Yamanote on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 and are traditional names for two areas of Tokyo, Japan. Yamanote refers to the affluent, upper-class areas of Tokyo west of the Imperial Palace.Iwanami Japanese dictionary, 6th Edition (2008), DVD version While citizens once considered it as consisting of Hongo,
and are traditional names for two areas of Tokyo, Japan. Yamanote refers to the affluent, upper-class areas of Tokyo west of the Imperial Palace.Iwanami Japanese dictionary, 6th Edition (2008), DVD version While citizens once considered it as consisting of Hongo,
 The terms' usage as geographic terms in modern times has changed. In '' Metropolis Magazine'', translator and scholar
The terms' usage as geographic terms in modern times has changed. In '' Metropolis Magazine'', translator and scholar
 The extent of the early Yamanote cannot be defined exactly, but in
The extent of the early Yamanote cannot be defined exactly, but in
 The term originally indicated just the three areas of Kanda,
The term originally indicated just the three areas of Kanda,
from Yahoo Japan's Encyclopedia, accessed on June 26, 2009 The use of either is still considered very low-class and rough. Shitamachi speakers are also supposedly less apt to use the elaborate word forms more characteristic of Yamanote Japanese. ''Yamanote kotoba'' and ''Shitamachi kotoba'' together form the so-called which, because of its influences from Western Japan, is a linguistic island within the ''Kantō region''.
 and are traditional names for two areas of Tokyo, Japan. Yamanote refers to the affluent, upper-class areas of Tokyo west of the Imperial Palace.Iwanami Japanese dictionary, 6th Edition (2008), DVD version While citizens once considered it as consisting of Hongo,
and are traditional names for two areas of Tokyo, Japan. Yamanote refers to the affluent, upper-class areas of Tokyo west of the Imperial Palace.Iwanami Japanese dictionary, 6th Edition (2008), DVD version While citizens once considered it as consisting of Hongo, Kōjimachi
is a district in Chiyoda, Tokyo.
History
Prior to the arrival of Tokugawa Ieyasu, the area was known as . The area developed as townspeople settled along the Kōshū Kaidō.
In 1878, the Kōjimachi area became , a ward of the city of Tokyo.
I ...
, Koishikawa
is a district of Bunkyo, Tokyo. It consists of five sub-areas, . In Koishikawa are located two well regarded gardens: the Koishikawa Botanical Garden (operated by the University of Tokyo) in Hakusan, and the Koishikawa Korakuen Garden in Kō ...
, Ushigome
is the name of a neighborhood in Shinjuku, Tokyo, and a former ward (牛込区 ''Ushigome-ku'') in the now-defunct Tokyo City. In 1947, when the 35 wards of Tokyo were reorganized into 23, it was merged with Yotsuya ward of Tokyo City and Yodobas ...
, Yotsuya
is a neighborhood in Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan.
It is a former ward (四谷区 ''Yotsuya-ku'') in the now-defunct Tokyo City. In 1947, when the 35 wards of Tokyo were reorganized into 23, it was merged with Ushigome ward of Tokyo City and Yo ...
, Akasaka, Aoyama and Azabu
is an area in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Built on a marshy area of foothills south of central Tokyo, its coverage roughly corresponds to that of the former Azabu Ward, presently consisting of nine official districts: Azabu-Jūban, Azabudai, Azabu ...
in the Bunkyō
is a Special wards of Tokyo, special ward located in Tokyo, Japan. Situated in the middle of the ward area, Bunkyō is a residential and educational center. Beginning in the Meiji period, literati like Natsume Sōseki, as well as scholars and pol ...
, Chiyoda (in part), Shinjuku, and Minato wards, its size has grown to include the Nakano, Suginami and Meguro
is a special ward in Tokyo, Japan. The English translation of its Japanese self-designation is Meguro City. The ward was founded on March 15, 1947.
Meguro is predominantly residential in character, but is also home to light industry, corporat ...
wards. Shitamachi is the traditional name for the area of Tokyo including today the Adachi, Arakawa, Chiyoda (in part), Chūō, Edogawa, Katsushika, Kōtō
is a special ward located in Tokyo Metropolis, Japan. The ward refers to itself as Kōtō City in English. As of May 1, 2015, the ward has an estimated population of 488,632, and a population density of 12,170 persons per km². The total area i ...
, Sumida, and Taitō
is a special ward located in Tokyo Metropolis, Japan. In English, it is known as Taitō City.
As of May 1, 2015, the ward has an estimated population of 186,276, and a population density of 18,420 persons per km2. The total area is . Thi ...
wards, the physically low part of the city along and east of the Sumida River.
