Yayoi (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The started at the beginning of the Neolithic in Japan, continued through the Bronze Age, and towards its end crossed into the Iron Age.
Since the 1980s, scholars have argued that a period previously classified as a transition from the

 The Yayoi period is generally accepted to date from 300 BCE to 300 CE. However, although highly controversial, radiocarbon evidence from organic samples attached to pottery shards may suggest a date up to 500 years earlier, between 1,000 BC and 800 BC. During this period Japan transitioned to a settled agricultural society using agricultural methods that were introduced to the country, initially in the Kyushu region, from Korea.
The earliest archaeological evidence of the Yayoi is found on northern
The Yayoi period is generally accepted to date from 300 BCE to 300 CE. However, although highly controversial, radiocarbon evidence from organic samples attached to pottery shards may suggest a date up to 500 years earlier, between 1,000 BC and 800 BC. During this period Japan transitioned to a settled agricultural society using agricultural methods that were introduced to the country, initially in the Kyushu region, from Korea.
The earliest archaeological evidence of the Yayoi is found on northern
 The origin of Yayoi culture and the
The origin of Yayoi culture and the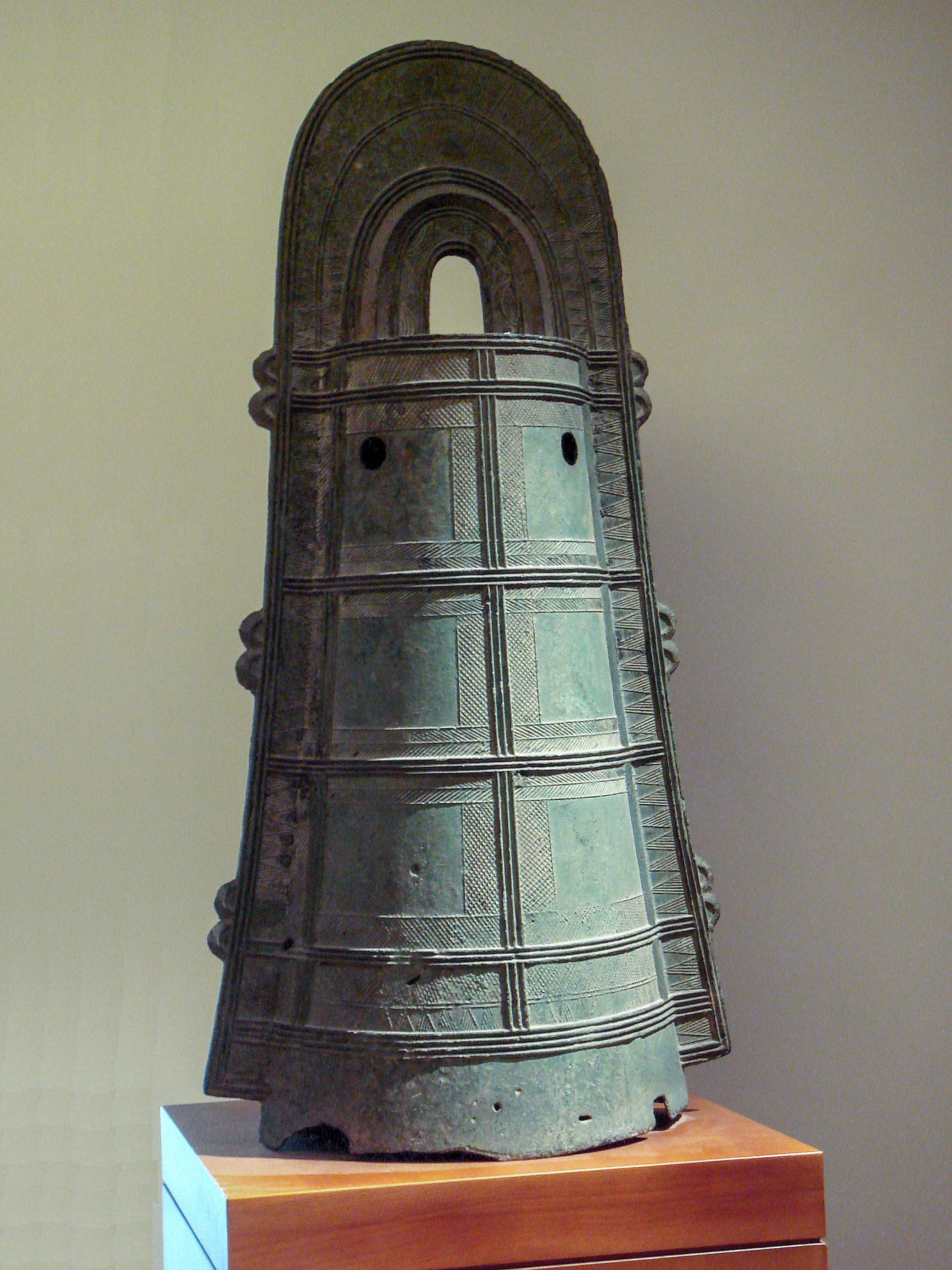  Some scholars claimed that Korean influence existed.
