Zadar Sankt Donat 04 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zadar ( , ; historically known as Zara (from
 Zadar faces the islands of Ugljan and Pašman (part of the Zadar Archipelago), from which it is separated by the narrow Zadar Strait. The promontory on which the old city stands used to be separated from the mainland by a deep moat which has since been filled. The harbour, to the north-east of the town, is safe and spacious.
Zadar faces the islands of Ugljan and Pašman (part of the Zadar Archipelago), from which it is separated by the narrow Zadar Strait. The promontory on which the old city stands used to be separated from the mainland by a deep moat which has since been filled. The harbour, to the north-east of the town, is safe and spacious.
 The archaeological remains have shown that the main centres of Liburnian territorial units or municipalities were already urbanized in the last centuries BC; before the Roman conquest, Zadar held a territory of more than in the 2nd century BC.
In the middle of the 2nd century BC, the Romans began to gradually invade the region. Although being first Roman enemies in the Adriatic Sea, the Liburnians, mostly stood aside in more than 230 years of Roman wars with the Illyrians, to protect their naval and trade connections in the sea. In 59 BC, Illyricum was assigned as a ''provincia'' (zone of responsibility) to
The archaeological remains have shown that the main centres of Liburnian territorial units or municipalities were already urbanized in the last centuries BC; before the Roman conquest, Zadar held a territory of more than in the 2nd century BC.
In the middle of the 2nd century BC, the Romans began to gradually invade the region. Although being first Roman enemies in the Adriatic Sea, the Liburnians, mostly stood aside in more than 230 years of Roman wars with the Illyrians, to protect their naval and trade connections in the sea. In 59 BC, Illyricum was assigned as a ''provincia'' (zone of responsibility) to  From the early days of Roman rule, Zadar gained its Roman urban character and developed into one of the most flourishing centres on the eastern Adriatic coast, a state of affairs which lasted for several hundred years. The town was organised according to the typical Roman street system with a rectangular street plan, a forum, thermae, a sewage and water supply system that came from lake Vrana, by way of a long aqueduct. It did not play a significant role in the Roman administration of Dalmatia, although the archaeological finds tell us about a significant growth of economy and culture.
From the early days of Roman rule, Zadar gained its Roman urban character and developed into one of the most flourishing centres on the eastern Adriatic coast, a state of affairs which lasted for several hundred years. The town was organised according to the typical Roman street system with a rectangular street plan, a forum, thermae, a sewage and water supply system that came from lake Vrana, by way of a long aqueduct. It did not play a significant role in the Roman administration of Dalmatia, although the archaeological finds tell us about a significant growth of economy and culture.
 At the beginning of the 9th century the Zadar bishop Donatus and the city duke Paul mediated in the dispute between the
At the beginning of the 9th century the Zadar bishop Donatus and the city duke Paul mediated in the dispute between the
 Zadar was especially devastated in 1202 after the Venetian Enrico Dandolo, Doge Enrico Dandolo used the crusaders, on their
Zadar was especially devastated in 1202 after the Venetian Enrico Dandolo, Doge Enrico Dandolo used the crusaders, on their  This did not break the spirit of the city, however. Its commerce was suffering due to a lack of autonomy under Venice, while it enjoyed considerable autonomy under the much more feudal Kingdom of Croatia-Hungary. A number of insurrections followed (1242–1243, 1320s, 1345–1346 – the latter resulted in a Siege of Zadar (1345–46), sixteen-month-long Venetian siege) which finally resulted in Zadar coming back under the crown of King Louis I of Hungary, Louis I of Croatia-Hungary under the Treaty of Zara, Treaty of Zadar, in 1358. After the War of Chioggia between Genoa and Venice, Chioggia concluded on 14 March 1381 an alliance with Zadar and Trogir against Venice, and finally Chioggia became better protected by Venice in 1412, because Šibenik became in 1412 the seat of the main customs office and the seat of the salt consumers office with a monopoly on the salt trade in Chioggia and on the whole
This did not break the spirit of the city, however. Its commerce was suffering due to a lack of autonomy under Venice, while it enjoyed considerable autonomy under the much more feudal Kingdom of Croatia-Hungary. A number of insurrections followed (1242–1243, 1320s, 1345–1346 – the latter resulted in a Siege of Zadar (1345–46), sixteen-month-long Venetian siege) which finally resulted in Zadar coming back under the crown of King Louis I of Hungary, Louis I of Croatia-Hungary under the Treaty of Zara, Treaty of Zadar, in 1358. After the War of Chioggia between Genoa and Venice, Chioggia concluded on 14 March 1381 an alliance with Zadar and Trogir against Venice, and finally Chioggia became better protected by Venice in 1412, because Šibenik became in 1412 the seat of the main customs office and the seat of the salt consumers office with a monopoly on the salt trade in Chioggia and on the whole
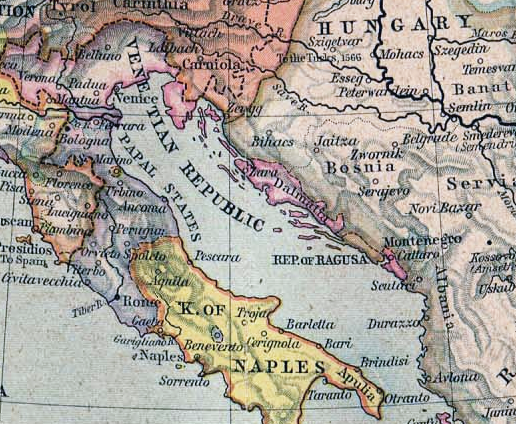 After the death of Louis I, Zadar came under the rule of Sigmund of Luxembourg and later Ladislaus of Naples, who, witnessing his loss of influence in Dalmatia, sold Zadar and his dynasty's rights to Dalmatia to Venice for 100,000 ducat (coin), ducats on 31 July 1409. Venice therefore obtained control over Zadar without a fight, but was confronted by the resistance and tensions of important Zadar families. These attempts were met with persecution and confiscation. Zadar remained the administrative seat of Dalmatia, but this time under the rule of Venice, which expanded over the whole Dalmatia, except the Republic of Ragusa/Dubrovnik. During that time Giorgio da Sebenico, a renaissance sculptor and architect, famous for his work on the Cathedral of Šibenik, was born in Zadar. Other important people followed, such as Luciano Laurana, Luciano and Francesco Laurana, known worldwide for their sculptures and buildings.
After the death of Louis I, Zadar came under the rule of Sigmund of Luxembourg and later Ladislaus of Naples, who, witnessing his loss of influence in Dalmatia, sold Zadar and his dynasty's rights to Dalmatia to Venice for 100,000 ducat (coin), ducats on 31 July 1409. Venice therefore obtained control over Zadar without a fight, but was confronted by the resistance and tensions of important Zadar families. These attempts were met with persecution and confiscation. Zadar remained the administrative seat of Dalmatia, but this time under the rule of Venice, which expanded over the whole Dalmatia, except the Republic of Ragusa/Dubrovnik. During that time Giorgio da Sebenico, a renaissance sculptor and architect, famous for his work on the Cathedral of Šibenik, was born in Zadar. Other important people followed, such as Luciano Laurana, Luciano and Francesco Laurana, known worldwide for their sculptures and buildings.
 The 16th and 17th centuries were noted in Zadar for Ottoman attacks. Ottomans captured the continental part of Zadar at the beginning of the 16th century and the city itself was all the time in the range of Turkish artillery. Due to that threat, the construction of a new system of castles and walls began. These defense systems changed the way the city looked. To make place for the pentagon castles many houses and churches were taken down, along with an entire suburb: Varoš of St. Martin. After the 40-year-long construction Zadar became the biggest fortified city in Dalmatia, empowered by a system of castles, bastions and canals filled with seawater. The city was supplied by the water from public city cisterns. During the complete makeover of Zadar, many new civic buildings were built, such as the City Lodge and City Guard on the Gospodski Square, several army barracks, but also some large new palaces.
In contrast to the insecurity and Ottoman sieges and destruction, an important culture evolved midst the city walls. During the 16th and the 17th centuries Zadar was still under the influence of the
The 16th and 17th centuries were noted in Zadar for Ottoman attacks. Ottomans captured the continental part of Zadar at the beginning of the 16th century and the city itself was all the time in the range of Turkish artillery. Due to that threat, the construction of a new system of castles and walls began. These defense systems changed the way the city looked. To make place for the pentagon castles many houses and churches were taken down, along with an entire suburb: Varoš of St. Martin. After the 40-year-long construction Zadar became the biggest fortified city in Dalmatia, empowered by a system of castles, bastions and canals filled with seawater. The city was supplied by the water from public city cisterns. During the complete makeover of Zadar, many new civic buildings were built, such as the City Lodge and City Guard on the Gospodski Square, several army barracks, but also some large new palaces.
In contrast to the insecurity and Ottoman sieges and destruction, an important culture evolved midst the city walls. During the 16th and the 17th centuries Zadar was still under the influence of the
 In 1797 with the Treaty of Campo Formio, the Republic of Venice, including Zadar, came under the Austrian Empire, Austrian crown. In 1806 it was briefly given to the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Kingdom of Italy, until in 1809 it was added to the French Illyrian Provinces. In November 1813 an Austrian force Siege of Zara (1813), blockaded the town with the assistance of two British Royal Navy frigates HMS Havannah (1811), HMS ''Havannah'' and HMS Weazel (1805), ''Weazle'' under the George Cadogan, 3rd Earl Cadogan, 3rd Earl of Cadogan. On 9 December the French garrison of Zadar capitulated, and by the end of the year all of Dalmatia was brought back under the control of the Austrian Empire. After the Congress of Vienna (1815) until 1918, the town (bilingual name ''Zara – Zadar'' ) remained part of the Austrian monarchy (Austria side after the compromise of 1867), head of the district of the same name, one of the 13 ''Bezirkshauptmannschaften'' in Kingdom of Dalmatia, Dalmatia. The Italian name was officially used before 1867. It remained also the capital of Dalmatia province (''Kronland'').
Although during the first half of the 19th century the city population stagnated due to low natural increase, the city started to spread from the old center; citizens from the old city created the new suburb of Stanovi in the north.
During the second half of the 19th century, there was constant increase of population due to economic growth and immigration. Under the pressure of the population increase, the city continued to spread to Voštarnica and Arbanasi quarters, and the bridge in the city port was built. Except being the administrative center of the province, agriculture, industry of liqueurs and trade were developed, many brotherhoods were established, similar to the Central European trade guilds. The southern city walls were torn down, new coastal facilities were built and Zadar became an ''open port''. As the city developed economically, it developed culturally. A large number of printshops, new libraries, archives, and theatres sprung up. At the end of the 19th century there was also stronger industrial development, with 27 small or big factories before the World War I.
