Yale Berzelius Society on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Yale University is a
 Yale traces its beginnings to "An Act for Liberty to Erect a Collegiate School", a would-be charter passed during a meeting in New Haven by the General Court of the
Yale traces its beginnings to "An Act for Liberty to Erect a Collegiate School", a would-be charter passed during a meeting in New Haven by the General Court of the  Known from its origin as the "Collegiate School", the institution opened in the home of its first
Known from its origin as the "Collegiate School", the institution opened in the home of its first
 In 1718, at the behest of either Rector
In 1718, at the behest of either Rector
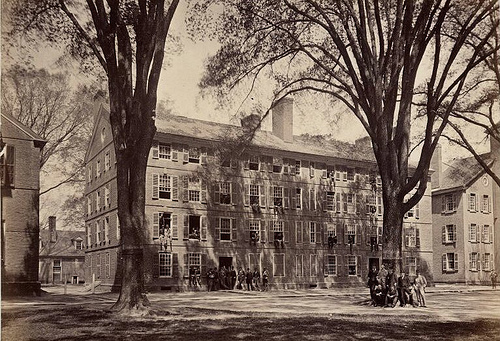
 Yale College undergraduates follow a
Yale College undergraduates follow a
 The Yale Report of 1828 was a dogmatic defense of the Latin and Greek curriculum against critics who wanted more courses in modern languages, mathematics, and science. Unlike higher education in Europe, there was no national curriculum for colleges and universities in the United States. In the competition for students and financial support, college leaders strove to keep current with demands for innovation. At the same time, they realized that a significant portion of their students and prospective students demanded a classical background. The Yale report meant the classics would not be abandoned. During this period, all institutions experimented with changes in the curriculum, often resulting in a dual-track curriculum. In the decentralized environment of higher education in the United States, balancing change with tradition was a common challenge because it was difficult for an institution to be completely modern or completely classical. A group of professors at Yale and New Haven Congregationalist ministers articulated a conservative response to the changes brought about by the Victorian culture. They concentrated on developing a person possessed of religious values strong enough to sufficiently resist temptations from within, yet flexible enough to adjust to the '-ism, isms' (professionalism, materialism, individualism, and consumerism) tempting him from without. William Graham Sumner, professor from 1872 to 1909, taught in the emerging disciplines of economics and sociology to overflowing classrooms of students. Sumner bested President Noah Porter, who disliked the social sciences and wanted Yale to lock into its traditions of classical education. Porter objected to Sumner's use of a textbook by Herbert Spencer that espoused agnostic materialism because it might harm students.
Until 1887, the legal name of the university was "The President and Fellows of Yale College, in New Haven." In 1887, under an act passed by the Connecticut General Assembly, Yale was renamed to the present "Yale University."
The Yale Report of 1828 was a dogmatic defense of the Latin and Greek curriculum against critics who wanted more courses in modern languages, mathematics, and science. Unlike higher education in Europe, there was no national curriculum for colleges and universities in the United States. In the competition for students and financial support, college leaders strove to keep current with demands for innovation. At the same time, they realized that a significant portion of their students and prospective students demanded a classical background. The Yale report meant the classics would not be abandoned. During this period, all institutions experimented with changes in the curriculum, often resulting in a dual-track curriculum. In the decentralized environment of higher education in the United States, balancing change with tradition was a common challenge because it was difficult for an institution to be completely modern or completely classical. A group of professors at Yale and New Haven Congregationalist ministers articulated a conservative response to the changes brought about by the Victorian culture. They concentrated on developing a person possessed of religious values strong enough to sufficiently resist temptations from within, yet flexible enough to adjust to the '-ism, isms' (professionalism, materialism, individualism, and consumerism) tempting him from without. William Graham Sumner, professor from 1872 to 1909, taught in the emerging disciplines of economics and sociology to overflowing classrooms of students. Sumner bested President Noah Porter, who disliked the social sciences and wanted Yale to lock into its traditions of classical education. Porter objected to Sumner's use of a textbook by Herbert Spencer that espoused agnostic materialism because it might harm students.
Until 1887, the legal name of the university was "The President and Fellows of Yale College, in New Haven." In 1887, under an act passed by the Connecticut General Assembly, Yale was renamed to the present "Yale University."
 Along with
Along with
 Milton Winternitz led the Yale School of Medicine as its dean from 1920 to 1935. Dedicated to the new scientific medicine established in Germany, he was equally fervent about "social medicine" and the study of humans in their culture and environment. He established the "Yale System" of teaching, with few lectures and fewer exams, and strengthened the full-time faculty system; he also created the graduate-level Yale School of Nursing and the psychiatry department and built numerous new buildings. Progress toward his plans for an Institute of Human Relations, envisioned as a refuge where social scientists would collaborate with biological scientists in a holistic study of humankind, unfortunately, lasted for only a few years before the opposition of resentful anti-Semitic colleagues drove him to resign.
Milton Winternitz led the Yale School of Medicine as its dean from 1920 to 1935. Dedicated to the new scientific medicine established in Germany, he was equally fervent about "social medicine" and the study of humans in their culture and environment. He established the "Yale System" of teaching, with few lectures and fewer exams, and strengthened the full-time faculty system; he also created the graduate-level Yale School of Nursing and the psychiatry department and built numerous new buildings. Progress toward his plans for an Institute of Human Relations, envisioned as a refuge where social scientists would collaborate with biological scientists in a holistic study of humankind, unfortunately, lasted for only a few years before the opposition of resentful anti-Semitic colleagues drove him to resign.
 Before World War II, most elite university faculties counted among their numbers few, if any, Jews, blacks, women, or other minorities; Yale was no exception. By 1980, this condition had been altered dramatically, as numerous members of those groups held faculty positions. Almost all members of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences—and some members of other faculties—teach undergraduate courses, more than 2,000 of which are offered annually.
Before World War II, most elite university faculties counted among their numbers few, if any, Jews, blacks, women, or other minorities; Yale was no exception. By 1980, this condition had been altered dramatically, as numerous members of those groups held faculty positions. Almost all members of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences—and some members of other faculties—teach undergraduate courses, more than 2,000 of which are offered annually.
Pamela Price
(civil rights attorney in California), and Lisa E. Stone (works at Anti-Defamation League). They were joined by Yale classics professor John “Jack” J. Winkler, who died in 1990. The lawsuit, brought partly by Catharine A. MacKinnon, Catharine MacKinnon, alleged rape, fondling, and offers of higher grades for sex by several Yale faculty, including Keith Brion, professor of flute and director of bands, political Science professo
Raymond Duvall
(now at the University of Minnesota), English professor Michael George Cooke, Michael Cooke, and coach of the field hockey team, Richard Kentwell. While unsuccessful in the courts, the legal reasoning behind the case changed the landscape of sex discrimination law and resulted in the establishment of Yale's Grievance Board and the Yale Women's Center. In March 2011 a Title IX complaint was filed against Yale by students and recent graduates, including editors of Yale's feminist magazine Broad Recognition, alleging that the university had a hostile sexual climate. In response, the university formed a Title IX steering committee to address complaints of sexual misconduct. Afterwards, universities and colleges throughout the US also established sexual harassment grievance procedures.
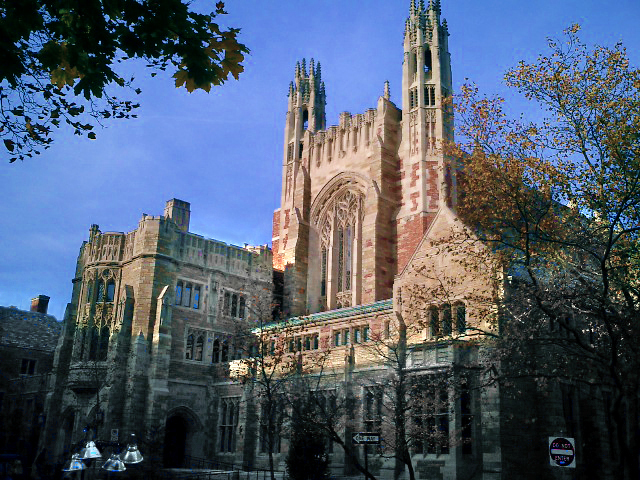

 Yale's central campus in
Yale's central campus in 
 Other examples of the Gothic style are on the Old Campus by architects like Henry Austin (architect), Henry Austin, Charles C. Haight and Russell Sturgis. Several are associated with members of the Vanderbilt family, including Vanderbilt Hall, Phelps Hall, St. Anthony Hall (a commission for member Frederick William Vanderbilt), the Mason, Sloane and Osborn laboratories, dormitories for the Sheffield Scientific School (the engineering and sciences school at Yale until 1956) and elements of Silliman College, the largest residential college.
The oldest building on campus, Connecticut Hall (built in 1750), is in the Georgian architecture, Georgian style. Georgian-style buildings erected from 1929 to 1933 include Timothy Dwight College, Pierson College, and Davenport College, except the latter's east, York Street façade, which was constructed in the Gothic architecture, Gothic style to coordinate with adjacent structures.
The Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library, designed by Gordon Bunshaft of Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, is one of the largest buildings in the world reserved exclusively for the preservation of rare books and manuscripts. The library includes a six-story above-ground tower of book stacks, filled with 180,000 volumes, that is surrounded by large translucent Vermont marble panels and a steel and granite truss. The panels act as windows and subdue direct sunlight while also diffusing the light in warm hues throughout the interior. Near the library is a sunken courtyard, with sculptures by Isamu Noguchi that are said to represent time (the pyramid), the sun (the circle), and chance (the cube). The library is located near the center of the university in Hewitt Quadrangle, which is now more commonly referred to as "Beinecke Plaza."
Alumnus Eero Saarinen, Finnish-American architect of such notable structures as the Gateway Arch in St. Louis, Washington Dulles International Airport main terminal, Bell Labs Holmdel Complex and the CBS Building in Manhattan, designed Ingalls Rink, dedicated in 1959, as well as the residential colleges Ezra Stiles and Morse. These latter were modeled after the medieval Italian hill town of San Gimignano – a prototype chosen for the town's pedestrian-friendly milieu and fortress-like stone towers. These tower forms at Yale act in counterpoint to the college's many Gothic spires and Georgian cupolas.
Other examples of the Gothic style are on the Old Campus by architects like Henry Austin (architect), Henry Austin, Charles C. Haight and Russell Sturgis. Several are associated with members of the Vanderbilt family, including Vanderbilt Hall, Phelps Hall, St. Anthony Hall (a commission for member Frederick William Vanderbilt), the Mason, Sloane and Osborn laboratories, dormitories for the Sheffield Scientific School (the engineering and sciences school at Yale until 1956) and elements of Silliman College, the largest residential college.
The oldest building on campus, Connecticut Hall (built in 1750), is in the Georgian architecture, Georgian style. Georgian-style buildings erected from 1929 to 1933 include Timothy Dwight College, Pierson College, and Davenport College, except the latter's east, York Street façade, which was constructed in the Gothic architecture, Gothic style to coordinate with adjacent structures.
The Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library, designed by Gordon Bunshaft of Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, is one of the largest buildings in the world reserved exclusively for the preservation of rare books and manuscripts. The library includes a six-story above-ground tower of book stacks, filled with 180,000 volumes, that is surrounded by large translucent Vermont marble panels and a steel and granite truss. The panels act as windows and subdue direct sunlight while also diffusing the light in warm hues throughout the interior. Near the library is a sunken courtyard, with sculptures by Isamu Noguchi that are said to represent time (the pyramid), the sun (the circle), and chance (the cube). The library is located near the center of the university in Hewitt Quadrangle, which is now more commonly referred to as "Beinecke Plaza."
Alumnus Eero Saarinen, Finnish-American architect of such notable structures as the Gateway Arch in St. Louis, Washington Dulles International Airport main terminal, Bell Labs Holmdel Complex and the CBS Building in Manhattan, designed Ingalls Rink, dedicated in 1959, as well as the residential colleges Ezra Stiles and Morse. These latter were modeled after the medieval Italian hill town of San Gimignano – a prototype chosen for the town's pedestrian-friendly milieu and fortress-like stone towers. These tower forms at Yale act in counterpoint to the college's many Gothic spires and Georgian cupolas.
 Notable nonresidential campus buildings and landmarks include Battell Chapel, Beinecke Rare Book Library, Harkness Tower, Ingalls Rink, Kline Biology Tower, Osborne Memorial Laboratories, Payne Whitney Gymnasium, Peabody Museum of Natural History, Sterling Hall of Medicine, Sterling Law Buildings, Sterling Memorial Library, Woolsey Hall, Yale Center for British Art, Yale University Art Gallery, Yale Art & Architecture Building, and the Paul Mellon Centre for Studies in British Art in London.
Yale's secret society buildings (some of which are called "tombs") were built both to be private yet unmistakable. A diversity of architectural styles is represented: Berzelius (secret society), Berzelius, Donn Barber in an austere cube with classical detailing (erected in 1908 or 1910); Book and Snake, Louis R. Metcalfe in a Greek Ionic style (erected in 1901); Elihu (secret society), Elihu, architect unknown but built in a American colonial architecture, Colonial style (constructed on an early 17th-century foundation although the building is from the 18th century); Mace and Chain, in a late colonial, early Victorian fashion, Victorian style (built in 1823). (Interior moulding is said to have belonged to Benedict Arnold);Manuscript Society, King-lui Wu with Dan Kiley responsible for landscaping and Josef Albers for the brickwork intaglio mural. Building constructed in a mid-century modern style; Scroll and Key, Richard Morris Hunt in a Moorish- or Islamic-inspired Beaux-Arts architecture, Beaux-Arts style (erected 1869–70); Skull and Bones, possibly Alexander Jackson Davis or Henry Austin (architect), Henry Austin in an Egyptian Revival, Egypto-Doric style utilizing Brownstone (in 1856 the first wing was completed, in 1903 the second wing, 1911 the Neo-Gothic towers in rear garden were completed); St. Elmo (secret society), St. Elmo, (former tomb) Kenneth MacKenzie Murchison, Kenneth M. Murchison, 1912, designs inspired by Elizabethan manor. Current location, brick colonial; and Wolf's Head (secret society), Wolf's Head, Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue, erected 1923–1924, Collegiate Gothic.
Notable nonresidential campus buildings and landmarks include Battell Chapel, Beinecke Rare Book Library, Harkness Tower, Ingalls Rink, Kline Biology Tower, Osborne Memorial Laboratories, Payne Whitney Gymnasium, Peabody Museum of Natural History, Sterling Hall of Medicine, Sterling Law Buildings, Sterling Memorial Library, Woolsey Hall, Yale Center for British Art, Yale University Art Gallery, Yale Art & Architecture Building, and the Paul Mellon Centre for Studies in British Art in London.
Yale's secret society buildings (some of which are called "tombs") were built both to be private yet unmistakable. A diversity of architectural styles is represented: Berzelius (secret society), Berzelius, Donn Barber in an austere cube with classical detailing (erected in 1908 or 1910); Book and Snake, Louis R. Metcalfe in a Greek Ionic style (erected in 1901); Elihu (secret society), Elihu, architect unknown but built in a American colonial architecture, Colonial style (constructed on an early 17th-century foundation although the building is from the 18th century); Mace and Chain, in a late colonial, early Victorian fashion, Victorian style (built in 1823). (Interior moulding is said to have belonged to Benedict Arnold);Manuscript Society, King-lui Wu with Dan Kiley responsible for landscaping and Josef Albers for the brickwork intaglio mural. Building constructed in a mid-century modern style; Scroll and Key, Richard Morris Hunt in a Moorish- or Islamic-inspired Beaux-Arts architecture, Beaux-Arts style (erected 1869–70); Skull and Bones, possibly Alexander Jackson Davis or Henry Austin (architect), Henry Austin in an Egyptian Revival, Egypto-Doric style utilizing Brownstone (in 1856 the first wing was completed, in 1903 the second wing, 1911 the Neo-Gothic towers in rear garden were completed); St. Elmo (secret society), St. Elmo, (former tomb) Kenneth MacKenzie Murchison, Kenneth M. Murchison, 1912, designs inspired by Elizabethan manor. Current location, brick colonial; and Wolf's Head (secret society), Wolf's Head, Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue, erected 1923–1924, Collegiate Gothic.

