Xueyantuo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
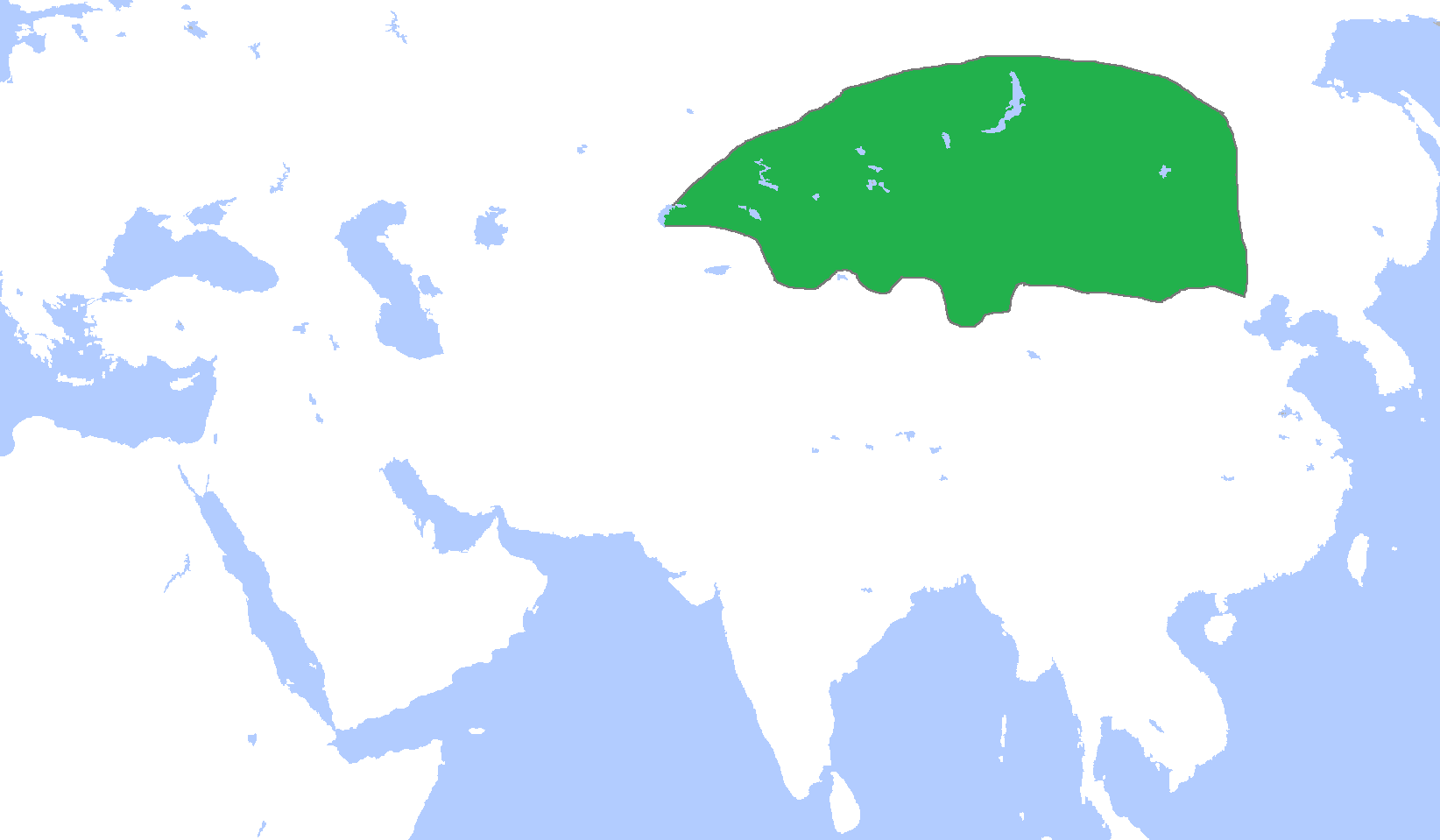 The Xueyantuo were an ancient Tiele tribe and
The Xueyantuo were an ancient Tiele tribe and
* ''
 The Xueyantuo were an ancient Tiele tribe and
The Xueyantuo were an ancient Tiele tribe and khaganate
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a Khan (title), khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribe, tribal chiefdom, principality, monarch ...
in Northeast Asia
Northeast Asia or Northeastern Asia is a geographical subregion of Asia; its northeastern landmass and islands are bounded by the Pacific Ocean.
