Yeovil Town Band on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Yeovil ( ) is a town and civil parish in the district of South Somerset, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somerset's southern border with Dorset, from London, south of Bristol, from Sherborne and from Taunton. The aircraft and defence industries which developed in the 20th century made it a target for bombing in the Second World War; they are still major employers. Yeovil Country Park, which includes Ninesprings, is one of several open spaces with educational, cultural and sporting facilities. Religious sites include the 14th-century Church of St John the Baptist. The town is on the A30 and A37 roads and has two railway stations.
 In the 1800s Yeovil was a glove-making centre, whose the population expanded fast. In the mid-19th century it became linked to the rest of Britain by a complex of railway lines, with competition between the
In the 1800s Yeovil was a glove-making centre, whose the population expanded fast. In the mid-19th century it became linked to the rest of Britain by a complex of railway lines, with competition between the
 Officially designated as Yeovil Municipal Borough in 1854, the town continued to lend its name to the area with the creation of the local government district of Yeovil on 1 April 1974, with the merging several neighbouring rural and urban districts, which is today known as South Somerset. Some suburbs fall within the civil parishes of
Officially designated as Yeovil Municipal Borough in 1854, the town continued to lend its name to the area with the creation of the local government district of Yeovil on 1 April 1974, with the merging several neighbouring rural and urban districts, which is today known as South Somerset. Some suburbs fall within the civil parishes of
 Yeovil is in the south of Somerset, close to the border with Dorset, from London, south of Bristol and from Taunton. It lies in the centre of the Yeovil Scarplands, a natural region of England. The suburbs include Summerlands, Hollands, Houndstone,
Yeovil is in the south of Somerset, close to the border with Dorset, from London, south of Bristol and from Taunton. It lies in the centre of the Yeovil Scarplands, a natural region of England. The suburbs include Summerlands, Hollands, Houndstone,
 AgustaWestland manufactures helicopters in Yeovil, and Normalair Garratt, (Honeywell) builder of aircraft oxygen systems, is also based there.
Yeovil's role as a centre of the aircraft and defence industries continued into the 21st century, despite attempts to diversify and the creation of industrial estates. In January 1986 a proposed sale of Westland Helicopters to the US
AgustaWestland manufactures helicopters in Yeovil, and Normalair Garratt, (Honeywell) builder of aircraft oxygen systems, is also based there.
Yeovil's role as a centre of the aircraft and defence industries continued into the 21st century, despite attempts to diversify and the creation of industrial estates. In January 1986 a proposed sale of Westland Helicopters to the US
 One symbol of Yeovil is "Jack the Treacle Eater", a folly consisting of a small archway topped by a turret with a statue on top. This stands in the village of Barwick, just to the south of the town. The hamstone Abbey Farm House was built about 1420 by John Stourton II, known as Jenkyn, as was Abbey Barn.
Hendford Manor in the town centre was built about 1720 and has since been converted into offices. It is a Grade II* listed building.
One symbol of Yeovil is "Jack the Treacle Eater", a folly consisting of a small archway topped by a turret with a statue on top. This stands in the village of Barwick, just to the south of the town. The hamstone Abbey Farm House was built about 1420 by John Stourton II, known as Jenkyn, as was Abbey Barn.
Hendford Manor in the town centre was built about 1720 and has since been converted into offices. It is a Grade II* listed building.
 Bus services linking the centre to Yeovil Junction are run by South West Coaches except on Sundays and bank holidays, when a service is operated by First West of England. The latter firm also operates a service to Pen Mill,
Yeovil has bus services from First West of England, First Hampshire & Dorset, South West Coaches,
Bus services linking the centre to Yeovil Junction are run by South West Coaches except on Sundays and bank holidays, when a service is operated by First West of England. The latter firm also operates a service to Pen Mill,
Yeovil has bus services from First West of England, First Hampshire & Dorset, South West Coaches,
 The
The
 The town's
The town's
School for Scoundrels
/ref> Later they were adapted by Barry Took for a BBC TV comedy series, ''One-Upmanship'' (1974–1978), starring Richard Briers and Peter Jones. Local band The Chesterfields released a single called "Last train to Yeovil" and pop band Bubblegum Splash a song called "18:10 to Yeovil Junction". The folk band Show of Hands wrote a song called "Yeovil Town" about violence and crime they experienced after playing a small gig in Yeovil. Yeovil is the home town of Gary Strang (played by Martin Clunes) in the TV comedy '' Men Behaving Badly''.