File:Jonathan Edwards Courtyard.jpg, Jonathan Edwards College courtyard
File:Branford Court spring 2.JPG, Branford College courtyard
File:Saybrook College Courtyard.jpg, Saybrook College's Killingworth Courtyard
File:Hopper College Courtyard.jpg, Hopper College courtyard
File:Berkeley College (South) at Yale.jpg, Berkeley College (Yale University), Berkeley College buildings
File:Trumbull College Courtyard.jpg, Trumbull College courtyard
File:Davenport College Courtyard.jpg, Davenport College courtyard
File:Pierson College Courtyard Yale.jpg, Pierson College courtyard
File:Silliman College Courtyard Yale.jpg, Silliman College courtyard
File:Timothy Dwight College courtyard.jpg, Timothy Dwight College courtyard
File:Morse College Courtyard.jpg, Morse College courtyard
File:Ezra Stiles Courtyard.jpg, Ezra Stiles College courtyard
File:Benjamin Franklin College Yale.jpg, Benjamin Franklin College courtyard
File:Pauli Murray College Yale.jpg, Pauli Murray College courtyard
 Yale supports 35 varsity athletic teams that compete in the
Yale supports 35 varsity athletic teams that compete in the  October 21, 2000, marked the dedication of Yale's fourth new boathouse in 157 years of collegiate rowing. The Gilder Boathouse is named to honor former Olympic rower Virginia Gilder '79 and her father Richard Gilder '54, who gave $4 million towards the $7.5 million project. Yale also maintains the Gales Ferry site where the heavyweight men's team trains for the Yale-Harvard Boat Race.
Yale crew is the oldest collegiate athletic team in America, and won Olympics, Olympic Games Gold Medal for men's eights in 1924 and 1956. The Yale Corinthian Yacht Club, founded in 1881, is the oldest collegiate sailing (sport), sailing club in the world.
In 1896, Yale and Johns Hopkins University, Johns Hopkins played the first known ice hockey game in the United States. Since 2006, the school's ice hockey clubs have played a commemorative game.
Yale students claim to have invented Frisbee, by tossing empty Frisbie Pie Company tins.
Yale athletics are supported by the Yale Precision Marching Band. "Precision" is used here ironically; the band is a scatter-style band that runs wildly between formations rather than actually marching. The band attends every home football game and many away, as well as most hockey and basketball games throughout the winter.
Yale intramural sports are also a significant aspect of student life. Students compete for their respective residential colleges, fostering a friendly rivalry. The year is divided into fall, winter, and spring seasons, each of which includes about ten different sports. About half the sports are coeducational. At the end of the year, the residential college with the most points (not all sports count equally) wins the Tyng Cup.
October 21, 2000, marked the dedication of Yale's fourth new boathouse in 157 years of collegiate rowing. The Gilder Boathouse is named to honor former Olympic rower Virginia Gilder '79 and her father Richard Gilder '54, who gave $4 million towards the $7.5 million project. Yale also maintains the Gales Ferry site where the heavyweight men's team trains for the Yale-Harvard Boat Race.
Yale crew is the oldest collegiate athletic team in America, and won Olympics, Olympic Games Gold Medal for men's eights in 1924 and 1956. The Yale Corinthian Yacht Club, founded in 1881, is the oldest collegiate sailing (sport), sailing club in the world.
In 1896, Yale and Johns Hopkins University, Johns Hopkins played the first known ice hockey game in the United States. Since 2006, the school's ice hockey clubs have played a commemorative game.
Yale students claim to have invented Frisbee, by tossing empty Frisbie Pie Company tins.
Yale athletics are supported by the Yale Precision Marching Band. "Precision" is used here ironically; the band is a scatter-style band that runs wildly between formations rather than actually marching. The band attends every home football game and many away, as well as most hockey and basketball games throughout the winter.
Yale intramural sports are also a significant aspect of student life. Students compete for their respective residential colleges, fostering a friendly rivalry. The year is divided into fall, winter, and spring seasons, each of which includes about ten different sports. About half the sports are coeducational. At the end of the year, the residential college with the most points (not all sports count equally) wins the Tyng Cup.
 Over its history, Yale has produced many distinguished alumni in a variety of fields, ranging from the public to private sector. According to 2020 data, around 71% of undergraduates join the workforce, while the next largest majority of 16.6% go on to attend graduate or professional schools. Yale graduates have been recipients of 252 Rhodes Scholarships, 123 Marshall Scholarships, 67 Harry S. Truman Scholarship, Truman Scholarships, 21 Churchill Scholarships, and 9 Mitchell Scholarships. The university is also the second largest producer of Fulbright Program, Fulbright Scholars, with a total of 1,199 in its history and has produced 89 MacArthur Fellows Program, MacArthur Fellows. The U.S. Department of State Bureau of Educational and Cultural Affairs ranked Yale fifth among research institutions producing the most 2020–2021 Fulbright Scholars. Additionally, 31 living billionaires are Yale alumni.
At Yale, one of the most popular undergraduate majors among Juniors and Seniors is political science, with many students going on to serve careers in government and politics. Former presidents who attended Yale for undergrad include William Howard Taft, George H. W. Bush, and George W. Bush while former presidents Gerald Ford and Bill Clinton attended Yale Law School. Former vice-president and influential antebellum era politician John C. Calhoun also graduated from Yale. Former world leaders include Italian prime minister Mario Monti, Turkish prime minister Tansu Çiller, Mexican president Ernesto Zedillo, German president Karl Carstens, Philippine president José Paciano Laurel, Latvian president Valdis Zatlers, Taiwanese premier Jiang Yi-huah, and Malawian president Peter Mutharika, among others. Prominent royals who graduated are Crown Princess Victoria of Sweden, and Olympia von und zu Arco-Zinneberg, Olympia Bonaparte, Princess Napoléon.
Over its history, Yale has produced many distinguished alumni in a variety of fields, ranging from the public to private sector. According to 2020 data, around 71% of undergraduates join the workforce, while the next largest majority of 16.6% go on to attend graduate or professional schools. Yale graduates have been recipients of 252 Rhodes Scholarships, 123 Marshall Scholarships, 67 Harry S. Truman Scholarship, Truman Scholarships, 21 Churchill Scholarships, and 9 Mitchell Scholarships. The university is also the second largest producer of Fulbright Program, Fulbright Scholars, with a total of 1,199 in its history and has produced 89 MacArthur Fellows Program, MacArthur Fellows. The U.S. Department of State Bureau of Educational and Cultural Affairs ranked Yale fifth among research institutions producing the most 2020–2021 Fulbright Scholars. Additionally, 31 living billionaires are Yale alumni.
At Yale, one of the most popular undergraduate majors among Juniors and Seniors is political science, with many students going on to serve careers in government and politics. Former presidents who attended Yale for undergrad include William Howard Taft, George H. W. Bush, and George W. Bush while former presidents Gerald Ford and Bill Clinton attended Yale Law School. Former vice-president and influential antebellum era politician John C. Calhoun also graduated from Yale. Former world leaders include Italian prime minister Mario Monti, Turkish prime minister Tansu Çiller, Mexican president Ernesto Zedillo, German president Karl Carstens, Philippine president José Paciano Laurel, Latvian president Valdis Zatlers, Taiwanese premier Jiang Yi-huah, and Malawian president Peter Mutharika, among others. Prominent royals who graduated are Crown Princess Victoria of Sweden, and Olympia von und zu Arco-Zinneberg, Olympia Bonaparte, Princess Napoléon. Yale alumni have had considerable presence in U.S. government in all three branches. On the Supreme Court of the United States, U.S. Supreme Court, 19 justices have been Yale alumni, including current Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, Associate Justices Sonia Sotomayor, Samuel Alito, Clarence Thomas, and Brett Kavanaugh. Numerous Yale alumni have been United States Senate, U.S. Senators, including current senators Michael Bennet, Richard Blumenthal, Cory Booker, Sherrod Brown, Chris Coons, Amy Klobuchar, Ben Sasse, and Sheldon Whitehouse. Current and former cabinet members include Secretaries of State John Kerry, Hillary Clinton, Cyrus Vance, and Dean Acheson; U.S. Secretaries of the Treasury Oliver Wolcott, Robert Rubin, Nicholas F. Brady, Steven Mnuchin, and Janet Yellen; U.S. Attorneys General Nicholas Katzenbach, John Ashcroft, and Edward H. Levi; and many others. Peace Corps founder and American diplomat Sargent Shriver and public official and urban planner Robert Moses are Yale alumni.
Yale alumni have had considerable presence in U.S. government in all three branches. On the Supreme Court of the United States, U.S. Supreme Court, 19 justices have been Yale alumni, including current Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, Associate Justices Sonia Sotomayor, Samuel Alito, Clarence Thomas, and Brett Kavanaugh. Numerous Yale alumni have been United States Senate, U.S. Senators, including current senators Michael Bennet, Richard Blumenthal, Cory Booker, Sherrod Brown, Chris Coons, Amy Klobuchar, Ben Sasse, and Sheldon Whitehouse. Current and former cabinet members include Secretaries of State John Kerry, Hillary Clinton, Cyrus Vance, and Dean Acheson; U.S. Secretaries of the Treasury Oliver Wolcott, Robert Rubin, Nicholas F. Brady, Steven Mnuchin, and Janet Yellen; U.S. Attorneys General Nicholas Katzenbach, John Ashcroft, and Edward H. Levi; and many others. Peace Corps founder and American diplomat Sargent Shriver and public official and urban planner Robert Moses are Yale alumni.
 Yale has produced numerous award-winning authors and influential writers, like Nobel Prize in Literature laureate Sinclair Lewis and Pulitzer Prize winners Stephen Vincent Benét, Thornton Wilder, Doug Wright, and David McCullough. Academy Awards, Academy Award winning actors, actresses, and directors include Jodie Foster, Paul Newman, Meryl Streep, Elia Kazan, George Roy Hill, Lupita Nyong'o, Oliver Stone, and Frances McDormand. Alumni from Yale have also made notable contributions to both music and the arts. Leading American composer from the 20th century Charles Ives, Broadway composer Cole Porter, Grammy Award, Grammy award winner David Lang (composer), David Lang, multi-Tony Award winner Composer and Musicologist Maury Yeston, and award-winning jazz pianist and composer Vijay Iyer all hail from Yale. Hugo Boss Prize winner Matthew Barney, famed American sculptor Richard Serra, President Barack Obama presidential portrait painter Kehinde Wiley, MacArthur Fellow and contemporary artist Sarah Sze, Pulitzer Prize for Editorial Cartooning, Pulitzer Prize winning cartoonist Garry Trudeau, and National Medal of Arts photorealist painter Chuck Close all graduated from Yale. Additional alumni include architect and Presidential Medal of Freedom winner Maya Lin, Pritzker Architecture Prize, Pritzker Prize winner Norman Foster, Baron Foster of Thames Bank, Norman Foster, and Gateway Arch designer Eero Saarinen. Journalists and pundits include Dick Cavett, Chris Cuomo, Anderson Cooper, William F. Buckley Jr., and Fareed Zakaria.
Yale has produced numerous award-winning authors and influential writers, like Nobel Prize in Literature laureate Sinclair Lewis and Pulitzer Prize winners Stephen Vincent Benét, Thornton Wilder, Doug Wright, and David McCullough. Academy Awards, Academy Award winning actors, actresses, and directors include Jodie Foster, Paul Newman, Meryl Streep, Elia Kazan, George Roy Hill, Lupita Nyong'o, Oliver Stone, and Frances McDormand. Alumni from Yale have also made notable contributions to both music and the arts. Leading American composer from the 20th century Charles Ives, Broadway composer Cole Porter, Grammy Award, Grammy award winner David Lang (composer), David Lang, multi-Tony Award winner Composer and Musicologist Maury Yeston, and award-winning jazz pianist and composer Vijay Iyer all hail from Yale. Hugo Boss Prize winner Matthew Barney, famed American sculptor Richard Serra, President Barack Obama presidential portrait painter Kehinde Wiley, MacArthur Fellow and contemporary artist Sarah Sze, Pulitzer Prize for Editorial Cartooning, Pulitzer Prize winning cartoonist Garry Trudeau, and National Medal of Arts photorealist painter Chuck Close all graduated from Yale. Additional alumni include architect and Presidential Medal of Freedom winner Maya Lin, Pritzker Architecture Prize, Pritzker Prize winner Norman Foster, Baron Foster of Thames Bank, Norman Foster, and Gateway Arch designer Eero Saarinen. Journalists and pundits include Dick Cavett, Chris Cuomo, Anderson Cooper, William F. Buckley Jr., and Fareed Zakaria. In business, Yale has had numerous alumni and former students go on to become founders of influential business, like William E. Boeing, William Boeing (Boeing, United Airlines), Briton Hadden and Henry Luce (Time (magazine), Time Magazine), Stephen A. Schwarzman (The Blackstone Group, Blackstone Group), Frederick W. Smith (FedEx), Juan Trippe (Pan Am), Harold Stanley (Morgan Stanley), Bing Gordon (Electronic Arts), and Ben Silbermann (Pinterest). Other business people from Yale include former chairman and CEO of Sears Holdings Edward Lampert, former Time Warner president Jeffrey Bewkes, former PepsiCo chairperson and CEO Indra Nooyi, sports agent Donald Dell, and investor/philanthropist Sir John Templeton,
Yale alumni distinguished in academia include literary critic and historian Henry Louis Gates, economists Irving Fischer, Mahbub ul Haq, and Nobel Prize laureate Paul Krugman; Nobel Prize in Physics laureates Ernest Lawrence and Murray Gell-Mann; Fields Medalist John G. Thompson; Human Genome Project leader and National Institutes of Health director Francis S. Collins; brain surgery pioneer Harvey Cushing; pioneering computer scientist Grace Hopper; influential mathematician and chemist Josiah Willard Gibbs; National Women's Hall of Fame inductee and biochemist Florence B. Seibert;
In business, Yale has had numerous alumni and former students go on to become founders of influential business, like William E. Boeing, William Boeing (Boeing, United Airlines), Briton Hadden and Henry Luce (Time (magazine), Time Magazine), Stephen A. Schwarzman (The Blackstone Group, Blackstone Group), Frederick W. Smith (FedEx), Juan Trippe (Pan Am), Harold Stanley (Morgan Stanley), Bing Gordon (Electronic Arts), and Ben Silbermann (Pinterest). Other business people from Yale include former chairman and CEO of Sears Holdings Edward Lampert, former Time Warner president Jeffrey Bewkes, former PepsiCo chairperson and CEO Indra Nooyi, sports agent Donald Dell, and investor/philanthropist Sir John Templeton,
Yale alumni distinguished in academia include literary critic and historian Henry Louis Gates, economists Irving Fischer, Mahbub ul Haq, and Nobel Prize laureate Paul Krugman; Nobel Prize in Physics laureates Ernest Lawrence and Murray Gell-Mann; Fields Medalist John G. Thompson; Human Genome Project leader and National Institutes of Health director Francis S. Collins; brain surgery pioneer Harvey Cushing; pioneering computer scientist Grace Hopper; influential mathematician and chemist Josiah Willard Gibbs; National Women's Hall of Fame inductee and biochemist Florence B. Seibert;
Gutenberg.org
Yale University also is mentioned in F. Scott Fitzgerald's novel ''The Great Gatsby''. The narrator, Nick Carraway, wrote a series of editorials for the ''Yale News'', and Tom Buchanan was "one of the most powerful Defensive end, ends that ever played football" for Yale.
''Documentary History of Yale University: Under the Original Charter of the Collegiate School of Connecticut, 1701–1745.''
