Yeovil Junction Railway Station on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
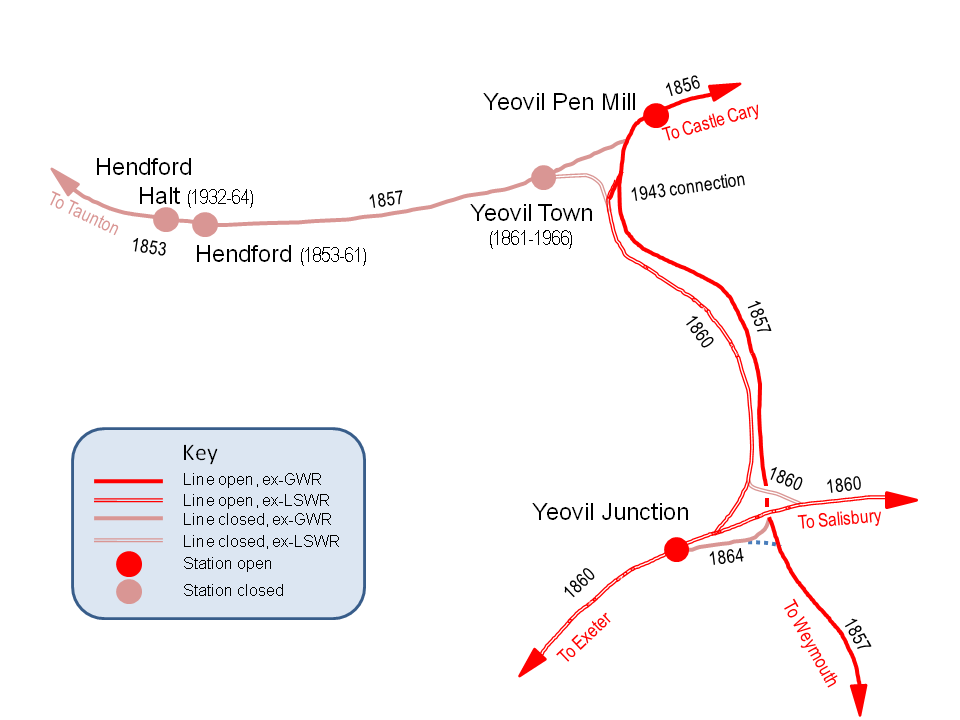
Yeovil Junction railway station is the busier, but less central, of two railway stations serving the town of
 The
The  Work started in 1907 to enlarge the station and was completed in 1909. The new northern platform was long with a track on either side; the northern track was for the Yeovil Town trains and the southern side was for main line services to London. The southern platform also had two tracks, the northern face for westbound trains and the opposite side was a goods siding. Two through tracks also passed between the platforms for non-stop trains. A footbridge at the west end connected the two platforms and extended over the branch track to the station forecourt. A second footbridge was erected at the east end of the station but was dismantled in 1920 and moved up the line to
Work started in 1907 to enlarge the station and was completed in 1909. The new northern platform was long with a track on either side; the northern track was for the Yeovil Town trains and the southern side was for main line services to London. The southern platform also had two tracks, the northern face for westbound trains and the opposite side was a goods siding. Two through tracks also passed between the platforms for non-stop trains. A footbridge at the west end connected the two platforms and extended over the branch track to the station forecourt. A second footbridge was erected at the east end of the station but was dismantled in 1920 and moved up the line to  On 1 January 1948 the Southern Railway was nationalised to become the
On 1 January 1948 the Southern Railway was nationalised to become the
 The first signal boxes were built in 1875. "Yeovil Junction No. 1" was on the north side of the line at the west of the station, and "Yeovil Junction No. 2" was at the opposite end. When the station was rebuilt in 1908 the No. 1 Box was replaced by a new 60-lever "Yeovil Junction East" situated between the main and branch lines; No. 2 box was extended and renamed "Yeovil Junction West". The latter was damaged in an accident on 20 August 1918 but was rebuilt. At the end of 1949 they were renamed again, the East Box becoming "Yeovil Junction A" and the West Box "Yeovil Junction B"
The 1967 rationalisation saw the closure of the B Box on 30 April but the A Box was retained to control movements on the branch to Yeovil Town and Pen Mill. A siding connection to the main line was controlled by "Yeovil Junction West Ground Frame", while "Yeovil Junction East Ground Frame" was used for a connection to the sidings on the south side of the main line. When the double track was reinstated to Sherborne the signal box frame was replaced with a Western Region one of 44 levers.