The term Northeast Asia was popularized during the 1930s by American historian and political scient ...
who were at one point vassals of the Göktürks, later aligning with the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdom ...
against the Eastern Göktürks.
Names
Xue
''Xue'' 薛 appeared earlier as ''Xinli'' 薪犁 in Sima Qian'sRecords of the Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese his ...
, vol. 110 but were not referred to again until the 7th century. Golden (2011) proposed that 薛 Xue's Old Turkic form ''Sir'' derived from Sanskrit '' Śrī'' "fortunate, auspicious"
Yantuo
The etymology of ''Yantuo'' 延陀 is much debated. It was first identified with ''Tarduš'', one of two divisions, besides ''Töliš'', of the short-lived Xueyantuo Qaghanate, by Western Orientalists (likeVilhelm Thomsen
Vilhelm Ludwig Peter Thomsen (25 January 1842 – 12 May 1927) was a Danish linguist and Turkologist. He successfully deciphered the Orkhon inscriptions which were discovered during the expedition of Nikolai Yadrintsev in 1889.
Early life and ...
) who considered ''Töliš'' and ''Tarduš'' to be tribal names. The ethnonym is thus reconstructable as Syr-Tardush. However, Chinese scholars viewed ''Töliš'' and ''Tarduš'' as names of political organizations or districts: for example, Cen Zhongmian viewed the Töliš-Tarduš division as east–west whereas Wang Jingru, citing New Book of Tang, viewed Töliš-Tarduš as north–south.
Sergey Klyastorny (2003:305), apud Golden (2018), proposed that Xueyantuo transcribed *Sir-Yamtar; in contrast to the tribal name ''Sir'', '' �šβaraYamtar'' appeared as a personal name of one companion of Kül Tigin
, native_name_lang = otk
, image = Turkic Head of Koltegin Statue (35324303410).jpg
, caption = Bust of Kul Tigin found at the Khoshoo Tsaidam burial site, in Khashaat, Arkhangai Province, Orkhon River valley. Located in the Na ...
, mentioned the eponymous inscription in his memory.
Tongdian
The ''Tongdian'' () is a Chinese institutional history and encyclopedia text. It covers a panoply of topics from high antiquity through the year 756, whereas a quarter of the book focuses on the Tang Dynasty. The book was written by Du You from 766 ...
recorded the origin of Yantuo: "During the reign of Murong Jun
Murong Jun (; 319–360), courtesy name Xuanying (宣英), formally Emperor Jingzhao of (Former) Yan ((前)燕景昭帝), was an emperor of the Former Yan. He was the dynasty's second ruler, but after first using the Jin dynasty-created title o ...
in the Former Yan, the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
chanyu ''Helatou'' (賀剌頭, "the leader of the Alat tribe") led his tribe of thirty-five thousand people and came to surrender. Yantuo people are probably their descendants." Based on this, Bao (2010) proposed that Yantuo people were the descendants of the Alat tribe, also known as Ala-Yundluğ; therefore, the name Yantuo was probably derived from Yundluğ, and Xueyantuo can be reconstructed as Sir-Yundluğ.
History
Initially the Xue and the Yantuo were two separate tribes.Tongdian
The ''Tongdian'' () is a Chinese institutional history and encyclopedia text. It covers a panoply of topics from high antiquity through the year 756, whereas a quarter of the book focuses on the Tang Dynasty. The book was written by Du You from 766 ...
states that: "Xueyantuo is a splinter tribe from Tiele. In the time of Former Yan mperorMurong Jun
Murong Jun (; 319–360), courtesy name Xuanying (宣英), formally Emperor Jingzhao of (Former) Yan ((前)燕景昭帝), was an emperor of the Former Yan. He was the dynasty's second ruler, but after first using the Jin dynasty-created title o ...
, Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
Shanyu Helaitou led his tribe, numbering 35,000, to come surrender. Yantuo are probably their descendants. With the Xue tribe antuolive intermixed. Thus the appellation Xueyantuo. The Khagan clan's surname is Yilitu. For generations they have been a strong nation." The rulers of Xueyantuo claimed to be originally named Xue (薛/偰), and that the name of the tribe was changed to Xueyantuo after the Xue defeated and merged the Yantuo into their tribe.
After Yishibo, the Xueyantuo founded a short-lived Qaghanate over the steppe under Zhenzhu Khan Zhenzhu may refer to:
* Zhenzhu Khan (died 645), khagan of Xueyantuo
*Zhenzhu Yabgu (died 659), claimant to the throne of Western Turkic Khaganate
*Zhenzhu Subdistrict, Zhen'an District, Dandong, Liaoning, China
*Zhen Zhu, a variety of the ornament ...
, his son Duomi Khan Duomi Khan (多彌可汗) (died 646), personal name Bazhuo (拔灼), full regal name Jialijulixueshaduomi Khan (頡利俱利薛沙多彌可汗), was a khan of the Xueyantuo. After the death of his father, the Zhenzhu Khan Yi'nan, he disputed with ...
and nephew Yitewushi Khan Yitewushi Khan (伊特勿失可汗), personal name Duomozhi (咄摩支), was the last khan of Xueyantuo.
Little is known about Duomozhi's background, other than that he was a nephew of Xueyantuo's greatest khan, the Zhenzhu Khan Yi'nan. In 646, du ...
, the last of whom eventually surrendered to the Tang dynasty.
In 605, Xueyantuo were attacked by the Western Türkic Chuluo Khagan. Consequently, they abandoned the Western Turks and established their own Kaganate under a leadership of Qibi tribe
Qibi tribe (; Middle Chinese: *''kʲiei-pɪ̯et''; Saka: ''Kāribari'') was a Turkic tribe and a part of Tiele confederation, then Toquz Oghuz and later Uyghur Khaganate. Most famous member of the tribe was Qibi Heli.
Area
According to the epig ...
's Yağmurčin Bağa-Qağan, retaining the control and income from the Turfan segment of the Silk Road. Later, Xueynatuo leader Yshbara was installed as a lesser Kagan Yetir (yeti er "seven tribes"). In the 610, Shekui (r. 610-617) ascended to the Western Turkic throne, both rulers renounced their Kagan ranks and rejoined the Western Türkic Kaganate. The next Western Türkic Tong-Yabgu-Kagan (r. 617-630) annexed all seven tribes of the Xueyantuo-headed Tiele confederation, which also included Uighur, Bayïrku, Ădiz, Tongra, Bugu and Barsil tribes. in 627 Xueyantuo leader led his tribes into the territory of the Eastern Türkic Kaganate, defeated the main force of the Kaganate led by the son of the reigning Illig Qaghan
Illig Qaghan (Old Turkic: ; ), born Ashina Duobi (), posthumous name
A posthumous name is an honorary name given mostly to the notable dead in East Asian culture. It is predominantly practiced in East Asian countries such as China, Korea, ...
, Yukuk Shad
Yukuk Shad (r. 638–642, died 653) reigned in the final days of the Western Turkic Khaganate. His name ''Yukuk'' means " owl", according to Gumilyov, or means "venerable", according to Gabain. His full title was 乙毗咄陆可汗 or Yipi Duolu ...
, and settled in the valley of river Tola
Tola may refer to:
Places
* Bella Tola, a mountain in the Pennine Alps in the Swiss canton of Valais
* La Tola, a town and municipality in the Nariño Department, Colombia
*Tola (Shakargarh), a village in Pakistan
* Tola, Rivas, a municipality ...
in the Northern Mongolia. After the victory, Uighur leader Yaoluoge Pusa assumed a title ''huo xielifa'' ( zh, 活頡利發 *''kat-elteber'' or *''war-hilitber'') and split from the confederation, and in 629 the Xueyantuo Yinan-erkin declared himself Inčü Bilge-Khagan of a new Xueyantuo Kaganate.
