Ytene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The New Forest is one of the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed
 Following
Following
File:Death of William Rufus.JPG, Death of
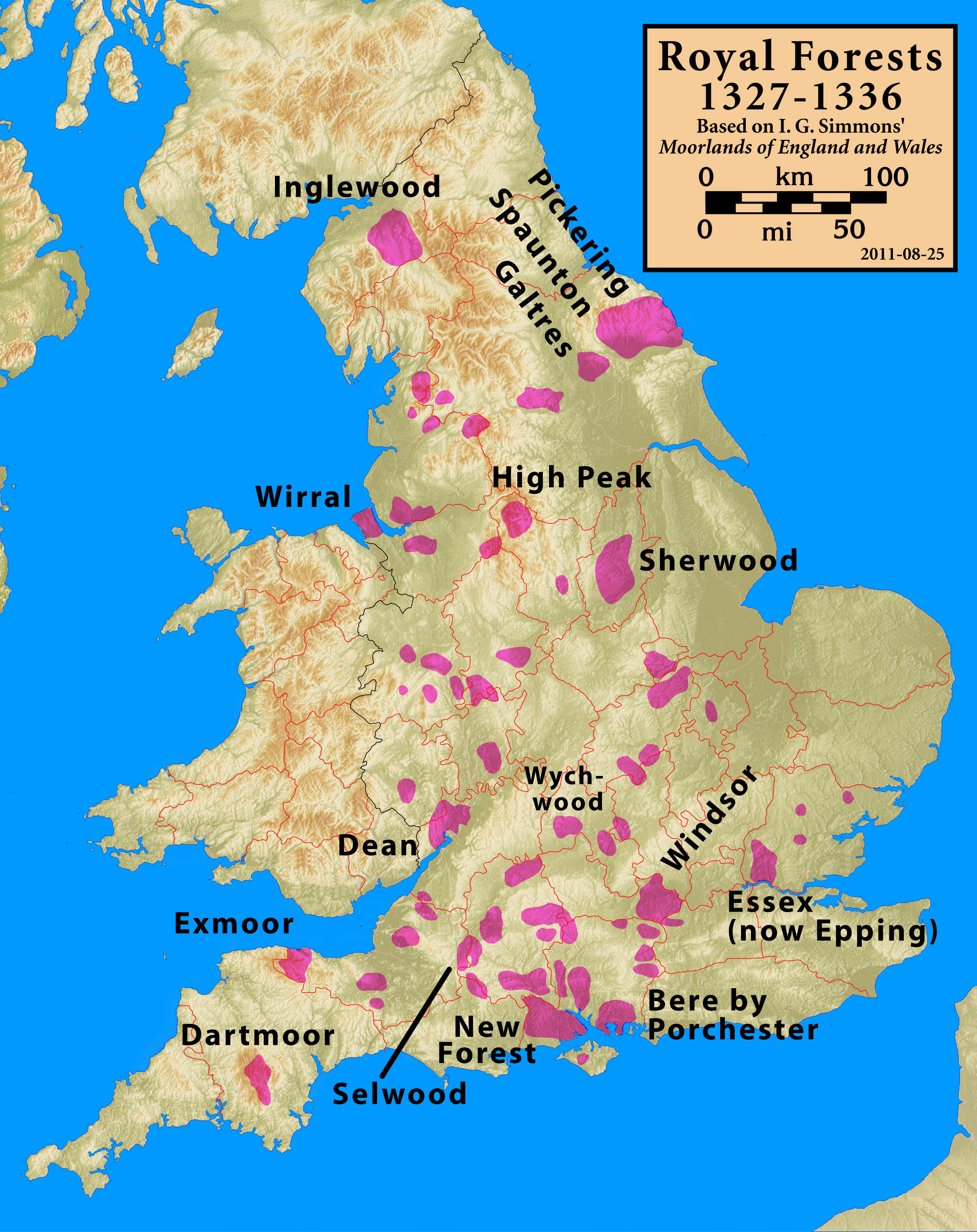
 Forest laws were enacted to preserve the New Forest as a location for royal
Forest laws were enacted to preserve the New Forest as a location for royal
 The New Forest National Park area covers , and the New Forest SSSI covers almost , making it the largest contiguous area of unsown vegetation in lowland Britain. It includes roughly:
* of broadleaved woodland
* of heathland and grassland
* of wet heathland
* of tree plantations (''woodland inclosures'') established since the 18th century, including planted by Forestry England since the 1920s.
The New Forest has also been classed as National Character Area No. 131 by
The New Forest National Park area covers , and the New Forest SSSI covers almost , making it the largest contiguous area of unsown vegetation in lowland Britain. It includes roughly:
* of broadleaved woodland
* of heathland and grassland
* of wet heathland
* of tree plantations (''woodland inclosures'') established since the 18th century, including planted by Forestry England since the 1920s.
The New Forest has also been classed as National Character Area No. 131 by
 All three British native species of snake inhabit the Forest. The adder (''
All three British native species of snake inhabit the Forest. The adder (''
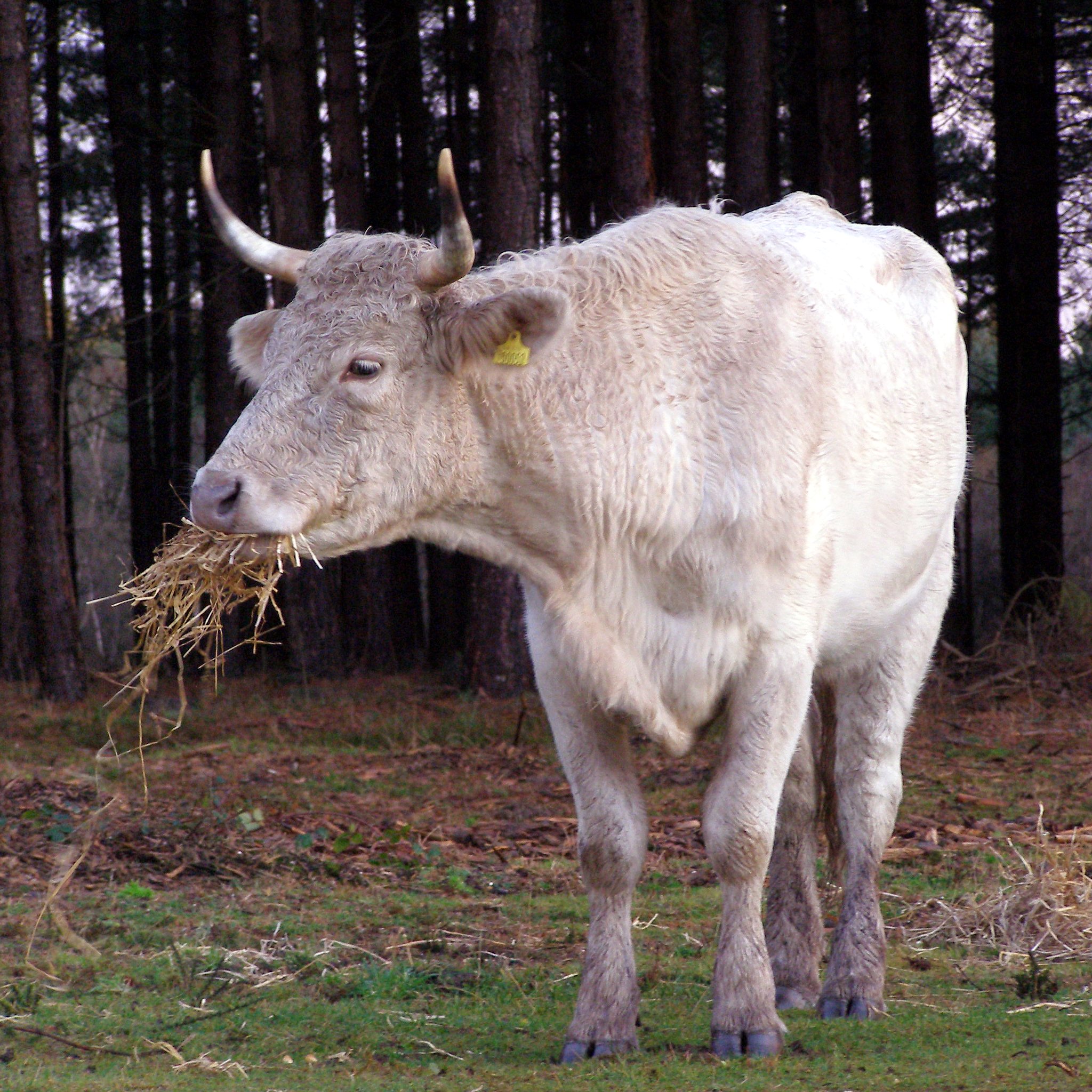
 Commoners' cattle, ponies and donkeys roam throughout the open heath and much of the woodland, and it is largely their grazing that maintains the open character of the Forest. They are also frequently seen in the Forest villages, where home and shop owners must take care to keep them out of gardens and shops. The
Commoners' cattle, ponies and donkeys roam throughout the open heath and much of the woodland, and it is largely their grazing that maintains the open character of the Forest. They are also frequently seen in the Forest villages, where home and shop owners must take care to keep them out of gardens and shops. The
 Consultations on the possible designation of a National Park in the New Forest were commenced by the
Consultations on the possible designation of a National Park in the New Forest were commenced by the

 * Bolderwood
* Bucklers Hard
* Beaulieu
*
* Bolderwood
* Bucklers Hard
* Beaulieu
*

The Official New Forest Tourism Website , Information on visiting the National ParkNew Forest National Park AuthorityNew Forest , Forestry EnglandNew Forest Gateway – Film, TV, Picture Resource / Historical Book Publications OnlineSAC designation including extensive technical description of habitats and species
*Designation as a national park:
( DEFRA press release, 28 June 2004)
New Forest National Park becomes a reality
( DEFRA press release, 24 February 2004)
The New Forest National Park
(
New Forest National Park Inquiry
from the Planning Inspectorate
Maps of the boundary
* {{SSSIs Wilts biological 1079 establishments in England English royal forests Forests and woodlands of Hampshire Forests and woodlands of Wiltshire Heathland Sites of Special Scientific Interest National parks in England Nature Conservation Review sites New Forest District Parks and open spaces in Hampshire Parks and open spaces in Wiltshire Protected areas established in 2005 Ramsar sites in England Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Hampshire Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Wiltshire South East England Special Areas of Conservation in England Woodland Sites of Special Scientific Interest Natural regions of England William the Conqueror
pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep, or sw ...
land, heath
A heath () is a shrubland habitat found mainly on free-draining infertile, acidic soils and characterised by open, low-growing woody vegetation. Moorland is generally related to high-ground heaths with—especially in Great Britain—a cooler a ...
land and forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
in Southern England
Southern England, or the South of England, also known as the South, is an area of England consisting of its southernmost part, with cultural, economic and political differences from the Midlands and the North. Officially, the area includes ...
, covering southwest Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
and southeast Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire ...
. It was proclaimed a royal forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the ...
by William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Norman ...