The remaining box was closed in March 2012, when the line between Salisbury and Exmouth Junction was re-signalled. Signalling here is now supervised from Basingstoke
The first signal boxes were built in 1875. "Yeovil Junction No. 1" was on the north side of the line at the west of the station, and "Yeovil Junction No. 2" was at the opposite end. When the station was rebuilt in 1908 the No. 1 Box was replaced by a new 60-lever "Yeovil Junction East" situated between the main and branch lines; No. 2 box was extended and renamed "Yeovil Junction West". The latter was damaged in an accident on 20 August 1918 but was rebuilt. At the end of 1949 they were renamed again, the East Box becoming "Yeovil Junction A" and the West Box "Yeovil Junction B"
The 1967 rationalisation saw the closure of the B Box on 30 April but the A Box was retained to control movements on the branch to Yeovil Town and Pen Mill. A siding connection to the main line was controlled by "Yeovil Junction West Ground Frame", while "Yeovil Junction East Ground Frame" was used for a connection to the sidings on the south side of the main line. When the double track was reinstated to Sherborne the signal box frame was replaced with a Western Region one of 44 levers.
The remaining box was closed in March 2012, when the line between Salisbury and Exmouth Junction was re-signalled. Signalling here is now supervised from Basingstoke
 South Western Railway operate services at least once per hour during the daytime to
South Western Railway operate services at least once per hour during the daytime to
Yeovil
Yeovil ( ) is a town and civil parish in the district of South Somerset, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somerset's southern border with ...
in England. The station is outside the town, in the village of Stoford. Although Yeovil is in Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
, the station was in Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset. Covering an area of , ...
until 1991. It is down the line from .
It was opened by the London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exeter ...
in 1860 on its London to Exeter line now known as the West of England Main Line
The West of England line (also known as the West of England Main Line) is a British railway line from , Hampshire, to in Devon, England. Passenger services run between London Waterloo station and Exeter; the line intersects with the Wessex Ma ...
. Today it is managed by South Western Railway and is also the home of the Yeovil Railway Centre.
History
 The
The Salisbury and Yeovil Railway
The Salisbury and Yeovil Railway linked Salisbury (Wiltshire), Gillingham (Dorset) and Yeovil (Somerset) in England. Opened in stages in 1859 and 1860, it formed a bridge route between the main London and South Western Railway (LSWR) network a ...
(S&YR) opened the final part of its line from on 1 June 1860. Near Bradford Abbas
Bradford Abbas is a village and civil parish in north west Dorset, England, southeast of Yeovil and southwest of Sherborne. The parish includes the small settlement of Saxon Maybank to the north. In the 2011 census the population of the parish ...
it crossed over the Wilts, Somerset and Weymouth line of the Great Western Railway (GWR) on a bridge, then ran alongside it and the Yeovil Branch Line of the Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) to reach that company’s terminus at , on the west side of Yeovil. Just a few weeks later, on 19 July, the London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exeter ...
(LSWR) opened its Yeovil and Exeter line. This left the S&YR at Bradford Abbas Junction and crossed over the GWR line to its own station at Yeovil Junction, and then continued on towards Exeter Queen Street. The station was a junction because another line led back to join the S&YR at River Junction, so trains could run from Exeter direct to Hendford (the terminus was moved to a joint B&ER/LSWR Yeovil Town railway station
Yeovil Town railway station was a railway station serving the town of Yeovil in Somerset, England. The station was on the Yeovil to Taunton Line and also had shuttle services to Pen Mill and Yeovil Junction stations. The station opened on 1 J ...
from 1 June 1861). The original eastwards connection from River Junction to Bradford Abbas was closed in 1870, after which most main line trains only called at Yeovil Junction where passengers could change onto a connecting train for the short journey to Yeovil Town. The LSWR operated all trains over the S&YR and bought the smaller company in 1878.