This Xueyantuo Kaganate was quickly recognized by the Tang Empire, as a counterweight against its enemy Eastern Türkic Kaganate. "Raising Yi'nan on Kagan throne was done under pressure from the Tang court interested in stripping El-kagan of the rights to the supreme power in the huge region, and also in final dismemberment of the Türkic state, a source of many conflicts on their northern borders." Xueyantuo provided military service by assisting the Tang Empire against the Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
in the 630s. The Xueyantuo's vast khaganate spanned from the Altai Mountains to the Gobi desert.
On March 27, 630, the Xueyantuo allied with the Tang to defeat the Eastern Qaghanate in the in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Yin Mountains
The Yin Mountains, also known by several other names, are a mountain range stretching across about of northern China. They form the southeastern border of the Gobi Desert and cross the Chinese provinces of Inner Mongolia and Hebei. Among othe ...
. Illig Qaghan
Illig Qaghan (Old Turkic: ; ), born Ashina Duobi (), posthumous name
A posthumous name is an honorary name given mostly to the notable dead in East Asian culture. It is predominantly practiced in East Asian countries such as China, Korea, ...
escaped, but was handed over to the Tang by his subordinate qaghan on May 2.
After Eastern Göktürk Illig Qaghan Ashina Duobi was defeated by Tang in 630, the Xueyantuo effectively took over control of the Eastern Göktürks' former territory, at times submissive to the Tang and at times warring with the Tang and the subsequent khan of the Eastern Göktürks that Tang supported, the Qilibi Khan
Qilibi Khan ( Chinese: 俟力苾可汗, (Pinyin): qílìbì kěhàn, ( Wade-Giles): ch'i-li-pi k'o-han, Middle Chinese: (Guangyun) , died 647), personal name Ashina Simo (阿史那思摩), Chinese name Li Simo (李思摩), full regal title Yiminish ...
Ashina Simo.
In 632 the Xueyantuo repulsed an army of Si Yabgu Qaghan from the Western Qaghanate, then subjugated the Qarluq at the Ulungur and Irtysh River, and then the Yenisei Kyrgyz tribes. In 634 one of their rivals, Dubu Qaghan (Ashina Shier), son of Chuluo Khan, who ruled much of the eastern half of the Western Qaghanate, was eliminated before escaping to the Tang dynasty.
After that they maintained a friendly relationship with the Tang until 639, when a raid on the Tang capital was planned by the Gökturks under Ashina Jiesheshuai
Ashina Jiesheshuai (; ''New Book of Tang'' Vol. 2'' Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 195. ''Old Book of Tang'' Vol. 194-1 ''New Book of Tang'' Vol. 215-1 Middle Chinese ( Guangyun) pronunciation: ; died 19 May 639) was a member of the Ashina clan of the ...
(阿史那结社率), who had been disparaged by the Tang emperor. He allied with his nephew Ashina Heluohu (阿史那贺逻鹘), choosing him as the leader of the raid on May 19. They were unsuccessful and over 40 rebels were executed. Heluohu was spared and expelled to the far south.
After this incident, an arraignment was made on August 13. A deportation of all Goktürks north of Ordos was carried out, in an attempt to restore the puppet Eastern Qaghanate as a barrier against the Xueyanto, in an attempt to distract them from the territorial competition in the west.
Among the Göktürk nobles, Ashina Simo was selected as the qaghan (Qilibi Khan
Qilibi Khan ( Chinese: 俟力苾可汗, (Pinyin): qílìbì kěhàn, ( Wade-Giles): ch'i-li-pi k'o-han, Middle Chinese: (Guangyun) , died 647), personal name Ashina Simo (阿史那思摩), Chinese name Li Simo (李思摩), full regal title Yiminish ...
) with his capital at the border. The plot failed, as he was unable to gather his people, many of his tribesmen having escaped to the south by 644 after a series of unsuccessful incursions by the Xueyantuo supported by the Tang dynasty. Defeats by the advancing Tang troops had made their tribal allies lose confidence in them. The crisis deepened the next year when a coup d'état took place within the clan.