The two regions have always been vaguely defined, as their identity was more based on culture and caste than on geography. While Tokugawa vassals of the warrior caste (hatamoto
A was a high ranking samurai in the direct service of the Tokugawa shogunate of feudal Japan. While all three of the shogunates in Japanese history had official retainers, in the two preceding ones, they were referred to as '' gokenin.'' Howev ...
and gokenin
A was initially a vassal of the shogunate of the Kamakura and the Muromachi periods.Iwanami Kōjien, "Gokenin" In exchange for protection and the right to become '' jitō'' (manor's lord), a ''gokenin'' had in times of peace the duty to protect ...
) lived in the hilly Yamanote, lower castes (merchants and artisans) lived in the marshy areas near the sea. This dual class and geographic division has remained strong through the centuries while evolving with the times and is still in common use today.Edogaku Jiten, Kōbunsha, 1984, pages 14, 15, and 16. Indeed, the two terms are now used also in other parts of the country. The term Yamanote still indicates a higher social status, and Shitamachi a lower one, even though ''de facto'' this is not always true.
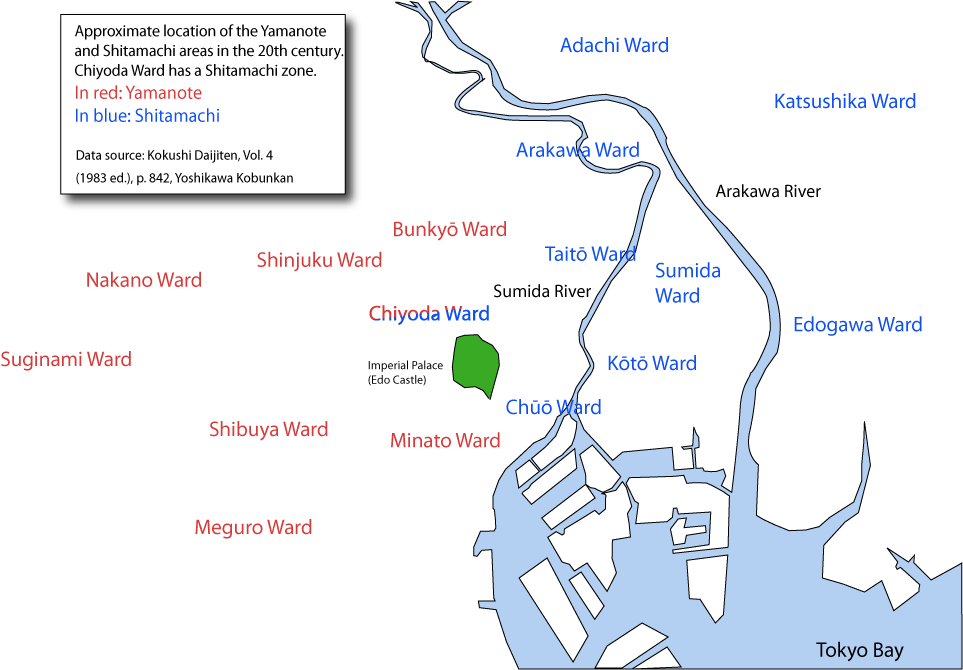
Both the Yamanote and the Shitamachi have grown gradually over the years, and the map above shows them as they are today.
History of the terms
When the Tokugawa regime moved its seat of power toEdo
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
, it granted most of the solid hilly regions to the military aristocracy and their families for residences, in part taking advantage of its cooler summer. Marshland around the mouths of the Sumida and Tone rivers, to the east of the castle, was filled in, with the flatlands that resulted becoming the area for merchants and craftsmen who supplied and worked for the aristocracy. Thus, from the beginning of its existence, Tokyo (the former Edo
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
) has been culturally and economically divided in two parts: the higher caste Yamanote, located on the hills of the Musashino Terrace
The , also translated as Musashino Platform and also named as Musashino Region, is a large tableland (known as a fluvial terrace) in the Kantō region of Honshu, Japan.
The Musashino Plateau is a plateau that extends between the Arakawa and Tama ...
, and the lower caste Shitamachi, literally "low town" or "low city", located next to the Sumida River. Although neither of the two was ever an official name, both stuck and are still in use. Both words are used with the same meaning in other parts of the country too. The term "Yamanote" is also used for example in Hokkaido, Oita, Yokohama and Osaka.
There are several theories about the etymology of the term Yamanote, in addition to its hilly location. In the book it is said that Tokugawa Ietsuna
was the fourth ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa dynasty of Japan who was in office from 1651 to 1680. He is considered the eldest son of Tokugawa Iemitsu, which makes him the grandson of Tokugawa Hidetada and the great-grandson of Tokugawa Ieyasu.