The station at this time had two platforms serving three tracks. The northern side was the track for trains to and London Waterloo
Waterloo station (), also known as London Waterloo, is a central London terminus on the National Rail network in the United Kingdom, in the Waterloo area of the London Borough of Lambeth. It is connected to a London Underground station of ...
; the middle track was covered by a train shed
A train shed is a building adjacent to a station building where the tracks and platforms of a railway station are covered by a roof. It is also known as an overall roof. Its primary purpose is to store and protect from the elements train car ...
and could be used from either platform and was for the trains to Yeovil Town; the southern track was for trains to Exeter. Goods traffic was handled on the north side of the main line, and a turntable
A phonograph, in its later forms also called a gramophone (as a trademark since 1887, as a generic name in the UK since 1910) or since the 1940s called a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogu ...
was placed on the south side. On 13 June 1864 a new line was opened from the GWR up to a goods station at Clifton Maybank on the south side of the LSWR station. The GWR was, until 1874, a broad gauge line and broad and standard gauge wagons could be brought alongside each other at Clifton Maybank to allow goods to be transhipped
Transshipment, trans-shipment or transhipment is the shipment of goods or containers to an intermediate destination, then to another destination.
One possible reason for transshipment is to change the means of transport during the journey (e.g. ...
between them.
 Work started in 1907 to enlarge the station and was completed in 1909. The new northern platform was long with a track on either side; the northern track was for the Yeovil Town trains and the southern side was for main line services to London. The southern platform also had two tracks, the northern face for westbound trains and the opposite side was a goods siding. Two through tracks also passed between the platforms for non-stop trains. A footbridge at the west end connected the two platforms and extended over the branch track to the station forecourt. A second footbridge was erected at the east end of the station but was dismantled in 1920 and moved up the line to
Work started in 1907 to enlarge the station and was completed in 1909. The new northern platform was long with a track on either side; the northern track was for the Yeovil Town trains and the southern side was for main line services to London. The southern platform also had two tracks, the northern face for westbound trains and the opposite side was a goods siding. Two through tracks also passed between the platforms for non-stop trains. A footbridge at the west end connected the two platforms and extended over the branch track to the station forecourt. A second footbridge was erected at the east end of the station but was dismantled in 1920 and moved up the line to Overton railway station
Overton railway station serves the village of Overton in Hampshire, England. It is located in the hamlet of Quidhampton.
It is down the line from . The station is served and managed by South Western Railway.
Services
South Western Railwa ...
. The goods yard was also extended in 1908 and new sidings were laid near the GWR exchange siding. The cost of the work was in excess of £47,000.
The LSWR became a part of the Southern Railway (SR) in 1923 as a result of the Railways Act 1921. The GWR’s Clifton Maybank branch closed on 7 June 1937. Wagons would in future be exchanged at Yeovil Town, but the GWR had to build a road for Mr Paul, the owner of a private siding which had connected with their line, so that he could bring his goods to the Clifton Maybank platform instead which was still served by the SR.
A new connection was established between the two companies during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
to allow trains direct access between Yeovil Junction and on the Weymouth line. This was opened on 13 October 1943 and offered a new route for trains of war materials as well as a diversion route in the event of bomb damage.
 On 1 January 1948 the Southern Railway was nationalised to become the
On 1 January 1948 the Southern Railway was nationalised to become the Southern Region of British Railways
The Southern Region was a region of British Railways from 1948 until 1992 when railways were re-privatised. The region ceased to be an operating unit in its own right in the 1980s. The region covered south London, southern England and the south ...