New Haven: Yale University Press, 1901. * French, Robert Dudley. ''The Memorial Quadrangle'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1929. * Furniss, Edgar S. ''The Graduate School of Yale'', New Haven, 1965. * Holden, Reuben A. ''Yale: A Pictorial History'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1967. * Kelley, Brooks Mather. ''Yale: A History''. New Haven: Yale University Press, 1999. ; * Kingsley, William L. ''Yale College. A Sketch of its History'', 2 vols. New York, 1879. * Mendenhall, Thomas C. ''The Harvard-Yale Boat Race, 1852–1924, and the Coming of Sport to the American College.'' (1993). 371 pp. * Nissenbaum, Stephen, ed. ''The Great Awakening at Yale College'' (1972). 263 pp. * Oren, Dan A. ''Joining the Club: A History of Jews and Yale'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1985.* Oviatt, Edwin. ''The Beginnings of Yale (1701–1726)'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1916. * * George Wilson Pierson, Pierson, George Wilson. ''Yale College, An Educational History (1871–1921)'', (Yale University Press, 1952); ''Yale, The University College (1921–1937)'', (Yale University Press, 1955) * Pierson, George Wilson. ''The Founding of Yale: The Legend of the Forty Folios'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1988. * Stevenson, Louise L. ''Scholarly Means to Evangelical Ends: The New Haven Scholars and the Transformation of Higher Learning in America, 1830–1890'' (1986). 221 pp. * Vincent Scully, Scully, Vincent ''et al.'', eds. ''Yale in New Haven: Architecture and Urbanism''. New Haven: Yale University, 2004. * Tucker, Louis Leonard. ''Connecticut's Seminary of Sedition: Yale College.'' Chester, Conn.: Pequot, 1973. 78 pp. * Warch, Richard. ''School of the Prophets: Yale College, 1701–1740.'' (1973). 339 pp. * Welch, Lewis Sheldon, and Walter Camp. ''Yale, her campus, class-rooms, and athletics'' (1900)
online
* *
Yale Athletics website
* {{Authority control Yale University, Buildings and structures in New Haven, Connecticut Colonial colleges Education in New Haven, Connecticut Educational institutions established in 1701 Non-profit organizations based in Connecticut Universities and colleges in New Haven County, Connecticut Tourist attractions in New Haven, Connecticut 1701 establishments in Connecticut Private universities and colleges in Connecticut
private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* " In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorde ...
research university
A research university or a research-intensive university is a university that is committed to research as a central part of its mission. They are the most important sites at which knowledge production occurs, along with "intergenerational kno ...
in New Haven, Connecticut
New Haven is a city in the U.S. state of Connecticut. It is located on New Haven Harbor on the northern shore of Long Island Sound in New Haven County, Connecticut and is part of the New York City metropolitan area. With a population of 134,02 ...
. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States
Higher education in the United States is an optional stage of formal learning following secondary education. Higher education is also referred as post-secondary education, third-stage, third-level, or tertiary education. It covers stages 5 to 8 ...
and among the most prestigious in the world. It is a member of the Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight schools ...
.
Chartered by the Connecticut Colony
The ''Connecticut Colony'' or ''Colony of Connecticut'', originally known as the Connecticut River Colony or simply the River Colony, was an English colony in New England which later became Connecticut. It was organized on March 3, 1636 as a settl ...
, the Collegiate School was established in 1701 by clergy to educate Congregational
Congregational churches (also Congregationalist churches or Congregationalism) are Protestant churches in the Calvinist tradition practising congregationalist church governance, in which each congregation independently and autonomously runs its ...
ministers before moving to New Haven in 1716. Originally restricted to theology and sacred language
A sacred language, holy language or liturgical language is any language that is cultivated and used primarily in church service or for other religious reasons by people who speak another, primary language in their daily lives.
Concept
A sacre ...
s, the curriculum began to incorporate humanities and sciences by the time of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
. In the 19th century, the college expanded into graduate and professional instruction, awarding the first PhD PHD or PhD may refer to:
* Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), an academic qualification
Entertainment
* '' PhD: Phantasy Degree'', a Korean comic series
* ''Piled Higher and Deeper'', a web comic
* Ph.D. (band), a 1980s British group
** Ph.D. (Ph.D. albu ...
in the United States in 1861 and organizing as a university in 1887. Yale's faculty and student populations grew after 1890 with rapid expansion of the physical campus and scientific research.
Yale is organized into fourteen constituent schools: the original undergraduate college, the Yale Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
The Yale Graduate School of Arts and Sciences is the graduate school of Yale University. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest graduate school in North America, and was the first North American graduate school to confer a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D ...
and twelve professional schools. While the university is governed by the Yale Corporation
The Yale Corporation, officially The President and Fellows of Yale College, is the governing body of Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut.
Assembly of corporation
The Corporation comprises 19 members:
* Three ex officio members: the Presiden ...
, each school's faculty oversees its curriculum and degree programs. In addition to a central campus in downtown New Haven
Downtown New Haven is the neighborhood located in the heart of the city of New Haven, Connecticut. It is made up of the original nine squares laid out in 1638 to form New Haven, including the New Haven Green, and the immediate surrounding central ...
, the university owns athletic facilities in western New Haven, a campus in West Haven
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some R ...
, and forests and nature preserves throughout New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
. , the university's endowment was valued at $42.3 billion, the second largest of any educational institution. The Yale University Library
The Yale University Library is the library system of Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut. Originating in 1701 with the gift of several dozen books to a new "Collegiate School," the library's collection now contains approximately 14.9 milli ...
, serving all constituent schools, holds more than 15 million volumes and is the third-largest academic library in the United States. Students compete in intercollegiate sports as the Yale Bulldogs
The Yale Bulldogs are the intercollegiate athletic teams that represent Yale University, located in New Haven, Connecticut. The school sponsors 35 varsity sports. The school has won two NCAA national championships in women's fencing, four in ...
in the NCAA
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges an ...
Division I – Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight schools ...
.
, 65 Nobel laureates, five Fields Medal
The Fields Medal is a prize awarded to two, three, or four mathematicians under 40 years of age at the International Congress of the International Mathematical Union (IMU), a meeting that takes place every four years. The name of the award ho ...
ists, four Abel Prize
The Abel Prize ( ; no, Abelprisen ) is awarded annually by the King of Norway to one or more outstanding mathematicians. It is named after the Norwegian mathematician Niels Henrik Abel (1802–1829) and directly modeled after the Nobel Prizes. ...
laureates, and three Turing Award
The ACM A. M. Turing Award is an annual prize given by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) for contributions of lasting and major technical importance to computer science. It is generally recognized as the highest distinction in compu ...
winners have been affiliated with Yale University. In addition, Yale has graduated many notable alumni
Notability is the property
of being worthy of notice, having fame, or being considered to be of a high degree of interest, significance, or distinction. It also refers to the capacity to be such. Persons who are notable due to public responsibi ...
, including five U.S. presidents
The president of the United States is the head of state and head of government of the United States, indirectly elected to a four-year term
Term may refer to:
* Terminology, or term, a noun or compound word used in a specific context, in pa ...
, 10 Founding Fathers
The following list of national founding figures is a record, by country, of people who were credited with establishing a state. National founders are typically those who played an influential role in setting up the systems of governance, (i.e. ...
, 19 U.S. Supreme Court Justices, 31 living billionaires, 54 College founders and presidents, many heads of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 "he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and le ...
, cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
members and governors
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political_regions, political region, ranking under the Head of State, head of state and in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of ...
. Hundreds of members of Congress
A Member of Congress (MOC) is a person who has been appointed or elected and inducted into an official body called a congress, typically to represent a particular constituency in a legislature. The term member of parliament (MP) is an equivalen ...
and many U.S. diplomats, 78 MacArthur Fellows, 252 Rhodes Scholars
The Rhodes Scholarship is an international postgraduate award for students to study at the University of Oxford, in the United Kingdom.
Established in 1902, it is the oldest graduate scholarship in the world. It is considered among the world' ...
, 123 Marshall Scholars
The Marshall Scholarship is a postgraduate scholarship for "intellectually distinguished young Americans ndtheir country's future leaders" to study at any university in the United Kingdom. It is widely considered one of the most prestigious sc ...
, 102 Guggenheim Fellows
Guggenheim Fellowships are Grant (money), grants that have been awarded annually since by the John Simon Guggenheim Memorial Foundation to those "who have demonstrated exceptional capacity for productive scholarship or exceptional creative abi ...
and nine Mitchell Scholars have been affiliated with the university. Yale is a member of the Big Three, along with Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
and Princeton
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the nine ...
. Yale's current faculty include 67 members of the National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nati ...
, 55 members of the National Academy of Medicine
The National Academy of Medicine (NAM), formerly called the Institute of Medicine (IoM) until 2015, is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Medicine is a part of the National Academies of Sciences, En ...
, 8 members of the National Academy of Engineering
The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Engineering is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy ...
, and 187 members of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and ...
. The college is, after normalization for institution size, the tenth-largest baccalaureate source of doctoral degree
A doctorate (from Latin ''docere'', "to teach"), doctor's degree (from Latin ''doctor'', "teacher"), or doctoral degree is an academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism ''li ...
recipients in the United States, and the largest such source within the Ivy League. It also is a top 10 (ranked seventh), after normalization for the number of graduates, baccalaureate source of some of the most notable scientists (Nobel, Fields, Turing prizes, or membership in National Academy of Sciences, National Academy of Medicine, or National Academy of Engineering).
History
Early history of Yale College
Origins
 Yale traces its beginnings to "An Act for Liberty to Erect a Collegiate School", a would-be charter passed during a meeting in New Haven by the General Court of the
Yale traces its beginnings to "An Act for Liberty to Erect a Collegiate School", a would-be charter passed during a meeting in New Haven by the General Court of the Colony of Connecticut
The ''Connecticut Colony'' or ''Colony of Connecticut'', originally known as the Connecticut River Colony or simply the River Colony, was an English colony in New England which later became Connecticut. It was organized on March 3, 1636 as a settl ...
on October 9, 1701. The Act was an effort to create an institution to train ministers and lay leadership for Connecticut. Soon after, a group of ten Congregational
Congregational churches (also Congregationalist churches or Congregationalism) are Protestant churches in the Calvinist tradition practising congregationalist church governance, in which each congregation independently and autonomously runs its ...
ministers, Samuel Andrew
Samuel Andrew (29 January 1656 – 24 January 1738) was an American Congregational clergyman and educator.
Early life
Samuel was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts, the eldest child of Samuel and Elizabeth (nee White) Andrew. The elder Samuel ...
, Thomas Buckingham, Israel Chauncy, Samuel Mather (nephew of Increase Mather
Increase Mather (; June 21, 1639 Old Style – August 23, 1723 Old Style) was a New England Puritan clergyman in the Massachusetts Bay Colony and president of Harvard College for twenty years (1681–1701). He was influential in the administrati ...
), Rev. James Noyes II (son of James Noyes
Rev. James Noyes (born 1608, Wiltshire, England – died 22 October 1656, Newbury, Massachusetts Bay Colony) was an English clergyman who emigrated to Massachusetts. He was a founder of Newbury, Massachusetts.
Biography
James Noyes was the fift ...
), James Pierpont, Abraham Pierson
Abraham Pierson (1646 – March 5, 1707) was an American Congregational minister who served as the first rector, from 1701 to 1707, and one of the founders of the Collegiate School — which later became Yale University.
Biography
He was ...
, Noadiah Russell The Reverend Noadiah Russell (22 July 1659 – 3 December 1713) was a Congregationalist minister, a founder and trustee of Yale College, and one of the framers of the Saybrook Platform.
Life
Russell was born in New Haven, Connecticut, the son of W ...
, Joseph Webb, and Timothy Woodbridge
Timothy Woodbridge (February 27, 1709 – May 10, 1774)Mitchell, p. 32. was an American missionary, deacon and schoolteacher, later a judge, representative, and Superintendent of Indian Affairs, from Springfield, Massachusetts, who spent most of ...
, all alumni
Alumni (singular: alumnus (masculine) or alumna (feminine)) are former students of a school, college, or university who have either attended or graduated in some fashion from the institution. The feminine plural alumnae is sometimes used for grou ...
of Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, met in the study of Reverend Samuel Russell
Samuel Russell (August 25, 1789 – May 5, 1862), was an American entrepreneur and trader, and founder of Russell & Company, the largest and most important American trading house in China from 1842 to its closing in 1891.
Early life
Russell ...
, located in Branford, Connecticut, to donate their books to form the school's library. The group, led by James Pierpont, is now known as "The Founders".
 Known from its origin as the "Collegiate School", the institution opened in the home of its first
Known from its origin as the "Collegiate School", the institution opened in the home of its first rector
Rector (Latin for the member of a vessel's crew who steers) may refer to:
Style or title
*Rector (ecclesiastical), a cleric who functions as an administrative leader in some Christian denominations
*Rector (academia), a senior official in an edu ...
, Abraham Pierson
Abraham Pierson (1646 – March 5, 1707) was an American Congregational minister who served as the first rector, from 1701 to 1707, and one of the founders of the Collegiate School — which later became Yale University.
Biography
He was ...
, who is today considered the first president of Yale. Pierson lived in Killingworth
Killingworth, formerly Killingworth Township, is a town in North Tyneside, England.
Killingworth was built as a planned town in the 1960s, next to Killingworth Village, which existed for centuries before the Township. Other nearby towns and ...
(now Clinton
Clinton is an English toponymic surname, indicating one's ancestors came from English places called Glympton or Glinton.Hanks, P. & Hodges, F. ''A Dictionary of Surnames''. Oxford University Press, 1988 Clinton has frequently been used as a given ...
). The school moved to Saybrook in 1703 when the first treasurer of Yale, Nathaniel Lynde, donated land and a building. In 1716, it moved to New Haven, Connecticut.
Meanwhile, there was a rift forming at Harvard between its sixth president, Increase Mather
Increase Mather (; June 21, 1639 Old Style – August 23, 1723 Old Style) was a New England Puritan clergyman in the Massachusetts Bay Colony and president of Harvard College for twenty years (1681–1701). He was influential in the administrati ...
, and the rest of the Harvard clergy, whom Mather viewed as increasingly liberal, ecclesiastically lax, and overly broad in Church polity
Ecclesiastical polity is the operational and governance structure of a church or of a Christian denomination. It also denotes the ministerial structure of a church and the authority relationships between churches. Polity relates closely to e ...
. The feud caused the Mathers to champion the success of the Collegiate School in the hope that it would maintain the Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Catholic Church, Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become m ...
religious orthodoxy in a way that Harvard had not. Rev. Jason Haven Jason Haven (March 2, 1733 – May 17, 1803) was the longest serving minister of the First Church and Parish in Dedham.
Personal life
Haven was born on March 2, 1733, in Framingham, Massachusetts. He was graduated from Harvard College in 1754. Whil ...
, the minister at the First Church and Parish in Dedham
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
, Massachusetts had been considered for the presidency on account of his orthodox theology and for "Neatness dignity and purity of Style hich
Ij ( fa, ايج, also Romanized as Īj; also known as Hich and Īch) is a village in Golabar Rural District, in the Central District of Ijrud County, Zanjan Province, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also ...
surpass those of all that have been mentioned," but was passed over due to his "very Valetudinary and infirm State of Health."
Naming and development
 In 1718, at the behest of either Rector
In 1718, at the behest of either Rector Samuel Andrew
Samuel Andrew (29 January 1656 – 24 January 1738) was an American Congregational clergyman and educator.
Early life
Samuel was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts, the eldest child of Samuel and Elizabeth (nee White) Andrew. The elder Samuel ...
or the colony's Governor Gurdon Saltonstall
Gurdon Saltonstall (27 March 1666 – 20 September 1724) was governor of the Colony of Connecticut from 1708 to 1724. Born into a distinguished family, Saltonstall became an accomplished and eminent Connecticut pastor. A close associate of Gover ...