In 1797 with the Treaty of Campo Formio, the Republic of Venice, including Zadar, came under the Austrian Empire, Austrian crown. In 1806 it was briefly given to the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Kingdom of Italy, until in 1809 it was added to the French Illyrian Provinces. In November 1813 an Austrian force Siege of Zara (1813), blockaded the town with the assistance of two British Royal Navy frigates HMS Havannah (1811), HMS ''Havannah'' and HMS Weazel (1805), ''Weazle'' under the George Cadogan, 3rd Earl Cadogan, 3rd Earl of Cadogan. On 9 December the French garrison of Zadar capitulated, and by the end of the year all of Dalmatia was brought back under the control of the Austrian Empire. After the Congress of Vienna (1815) until 1918, the town (bilingual name ''Zara – Zadar'' ) remained part of the Austrian monarchy (Austria side after the compromise of 1867), head of the district of the same name, one of the 13 ''Bezirkshauptmannschaften'' in Kingdom of Dalmatia, Dalmatia. The Italian name was officially used before 1867. It remained also the capital of Dalmatia province (''Kronland'').
Although during the first half of the 19th century the city population stagnated due to low natural increase, the city started to spread from the old center; citizens from the old city created the new suburb of Stanovi in the north.
During the second half of the 19th century, there was constant increase of population due to economic growth and immigration. Under the pressure of the population increase, the city continued to spread to Voštarnica and Arbanasi quarters, and the bridge in the city port was built. Except being the administrative center of the province, agriculture, industry of liqueurs and trade were developed, many brotherhoods were established, similar to the Central European trade guilds. The southern city walls were torn down, new coastal facilities were built and Zadar became an ''open port''. As the city developed economically, it developed culturally. A large number of printshops, new libraries, archives, and theatres sprung up. At the end of the 19th century there was also stronger industrial development, with 27 small or big factories before the World War I.
 After 1848, Italian and Croatian nationalistic ideas arrived in the city, which became divided between the Croats and the Italians, both of whom founded their respective political parties.
There are conflicting sources for both sides claiming to have formed the majority in Zadar in this period. The archives of the official Austro-Hungarian censuses conducted around the end of 19th century show that Italian was the primary language spoken by the majority of the people in the city (9,018 Italians and 2,551 Croatians in 1900), but only by a third of the population in the entire county (9,234 vs. 21,753 the same year).
During the 19th century, the conflict between Zadar's Italian and Croatian communities grew in intensity and changed its nature. Until the beginning of the century it had been of moderate intensity and mainly of a class nature (under Venetian rule the Italians were employed in the most profitable activities, such as trade and administration). With the development of the modern concept of national identity across Europe, national conflicts started to mark the political life of Zadar.
After 1848, Italian and Croatian nationalistic ideas arrived in the city, which became divided between the Croats and the Italians, both of whom founded their respective political parties.
There are conflicting sources for both sides claiming to have formed the majority in Zadar in this period. The archives of the official Austro-Hungarian censuses conducted around the end of 19th century show that Italian was the primary language spoken by the majority of the people in the city (9,018 Italians and 2,551 Croatians in 1900), but only by a third of the population in the entire county (9,234 vs. 21,753 the same year).
During the 19th century, the conflict between Zadar's Italian and Croatian communities grew in intensity and changed its nature. Until the beginning of the century it had been of moderate intensity and mainly of a class nature (under Venetian rule the Italians were employed in the most profitable activities, such as trade and administration). With the development of the modern concept of national identity across Europe, national conflicts started to mark the political life of Zadar.
 During the second part of the 19th century, Zadar was subject to the same policy enacted by the
During the second part of the 19th century, Zadar was subject to the same policy enacted by the
 Nazi Germany, Germany, Italy, and other Axis Powers, Invasion of Yugoslavia, invaded the Kingdom of Yugoslavia on 6 April 1941. Zadar held a force of 9,000 and was one of the starting points of the invasion. The force reached Šibenik and Split on 15 April (2 days before surrender). Civilians were previously evacuated to Ancona . Occupying Mostar and Dubrovnik, on 17 April they met invading troops that had started out from Italian-occupied Albania. On 17 April the Yugoslav government surrendered, faced with the Wehrmacht's overwhelming superiority.
Benito Mussolini, Mussolini required the newly formed Nazi puppet-state, the so-called Independent State of Croatia (NDH) to hand over almost all of Dalmatia (including Split) to Italy under the Treaties of Rome (1941), Rome Treaties.
The city became the center of a new Italian territorial entity, the Governorate of Dalmatia, including the enlarged province of Zara (now Zadar), the province of Cattaro (now Kotor), and the province of Spalato (Split, Croatia, Split).
Under Italian rule, the Croats were subjected to a policy of forced assimilation. This created immense resentment among the Yugoslav people. The Yugoslav Partisans, Yugoslav Partisan movement took root in Zadar, even though more than 70% of population of Zadar was Italian.
After Mussolini was removed from power on 25 July 1943, Armistice with Italy, Italy signed an armistice with the Allies, which was announced on 8 September 1943, and the Italian army collapsed. Then on 12 September 1943, Gran Sasso raid, Mussolini was rescued by the Germans, and formed the Nazi-puppet Italian Social Republic. German troops (114th Jäger Division) entered Zadar on 10 September and took over. This avoided a temporary liberation by Partisans, as was the case in Split and Šibenik. Zadar was placed under the control of the Italian Social Republic.
The NDH proclaimed the Treaty of Rome to be void and occupied Dalmatia with German support. But the NDH was prevented from taking over Zadar on the grounds that Zadar itself was not subject to the conditions of the 1941 Treaty of Rome. Despite this, NDH leader Ante Pavelić designated Zadar as the capital of the Sidraga-Ravni Kotari County, although the county administrator could not enter the city.
During World War II, Zadar was Bombing of Zadar in World War II, bombed by the Allies, from November 1943 to October 1944. Estimated fatalities range from under 1,000, up to as many as 4,000 of the city's 20,000 inhabitants. Over the course of the bombing, 80% of the city's buildings were destroyed. Zadar has been called the "Dresden of the Adriatic" because of perceived similarities to the Bombing of Dresden in World War II, Allied bombing of Dresden.
In late October 1944, the German army and most of the Italian civilian administration abandoned the city, except the Vice Prefect Giacomo Vuxani. On 31 October 1944, the Yugoslav Partisans, Partisans seized the city, until then a part of Mussolini's Italian Social Republic. At the start of World War II, Zadar had a population of 24,000; by the end of 1944, this had decreased to 6,000. Though controlled by the Partisans, Zadar remained under nominal Italian sovereignty until the Paris Peace Treaties, 1947, Paris Peace Treaties that took effect on 15 September 1947. After the war Dalmatian Italians of Zadar left Yugoslavia towards Italy (Istrian-Dalmatian exodus).
Nazi Germany, Germany, Italy, and other Axis Powers, Invasion of Yugoslavia, invaded the Kingdom of Yugoslavia on 6 April 1941. Zadar held a force of 9,000 and was one of the starting points of the invasion. The force reached Šibenik and Split on 15 April (2 days before surrender). Civilians were previously evacuated to Ancona . Occupying Mostar and Dubrovnik, on 17 April they met invading troops that had started out from Italian-occupied Albania. On 17 April the Yugoslav government surrendered, faced with the Wehrmacht's overwhelming superiority.
Benito Mussolini, Mussolini required the newly formed Nazi puppet-state, the so-called Independent State of Croatia (NDH) to hand over almost all of Dalmatia (including Split) to Italy under the Treaties of Rome (1941), Rome Treaties.
The city became the center of a new Italian territorial entity, the Governorate of Dalmatia, including the enlarged province of Zara (now Zadar), the province of Cattaro (now Kotor), and the province of Spalato (Split, Croatia, Split).
Under Italian rule, the Croats were subjected to a policy of forced assimilation. This created immense resentment among the Yugoslav people. The Yugoslav Partisans, Yugoslav Partisan movement took root in Zadar, even though more than 70% of population of Zadar was Italian.
After Mussolini was removed from power on 25 July 1943, Armistice with Italy, Italy signed an armistice with the Allies, which was announced on 8 September 1943, and the Italian army collapsed. Then on 12 September 1943, Gran Sasso raid, Mussolini was rescued by the Germans, and formed the Nazi-puppet Italian Social Republic. German troops (114th Jäger Division) entered Zadar on 10 September and took over. This avoided a temporary liberation by Partisans, as was the case in Split and Šibenik. Zadar was placed under the control of the Italian Social Republic.
The NDH proclaimed the Treaty of Rome to be void and occupied Dalmatia with German support. But the NDH was prevented from taking over Zadar on the grounds that Zadar itself was not subject to the conditions of the 1941 Treaty of Rome. Despite this, NDH leader Ante Pavelić designated Zadar as the capital of the Sidraga-Ravni Kotari County, although the county administrator could not enter the city.
During World War II, Zadar was Bombing of Zadar in World War II, bombed by the Allies, from November 1943 to October 1944. Estimated fatalities range from under 1,000, up to as many as 4,000 of the city's 20,000 inhabitants. Over the course of the bombing, 80% of the city's buildings were destroyed. Zadar has been called the "Dresden of the Adriatic" because of perceived similarities to the Bombing of Dresden in World War II, Allied bombing of Dresden.
In late October 1944, the German army and most of the Italian civilian administration abandoned the city, except the Vice Prefect Giacomo Vuxani. On 31 October 1944, the Yugoslav Partisans, Partisans seized the city, until then a part of Mussolini's Italian Social Republic. At the start of World War II, Zadar had a population of 24,000; by the end of 1944, this had decreased to 6,000. Though controlled by the Partisans, Zadar remained under nominal Italian sovereignty until the Paris Peace Treaties, 1947, Paris Peace Treaties that took effect on 15 September 1947. After the war Dalmatian Italians of Zadar left Yugoslavia towards Italy (Istrian-Dalmatian exodus).
