XB-51 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Martin XB-51 was an American
 This unorthodox design, first flying on 28 October 1949, was fitted with three
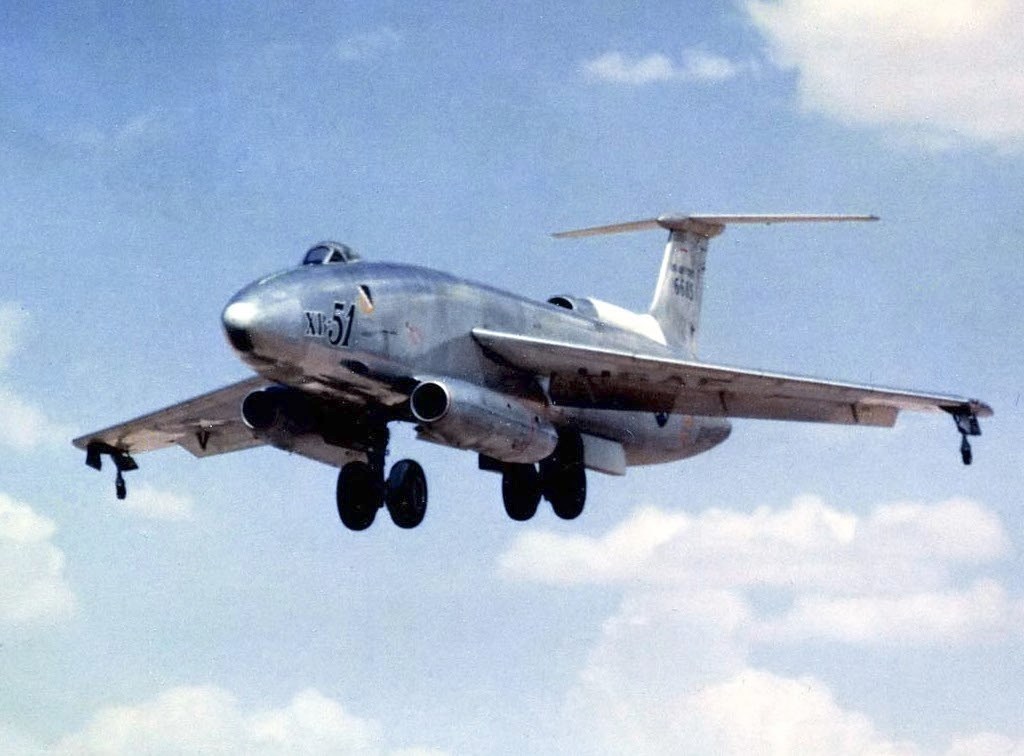
This unorthodox design, first flying on 28 October 1949, was fitted with three  The main landing gear consisted of dual wheel sets in tandem in the fuselage, similar to the Boeing B-47 Stratojet, with outrigger wheels at the wingtips (originally proved on a modified Martin B-26 Marauder named "Middle River Stump Jumper"Winchester 2005, p. 144.). The XB-51 was a large but aerodynamically "clean" design which incorporated nearly all major systems internally. The aircraft was fitted with a rotating bomb bay, a Martin trademark; bombs could also be carried externally up to a maximum load of 10,400 lb (4,700 kg), although the specified basic mission required only a 4,000 lb (1,814 kg) bombload.
The main landing gear consisted of dual wheel sets in tandem in the fuselage, similar to the Boeing B-47 Stratojet, with outrigger wheels at the wingtips (originally proved on a modified Martin B-26 Marauder named "Middle River Stump Jumper"Winchester 2005, p. 144.). The XB-51 was a large but aerodynamically "clean" design which incorporated nearly all major systems internally. The aircraft was fitted with a rotating bomb bay, a Martin trademark; bombs could also be carried externally up to a maximum load of 10,400 lb (4,700 kg), although the specified basic mission required only a 4,000 lb (1,814 kg) bombload."Pivoting Bomb-bay Door Permits Accurate Drops at High-Speeds."