, featuring in the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
.
It is the home of the New Forest Commoners, whose ancient rights of common pasture are still recognised and exercised, enforced by official verderers and agisters. In the 18th century, the New Forest became a source of timber for the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
. It remains a habitat for many rare birds and mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
.
It is a biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest. Several areas are Geological Conservation Review
The Geological Conservation Review (GCR) is produced by the UK's Joint Nature Conservation Committee and is designed to identify those sites of national and international importance needed to show all the key scientific elements of the geological ...
and Nature Conservation Review
''A Nature Conservation Review'' is a two-volume work by Derek Ratcliffe, published by Cambridge University Press in 1977. It set out to identify the most important places for nature conservation in Great Britain. It is often known by the initial ...
sites. It is a Special Area of Conservation
A Special Area of Conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the ''Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. They are to protect the 220 habitats and a ...
, a Ramsar site and a Special Protection Area
A Special Protection Area (SPA) is a designation under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds. Under the Directive, Member States of the European Union (EU) have a duty to safeguard the habitats of migratory birds and certa ...
. Copythorne Common
Copythorne Common is a nature reserve west of Southampton in Hampshire. It is managed by the Hampshire and Isle of Wight Wildlife Trust. It is part of the New Forest, which is a Special Area of Conservation and a Site of Special Scientific Inter ...
is managed by the Hampshire and Isle of Wight Wildlife Trust
Hampshire and Isle of Wight Wildlife Trust is a Wildlife Trust with 27,000 members across the counties of Hampshire and the Isle of Wight, England.
The trust describes itself as the leading local wildlife conservation charity in Hampshire and th ...
, Kingston Great Common is a national nature reserve and New Forest Northern Commons is managed by the National Trust
The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and ...
.
The New Forest covers two parliamentary constituencies
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other poli ...
; New Forest East and New Forest West.
Prehistory
Like much of England, the site of the New Forest was oncedeciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
woodland, recolonised by birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains ...
and eventually beech and oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
after the withdrawal of the ice sheets starting around 12,000 years ago. Some areas were cleared for cultivation from the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
onwards; the poor quality of the soil in the New Forest meant that the cleared areas turned into heathland "waste", which may have been used even then as grazing land for horses.
There was still a significant amount of woodland in this part of Britain, but this was gradually reduced, particularly towards the end of the Middle Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
around 250–100 BC, and most importantly the 12th and 13th centuries, and of this essentially all that remains today is the New Forest.
There are around 250 round barrows within its boundaries, and scattered boiling mounds, and it also includes about 150 scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and d ...
s. One such barrow in particular may represent the only known inhumation
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objec ...
burial of the Early Iron Age and the only known Hallstatt culture burial in Britain; however, the acidity of the soil means that bone very rarely survives.
History
 Following
Following Anglo-Saxon settlement
The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain is the process which changed the language and culture of most of what became England from Romano-British to Germanic. The Germanic-speakers in Britain, themselves of diverse origins, eventually develope ...
in Britain, according to Florence of Worcester Florence of Worcester (died 1118), known in Latin as Florentius, was a monk of Worcester, who played some part in the production of the '' Chronicon ex chronicis'', a Latin world chronicle which begins with the creation and ends in 1140.Keynes, "Fl ...