. January 1963 saw all the lines in the area transferred to the Western Region and this was soon followed by the ''Reshaping of British Railways
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the ...
'' report. Yeovil Town closed to passengers on 2 October 1966, the branch service then operated to Pen Mill until it was withdrawn entirely on 4 May 1968. The main line had been rationalised on 11 June 1967 – Yeovil was now in the middle of a single track section between Sherborne and . This soon proved a rationalisation too far and the double track was restored between Sherborne and Yeovil Junction on 1 October 1967 but all trains had to use the eastbound main line platform. On 26 March 1975 the former branch platform was reopened as a through line so that two trains could use the station at the same time. A limited passenger service to Yeovil Pen Mill was reinstated in 2015 since when this has gradually increased in frequency.
A permanent way depot was established in the old goods yard on the north side of the station in 1965. A small Ruston and Hornsby
Ruston & Hornsby was an industrial equipment manufacturer in Lincoln, England founded in 1918. The company is best known as a manufacturer of narrow and standard gauge diesel locomotives and also of steam shovels. Other products included cars ...
four-wheel diesel locomotive number DS1169 was kept here for shunting until 1972. In 2001 the area was used by the Somerset and Dorset Locomotive Company as a depot for its fleet of hire locomotives, although this use has now ceased. The turntable has been retained on the south side of the line and is often used for turning the locomotives of steam-hauled excursions. This and the Clifton Maybank site has been the home of the Yeovil Railway Centre since 1993.
Signalling
 The first signal boxes were built in 1875. "Yeovil Junction No. 1" was on the north side of the line at the west of the station, and "Yeovil Junction No. 2" was at the opposite end. When the station was rebuilt in 1908 the No. 1 Box was replaced by a new 60-lever "Yeovil Junction East" situated between the main and branch lines; No. 2 box was extended and renamed "Yeovil Junction West". The latter was damaged in an accident on 20 August 1918 but was rebuilt. At the end of 1949 they were renamed again, the East Box becoming "Yeovil Junction A" and the West Box "Yeovil Junction B"
The 1967 rationalisation saw the closure of the B Box on 30 April but the A Box was retained to control movements on the branch to Yeovil Town and Pen Mill. A siding connection to the main line was controlled by "Yeovil Junction West Ground Frame", while "Yeovil Junction East Ground Frame" was used for a connection to the sidings on the south side of the main line. When the double track was reinstated to Sherborne the signal box frame was replaced with a Western Region one of 44 levers.
The remaining box was closed in March 2012, when the line between Salisbury and Exmouth Junction was re-signalled. Signalling here is now supervised from Basingstoke
The first signal boxes were built in 1875. "Yeovil Junction No. 1" was on the north side of the line at the west of the station, and "Yeovil Junction No. 2" was at the opposite end. When the station was rebuilt in 1908 the No. 1 Box was replaced by a new 60-lever "Yeovil Junction East" situated between the main and branch lines; No. 2 box was extended and renamed "Yeovil Junction West". The latter was damaged in an accident on 20 August 1918 but was rebuilt. At the end of 1949 they were renamed again, the East Box becoming "Yeovil Junction A" and the West Box "Yeovil Junction B"
The 1967 rationalisation saw the closure of the B Box on 30 April but the A Box was retained to control movements on the branch to Yeovil Town and Pen Mill. A siding connection to the main line was controlled by "Yeovil Junction West Ground Frame", while "Yeovil Junction East Ground Frame" was used for a connection to the sidings on the south side of the main line. When the double track was reinstated to Sherborne the signal box frame was replaced with a Western Region one of 44 levers.
The remaining box was closed in March 2012, when the line between Salisbury and Exmouth Junction was re-signalled. Signalling here is now supervised from Basingstoke Rail Operating Centre
A rail operating centre (ROC) is a building that houses all signallers, signalling equipment, ancillaries and operators for a specific region or route on the United Kingdom's main rail network. The ROC supplants the work of several other signa ...
.