''Popular Mechanics'', February 1954, p. 126. Eight 20 mm cannon mounted in the nose would have been installed in production aircraft. Crew was a pilot under a "fighter"-type bubble canopy and a Short-range navigation and bombing system (SHORAN) operator/navigator in a compartment located lower than and to the rear of the cockpit (only a small observation window was provided).Winchester 2005, p. 145. Both crew members were provided with a pressurized, air conditioned environment, equipped with upward-firing ejection seats.Winchester 2005, p. 145. The XB-51 was the first Martin aircraft equipped with ejection seats, these being of their own design.Tuttle, Jim. ''Eject! The Complete History of U.S. Aircraft Escape Systems''. St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI Publishing Company, 2002. .
 In 1950, the
In 1950, the
USAF Museum: XB-51
* {{Authority control B-51 Trijets B-51, Martin Variable-incidence-wing aircraft T-tail aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1949 Mid-wing aircraft
trijet
A trijet is a jet aircraft powered by three jet engines. In general, passenger airline trijets are considered to be second-generation jet airliners, due to their innovative engine locations, in addition to the advancement of turbofan technology. ...
ground-attack aircraft
An attack aircraft, strike aircraft, or attack bomber is a tactical military aircraft that has a primary role of carrying out airstrikes with greater precision than bombers, and is prepared to encounter strong low-level air defenses while pres ...
. It was designed in 1945 and made its maiden flight in 1949. It was originally designed as a bomber for the United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
under specification V-8237-1 and was designated XA-45. The "A" ground-attack classification was eliminated the next year, and the XB-51 designation was assigned instead. The requirement was for low-level bombing and close support. The XB-51 lost out in evaluation to the English Electric Canberra
The English Electric Canberra is a British first-generation, jet-powered medium bomber. It was developed by English Electric during the mid- to late 1940s in response to a 1944 Air Ministry requirement for a successor to the wartime de Havil ...
which - built by Martin - entered service as the Martin B-57 Canberra
The Martin B-57 Canberra is an American-built, twin-engined tactical bomber and reconnaissance aircraft that entered service with the United States Air Force (USAF) in 1953. The B-57 is a license-built version of the British English Electric C ...
.
Design and development
 This unorthodox design, first flying on 28 October 1949, was fitted with three
This unorthodox design, first flying on 28 October 1949, was fitted with three General Electric J47
The General Electric J47 turbojet (GE company designation TG-190) was developed by General Electric from its earlier J35. It first flew in May 1948. The J47 was the first axial-flow turbojet approved for commercial use in the United States. It ...
engines - an unusual number for a combat aircraft - two underneath the forward fuselage in pods, and one at the extreme tail with the intake at the base of the tailfin. The innovative, variable incidence wings, swept at 35° and with 6° anhedral, were equipped with leading edge slats and full-width flaps. Spoilers gave most of the roll control and undersized ailerons provided feel for the pilot. The combination of variable incidence and slotted flaps gave a shorter takeoff run. Four 954 lb (4.24 kN) thrust Rocket-Assisted Take Off
JATO (acronym for jet-assisted take-off) is a type of assisted take-off for helping overloaded aircraft into the air by providing additional thrust in the form of small rockets. The term ''JATO'' is used interchangeably with the (more specific ...
(RATO) bottles with a 14-second burn duration could be fitted to the rear fuselage to improve takeoff performance. Spectacular launches were a feature of later test flights.Winchester 2005, p. 144.
 The main landing gear consisted of dual wheel sets in tandem in the fuselage, similar to the Boeing B-47 Stratojet, with outrigger wheels at the wingtips (originally proved on a modified Martin B-26 Marauder named "Middle River Stump Jumper"Winchester 2005, p. 144.). The XB-51 was a large but aerodynamically "clean" design which incorporated nearly all major systems internally. The aircraft was fitted with a rotating bomb bay, a Martin trademark; bombs could also be carried externally up to a maximum load of 10,400 lb (4,700 kg), although the specified basic mission required only a 4,000 lb (1,814 kg) bombload.