Yeovil Town CouncilEconomy of Yeovil
{{Authority control Towns in South Somerset Civil parishes in Somerset Market towns in Somerset
History
Archaeological surveys have yielded Palaeolithic burial and settlement sites mainly to the south of the modern town, particularly in Hendford, where a Bronze Age golden torc (twisted collar) was found. Yeovil is on the mainRoman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
from Dorchester to the Fosse Way
The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia (Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis (Ilchester), Aquae Sulis ( Bath), Corini ...
at Ilchester. The route of the old road is aligned with the A37 from Dorchester, Hendford Hill, Rustywell, across the Westland site, to Larkhill Road and Vagg Lane, rejoining the A37 at the ''Halfway House'' pub in the Ilchester Road. The Westland site has evidence of a small Roman town. There were several Roman villas (estates) in the area. Finds have been made at East Coker, West Coker and Lufton.
Medieval times
Yeovil was first named in a Saxon charter dated 880 as Gifle. It derives from the Celtic river-name ''gifl'' "forked river", an earlier name of the River Yeo. The estate was bequeathed in the will of KingAlfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bot ...
to his youngest son Aethelweard. It was recorded in the Domesday Book as ''Givele'', a thriving market community. The parish of Yeovil was part of the Stone Hundred. After the Norman Conquest, the manor, later known as Hendford, was granted to the Count of Eu
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New Yor ...
and his tenant Hugh Maltravers, whose descendants became Earls of Arundel and held the lordship until 1561. In 1205 it was granted a charter by King John King John may refer to:
Rulers
* John, King of England (1166–1216)
* John I of Jerusalem (c. 1170–1237)
* John Balliol, King of Scotland (c. 1249–1314)
* John I of France (15–20 November 1316)
* John II of France (1319–1364)
* John I o ...
. By the 14th century, the town had gained the right to elect a portreeve.
The Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
exacted a heavy toll, killing about half the population.
In 1499 a major fire destroyed many wooden, thatch-roofed buildings in the town. Yeovil suffered further fires in 1620 and 1643.
Ownership
After the dissolution of the monasteries the lord of the manor was the family of John Horsey of Clifton Maybank from 1538 to 1610 followed by the Phelips family until 1846 when it passed to the Harbins ofNewton Surmaville
Newton Surmaville is a stately home with gardens and a park south of Yeovil, Somerset in the district of South Somerset, in England. It lies just outside the town in the parish of Barwick.
House
The house, which is also known as Newton Hous ...
. Babylon Hill across the River Yeo to the south east of the town was the site of a minor skirmish, the Battle of Babylon Hill, during the English Civil War, which resulted in the Earl of Bedford's Roundheads forcing back Sir Ralph Hopton
Ralph Hopton, 1st Baron Hopton, (159628 September 1652), was an English politician, soldier and landowner. During the 1642 to 1646 First English Civil War, he served as Royalist commander in the West Country, and was made Baron Hopton of ...
's Cavaliers to Sherborne.
Development
 In the 1800s Yeovil was a glove-making centre, whose the population expanded fast. In the mid-19th century it became linked to the rest of Britain by a complex of railway lines, with competition between the
In the 1800s Yeovil was a glove-making centre, whose the population expanded fast. In the mid-19th century it became linked to the rest of Britain by a complex of railway lines, with competition between the broad gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union (CIS ...
lines of the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
(GWR) and the standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
lines of the London and South Western Railway (LSWR). In 1853 the Great Western Railway line was opened between Taunton and Yeovil.
The town's first railway was a branch line from the Bristol and Exeter Railway
The Bristol & Exeter Railway (B&ER) was an English railway company formed to connect Bristol and Exeter. It was built on the broad gauge and its engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. It opened in stages between 1841 and 1844. It was allied with ...