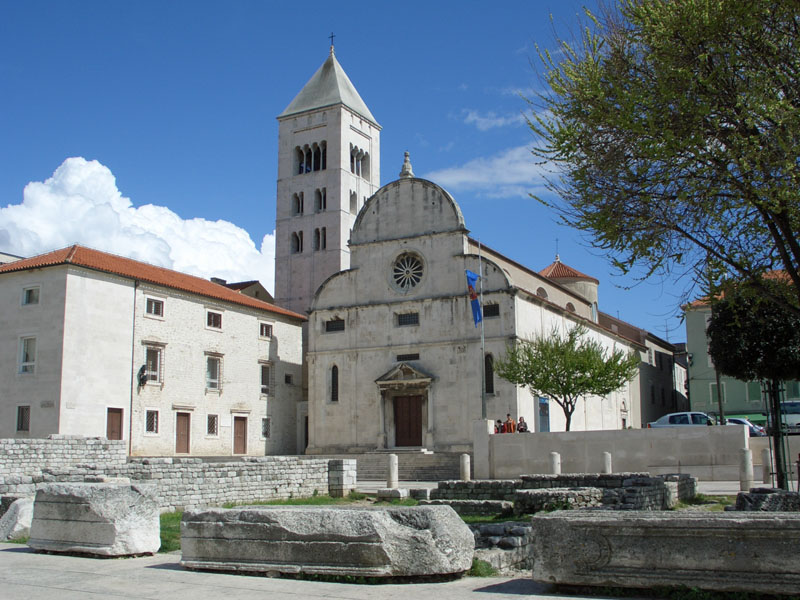



 During the Middle Ages, Zadar fully gained its urban aspect, which has been maintained until today. In the first half of the 16th century, Venice fortified the town with a new system of defensive walls on the side facing land. In the course of the century architectural building in the
During the Middle Ages, Zadar fully gained its urban aspect, which has been maintained until today. In the first half of the 16th century, Venice fortified the town with a new system of defensive walls on the side facing land. In the course of the century architectural building in the
 The first university of Zadar was mentioned in writing as early as in 1396 and it was a part of a Dominican Order, Dominican monastery. It closed in 1807.
Between the 15th and 17th centuries Zadar was an important Italian Renaissance, Renaissance center, producing an array of Italian Dalmatians, Italian Dalmatia architects, sculptors, painters and scholars such as Giorgio da Sebenico, Luciano Laurana, Laurana and Francesco Laurana, Giorgio Ventura, Andrea Meldolla and Giovanni Francesco Fortunio (who wrote the first Italian grammar book).
Zadar was, along with Split, Croatia, Split and Dubrovnik, also one of the centres of the development of Croatian literature. The 15th and 16th centuries were marked by important activities of Croatians writing in the national language: Jerolim Vidolić, Petar Zoranić (who wrote the first Croatian novel, Planine), Brne Karnarutić, Juraj Baraković, Šime Budinić.
Under French rule (1806–1810), the first Dalmatian newspaper ''Il Regio Dalmata – Kraglski Dalmatin'' was published in Zadar. It was printed in Italian and Croatian; this last used for the first time in a newspaper.
In the second half of the 19th century, Zadar was a centre of the movement for the cultural and national revivals in Dalmatia (Italian and Croatian).
Today Zadar's cultural institutions include:
* The Croatian Theatre House
* The National Museum
* The Archaeological Museum (established in 1830)
* The Museum of Ancient Glass
* The University of Zadar (founded in 1396, active until 1807 and refounded in 2002)
* The Maritime Museum
* Permanent Exhibition of Sacral Art
* Croatian Singing Musical Society Zoranić (established 1885)
* Musical Evenings in St. Donatus (established 1961)
* International Choirs Competition (established 1997)
* Arsenal Zadar
The first university of Zadar was mentioned in writing as early as in 1396 and it was a part of a Dominican Order, Dominican monastery. It closed in 1807.
Between the 15th and 17th centuries Zadar was an important Italian Renaissance, Renaissance center, producing an array of Italian Dalmatians, Italian Dalmatia architects, sculptors, painters and scholars such as Giorgio da Sebenico, Luciano Laurana, Laurana and Francesco Laurana, Giorgio Ventura, Andrea Meldolla and Giovanni Francesco Fortunio (who wrote the first Italian grammar book).
Zadar was, along with Split, Croatia, Split and Dubrovnik, also one of the centres of the development of Croatian literature. The 15th and 16th centuries were marked by important activities of Croatians writing in the national language: Jerolim Vidolić, Petar Zoranić (who wrote the first Croatian novel, Planine), Brne Karnarutić, Juraj Baraković, Šime Budinić.
Under French rule (1806–1810), the first Dalmatian newspaper ''Il Regio Dalmata – Kraglski Dalmatin'' was published in Zadar. It was printed in Italian and Croatian; this last used for the first time in a newspaper.
In the second half of the 19th century, Zadar was a centre of the movement for the cultural and national revivals in Dalmatia (Italian and Croatian).
Today Zadar's cultural institutions include:
* The Croatian Theatre House
* The National Museum
* The Archaeological Museum (established in 1830)
* The Museum of Ancient Glass
* The University of Zadar (founded in 1396, active until 1807 and refounded in 2002)
* The Maritime Museum
* Permanent Exhibition of Sacral Art
* Croatian Singing Musical Society Zoranić (established 1885)
* Musical Evenings in St. Donatus (established 1961)
* International Choirs Competition (established 1997)
* Arsenal Zadar
 The administrative area of the City of Zadar includes the nearby villages of Babindub, Crno, Kožino and Petrčane, as well as the islands of Ist (island), Ist, Iž, Molat, Olib, Premuda, Rava (island), Rava and Silba. The total city area, including the islands, covers 194 km2.
Zadar is divided into 21 local districts: Arbanasi, Bili Brig, Bokanjac, Brodarica, Crvene Kuće, Diklo, Dračevac, Jazine I, Jazine II, Maslina, Novi Bokanjac, Poluotok, Ploča, Puntamika, Ričina, Sinjoretovo, Smiljevac, Stanovi, Vidikovac, Višnjik, Voštarnica.
The current mayor of Zadar is Branko Dukić (Croatian Democratic Union, HDZ). He was elected for a second term on 2021 Croatian local elections, local elections held on 21 May 2021. The City Council is composed of 27 representatives.
The administrative area of the City of Zadar includes the nearby villages of Babindub, Crno, Kožino and Petrčane, as well as the islands of Ist (island), Ist, Iž, Molat, Olib, Premuda, Rava (island), Rava and Silba. The total city area, including the islands, covers 194 km2.
Zadar is divided into 21 local districts: Arbanasi, Bili Brig, Bokanjac, Brodarica, Crvene Kuće, Diklo, Dračevac, Jazine I, Jazine II, Maslina, Novi Bokanjac, Poluotok, Ploča, Puntamika, Ričina, Sinjoretovo, Smiljevac, Stanovi, Vidikovac, Višnjik, Voštarnica.
The current mayor of Zadar is Branko Dukić (Croatian Democratic Union, HDZ). He was elected for a second term on 2021 Croatian local elections, local elections held on 21 May 2021. The City Council is composed of 27 representatives.
 There are nine primary education, primary schools and 16 secondary education, secondary schools, including six gymnasium (school), gymnasiums, in Zadar.
There are nine primary education, primary schools and 16 secondary education, secondary schools, including six gymnasium (school), gymnasiums, in Zadar.

 The basketball club is KK Zadar, the football club NK Zadar, and the local handball club RK Zadar. The bowling club Kuglački klub Zadar is also very successful. Zadar is also the hometown of Croatian team handball, handball player Ivan Ninčević and soccer, football players Luka Modrić, Dado Pršo, Šime Vrsaljko and Danijel Subašić.
Other Sports:
Badminton: Badminton club Zadar
The basketball club is KK Zadar, the football club NK Zadar, and the local handball club RK Zadar. The bowling club Kuglački klub Zadar is also very successful. Zadar is also the hometown of Croatian team handball, handball player Ivan Ninčević and soccer, football players Luka Modrić, Dado Pršo, Šime Vrsaljko and Danijel Subašić.
Other Sports:
Badminton: Badminton club Zadar
Zadar Tourist Board
ZD portal
City of Zadar official web page
{{Authority control Zadar, Articles containing video clips Cities and towns in Croatia Illyrian Croatia Kingdom of Dalmatia Mediterranean port cities and towns in Croatia Populated coastal places in Croatia Populated places established in the 9th century BC Populated places in Zadar County Ports and harbours of Croatia Cities in ancient Illyria Roman towns and cities in Croatia Territories of the Republic of Venice Former exclaves
Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
and Italian: ); see also other names
Other often refers to:
* Other (philosophy), a concept in psychology and philosophy
Other or The Other may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''The Other'' (1913 film), a German silent film directed by Max Mack
* ''The Other'' (1930 film), ...
), is the oldest continuously inhabited Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
n city. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar serves as the seat of Zadar County and of the wider northern Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
n region. The city proper covers with a population of 75,082 , making it the second-largest city of the region of Dalmatia and the fifth-largest city in the country.
Today, Zadar is a historical center of Dalmatia, Zadar County's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, educational, and transportation centre. Zadar is also the episcopal see
An episcopal see is, in a practical use of the phrase, the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, mak ...
of the Archdiocese of Zadar
The Archdiocese of Zadar ( hr, Zadarska nadbiskupija; la, Archidioecesis Iadrensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic church in Croatia.The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper ''The Sunday Times'' (fou ...
'' and "Croatia's new capital of cool" by ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
''.
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
's World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
list included the fortified city of Zadar as part of Venetian Works of Defence between 15th and 17th centuries: ''Stato da Terra'' – western ''Stato da Mar'' in 2017.
Etymology and historical names
The name of the city of Zadar emerged as ''Iadera'' and ''Iader'' in ancient times, possibly ‘’’Iavdera/ Ia·vídera’’’ (or a slightly corrupted version as Iaudera), most likely drawing from the ancient school of thought dealing with angles and levels of SIGHT, but the origin of the name is older. It was most probably related to a hydrographical term, coined by an ancient Mediterranean people and their Pre-Indo-European language. They transmitted it to later settlers, theLiburnians
The Liburnians or Liburni ( grc, Λιβυρνοὶ) were an ancient tribe inhabiting the district called Liburnia, a coastal region of the northeastern Adriatic between the rivers ''Arsia'' ( Raša) and ''Titius'' ( Krka) in what is now Croatia ...
. The name of the Liburnian settlement was first mentioned by a Greek inscription from Pharos ( Stari grad) on the island of Hvar in 384 BC, where the citizens of Zadar were noted as (''Iadasinoi''). According to the Greek source Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax the city was (''Idassa''), probably a Greek transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
of the original Liburnian expression.
During Antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
the name was often recorded in sources in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
in two forms: ''Iader'' in the inscriptions and in the writings of classic writers, ''Iadera'' predominantly among the late Antiquity writers, while usual ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
s were ''Iadestines'' and ''Iadertines''. The accent was on the first syllable in both Iader and Iadera forms, which influenced the early-Medieval Dalmatian forms ''Jadra'', ''Jadera'' and ''Jadertina'', where the accent kept its original place.
In Dalmatian, ''Jadra'' (''Jadera'') was pronounced ''Zadra'' (''Zadera''), due to the phonetic transformation of ''Ja''- to ''Za''-. That change was also reflected in the Croatian name ''Zadar'' (recorded as ''Zader'' in the 12th century), developed from masculine ''Zadъrъ''. An ethnonym graphic ''Jaderani'' from the legend of Saint Chrysogonus in the 9th century, was identical to the initial old-Slavic form ''Zadъrane'', or Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
Croatian ''Zadrani''.