(d. 1118), the area became the site of the Jutish kingdom of ''Ytene''; this name was the genitive plural
In grammar, the genitive case (abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can al ...
of ''Yt'' meaning "Jute", i.e. "of the Jutes". The Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nation ...
were one of the early Anglo-Saxon tribal groups who colonised this area of southern Hampshire.
Following the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Con ...
, the New Forest was proclaimed a royal forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the ...
, in about 1079, by William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Norman ...
. It was used for royal hunts, mainly of deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
. It was created at the expense of more than 20 small hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
s and isolated farmstead
A homestead is an isolated dwelling, especially a farmhouse, and adjacent outbuildings, typically on a large agricultural holding such as a ranch or station.
In North America the word "homestead" historically referred to land claimed by a set ...
s; hence it was then 'new' as a single compact area.
The New Forest was first recorded as ''Nova Foresta'' in Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
in 1086, where a section devoted to it is interpolated between lands of the king's thegn
In Anglo-Saxon England, thegns were aristocratic landowners of the second rank, below the ealdormen who governed large areas of England. The term was also used in early medieval Scandinavia for a class of retainers. In medieval Scotland, there ...
s and the town of Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Po ...
; it is the only forest that the book describes in detail. Twelfth-century chroniclers alleged that William had created the forest by evicting the inhabitants of 36 parishes, reducing a flourishing district to a wasteland; however, this account is thought dubious by most historians, as the poor soil in much of the area is believed to have been incapable of supporting large-scale agriculture, and significant areas appear to have always been uninhabited.
Two of William's sons died in the forest: Prince Richard sometime between 1069 and 1075, and King William II (William Rufus) in 1100. Though many claim the latter is due to an inaccurate arrow shot from his hunting companion, ocal folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging ...
asserted that this was punishment for the crimes committed by William when he created his New Forest; 17th-century writer Richard Blome provides detail:
In this County antshireis New-Forest, formerly called Ytene, being about 30 miles in compass; in which said tract William the Conqueror (for the making of the said Forest a harbour for Wild-beasts for his Game) caused 36 Parish Churches, with all the Houses thereto belonging, to be pulled down, and the poor Inhabitants left succourless of house or home. But this wicked act did not long go unpunished, for his Sons felt the smart thereof; Richard being blasted with a pestilent Air; Rufus shot through with an Arrow; and Henry his Grand-child, by Robert his eldest son, as he pursued his Game, was hanged among the boughs, and so dyed. This Forest at present affordeth great variety of Game, where his Majesty oft-times withdraws himself for his divertisement.The reputed spot of Rufus's death is marked with a stone known as the Rufus Stone. John White, Bishop of Winchester, said of the forest:
From God and Saint King Rufus did Churches take, From Citizens town-court, and mercate place, From Farmer lands: New Forrest for to make, In Beaulew tract, where whiles the King in chase Pursues the hart, just vengeance comes apace, And King pursues. Tirrell him seing not, Unwares him flew with dint of arrow shot.The common rights were confirmed by statute in 1698. The New Forest became a source of timber for the
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
, and plantations were created in the 18th century for this purpose. In the Great Storm of 1703
The great storm of 1703 was a destructive extratropical cyclone that struck central and southern England on 26 November 1703. High winds caused 2,000 chimney stacks to collapse in London and damaged the New Forest, which lost 4,000 oaks. Ships wer ...
, about 4000 oak trees were lost.
The naval plantations encroached on the rights of the Commoners, but the Forest gained new protection under the New Forest Act 1877, which confirmed the historic rights of the Commoners and entrenched that the total of enclosures was henceforth not to exceed at any time. It also reconstituted the Court of Verderers as representatives of the Commoners (rather than the Crown).
, roughly 90% of the New Forest is still owned by the Crown. The Crown lands have been managed by Forestry England since 1923 and most of the Crown lands now fall inside the new National Park.
Felling of broadleaved trees, and their replacement by conifers, began during the First World War to meet the wartime demand for wood. Further encroachments were made during the Second World War. This process is today being reversed in places, with some plantations being returned to heathland or broadleaved woodland. Rhododendron remains a problem.
During the Second World War, an area of the forest, Ashley Range, was used as a bombing range. During 1941–1945, the Beaulieu, Hampshire
Beaulieu ( ) is a small village located on the southeastern edge of the New Forest national park in Hampshire, England, and home to both Palace House and the British National Motor Museum.
History
The name Beaulieu comes etymological ...
Estate of Lord Montagu in the New Forest was the site of group B finishing schools for agents operated by the Special Operations Executive
The Special Operations Executive (SOE) was a secret British World War II organisation. It was officially formed on 22 July 1940 under Minister of Economic Warfare Hugh Dalton, from the amalgamation of three existing secret organisations. Its pu ...
(SOE) between 1941 and 1945. (One of the trainers was Kim Philby
Harold Adrian Russell "Kim" Philby (1 January 191211 May 1988) was a British intelligence officer and a double agent for the Soviet Union. In 1963 he was revealed to be a member of the Cambridge Five, a spy ring which had divulged British secr ...
who was later found to be part of a spy ring passing information to the Soviets.) In 2005, a special exhibition was mounted at the Estate, with a video showing photographs from that era as well as voice recordings of former SOE trainers and agents.
Further New Forest Acts followed in 1949, 1964 and 1970. The New Forest became a Site of Special Scientific Interest in 1971, and was granted special status as the New Forest Heritage Area in 1985, with additional planning controls added in 1992. The New Forest was proposed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in June 1999, but UNESCO did not take up the nomination. It became a National Park in March 2005, transferring a wide variety of planning and control decisions to the New Forest National Park Authority, who work alongside the local authorities, land owners and crown estates in managing the New Forest.
William Rufus
William II ( xno, Williame; – 2 August 1100) was King of England from 26 September 1087 until his death in 1100, with powers over Normandy and influence in Scotland. He was less successful in extending control into Wales. The third so ...
File:Rufus Stone.jpg, The Rufus Stone Memorial
File:NewForestIbsleyww2.jpg, WW2 remains at Ibsley
Common rights

 Forest laws were enacted to preserve the New Forest as a location for royal
Forest laws were enacted to preserve the New Forest as a location for royal deer hunting
Deer hunting is hunting for deer for meat and sport, an activity which dates back tens of thousands of years. Venison, the name for deer meat, is a nutritious and natural food source of animal protein that can be obtained through deer hunting. ...
, and interference with the king's deer and its forage was punished. However, the inhabitants of the area (''commoners
A commoner, also known as the ''common man'', ''commoners'', the ''common people'' or the ''masses'', was in earlier use an ordinary person in a community or nation who did not have any significant social status, especially a member of neither ...
'') had pre-existing ''rights of common'': to turn horses and cattle (but only rarely sheep) out into the Forest to graze (''common pasture''), to gather fuel wood ('' estovers''), to cut peat for fuel (''turbary
Turbary is the ancient right to cut turf, or peat, for fuel on a particular area of bog. The word may also be used to describe the associated piece of bog or peatland and, by extension, the material extracted from the turbary. Turbary rights, whic ...