Some scholars claimed that Korean influence existed.  However, some scholars argue that the rapid increase of roughly four million people in Japan between the Jōmon and Yayoi periods cannot be explained by migration alone. They attribute the increase primarily to a shift from a hunter-gatherer to an agricultural diet on the islands, with the introduction of rice. It is quite likely that rice cultivation and its subsequent deification allowed for a slow and gradual population increase. Regardless, there is archaeological evidence that supports the idea that there was an influx of farmers from the continent to Japan that absorbed or overwhelmed the native hunter-gatherer population.
Some pieces of Yayoi pottery clearly show the influence of Jōmon ceramics. In addition, the Yayoi lived in the same type of pit or circular dwelling as that of the Jōmon. Other examples of commonality are chipped stone tools for hunting, bone tools for fishing, shells in bracelet construction, and lacquer decoration for vessels and accessories.
According to several linguists, Japonic was present on large parts of the southern Korean peninsula. These "Peninsular Japonic languages" were replaced by Koreanic-speakers (possibly belonging to the Han-branch) likely causing the Yayoi migration.Vovin, Alexander (2013). "From Koguryo to Tamna: Slowly riding to the South with speakers of Proto-Korean". ''Korean Linguistics''. 15 (2): 222–240. Similarly Whitman (2012) suggests that the Yayoi are not related to the proto-Koreans but that they were present on the Korean peninsula during the Mumun pottery period. According to him, Japonic arrived in the Korean peninsula around 1500 BC and was brought to the Japanese archipelago by the Yayoi at around 950 BC. The language family associated with both Mumun and Yayoi culture is Japonic. Koreanic arrived later from Manchuria to the Korean peninsula at around 300 BC and coexist with the descendants of the Japonic Mumun cultivators (or assimilated them). Both had influence on each other and a later
However, some scholars argue that the rapid increase of roughly four million people in Japan between the Jōmon and Yayoi periods cannot be explained by migration alone. They attribute the increase primarily to a shift from a hunter-gatherer to an agricultural diet on the islands, with the introduction of rice. It is quite likely that rice cultivation and its subsequent deification allowed for a slow and gradual population increase. Regardless, there is archaeological evidence that supports the idea that there was an influx of farmers from the continent to Japan that absorbed or overwhelmed the native hunter-gatherer population.
Some pieces of Yayoi pottery clearly show the influence of Jōmon ceramics. In addition, the Yayoi lived in the same type of pit or circular dwelling as that of the Jōmon. Other examples of commonality are chipped stone tools for hunting, bone tools for fishing, shells in bracelet construction, and lacquer decoration for vessels and accessories.
According to several linguists, Japonic was present on large parts of the southern Korean peninsula. These "Peninsular Japonic languages" were replaced by Koreanic-speakers (possibly belonging to the Han-branch) likely causing the Yayoi migration.Vovin, Alexander (2013). "From Koguryo to Tamna: Slowly riding to the South with speakers of Proto-Korean". ''Korean Linguistics''. 15 (2): 222–240. Similarly Whitman (2012) suggests that the Yayoi are not related to the proto-Koreans but that they were present on the Korean peninsula during the Mumun pottery period. According to him, Japonic arrived in the Korean peninsula around 1500 BC and was brought to the Japanese archipelago by the Yayoi at around 950 BC. The language family associated with both Mumun and Yayoi culture is Japonic. Koreanic arrived later from Manchuria to the Korean peninsula at around 300 BC and coexist with the descendants of the Japonic Mumun cultivators (or assimilated them). Both had influence on each other and a later
 The earliest written records about people in Japan are from
The earliest written records about people in Japan are from
 The ''Wei Zhi'' (), which is part of the Records of the three Kingdoms, first mentions
The ''Wei Zhi'' (), which is part of the Records of the three Kingdoms, first mentions 最古級の奈良・桜井“3兄弟古墳”、形状ほぼ判明 卑弥呼の時代に相次いで築造
, Sankei Shimbun, March 6, 2008 Some scholars assume that the Hashihaka kofun in Makimuku was the tomb of Himiko. Its relation to the origin of the Yamato polity in the following
Yayoi Culture
Department of Asian Art, The Metropolitan Museum of Art
a
An article
by Richard Hooker on the Yayoi and the Jōmon.