The Dalmatian names ''Jadra'', ''Jadera'' were transferred to other languages; in Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
(hyper-urbanism in the 9th century) and , Hungarian , Tuscan ''Giara'', Latin ''Iadora'' and ''Diadora'' (Constantine VII
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Emperor of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Kar ...
in ''De Administrando Imperio
''De Administrando Imperio'' ("On the Governance of the Empire") is the Latin title of a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Eastern Roman Emperor Constantine VII. The Greek title of the work is ("To yown son Romanos"). It is a domes ...
'', 10th century, probably an error in the transcription of ), Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligib ...
''Jadres'' (Geoffroy de Villehardouin in the chronicles of the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
in 1202), Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
''Jādhara'' () and ''Jādara'' () ( Al-Idrisi, 12th century), ''Iadora'' (Guido, 12th century), Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
''Jazara'', ''Jara'', ''Sarra'' (14th century) and the others.
Jadera became Zara when it fell under the authority of the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
in the 15th century. Zara was later used by the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
in the 19th century, but it was provisionally changed to Zadar/Zara from 1910 to 1920; from 1920 to 1947 the city became part of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
as Zara, and finally was named ''Zadar'' in 1947.
Geography
 Zadar faces the islands of Ugljan and Pašman (part of the Zadar Archipelago), from which it is separated by the narrow Zadar Strait. The promontory on which the old city stands used to be separated from the mainland by a deep moat which has since been filled. The harbour, to the north-east of the town, is safe and spacious.
Zadar faces the islands of Ugljan and Pašman (part of the Zadar Archipelago), from which it is separated by the narrow Zadar Strait. The promontory on which the old city stands used to be separated from the mainland by a deep moat which has since been filled. The harbour, to the north-east of the town, is safe and spacious.
Climate
Zadar has a borderline humid subtropical (''Cfa'') andMediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
(''Csa''). Zadar has mild, wet winters and very warm, humid summers. July and August are the hottest months, with an average high temperature around . The highest temperature ever was on 5 August 2017 at the Zadar Zemunik station (records since 1981) and at the old Zadar climate station on 6 August 2022 (records since 1961). Temperatures can consistently reach over during the summer months, but during spring and autumn may also reach almost every year. Temperatures below are rare, and are not maintained for more than a few days. January is the coldest month, with an average temperature around . The recorded the lowest temperature ever in Zadar was on 28 February 2018 at the Zadar Zemunik weather station and on 23 January 1963 at the old Zadar climate station. Through July and August temperature has never dropped below . October and November are the wettest months, with a total precipitation of about , respectively. July is the driest month, with a total precipitation of around . Winter is the wettest season, however it can rain in Zadar at any time of the year. Snow is exceedingly rare, but it may fall in December, January, February and much more rarely in March. On average Zadar has 1.4 days of snow a year, but it is more likely that the snow does not fall. Also the sea temperature is from in February to in July and August, but is possible to swim from May until October, sometimes even by November. Sometimes in February the sea temperature can drop to only and in July exceed .
History
Prehistory
The district of present-day Zadar has been populated since prehistoric times. The earliest evidence of human life comes from the LateStone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
, while numerous settlements have been dated as early as the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
. Before the Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo ...
, the area was inhabited by an ancient Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
people of a pre-Indo-European culture. They assimilated with the Indo-Europeans who settled between the 4th and 2nd millennium BC into a new ethnical unity, that of the Liburnians
The Liburnians or Liburni ( grc, Λιβυρνοὶ) were an ancient tribe inhabiting the district called Liburnia, a coastal region of the northeastern Adriatic between the rivers ''Arsia'' ( Raša) and ''Titius'' ( Krka) in what is now Croatia ...
. Zadar was a Liburnian settlement, laid out in the 9th century BC, built on a small stone islet and embankments where the old city stands and tied to the mainland by the overflown narrow isthmus, which created a natural port in its northern strait.
Antiquity
The Liburnians, an Illyrian tribe, were known as great sailors and merchants, but also had a reputation for piracy in the later years. By the 7th century BC, Zadar had become an important centre for their trading activities with thePhoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns, Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, rou ...
, Ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cultu ...
and other Mediterranean peoples. Its population at that time is estimated at 2,000. From the 9th to the 6th century there was certain cultural unity in the Adriatic Sea, with the general Liburninan seal, whose naval supremacy meant both political and economical authority through several centuries. Due to its geographical position, Zadar developed into a main seat of the Liburnian thalassocracy and took a leading role in the Liburnian ''tetradekapolis'', an organization of 14 communes.
The people of Zadar, ''Iadasinoi'', were first mentioned in 384 BC as the allies of the natives of Hvar and the leaders of an eastern Adriatic coast coalition in the fight against the Greek colonizers. An expedition of 10,000 men in 300 ships sailed out from Zadar and laid siege to the Greek colony Pharos
The Lighthouse of Alexandria, sometimes called the Pharos of Alexandria (; Ancient Greek: ὁ Φάρος τῆς Ἀλεξανδρείας, contemporary Koine ), was a lighthouse built by the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, during the re ...
in the island of Hvar, but the Syracusan
Syracuse ( ; it, Siracusa ; scn, Sarausa ), ; grc-att, Συράκουσαι, Syrákousai, ; grc-dor, Συράκοσαι, Syrā́kosai, ; grc-x-medieval, Συρακοῦσαι, Syrakoûsai, ; el, label=Modern Greek, Συρακούσε� ...
fleet of ''Dionysus'' was alerted and attacked the siege fleet. The naval victory went to the Greeks which allowed them relatively safer further colonization in the southern Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ...
.
 The archaeological remains have shown that the main centres of Liburnian territorial units or municipalities were already urbanized in the last centuries BC; before the Roman conquest, Zadar held a territory of more than in the 2nd century BC.
In the middle of the 2nd century BC, the Romans began to gradually invade the region. Although being first Roman enemies in the Adriatic Sea, the Liburnians, mostly stood aside in more than 230 years of Roman wars with the Illyrians, to protect their naval and trade connections in the sea. In 59 BC, Illyricum was assigned as a ''provincia'' (zone of responsibility) to
The archaeological remains have shown that the main centres of Liburnian territorial units or municipalities were already urbanized in the last centuries BC; before the Roman conquest, Zadar held a territory of more than in the 2nd century BC.
In the middle of the 2nd century BC, the Romans began to gradually invade the region. Although being first Roman enemies in the Adriatic Sea, the Liburnians, mostly stood aside in more than 230 years of Roman wars with the Illyrians, to protect their naval and trade connections in the sea. In 59 BC, Illyricum was assigned as a ''provincia'' (zone of responsibility) to Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
and Liburnian Iadera became a Roman municipium
In ancient Rome, the Latin term (pl. ) referred to a town or city. Etymologically, the was a social contract among ("duty holders"), or citizens of the town. The duties () were a communal obligation assumed by the in exchange for the privi ...
.
The Liburnian naval force was dragged into the Roman civil war between Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
and Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
in 49 BC, partially by force, partially because of the local interests of the participants, the Liburnian cities. Caesar was supported by the urban Liburnian centres, like ''Iader'' (Zadar), ''Aenona'' ( Nin) and ''Curicum'' (Krk
Krk (; it, Veglia; ruo, Krk; dlm, label= Vegliot Dalmatian, Vikla; la, Curicta; grc-gre, Κύρικον, Kyrikon) is a Croatian island in the northern Adriatic Sea, located near Rijeka in the Bay of Kvarner and part of Primorje-Gorski Kota ...
), while the city of ''Issa'' ( Vis) and the rest of the Liburnians gave their support to Pompey. In 49 BC near the island of Krk, the "Navy of Zadar", equipped by the fleets of a few Liburnian cities and supported by some Roman ships, lost an important naval battle against Pompey supporting the "Liburnian navy". The civil war was prolonged until the end of 48 BC, when Caesar rewarded his supporters in Liburnian ''Iader'' and Dalmatian ''Salona
Salona ( grc, Σάλωνα) was an ancient city and the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia. Salona is located in the modern town of Solin, next to Split, in Croatia.
Salona was founded in the 3rd century BC and was mostly destroyed in t ...
'', by giving the status of the Roman colonies
Colonies in antiquity were post-Iron Age city-states founded from a mother-city (its "metropolis"), not from a territory-at-large. Bonds between a colony and its metropolis remained often close, and took specific forms during the period of classic ...
to their communities. Thus the city was granted the title ''colonia Iulia Iader'', after its founder, and in the next period some of the Roman colonists (mostly legionary
The Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius'', plural ''legionarii'') was a professional heavy infantryman of the Roman army after the Marian reforms. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the late Republi ...
veterans) settled there.
The real establishment of the Roman province of Illyricum occurred not earlier than 33 BC and Octavian's military campaign in Illyria and Liburnia, when the Liburnians finally lost their naval independence and their galleys and sailors were incorporated into the Roman naval fleets.
 From the early days of Roman rule, Zadar gained its Roman urban character and developed into one of the most flourishing centres on the eastern Adriatic coast, a state of affairs which lasted for several hundred years. The town was organised according to the typical Roman street system with a rectangular street plan, a forum, thermae, a sewage and water supply system that came from lake Vrana, by way of a long aqueduct. It did not play a significant role in the Roman administration of Dalmatia, although the archaeological finds tell us about a significant growth of economy and culture.
From the early days of Roman rule, Zadar gained its Roman urban character and developed into one of the most flourishing centres on the eastern Adriatic coast, a state of affairs which lasted for several hundred years. The town was organised according to the typical Roman street system with a rectangular street plan, a forum, thermae, a sewage and water supply system that came from lake Vrana, by way of a long aqueduct. It did not play a significant role in the Roman administration of Dalmatia, although the archaeological finds tell us about a significant growth of economy and culture.
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
did not bypass the Roman province of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
. Already by the end of the 3rd century Zadar had its own bishop and founding of its Christian community took place; a new religious centre was built north of the forum together with a basilica and a baptistery, as well as other ecclesiastical buildings. According to some estimates, in the 4th century it had probably around ten thousand citizens, including the population from its ''ager
Ager or AGER may refer to:
*Ager (surname)
*Ager (river), a river in Upper Austria
*Àger, a municipality in Catalonia, Spain
*Viscounty of Àger, a medieval Catalan jurisdiction that branched off the County of Urgell
*Ager, California, unincorpo ...
'', the nearby islands and hinterland, an admixture of the indigenous Liburnians and Roman colonists.
Early Middle Ages
During theMigration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
and the Barbarian invasions, Zadar was one of the remaining Dalmatian city-states, but it stagnated. In 441 and 447 Dalmatia was ravaged by the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
, after the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rul ...