''), to dig clay ('' marl''), and to turn out pigs between September and November to eat fallen acorns and beechnuts ('' pannage'' or ''mast''). There were also licences granted to gather bracken
Bracken (''Pteridium'') is a genus of large, coarse ferns in the family Dennstaedtiaceae. Ferns (Pteridophyta) are vascular plants that have alternating generations, large plants that produce spores and small plants that produce sex cells (eggs ...
after Michaelmas Day
Michaelmas ( ; also known as the Feast of Saints Michael, Gabriel, and Raphael, the Feast of the Archangels, or the Feast of Saint Michael and All Angels) is a Christian festival observed in some Western liturgical calendars on 29 September, an ...
(29 September) as litter for animals (''fern'').
Along with grazing, pannage is still an important part of the Forest's ecology. Pigs can eat acorns without problem, but for ponies and cattle, large quantities of acorns can be poisonous. Pannage always lasts at least 60 days, but the start date varies according to the weather – and when the acorns fall. The verderers decide when pannage will start each year. At other times the pigs must be taken in and kept on the owner's land, with the exception that pregnant sows, known as ''privileged sows'', are always allowed out providing they are not a nuisance and return to the Commoner's holding at night (they must not be "''levant'' and ''couchant''" in the Forest, that is, they may not consecutively feed ''and'' sleep there). This last is an established practice rather than a formal right.
The principle of levancy and couchancy applies generally to the right of pasture. Commoners must have backup land, outside the Forest, to accommodate these depastured animals when necessary, for example during a foot-and-mouth disease epidemic.
Commons rights are attached to particular plots of land (or in the case of turbary, to particular hearths), and different land has different rights – and some of this land is some distance from the Forest itself. Rights to graze ponies and cattle are not for a fixed number of animals, as is often the case on other commons. Instead a "marking fee" is paid for each animal each year by the owner. The marked animal's tail is trimmed by the local agister (verderers' official), with each of the four or five forest agisters using a different trimming pattern. Ponies are branded with the owner's brand mark; cattle may be branded, or nowadays may have the brand mark on an ear tag. Grazing of Commoners' ponies and cattle is an essential part of the management of the forest, helping to maintain the heathland, bog, grassland and wood-pasture habitats and their associated wildlife.
Recently this ancient practice has come under pressure as benefitting houses pass to owners with no interest in commoning. Existing families with a new generation heavily rely on inheritance of, rather than mostly the expensive purchase of, a benefitting house with paddock or farm.
The Verderers and Commoners' Defence Association has fought back against these allied economic threats. The EU Basic Payment Scheme
On 26 June 2003, EU farm ministers adopted a fundamental reform of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and introduced a new Single Payment Scheme (SPS or Single Farm Payment) for direct subsidy payments to landowners.
The system of subsidy appli ...
(BPS) helped some Commoners significantly. Commoners marking animals for grazing can claim about £200 per cow per year, and about £160 for a pony, and if participating in the stewardship scheme, more. With 10 cattle and 40 ponies, a Commoner qualifying for both schemes would receive over £8,000 a year, and more if they put out pigs: net of marking fees, feed and veterinary costs this part-time level of involvement across a family is calculated to give annual income in the thousands of pounds in most years. Whether those subsidies will survive Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC ...
is unclear. The BPS payment is based on the number of animals marked for the Forest, whether or not these are actually turned out. The livestock actually grazing the Forest are therefore considerably fewer than those marked.
Geography
 The New Forest National Park area covers , and the New Forest SSSI covers almost , making it the largest contiguous area of unsown vegetation in lowland Britain. It includes roughly:
* of broadleaved woodland
* of heathland and grassland
* of wet heathland
* of tree plantations (''woodland inclosures'') established since the 18th century, including planted by Forestry England since the 1920s.
The New Forest has also been classed as National Character Area No. 131 by
The New Forest National Park area covers , and the New Forest SSSI covers almost , making it the largest contiguous area of unsown vegetation in lowland Britain. It includes roughly:
* of broadleaved woodland
* of heathland and grassland
* of wet heathland
* of tree plantations (''woodland inclosures'') established since the 18th century, including planted by Forestry England since the 1920s.
The New Forest has also been classed as National Character Area No. 131 by Natural England
Natural England is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. It is responsible for ensuring that England's natural environment, including its land, flora and fauna, ...
. The NCA covers an area of and is bounded by the Dorset Heaths and Dorset Downs
The Dorset Downs are an area of chalk downland in the centre of the county Dorset in south west England. The downs are the most western part of a larger chalk formation which also includes (from west to east) Cranborne Chase, Salisbury Plain, H ...
to the west, the West Wiltshire Downs to the north and the South Hampshire Lowlands and South Coast Plain to the east.
The New Forest is drained to the south by three rivers, Lymington River
The Lymington River drains part of the New Forest in Hampshire in southern England. Numerous headwaters to the west of Lyndhurst give rise to the river, including Highland Water, Bratley Water and Fletchers Water. From Brockenhurst the river r ...
, Beaulieu River
The Beaulieu River ( ), formerly known as the River Exe, is a small river draining much of the central New Forest in Hampshire, southern England. The river has many small upper branches and its farthest source is from its -long tidal estuary. ...
and Avon Water
Avon Water, also known locally as the River Avon, is a river in Scotland, and a tributary of the River Clyde.
Course
The Avon Water rises in the hills on the boundary between East Ayrshire and South Lanarkshire, close to the head of the ...
, and to the west by the Latchmore Brook, Dockens Water, Linford Brook and other streams.
The highest point in the New Forest is Pipers Wait, near Nomansland
No man's land is an unoccupied area between two opposing positions.
No man's land (Latrun) is an example.
No Man's Land, No-man's land or Nomansland may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* No Man's Land, Cornwall, England
* No Man's Land ...
. Its summit is above sea level.
The Geology of the New Forest consists mainly of sedimentary rock, in the centre of a sedimentary basin known as the Hampshire Basin.
Wildlife
The ecological value of the New Forest is enhanced by the relatively large areas of lowland habitats, lost elsewhere, which have survived. There are several kinds of important lowland habitat including valley bogs,alder carr An alder carr is a particular type of carr, i.e. waterlogged wooded terrain populated with alder trees.
Examples
* Alder Carr, Hildersham
* Alderfen Broad
* Fawley Ford on the Beaulieu River
* Biebrza National Park
* Fen Alder Carr
* Harsto ...
, wet heath
A heath () is a shrubland habitat found mainly on free-draining infertile, acidic soils and characterised by open, low-growing woody vegetation. Moorland is generally related to high-ground heaths with—especially in Great Britain—a cooler a ...
s, dry heaths and deciduous woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (se ...
. The area contains a profusion of rare wildlife, including the New Forest cicada
The cicadas () are a superfamily, the Cicadoidea, of insects in the order Hemiptera (true bugs). They are in the suborder Auchenorrhyncha, along with smaller jumping bugs such as leafhoppers and froghoppers. The superfamily is divided into tw ...
'' Cicadetta montana'', the only cicada native to Great Britain, although the last unconfirmed sighting was in 2000. The wet heaths are important for rare plants, such as marsh gentian ('' Gentiana pneumonanthe'') and marsh clubmoss (''Lycopodiella inundata
''Lycopodiella inundata'' is a species of club moss known by the common names inundated club moss, marsh clubmoss and northern bog club moss. It has a circumpolar and circumboreal distribution, occurring throughout the northern Northern Hemisph ...
'') and other important species include the wild gladiolus ('' Gladiolus illyricus'').