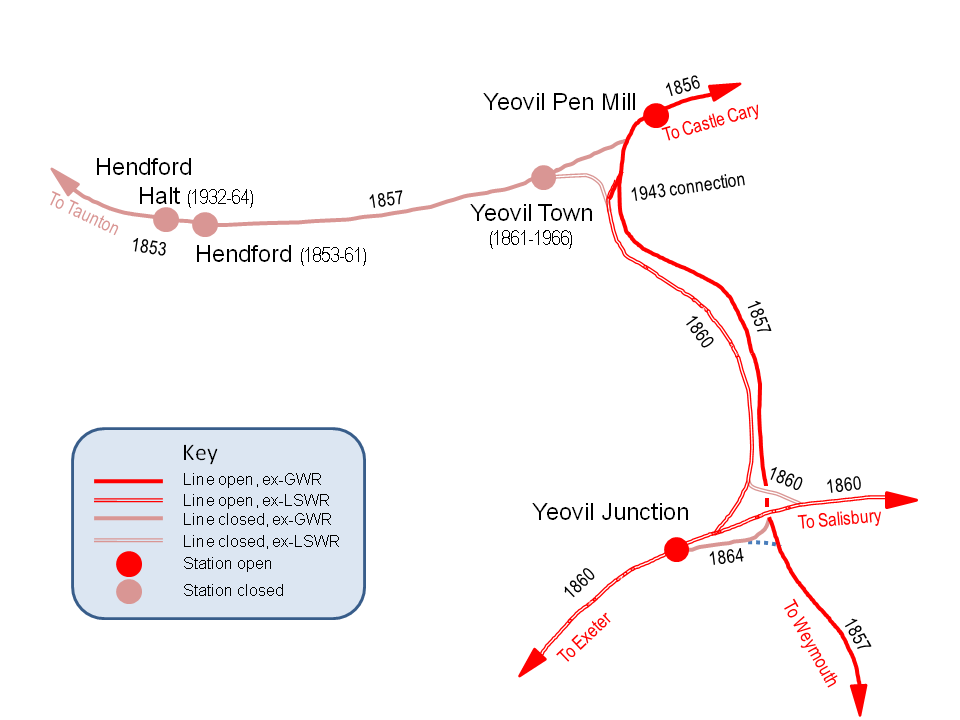
near Taunton to a terminus at on the western side of the town, which opened on 1 October 1853. As an associate of the GWR, this was a broad-gauge line. The GWR itself opened Yeovil Pen Mill railway station on the east side of the town as part of its route from London on 1 September 1856, extended to Weymouth on 1 January 1857), and the original line from Taunton connected with this. The LSWR route from London reached Hendford on 1 June 1860, but a month later the town was by-passed by an extension of the LSWR to Exeter. A new station at was provided south of the town from where passengers could catch a connecting service to Hendford. On 1 June 1861 passenger trains were withdrawn from Hendford and transferred to a new, more central, Yeovil Town railway station.
In 1854, the town gained borough status and had its first mayor. In the early 20th century Yeovil had around 11,000 inhabitants and was dominated by the defence industry, making it a target of German raids during World War II. The worst bombing was in 1940 and continued until 1942. During that time 107 high-explosive bombs fell on the town, 49 people died, 68 houses were totally destroyed and 2,377 damaged.
Industrial businesses developed round the Hendford railway goods station to such a degree that a small was opened on 2 May 1932 for passengers, but the growth of road transport and a desire to rationalise the rail network led to half of the railway stations in Yeovil being closed in 1964. First to go was Hendford Halt, closed on 15 June along with the line to Taunton, then closed on 2 October. Long-distance trains from Pen Mill were withdrawn on 11 September 1961, leaving only with a service to London, but the service between there and Pen Mill, the two remaining stations, was also withdrawn from 5 May 1968.
As a former centre of Britain's leather industry, the town is post-industrial in character. Journalist John Harris, for instance, described the towns Taunton, Yeovil and Bridgwater as a "post-industrial, hardscrabble place that contain 19 of the council wards in the 20% of English areas classed as the most deprived."
Governance

 Officially designated as Yeovil Municipal Borough in 1854, the town continued to lend its name to the area with the creation of the local government district of Yeovil on 1 April 1974, with the merging several neighbouring rural and urban districts, which is today known as South Somerset. Some suburbs fall within the civil parishes of
Officially designated as Yeovil Municipal Borough in 1854, the town continued to lend its name to the area with the creation of the local government district of Yeovil on 1 April 1974, with the merging several neighbouring rural and urban districts, which is today known as South Somerset. Some suburbs fall within the civil parishes of Yeovil Without
Yeovil Without is a civil parish in the South Somerset district of Somerset, England.
It lies on the northern edge of Yeovil. It includes both suburbs of Yeovil, including the Bucklers Mead development, and rural areas including the hamlets of Y ...
and Brympton
Brympton is a civil parish and electoral ward in Somerset, England. The parish is situated on the north-west edge of Yeovil in the South Somerset district. The parish/ward has a population of 7,308. The civil parish covers the western part of t ...