The main landing gear consisted of dual wheel sets in tandem in the fuselage, similar to the Boeing B-47 Stratojet, with outrigger wheels at the wingtips (originally proved on a modified Martin B-26 Marauder named "Middle River Stump Jumper"Winchester 2005, p. 144.). The XB-51 was a large but aerodynamically "clean" design which incorporated nearly all major systems internally. The aircraft was fitted with a rotating bomb bay, a Martin trademark; bombs could also be carried externally up to a maximum load of 10,400 lb (4,700 kg), although the specified basic mission required only a 4,000 lb (1,814 kg) bombload.''Popular Mechanics'', February 1954, p. 126. Eight 20 mm cannon mounted in the nose would have been installed in production aircraft. Crew was a pilot under a "fighter"-type bubble canopy and a Short-range navigation and bombing system (SHORAN) operator/navigator in a compartment located lower than and to the rear of the cockpit (only a small observation window was provided).Winchester 2005, p. 145. Both crew members were provided with a pressurized, air conditioned environment, equipped with upward-firing ejection seats.Winchester 2005, p. 145. The XB-51 was the first Martin aircraft equipped with ejection seats, these being of their own design.Tuttle, Jim. ''Eject! The Complete History of U.S. Aircraft Escape Systems''. St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI Publishing Company, 2002. .
Operational history
 In 1950, the
In 1950, the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal ...
issued a new requirement based on early Korean war
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
experience for a night intruder/bomber to replace the Douglas A-26 Invader. The XB-51 was entered, as well as the Avro Canada CF-100 and English Electric Canberra
The English Electric Canberra is a British first-generation, jet-powered medium bomber. It was developed by English Electric during the mid- to late 1940s in response to a 1944 Air Ministry requirement for a successor to the wartime de Havil ...
; the XB-51 and Canberra emerged from these as the favorites.
Test flights showed the XB-51 to be highly maneuverable at low altitudes and substantially faster than the Canberra and faster than most fighter aircraft of the era. However, the XB-51's endurance was significantly lower than that of the Canberra and this factor was decisive in its cancellation. In addition, a load limiting factor of only 3.67 ''g'' (36 m/s2) meant that the general strength of the airframe was relatively low and would prevent tight turns while fully loaded. Additionally, the tandem main gear plus outriggers of the XB-51 were thought unsuitable for the requirement to fly from emergency forward airfield Advance airfield and forward airfield are military terms for a relatively primitive ad-hoc airfield used for refueling and re-arming air units as part of forward operations near the enemy. Also called advanced airfield for its advanced position, not ...
s.
While the XB-51 was not selected for procurement, it was decided that Martin would build 250 Canberras under license, under the designation B-57. Furthermore, Martin's rotating bomb bay would be incorporated into production variants of the B-57. A "Super Canberra", incorporating other XB-51 features, such as swept wings and tail-planes, was also proposed. This aircraft – although it promised much better speed and performance than the B-57 – never reached the prototype stage, mainly because the many changes would have taken too long to implement and test, before it could be put into production.
Flights by the XB-51 prototype, ''46-685'', continued, for general research purposes, following the project's official cancellation by the USAF. A second prototype, ''46-686'', which first flew in 1950, crashed during low-level aerobatics on 9 May 1952, killing pilot Major Neil H. Lathrop. ''46-685'' continued to fly, including an appearance in the film '' Toward the Unknown'' as the "Gilbert XF-120" fighter.A few seconds of test flight footage of an XB-51 also appeared in the 1951 '' Tales of Tomorrow'' episode "Plague From Space". Note: Although the XB-51 did not receive an official name, "Panther" had been suggested by the company. The surviving prototype was en- route to Eglin AFB to shoot additional footage when it crashed during takeoff, following a refueling stop in El Paso, Texas, on 25 March 1956.
