, Our Home Supercluster
External links
* Vimeo"Laniakea Supercluster"
Daniel Pomarède, 4 September 2014—video representation of the findings of the discovery paper * YouTube
"Laniakea: Our Home Supercluster"
Nature Video, 3 September 2014—Redrawing the boundaries of the cosmic map, they redefine our home supercluster and name it Laniakea. {{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Solar System, Science 201409?? Galaxy superclusters