Comprehensive Database of Archaeological Site Reports in Japan
Nara National Research Institute for Cultural Properties
{{DEFAULTSORT:Yayoi Period Japanese eras Ancient peoples Archaeological cultures of East Asia 4th-century BC establishments in Japan 4th-century disestablishments in Japan
Jōmon period
The is the time in Japanese history, traditionally dated between 6,000–300 BCE, during which Japan was inhabited by a diverse hunter-gatherer and early agriculturalist population united through a common Jōmon culture, which reached a c ...
should be reclassified as Early Yayoi. The date of the beginning of this transition is controversial, with estimates ranging from the 10th to the 3rd centuries BC.
The period is named after the neighbourhood of Tokyo where archaeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
first uncovered artifacts and features from that era in the late 19th century. Distinguishing characteristics of the Yayoi period include the appearance of new Yayoi pottery styles and the start of an intensive rice agriculture in paddy field
A paddy field is a flooded field (agriculture), field of arable land used for growing Aquatic plant, semiaquatic crops, most notably rice and taro. It originates from the Neolithic rice-farming cultures of the Yangtze River basin in sout ...
s. A hierarchical social class
A social class is a grouping of people into a set of Dominance hierarchy, hierarchical social categories, the most common being the Upper class, upper, Middle class, middle and Working class, lower classes. Membership in a social class can for ...
structure dates from this period and has its origin in China. Techniques in metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
based on the use of bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
and iron were also introduced from China via Korea to Japan in this period.
The Yayoi followed the Jōmon period and Yayoi culture flourished in a geographic area from southern Kyūshū
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
to northern Honshū
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island separa ...
. Archaeological evidence supports the idea that during this time, an influx of farmers (Yayoi People) from the Korean Peninsula to Japan overwhelmed and mixed with the native predominantly hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
population (Jomon).
Features

 The Yayoi period is generally accepted to date from 300 BCE to 300 CE. However, although highly controversial, radiocarbon evidence from organic samples attached to pottery shards may suggest a date up to 500 years earlier, between 1,000 BC and 800 BC. During this period Japan transitioned to a settled agricultural society using agricultural methods that were introduced to the country, initially in the Kyushu region, from Korea.
The earliest archaeological evidence of the Yayoi is found on northern
The Yayoi period is generally accepted to date from 300 BCE to 300 CE. However, although highly controversial, radiocarbon evidence from organic samples attached to pottery shards may suggest a date up to 500 years earlier, between 1,000 BC and 800 BC. During this period Japan transitioned to a settled agricultural society using agricultural methods that were introduced to the country, initially in the Kyushu region, from Korea.
The earliest archaeological evidence of the Yayoi is found on northern Kyūshū
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
, but that is still debated. Yayoi culture quickly spread to the main island of Honshū, mixing with native Jōmon culture.
The name Yayoi is borrowed from a location in Tokyo where pottery of the Yayoi period was first found. Yayoi pottery was simply decorated and produced using the same coiling technique previously used in Jōmon pottery. Yayoi craft specialists made bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
ceremonial bells ('' dōtaku''), mirrors, and weapons. By the 1st century AD, Yayoi people began using iron agricultural tools and weapons.