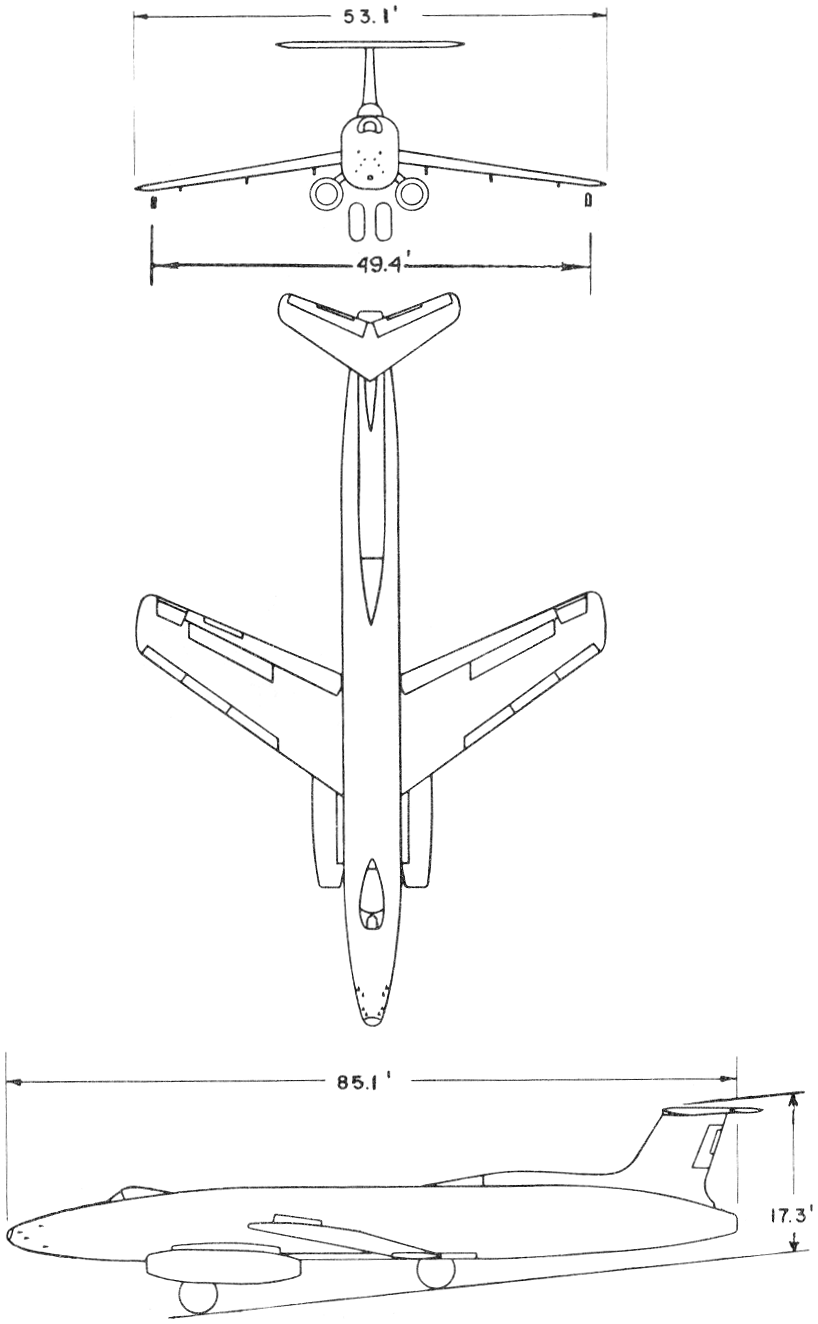
Specifications (XB-51)

See also
References
Notes
Bibliography
* Andrade, John M. ''U.S. Military Aircraft Designations and Serials since 1909''. Earl Shilton, Leicester, UK: Midland Counties Publications, 1979. . * Boyne, Walter. "Attack, The Story of the XB-51, Martin's Phantom Strike Ship!" ''Airpower'', Volume 8, No. 4, July 1978. * Jones, Lloyd S. ''U.S. Bombers, B-1 1928 to B-1 1980s''. Fallbrook, California: Aero Publishers, 1962, second edition 1974. . * Mikesh, Robert C. B-57 Canberra At War 1964-1972''. London: Ian Allan, 1980. . * Winchester, Jim. "Martin XB-51." ''Concept Aircraft: Prototypes, X-Planes and Experimental Aircraft''. Kent, UK: Grange Books plc., 2005. .External links
USAF Museum: XB-51
* {{Authority control B-51 Trijets B-51, Martin Variable-incidence-wing aircraft T-tail aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1949 Mid-wing aircraft