E ...
's (1641–1680) younger brother Tsunashige was given two suburban residences, one in and another in Yamanote, so it is possible that the opposite of Yamanote was not Shitamachi, but Umite. However, with the progressive construction of landfills in the Sumida estuary and the urbanization of the area, gradually Shitamachi replaced Umite. The pairing of Yamanote - Shitamachi is well attested in records of the spoken language as early as 1650, and from that time appears often in documents and books. The warrior/merchant distinction between Yamanote and Shitamachi was also well established early on.
Geography
 The terms' usage as geographic terms in modern times has changed. In '' Metropolis Magazine'', translator and scholar
The terms' usage as geographic terms in modern times has changed. In '' Metropolis Magazine'', translator and scholar Edward Seidensticker
Edward George Seidensticker (February 11, 1921 – August 26, 2007) was an American noted post-World War II scholar, historian, and preeminent translator of classical and contemporary Japanese literature. His English translation of the epic '' Th ...
believes that the dividing line goes from Ginza to Shinjuku, and "north" and "south" are more accurate terms. Seidensticker also describes how the economic and cultural centers have moved from Ginza and Nihonbashi
is a business district of Chūō, Tokyo, Japan which grew up around the bridge of the same name which has linked two sides of the Nihonbashi River at this site since the 17th century. The first wooden bridge was completed in 1603. The current ...
to Shinjuku, Ikebukuro, Shibuya, and Shinagawa.
Yamanote
Kyokutei Bakin
(), a.k.a. (, 4 July 1767 – 1 December 1848), was a Japanese novelist of the Edo period. Born (), he wrote under the pen name (). Later in life he took the pen name (). Modern scholarship generally refers to him as , or just as n. He is ...
's work ''Gendō Hōgen'' of 1818 (therefore during the Edo period) it is said that "Yotsuya, Aoyama, Ichigaya, Koishikawa and Hongō constitute Yamanote", and occupied therefore more or less a part each of today's Shinjuku, Bunkyo and Minato. Yamanote was originally considered more rustic and Shitamachi more sophisticated. It was only with the Meiji restoration that this changed because of the influx of intellectuals into its wards.
The extent of the Yamanote changed little during the Meiji era. In 1894 it was described as consisting of Hongo, Koishikawa, Ushigome, Yotsuya, Akasaka, and Azabu. After the great earthquake of 1923 and again after the second world war, the Yamanote started to expand. As a result, today's Yamanote extends, in the eyes of the young, even further than Shinjuku, Bunkyo and Minato, to Suginami, Setagaya, Nakano, and even to Kichijōji or Denen-chōfu. What used to be the hilly area within the Yamanote line has now expanded west on the Musashino Plateau. Bunkyo and Minato are generally considered Yamanote, however, some districts (Nezu and Sendagi in Bunkyo, and Shinbashi
, sometimes transliterated Shimbashi, is a district of Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Name
Read literally, the characters in Shinbashi mean "new bridge".
History
The area was the site of a bridge built across the Shiodome River in 1604. The river was la ...
in Minato) are typically Shitamachi.
Today, the Yamanote Line is one of Tokyo's busiest and most important commuter rail lines. Originally thus named in 1909, when the line only connected Shinagawa to Akabane in the Yamanote area, the line was extended into its present loop in 1925, connecting Shitamachi areas like Ueno, Kanda, Yurakucho and Shinbashi as well. is colloquially known as , or sometimes "Yamate Street", after the Yamanote region, as well.
Shitamachi
 The term originally indicated just the three areas of Kanda,
The term originally indicated just the three areas of Kanda, Nihonbashi
is a business district of Chūō, Tokyo, Japan which grew up around the bridge of the same name which has linked two sides of the Nihonbashi River at this site since the 17th century. The first wooden bridge was completed in 1603. The current ...
and Kyōbashi but, as the city grew, it came to cover also the areas mentioned above. Shitamachi was the center of Edo, so much so that the two were often thought of as coterminous. While Shitamachi was not in fact synonymous with Edo, there was originally a certain "conflation" of the two terms, and those born in Shitamachi are typically considered true Edokko, children of Edo. This conflation is evident in the Edo period habit of saying "I am going to Edo" to mean going from the area around Fukagawa in Kōtō ward to anywhere east of the Sumida river.
While the Yamanote grew west on the Musashino Plateau, in time the Shitamachi expanded east beyond the Arakawa river, and now includes the Chūō, Kōtō (Fukagawa), Sumida, and Taitō wards, plus part of Chiyoda ward.