On August 1, 646, the Xueyantuo were defeated by the Uyghur (Huihe, 回纥) and the Tang. The Xueyantuo's Duomi Khan Duomi Khan (多彌可汗) (died 646), personal name Bazhuo (拔灼), full regal name Jialijulixueshaduomi Khan (頡利俱利薛沙多彌可汗), was a khan of the Xueyantuo. After the death of his father, the Zhenzhu Khan Yi'nan, he disputed with ...
, Bazhuo, was killed by the Uyghur. A Tang army led by the general Li Daozong Li Daozong () (603?-656?Historical accounts indicate that Li Daozong died at the age of 53, and died during the journey to his place of exile after he was exiled in 653, without reaching the place of exile. That appears to be some evidence that he ...
, the Prince of Jiangxia, crushed the Xueyantuo forces. The last Xueyantuo khan, the Yitewushi Khan Yitewushi Khan (伊特勿失可汗), personal name Duomozhi (咄摩支), was the last khan of Xueyantuo.
Little is known about Duomozhi's background, other than that he was a nephew of Xueyantuo's greatest khan, the Zhenzhu Khan Yi'nan. In 646, du ...
Duomozhi, surrendered. Their remnants were destroyed two years later, on September 15. The Sir re-appeared later as '' lï Sir'' "Six Sir Tribes", subjects of the Latter Turk ruler Bilge Khagan
Bilge Qaghan ( otk, 𐰋𐰃𐰠𐰏𐰀:𐰴𐰍𐰣, Bilgä Qaγan; ; 683 – 25 November 734) was the fourth Qaghan of the Second Turkic Khaganate. His accomplishments were described in the Orkhon inscriptions.
Names
As was the custom, his ...
; Klyashtorny controversially proposed that Sir were precursors to Kipchaks.
Xueyantuo's relationship with the later Shatuo Turks is contested. The epitaph of Shatuo leader Li Keyong
Li Keyong () (October 24, 856 – February 24, 908) was a Chinese military general and politician of Shatuo ethnicity, and from January 896 a Prince of Jin (, ''Jin Wang''), which would become an independent state after the fall of the Tang dyn ...
states that his clan's progenitor was "Yidu, Lord of the Xueyantuo country, an unrivaled general" (益度、薛延陀國君、無敵將軍). However, Chinese chroniclers also traced the Shatuo's origins to a Tiele chief named *''Bayar'' (拔也 ''Baye'') ~ *''Bayïrku'' (拔也古 ''Bayegu'') or Western Turkic ''Chuyue'' 處月 (often identified with Chigils
The Chigil (Chihil, and also (D)Jigil, Cihil, Chiyal) were a Turkic tribe known from the 7th century CE as living around Issyk Kul lake area. They were considered to be descended from the tribe Chuyue, who were of mixed Yueban- Western Turkic or ...
).
Khans of Xueyantuo
* Yishibo (乙失缽), the Yiedie Khan (也咥可汗) (?-628?) * Yi'nan (夷男), the Zhenzhupiqie Khan (真珠毗伽可汗) or, in short, Zhenzhu Khan (真珠可汗) (628-645) * Bazhuo (拔灼), the Jialijulishixueshaduomi Khan (頡利俱力失薛沙多彌可汗) or, in short, Duomi Khan (多彌可汗) (645-646) * Duomozhi (咄摩支), the Yitewushi Khan (伊特勿失可汗) (646)Under Second Turkic Khaganate
* Küli Čur, Ïšbara Bilge Küli Čur (?-c. 723)Surname of Khans
The surname of Xueyantuo's khans is uncertain, although modern Chinese historian Bo Yang lists their surname as "Yishi" in his edition (also known as the ''Bo Yang Edition'') of the ''Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song (960–1127), Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959&n ...
'', but without citing a source. It is possible that Bo was influenced by the ''Tongdian
The ''Tongdian'' () is a Chinese institutional history and encyclopedia text. It covers a panoply of topics from high antiquity through the year 756, whereas a quarter of the book focuses on the Tang Dynasty. The book was written by Du You from 766 ...