As the Yayoi population increased, the society became more stratified and complex. They wove textiles
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
, lived in permanent farming villages, and constructed buildings with wood and stone. They also accumulated wealth through land ownership and the storage of grain. Such factors promoted the development of distinct social classes. Contemporary Chinese sources described the people as having tattoos and other bodily markings which indicated differences in social status. Yayoi chiefs, in some parts of Kyūshū, appear to have sponsored, and politically manipulated, trade in bronze and other prestige objects. That was made possible by the introduction of an irrigated, wet-rice agriculture from the Yangtze estuary in southern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
via the Ryukyu Islands or Korean Peninsula. Wet-rice agriculture led to the development and growth of a sedentary, agrarian society in Japan. Local political and social developments in Japan were more important than the activities of the central authority within a stratified society.
Direct comparisons between Jōmon and Yayoi skeletons show that the two peoples are noticeably distinguishable. The Jōmon tended to be shorter, with relatively longer forearms and lower legs, more deep-set eyes, shorter and wider faces, and much more pronounced facial topography. They also have strikingly raised brow ridges, noses, and nose bridges. Yayoi people, on the other hand, averaged 2.5 cm - 5 cm taller, with shallow-set eyes, high and narrow faces, and flat brow ridges and noses. By the Kofun period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is ...
, almost all skeletons excavated in Japan except those of the Ainu
Ainu or Aynu may refer to:
*Ainu people, an East Asian ethnic group of Japan and the Russian Far East
*Ainu languages, a family of languages
**Ainu language of Hokkaido
**Kuril Ainu language, extinct language of the Kuril Islands
**Sakhalin Ainu la ...
are of the Yayoi type with some having small Jomon admixture, resembling those of modern-day Japanese.
History
Origin of the Yayoi people
 The origin of Yayoi culture and the
The origin of Yayoi culture and the Yayoi people
The were an ancient ethnicity that migrated to the Japanese archipelago from Korea and China during the Yayoi period (300 BCE–300 CE). Although highly controversial, a single study that utilized radiometric dating techniques inconclusively ...
has long been debated. The earliest archaeological sites are Itazuke or Nabata in the northern part of Kyūshū. Contacts between fishing communities on this coast and the southern coast of Korea date from the Jōmon period, as witnessed by the exchange of trade items such as fishhooks and obsidian. During the Yayoi period, cultural features from Korea and China arrived in this area at various times over several centuries, and later spread to the south and east. This was a period of mixture between immigrants and the indigenous population, and between new cultural influences and existing practices.
Chinese influence was obvious in the bronze and copper weapons, dōkyō, dōtaku, as well as irrigated paddy rice cultivation. Three major symbols of Yayoi culture are the bronze mirror, the bronze sword, and the royal seal stone.
Between 1996 and 1999, a team led by Satoshi Yamaguchi, a researcher at Japan's National Museum of Nature and Science
The is in the northeast corner of Ueno Park in Tokyo. The museum has exhibitions on pre-Meiji period, Meiji science in Japan. It is the venue of the taxidermied bodies of the legendary dogs Hachikō and Taro and Jiro. A life-size blue whale mode ...
, compared Yayoi remains found in Japan's Yamaguchi and Fukuoka prefectures with those from China's coastal Jiangsu province and found many similarities between the Yayoi and the Jiangsu remains.
 Some scholars claimed that Korean influence existed.
Some scholars claimed that Korean influence existed. Mark J. Hudson
Mark James Hudson (born 10 July 1963, in Roade) is a British archaeologist interested in multicultural Japan. His initial areas of specialization were the Jōmon period and the Yayoi period.Society for East Asian Archaeology (SEAA) Member news ...
has cited archaeological evidence that included "bounded paddy fields, new types of polished stone tools, wooden farming implements, iron tools, weaving technology, ceramic storage jars, exterior bonding of clay coils in pottery fabrication, ditched settlements, domesticated pigs, and jawbone rituals". The migrant transfusion from the Korean peninsula gains strength because Yayoi culture began on the north coast of Kyūshū, where Japan is closest to Korea. Yayoi pottery, burial mounds, and food preservation
Food preservation includes processes that make food more resistant to microorganism growth and slow the oxidation of fats. This slows down the decomposition and rancidification process. Food preservation may also include processes that inhibit ...
were discovered to be very similar to the pottery of southern Korea.
 However, some scholars argue that the rapid increase of roughly four million people in Japan between the Jōmon and Yayoi periods cannot be explained by migration alone. They attribute the increase primarily to a shift from a hunter-gatherer to an agricultural diet on the islands, with the introduction of rice. It is quite likely that rice cultivation and its subsequent deification allowed for a slow and gradual population increase. Regardless, there is archaeological evidence that supports the idea that there was an influx of farmers from the continent to Japan that absorbed or overwhelmed the native hunter-gatherer population.