, Cotton Mather
Cotton Mather (; February 12, 1663 – February 13, 1728) was a New England Puritan clergyman and a prolific writer. Educated at Harvard College, in 1685 he joined his father Increase as minister of the Congregationalist Old North Meeting H ...
contacted the successful Boston-born businessman Elihu Yale
Elihu Yale (5 April 1649 – 8 July 1721) was a British-American colonial administrator and philanthropist. Although born in Boston, Massachusetts, he only lived in America as a child, spending the rest of his life in England, Wales and India ...
to ask him for financial help in constructing a new building for the college. Through the persuasion of Jeremiah Dummer
Jeremiah Dummer (1681 – May 19, 1739) was an important colonial figure for New England in the early 18th century. His most significant contributions to American history were his ''A Defense of the New England Charters'' and his role in the for ...
, Yale, who had made a fortune in Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
while working for the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
as the first president of Fort St. George
Fort St. George (or historically, White Town) is a fortress in the coastal city of Chennai, India. Founded in 1639, it was the first English (later British) fortress in India. The construction of the fort provided the impetus for further ...
(largely through secret contracts with Madras merchants that were illegal under Company policy), donated nine bales of goods, which were sold for more than £560, a substantial sum of money at the time. Cotton Mather suggested that the school change its name to "Yale College." The Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
name Yale is the Anglicized spelling of the Iâl
Ial or Yale ( cy, Iâl) was a commote of medieval Wales within the cantref of Maelor in the Kingdom of Powys. When the Kingdom was divided in 1160, Maelor became part of the Princely realm of Powys Fadog (Lower Powys or Madog's Powys), and belon ...
, which the family estate at Plas yn Iâl, near the village of Llandegla
Llandegla or Llandegla-yn-Iâl is a village and community in the county of Denbighshire in Wales. In the 2011 census, the community had a population of 567.
Name
The village's name is Welsh for the "Parish of Saint Tecla", which honours th ...
, was called.
Meanwhile, a Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
graduate working in England convinced some 180 prominent intellectuals to donate books to Yale. The 1714 shipment of 500 books represented the best of modern English literature, science, philosophy and theology at the time. It had a profound effect on intellectuals at Yale. Undergraduate Jonathan Edwards Jonathan Edwards may refer to:
Musicians
*Jonathan and Darlene Edwards, pseudonym of bandleader Paul Weston and his wife, singer Jo Stafford
*Jonathan Edwards (musician) (born 1946), American musician
** ''Jonathan Edwards'' (album), debut album ...
discovered John Locke's works and developed his original theology known as the "new divinity." In 1722 the rector and six of his friends, who had a study group to discuss the new ideas, announced that they had given up Calvinism, become Arminians
Arminianism is a branch of Protestantism based on the theological ideas of the Dutch Reformed theologian Jacobus Arminius (1560–1609) and his historic supporters known as Remonstrants. Dutch Arminianism was originally articulated in the ''Rem ...
, and joined the Church of England. They were ordained in England and returned to the colonies as missionaries for the Anglican faith. Thomas Clapp
Thomas Clap or Thomas Clapp (June 26, 1703 – January 7, 1767) was an American academic and educator, a Congregational church, Congregational minister, and college administrator. He was both the fifth Rector (academia), rector and the earliest of ...
became president in 1745 and while he attempted to return the college to Calvinist orthodoxy, he did not close the library. Other students found Deist books in the library.
Curriculum
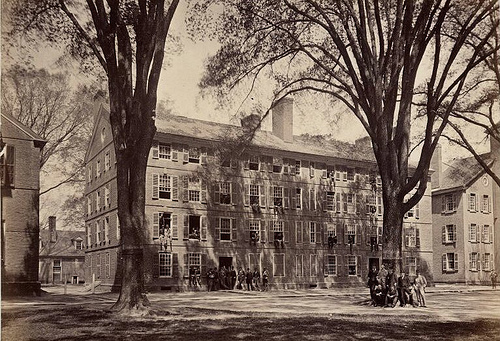
 Yale College undergraduates follow a
Yale College undergraduates follow a liberal arts
Liberal arts education (from Latin "free" and "art or principled practice") is the traditional academic course in Western higher education. ''Liberal arts'' takes the term ''art'' in the sense of a learned skill rather than specifically the ...
curriculum with departmental majors
Jonathan Michael Majors (born September 7, 1989)Majors in is an American actor. He rose to prominence after starring in the independent feature film ''The Last Black Man in San Francisco'' (2019). In 2020, he garnered wider notice for portraying ...
and is organized into a social system of residential colleges
A residential college is a division of a university that places academic activity in a community setting of students and faculty, usually at a residence and with shared meals, the college having a degree of autonomy and a federated relationship wi ...
.
Yale was swept up by the great intellectual movements of the period—the Great Awakening
Great Awakening refers to a number of periods of religious revival in American Christian history. Historians and theologians identify three, or sometimes four, waves of increased religious enthusiasm between the early 18th century and the late ...
and the Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
—due to the religious and scientific interests of presidents Thomas Clap
Thomas Clap or Thomas Clapp (June 26, 1703 – January 7, 1767) was an American academic and educator, a Congregational minister, and college administrator. He was both the fifth rector and the earliest official to be called "president" of Yale Co ...
and Ezra Stiles
Ezra Stiles ( – May 12, 1795) was an American educator, academic, Congregationalist minister, theologian, and author. He is noted as the seventh president of Yale College (1778–1795) and one of the founders of Brown University. According ...
. They were both instrumental in developing the scientific curriculum at Yale while dealing with wars, student tumults, graffiti, "irrelevance" of curricula, desperate need for endowment and disagreements with the Connecticut legislature
The Connecticut General Assembly (CGA) is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It is a bicameral body composed of the 151-member House of Representatives and the 36-member Senate. It meets in the state capital, Hartford. Ther ...
.
Serious American students of theology and divinity, particularly in New England, regarded Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
as a classical language
A classical language is any language with an independent literary tradition and a large and ancient body of written literature. Classical languages are typically dead languages, or show a high degree of diglossia, as the spoken varieties of the ...
, along with Greek and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, and essential for the study of the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
in the original words. The Reverend Ezra Stiles
Ezra Stiles ( – May 12, 1795) was an American educator, academic, Congregationalist minister, theologian, and author. He is noted as the seventh president of Yale College (1778–1795) and one of the founders of Brown University. According ...
, president of the college from 1778 to 1795, brought with him his interest in the Hebrew language as a vehicle for studying ancient Biblical texts in their original language (as was common in other schools), requiring all freshmen to study Hebrew (in contrast to Harvard, where only upperclassmen were required to study the language) and is responsible for the Hebrew phrase אורים ותמים (Urim and Thummim
In the Hebrew Bible, the Urim ( he, ''ʾŪrīm'', "lights") and the Thummim ( he, ''Tummīm'', meaning uncertain, possibly "perfections") are elements of the ''hoshen'', the breastplate worn by the High Priest attached to the ephod. They are ...
) on the Yale seal. A 1746 graduate of Yale, Stiles came to the college with experience in education, having played an integral role in the founding of Brown University
Brown University is a private research university in Providence, Rhode Island. Brown is the seventh-oldest institution of higher education in the United States, founded in 1764 as the College in the English Colony of Rhode Island and Providenc ...
, in addition to having been a minister. Stiles' greatest challenge occurred in July 1779 when British forces occupied New Haven and threatened to raze the college. However, Yale graduate Edmund Fanning (colonial administrator), Edmund Fanning, secretary to the British general in command of the occupation, intervened and the college was saved. In 1803, Fanning was granted an honorary degree LL.D. for his efforts.
Students
As the only college in Connecticut from 1701 to 1823, Yale educated the sons of the elite. Punishable offenses for students included cardplaying, tavern-going, destruction of college property, and acts of disobedience to college authorities. During this period, Harvard was distinctive for the stability and maturity of its tutor corps, while Yale had youth and zeal on its side. The emphasis on classics gave rise to a number of private student societies, open only by invitation, which arose primarily as forums for discussions of modern scholarship, literature and politics. The first such organizations were debating societies: Crotonia (literary society), Crotonia in 1738, Linonia in 1753 and Brothers in Unity in 1768. Linonia and Brothers in Unity continue to exist today with commemorations to them can be found with names given to campus structures, like Brothers in Unity Courtyard in Branford College.19th century
 The Yale Report of 1828 was a dogmatic defense of the Latin and Greek curriculum against critics who wanted more courses in modern languages, mathematics, and science. Unlike higher education in Europe, there was no national curriculum for colleges and universities in the United States. In the competition for students and financial support, college leaders strove to keep current with demands for innovation. At the same time, they realized that a significant portion of their students and prospective students demanded a classical background. The Yale report meant the classics would not be abandoned. During this period, all institutions experimented with changes in the curriculum, often resulting in a dual-track curriculum. In the decentralized environment of higher education in the United States, balancing change with tradition was a common challenge because it was difficult for an institution to be completely modern or completely classical. A group of professors at Yale and New Haven Congregationalist ministers articulated a conservative response to the changes brought about by the Victorian culture. They concentrated on developing a person possessed of religious values strong enough to sufficiently resist temptations from within, yet flexible enough to adjust to the '-ism, isms' (professionalism, materialism, individualism, and consumerism) tempting him from without. William Graham Sumner, professor from 1872 to 1909, taught in the emerging disciplines of economics and sociology to overflowing classrooms of students. Sumner bested President Noah Porter, who disliked the social sciences and wanted Yale to lock into its traditions of classical education. Porter objected to Sumner's use of a textbook by Herbert Spencer that espoused agnostic materialism because it might harm students.
Until 1887, the legal name of the university was "The President and Fellows of Yale College, in New Haven." In 1887, under an act passed by the Connecticut General Assembly, Yale was renamed to the present "Yale University."
The Yale Report of 1828 was a dogmatic defense of the Latin and Greek curriculum against critics who wanted more courses in modern languages, mathematics, and science. Unlike higher education in Europe, there was no national curriculum for colleges and universities in the United States. In the competition for students and financial support, college leaders strove to keep current with demands for innovation. At the same time, they realized that a significant portion of their students and prospective students demanded a classical background. The Yale report meant the classics would not be abandoned. During this period, all institutions experimented with changes in the curriculum, often resulting in a dual-track curriculum. In the decentralized environment of higher education in the United States, balancing change with tradition was a common challenge because it was difficult for an institution to be completely modern or completely classical. A group of professors at Yale and New Haven Congregationalist ministers articulated a conservative response to the changes brought about by the Victorian culture. They concentrated on developing a person possessed of religious values strong enough to sufficiently resist temptations from within, yet flexible enough to adjust to the '-ism, isms' (professionalism, materialism, individualism, and consumerism) tempting him from without. William Graham Sumner, professor from 1872 to 1909, taught in the emerging disciplines of economics and sociology to overflowing classrooms of students. Sumner bested President Noah Porter, who disliked the social sciences and wanted Yale to lock into its traditions of classical education. Porter objected to Sumner's use of a textbook by Herbert Spencer that espoused agnostic materialism because it might harm students.
Until 1887, the legal name of the university was "The President and Fellows of Yale College, in New Haven." In 1887, under an act passed by the Connecticut General Assembly, Yale was renamed to the present "Yale University."
Sports and debate
The Revolutionary War soldier Nathan Hale (Yale 1773) was the archetype of the Yale ideal in the early 19th century: a manly yet aristocratic scholar, equally well-versed in knowledge and sports, and a patriot who "regretted" that he "had but one life to lose" for his country. Western painter Frederic Remington (Yale 1900) was an artist whose heroes gloried in the combat and tests of strength in the Wild West. The fictional, turn-of-the-20th-century Yale man Frank Merriwell embodied this same heroic ideal without racial prejudice, and his fictional successor Frank Stover in the novel ''Stover at Yale'' (1911) questioned the business mentality that had become prevalent at the school. Increasingly the students turned to athletic stars as their heroes, especially since winning the big game became the goal of the student body, the alumni, and the team itself. Along with
Along with Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
and Princeton
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the nine ...
, Yale students rejected British concepts about 'amateurism' in sports and constructed athletic programs that were uniquely American, such as football. The Harvard–Yale football rivalry began in 1875. Between 1892, when Harvard and Yale met in one of the first intercollegiate debates, and in 1909 (the year of the first Triangular Debate of Harvard, Yale and Princeton) the rhetoric, symbolism, and metaphors used in athletics were used to frame these early debates. Debates were covered on front pages of college newspapers and emphasized in yearbooks, and team members even received the equivalent of Varsity letter, athletic letters for their jackets. There were also rallies to send off the debating teams to matches, but the debates never attained the broad appeal that athletics enjoyed. One reason may be that debates do not have a clear winner, as is the case in sports, and that scoring is subjective. In addition, with late 19th-century concerns about the impact of modern life on the human body, athletics offered hope that neither the individual nor the society was coming apart.
In 1909–10, football faced a crisis resulting from the failure of the previous reforms of 1905–06, which sought to solve the problem of serious injuries. There was a mood of alarm and mistrust, and, while the crisis was developing, the presidents of Harvard, Yale, and Princeton developed a project to reform the sport and forestall possible radical changes forced by government upon the sport. Presidents Arthur Twining Hadley, Arthur Hadley of Yale, A. Lawrence Lowell of Harvard, and Woodrow Wilson of Princeton worked to develop moderate reforms to reduce injuries. Their attempts, however, were reduced by rebellion against the rules committee and the formation of the Intercollegiate Athletic Association. While the big three had attempted to operate independently of the majority, the changes pushed did reduce injuries.
Expansion
Starting with the addition of the Yale School of Medicine in 1810, the college expanded gradually from then on, establishing the Yale Divinity School in 1822, Yale Law School in 1822, theYale Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
The Yale Graduate School of Arts and Sciences is the graduate school of Yale University. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest graduate school in North America, and was the first North American graduate school to confer a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D ...
in 1847, the now-defunct Sheffield Scientific School in 1847,Sheffield was originally named Yale Scientific School; it was renamed in 1861 after a major donation from Joseph E. Sheffield. and the Yale School of Art, Yale School of Fine Arts in 1869. In 1887, under the presidency of Timothy Dwight V, Yale College was renamed to Yale University, and the former name was subsequently applied only to the undergraduate college. The university would continue to expand greatly into the 20th and 21st century, adding the Yale School of Music in 1894, the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies in 1900, the Yale School of Public Health in 1915, the Yale School of Architecture in 1916, the Yale School of Nursing 1923, the Yale School of Drama in 1955, the Yale School of Management in 1976, and the Jackson School of Global Affairs which is planned to open in 2022. The Sheffield Scientific School would also reorganize its relationship with the university to teach only undergraduate courses.
Expansion caused controversy about Yale's new roles. Noah Porter, a moral philosopher, was president from 1871 to 1886. During an age of tremendous expansion in higher education, Porter resisted the rise of the new research university, claiming that an eager embrace of its ideals would corrupt undergraduate education. Many of Porter's contemporaries criticized his administration, and historians since have disparaged his leadership. Historian George Levesque argues Porter was not a simple-minded reactionary, uncritically committed to tradition, but a principled and selective conservative. Levesque continues, saying he did not endorse everything old or reject everything new; rather, he sought to apply long-established ethical and pedagogical principles to a rapidly changing culture. Levesque concludes, noting he may have misunderstood some of the challenges of his time, but he correctly anticipated the enduring tensions that have accompanied the emergence and growth of the modern university.
20th century
Medicine
 Milton Winternitz led the Yale School of Medicine as its dean from 1920 to 1935. Dedicated to the new scientific medicine established in Germany, he was equally fervent about "social medicine" and the study of humans in their culture and environment. He established the "Yale System" of teaching, with few lectures and fewer exams, and strengthened the full-time faculty system; he also created the graduate-level Yale School of Nursing and the psychiatry department and built numerous new buildings. Progress toward his plans for an Institute of Human Relations, envisioned as a refuge where social scientists would collaborate with biological scientists in a holistic study of humankind, unfortunately, lasted for only a few years before the opposition of resentful anti-Semitic colleagues drove him to resign.