Several species of sundew
''Drosera'', which is commonly known as the sundews, is one of the largest genera of carnivorous plants, with at least 194 species. 2 volumes. These members of the family Droseraceae lure, capture, and digest insects using stalked mucilaginou ...
are found, as well as many unusual insect species, including the southern damselfly (''Coenagrion mercuriale
''Coenagrion mercuriale'', the southern damselfly, is a species of damselfly in the family Coenagrionidae. It is found in Algeria, Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Morocco, the Netherlands, Portugal, Romania, ...
''), large marsh grasshopper ('' Stethophyma grossum'') and the mole cricket (''Gryllotalpa gryllotalpa
''Gryllotalpa gryllotalpa'', commonly known as the European mole cricket, is widespread in Europe and has been introduced to the eastern United States. The scientific name is derived from the Latin 'gryllus' meaning a cricket and 'talpa', a mole ...
''), all rare in Britain. In 2009, 500 adult southern damselflies were captured and released in the Venn Ottery nature reserve in Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
, which is owned and managed by the Devon Wildlife Trust
The Devon Wildlife Trust is a member of The Wildlife Trusts partnership covering the county of Devon, England. It is a registered charity, established in 1962 as the Devon Naturalists Trust, and its aim is to safeguard the future of the county's ...
. The Forest is an important stronghold for a rich variety of fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, and although these have been heavily gathered in the past, there are control measures now in place to manage this.
Birds
Specialist heathland birds are widespread, includingDartford warbler
The Dartford warbler (''Curruca undata'') is a typical warbler from the warmer parts of western Europe and northwestern Africa. It is a small warbler with a long thin tail and a thin pointed bill. The adult male has grey-brown upperparts and is ...
(''Curruca undata''), woodlark
The woodlark or wood lark (''Lullula arborea'') is the only extant species in the lark genus ''Lullula''. It is found across most of Europe, the Middle East, western Asia and the mountains of north Africa. It is mainly resident (non- migratory) ...
(''Lullula arborea''), northern lapwing (''Vanellus vanellus''), Eurasian curlew
The Eurasian curlew or common curlew (''Numenius arquata'') is a very large wader in the family Scolopacidae. It is one of the most widespread of the curlews, breeding across temperate Europe and Asia. In Europe, this species is often referred ...
(''Numenius arquata''), European nightjar
The European nightjar (''Caprimulgus europaeus''), common goatsucker, Eurasian nightjar or just nightjar, is a crepuscular and nocturnal bird in the nightjar family that breeds across most of Europe and the Palearctic to Mongolia and Northwest ...
(''Caprimulgus europaeus''), Eurasian hobby
The Eurasian hobby (''Falco subbuteo'') or just hobby, is a small, slim falcon. It belongs to a rather close-knit group of similar falcons often considered a subgenus '' Hypotriorchis''.
Taxonomy and systematics
The first formal description of ...
(''Falco subbuteo''), European stonechat
The European stonechat (''Saxicola rubicola'') is a small passerine bird that was formerly classed as a subspecies of the common stonechat. Long considered a member of the thrush family, Turdidae, genetic evidence has placed it and its relat ...
(''Saxicola rubecola''), common redstart (''Phoenicurus phoenicurus'') and tree pipit
The tree pipit (''Anthus trivialis'') is a small passerine bird which breeds across most of Europe and the Palearctic as far East as the East Siberian Mountains. It is a long-distance migrant moving in winter to Africa and southern Asia. The s ...
(''Anthus sylvestris''). As in much of Britain common snipe
The common snipe (''Gallinago gallinago'') is a small, stocky wader native to the Old World.
The breeding habitats are marshes, bogs, tundra and wet meadows throughout the Palearctic. In the north, the distribution limit extends from Iceland ov ...
(''Gallinago gallinago'') and meadow pipit
The meadow pipit (''Anthus pratensis'') is a small passerine bird, which breeds in much of the Palearctic, from southeastern Greenland and Iceland east to just east of the Ural Mountains in Russia, and south to central France and Romania; an isol ...
(''Anthus trivialis'') are common as wintering birds, but in the Forest they still also breed in many of the bogs and heaths respectively.
Woodland birds include wood warbler
The wood warbler (''Phylloscopus sibilatrix'') is a common and widespread leaf warbler which breeds throughout northern and temperate Europe, and just into the extreme west of Asian Russia in the southern Ural Mountains.
This warbler is stro ...
(''Phylloscopus sibilatrix''), stock dove (''Columba oenas''), European honey buzzard
The European honey buzzard (''Pernis apivorus''), also known as the pern or common pern, is a bird of prey in the family Accipitridae.
Etymology
Despite its English name, this species is more closely related to kites of the genera '' Leptodon'' a ...
(''Pernis apivorus'') and northern goshawk (''Accipiter gentilis''). Common buzzard (''Buteo buteo'') is very common and common raven
The common raven (''Corvus corax'') is a large all-black passerine bird. It is the most widely distributed of all corvids, found across the Northern Hemisphere. It is a raven known by many names at the subspecies level; there are at least ...
(''Corvus corax'') is spreading. Birds seen more rarely include red kite
The red kite (''Milvus milvus'') is a medium-large bird of prey in the family Accipitridae, which also includes many other diurnal raptors such as eagles, buzzards, and harriers. The species currently breeds in the Western Palearctic region o ...
(''Milvus milvus''), wintering great grey shrike
The great grey shrike (''Lanius excubitor'') is a large and predatory songbird species in the shrike family (Laniidae). It forms a superspecies with its parapatric southern relatives, the Iberian grey shrike (''L. meridionalis''), the Chinese ...
(''Lanius exubitor'') and hen harrier
The hen harrier (''Circus cyaneus'') is a bird of prey. It breeds in Eurasia. The term "hen harrier" refers to its former habit of preying on free-ranging fowl.
It migrates to more southerly areas in winter. Eurasian birds move to southern Eur ...
(''Circus cyaneus'') and migrating ring ouzel
The ring ouzel (''Turdus torquatus'') is a mainly European member of the thrush family Turdidae. It is a medium-sized thrush, in length and weighing . The male is predominantly black with a conspicuous white crescent across its breast. Females ...
(''Turdus torquatus'') and northern wheatear
The northern wheatear or wheatear (''Oenanthe oenanthe'') is a small passerine bird that was formerly classed as a member of the thrush family Turdidae, but is now more generally considered to be an Old World flycatcher, Muscicapidae. It is th ...
(''Oenanthe oenanthe'').
Reptiles and amphibians
 All three British native species of snake inhabit the Forest. The adder (''
All three British native species of snake inhabit the Forest. The adder (''Vipera berus
''Vipera berus'', the common European adderMallow D, Ludwig D, Nilson G. (2003). ''True Vipers: Natural History and Toxinology of Old World Vipers''. Malabar, Florida: Krieger Publishing Company. . or common European viper,Stidworthy J. (1974). ...
'') is the most common, being found on open heath and grassland. The grass snake
The grass snake (''Natrix natrix''), sometimes called the ringed snake or water snake, is a Eurasian non-venomous colubrid snake. It is often found near water and feeds almost exclusively on amphibians.
Subspecies
Many subspecies are recognized ...