Some pieces of Yayoi pottery clearly show the influence of Jōmon ceramics. In addition, the Yayoi lived in the same type of pit or circular dwelling as that of the Jōmon. Other examples of commonality are chipped stone tools for hunting, bone tools for fishing, shells in bracelet construction, and lacquer decoration for vessels and accessories.
According to several linguists, Japonic was present on large parts of the southern Korean peninsula. These "Peninsular Japonic languages" were replaced by Koreanic-speakers (possibly belonging to the Han-branch) likely causing the Yayoi migration.Vovin, Alexander (2013). "From Koguryo to Tamna: Slowly riding to the South with speakers of Proto-Korean". ''Korean Linguistics''. 15 (2): 222–240. Similarly Whitman (2012) suggests that the Yayoi are not related to the proto-Koreans but that they were present on the Korean peninsula during the Mumun pottery period. According to him, Japonic arrived in the Korean peninsula around 1500 BC and was brought to the Japanese archipelago by the Yayoi at around 950 BC. The language family associated with both Mumun and Yayoi culture is Japonic. Koreanic arrived later from Manchuria to the Korean peninsula at around 300 BC and coexist with the descendants of the Japonic Mumun cultivators (or assimilated them). Both had influence on each other and a later
However, some scholars argue that the rapid increase of roughly four million people in Japan between the Jōmon and Yayoi periods cannot be explained by migration alone. They attribute the increase primarily to a shift from a hunter-gatherer to an agricultural diet on the islands, with the introduction of rice. It is quite likely that rice cultivation and its subsequent deification allowed for a slow and gradual population increase. Regardless, there is archaeological evidence that supports the idea that there was an influx of farmers from the continent to Japan that absorbed or overwhelmed the native hunter-gatherer population.
Some pieces of Yayoi pottery clearly show the influence of Jōmon ceramics. In addition, the Yayoi lived in the same type of pit or circular dwelling as that of the Jōmon. Other examples of commonality are chipped stone tools for hunting, bone tools for fishing, shells in bracelet construction, and lacquer decoration for vessels and accessories.
According to several linguists, Japonic was present on large parts of the southern Korean peninsula. These "Peninsular Japonic languages" were replaced by Koreanic-speakers (possibly belonging to the Han-branch) likely causing the Yayoi migration.Vovin, Alexander (2013). "From Koguryo to Tamna: Slowly riding to the South with speakers of Proto-Korean". ''Korean Linguistics''. 15 (2): 222–240. Similarly Whitman (2012) suggests that the Yayoi are not related to the proto-Koreans but that they were present on the Korean peninsula during the Mumun pottery period. According to him, Japonic arrived in the Korean peninsula around 1500 BC and was brought to the Japanese archipelago by the Yayoi at around 950 BC. The language family associated with both Mumun and Yayoi culture is Japonic. Koreanic arrived later from Manchuria to the Korean peninsula at around 300 BC and coexist with the descendants of the Japonic Mumun cultivators (or assimilated them). Both had influence on each other and a later founder effect
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using ...
diminished the internal variety of both language families.
Languages
Most linguists and archaeologists agree that theJaponic language family
Japonic or Japanese–Ryukyuan, sometimes also Japanic, is a language family comprising Japanese, spoken in the main islands of Japan, and the Ryukyuan languages, spoken in the Ryukyu Islands. The family is universally accepted by linguists, and ...
was introduced to and spread through the archipelago during the Yayoi period.