.
Yeovil still has a town council, which took over the functions of the Charter Trustees in 1982. It has responsibility for the management of recreational and leisure facilities, open spaces and play areas. In 2005, Yeovil Town Council became the first large council in Somerset to be awarded Quality Town Council status. Yeovil Town Council is based at the Town House.
There are five electoral wards covering Yeovil.
Yeovil is a county constituency represented in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It elects one Member of Parliament (MP). It covers the Somerset towns of Yeovil, Chard
Chard or Swiss chard (; ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'', Cicla Group and Flavescens Group) is a green leafy vegetable. In the cultivars of the Flavescens Group, the leaf stalks are large and often prepared separately from the leaf blade; ...
, Crewkerne and Ilminster. Until 1983 Somerset was split into four constituencies and Yeovil constituency also covered Ilchester, Martock and Somerton, but these were moved into the new constituency of Somerton and Frome
Somerton and Frome is a constituency in Somerset represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2015 by David Warburton, who was elected as a Conservative, but currently sits as an Independent after losing the Conservative whip in ...
. From the 2010 general election, Yeovil constituency regained Ilchester, to equalise the constituency populations. The Boundary Commission for England estimate that the electorate of Yeovil constituency after the boundary changes to be 77,049. The current MP is Marcus Fysh of the Conservative Party.
Geography
 Yeovil is in the south of Somerset, close to the border with Dorset, from London, south of Bristol and from Taunton. It lies in the centre of the Yeovil Scarplands, a natural region of England. The suburbs include Summerlands, Hollands, Houndstone,
Yeovil is in the south of Somerset, close to the border with Dorset, from London, south of Bristol and from Taunton. It lies in the centre of the Yeovil Scarplands, a natural region of England. The suburbs include Summerlands, Hollands, Houndstone, Preston Plucknett
Preston Plucknett is a suburb of Yeovil in Somerset, England. It was once a small village, and a separate civil parish until 1930, when it was absorbed into the neighbouring parishes of Yeovil, Brympton and West Coker. It was listed in the D ...
, Penn Mill, New Town, Hendford, Old Town, Forest Hill, Abbey Manor, Great Lyde. Outlying villages include East Coker, West Coker, Hardington Mandeville, Evershot, Halstock, Stoford, Barwick, Sutton Bingham
Closworth is a village and civil parish in Somerset, England, south of Yeovil in the South Somerset district, on the border with Dorset. The village has a population of 220.
The parish includes the villages of Pendomer and Sutton Bingham, the lo ...
, Mudford and Yetminster
Yetminster is a village and civil parish in the English county of Dorset. It lies south-west of Sherborne. It is sited on the River Wriggle, a tributary of the River Yeo, and is built almost entirely of honey-coloured limestone, which gives ...
. Other nearby villages include Bradford Abbas, Thornford Corscombe, Montacute
Montacute is a village and civil parishes in England, civil parish in Somerset, England, west of Yeovil. The village has a population of 831 (2011 census). The name Montacute is thought by some to derive from the Latin "Mons Acutus", referrin ...
(with Montacute House) and Pendomer
Closworth is a village and civil parish in Somerset, England, south of Yeovil in the South Somerset district, on the border with Dorset. The village has a population of 220.
The parish includes the villages of Pendomer and Sutton Bingham, the lo ...
. The village of Brympton
Brympton is a civil parish and electoral ward in Somerset, England. The parish is situated on the north-west edge of Yeovil in the South Somerset district. The parish/ward has a population of 7,308. The civil parish covers the western part of t ...
, now almost a suburb of Yeovil, contains the medieval manor
Manor may refer to:
Land ownership
*Manorialism or "manor system", the method of land ownership (or "tenure") in parts of medieval Europe, notably England
*Lord of the manor, the owner of an agreed area of land (or "manor") under manorialism
*Man ...
of Brympton d'Evercy. Tintinhull, also close to Yeovil, features the National Trust-owned Tintinhull House and Gardens.
Ninesprings Country Park is in the south-east near Penn Hill, linked by a cycle way along the route of the old railway to Riverside Walk, Wyndham Hill and Summerhouse Hill, forming the Yeovil Country Park.