, in 481 Dalmatia became part of the Ostrogothic kingdom, which, besides Italy, already included the more northerly parts of Illyricum, i.e. Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
and Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celts, Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were th ...
.
In the 5th century, under the rule of the Ostrogothic Kingdom, Zadar became poor with many civic buildings ruined due to its advanced age. About the same time (6th century) it was hit by an earthquake, which destroyed entire complexes of monumental Roman architecture, whose parts would later serve as material for building houses. This caused a loss of population and created demographic changes in the city, then gradually repopulated by the inhabitants from its hinterland. However, during six decades of Gothic rule, the Goths saved those old Roman Municipal institutions that were still in function, while religious life in Dalmatia even intensified in the last years, so that there was a need for the foundation of additional bishoprics.
In 536, the Byzantine emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
Justinian the Great
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
started a military campaign to reconquer the territories of the former Western Empire (see Gothic War Gothic War may refer to:
*Gothic War (248–253), battles and plundering carried out by the Goths and their allies in the Roman Empire.
*Gothic War (367–369), a war of Thervingi against the Eastern Roman Empire in which the Goths retreated to Mont ...
); and in 553 Zadar passed to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. In 568, Dalmatia was devastated by an Avar invasion; although further waves of attacks by Avar and Slav tribes kept up the pressure, it was the only city which survived due to its protective belt of inland plains. The Dalmatian capital Salona
Salona ( grc, Σάλωνα) was an ancient city and the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia. Salona is located in the modern town of Solin, next to Split, in Croatia.
Salona was founded in the 3rd century BC and was mostly destroyed in t ...
was captured and destroyed in the 640s, so Zadar became the new seat of the Byzantine archonty of Dalmatia, territorially reduced to a few coastal cities with their agers and municipal lands at the coast and the islands nearby. The prior of Zadar had jurisdiction over all Byzantine Dalmatia, so Zadar enjoyed metropolitan status at the eastern Adriatic coast. At this time rebuilding began to take place in the city.
 At the beginning of the 9th century the Zadar bishop Donatus and the city duke Paul mediated in the dispute between the
At the beginning of the 9th century the Zadar bishop Donatus and the city duke Paul mediated in the dispute between the Holy Roman empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
under Pepin and the Byzantine Empire. The Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
held Zadar for a short time, but the city was returned to Byzantium by a decision of the 812 Treaty of Aachen.
Zadar's economy revolved around the sea, fishing and sea trade in the first centuries of the Middle Ages. Thanks to saved Antique ager, adjusted municipal structure and a new strategic position, it became the most important city between the Kvarner islands and Kaštela
Kaštela (;) is a town in Split-Dalmatia County. The town is an agglomeration of seven individual settlements which are administered as a single municipality with populations individually ranging from 3,000 to 7,000 residents. The town is locat ...
Bay. Byzantine Dalmatia was not territorially unified, but an alliance of city municipalities headed by Zadar, and the large degree of city autonomy allowed the development of Dalmatian cities as free communes. Forced to turn their attention seawards, the inhabitants of Zadar focused on shipping, and the city became a naval power to rival Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
. The citizens were Dalmatian speakers, but from the 7th century Croatian started to spread in the region, becoming predominant in the inland and the islands to the end of the 9th century.
The Mediterranean and Adriatic cities developed significantly during a period of peace from the last decades of the 9th to the middle of the 10th century. Especially favourable conditions for navigation in the Adriatic Sea occurred since the Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia Pe ...
raids had finished. Also the adjustment of relations with the Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, G ...
enabled Zadar merchants to trade with its rich agriculture hinterland where the Kingdom of Croatia Kingdom of Croatia may refer to:
* Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), an independent medieval kingdom
* Croatia in personal union with Hungary (1102–1526), a kingdom in personal union with the Kingdom of Hungary
* Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg) (152 ...
had formed, and trade and political links with Zadar began to develop. Croatian settlers began to arrive, becoming commonplace by the 10th century, occupying all city classes, as well as important posts, like those of prior, judge, priest and others. In 925, Tomislav
Tomislav (, ) is a masculine given name of Slavic origin, that is widespread amongst the South Slavs.
The meaning of the name ''Tomislav'' is thought to have derived from the Old Slavonic verb "'' tomiti''" or "'' tomit" meaning to "''languish ...
, the Duke of Croatian Dalmatia, united Croatian Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
and Pannonia establishing the Croatian Kingdom.
Following the dynastic struggle between the descendants of king Stjepan Držislav Stjepan is a Croatian masculine given name, variant of Stephen, used by ijekavian speakers.
In Croatia, the name Stjepan was among the top ten most common masculine given names in the decades up to 1969.
Notable people with the name include:
* S ...
after his death in 997, the city was besieged
Besieged may refer to:
* the state of being under siege
* ''Besieged'' (film), a 1998 film by Bernardo Bertolucci
{{disambiguation ...
in 998 by the army of the Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
emperor Samuel
Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the bibl ...
but managed to defend itself.
High Middle Ages
At the time of Zadar's medieval development, the city became a threat to Venice's ambitions, because of its strategic position at the centre of the eastern Adriatic coast. In 998, Zadar sought Venetian protection against the Neretvian pirates. The Venetians were quick to fully exploit this opportunity: in 998 a fleet commanded by DogePietro Orseolo II
Pietro II Orseolo (961−1009) was the Doge of Venice from 991 to 1009.
He began the period of eastern expansion of Venice that lasted for the better part of 500 years. He secured his influence in the Dalmatian Romanized settlements from the Croa ...
, after having defeated pirates, landed in Korčula and Lastovo. Dalmatia was taken by surprise and offered little serious resistance. Trogir was the exception and was subjected to Venetian rule only after a bloody struggle, whereas Dubrovnik was forced to pay tribute. Tribute previously paid by Zadar to Croatian kings, was redirected to Venice, a state of affairs which lasted for several years.
Zadar citizens started to work for the full independence of Zadar and from the 1030s the city was formally a vassal of the Byzantine Empire. The head of this movement was the mightiest Zadar patrician (post-Roman Europe), patrician family – the House of Madi, Madi. After negotiations with Byzantium, Zadar was attached to the Croatian state led by king Petar Krešimir IV of Croatia, Petar Krešimir IV in 1069. Later, after the death of king Dmitar Zvonimir in 1089 and ensuing dynastic run-ins, in 1105 Zadar accepted the rule of the first Croato-Hungarian king, Coloman, King of Hungary.
In the meantime Venice developed into a true trading force in the Adriatic and started attacks on Zadar. The city was repeatedly invaded by Venice between 1111 and 1154 and then once more between 1160 and 1183, when it finally rebelled, appealing to the Pope and to the Croato-Hungarian throne for protection.
 Zadar was especially devastated in 1202 after the Venetian Enrico Dandolo, Doge Enrico Dandolo used the crusaders, on their
Zadar was especially devastated in 1202 after the Venetian Enrico Dandolo, Doge Enrico Dandolo used the crusaders, on their Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
to Palestine (region), Palestine, to lay siege to the city. The crusaders were obliged to pay Venice for sea transport to Egypt. As they were not able to produce enough money, the Venetians used them to initiate the Siege of Zadar, when the city was ransacked, demolished and robbed. Emeric of Hungary, Emeric, king of Croatia and Hungary, condemned the crusade, because of an argument about the possible heresy committed by God's army in attacking a Christian city. Nonetheless, Zadar was devastated and captured, with the population escaping into the surrounding countryside. Pope Innocent III excommunicated the Venetians and crusaders involved in the siege.
Two years later (1204), under the leadership of the Croatian nobleman Domald of Sidraga, Domald from Šibenik, most of the refugees returned and liberated the city from what remained of the crusader force. In 1204 Domald was ''comes'' (duke) of Zadar, but the following year (1205) Venetian authority was re-established and a peace agreement signed with hard conditions for the citizens. The only profit which the Communal Council of Zadar derived from this was one third of the city's harbour taxes, probably insufficient even for the most indispensable communal needs.
 This did not break the spirit of the city, however. Its commerce was suffering due to a lack of autonomy under Venice, while it enjoyed considerable autonomy under the much more feudal Kingdom of Croatia-Hungary. A number of insurrections followed (1242–1243, 1320s, 1345–1346 – the latter resulted in a Siege of Zadar (1345–46), sixteen-month-long Venetian siege) which finally resulted in Zadar coming back under the crown of King Louis I of Hungary, Louis I of Croatia-Hungary under the Treaty of Zara, Treaty of Zadar, in 1358. After the War of Chioggia between Genoa and Venice, Chioggia concluded on 14 March 1381 an alliance with Zadar and Trogir against Venice, and finally Chioggia became better protected by Venice in 1412, because Šibenik became in 1412 the seat of the main customs office and the seat of the salt consumers office with a monopoly on the salt trade in Chioggia and on the whole
This did not break the spirit of the city, however. Its commerce was suffering due to a lack of autonomy under Venice, while it enjoyed considerable autonomy under the much more feudal Kingdom of Croatia-Hungary. A number of insurrections followed (1242–1243, 1320s, 1345–1346 – the latter resulted in a Siege of Zadar (1345–46), sixteen-month-long Venetian siege) which finally resulted in Zadar coming back under the crown of King Louis I of Hungary, Louis I of Croatia-Hungary under the Treaty of Zara, Treaty of Zadar, in 1358. After the War of Chioggia between Genoa and Venice, Chioggia concluded on 14 March 1381 an alliance with Zadar and Trogir against Venice, and finally Chioggia became better protected by Venice in 1412, because Šibenik became in 1412 the seat of the main customs office and the seat of the salt consumers office with a monopoly on the salt trade in Chioggia and on the whole Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
. After the death of Louis, Zadar recognized the rule of king Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Sigismund, and after him, that of Ladislaus of Naples. During his reign Croatia-Hungary was enveloped in a bloody civil war. In 1409, Venice, seeing that Ladislaus was about to be defeated, and eager to exploit the situation despite its relative military weakness, offered to buy his "rights" on Dalmatia for a mere 100,000 ducats. Knowing he had lost the region in any case, Ladislaus accepted. Zadar was, thus sold back to the Venetians for a paltry sum.
The population of Zadar during the Medieval period was predominantly Croatian, according to numerous archival documents, and Croatian was used in liturgy, as shown by the writings of cardinal Boson, who followed Pope Alexander III en route to Venice in 1177. When the papal ships took shelter in the harbour of Zadar, the inhabitants greeted the Pope by singing lauds and canticles in Croatian.
Even though interspersed by sieges and destruction, the time between the 11th and 14th centuries was the golden age of Zadar. Thanks to its political and trading achievements, and also to its skilled seamen, Zadar played an important role among the cities on the east coast of the Adriatic. This affected its appearance and culture: many churches, rich monasteries and palaces for powerful families were built, together with the Chest of Saint Simeon. One of the best examples of the culture and prosperity of Zadar at that time was the founding of the University of Zadar, built in 1396 by the Dominican Order (the oldest university in present-day Croatia).