'', which refers to the Xueyantuo surname as ''Yilitu'' 壹利吐, ''Yiliduo'' 一利咄 as in ''Cefu Yuangui
''Cefu Yuangui'' (冊府元龜) is the largest ''leishu'' (encyclopedia) compiled during the Chinese Song Dynasty (AD 960–1279). It was the last of the '' Four Great Books of Song'', the previous three having been published in the 10th cen ...
'', ''Yilidie'' 壹利咥 as in '' New Book of Tang''. Li Keyong
Li Keyong () (October 24, 856 – February 24, 908) was a Chinese military general and politician of Shatuo ethnicity, and from January 896 a Prince of Jin (, ''Jin Wang''), which would become an independent state after the fall of the Tang dyn ...
's epitaph also records his alleged Xueyantuo ancestor's name as ''Yidu'' 益度.
According to Cen Zhongmian, the aforementioned names are related to a variant of ''elteris''. Duan Lianqin asserted that the name Yishibo (Yiedie Khan) can also be read interchangeably as Yedie (也咥). The ''Zizhi Tongjian'', in the original, referred to one ethnic Xueyantuo general named Duomo, possibly the Yitewushi Khan (after he became a Tang general) by the family name of XueSee ''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 204.—although the ''Tang Huiyao
The ''Tang Huiyao'' () is an institutional history of Tang dynasty compiled by Wang Pu and presented it to Emperor Taizu of Song in 961. The book contains 100 volumes and 514 sections, it has an abundant content for the period before 846, and scar ...
'' indicated that it was not the same person, as it indicated that the Yitewushi Khan died during Emperor Taizong's reign.''Tang Huiyao'', vol. 96Surnames of Xueyantuo
* Li (李) * Liu (刘) * Xie (偰) * Xue (薛) *Zhang Zhang may refer to:
Chinese culture, etc.
* Zhang (surname) (張/张), common Chinese surname
** Zhang (surname 章), a rarer Chinese surname
* Zhang County (漳县), of Dingxi, Gansu
* Zhang River (漳河), a river flowing mainly in Henan
* ''Zha ...
(張)
See also
* List of Turkic dynasties and countries * Timeline of Turks (500-1300) * Xue * Selenga River *Later Tang
Tang, known in historiography as the Later Tang, was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China and the second of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period in Chinese history.
The first three of the Later Tang's four ...
* Sir-Kıvchak
References
Citations
Sources
* Bo Yang. ''Modern Chinese Edition of Zizhi Tongjian (Vol. 45)''. Taipei: Yuan-Liou Publishing Co. Ltd . * Duan Lianqin (1988a). ''Xueyantuo During the Period of Sui and Tang''. Xi'an: Sanqin Press. . * Duan Lianqin (1988b). ''Dingling, Gaoju and Tiele''. Shanghai: Shanghai People's Press. . * '' New Book of Tang'', vol. 217, part* ''
Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song (960–1127), Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959&n ...
'', vols. :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷192, 192, 193, 194
Year 194 (Roman numerals, CXCIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Septimius and Septimius (or, less frequently, year 9 ...
, 195
Year 195 ( CXCV) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scrapula and Clemens (or, less frequently, year 948 ''Ab urbe cond ...
, 196, 197, 198
__NOTOC__
Year 198 (CXCVIII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sergius and Gallus (or, less frequently, year 951 ''Ab u ...
, 199.
* Zuev Yu.A. "Xueyantuo Khaganate and Kimeks. ( Contributionto Turkic ethnogeography of Central Asia in the middle of 7th century)" in ''Shygys'', Oriental Studies Institute, Almaty (2004), No 1 pp 11–21, No 2 pp 3–26 (in Russian)
* Zuev Yu.A., ''Horse Tamgas from Vassal Princedoms'' (Translation of Chinese composition "Tanghuyao" of 8-10th centuries), Kazakh SSR Academy of Sciences, Alma-Ata, I960, (In Russian)
{{Turkic peoples
Turkic peoples of Asia
Ancient peoples of China
7th century in China
Ancient peoples of Russia
Nomadic groups in Eurasia
History of Mongolia
Historical Turkic states
Tang dynasty
Former countries in Chinese history
7th-century establishments in China
646 disestablishments
7th-century disestablishments in China
Göktürks