Climate
Like the rest of South West England, Yeovil has a temperate climate generally wetter and milder than the rest of the country. The annual mean temperature is about and shows seasonal and diurnal variation, but the sea has a modifying effect. January is the coldest month, with mean minimum temperatures between and . July and August are the warmest months, with mean daily maxima around . The south-west of England is in a favoured location for the Azores high pressure zone, when it extends north-eastwards towards the UK, particularly in summer. However, convective cloud often forms inland, especially near hills, reducing the number of hours of sunshine, whose annual average annual is about 1,700 hours. Rainfall tends to be associated with Atlantic depressions or with convection. The Atlantic depressions are more vigorous in autumn and winter, when most of the rain that falls in the south-west is from that source. Average rainfall is about . November to March have the highest mean wind speeds, with June to August having the lightest winds. The predominant wind direction is from the south-west.Demography
At the 2011 census, the population of the built-up area (which extends beyond Yeovil civil parish to include the urban parts ofYeovil Without
Yeovil Without is a civil parish in the South Somerset district of Somerset, England.
It lies on the northern edge of Yeovil. It includes both suburbs of Yeovil, including the Bucklers Mead development, and rural areas including the hamlets of Y ...
and Brympton
Brympton is a civil parish and electoral ward in Somerset, England. The parish is situated on the north-west edge of Yeovil in the South Somerset district. The parish/ward has a population of 7,308. The civil parish covers the western part of t ...
parishes) was 45,784, forming 28% of the population of South Somerset district.
Economy
 AgustaWestland manufactures helicopters in Yeovil, and Normalair Garratt, (Honeywell) builder of aircraft oxygen systems, is also based there.
Yeovil's role as a centre of the aircraft and defence industries continued into the 21st century, despite attempts to diversify and the creation of industrial estates. In January 1986 a proposed sale of Westland Helicopters to the US
AgustaWestland manufactures helicopters in Yeovil, and Normalair Garratt, (Honeywell) builder of aircraft oxygen systems, is also based there.
Yeovil's role as a centre of the aircraft and defence industries continued into the 21st century, despite attempts to diversify and the creation of industrial estates. In January 1986 a proposed sale of Westland Helicopters to the US Sikorsky Aircraft
Sikorsky Aircraft is an American aircraft manufacturer based in Stratford, Connecticut. It was established by aviation pioneer Igor Sikorsky in 1923 and was among the first companies to manufacture helicopters for civilian and military use.
Pre ...
group led to the Westland affair, a crisis in the Thatcher government, resignation of Michael Heseltine as Secretary of State for Defence, and two weeks later of Secretary of State for Trade and Industry Leon Brittan, who admitted leaking a governmental law officer's letter harshly critical of Heseltine. AgustaWestland, created through the acquisition of Westland by Finmeccanica in 2000, remains the main employer in Yeovil.
Yeovil Aerodrome
Yeovil Aerodrome , sometimes known as Yeovil/Westland (to avoid confusion with nearby RNAS Yeovilton), is located in Yeovil, Somerset, England, west of the town centre.
Yeovil Aerodrome has a CAA Ordinary Licence (Number P482) that allows fli ...
, (sometimes known as Yeovil/Westland "Judwin" to avoid confusion with nearby RNAS Yeovilton), is west of the town centre. British defence giant BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh-largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenues. ...
also runs a site producing high-integrity networked software, mainly for the armed forces.
Screwfix Direct
Screwfix is a retailer of trade tools, accessories and hardware products based in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1979 as the Woodscrew Supply Company, the company was acquired in July 1999 by Kingfisher plc, which also owns B&Q, and is listed o ...
based in Houndstone started life as Woodscrew Supply Company in 1979. It is now a subsidiary of Kingfisher plc. The company warehouse relocated to Stoke-on-Trent
Stoke-on-Trent (often abbreviated to Stoke) is a city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Staffordshire, England, with an area of . In 2019, the city had an estimated population of 256,375. It is the largest settlement ...
after failing to gain planning permission for expansion.
Quedam Shopping Centre has some 45 shops: the usual high-street chains, several independents, and a multi-storey car park with about 650 spaces.
In 2015, leather manufacturer Pittards bought back its 1964 purpose-built tannery in Sherborne Road, Yeovil.
Landmarks
 One symbol of Yeovil is "Jack the Treacle Eater", a folly consisting of a small archway topped by a turret with a statue on top. This stands in the village of Barwick, just to the south of the town. The hamstone Abbey Farm House was built about 1420 by John Stourton II, known as Jenkyn, as was Abbey Barn.
Hendford Manor in the town centre was built about 1720 and has since been converted into offices. It is a Grade II* listed building.