15th to 18th centuries
 After the death of Louis I, Zadar came under the rule of Sigmund of Luxembourg and later Ladislaus of Naples, who, witnessing his loss of influence in Dalmatia, sold Zadar and his dynasty's rights to Dalmatia to Venice for 100,000 ducat (coin), ducats on 31 July 1409. Venice therefore obtained control over Zadar without a fight, but was confronted by the resistance and tensions of important Zadar families. These attempts were met with persecution and confiscation. Zadar remained the administrative seat of Dalmatia, but this time under the rule of Venice, which expanded over the whole Dalmatia, except the Republic of Ragusa/Dubrovnik. During that time Giorgio da Sebenico, a renaissance sculptor and architect, famous for his work on the Cathedral of Šibenik, was born in Zadar. Other important people followed, such as Luciano Laurana, Luciano and Francesco Laurana, known worldwide for their sculptures and buildings.
After the death of Louis I, Zadar came under the rule of Sigmund of Luxembourg and later Ladislaus of Naples, who, witnessing his loss of influence in Dalmatia, sold Zadar and his dynasty's rights to Dalmatia to Venice for 100,000 ducat (coin), ducats on 31 July 1409. Venice therefore obtained control over Zadar without a fight, but was confronted by the resistance and tensions of important Zadar families. These attempts were met with persecution and confiscation. Zadar remained the administrative seat of Dalmatia, but this time under the rule of Venice, which expanded over the whole Dalmatia, except the Republic of Ragusa/Dubrovnik. During that time Giorgio da Sebenico, a renaissance sculptor and architect, famous for his work on the Cathedral of Šibenik, was born in Zadar. Other important people followed, such as Luciano Laurana, Luciano and Francesco Laurana, known worldwide for their sculptures and buildings.
 The 16th and 17th centuries were noted in Zadar for Ottoman attacks. Ottomans captured the continental part of Zadar at the beginning of the 16th century and the city itself was all the time in the range of Turkish artillery. Due to that threat, the construction of a new system of castles and walls began. These defense systems changed the way the city looked. To make place for the pentagon castles many houses and churches were taken down, along with an entire suburb: Varoš of St. Martin. After the 40-year-long construction Zadar became the biggest fortified city in Dalmatia, empowered by a system of castles, bastions and canals filled with seawater. The city was supplied by the water from public city cisterns. During the complete makeover of Zadar, many new civic buildings were built, such as the City Lodge and City Guard on the Gospodski Square, several army barracks, but also some large new palaces.
In contrast to the insecurity and Ottoman sieges and destruction, an important culture evolved midst the city walls. During the 16th and the 17th centuries Zadar was still under the influence of the
The 16th and 17th centuries were noted in Zadar for Ottoman attacks. Ottomans captured the continental part of Zadar at the beginning of the 16th century and the city itself was all the time in the range of Turkish artillery. Due to that threat, the construction of a new system of castles and walls began. These defense systems changed the way the city looked. To make place for the pentagon castles many houses and churches were taken down, along with an entire suburb: Varoš of St. Martin. After the 40-year-long construction Zadar became the biggest fortified city in Dalmatia, empowered by a system of castles, bastions and canals filled with seawater. The city was supplied by the water from public city cisterns. During the complete makeover of Zadar, many new civic buildings were built, such as the City Lodge and City Guard on the Gospodski Square, several army barracks, but also some large new palaces.
In contrast to the insecurity and Ottoman sieges and destruction, an important culture evolved midst the city walls. During the 16th and the 17th centuries Zadar was still under the influence of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, which had created an environment in which Renaissance art, arts and Renaissance literature, literature could flourish, despite the ongoing conflicts outside the city walls. This period saw the rise of many important Italian Renaissance figures, such as the painters Giorgio Ventura and Andrea Meldolla, and the humanist scholar Giovanni Francesco Fortunio, who wrote the first Italian grammar book. Meanwhile, the activity of the Croatian writers and poets became prolific (Jerolim Vidolić, Petar Zoranić, Brne Karnarutić, Juraj Baraković, Šime Budinić).
During the continuous Ottoman danger the population stagnated by a significant degree along with the economy. During the 16th and 17th centuries several large-scale epidemics of bubonic plague erupted in the city. After more than 150 years of Turkish threat Zadar was not only scarce in population, but also in material wealth. Venice sent new colonists and, under the firm hand of archbishop Vicko Zmajević, the Arbanasi (Catholic Albanian refugees) settled in the city, forming a new suburb. Despite the shortage of money, the Teatro Nobile (Theater for Nobility) was built in 1783. It functioned for over 100 years.
19th and 20th centuries
 In 1797 with the Treaty of Campo Formio, the Republic of Venice, including Zadar, came under the Austrian Empire, Austrian crown. In 1806 it was briefly given to the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Kingdom of Italy, until in 1809 it was added to the French Illyrian Provinces. In November 1813 an Austrian force Siege of Zara (1813), blockaded the town with the assistance of two British Royal Navy frigates HMS Havannah (1811), HMS ''Havannah'' and HMS Weazel (1805), ''Weazle'' under the George Cadogan, 3rd Earl Cadogan, 3rd Earl of Cadogan. On 9 December the French garrison of Zadar capitulated, and by the end of the year all of Dalmatia was brought back under the control of the Austrian Empire. After the Congress of Vienna (1815) until 1918, the town (bilingual name ''Zara – Zadar'' ) remained part of the Austrian monarchy (Austria side after the compromise of 1867), head of the district of the same name, one of the 13 ''Bezirkshauptmannschaften'' in Kingdom of Dalmatia, Dalmatia. The Italian name was officially used before 1867. It remained also the capital of Dalmatia province (''Kronland'').
Although during the first half of the 19th century the city population stagnated due to low natural increase, the city started to spread from the old center; citizens from the old city created the new suburb of Stanovi in the north.
During the second half of the 19th century, there was constant increase of population due to economic growth and immigration. Under the pressure of the population increase, the city continued to spread to Voštarnica and Arbanasi quarters, and the bridge in the city port was built. Except being the administrative center of the province, agriculture, industry of liqueurs and trade were developed, many brotherhoods were established, similar to the Central European trade guilds. The southern city walls were torn down, new coastal facilities were built and Zadar became an ''open port''. As the city developed economically, it developed culturally. A large number of printshops, new libraries, archives, and theatres sprung up. At the end of the 19th century there was also stronger industrial development, with 27 small or big factories before the World War I.
In 1797 with the Treaty of Campo Formio, the Republic of Venice, including Zadar, came under the Austrian Empire, Austrian crown. In 1806 it was briefly given to the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Kingdom of Italy, until in 1809 it was added to the French Illyrian Provinces. In November 1813 an Austrian force Siege of Zara (1813), blockaded the town with the assistance of two British Royal Navy frigates HMS Havannah (1811), HMS ''Havannah'' and HMS Weazel (1805), ''Weazle'' under the George Cadogan, 3rd Earl Cadogan, 3rd Earl of Cadogan. On 9 December the French garrison of Zadar capitulated, and by the end of the year all of Dalmatia was brought back under the control of the Austrian Empire. After the Congress of Vienna (1815) until 1918, the town (bilingual name ''Zara – Zadar'' ) remained part of the Austrian monarchy (Austria side after the compromise of 1867), head of the district of the same name, one of the 13 ''Bezirkshauptmannschaften'' in Kingdom of Dalmatia, Dalmatia. The Italian name was officially used before 1867. It remained also the capital of Dalmatia province (''Kronland'').
Although during the first half of the 19th century the city population stagnated due to low natural increase, the city started to spread from the old center; citizens from the old city created the new suburb of Stanovi in the north.
During the second half of the 19th century, there was constant increase of population due to economic growth and immigration. Under the pressure of the population increase, the city continued to spread to Voštarnica and Arbanasi quarters, and the bridge in the city port was built. Except being the administrative center of the province, agriculture, industry of liqueurs and trade were developed, many brotherhoods were established, similar to the Central European trade guilds. The southern city walls were torn down, new coastal facilities were built and Zadar became an ''open port''. As the city developed economically, it developed culturally. A large number of printshops, new libraries, archives, and theatres sprung up. At the end of the 19th century there was also stronger industrial development, with 27 small or big factories before the World War I.
 After 1848, Italian and Croatian nationalistic ideas arrived in the city, which became divided between the Croats and the Italians, both of whom founded their respective political parties.
There are conflicting sources for both sides claiming to have formed the majority in Zadar in this period. The archives of the official Austro-Hungarian censuses conducted around the end of 19th century show that Italian was the primary language spoken by the majority of the people in the city (9,018 Italians and 2,551 Croatians in 1900), but only by a third of the population in the entire county (9,234 vs. 21,753 the same year).
During the 19th century, the conflict between Zadar's Italian and Croatian communities grew in intensity and changed its nature. Until the beginning of the century it had been of moderate intensity and mainly of a class nature (under Venetian rule the Italians were employed in the most profitable activities, such as trade and administration). With the development of the modern concept of national identity across Europe, national conflicts started to mark the political life of Zadar.
After 1848, Italian and Croatian nationalistic ideas arrived in the city, which became divided between the Croats and the Italians, both of whom founded their respective political parties.
There are conflicting sources for both sides claiming to have formed the majority in Zadar in this period. The archives of the official Austro-Hungarian censuses conducted around the end of 19th century show that Italian was the primary language spoken by the majority of the people in the city (9,018 Italians and 2,551 Croatians in 1900), but only by a third of the population in the entire county (9,234 vs. 21,753 the same year).
During the 19th century, the conflict between Zadar's Italian and Croatian communities grew in intensity and changed its nature. Until the beginning of the century it had been of moderate intensity and mainly of a class nature (under Venetian rule the Italians were employed in the most profitable activities, such as trade and administration). With the development of the modern concept of national identity across Europe, national conflicts started to mark the political life of Zadar.
 During the second part of the 19th century, Zadar was subject to the same policy enacted by the
During the second part of the 19th century, Zadar was subject to the same policy enacted by the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
in History of South Tyrol, South-Tyrol, the Austrian Littoral and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
and consisting in fostering the local German or Croatian culture at the expense of the Italian. In Zadar and generally throughout Dalmatia, the Austrian policy had the objective to reduce the possibility of any future territorial claim by the Kingdom of Italy.