The center of Ueno in Taitō lies at the heart of the old Shitamachi and still has several museums and a concert hall. Today the immediate area, due to its close proximity to a major transportation hub, retains high land value. The Shitamachi Museum in Ueno is dedicated to the area's way of life and culture, with models of old environments and buildings. The Edo-Tokyo Museum
The is a historical museum located at 1-4-1 Yokoami, Sumida-Ku, Tokyo in the Ryogoku district. The museum opened in March 1993 to preserve Edo's cultural heritage, and features city models of Edo and Tokyo between 1590 (just prior to t ...
, in Tokyo's Ryogoku district, also has exhibits on Shitamachi.
Bunkyo and Minato are generally considered Yamanote, however, Nezu and Sendagi in eastern Bunkyo, and Shinbashi
, sometimes transliterated Shimbashi, is a district of Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Name
Read literally, the characters in Shinbashi mean "new bridge".
History
The area was the site of a bridge built across the Shiodome River in 1604. The river was la ...
in northeastern Minato are typical Shitamachi districts.
List of districts
Wards with both Yamanote and Shitamachi districts
* Chiyoda ward: **Shitamachi: all of Kanda area **Yamanote: all of Kojimachi area * Minato ward: **Shitamachi:Shinbashi
, sometimes transliterated Shimbashi, is a district of Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Name
Read literally, the characters in Shinbashi mean "new bridge".
History
The area was the site of a bridge built across the Shiodome River in 1604. The river was la ...
, Higashi-Shinbashi
is a district of Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Shinbashi is a mainly business and entertainment district of central Tokyo, south of Hibiya Park and the Imperial Palace Tokyo.
Education
Minato City Board of Education operates public elementary and ...
(Shiodome) and Nishi-Shinbashi
is a district of Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It is home to Toei Mita Line subway stations including Onarimon Station and Uchisaiwaichō Station, as well as medical school Jikei University School of Medicine.
Education
Minato City Board of Educati ...
**Yamanote:
***all of Azabu
is an area in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Built on a marshy area of foothills south of central Tokyo, its coverage roughly corresponds to that of the former Azabu Ward, presently consisting of nine official districts: Azabu-Jūban, Azabudai, Azabu ...
area (including Azabu-Jūban
is a district of Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It consists of 1 to 4-chōme. Azabu-Jūban Station is located in this district.
Azabu-Juban is a residential area in central Tokyo with a mixture of Japanese shops, restaurants and bars. The convenience ...
, Nishi-Azabu
is a district of Minato, Tokyo, Japan, which was a part of the former Azabu Ward.
Nishiazabu is bordered by Minami-Aoyama on the north and west, Hiroo (Shibuya) on the south, Moto-Azabu on the southeast, and Roppongi on the northeast.
The Fuj ...
and Roppongi)
***all of Akasaka area (including Akasaka and Aoyama)
* Bunkyo ward:
**Shitamachi: Nezu and Sendagi
**Yamanote:
***all of Hongo area, except for Nezu and Sendagi
***all of Koishikawa
is a district of Bunkyo, Tokyo. It consists of five sub-areas, . In Koishikawa are located two well regarded gardens: the Koishikawa Botanical Garden (operated by the University of Tokyo) in Hakusan, and the Koishikawa Korakuen Garden in Kō ...
area
All Shitamachi districts
*Chuo ward (includingNihonbashi
is a business district of Chūō, Tokyo, Japan which grew up around the bridge of the same name which has linked two sides of the Nihonbashi River at this site since the 17th century. The first wooden bridge was completed in 1603. The current ...
, Kyobashi and Ginza)
*Taito ward (including Ueno, Yanaka and Asakusa
is a district in Taitō, Tokyo, Japan. It is known as the location of the Sensō-ji, a Buddhist temple dedicated to the bodhisattva Kannon. There are several other temples in Asakusa, as well as various festivals, such as the .
History
T ...