One symbol of Yeovil is "Jack the Treacle Eater", a folly consisting of a small archway topped by a turret with a statue on top. This stands in the village of Barwick, just to the south of the town. The hamstone Abbey Farm House was built about 1420 by John Stourton II, known as Jenkyn, as was Abbey Barn.
Hendford Manor in the town centre was built about 1720 and has since been converted into offices. It is a Grade II* listed building. Newton Surmaville
Newton Surmaville is a stately home with gardens and a park south of Yeovil, Somerset in the district of South Somerset, in England. It lies just outside the town in the parish of Barwick.
House
The house, which is also known as Newton Hous ...
is a small park and house also known as Newton House, built in 1608–1612 for Robert Harbin, a Yeovil merchant. It is a Grade I listed building.
Yeovil's two theatres are the Octagon, and the Swan, now a ten-screen cinema and 18-lane tenpin bowling alley.
Yeovil District Hospital NHS Foundation Trust provides local health services.
Yeovil Railway Centre is a small museum created in 1993 in response to British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British rai ...
's decision to remove the turntable from Yeovil Junction. About of track along the Clifton Maybank spur is used for demonstration trains.
Transport
The two railway stations serve separate lines.Yeovil Pen Mill
Yeovil Pen Mill railway station is one of two stations serving the town of Yeovil, Somerset, England. The station is situated just under a mile to the east of the town centre. The station is located south of , on the Heart of Wessex Line. The ...
is on the Bristol to Weymouth line, served by Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
services, and Yeovil Junction
Yeovil Junction railway station is the busier, but less central, of two railway stations serving the town of Yeovil in England. The station is outside the town, in the village of Stoford. Although Yeovil is in Somerset, the station was in Dor ...
is on the London Waterloo to Exeter line served by South Western Railway. Both are some distance from the centre of Yeovil: Pen Mill just under to the east and Junction just over to the south.
 Bus services linking the centre to Yeovil Junction are run by South West Coaches except on Sundays and bank holidays, when a service is operated by First West of England. The latter firm also operates a service to Pen Mill,
Yeovil has bus services from First West of England, First Hampshire & Dorset, South West Coaches,
Bus services linking the centre to Yeovil Junction are run by South West Coaches except on Sundays and bank holidays, when a service is operated by First West of England. The latter firm also operates a service to Pen Mill,
Yeovil has bus services from First West of England, First Hampshire & Dorset, South West Coaches, Stagecoach South West
Stagecoach South West is a bus operator providing services in Devon and East Cornwall along with coach services to Bristol. It is a subsidiary of Stagecoach.
History Devon General
The Devon General Omnibus and Touring Company commenced operat ...
and , and coach services from National Express, Berrys Coaches
Berrys Coaches is a coach operator based in Taunton, Somerset. It was established in 1920 and is still a family owned business today.
Superfast coach services
Berrys started operating a service between Somerset and London following deregulati ...
and South West Tours. Many of the listed services serve Yeovil College. All bus routes except First West of England local routes towards the Western side of the town serve Yeovil bus station. North Dorset Community Accessible Transport (NORDCAT) provides a bookable service to places without other forms of public transport.
The town is on the A30 – the main route between London and the South West until it was supplanted by the A303 to its north. Junction 25 of the M5 motorway, giving access to Bristol and the Midlands, is about to the west, near Taunton. Yeovil is also on the mainly single-carriageway A37 north–south road between Bristol and Weymouth.
Education
Further education
Further education (often abbreviated FE) in the United Kingdom and Ireland is education in addition to that received at secondary school, that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. I ...
in Yeovil is mainly offered by Yeovil College, with land-based studies available at a Yeovil centre of Bridgwater College, and some provision through private providers. The town also has a higher education centre, University Centre Yeovil, whose main degree-awarding body is Bournemouth University, with University of the West of England offering some courses.
Secondary education in Yeovil is provided by four schools: Westfield Academy on Stiby Road; Preston School, with actress Sarah Parish among its past pupils; and Bucklers Mead Academy with past pupils including Sir Ian Botham.
Places of worship
 The
The Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
Church of St John The Baptist dates from the late 14th century. Its -high tower is in four stages, with set-back offset corner buttresses. It is capped by openwork balustrading matching the 19th-century parapets. There are two-light late 14th-century windows on all sides at bell-ringing and bell-chamber levels, the latter having fine pierced stonework grilles. There is a stair turret to the north-west corner, with a weather vane termination. The church is a Grade I listed building.