(''Natrix natrix'') prefers the damper environment of the valley mires. The rare smooth snake ('' Coronella austriaca'') occurs on sandy hillsides with heather and gorse. It was mainly adders which were caught by Brusher Mills (1840–1905), the "New Forest Snake Catcher". He caught many thousands in his lifetime, sending some to London Zoo as food for their animals. A pub
A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and was ...
in Brockenhurst
Brockenhurst is the largest village by population within the New Forest in Hampshire, England. The nearest city is Southampton some to the North East, while Bournemouth is also nearby, South West. Surrounding towns and villages include Beaul ...
is named ''The Snakecatcher'' in his memory. All British snakes are now legally protected, and so the New Forest snakes are no longer caught.
A programme to reintroduce the sand lizard
The sand lizard (''Lacerta agilis'') is a lacertid lizard distributed across most of Europe from France and across the continent to Lake Baikal in Russia. It does not occur in European Turkey. Its distribution is often patchy. In the sand lizard' ...
(''Lacerta agilis'') started in 1989 and the great crested newt
The northern crested newt, great crested newt or warty newt (''Triturus cristatus'') is a newt species native to Great Britain, northern and central continental Europe and parts of Western Siberia. It is a large newt, with females growing up to ...
(''Triturus cristatus'') already breeds in many locations.
Sand lizards in a captive breeding and reintroduction programme together with adders, grass snakes, smooth snake
The smooth snake (''Coronella austriaca'')Street D (1979). ''The Reptiles of Northern and Central Europe''. London: B.T. Batsford Ltd. 268 pp. . is a species of non-venomous snake in the family Colubridae. The species is found in northern and cen ...
s, frogs
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" '' Triadobatrachus'' is ...
and toads
Toad is a common name for certain frogs, especially of the family Bufonidae, that are characterized by dry, leathery skin, short legs, and large bumps covering the parotoid glands.
A distinction between frogs and toads is not made in scienti ...
can be seen at The New Forest Reptile Centre about two miles east of Lyndhurst. The centre was established in 1969 by Derek Thomson MBE, a Forestry England keeper, who was also involved in establishing the deer viewing platform at nearby Bolderwood.
Ponies, cattle, donkeys, pigs
 Commoners' cattle, ponies and donkeys roam throughout the open heath and much of the woodland, and it is largely their grazing that maintains the open character of the Forest. They are also frequently seen in the Forest villages, where home and shop owners must take care to keep them out of gardens and shops. The
Commoners' cattle, ponies and donkeys roam throughout the open heath and much of the woodland, and it is largely their grazing that maintains the open character of the Forest. They are also frequently seen in the Forest villages, where home and shop owners must take care to keep them out of gardens and shops. The New Forest pony
The New Forest pony is one of the recognised mountain and moorland or native pony breeds of the British Isles. Height varies from around ; ponies of all heights should be strong, workmanlike, and of a good riding type. They are valued for hardi ...
is one of the indigenous horse breeds of the British Isles, and is one of the New Forest's most famous attractions – most of the Forest ponies are of this breed, but there are also some Shetlands
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the no ...
and their crossbreed
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. ''Crossbreeding'', sometimes called "designer crossbreeding", is the process of breeding such an organism, While crossbreeding is used to mai ...
s.
Cattle are of various breeds, most commonly Galloways and their crossbreeds, but also various other hardy types such as Highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Albania
* Dukagjin Highlands
Armenia
* Armenian Highlands
Australia
*Sou ...
, Herefords, Dexters, Kerries and British whites. The pigs used for pannage, during the autumn months, are now of various breeds, but the New Forest was the original home of the Wessex Saddleback
The Wessex Saddleback or Wessex Pig is a breed of domestic pig originating in the West Country of England, (Wessex), especially in Wiltshire and the New Forest area of Hampshire. It is black, with white forequarters. In Britain it was amalgamated ...
, now extinct in Britain.
Deer
Numerous deer live in the Forest; they are usually rather shy and tend to stay out of sight when people are around, but are surprisingly bold at night, even when a car drives past.Fallow deer
''Dama'' is a genus of deer in the subfamily Cervinae, commonly referred to as fallow deer.
Name
The name fallow is derived from the deer's pale brown colour. The Latin word ''dāma'' or ''damma'', used for roe deer, gazelles, and antelopes ...
(''Dama dama'') are the most common, followed by roe deer
The roe deer (''Capreolus capreolus''), also known as the roe, western roe deer, or European roe, is a species of deer. The male of the species is sometimes referred to as a roebuck. The roe is a small deer, reddish and grey-brown, and well-adapt ...
(''Capreolus capreolus'') and red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of we ...
(''Cervus elaphus''). There are also smaller populations of the introduced sika deer
The sika deer (''Cervus nippon''), also known as the Northern spotted deer or the Japanese deer, is a species of deer native to much of East Asia and introduced to other parts of the world. Previously found from northern Vietnam in the south to ...
(''Cervus nippon'') and muntjac
Muntjacs ( ), also known as the barking deer or rib-faced deer, (URL is Google Books) are small deer of the genus ''Muntiacus'' native to South Asia and Southeast Asia. Muntjacs are thought to have begun appearing 15–35 million years ago, ...
(''Muntiacus reevesii'').
Other mammals
The red squirrel (''Sciurus vulgaris'') survived in the Forest until the 1970s – longer than most places in lowland Britain (though it still occurs on The Isle of Wight and the nearbyBrownsea Island
Brownsea Island is the largest of the islands in Poole Harbour in the county of Dorset, England. The island is owned by the National Trust with the northern half managed by the Dorset Wildlife Trust. Much of the island is open to the public and ...
). It is now fully supplanted in the Forest by the introduced North American grey squirrel
The eastern gray squirrel (''Sciurus carolinensis''), also known, particularly outside of North America, as simply the grey squirrel, is a tree squirrel in the genus ''Sciurus''. It is native to eastern North America, where it is the most prodi ...
(''Sciurus carolinensis''). The European polecat
The European polecat (''Mustela putorius''), also known as the common polecat, black polecat, or forest polecat, is a species of mustelid native to western Eurasia and North Africa. It is of a generally dark brown colour, with a pale underbell ...
(''Mustela putorius'') has recolonised the western edge of the Forest in recent years. European otter
The Eurasian otter (''Lutra lutra''), also known as the European otter, Eurasian river otter, common otter, and Old World otter, is a semiaquatic mammal native to Eurasia. The most widely distributed member of the otter subfamily (Lutrinae) of th ...
(''Lutra lutra'') occurs along watercourses, as well as the introduced American mink
The American mink (''Neogale vison'') is a semiaquatic species of mustelid native to North America, though human intervention has expanded its range to many parts of Europe, Asia and South America. Because of range expansion, the American mink i ...
(''Neogale vison'').
Conservation measures
The New Forest is designated as a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI), an EUSpecial Area of Conservation
A Special Area of Conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the ''Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. They are to protect the 220 habitats and a ...
(SAC), a Special Protection Area
A Special Protection Area (SPA) is a designation under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds. Under the Directive, Member States of the European Union (EU) have a duty to safeguard the habitats of migratory birds and certa ...
for birds (SPA), and a Ramsar Site; it also has its own Biodiversity Action Plan (BAP).Settlements
The New Forest itself gives its name to the New Forest district ofHampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
, and the National Park area, of which it forms the core.