Milton Winternitz led the Yale School of Medicine as its dean from 1920 to 1935. Dedicated to the new scientific medicine established in Germany, he was equally fervent about "social medicine" and the study of humans in their culture and environment. He established the "Yale System" of teaching, with few lectures and fewer exams, and strengthened the full-time faculty system; he also created the graduate-level Yale School of Nursing and the psychiatry department and built numerous new buildings. Progress toward his plans for an Institute of Human Relations, envisioned as a refuge where social scientists would collaborate with biological scientists in a holistic study of humankind, unfortunately, lasted for only a few years before the opposition of resentful anti-Semitic colleagues drove him to resign.
Faculty
 Before World War II, most elite university faculties counted among their numbers few, if any, Jews, blacks, women, or other minorities; Yale was no exception. By 1980, this condition had been altered dramatically, as numerous members of those groups held faculty positions. Almost all members of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences—and some members of other faculties—teach undergraduate courses, more than 2,000 of which are offered annually.
Before World War II, most elite university faculties counted among their numbers few, if any, Jews, blacks, women, or other minorities; Yale was no exception. By 1980, this condition had been altered dramatically, as numerous members of those groups held faculty positions. Almost all members of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences—and some members of other faculties—teach undergraduate courses, more than 2,000 of which are offered annually.
Women
In 1793, Lucinda Foote passed the entrance exams for Yale College, but was rejected by the president on the basis of her gender. Women studied at Yale University as early as 1892, in graduate-level programs at theYale Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
The Yale Graduate School of Arts and Sciences is the graduate school of Yale University. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest graduate school in North America, and was the first North American graduate school to confer a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D ...
. The first seven women to earn PhDs at Yale received their degrees in 1894: Elizabeth Deering Hanscom, Cornelia H. B. Rogers, Sara Bulkley Rogers, Margaretta Palmer, Mary Augusta Scott, Laura Johnson Wylie, and Charlotte Fitch Roberts. There is a portrait of these seven women in Sterling Memorial Library, painted by Brenda Zlamany.
In 1966, Yale began discussions with its sister school Vassar College about merging to foster coeducation at the undergraduate level. Vassar, then all-female and part of the Seven Sisters (colleges), Seven Sisters—elite higher education schools that historically served as sister institutions to the Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight schools ...
when most Ivy League institutions still only admitted men—tentatively accepted, but then declined the invitation. Both schools introduced coeducation independently in 1969. Amy Solomon was the first woman to register as a Yale undergraduate; she was also the first woman at Yale to join an undergraduate society, St. Anthony Hall. The undergraduate class of 1973 was the first class to have women starting from freshman year; at the time, all undergraduate women were housed in Vanderbilt Hall at the south end of Old Campus.
A decade into co-education, student assault and harassment by faculty became the impetus for the trailblazing lawsuit Alexander v. Yale. In the late 1970s, a group of students and one faculty member sued Yale for its failure to curtail campus sexual harassment by especially male faculty. The case was partly built from a 1977 report authored by plaintiff Ann Olivarius, now a feminist attorney known for fighting sexual harassment, "A report to the Yale Corporation from the Yale Undergraduate Women's Caucus." This case was the first to use Title IX to argue and establish that the sexual harassment of female students can be considered illegal sex discrimination. The plaintiffs in the case were Olivarius, Ronni Alexander (now a professor at Kobe University, Japan), Margery Reifler (works in the Los Angeles film industry)Pamela Price
(civil rights attorney in California), and Lisa E. Stone (works at Anti-Defamation League). They were joined by Yale classics professor John “Jack” J. Winkler, who died in 1990. The lawsuit, brought partly by Catharine A. MacKinnon, Catharine MacKinnon, alleged rape, fondling, and offers of higher grades for sex by several Yale faculty, including Keith Brion, professor of flute and director of bands, political Science professo
Raymond Duvall
(now at the University of Minnesota), English professor Michael George Cooke, Michael Cooke, and coach of the field hockey team, Richard Kentwell. While unsuccessful in the courts, the legal reasoning behind the case changed the landscape of sex discrimination law and resulted in the establishment of Yale's Grievance Board and the Yale Women's Center. In March 2011 a Title IX complaint was filed against Yale by students and recent graduates, including editors of Yale's feminist magazine Broad Recognition, alleging that the university had a hostile sexual climate. In response, the university formed a Title IX steering committee to address complaints of sexual misconduct. Afterwards, universities and colleges throughout the US also established sexual harassment grievance procedures.
Class
Yale, like other Ivy League schools, instituted policies in the early 20th century designed to maintain the proportion of white Protestants from notable families in the student body (see ''numerus clausus''), and was one of the last of the Ivies to eliminate such preferences, beginning with the class of 1970.21st century
In 2006, Yale and Peking University (PKU) established a Joint Undergraduate Program in Beijing, an exchange program allowing Yale students to spend a semester living and studying with PKU honor students. In July 2012, the Yale University-PKU Program ended due to weak participation. In 2007 outgoing Yale President Rick Levin characterized Yale's institutional priorities: "First, among the nation's finest research universities, Yale is distinctively committed to excellence in undergraduate education. Second, in our graduate and professional schools, as well as in Yale College, we are committed to the education of leaders." In 2009, former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister Tony Blair picked Yale as one location – the others being Britain's Durham University and Universiti Teknologi Mara – for the Tony Blair Faith Foundation's United States Faith and Globalization Initiative. As of 2009, former Mexican President Ernesto Zedillo is the director of the Yale Center for the Study of Globalization and teaches an undergraduate seminar, "Debating Globalization". As of 2009, former presidential candidate and DNC chair Howard Dean teaches a residential college seminar, "Understanding Politics and Politicians". Also in 2009, an alliance was formed among Yale, University College London, and both schools' affiliated hospital complexes to conduct research focused on the direct improvement of patient care—a growing field known as translational medicine. President Richard Levin noted that Yale has hundreds of other partnerships across the world, but "no existing collaboration matches the scale of the new partnership with UCL". In August 2013, a new partnership with the National University of Singapore led to the opening of Yale-NUS College in Singapore, a joint effort to create a new liberal arts college in Asia featuring a curriculum including both Western and Asian traditions. In 2017, having been suggested for decades, Yale University renamed Calhoun College, named for Slavery in the United States, slave owner, anti-abolitionist, and white supremacist Vice President John C. Calhoun (it is now Hopper College, after Grace Hopper). In 2020, in the wake of George Floyd protests, protests around the world focused on racial relations and criminal justice reform, the #CancelYale tag was used on social media to demand that Elihu Yale's name be removed from Yale University. Most support for the change stemmed from politically conservative pundits, such as Mike Cernovich and Ann Coulter, satirizing perceived excesses of online cancel culture. Yale was Madras Presidency, president of Fort. St George in Madras, a fort of theEast India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
in India, which was one of the biggest corporation in the world at the time. The company traded textiles, goods, diamonds, cotton, spices, among others, and was involved in the slave trade in India, with a private army of 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of Britain.
His singularly large donation of paintings and books to the college led some critics to argue that Yale relied on money related to the slave-trade for its first scholarships and endowments.
In August 2020, the US United States Department of Justice, Justice Department sued Yale for alleged discrimination against Asian and white candidates on the basis of their race through affirmative action admission policies. In early February 2021, under the new Biden administration, the Justice Department withdrew the lawsuit. The group, Students for Fair Admissions, known for a similar Students for Fair Admissions v. President and Fellows of Harvard College, lawsuit against Harvard alleging the same issue, plans to refile the lawsuit.
Yale alumni in politics
The ''Boston Globe'' wrote that "if there's one school that can lay claim to educating the nation's top national leaders over the past three decades, it's Yale".''Boston Globe'' November 17, 2002, Magazine, p. 6 Yale alumni were represented on the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic or Republican Party (United States), Republican ticket in every U.S. presidential election between 1972 and 2004. Yale-educated presidents since the end of the Vietnam War include Gerald Ford, George H. W. Bush, Bill Clinton, and George W. Bush, and major-party nominees during this period include Hillary Clinton (2016), John Kerry (2004), Joseph Lieberman (vice president, 2000), and Sargent Shriver (vice president, 1972). Other Yale alumni who have made serious bids for the presidency during this period include Amy Klobuchar (2020), Tom Steyer (2020), Ben Carson (2016), Howard Dean (2004), Gary Hart (1984 and 1988), Paul Tsongas (1992), Pat Robertson (1988) and Jerry Brown (1976, 1980, 1992). Several explanations have been offered for Yale's representation in national elections since the end of the Vietnam War. Various sources note the spirit of campus activism that has existed at Yale since the 1960s, and the intellectual influence of Reverend William Sloane Coffin on many of the future candidates.''Los Angeles Times'' October 4, 2000, p. E1 Yale President Richard Levin attributes the run to Yale's focus on creating "a laboratory for future leaders," an institutional priority that began during the tenure of Yale Presidents Alfred Whitney Griswold and Kingman Brewster. Richard H. Brodhead, former dean of Yale College and now president of Duke University, stated: "We do give very significant attention to orientation to the community in our admissions, and there is a very strong tradition of volunteerism at Yale." Yale historian Gaddis Smith notes "an ethos of organized activity" at Yale during the 20th century that led John Kerry to lead the Yale Political Union's Liberal Party, George Pataki the Conservative Party, and Joseph Lieberman to manage the ''Yale Daily News''. Camille Paglia points to a history of networking and elitism: "It has to do with a web of friendships and affiliations built up in school." CNN suggests that George W. Bush benefited from preferential admissions policies for the "son and grandson of alumni", and for a "member of a politically influential family". ''New York Times'' correspondent Elisabeth Bumiller and ''The Atlantic Monthly'' correspondent James Fallows credit the culture of community and cooperation that exists between students, faculty, and administration, which downplays self-interest and reinforces commitment to others. During the 1988 presidential election, George H. W. Bush (Yale '48) derided Michael Dukakis for having "foreign-policy views born in Harvard Yard's boutique". When challenged on the distinction between Dukakis' Harvard connection and his own Yale background, he said that, unlike Harvard, Yale's reputation was "so diffuse, there isn't a symbol, I don't think, in the Yale situation, any symbolism in it" and said Yale did not share Harvard's reputation for "liberalism and elitism". In 2004 Howard Dean stated, "In some ways, I consider myself separate from the other three (Yale) candidates of 2004. Yale changed so much between the class of '68 and the class of '71. My class was the first class to have women in it; it was the first class to have a significant effort to recruit African Americans. It was an extraordinary time, and in that span of time is the change of an entire generation".Administration and organization
Leadership
The President and Fellows of Yale College, also known as the Yale Corporation, or board of trustees, is the governing body of the university and consists of thirteen standing committees with separate responsibilities outlined in the by-laws. The corporation has 19 members: three Ex officio member, ex officio members, ten successor trustees, and six elected alumni fellows. The university has three major academic components: Yale College (the undergraduate program), the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, and the twelve professional schools. Yale's former president Richard C. Levin was, at the time, one of the highest paid university presidents in the United States with a 2008 salary of $1.5 million. Yale's succeeding president Peter Salovey ranks 40th with a 2020 salary of $1.16 million. The Yale Provost's Office and similar executive positions have launched several women into prominent university executive positions. In 1977, Provost Hanna Holborn Gray was appointed interim president of Yale and later went on to become president of the University of Chicago, being the first woman to hold either position at each respective school. In 1994, Provost Judith Rodin became the first permanent female president of an Ivy League institution at the University of Pennsylvania. In 2002, Provost Alison Richard became the vice-chancellor of the University of Cambridge. In 2003, the dean of the Divinity School, Rebecca Chopp, was appointed president of Colgate University and later went on to serve as the president of the Swarthmore College in 2009, and then the first female chancellor of the University of Denver in 2014. In 2004, Provost Susan Hockfield, Dr. Susan Hockfield became the president of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. In 2004, Dean of the Nursing school, Catherine Gilliss, was appointed the dean of Duke University's School of Nursing and vice chancellor for nursing affairs. In 2007, Deputy Provost H. Kim Bottomly was named president of Wellesley College. Similar examples for men who have served in Yale leadership positions can also be found. In 2004, Dean of Yale College Richard H. Brodhead was appointed as the president of Duke University. In 2008, Provost Andrew D. Hamilton, Andrew Hamilton was confirmed to be the vice chancellor of the University of Oxford.Staff and labor unions
Yale University staff are represented by several different unions. Clerical and technical workers are represented by Local 34, and service and maintenance workers are represented by Local 35, both of the same union affiliate UNITE HERE. Unlike similar institutions, Yale has consistently refused to recognize its graduate student union, Local 33 (another affiliate of UNITE HERE), citing claims that the union's elections were undemocratic and how graduate students are not employees; the move to not recognize the union has been criticized by the American Federation of Teachers. In addition, officers of the Yale University Police Department are represented by the Yale Police Benevolent Association, which affiliated in 2005 with the Connecticut Organization for Public Safety Employees. Yale security officers joined the International Union of Security, Police and Fire Professionals of America in late 2010, even though the Yale administration contested the election. In October 2014, after deliberation, Yale security decided to form a new union, the Yale University Security Officers Association, which has since represented the campus security officers. Yale has a history of difficult and prolonged labor negotiations, often culminating in strikes. There have been at least eight strikes since 1968, and ''The New York Times'' wrote that Yale has a reputation as having the worst record of labor tension of any university in the U.S. Moreover, Yale has been accused by the AFL–CIO of failing to treat workers with respect, as well as not renewing contracts with professors over involvement in campus labor issues. Yale has responded to strikes with claims over mediocre union participation and the benefits of their contracts.Campus

 Yale's central campus in
Yale's central campus in downtown New Haven
Downtown New Haven is the neighborhood located in the heart of the city of New Haven, Connecticut. It is made up of the original nine squares laid out in 1638 to form New Haven, including the New Haven Green, and the immediate surrounding central ...
covers and comprises its main, historic campus and a medical campus adjacent to the Yale–New Haven Hospital. In western New Haven, the university holds of athletic facilities, including the Yale Golf Course. In 2008, Yale purchased the 17-building, former Bayer, Bayer HealthCare complex in West Haven
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some R ...
, Connecticut, the buildings of which are now used as laboratory and research space. Yale also owns seven forests in Connecticut, Vermont, and New Hampshire—the largest of which is the Yale-Myers Forest in Connecticut's Quiet Corner—and nature preserves including Thimble Islands, Horse Island.
Yale is noted for its largely Collegiate Gothic campus as well as several iconic modern buildings commonly discussed in architectural history survey courses: Louis Kahn's Yale Art Gallery and Center for British Art, Eero Saarinen's Ingalls Rink and Ezra Stiles and Morse Colleges, and Paul Rudolph (architect), Paul Rudolph's Yale Art and Architecture Building, Art & Architecture Building. Yale also owns and has restored many noteworthy 19th-century mansions along Hillhouse Avenue, which was considered the most beautiful street in America by Charles Dickens when he visited the United States in the 1840s. In 2011, Travel+Leisure listed the Yale campus as one of the most beautiful in the United States.
Many of Yale's buildings were constructed in the Collegiate Gothic architecture style from 1917 to 1931, financed largely by Edward S. Harkness, including the Yale Drama School. Stone sculpture built into the walls of the buildings portray contemporary college personalities, such as a writer, an athlete, a tea-drinking socialite, and a student who has fallen asleep while reading. Similarly, the decorative friezes on the buildings depict contemporary scenes, like a policemen chasing a robber and arresting a prostitute (on the wall of the Law School), or a student relaxing with a mug of beer and a cigarette. The architect, James Gamble Rogers, faux-aged these buildings by splashing the walls with acid, deliberately breaking their lead glass, leaded glass windows and repairing them in the style of the Middle Ages, and creating niches for decorative statuary but leaving them empty to simulate loss or theft over the ages. In fact, the buildings merely simulate Middle Ages architecture, for though they appear to be constructed of solid stone blocks in the authentic manner, most actually have steel framing as was commonly used in 1930. One exception is Harkness Tower, tall, which was originally a free-standing stone structure. It was reinforced in 1964 to allow the installation of the Yale Memorial Carillon.