Yeovil has a Roman Catholic Holy Ghost Church, three Methodist churches (Preston Road, St Marks, Chelston Avenue, and Vicarage Street), a Baptist church in South Street, the Salvation Army
Salvation (from Latin: ''salvatio'', from ''salva'', 'safe, saved') is the state of being saved or protected from harm or a dire situation. In religion and theology, ''salvation'' generally refers to the deliverance of the soul from sin and its c ...
, Elim Pentecostal Church, Yeovil Community Church (Evangelical, based at The GateWay), Yeovil Family Church (New Frontiers), and several other Anglican churches.
There is a mosque on Sherborne Road which was opened to worshippers in May 2017.
Sport
 The town's
The town's football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
team, Yeovil Town F.C., plays in green and white livery at Huish Park
Huish Park is a football stadium located in Yeovil, Somerset, England. The stadium has been home to Yeovil Town F.C. since its completion in 1990, following their relocation from Huish. Huish Park has a capacity of 9,565 (of which two stands are ...
, and currently competes in the National League. Known as the "Glovers" (referring to the town's glove-making past), it was founded in 1895 and won, as Football Conference (the then name of National League) champions in 2003, promotion to the English Football League for the first time in its history. It had achieved numerous FA Cup victories over Football League
The English Football League (EFL) is a league of professional football clubs from England and Wales. Founded in 1888 as the Football League, the league is the oldest such competition in the world. It was the top-level football league in Engla ...
sides in the past 50 years, and since joining the League has won promotion again – as League Two champions in 2005 and League One play-off winners in 2013. However, the stay in tier 2 of English football only lasted for a season. In women's football, Yeovil Town L.F.C. was founded in 1990 and won promotion to England's highest tier, the FA Women's Super League, in 2016.
Other football teams in the town include Westland's Sports Football Club, which plays at Alvington Lane, and Pen Mill Football Club.
Yeovil Olympiads Athletics Club, founded in 1969, has produced many international athletes. The first was Eric Berry, who came 6th in the 1973 European Juniors in the hammer event. Olympians who started with the club include Max Robertson and Gary Jennings Garry or Gary Jennings may refer to:
*Gary Jennings (author) (1928–1999), American novelist
*Garry Jennings, English rock guitarist active since 1985
*Gary Jennings (athlete) (born 1972), English Olympic hurdler
*Gary Jennings Jr.
Gary Jennin ...
, both 400-metre hurdlers.
Yeovil is home to Ivel Barbarians Rugby Club, formed in 1995 by a merger of the Yeovil and Westlands clubs. South Somerset Warriors formed in 2010 and played in the South West Division of the Rugby League Conference until it folded in 2011.
The Goldenstones Pool and Leisure Centre provides a swimming pool, a teaching pool, a gym, sauna, steam room, spectator area and workout studio. Preston Sports Centre has undergone an £800,000 refurbishment, which included adding a gym and dance studio.
In late July 2007, South Somerset District Council plans were made public by the '' Western Gazette'' to build a £21-million Yeovil Sports Zone on Yeovil Recreation Ground, which has been a popular open green space with the local community for over 70 years. Residents fought to protect it, leading to rejection of the proposals in 2009, and further consultations in 2010.
The recreation space known as Mudford Rec was frequented by England cricket star Ian Botham
Ian Terence Botham, Baron Botham, (born 24 November 1955) is an English cricket commentator, member of the House of Lords, a former cricketer who has been chairman of Durham County Cricket Club since 2017 and charity fundraiser.
Hailed as one ...
during a childhood stay in Yeovil. Another regeneration project would have meant demolishing Foundry House, a former glove factory, but a local campaign led to this becoming a listed building. It will now be converted into a restaurant and offices and new shop and houses built on the surrounding site.
Popular culture
Yeovil is known inThomas Hardy
Thomas Hardy (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Word ...
's Wessex as "Ivell". It is also one of three main locations in John Cowper Powys
John Cowper Powys (; 8 October 187217 June 1963) was an English philosopher, lecturer, novelist, critic and poet born in Shirley, Derbyshire, where his father was vicar of the parish church in 1871–1879. Powys appeared with a volume of verse ...
's 1929 novel, ''Wolf Solent
''Wolf Solent'' is a novel by John Cowper Powys (1872–1963) that was written while he was based in Patchin Place, New York City, and travelling around the US as a lecturer. It was published by Simon and Schuster in May 1929 in New York. The Br ...