The Forest itself is dominated by four larger 'defined' villages, Sway, Brockenhurst
Brockenhurst is the largest village by population within the New Forest in Hampshire, England. The nearest city is Southampton some to the North East, while Bournemouth is also nearby, South West. Surrounding towns and villages include Beaul ...
, Lyndhurst and Ashurst, with several smaller villages such as Burley, Beaulieu, Godshill
Godshill is a village and civil parish on the Isle of Wight, England, with a population of 1,459 at the 2011 Census. It lies between Newport and Ventnor in the southeast of the island.
History
Godshill is one of the ancient parishes that exis ...
, Fritham
Fritham is a small village in Hampshire, England. It lies in the north of the New Forest, near the Wiltshire border. It is in the civil parish of Bramshaw.
History
The name Fritham may be derived from Old English meaning a cultivated plot (''ha ...
, Nomansland
No man's land is an unoccupied area between two opposing positions.
No man's land (Latrun) is an example.
No Man's Land, No-man's land or Nomansland may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* No Man's Land, Cornwall, England
* No Man's Land ...
, and Minstead
Minstead is a small village and civil parish in the New Forest, Hampshire, about north of Lyndhurst. There is a shop and a pub, the ''Trusty Servant''. Sir Arthur Conan Doyle's grave is under a large tree at the back of the 13th century Al ...
also lying within or immediately adjacent. Outside of the National Park Area in New Forest District, several clusters of larger towns frame the area – Totton and the Waterside settlements (Marchwood
Marchwood is a village and civil parish located in Hampshire, England, United Kingdom. It lies between Totton and Hythe on the western shore of Southampton Water and directly east of the New Forest. The population of the village in the 20 ...
, Dibden, Hythe, Fawley) to the East, Christchurch
Christchurch ( ; mi, Ōtautahi) is the largest city in the South Island of New Zealand and the seat of the Canterbury Region. Christchurch lies on the South Island's east coast, just north of Banks Peninsula on Pegasus Bay. The Avon Rive ...
, New Milton
New Milton is a market town in southwest Hampshire, England. To the north is in the New Forest and to the south the coast at Barton-on-Sea. The town is equidistant between Lymington and Christchurch, 6 miles (10 km) away.
History
Ne ...
, Milford on Sea
Milford on Sea, often hyphenated, is a large village or small town and a civil parish on the Hampshire coast. The parish had a population of 4,660 at the 2011 census and is centred about south of Lymington. Tourism and businesses for quite pr ...
, and Lymington
Lymington is a port town on the west bank of the Lymington River on the Solent, in the New Forest district of Hampshire, England. It faces Yarmouth, Isle of Wight, to which there is a car ferry service operated by Wightlink. It is within the ...
to the South, and Fordingbridge
Fordingbridge is a town and broader civil parish with a population of 6,000 on the River Avon in the New Forest District of Hampshire, England, near the Dorset and Wiltshire borders and on the edge of the New Forest, famed for its late medieva ...
and Ringwood to the West.
New Forest National Park
Countryside Agency
The Countryside Agency was a statutory body set up in England in 1999 with the task of improving the quality of the rural environment and the lives of those living in it. The agency was dissolved in 2006 and its functions dispersed among other bod ...
in 1999. An order to create the park was made by the Agency on 24 January 2002 and submitted to the Secretary of State for confirmation in February 2002. Following objections from seven local authorities and others, a public inquiry was held from 8 October 2002 to 10 April 2003, and concluded by endorsing the proposal with some detailed changes to the boundary of the area to be designated.
On 28 June 2004, Rural Affairs Minister Alun Michael confirmed the government's intention to designate the area as a National Park, with further detailed boundary adjustments. The area was formally designated as such on 1 March 2005. A national park authority
A national park authority is a special term used in Great Britain for legal bodies charged with maintaining a national park of which, as of October 2021, there are ten in England, three in Wales and two in Scotland. The powers and duties of all suc ...
for the New Forest was established on 1 April 2005 and assumed its full statutory powers on 1 April 2006.
Forestry England retain their powers to manage the Crown land within the Park. The Verderers under the New Forest Acts also retain their responsibilities, and the park authority is expected to co-operate with these bodies, the local authorities, English Nature
English Nature was the United Kingdom government agency that promoted the conservation of wildlife, geology and wild places throughout England between 1990 and 2006. It was a non-departmental public body funded by the Department for Environmen ...
and other interested parties.
The designated area of the National Park covers and includes many existing SSSIs. It has a population of about 38,000 (it excludes most of the 170,256 people who live in the New Forest
The New Forest is one of the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed pasture land, heathland and forest in Southern England, covering southwest Hampshire and southeast Wiltshire. It was proclaimed a royal forest by William the Conqueror, fea ...
local government district). As well as most of the New Forest district of Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
, it takes in the South Hampshire Coast Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty
An Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB; , AHNE) is an area of countryside in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland, that has been designated for conservation due to its significant landscape value. Areas are designated in recognition of ...
, a small corner of Test Valley
Test Valley is a local government district and borough in Hampshire, England, named after the valley of the River Test. Its council is based in Andover.
The borough was formed on 1 April 1974 by a merger of the boroughs of Andover and Romsey, a ...
district around the village of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
and part of Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire ...
south-east of Redlynch.
However, the area covered by the Park does not include all the areas initially proposed: it excludes most of the valley of the River Avon to the west of the Forest and Dibden Bay to the east. Two challenges were made to the designation order, by Meyrick Estate Management Ltd in relation to the inclusion of Hinton Admiral Park, and by RWE NPower Plc in relation to the inclusion of Fawley Power Station
Fawley Power Station was an oil-fired power station located on the western side of Southampton Water, between the villages of Fawley and Calshot in Hampshire, England. Its chimney was a prominent (and navigationally useful) landmark, but it ...
. The second challenge was settled out of court, with the power station being excluded. The High Court upheld the first challenge; but an appeal against the decision was then heard by the Court of Appeal in Autumn 2006. The final ruling, published on 15 February 2007, found in favour of the challenge by Meyrick Estate Management Ltd, and the land at Hinton Admiral Park is therefore excluded from the New Forest National Park. The total area of land initially proposed for inclusion but ultimately left out of the Park is around .
Visitor attractions and places

 * Bolderwood
* Bucklers Hard
* Beaulieu
*
* Bolderwood
* Bucklers Hard
* Beaulieu
*Exbury Gardens
Exbury Gardens is a informal woodland garden in Hampshire, England with large collections of rhododendrons, azaleas and camellias, and is often considered the finest garden of its type in the United Kingdom. Exbury holds the national collectio ...
*Hythe Pier
Hythe Pier, the Hythe Pier Railway and the Hythe Ferry provide a link between the English port city of Southampton and the Hampshire village of Hythe on the west side of Southampton Water. It is used both by commuters and tourists, and forms a ...
*Lymington
Lymington is a port town on the west bank of the Lymington River on the Solent, in the New Forest district of Hampshire, England. It faces Yarmouth, Isle of Wight, to which there is a car ferry service operated by Wightlink. It is within the ...
* New Forest Show
* New Forest Tour
* New Forest Wildlife Park
Politics
The New Forest is represented by twoMembers of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
; in New Forest East and New Forest West.