Emergence of ''Wo'' in Chinese history texts
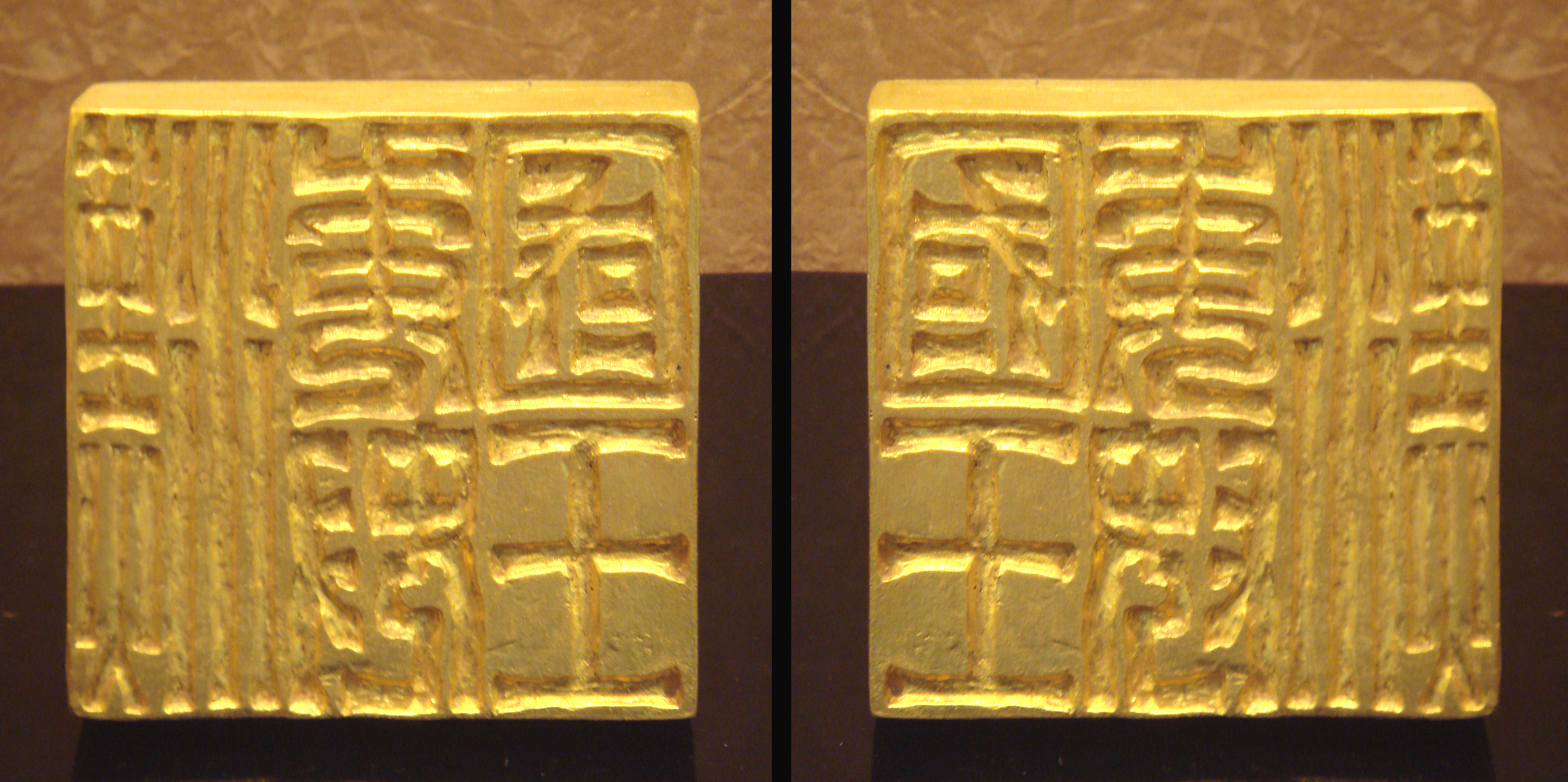
 The earliest written records about people in Japan are from
The earliest written records about people in Japan are from Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
sources from this period. Wo, the pronunciation of an early Chinese name for Japan, was mentioned in 57 AD; the Na state of Wo received a golden seal from the Emperor Guangwu
Emperor Guangwu of Han (; 15 January 5 BC – 29 March AD 57), born Liu Xiu (), courtesy name Wenshu (), was a Chinese monarch. He served as an emperor of the Han dynasty by restoring the dynasty in AD 25, thus founding the Eastern Han (Later ...
of the Later Han dynasty. This event was recorded in the ''Book of the Later Han
The ''Book of the Later Han'', also known as the ''History of the Later Han'' and by its Chinese name ''Hou Hanshu'' (), is one of the Twenty-Four Histories and covers the history of the Han dynasty from 6 to 189 CE, a period known as the Later ...