Accidents and incidents
There have been a number of accidents at Yeovil Junction over the years, although most were minor with few injuries. * 20 September 1860 – the rear coach of a Yeovil Junction to Hendford train derailed on the points leading onto the branch. * October 1860 – a goods train going towards Hendford collided with a passenger train coming the other way. * 12 June 1886 – a collision between a goods train and a passenger train to Yeovil Town due to confusing signals. * 13 July 1887 – a locomotive collided with the coaches to which it was going to couple, knocking them almost along the track and injuring nine passengers. * 26 July 1887 – an empty passenger carriage derailed while it was being added to a London train. * 4 July 1914 – a coupling of an eastbound goods train broke. The rear part collided with the front from Yeovil Junction, knocking the wooden upper storey off the West signal box. * 20 August 1918 – a collision between locomotives occurred due to the signalman not following rules.Location
The entrance to the station is across the footbridge from the car park on the north side of the line. The garage in the middle of the car park is the station’s originalgoods shed
A goods shed is a railway building designed for storing goods before or after carriage in a train. A typical goods shed will have a track running through it to allow goods wagons to be unloaded under cover, although sometimes they were built ...
, and the remaining goods sidings are at the end of the car park. Descending from the footbridge to the platform
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
brings passengers to the main station offices, which are built from red bricks with red glazed abutments. A second similar building at the east end of the platform is the station buffet which still contains its original (1908) counter. Now known as "Peppers", in 2009 it appeared in a list of "highly commended" station cafes published in ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
'' but came under new management in 2011.
Platform layout
Tracks serve both sides of the platform and are each signalled for trains to run in either direction. Beyond the east end of the platform was the signal box, now demolished. The tracks to London are on its right, and the single track to Yeovil Pen Mill is on its left. No regular passenger services operated over this route from 1968 until December 2015 when a limited service was introduced between London Waterloo and Yeovil Pen Mill via Yeovil Junction. Opposite the main platform the old eastbound through line has been lifted but the westbound line is retained as a siding, accessible only from the east end of the station. Beyond is the old westbound platform which is no longer connected to the main station but is used by occasional visiting steam trains and by the Yeovil Railway Centre which lies to the south. Theturntable
A phonograph, in its later forms also called a gramophone (as a trademark since 1887, as a generic name in the UK since 1910) or since the 1940s called a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogu ...
is at the right of their railway centre. It makes use of tracks to the left which are on the site of the old GWR Clifton Maybank goods depot. At the far end is a raised earthwork that looks like it once carried another siding, but it is in fact part of the original scheme of 1864 which envisaged another link from Clifton Maybank southwards towards which was never completed.
Services
London Waterloo
Waterloo station (), also known as London Waterloo, is a central London terminus on the National Rail network in the United Kingdom, in the Waterloo area of the London Borough of Lambeth. It is connected to a London Underground station of ...
and . A limited service operates to , some of which then continue to London Waterloo via .
There are bus services to Yeovil
Yeovil ( ) is a town and civil parish in the district of South Somerset, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somerset's southern border with ...
and the nearby village of Barwick, these are provided by South West Coaches service 68.
Connection by bus to Yeovil Pen Mill
Yeovil Pen Mill railway station is one of two stations serving the town of Yeovil, Somerset, England. The station is situated just under a mile to the east of the town centre. The station is located south of , on the Heart of Wessex Line. The ...
is accessible via a change at Yeovil Bus Station (using South West Coaches Services 68 & 70). This runs roughly 0700 to 1810 Monday to Saturday (except Public Holidays).
See also
*Southern Railway routes west of Salisbury
This article describes the history and operation of the railway routes west of Salisbury built by the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) and allied companies, which ultimately became part of the Southern Railway in the United Kingdom. Salisb ...
References
{{SWT Stations, Salisbury=y, Suburban None=y, IL None=y Buildings and structures in Yeovil Railway stations in Somerset Former London and South Western Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1860 Railway stations served by South Western Railway Rail junctions in England DfT Category D stations