''.
Yeovil is the location for the fictional ''School of Lifemanship'' in a series of novels by Stephen Potter
Stephen Meredith Potter (1 February 1900 – 2 December 1969) was a British writer best known for his parodies of self-help books, and their film and television derivatives.
After leaving school in the last months of the First World War he wa ...
: ''Gamesmanship'' (1947), ''Lifemanship'' (1950), ''One-Upmanship'' (1952), ''Supermanship'' (1958), ''Anti-Woo'' (1965) and ''The Complete Golf Gamesmanship'' (1968). These were adapted for the 1960 film '' School for Scoundrels'', starring Alastair Sim, Terry-Thomas, Ian Carmichael and Irene Handl.Internet Movie DatabaseSchool for Scoundrels
/ref> Later they were adapted by Barry Took for a BBC TV comedy series, ''One-Upmanship'' (1974–1978), starring Richard Briers and Peter Jones. Local band The Chesterfields released a single called "Last train to Yeovil" and pop band Bubblegum Splash a song called "18:10 to Yeovil Junction". The folk band Show of Hands wrote a song called "Yeovil Town" about violence and crime they experienced after playing a small gig in Yeovil. Yeovil is the home town of Gary Strang (played by Martin Clunes) in the TV comedy '' Men Behaving Badly''.
International tie
Johannesburg, South Africa, has a suburb called Yeoville, so named in 1890 by Thomas Yeo Sherwell, a native of Yeovil in England. He named the streets after his sons, friends and business associates.Notable people
Among several notable Yeovil people, Robert Harbin, born in 1526, was a mercer by profession, who lived and died in Yeovil and is buried in St John the Baptist Church. His house,Newton Surmaville
Newton Surmaville is a stately home with gardens and a park south of Yeovil, Somerset in the district of South Somerset, in England. It lies just outside the town in the parish of Barwick.
House
The house, which is also known as Newton Hous ...
, was completed on the edge of the town in 1612. He was granted a coat of arms in May 1612 and given the title "Gentleman", but not knighted. Stukeley Westcott
Stukely Westcott (1592 – 12 January 1677) was one of the founding settlers of the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations and one of the original members of the first Baptist Church in America, established by Roger Williams in ...
was an early American settler (17th century) and co-founder with Roger Williams
Roger Williams (21 September 1603between 27 January and 15 March 1683) was an English-born New England Puritan minister, theologian, and author who founded Providence Plantations, which became the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantation ...
and 11 others, of Providence, Rhode Island (1636), an early American asylum of religious freedom.
Alison Adburgham
Alison Adburgham (28 January 1912 – 23 May 1997) was an English journalist, author and social historian, best known for her work as fashion editor of ''The Guardian'' newspaper, a position she held for 20 years. Along with Prudence Glynn of ' ...
(1912–1997), social historian and fashion journalist, was born in Yeovil, as were film historian William K. Everson in 1929, and traditionalist Catholic writer and public figure Michael T. Davies in 1936.
Sportspeople from Yeovil include Luton Town defender Martin Cranie
Martin James Cranie (born 26 September 1986) is an English professional association football, footballer who is currently a free agent. He most recently played as a centre back and right back for EFL Championship, Championship club Luton Town F. ...
, Olympic pentathlete Sam Weale
Samuel "Sammy" Weale (born 9 February 1982) is a British modern pentathlon, modern pentathlete who has competed at the Olympic Games. Weale competed for Great Britain at the 2008 Summer Olympics, in Beijing, China, and finished 10th in the Modern ...
, and his twin brother Chris Weale
Christopher Weale (born 9 February 1982) is a former English professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper. He is currently director of football at Sherborne School.
Career
Yeovil Town
Born in Yeovil, Somerset, Weale was a product of Yeov ...
, who is a former professional goalkeeper. Heather Stanning, a gold-medallist rower in the 2012 Olympic Games, was born in Yeovil.
England Women's Rugby World Cup winner 2014 and freedom of the town holder Marlie Packer is from Yeovil.
The arts are represented by Jim Cregan, a guitarist with Steve Harley & Cockney Rebel, musician John Parish, and his younger sister, actress Sarah Parish. Artist Flora Twort was born in Yeovil in 1893.
See also
* RNAS Yeovilton (HMS Heron)References
External links
*Yeovil Town Council
{{Authority control Towns in South Somerset Civil parishes in Somerset Market towns in Somerset