Italy (1918–1947)
In 1915, Italy entered World War I under the provisions set in the Treaty of London (1915), Treaty of London. In exchange for its participation with the Triple Entente and in the event of victory, Italy was to obtain the following territory in northern Dalmatia, including Zadar, Šibenik and most of the Dalmatian islands, exceptKrk
Krk (; it, Veglia; ruo, Krk; dlm, label= Vegliot Dalmatian, Vikla; la, Curicta; grc-gre, Κύρικον, Kyrikon) is a Croatian island in the northern Adriatic Sea, located near Rijeka in the Bay of Kvarner and part of Primorje-Gorski Kota ...
and Rab. At the end of the war, Italian military forces invaded Dalmatia and seized control of Zara, with Admiral Enrico Millo being proclaimed the governor of Dalmatia.A. Rossi. ''The Rise of Italian Fascism: 1918–1922''. New York, New York, USA: Routledge, 2010. P. 47. Famous Italian nationalist Gabriele d'Annunzio supported the seizure of Dalmatia, and proceeded to Zadar in an Italian warship in December 1918.
During 1918, political life in Zadar intensified. The collapse of the Austro-Hungarian monarchy led to the renewal of national conflicts in the city. With the arrival of an Italian army of occupation in the city on 4 November 1918, the Italian faction gradually assumed control, a process which was completed on 5 December when it took over the governorship. With the Treaty of Versailles (10 January 1920) Italian claims on Dalmatia contained in the Treaty of London (1915), Treaty of London were nullified, but later on the agreements between the Kingdom of Italy and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes set in the Treaty of Rapallo, 1920, Treaty of Rapallo (12 November 1920) gave Zadar with other small local territories to Italy.
The Zadar enclave, a total of , included the city of Zadar, the municipalities of Bokanjac, Arbanasi, Crno, part of Diklo (a total of 51 km2 of territory and 17,065 inhabitants) and the islands of Lastovo and Palagruža (, 1,710 inhabitants). The territory was organized into a small Italian province, the province of Zara. According to the 1921 census, in the ''comune'' of Zara there were 12,075 Dalmatian Italians and 1,255 Croatians.
World War II
 Nazi Germany, Germany, Italy, and other Axis Powers, Invasion of Yugoslavia, invaded the Kingdom of Yugoslavia on 6 April 1941. Zadar held a force of 9,000 and was one of the starting points of the invasion. The force reached Šibenik and Split on 15 April (2 days before surrender). Civilians were previously evacuated to Ancona . Occupying Mostar and Dubrovnik, on 17 April they met invading troops that had started out from Italian-occupied Albania. On 17 April the Yugoslav government surrendered, faced with the Wehrmacht's overwhelming superiority.
Benito Mussolini, Mussolini required the newly formed Nazi puppet-state, the so-called Independent State of Croatia (NDH) to hand over almost all of Dalmatia (including Split) to Italy under the Treaties of Rome (1941), Rome Treaties.
The city became the center of a new Italian territorial entity, the Governorate of Dalmatia, including the enlarged province of Zara (now Zadar), the province of Cattaro (now Kotor), and the province of Spalato (Split, Croatia, Split).
Under Italian rule, the Croats were subjected to a policy of forced assimilation. This created immense resentment among the Yugoslav people. The Yugoslav Partisans, Yugoslav Partisan movement took root in Zadar, even though more than 70% of population of Zadar was Italian.
After Mussolini was removed from power on 25 July 1943, Armistice with Italy, Italy signed an armistice with the Allies, which was announced on 8 September 1943, and the Italian army collapsed. Then on 12 September 1943, Gran Sasso raid, Mussolini was rescued by the Germans, and formed the Nazi-puppet Italian Social Republic. German troops (114th Jäger Division) entered Zadar on 10 September and took over. This avoided a temporary liberation by Partisans, as was the case in Split and Šibenik. Zadar was placed under the control of the Italian Social Republic.
The NDH proclaimed the Treaty of Rome to be void and occupied Dalmatia with German support. But the NDH was prevented from taking over Zadar on the grounds that Zadar itself was not subject to the conditions of the 1941 Treaty of Rome. Despite this, NDH leader Ante Pavelić designated Zadar as the capital of the Sidraga-Ravni Kotari County, although the county administrator could not enter the city.
During World War II, Zadar was Bombing of Zadar in World War II, bombed by the Allies, from November 1943 to October 1944. Estimated fatalities range from under 1,000, up to as many as 4,000 of the city's 20,000 inhabitants. Over the course of the bombing, 80% of the city's buildings were destroyed. Zadar has been called the "Dresden of the Adriatic" because of perceived similarities to the Bombing of Dresden in World War II, Allied bombing of Dresden.
In late October 1944, the German army and most of the Italian civilian administration abandoned the city, except the Vice Prefect Giacomo Vuxani. On 31 October 1944, the Yugoslav Partisans, Partisans seized the city, until then a part of Mussolini's Italian Social Republic. At the start of World War II, Zadar had a population of 24,000; by the end of 1944, this had decreased to 6,000. Though controlled by the Partisans, Zadar remained under nominal Italian sovereignty until the Paris Peace Treaties, 1947, Paris Peace Treaties that took effect on 15 September 1947. After the war Dalmatian Italians of Zadar left Yugoslavia towards Italy (Istrian-Dalmatian exodus).
Nazi Germany, Germany, Italy, and other Axis Powers, Invasion of Yugoslavia, invaded the Kingdom of Yugoslavia on 6 April 1941. Zadar held a force of 9,000 and was one of the starting points of the invasion. The force reached Šibenik and Split on 15 April (2 days before surrender). Civilians were previously evacuated to Ancona . Occupying Mostar and Dubrovnik, on 17 April they met invading troops that had started out from Italian-occupied Albania. On 17 April the Yugoslav government surrendered, faced with the Wehrmacht's overwhelming superiority.
Benito Mussolini, Mussolini required the newly formed Nazi puppet-state, the so-called Independent State of Croatia (NDH) to hand over almost all of Dalmatia (including Split) to Italy under the Treaties of Rome (1941), Rome Treaties.
The city became the center of a new Italian territorial entity, the Governorate of Dalmatia, including the enlarged province of Zara (now Zadar), the province of Cattaro (now Kotor), and the province of Spalato (Split, Croatia, Split).
Under Italian rule, the Croats were subjected to a policy of forced assimilation. This created immense resentment among the Yugoslav people. The Yugoslav Partisans, Yugoslav Partisan movement took root in Zadar, even though more than 70% of population of Zadar was Italian.
After Mussolini was removed from power on 25 July 1943, Armistice with Italy, Italy signed an armistice with the Allies, which was announced on 8 September 1943, and the Italian army collapsed. Then on 12 September 1943, Gran Sasso raid, Mussolini was rescued by the Germans, and formed the Nazi-puppet Italian Social Republic. German troops (114th Jäger Division) entered Zadar on 10 September and took over. This avoided a temporary liberation by Partisans, as was the case in Split and Šibenik. Zadar was placed under the control of the Italian Social Republic.
The NDH proclaimed the Treaty of Rome to be void and occupied Dalmatia with German support. But the NDH was prevented from taking over Zadar on the grounds that Zadar itself was not subject to the conditions of the 1941 Treaty of Rome. Despite this, NDH leader Ante Pavelić designated Zadar as the capital of the Sidraga-Ravni Kotari County, although the county administrator could not enter the city.
During World War II, Zadar was Bombing of Zadar in World War II, bombed by the Allies, from November 1943 to October 1944. Estimated fatalities range from under 1,000, up to as many as 4,000 of the city's 20,000 inhabitants. Over the course of the bombing, 80% of the city's buildings were destroyed. Zadar has been called the "Dresden of the Adriatic" because of perceived similarities to the Bombing of Dresden in World War II, Allied bombing of Dresden.
In late October 1944, the German army and most of the Italian civilian administration abandoned the city, except the Vice Prefect Giacomo Vuxani. On 31 October 1944, the Yugoslav Partisans, Partisans seized the city, until then a part of Mussolini's Italian Social Republic. At the start of World War II, Zadar had a population of 24,000; by the end of 1944, this had decreased to 6,000. Though controlled by the Partisans, Zadar remained under nominal Italian sovereignty until the Paris Peace Treaties, 1947, Paris Peace Treaties that took effect on 15 September 1947. After the war Dalmatian Italians of Zadar left Yugoslavia towards Italy (Istrian-Dalmatian exodus).
SFR Yugoslavia (1947–1991)
In 1947, Zadar became part of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the Socialist Republic of Croatia. In the first decade after the war, the city's population increase was slow and still did not reach its pre-war numbers. The Italian exodus from the city continued and in a few years was almost total. It is estimated that around 10,000 Italians emigrated from Zadar. In October 1953, the last Italian schools in the area were closed. Today the Italian community counts only a few hundred people, gathered into a local community (''Comunità degli Italiani di Zara''). The city recorded a large population increase in the late 1950s and the 1960s, mainly due to immigration as the government encouraged migration from rural areas to urban centers and their industrial development. Construction of the Adriatic Highway, railway and civil airport contributed to the development of Tourism in Croatia, tourism and the accessibility of Zadar. Population growth slowed down in the following decades. In the late 1980s, due to the economic crisis in Yugoslavia, Zadar's economy began stagnating.Croatian War of Independence (1991–1995)
In 1990, Serbs of Croatia, Serb separatists from Dalmatian Hinterland sealed roads and effectively blocked Dalmatia from the rest of Croatia during the Log Revolution. In March 1991, the Croatian War of Independence broke out that affected Zadar and its surroundings. A number of non-Serbs were expelled from the area and several Croatian policemen were killed resulting in the 1991 anti-Serb riot in Zadar. Serbs at that time accounted for about 14% of the population. The Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and forces of the SAO Krajina occupied parts of Zadar's hinterland, converged on the city and subjected it to artillery bombardment during the Battle of Zadar. Along with other Croatian towns in the area, Serb forces shelled Zadar sporadically, damaging buildings and homes as well asUNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
protected sites. Serb forces also attacked a number of nearby towns and villages, the most brutal attack being the Škabrnja massacre in which Krajina Territorial Defense (Yugoslavia), Territorial Defense troops killed 62 Croatian civilians and five prisoners of war.
Land connections with Zagreb were severed for over a year. The only link between the north and south of the country was via the island of Pag (island), Pag. The siege of the city lasted from 1991 until January 1993 when Zadar and the surrounding area came under the control of Croatian forces and the bridge link with the rest of Croatia was reestablished in Operation Maslenica. Attacks on the city continued until Operation Storm, the end of the war in 1995.
Some of the countryside along the No. 8 highway running north east is still sectioned off due to land mines.
Main sights


Architecture
Zadar gained its urbanization, urban structure in Roman times; during the time ofJulius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
and Emperor Augustus, the town was fortified and the city walls with towers and gates were built. On the western side of the town were the Forum (Roman), forum, the basilica and the temple, while outside the town were the amphitheatre and cemetery, cemeteries. The aqueduct (watercourse), aqueduct which supplied the town with water is partially preserved. Inside the ancient town, a medieval town had developed with a series of Church (building), churches and monastery, monasteries being built.