Cultural references
There is an allusion to the foundation of the New Forest in an end-rhyming poem found in thePeterborough Chronicle
The ''Peterborough Chronicle'' (also called the Laud manuscript and the E manuscript) is a version of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicles'' originally maintained by the monks of Peterborough Abbey in Cambridgeshire. It contains unique information abo ...
's entry for 1087, ''The Rime of King William
"The Rime of King William" is an Old English poem that tells the death of William the Conqueror. The Rime was a part of the only entry for the year of 1087 (though improperly dated 1086) in the "Peterborough Chronicle/Laud Manuscript." In this e ...
''.
The Forest forms a backdrop to numerous books. ''The Children of the New Forest
''The Children of the New Forest'' is a children's novel published in 1847 by Frederick Marryat. It is set in the time of the English Civil War and the Commonwealth. The story follows the fortunes of the four Beverley children who are orphane ...
'' is a children's novel published in 1847 by Frederick Marryat, set in the time of the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
. Charles Kingsley's ''A New Forest Ballad'' (1847) mentions several New Forest locations, including Ocknell Plain, Bradley ratley
Ratley is a village in the civil parish of Ratley and Upton, Stratford-on-Avon District, Warwickshire, England. The population of the civil parish in 2011 was 327. It is on the northwest side of the Edge Hill escarpment about above sea level. ...
Water, Burley Walk and Lyndhurst churchyard. Edward Rutherfurd's work of historical fiction, '' The Forest'' is based in the New Forest in the period from 1099 to 2000. The Forest is also a setting of the ''Warriors'' novel series, in which the 'Forest Territories' was initially based on New Forest.
The New Forest and southeast England, around the 12th century, is a prominent setting in Ken Follett
Kenneth Martin Follett, (born 5 June 1949) is a British author of thrillers and historical novels who has sold more than 160 million copies of his works.
Many of his books have achieved high ranking on best seller lists. For example, in the ...
's novel ''The Pillars of the Earth
''The Pillars of the Earth'' is a historical novel by British author Ken Follett published in 1989 about the building of a cathedral in the fictional town of Kingsbridge, England. Set in the 12th century, the novel covers the time between the ...
''. It is also a prominent setting in Elizabeth George
Susan Elizabeth George (born February 26, 1949) is an American writer of mystery novels set in Great Britain.
She is best known for a series of novels featuring Inspector Thomas Lynley. The 21st book in the series appeared in January 2022. ...
's novel ''This Body of Death''. Oberon, Titania and the other Shakespearean fairies live in a rapidly diminishing Sherwood Forest whittled away by urban development in the fantasy novel A Midsummer's Nightmare by Garry Kilworth. On Midsummer's Eve, a most auspicious day, the fairies embark on the long journey to the New Forest in Hampshire where the fairies' magic will be restored to its former glory.

Notable residents
* Eric Ashby (1918–2003), naturalist and wildlife cameraman * Alice Bentinck (born 1986), co-founder and COO ofEntrepreneur First
Entrepreneur First is an international talent investor, which supports individuals in building technology companies. Founded in 2011 by Matt Clifford and Alice Bentinck, the company has offices in Toronto, London, Berlin, Paris, Singapore, a ...
, London
* William Arnold Bromfield (1801–1851), English botanist
*Sir Arthur Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for '' A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Ho ...
(1869–1930), author
* Harry Warner Farnall (1838–1891), New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
politician
*Gerald Gardner
Gerald Brosseau Gardner (13 June 1884 – 12 February 1964), also known by the craft name Scire, was an English Wiccan, as well as an author and an amateur anthropology, anthropologist and archaeology, archaeologist. He was instrumental in bri ...
(1884–1964), founder of Gardnerian Wicca
* Steff Gaulter (born 1976), weather forecaster
* Pam Gems (1925–2011), English playwright
* Arthur Sumner Gibson (1844–1927), rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
international
* Edgar Gibson (1848–1924), 31st Bishop of Gloucester
The Bishop of Gloucester is the ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Gloucester in the Province of Canterbury.
The diocese covers the County of Gloucestershire and part of the County of Worcestershire. The see's centre of governan ...
* Clifford Hall (1902–1982), English cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by str ...
er
* Frederick Harold (1888–1964), English cricketer
* Gerry Hill (1913–2006), English cricketer
* Ralph Hollins (born 1931), naturalist
* Mark Kermode (born 1963), film critic
Film criticism is the analysis and evaluation of films and the film medium. In general, film criticism can be divided into two categories: journalistic criticism that appears regularly in newspapers, magazines and other popular mass-media outl ...
and musician
* Sybil Leek (1917–1982), witch, author, astrologer
* Sir Charles Lyell (1797–1875), Victorian geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, althoug ...
and polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
*Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale (; 12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the Crimean War, i ...
(1820–1910), nurse
*Chris Packham
Christopher Gary Packham CBE (born 4 May 1961) is an English naturalist, nature photographer, television presenter and author, best known for his television work including the CBBC children's nature series '' The Really Wild Show'' from 1986 ...
(born 1961), naturalist and broadcaster
References
Further reading
The following out-of-copyright books can be read online or downloaded: * * * Extracts from the above texts have been brought together by the New Forest author and cultural historian Ian McKay in his anthologies: * * These anthologies also include writings byWilliam Cobbett
William Cobbett (9 March 1763 – 18 June 1835) was an English pamphleteer, journalist, politician, and farmer born in Farnham, Surrey. He was one of an agrarian faction seeking to reform Parliament, abolish "rotten boroughs", restrain foreign ...
, Daniel Defoe, William Gilpin, William Howitt
William Howitt (18 December 1792 – 3 March 1879), was a prolific English writer on history and other subjects. Howitt Primary Community School in Heanor, Derbyshire, is named after him and his wife.
Biography
Howitt was born at Heanor, Derbysh ...
, W. H. Hudson, and Heywood Sumner
George Heywood Maunoir Sumner (1853–1940) was originally an English painter, illustrator and craftsman, closely involved with the Arts and Crafts movement and the late-Victorian London art world. In his mid-forties he relocated to Cuckoo Hill, ...
.
*
External links
The Official New Forest Tourism Website , Information on visiting the National Park
*Designation as a national park:
( DEFRA press release, 28 June 2004)
New Forest National Park becomes a reality
( DEFRA press release, 24 February 2004)
The New Forest National Park
(
Countryside Agency
The Countryside Agency was a statutory body set up in England in 1999 with the task of improving the quality of the rural environment and the lives of those living in it. The agency was dissolved in 2006 and its functions dispersed among other bod ...
press release, 1 March 2005)
New Forest National Park Inquiry
from the Planning Inspectorate
Maps of the boundary
* {{SSSIs Wilts biological 1079 establishments in England English royal forests Forests and woodlands of Hampshire Forests and woodlands of Wiltshire Heathland Sites of Special Scientific Interest National parks in England Nature Conservation Review sites New Forest District Parks and open spaces in Hampshire Parks and open spaces in Wiltshire Protected areas established in 2005 Ramsar sites in England Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Hampshire Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Wiltshire South East England Special Areas of Conservation in England Woodland Sites of Special Scientific Interest Natural regions of England William the Conqueror