 Other examples of the Gothic style are on the Old Campus by architects like Henry Austin (architect), Henry Austin, Charles C. Haight and Russell Sturgis. Several are associated with members of the Vanderbilt family, including Vanderbilt Hall, Phelps Hall, St. Anthony Hall (a commission for member Frederick William Vanderbilt), the Mason, Sloane and Osborn laboratories, dormitories for the Sheffield Scientific School (the engineering and sciences school at Yale until 1956) and elements of Silliman College, the largest residential college.
The oldest building on campus, Connecticut Hall (built in 1750), is in the Georgian architecture, Georgian style. Georgian-style buildings erected from 1929 to 1933 include Timothy Dwight College, Pierson College, and Davenport College, except the latter's east, York Street façade, which was constructed in the Gothic architecture, Gothic style to coordinate with adjacent structures.
The Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library, designed by Gordon Bunshaft of Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, is one of the largest buildings in the world reserved exclusively for the preservation of rare books and manuscripts. The library includes a six-story above-ground tower of book stacks, filled with 180,000 volumes, that is surrounded by large translucent Vermont marble panels and a steel and granite truss. The panels act as windows and subdue direct sunlight while also diffusing the light in warm hues throughout the interior. Near the library is a sunken courtyard, with sculptures by Isamu Noguchi that are said to represent time (the pyramid), the sun (the circle), and chance (the cube). The library is located near the center of the university in Hewitt Quadrangle, which is now more commonly referred to as "Beinecke Plaza."
Alumnus Eero Saarinen, Finnish-American architect of such notable structures as the Gateway Arch in St. Louis, Washington Dulles International Airport main terminal, Bell Labs Holmdel Complex and the CBS Building in Manhattan, designed Ingalls Rink, dedicated in 1959, as well as the residential colleges Ezra Stiles and Morse. These latter were modeled after the medieval Italian hill town of San Gimignano – a prototype chosen for the town's pedestrian-friendly milieu and fortress-like stone towers. These tower forms at Yale act in counterpoint to the college's many Gothic spires and Georgian cupolas.
Other examples of the Gothic style are on the Old Campus by architects like Henry Austin (architect), Henry Austin, Charles C. Haight and Russell Sturgis. Several are associated with members of the Vanderbilt family, including Vanderbilt Hall, Phelps Hall, St. Anthony Hall (a commission for member Frederick William Vanderbilt), the Mason, Sloane and Osborn laboratories, dormitories for the Sheffield Scientific School (the engineering and sciences school at Yale until 1956) and elements of Silliman College, the largest residential college.
The oldest building on campus, Connecticut Hall (built in 1750), is in the Georgian architecture, Georgian style. Georgian-style buildings erected from 1929 to 1933 include Timothy Dwight College, Pierson College, and Davenport College, except the latter's east, York Street façade, which was constructed in the Gothic architecture, Gothic style to coordinate with adjacent structures.
The Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library, designed by Gordon Bunshaft of Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, is one of the largest buildings in the world reserved exclusively for the preservation of rare books and manuscripts. The library includes a six-story above-ground tower of book stacks, filled with 180,000 volumes, that is surrounded by large translucent Vermont marble panels and a steel and granite truss. The panels act as windows and subdue direct sunlight while also diffusing the light in warm hues throughout the interior. Near the library is a sunken courtyard, with sculptures by Isamu Noguchi that are said to represent time (the pyramid), the sun (the circle), and chance (the cube). The library is located near the center of the university in Hewitt Quadrangle, which is now more commonly referred to as "Beinecke Plaza."
Alumnus Eero Saarinen, Finnish-American architect of such notable structures as the Gateway Arch in St. Louis, Washington Dulles International Airport main terminal, Bell Labs Holmdel Complex and the CBS Building in Manhattan, designed Ingalls Rink, dedicated in 1959, as well as the residential colleges Ezra Stiles and Morse. These latter were modeled after the medieval Italian hill town of San Gimignano – a prototype chosen for the town's pedestrian-friendly milieu and fortress-like stone towers. These tower forms at Yale act in counterpoint to the college's many Gothic spires and Georgian cupolas.
Notable nonresidential campus buildings
 Notable nonresidential campus buildings and landmarks include Battell Chapel, Beinecke Rare Book Library, Harkness Tower, Ingalls Rink, Kline Biology Tower, Osborne Memorial Laboratories, Payne Whitney Gymnasium, Peabody Museum of Natural History, Sterling Hall of Medicine, Sterling Law Buildings, Sterling Memorial Library, Woolsey Hall, Yale Center for British Art, Yale University Art Gallery, Yale Art & Architecture Building, and the Paul Mellon Centre for Studies in British Art in London.
Yale's secret society buildings (some of which are called "tombs") were built both to be private yet unmistakable. A diversity of architectural styles is represented: Berzelius (secret society), Berzelius, Donn Barber in an austere cube with classical detailing (erected in 1908 or 1910); Book and Snake, Louis R. Metcalfe in a Greek Ionic style (erected in 1901); Elihu (secret society), Elihu, architect unknown but built in a American colonial architecture, Colonial style (constructed on an early 17th-century foundation although the building is from the 18th century); Mace and Chain, in a late colonial, early Victorian fashion, Victorian style (built in 1823). (Interior moulding is said to have belonged to Benedict Arnold);Manuscript Society, King-lui Wu with Dan Kiley responsible for landscaping and Josef Albers for the brickwork intaglio mural. Building constructed in a mid-century modern style; Scroll and Key, Richard Morris Hunt in a Moorish- or Islamic-inspired Beaux-Arts architecture, Beaux-Arts style (erected 1869–70); Skull and Bones, possibly Alexander Jackson Davis or Henry Austin (architect), Henry Austin in an Egyptian Revival, Egypto-Doric style utilizing Brownstone (in 1856 the first wing was completed, in 1903 the second wing, 1911 the Neo-Gothic towers in rear garden were completed); St. Elmo (secret society), St. Elmo, (former tomb) Kenneth MacKenzie Murchison, Kenneth M. Murchison, 1912, designs inspired by Elizabethan manor. Current location, brick colonial; and Wolf's Head (secret society), Wolf's Head, Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue, erected 1923–1924, Collegiate Gothic.
Notable nonresidential campus buildings and landmarks include Battell Chapel, Beinecke Rare Book Library, Harkness Tower, Ingalls Rink, Kline Biology Tower, Osborne Memorial Laboratories, Payne Whitney Gymnasium, Peabody Museum of Natural History, Sterling Hall of Medicine, Sterling Law Buildings, Sterling Memorial Library, Woolsey Hall, Yale Center for British Art, Yale University Art Gallery, Yale Art & Architecture Building, and the Paul Mellon Centre for Studies in British Art in London.
Yale's secret society buildings (some of which are called "tombs") were built both to be private yet unmistakable. A diversity of architectural styles is represented: Berzelius (secret society), Berzelius, Donn Barber in an austere cube with classical detailing (erected in 1908 or 1910); Book and Snake, Louis R. Metcalfe in a Greek Ionic style (erected in 1901); Elihu (secret society), Elihu, architect unknown but built in a American colonial architecture, Colonial style (constructed on an early 17th-century foundation although the building is from the 18th century); Mace and Chain, in a late colonial, early Victorian fashion, Victorian style (built in 1823). (Interior moulding is said to have belonged to Benedict Arnold);Manuscript Society, King-lui Wu with Dan Kiley responsible for landscaping and Josef Albers for the brickwork intaglio mural. Building constructed in a mid-century modern style; Scroll and Key, Richard Morris Hunt in a Moorish- or Islamic-inspired Beaux-Arts architecture, Beaux-Arts style (erected 1869–70); Skull and Bones, possibly Alexander Jackson Davis or Henry Austin (architect), Henry Austin in an Egyptian Revival, Egypto-Doric style utilizing Brownstone (in 1856 the first wing was completed, in 1903 the second wing, 1911 the Neo-Gothic towers in rear garden were completed); St. Elmo (secret society), St. Elmo, (former tomb) Kenneth MacKenzie Murchison, Kenneth M. Murchison, 1912, designs inspired by Elizabethan manor. Current location, brick colonial; and Wolf's Head (secret society), Wolf's Head, Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue, erected 1923–1924, Collegiate Gothic.
Sustainability
Yale's Office of Sustainability develops and implements sustainability practices at Yale. Yale is committed to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions 10% below 1990 levels by 2020. As part of this commitment, the university allocates renewable energy credits to offset some of the energy used by residential colleges. Eleven campus buildings are candidates for LEED design and certification. Yale Sustainable Food Project initiated the introduction of local, organic vegetables, fruits, and beef to all residential college dining halls. Yale was listed as a Campus Sustainability Leader on the Sustainable Endowments Institute's College Sustainability Report Card 2008, and received a "B+" grade overall. * Grove Street Cemetery, New Haven * Marsh Botanical Garden * Yale Sustainable Food Project, Yale Sustainable Food Program FarmRelationship with New Haven
Yale is the largest taxpayer and employer in the City of New Haven, and has often buoyed the city's economy and communities. Yale, however, has consistently opposed paying a tax on its academic property. Yale's Yale University Art Gallery, Art Galleries, along with many other university resources, are free and openly accessible. Yale also funds the New Haven, Connecticut#New Haven Promise, New Haven Promise program, paying full tuition for eligible students from New Haven public schools.Town–gown relations
Yale has a complicated relationship with its home city; for example, thousands of students volunteer every year in myriad community organizations, but city officials, who decry Yale's exemption from local property taxes, have long pressed the university to do more to help. Under President Levin, Yale has financially supported many of New Haven's efforts to reinvigorate the city. Evidence suggests that the town and gown relationships are mutually beneficial. Still, the economic power of the university increased dramatically with its financial success amid a decline in the local economy.Campus safety
Several campus safety strategies have been pioneered at Yale. The first campus police force was founded at Yale in 1894, when the university contracted city police officers to exclusively cover the campus. Later hired by the university, the officers were originally brought in to quell unrest between students and city residents and curb destructive student behavior. In addition to the Yale Police Department, a variety of safety services are available including blue phones, a safety escort, and 24-hour shuttle service. In the 1970s and 1980s, Connecticut locations by per capita income, poverty and violent crime rose in New Haven, dampening Yale's student and faculty recruiting efforts. Between 1990 and 2006, New Haven's crime rate fell by half, helped by a community policing, community policing strategy by the New Haven Police Department, New Haven Police and Yale's campus became the safest among the Ivy League and other peer schools. In 2004, the national non-profit watchdog group Security on Campus filed a complaint with the U.S. Department of Education, accusing Yale of under-reporting rape and sexual assaults. In April 2021, Yale announced that it will require students to receive a COVID-19 vaccine as a condition of being on campus during the fall 2021 term.Academics
Admissions
Undergraduate admission to Yale College is considered "most selective" by ''U.S. News & World Report, U.S. News''. In 2022, Yale accepted 2,234 students to the Class of 2026 out of 50,015 applicants, for an acceptance rate of 4.46%. 98% of students graduate within six years. Through its program of need-based financial aid, Yale commits to meet the full demonstrated financial need of all applicants. Most financial aid is in the form of grants and scholarships that do not need to be paid back to the university, and the average need-based aid grant for the Class of 2017 was $46,395. 15% of Yale College students are expected to have no parental contribution, and about 50% receive some form of financial aid. About 16% of the Class of 2013 had some form of student loan debt at graduation, with an average debt of $13,000 among borrowers. For 2019, Yale ranked second in enrollment of recipients of the National Merit Scholarship Program, National Merit $2,500 Scholarship (140 scholars). Half of all Yale undergraduates are women, more than 39% are ethnic minority U.S. citizens (19% are underrepresented minorities), and 10.5% are international students. 55% attended public schools and 45% attended private, religious, or international schools, and 97% of students were in the top 10% of their high school class. Every year, Yale College also admits a small group of non-traditional students through the Eli Whitney Students Program.Collections

Yale University Library
The Yale University Library is the library system of Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut. Originating in 1701 with the gift of several dozen books to a new "Collegiate School," the library's collection now contains approximately 14.9 milli ...
, which holds over 15 million volumes, is the third-largest university collection in the United States. The main library, Sterling Memorial Library, contains about 4 million volumes, and other holdings are dispersed at subject and location libraries.
Rare books are found in several Yale collections. The Beinecke Rare Book Library has a large collection of rare books and manuscripts. The Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library includes important historical medical texts, including an impressive collection of rare books, as well as historical medical instruments. The Lewis Walpole Library contains the largest collection of 18th‑century British literary works. The Elizabethan Club, technically a private organization, makes its Elizabethan folios and first editions available to qualified researchers through Yale.
Yale's museum collections are also of international stature. The Yale University Art Gallery, the country's first university-affiliated art museum, contains more than 200,000 works, including Old Masters and important collections of modern art, in the Swartwout and Kahn buildings. The latter, Louis Kahn's first large-scale American work (1953), was renovated and reopened in December 2006. The Yale Center for British Art, the largest collection of British art outside of the UK, grew from a gift of Paul Mellon and is housed in another Kahn-designed building.
The Peabody Museum of Natural History in New Haven is used by school children and contains research collections in anthropology, archaeology, and the natural environment. The Yale University Collection of Musical Instruments, affiliated with the Yale School of Music, is perhaps the least-known of Yale's collections because its hours of opening are restricted.
The museums once housed the artifacts brought to the United States from Peru by Yale history professor Hiram Bingham III, Hiram Bingham in his Yale-financed expedition to Machu Picchu in 1912 – when the removal of such artifacts was legal. The artifacts were restored to Peru in 2012.
Rankings
The ''U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Yale third among U.S. national universities for 2016, as it had for each of the previous sixteen years. Yale University is Higher education accreditation in the United States, accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education. Internationally, Yale was ranked 11th in the 2016 Academic Ranking of World Universities, tenth in the 2016–17 Nature Index for quality of scientific research output, and tenth in the 2016 CWUR World University Rankings. The university was also ranked sixth in the 2016 Times Higher Education (THE) Global University Employability Rankings and eighth in the Academic World Reputation Rankings. In 2019, it ranked 27th among the universities around the world by ''SCImago Institutions Rankings''.Faculty, research, and intellectual traditions
Yale is a member of the Association of American Universities (AAU) and is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". According to the National Science Foundation, Yale spent $990 million on research and development in 2018, ranking it 15th in the nation. Yale's current faculty include 67 members of theNational Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nati ...
, 55 members of the National Academy of Medicine
The National Academy of Medicine (NAM), formerly called the Institute of Medicine (IoM) until 2015, is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Medicine is a part of the National Academies of Sciences, En ...
, 8 members of the National Academy of Engineering
The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Engineering is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy ...
, and 187 members of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and ...
. The college is, after normalization for institution size, the tenth-largest baccalaureate source of doctoral degree
A doctorate (from Latin ''docere'', "to teach"), doctor's degree (from Latin ''doctor'', "teacher"), or doctoral degree is an academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism ''li ...
recipients in the United States, and the largest such source within the Ivy League. It also is a top 10 (ranked seventh) baccalaureate source (after normalization for the number of graduates) of some of the most notable scientists ( Nobel, Fields Medal, Fields, Turing Award, Turing prizes, or membership in National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nati ...
, National Academy of Engineering
The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Engineering is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy ...
, or National Academy of Medicine
The National Academy of Medicine (NAM), formerly called the Institute of Medicine (IoM) until 2015, is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Medicine is a part of the National Academies of Sciences, En ...
).