 During the Middle Ages, Zadar fully gained its urban aspect, which has been maintained until today. In the first half of the 16th century, Venice fortified the town with a new system of defensive walls on the side facing land. In the course of the century architectural building in the
During the Middle Ages, Zadar fully gained its urban aspect, which has been maintained until today. In the first half of the 16th century, Venice fortified the town with a new system of defensive walls on the side facing land. In the course of the century architectural building in the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
style was continued and defensive trenches (Foša) were also built. They were completely buried during the Italian occupation until that in 1873, under Austrian rule, the ramparts of Zadar were converted from fortifications into elevated promenades commanding extensive seaward and landward views, thus being the wall lines preserved; of its four old gates one, the Porta Marina, incorporates the relics of a Roman arch, and another, the Porta di Terraferma, was designed in the 16th century by the Veronese artist Michele Sanmicheli. In the bombardments during the Second World War entire blocks were destroyed, but some structures survived.
Most important landmarks include:
* Roman Forum (Roman), Forum – the largest on the eastern side of the Adriatic, founded by the first Roman Emperor Augustus, as shown by two stone inscriptions about its completion dating from the 3rd century.
* Most Roman remains were used in the construction of the fortifications, but two squares are embellished with lofty marble columns; a Roman tower stands on the eastern side of the town; and some remains of a Roman aqueduct may be seen outside the ramparts.
* Church of St. Donatus – a monumental round building from the 9th century in pre-Romanesque style, traditionally but erroneously said to have been erected on the site of a temple of Juno. It is the most important preserved structure of its period in Dalmatia; the massive dome of the Rotunda (architecture), rotunda is surrounded by a vaulted gallery in two stories which also extends around the three apses to the east. The church treasury contains some of the finest Dalmatian metalwork; notably the pastoral staff of Bishop Valaresso (1460).
* Cathedral of St. Anastasia, Zadar, St. Anastasia's Cathedral (Croatian: ''Sv. Stošija''), basilica in Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style built in the 12th to 13th century (high Romanesque style), the largest cathedral in Dalmatia.
* The churches of Saint Chrysogonus, St. Chrysogonus and St. Simeon are also architectural examples in the Romanesque style. The latter houses the ark or reliquary of St. Simeon (1380), made in gilted silver by Francesco Antonio da Milano under commission of queen Elizabeth of Hungary.
* St Chrysogonus's Church – monumental Romanesque church of very fine proportions and refined Romanesque ornaments.
* St Elijah's Church (Croatian: ''Sv. Ilija'')
* St Francis' Church, Gothic styled church, site of the signing of the Zadar Peace Treaty 1358. Its choir is home to several carved stalls, executed in 1394 by the Venetian Giovanni di Giacomo da Borgo San Sepolcro.
* Five Wells Square
* St. Mary's Church, Zadar, St Mary's Church, which retains a fine Romanesque campanile from 1105, belongs to a Benedictine Convent founded in 1066 by a noblewoman of Zadar by the name of Cika with the permanent Ecclesiastical art exhibition "The Gold and Silver of Zadar".
* The Citadel. Built in 1409 southwest of the Land Gate, it has remained the same to this day.
* The Land Gate – built to a design by the Venetian architect Michele Sanmicheli in 1543
* The unique sea organ
* The Great Arsenal
* Among the other chief buildings are the Loggia del Comune, rebuilt in 1565, and containing a public library; the old palace of the priors, now the governor's residence; and the episcopal palaces.
Culture
City government
 The administrative area of the City of Zadar includes the nearby villages of Babindub, Crno, Kožino and Petrčane, as well as the islands of Ist (island), Ist, Iž, Molat, Olib, Premuda, Rava (island), Rava and Silba. The total city area, including the islands, covers 194 km2.
Zadar is divided into 21 local districts: Arbanasi, Bili Brig, Bokanjac, Brodarica, Crvene Kuće, Diklo, Dračevac, Jazine I, Jazine II, Maslina, Novi Bokanjac, Poluotok, Ploča, Puntamika, Ričina, Sinjoretovo, Smiljevac, Stanovi, Vidikovac, Višnjik, Voštarnica.
The current mayor of Zadar is Branko Dukić (Croatian Democratic Union, HDZ). He was elected for a second term on 2021 Croatian local elections, local elections held on 21 May 2021. The City Council is composed of 27 representatives.
The administrative area of the City of Zadar includes the nearby villages of Babindub, Crno, Kožino and Petrčane, as well as the islands of Ist (island), Ist, Iž, Molat, Olib, Premuda, Rava (island), Rava and Silba. The total city area, including the islands, covers 194 km2.
Zadar is divided into 21 local districts: Arbanasi, Bili Brig, Bokanjac, Brodarica, Crvene Kuće, Diklo, Dračevac, Jazine I, Jazine II, Maslina, Novi Bokanjac, Poluotok, Ploča, Puntamika, Ričina, Sinjoretovo, Smiljevac, Stanovi, Vidikovac, Višnjik, Voštarnica.
The current mayor of Zadar is Branko Dukić (Croatian Democratic Union, HDZ). He was elected for a second term on 2021 Croatian local elections, local elections held on 21 May 2021. The City Council is composed of 27 representatives.
Mayoral election
The City Council is composed of 27 representatives from the following political parties:Population
Zadar is the fifth largest city in Croatia and the second largest in Dalmatia, with a population of 75,082 according to the 2011 census. The 2001 census showed Zadar with a population of 72,718, with 93% of its citizens being ethnic Croats.Economy
Major industries include tourism, traffic, seaborne trade, agriculture, fishing and fish farming activities; metal manufacturing and mechanical engineering industries; chemicals and non-metal industry; and banking. Some of the largest companies with headquarters in Zadar are: * Tankerska plovidba (maritime transport) * Cromaris (food industry) * Bakmaz (retail) * Sonik (retail) * Turisthotel (tourism) * Maraska (food industry) * Punta Sakla (tourism) * Intermod (furniture retail and tourism) * Adria, Mardešić (fish production) * Vodovod (water supply) * OTP Bank Hrvatska (finance industry) * SAS (machine tools) * Aluflexpack (production of flexible packaging) * Arsenal Holdings (tourism) * Liburnija (transportation) The farmland just northeast of Zadar, '' Ravni Kotari'', is a well known source of marasca cherry, cherries. Distilleries in Zadar have produced Maraschino since the 16th century.Education
 There are nine primary education, primary schools and 16 secondary education, secondary schools, including six gymnasium (school), gymnasiums, in Zadar.
There are nine primary education, primary schools and 16 secondary education, secondary schools, including six gymnasium (school), gymnasiums, in Zadar.
University
University of Zadar was founded by the Dominican Order, Dominicans in 1396 as ''Universitas Iadertina'', a theological seminary. It was the first institute of higher learning in the country. In 1807 it ceased to become an independent institution and its functions were taken over by other local universities. In 1956 the University of Zagreb, the country's second oldest university, re-established it as its satellite Faculty of Arts campus. The Faculty later became a part of the University of Split, and in 2003, a full-fledged independent university. University comprises 25 departments with more than 6.000 students.Science
In 1998, Zadar hosted the Central European Olympiad in Informatics (CEOI).
Transportation
In the 20th century, roads became more important than sea routes, but Zadar remained an important traffic point. The main road along the Adriatic passes through the city. In the immediate vicinity, there is the A1 (Croatia), Zagreb-Dubrovnik highway, finished up to Split in 2005. Zadrans can access to the highway by two interchanges: Zadar 1 exit in the north and Zadar 2 highway hub near Zemunik in the south. The southern interchange is connected to Zadar port of Gaženica by the D424 (Croatia), D424 expressway. Today, buses are the only kind of ground public transportation with which one can reach Zadar. Zadar's bus station is used by both inter-city buses (which provide Zadar's connection with the rest of the country) and buses operated by the company "Liburnija" which provide public transit to the city of Zadar and its suburbs. Since 1966, during the time of Yugoslavia, railway has linked Zadar with Knin, where it joins the mainline from Zagreb to Split. However, all passenger trains between Knin and Zadar are since 2013 replaced with the buses that run in organisation of the national railway company Croatian Railways. Zadar also has an international ferry line to Ancona in Italy. Ships also connect Zadar with islands of its archipelago from two ferry ports: one located in the town center serving catamaran services and the other one located in the south suburb of Gaženica serving ferry and distant services. Zadar International Airport is located in Zemunik, around to the east of Zadar and accessible via the expressway. The airport is experiencing year on year an average of 30% increase in passenger traffic mainly due to arrivals of lowcost carriers (Ryanair, InterSky, JobAir, etc.) connecting Zadar from the end of March through October with over 20 cities throughout Europe.Sports
 The basketball club is KK Zadar, the football club NK Zadar, and the local handball club RK Zadar. The bowling club Kuglački klub Zadar is also very successful. Zadar is also the hometown of Croatian team handball, handball player Ivan Ninčević and soccer, football players Luka Modrić, Dado Pršo, Šime Vrsaljko and Danijel Subašić.
Other Sports:
Badminton: Badminton club Zadar
The basketball club is KK Zadar, the football club NK Zadar, and the local handball club RK Zadar. The bowling club Kuglački klub Zadar is also very successful. Zadar is also the hometown of Croatian team handball, handball player Ivan Ninčević and soccer, football players Luka Modrić, Dado Pršo, Šime Vrsaljko and Danijel Subašić.
Other Sports:
Badminton: Badminton club Zadar
International relations
Zadar is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned, or maintains cultural, economic and educational ties with: * Dundee, Scotland, United Kingdom * Reggio Emilia,Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
* Romans-sur-Isère, France
* Fürstenfeldbruck, Germany
* Székesfehérvár, Hungary
* Padua, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
* Iquique, Chile
* Banská Bystrica, Slovakia
* Milwaukee, United States
See also
* Archdiocese of Zadar * Stato da Màr * Bombing of Zadar in World War II * Siege of Zadar (1345–46) * History of Croatia * History of Dalmatia * Krešimir Ćosić Hall * Liburnia * Ottavio Missoni * The church and monastery of St. Michael in Zadar - Croatia * List of people from Zadar * List of people from Zadar CountyReferences
Sources
* * *External links
Zadar Tourist Board
ZD portal
City of Zadar official web page
{{Authority control Zadar, Articles containing video clips Cities and towns in Croatia Illyrian Croatia Kingdom of Dalmatia Mediterranean port cities and towns in Croatia Populated coastal places in Croatia Populated places established in the 9th century BC Populated places in Zadar County Ports and harbours of Croatia Cities in ancient Illyria Roman towns and cities in Croatia Territories of the Republic of Venice Former exclaves