)
*Arakawa ward
*Sumida ward
*Koto ward
*Edogawa ward
*Katsushika ward
*Adachi ward
All Yamanote districts
*Shibuya ward *Shinjuku ward *Nakano ward *Suginami ward *Meguro wardDifferences between Yamanote and Shitamachi in the popular imagination
The distinction between the two areas has been called "one of the most fundamental social, subcultural, and geographic demarcations in contemporary Tokyo." While the distinction has become "geographically fuzzy, or almost non-existent...it survives symbolically because it carries the historical meaning of class boundary, the samurai having been replaced by modern white collar commuters and professionals." Generally speaking, the term Yamanote has a connotation of "distant and cold, if rich and trendy", whereas "Shitamachi people are deemed honest, forthright and reliable". These differences encompass speech, community, profession and appearance. There is also an overarching difference based on notions of modernity and tradition. The inhabitants of Yamanote were thought of as espousing modernising ideals for their country, based on Western models. The people of Shitamachi, on the other hand, came to be seen as representatives of the old order and defenders of traditional cultural forms.Speech
The modern Japanese word meaning "dialect of the Yamanote", takes its name from the region. It is characterized by a relative lack of regional inflections, by a well-developed set of honorifics (''keigo
The Japanese language has a system of honorific speech, referred to as , parts of speech that show respect. Their use is mandatory in many social situations. Honorifics in Japanese may be used to emphasize social distance or disparity in rank, ...
''), and by linguistic influences from Western Japan. After the Meiji Restoration it became the standard language spoken in public schools and therefore the basis of modern Japanese ('' hyōjungo''), which is spoken all over the country. The Yamanote accent is now considered to be standard Japanese, "making the ''shitamachi'' man a speaker of a dialect". The origins of the difference arise from the presence of '' daimyōs'' and their vassals, and the continuous influx of soldiers from the provinces.
Phrases such as meaning "Shitamachi dialect", and meaning "Shitamachi style" are still in use, and refer to certain characteristics and roughness in Shitamachi speech. The lack of distinction between the two phonemes ''hi'' and ''shi'' (so that ''hitotsu'' ("one)" is pronounced ''shitotsu'') is typical of the ''Shitamachi kotoba''. Another characteristic trait is the pronunciation of the sound ''-ai'' as for example in ''wakaranai'' (''I don't know'' or ''I don't understand'') or ''-oi'' as in ''osoi'' (slow) as ''-ee'' (''wakaranee'' or ''osee'').Tōkyō-gofrom Yahoo Japan's Encyclopedia, accessed on June 26, 2009 The use of either is still considered very low-class and rough. Shitamachi speakers are also supposedly less apt to use the elaborate word forms more characteristic of Yamanote Japanese. ''Yamanote kotoba'' and ''Shitamachi kotoba'' together form the so-called which, because of its influences from Western Japan, is a linguistic island within the ''Kantō region''.
Profession
The division between samurai and merchant has carried on into the modern day. Shitamachi is associated with petty entrepreneurs, restaurant owners, small shop-owners and workshops, while Yamanote suggests the business executive, and the office worker.Attitude
Until World War II, the Shitamachi people did not give "a damn about tomorrow". Older locals were proud of not having gone far from the neighborhood. The March 1945bombing of Tokyo
The was a series of firebombing air raids by the United States Army Air Force during the Pacific campaigns of World War II. Operation Meetinghouse, which was conducted on the night of 9–10 March 1945, is the single most destructive bombi ...
wiped out the Shitamachi area and one hundred thousand lives.
The development associated to the 1964 Summer Olympics
The , officially the and commonly known as Tokyo 1964 ( ja, 東京1964), were an international multi-sport event held from 10 to 24 October 1964 in Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo had been awarded the organization of the 1940 Summer Olympics, but this ho ...
and the Tokyo Metropolitan Expressway
is a network of toll expressways in the Greater Tokyo Area of Japan. It is operated and maintained by the .
Most routes are grade-separated (elevated roads or tunnels) and central routes have many sharp curves and multi-lane merges that requ ...
further eroded the alley lifestyle.
In spite of this, the Shitamachi mindset still values living for the moment and present pleasures.
Clinging to something is unfashionable and one should be ready to weather disaster and start over.
The Shitamachi boom
Alongside the long drive for modernisation that had characterised Japan's post-restoration
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state and may refer to:
* Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage
** Audio restoration
** Film restoration
** Image restoration
** Textile restoration
*Restoration ecology
* ...
history, Shitamachi was marginalised for the larger part of the 20th century. In the words of one sociologist, "it was increasingly confined to a defensive position, guarding old traditions and old social norms". After a long period of post-war economic decline, in the 1980s a "Shitamachi boom" emerged, with increased interest in and celebration of Shitamachi culture and history, in particular that of the Edo Period. Shitamachi culture is thus depicted as more authentic and traditional (while Yamanote Tokyo is the present and future), and its valorisation has been described as a refuge from the rapid modernisation of the economic boom years. Popular television dramas, comedy and documentary now "rarefy an often idealised notion of the Edokko, with the same intensity and nostalgia afforded an endangered species".Buckley, S. (2002) "Shitamachi", in ''Encyclopedia of contemporary Japanese culture''. Taylor & Francis p. 457
References
{{reflist Edo Areas of Tokyo