Yale's English and Comparative Literature departments were part of the New Criticism movement. Of the New Critics, Robert Penn Warren, W.K. Wimsatt, and Cleanth Brooks were all Yale faculty. Later, the Yale Comparative literature department became a center of American deconstruction. Jacques Derrida, the father of deconstruction, taught at the department of comparative literature from the late 1970s to mid-1980s. Several other Yale faculty members were also associated with deconstruction, forming the so-called "Yale school (deconstruction), Yale School". These included Paul de Man who taught in the Departments of Comparative Literature and French, J. Hillis Miller, Geoffrey Hartman (both taught in the Departments of English and Comparative Literature), and Harold Bloom (English), whose theoretical position was always somewhat specific, and who ultimately took a very different path from the rest of this group. Yale's history department has also originated important intellectual trends. Historians C. Vann Woodward and David Brion Davis are credited with beginning in the 1960s and 1970s an important stream of American South, southern historians; likewise, David Montgomery (historian), David Montgomery, a labor historian, advised many of the current generation of labor historians in the country. Yale's Music School and department fostered the growth of Music Theory in the latter half of the 20th century. The ''Journal of Music Theory'' was founded there in 1957; Allen Forte and David Lewin were influential teachers and scholars.
Since the late 1960s, Yale produces social sciences and policy research through its Yale Institution for Social and Policy Studies, Institution for Social and Policy Studies (ISPS).
In addition to eminent faculty members, Yale research relies heavily on the presence of roughly 1200 postdoctoral researcher, Postdocs from various national and international origin working in the multiple laboratories in the sciences, social sciences, humanities, and professional schools of the university. The university progressively recognized this working force with the recent creation of the Office for Postdoctoral Affairs and the Yale Postdoctoral Association.
Campus life
Yale is a research university, with the majority of its students in the Graduate school, graduate and Professional school, professional schools. Undergraduate education, Undergraduates, or Yale College students, come from a variety of ethnic, national, socioeconomic, and personal backgrounds. Of the 2010–2011 freshman class, 10% are non‑U.S. citizens, while 54% went to public high schools. The median family income of Yale students is $192,600, with 57% of students coming from the top 10% highest-earning families and 16% from the bottom 60%.Residential colleges
Yale's residential college system was established in 1933 by Edward S. Harkness, who admired the social intimacy of Oxford and Cambridge and donated significant funds to found similar Collegiate university, colleges at Yale and Harvard. Though Yale's colleges resemble their English precursors organizationally and architecturally, they are Collegiate university#Dependent colleges, dependent entities of Yale College and have limited autonomy. The colleges are led by a head and an academic dean, who reside in the college, and university faculty and affiliates constitute each college's fellowship. Colleges offer their own seminars, social events, and speaking engagements known as "Master's Teas," but do not contain programs of study or academic departments. All other undergraduate courses are taught by the Faculty of Arts and Sciences and are open to members of any college. All undergraduates are members of a college, to which they are assigned before their freshman year, and 85 percent live in the college quadrangle or a college-affiliated dormitory. While the majority of upperclassman live in the colleges, most on-campus freshmen live on the Old Campus, the university's oldest precinct. While Harkness' original colleges were Georgian architecture, Georgian Revival or Collegiate Gothic in style, two colleges constructed in the 1960s, Morse College, Morse and Ezra Stiles College, Ezra Stiles Colleges, have modernist designs. All twelve college quadrangles are organized around a courtyard, and each has a dining hall, courtyard, library, common room, and a range of student facilities. The twelve colleges are named for important alumni or significant places in university history. In 2017, the university opened two new colleges near Science Hill (Yale University), Science Hill.Calhoun College
Since the 1960s, John C. Calhoun's white supremacy, white supremacist beliefs and pro-slavery leadership had prompted calls to rename the college or remove its tributes to Calhoun. The racially motivated Charleston church shooting, church shooting in Charleston, South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina, led to renewed calls in the summer of 2015 for Calhoun College, one of 12 residential colleges, to be renamed. In July 2015 students signed a petition calling for the name change. They argued in the petition that—while Calhoun was respected in the 19th century as an "extraordinary American statesman"—he was "one of the most prolific defenders of slavery and white supremacy" in the history of the United States. In August 2015, Yale President Peter Salovey addressed the Freshman Class of 2019 in which he responded to the racial tensions but explained why the college would not be renamed. He described Calhoun as "a notable political theorist, a vice president to two different U.S. presidents, a secretary of war and of state, and a congressman and senator representing South Carolina". He acknowledged that Calhoun also "believed that the highest forms of civilization depend on involuntary servitude. Not only that, but he also believed that the races he thought to be inferior, black people in particular, ought to be subjected to it for the sake of their own best interests." Student activism about this issue increased in the fall of 2015, and included further protests sparked by controversy surrounding an administrator's comments on the potential positive and negative implications of students who wear Halloween costumes that are culturally sensitive. Campus-wide discussions expanded to include critical discussion of the experiences of women of color on campus, and the realities of racism in undergraduate life. The protests were sensationalized by the media and led to the labelling of some students as being members of Generation Snowflake. In April 2016, Salovey announced that "despite decades of vigorous alumni and student protests," Calhoun's name will remain on the Yale residential college explaining that it is preferable for Yale students to live in Calhoun's "shadow" so they will be "better prepared to rise to the challenges of the present and the future". He claimed that if they removed Calhoun's name, it would "obscure" his "legacy of slavery rather than addressing it". "Yale is part of that history" and "We cannot erase American history, but we can confront it, teach it and learn from it." One change that will be issued is the title of "master" for faculty members who serve as residential college leaders will be renamed to "head of college" due to its connotation of slavery. Despite this apparently conclusive reasoning, Salovey announced that Calhoun College would be renamed for groundbreaking computer scientist Grace Murray Hopper in February 2017. This renaming decision received a range of responses from Yale students and alumni.Student organizations
In 2014, Yale had 385 registered student organizations, plus an additional one hundred groups in the process of registration. The university hosts a variety of student journals, magazines, and newspapers. The Yale Literary Magazine, founded in February 1836, is the oldest student literary magazine in the United States. Established in 1872, ''The Yale Record'' is the world's oldest humor magazine. Newspapers include the ''Yale Daily News'', which was first published in 1878, and the weekly ''Yale Herald'', which was first published in 1986. The ''Yale Journal of Medicine & Law'' is a biannual magazine that explores the intersection of Health law, law and medicine. Dwight Hall, an independent, non-profit community service organization, oversees more than 2,000 Yale undergraduates working on more than 70 community service initiatives in New Haven. The Yale College Council runs several agencies that oversee campus wide activities and student services. The Yale Dramatic Association and Bulldog Productions cater to the theater and film communities, respectively. In addition, the Yale Drama Coalition serves to coordinate between and provide resources for the various Sudler Fund sponsored theater productions which run each weekend. WYBC Yale Radio is the campus's radio station, owned and operated by students. While students used to broadcast on AM and FM frequencies, they now have an Internet-only stream. The Yale College Council (YCC) serves as the campus's undergraduate student government. All registered student organizations are regulated and funded by a subsidiary organization of the YCC, known as the Undergraduate Organizations Funding Committee (UOFC). The Graduate and Professional Student Senate (GPSS) serves as Yale's graduate and professional student government. The Yale Political Union (YPU) is a debate society founded in 1934 to host student discussions on a wide variety of topics. It is advised by alumni political leaders such as John Kerry and George Pataki. The Yale International Relations Association (YIRA) functions as the umbrella organization for the university's top-ranked Model UN team. YIRA also has a Europe-based offshoot, Yale Model Government Europe, other Model UN conferences such as YMUN, YMUN Korea, YMUN Taiwan and Yale Model African Union (YMAU), and educational programs such as the Yale Review of International Studies (YRIS), Yale International Relations Leadership Institute, and Hemispheres. The campus includes several fraternities and sororities. The campus features at least 18 a cappella groups, the most famous of which is The Whiffenpoofs, which from its founding in 1909 until 2018 was made up solely of senior men. Yale's secret society, secret societies Secret Societies at Yale University, include Skull and Bones, Scroll and Key, Wolf's Head (secret society), Wolf's Head, Book and Snake, Elihu (secret society), Elihu, Berzelius (secret society), Berzelius, St. Elmo (secret society), St. Elmo, Manuscript Society, Manuscript, Brothers in Unity, Linonia, St. Anthony Hall, Shabtai (society), Shabtai, Myth and Sword, Daughters of Sovereign Government (DSG), Mace and Chain, ISO, and Sage and Chalice, among others. The two oldest existing honor societies are the Aurelian Honor Society, Aurelian (1910) and the Torch Honor Society (1916). The Elizabethan Club, a social club, has a membership of undergraduates, graduates, faculty and staff with literary or artistic interests. Membership is by invitation. Members and their guests may enter the "Lizzie's" premises for conversation and tea. The club owns first editions of a Shakespeare Folio, several Shakespeare Quartos, and a first edition of Milton's ''Paradise Lost'', among other important literary texts.Traditions
Yale seniors at graduation smash clay pipes underfoot to symbolize passage from their "Bright College Years, bright college years," though in recent history the pipes have been replaced with "bubble pipes". ("Bright College Years," the university's alma mater, was penned in 1881 by Henry Strong Durand, Henry Durand, Class of 1881, to the tune of ''Die Wacht am Rhein''.) Yale's student tour guides tell visitors that students consider it good luck to rub the toe of the statue of Theodore Dwight Woolsey on Old Campus; however, actual students rarely do so. In the second half of the 20th century Bladderball, a campus-wide game played with a large inflatable ball, became a popular tradition but was banned by administration due to safety concerns. In spite of administration opposition, students revived the game in 2009, 2011, and 2014.Athletic
 Yale supports 35 varsity athletic teams that compete in the
Yale supports 35 varsity athletic teams that compete in the Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight schools ...
Conference, the Eastern College Athletic Conference, the New England Intercollegiate Sailing Association. Yale athletic teams compete intercollegiately at the National Collegiate Athletic Association, NCAA Division I level. Like other members of the Ivy League, Yale does not offer athletic scholarships.
Yale has numerous athletic facilities, including the Yale Bowl (the nation's first natural "bowl" stadium, and prototype for such stadiums as the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum and the Rose Bowl (stadium), Rose Bowl), located at The Walter Camp Field athletic complex, and the Payne Whitney Gymnasium, the second-largest indoor athletic complex in the world.
In May 2018, the men's lacrosse team defeated the Duke Blue Devils to claim their first ever NCAA Division I Men's Lacrosse Championship, and are the first Ivy League school to win the title since the Princeton Tigers in 2001.
In 2016, the men's basketball team won the Ivy League Championship title for the first time in 54 years, earning a spot in the NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament. In the first round of the tournament, the Bulldogs beat the Baylor Bears 79–75 in the school's first-ever tournament win. October 21, 2000, marked the dedication of Yale's fourth new boathouse in 157 years of collegiate rowing. The Gilder Boathouse is named to honor former Olympic rower Virginia Gilder '79 and her father Richard Gilder '54, who gave $4 million towards the $7.5 million project. Yale also maintains the Gales Ferry site where the heavyweight men's team trains for the Yale-Harvard Boat Race.
Yale crew is the oldest collegiate athletic team in America, and won Olympics, Olympic Games Gold Medal for men's eights in 1924 and 1956. The Yale Corinthian Yacht Club, founded in 1881, is the oldest collegiate sailing (sport), sailing club in the world.
In 1896, Yale and Johns Hopkins University, Johns Hopkins played the first known ice hockey game in the United States. Since 2006, the school's ice hockey clubs have played a commemorative game.
Yale students claim to have invented Frisbee, by tossing empty Frisbie Pie Company tins.
Yale athletics are supported by the Yale Precision Marching Band. "Precision" is used here ironically; the band is a scatter-style band that runs wildly between formations rather than actually marching. The band attends every home football game and many away, as well as most hockey and basketball games throughout the winter.
Yale intramural sports are also a significant aspect of student life. Students compete for their respective residential colleges, fostering a friendly rivalry. The year is divided into fall, winter, and spring seasons, each of which includes about ten different sports. About half the sports are coeducational. At the end of the year, the residential college with the most points (not all sports count equally) wins the Tyng Cup.
October 21, 2000, marked the dedication of Yale's fourth new boathouse in 157 years of collegiate rowing. The Gilder Boathouse is named to honor former Olympic rower Virginia Gilder '79 and her father Richard Gilder '54, who gave $4 million towards the $7.5 million project. Yale also maintains the Gales Ferry site where the heavyweight men's team trains for the Yale-Harvard Boat Race.
Yale crew is the oldest collegiate athletic team in America, and won Olympics, Olympic Games Gold Medal for men's eights in 1924 and 1956. The Yale Corinthian Yacht Club, founded in 1881, is the oldest collegiate sailing (sport), sailing club in the world.
In 1896, Yale and Johns Hopkins University, Johns Hopkins played the first known ice hockey game in the United States. Since 2006, the school's ice hockey clubs have played a commemorative game.
Yale students claim to have invented Frisbee, by tossing empty Frisbie Pie Company tins.
Yale athletics are supported by the Yale Precision Marching Band. "Precision" is used here ironically; the band is a scatter-style band that runs wildly between formations rather than actually marching. The band attends every home football game and many away, as well as most hockey and basketball games throughout the winter.
Yale intramural sports are also a significant aspect of student life. Students compete for their respective residential colleges, fostering a friendly rivalry. The year is divided into fall, winter, and spring seasons, each of which includes about ten different sports. About half the sports are coeducational. At the end of the year, the residential college with the most points (not all sports count equally) wins the Tyng Cup.
Song
Notable among the songs commonly played and sung at events such as graduation, commencement, convocation, alumni gatherings, and athletic games are the alma mater, "Bright College Years". Despite its popularity, "Boola Boola" is not the official fight song, albeit being the origin of the university's unofficial motto. The official Yale fight song, "Bulldog" was written by Cole Porter during his undergraduate days and is sung after touchdowns during a football game. Additionally, two other songs, "Down the Field" by C.W. O'Conner, and "Bingo Eli Yale", also by Cole Porter, are still sung at football games. According to ''College Fight Songs: An Annotated Anthology'' published in 1998, "Down the Field" ranks as the fourth-greatest fight song of all time.Mascot
The school mascot is "Handsome Dan", the Yale bulldog, and the Yale fight song contains the refrain, "Bulldog, bulldog, bow wow wow." The school color, since 1894, is Yale Blue. Yale's Handsome Dan is believed to be the first college mascot in America, having been established in 1889.Notable people
Benefactors
Yale has had many financial supporters, but some stand out by the magnitude or timeliness of their contributions. Among those who have made large donations commemorated at the university are:Elihu Yale
Elihu Yale (5 April 1649 – 8 July 1721) was a British-American colonial administrator and philanthropist. Although born in Boston, Massachusetts, he only lived in America as a child, spending the rest of his life in England, Wales and India ...
; Jeremiah Dummer
Jeremiah Dummer (1681 – May 19, 1739) was an important colonial figure for New England in the early 18th century. His most significant contributions to American history were his ''A Defense of the New England Charters'' and his role in the for ...
; the Harkness Tower, Harkness family (Edward S. Harkness, Edward, Anna M. Harkness, Anna, and William Harkness, William); the Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library, Beinecke family (Edwin, Frederick W. Beinecke, Frederick, and Walter); John William Sterling; Payne Whitney; Joseph Earl Sheffield, Paul Mellon, Charles B. G. Murphy, Joseph Tsai, and William K. Lanman. The Yale Class of 1954, led by Richard Gilder, donated $70 million in commemoration of their 50th reunion. Charles B. Johnson, a 1954 graduate of Yale College, pledged a $250 million gift in 2013 to support the construction of two new residential colleges. The colleges have been named respectively in honor of Pauli Murray and Benjamin Franklin. A $100 million contribution by Stephen Adams (business), Stephen Adams enabled the Yale School of Music to become tuition-free and the Adams Center for Musical Arts to be built.