'' compiled by Fan Ye in the 5th century. The seal itself was discovered in northern Kyūshū in the 18th century. Wo was also mentioned in 257 in the ''Wei zhi'', a section of the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220– ...
'' compiled by the 3rd-century scholar Chen Shou.
Early Chinese historians described Wo as a land of hundreds of scattered tribal communities rather than the unified land with a 700-year tradition as laid out in the 8th-century work '' Nihon Shoki'', a partly mythical, partly historical account of Japan which dates the foundation of the country at 660 BC. Archaeological evidence also suggests that frequent conflicts between settlements or statelets broke out in the period. Many excavated settlements were moated or built at the tops of hills. Headless human skeletons discovered in Yoshinogari site are regarded as typical examples of finds from the period. In the coastal area of the Inland Sea
An inland sea (also known as an epeiric sea or an epicontinental sea) is a continental body of water which is very large and is either completely surrounded by dry land or connected to an ocean by a river, strait, or "arm of the sea". An inland se ...
, stone arrowheads are often found among funerary objects.
Third-century Chinese sources reported that the Wa people
The Wa people ( Wa: Vāx; my, ဝလူမျိုး, ; ; th, ว้า) are a Southeast Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in Northern Myanmar, in the northern part of Shan State and the eastern part of Kachin State, near and along Myanm ...
lived on raw fish, vegetables, and rice served on bamboo and wooden trays, clapped their hands in worship (something still done in Shinto shrine
A is a structure whose main purpose is to house ("enshrine") one or more ''kami'', the deities of the Shinto religion.
Overview
Structurally, a Shinto shrine typically comprises several buildings.
The '' honden''Also called (本殿, meani ...
s today), and built earthen-grave mounds. They also maintained vassal-master relations, collected taxes, had provincial granaries and markets, and observed mourning. Society was characterised by violent struggles.
Yamataikoku
 The ''Wei Zhi'' (), which is part of the Records of the three Kingdoms, first mentions
The ''Wei Zhi'' (), which is part of the Records of the three Kingdoms, first mentions Yamataikoku
Yamatai or Yamatai-koku is the Sino-Japanese name of an ancient country in Wa (Japan) during the late Yayoi period The Chinese text ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' first recorded the name as () or (; using reconstructed Middle Chinese p ...
and Queen Himiko in the 3rd century. According to the record, Himiko assumed the throne of Wa, as a spiritual leader, after a major civil war. Her younger brother was in charge of the affairs of state, including diplomatic relations with the Chinese court of the Kingdom of Wei. When asked about their origins by the Wei embassy, the people of Wa claimed to be descendants of the Taibo of Wu, a historic figure of the Wu Kingdom around the Yangtze Delta of China.
For many years, the location of Yamataikoku and the identity of Queen Himiko have been subject of research. Two possible sites, Yoshinogari Yoshinogari may refer to:
* Yoshinogari, Saga, Japan ( :ja:吉野ヶ里町).
* Yoshinogari site, a prehistoric site located in Yoshinogari, Saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated o ...
in Saga Prefecture and Makimuku in Nara Prefecture have been suggested. Recent archaeological research in Makimuku suggests that Yamataikoku was located in the area., Sankei Shimbun, March 6, 2008 Some scholars assume that the Hashihaka kofun in Makimuku was the tomb of Himiko. Its relation to the origin of the Yamato polity in the following
Kofun period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is ...
is also under debate.
See also
*Japanese era name
The , also known as , is the first of the two elements that identify years in the Japanese era calendar scheme. The second element is a number which indicates the year number within the era (with the first year being ""), followed by the literal ...
* Ainu people
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Y ...
* Emishi people
* Yayoi people
The were an ancient ethnicity that migrated to the Japanese archipelago from Korea and China during the Yayoi period (300 BCE–300 CE). Although highly controversial, a single study that utilized radiometric dating techniques inconclusively ...
* Wa (Japan)
References
Books cited
* * *External links
Yayoi Culture
Department of Asian Art, The Metropolitan Museum of Art
a
by Richard Hooker on the Yayoi and the Jōmon.
Comprehensive Database of Archaeological Site Reports in Japan
Nara National Research Institute for Cultural Properties
{{DEFAULTSORT:Yayoi Period Japanese eras Ancient peoples Archaeological cultures of East Asia 4th-century BC establishments in Japan 4th-century disestablishments in Japan