Notable alumni
 Over its history, Yale has produced many distinguished alumni in a variety of fields, ranging from the public to private sector. According to 2020 data, around 71% of undergraduates join the workforce, while the next largest majority of 16.6% go on to attend graduate or professional schools. Yale graduates have been recipients of 252 Rhodes Scholarships, 123 Marshall Scholarships, 67 Harry S. Truman Scholarship, Truman Scholarships, 21 Churchill Scholarships, and 9 Mitchell Scholarships. The university is also the second largest producer of Fulbright Program, Fulbright Scholars, with a total of 1,199 in its history and has produced 89 MacArthur Fellows Program, MacArthur Fellows. The U.S. Department of State Bureau of Educational and Cultural Affairs ranked Yale fifth among research institutions producing the most 2020–2021 Fulbright Scholars. Additionally, 31 living billionaires are Yale alumni.
At Yale, one of the most popular undergraduate majors among Juniors and Seniors is political science, with many students going on to serve careers in government and politics. Former presidents who attended Yale for undergrad include William Howard Taft, George H. W. Bush, and George W. Bush while former presidents Gerald Ford and Bill Clinton attended Yale Law School. Former vice-president and influential antebellum era politician John C. Calhoun also graduated from Yale. Former world leaders include Italian prime minister Mario Monti, Turkish prime minister Tansu Çiller, Mexican president Ernesto Zedillo, German president Karl Carstens, Philippine president José Paciano Laurel, Latvian president Valdis Zatlers, Taiwanese premier Jiang Yi-huah, and Malawian president Peter Mutharika, among others. Prominent royals who graduated are Crown Princess Victoria of Sweden, and Olympia von und zu Arco-Zinneberg, Olympia Bonaparte, Princess Napoléon.
Over its history, Yale has produced many distinguished alumni in a variety of fields, ranging from the public to private sector. According to 2020 data, around 71% of undergraduates join the workforce, while the next largest majority of 16.6% go on to attend graduate or professional schools. Yale graduates have been recipients of 252 Rhodes Scholarships, 123 Marshall Scholarships, 67 Harry S. Truman Scholarship, Truman Scholarships, 21 Churchill Scholarships, and 9 Mitchell Scholarships. The university is also the second largest producer of Fulbright Program, Fulbright Scholars, with a total of 1,199 in its history and has produced 89 MacArthur Fellows Program, MacArthur Fellows. The U.S. Department of State Bureau of Educational and Cultural Affairs ranked Yale fifth among research institutions producing the most 2020–2021 Fulbright Scholars. Additionally, 31 living billionaires are Yale alumni.
At Yale, one of the most popular undergraduate majors among Juniors and Seniors is political science, with many students going on to serve careers in government and politics. Former presidents who attended Yale for undergrad include William Howard Taft, George H. W. Bush, and George W. Bush while former presidents Gerald Ford and Bill Clinton attended Yale Law School. Former vice-president and influential antebellum era politician John C. Calhoun also graduated from Yale. Former world leaders include Italian prime minister Mario Monti, Turkish prime minister Tansu Çiller, Mexican president Ernesto Zedillo, German president Karl Carstens, Philippine president José Paciano Laurel, Latvian president Valdis Zatlers, Taiwanese premier Jiang Yi-huah, and Malawian president Peter Mutharika, among others. Prominent royals who graduated are Crown Princess Victoria of Sweden, and Olympia von und zu Arco-Zinneberg, Olympia Bonaparte, Princess Napoléon. Yale alumni have had considerable presence in U.S. government in all three branches. On the Supreme Court of the United States, U.S. Supreme Court, 19 justices have been Yale alumni, including current Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, Associate Justices Sonia Sotomayor, Samuel Alito, Clarence Thomas, and Brett Kavanaugh. Numerous Yale alumni have been United States Senate, U.S. Senators, including current senators Michael Bennet, Richard Blumenthal, Cory Booker, Sherrod Brown, Chris Coons, Amy Klobuchar, Ben Sasse, and Sheldon Whitehouse. Current and former cabinet members include Secretaries of State John Kerry, Hillary Clinton, Cyrus Vance, and Dean Acheson; U.S. Secretaries of the Treasury Oliver Wolcott, Robert Rubin, Nicholas F. Brady, Steven Mnuchin, and Janet Yellen; U.S. Attorneys General Nicholas Katzenbach, John Ashcroft, and Edward H. Levi; and many others. Peace Corps founder and American diplomat Sargent Shriver and public official and urban planner Robert Moses are Yale alumni.
Yale alumni have had considerable presence in U.S. government in all three branches. On the Supreme Court of the United States, U.S. Supreme Court, 19 justices have been Yale alumni, including current Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, Associate Justices Sonia Sotomayor, Samuel Alito, Clarence Thomas, and Brett Kavanaugh. Numerous Yale alumni have been United States Senate, U.S. Senators, including current senators Michael Bennet, Richard Blumenthal, Cory Booker, Sherrod Brown, Chris Coons, Amy Klobuchar, Ben Sasse, and Sheldon Whitehouse. Current and former cabinet members include Secretaries of State John Kerry, Hillary Clinton, Cyrus Vance, and Dean Acheson; U.S. Secretaries of the Treasury Oliver Wolcott, Robert Rubin, Nicholas F. Brady, Steven Mnuchin, and Janet Yellen; U.S. Attorneys General Nicholas Katzenbach, John Ashcroft, and Edward H. Levi; and many others. Peace Corps founder and American diplomat Sargent Shriver and public official and urban planner Robert Moses are Yale alumni.
 Yale has produced numerous award-winning authors and influential writers, like Nobel Prize in Literature laureate Sinclair Lewis and Pulitzer Prize winners Stephen Vincent Benét, Thornton Wilder, Doug Wright, and David McCullough. Academy Awards, Academy Award winning actors, actresses, and directors include Jodie Foster, Paul Newman, Meryl Streep, Elia Kazan, George Roy Hill, Lupita Nyong'o, Oliver Stone, and Frances McDormand. Alumni from Yale have also made notable contributions to both music and the arts. Leading American composer from the 20th century Charles Ives, Broadway composer Cole Porter, Grammy Award, Grammy award winner David Lang (composer), David Lang, multi-Tony Award winner Composer and Musicologist Maury Yeston, and award-winning jazz pianist and composer Vijay Iyer all hail from Yale. Hugo Boss Prize winner Matthew Barney, famed American sculptor Richard Serra, President Barack Obama presidential portrait painter Kehinde Wiley, MacArthur Fellow and contemporary artist Sarah Sze, Pulitzer Prize for Editorial Cartooning, Pulitzer Prize winning cartoonist Garry Trudeau, and National Medal of Arts photorealist painter Chuck Close all graduated from Yale. Additional alumni include architect and Presidential Medal of Freedom winner Maya Lin, Pritzker Architecture Prize, Pritzker Prize winner Norman Foster, Baron Foster of Thames Bank, Norman Foster, and Gateway Arch designer Eero Saarinen. Journalists and pundits include Dick Cavett, Chris Cuomo, Anderson Cooper, William F. Buckley Jr., and Fareed Zakaria.
Yale has produced numerous award-winning authors and influential writers, like Nobel Prize in Literature laureate Sinclair Lewis and Pulitzer Prize winners Stephen Vincent Benét, Thornton Wilder, Doug Wright, and David McCullough. Academy Awards, Academy Award winning actors, actresses, and directors include Jodie Foster, Paul Newman, Meryl Streep, Elia Kazan, George Roy Hill, Lupita Nyong'o, Oliver Stone, and Frances McDormand. Alumni from Yale have also made notable contributions to both music and the arts. Leading American composer from the 20th century Charles Ives, Broadway composer Cole Porter, Grammy Award, Grammy award winner David Lang (composer), David Lang, multi-Tony Award winner Composer and Musicologist Maury Yeston, and award-winning jazz pianist and composer Vijay Iyer all hail from Yale. Hugo Boss Prize winner Matthew Barney, famed American sculptor Richard Serra, President Barack Obama presidential portrait painter Kehinde Wiley, MacArthur Fellow and contemporary artist Sarah Sze, Pulitzer Prize for Editorial Cartooning, Pulitzer Prize winning cartoonist Garry Trudeau, and National Medal of Arts photorealist painter Chuck Close all graduated from Yale. Additional alumni include architect and Presidential Medal of Freedom winner Maya Lin, Pritzker Architecture Prize, Pritzker Prize winner Norman Foster, Baron Foster of Thames Bank, Norman Foster, and Gateway Arch designer Eero Saarinen. Journalists and pundits include Dick Cavett, Chris Cuomo, Anderson Cooper, William F. Buckley Jr., and Fareed Zakaria. In business, Yale has had numerous alumni and former students go on to become founders of influential business, like William E. Boeing, William Boeing (Boeing, United Airlines), Briton Hadden and Henry Luce (Time (magazine), Time Magazine), Stephen A. Schwarzman (The Blackstone Group, Blackstone Group), Frederick W. Smith (FedEx), Juan Trippe (Pan Am), Harold Stanley (Morgan Stanley), Bing Gordon (Electronic Arts), and Ben Silbermann (Pinterest). Other business people from Yale include former chairman and CEO of Sears Holdings Edward Lampert, former Time Warner president Jeffrey Bewkes, former PepsiCo chairperson and CEO Indra Nooyi, sports agent Donald Dell, and investor/philanthropist Sir John Templeton,
Yale alumni distinguished in academia include literary critic and historian Henry Louis Gates, economists Irving Fischer, Mahbub ul Haq, and Nobel Prize laureate Paul Krugman; Nobel Prize in Physics laureates Ernest Lawrence and Murray Gell-Mann; Fields Medalist John G. Thompson; Human Genome Project leader and National Institutes of Health director Francis S. Collins; brain surgery pioneer Harvey Cushing; pioneering computer scientist Grace Hopper; influential mathematician and chemist Josiah Willard Gibbs; National Women's Hall of Fame inductee and biochemist Florence B. Seibert;
In business, Yale has had numerous alumni and former students go on to become founders of influential business, like William E. Boeing, William Boeing (Boeing, United Airlines), Briton Hadden and Henry Luce (Time (magazine), Time Magazine), Stephen A. Schwarzman (The Blackstone Group, Blackstone Group), Frederick W. Smith (FedEx), Juan Trippe (Pan Am), Harold Stanley (Morgan Stanley), Bing Gordon (Electronic Arts), and Ben Silbermann (Pinterest). Other business people from Yale include former chairman and CEO of Sears Holdings Edward Lampert, former Time Warner president Jeffrey Bewkes, former PepsiCo chairperson and CEO Indra Nooyi, sports agent Donald Dell, and investor/philanthropist Sir John Templeton,
Yale alumni distinguished in academia include literary critic and historian Henry Louis Gates, economists Irving Fischer, Mahbub ul Haq, and Nobel Prize laureate Paul Krugman; Nobel Prize in Physics laureates Ernest Lawrence and Murray Gell-Mann; Fields Medalist John G. Thompson; Human Genome Project leader and National Institutes of Health director Francis S. Collins; brain surgery pioneer Harvey Cushing; pioneering computer scientist Grace Hopper; influential mathematician and chemist Josiah Willard Gibbs; National Women's Hall of Fame inductee and biochemist Florence B. Seibert; Turing Award
The ACM A. M. Turing Award is an annual prize given by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) for contributions of lasting and major technical importance to computer science. It is generally recognized as the highest distinction in compu ...
recipient Ron Rivest; inventors Samuel F.B. Morse and Eli Whitney; Nobel Prize in Chemistry laureate John B. Goodenough; lexicographer Noah Webster; and theologians Jonathan Edwards Jonathan Edwards may refer to:
Musicians
*Jonathan and Darlene Edwards, pseudonym of bandleader Paul Weston and his wife, singer Jo Stafford
*Jonathan Edwards (musician) (born 1946), American musician
** ''Jonathan Edwards'' (album), debut album ...
and Reinhold Niebuhr.
In the sporting arena, Yale alumni include baseball players Ron Darling and Craig Breslow and baseball executives Theo Epstein and George Weiss (baseball), George Weiss; football players Calvin Hill, Gary Fencik, Gary Fenick, Amos Alonzo Stagg, and "the Father of American Football" Walter Camp; ice hockey players Chris Higgins (ice hockey), Chris Higgins and Olympian Helen Resor (ice hockey), Helen Resor; Olympic figure skaters Sarah Hughes and Nathan Chen; nine-time U.S. Squash men's champion Julian Illingworth; Olympic swimmer Don Schollander; Olympic rowers Josh West and Rusty Wailes; Olympic sailor Stuart McNay; Olympic runner Frank Shorter; and others.
In fiction and popular culture
Yale University is a cultural referent as an institution that produces some of the most elite members of society and its grounds, alumni, and students have been prominently portrayed in fiction and U.S. popular culture. For example, Owen Johnson (writer), Owen Johnson's novel ''Stover at Yale'' follows the college career of Dink Stover, and Frank Merriwell, the model for all later juvenile sports fiction, plays football, baseball, crew, and track at Yale while solving mysteries and righting wrongs.The text of ''Frank Merriwell at Yale'' is published online by Project GutenbergGutenberg.org
Yale University also is mentioned in F. Scott Fitzgerald's novel ''The Great Gatsby''. The narrator, Nick Carraway, wrote a series of editorials for the ''Yale News'', and Tom Buchanan was "one of the most powerful Defensive end, ends that ever played football" for Yale.
Notes
References
Further reading
* William F. Buckley Jr., Buckley, William F. Jr. ''God and Man at Yale'', 1951. * Dana, Arnold G. ''Yale Old and New'', 78 vols. personal scrapbook, 1942. * Deming, Clarence. ''Yale Yesterdays'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1915. * Dexter, Franklin Bowditch. ''Biographical Sketches of Graduates of Yale: Yale College with Annals of the College History, 6 vols. New York, 1885–1912.'' * Dexter, Franklin Bowditch''Documentary History of Yale University: Under the Original Charter of the Collegiate School of Connecticut, 1701–1745.''
New Haven: Yale University Press, 1901. * French, Robert Dudley. ''The Memorial Quadrangle'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1929. * Furniss, Edgar S. ''The Graduate School of Yale'', New Haven, 1965. * Holden, Reuben A. ''Yale: A Pictorial History'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1967. * Kelley, Brooks Mather. ''Yale: A History''. New Haven: Yale University Press, 1999. ; * Kingsley, William L. ''Yale College. A Sketch of its History'', 2 vols. New York, 1879. * Mendenhall, Thomas C. ''The Harvard-Yale Boat Race, 1852–1924, and the Coming of Sport to the American College.'' (1993). 371 pp. * Nissenbaum, Stephen, ed. ''The Great Awakening at Yale College'' (1972). 263 pp. * Oren, Dan A. ''Joining the Club: A History of Jews and Yale'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1985.* Oviatt, Edwin. ''The Beginnings of Yale (1701–1726)'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1916. * * George Wilson Pierson, Pierson, George Wilson. ''Yale College, An Educational History (1871–1921)'', (Yale University Press, 1952); ''Yale, The University College (1921–1937)'', (Yale University Press, 1955) * Pierson, George Wilson. ''The Founding of Yale: The Legend of the Forty Folios'', New Haven, Yale University Press, 1988. * Stevenson, Louise L. ''Scholarly Means to Evangelical Ends: The New Haven Scholars and the Transformation of Higher Learning in America, 1830–1890'' (1986). 221 pp. * Vincent Scully, Scully, Vincent ''et al.'', eds. ''Yale in New Haven: Architecture and Urbanism''. New Haven: Yale University, 2004. * Tucker, Louis Leonard. ''Connecticut's Seminary of Sedition: Yale College.'' Chester, Conn.: Pequot, 1973. 78 pp. * Warch, Richard. ''School of the Prophets: Yale College, 1701–1740.'' (1973). 339 pp. * Welch, Lewis Sheldon, and Walter Camp. ''Yale, her campus, class-rooms, and athletics'' (1900)
online
* *
Secret societies
* * * *External links
*Yale Athletics website
* {{Authority control Yale University, Buildings and structures in New Haven, Connecticut Colonial colleges Education in New Haven, Connecticut Educational institutions established in 1701 Non-profit organizations based in Connecticut Universities and colleges in New Haven County, Connecticut Tourist attractions in New Haven, Connecticut 1701 establishments in Connecticut Private universities and colleges in Connecticut