X-rays on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy
 Before their discovery in 1895, X-rays were just a type of unidentified radiation emanating from experimental
Before their discovery in 1895, X-rays were just a type of unidentified radiation emanating from experimental
 An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) li ...
. Most X-rays have a wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re ...
, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV Kev can refer to:
Given name
* Kev Adams, French comedian, actor, screenwriter and film producer born Kevin Smadja in 1991
* Kevin Kev Carmody (born 1946), Indigenous Australian singer-songwriter
* Kev Coghlan (born 1988), Scottish Grand Prix moto ...
. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
s. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen
Wilhelm may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* William Charles John Pitcher, costume designer known professionally as "Wilhelm"
* Wilhelm (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname
Other uses
* Mount ...
, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. For example, chest X-rays can spot pneumonia. Mammograms use X-rays to look for breast cancer.
History
Pre-Röntgen observations and research
 Before their discovery in 1895, X-rays were just a type of unidentified radiation emanating from experimental
Before their discovery in 1895, X-rays were just a type of unidentified radiation emanating from experimental discharge tube
A gas-filled tube, also commonly known as a discharge tube or formerly as a Plücker tube, is an arrangement of electrodes in a gas within an insulating, temperature-resistant envelope. Gas-filled tubes exploit phenomena related to electric ...
s. They were noticed by scientists investigating cathode ray
Cathode rays or electron beam (e-beam) are streams of electrons observed in discharge tubes. If an evacuated glass tube is equipped with two electrodes and a voltage is applied, glass behind the positive electrode is observed to glow, due to el ...
s produced by such tubes, which are energetic electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
beams that were first observed in 1869. Many of the early Crookes tube
A Crookes tube (also Crookes–Hittorf tube) is an early experimental electrical discharge tube, with partial vacuum, invented by English physicist William Crookes and others around 1869-1875, in which cathode rays, streams of electrons, were ...
s (invented around 1875) undoubtedly radiated X-rays, because early researchers noticed effects that were attributable to them, as detailed below. Crookes tubes created free electrons by ionization
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecul ...
of the residual air in the tube by a high DC voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to ...
of anywhere between a few kilovolts and 100 kV. This voltage accelerated the electrons coming from the cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in wh ...
to a high enough velocity that they created X-rays when they struck the anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic ...
or the glass wall of the tube.
The earliest experimenter thought to have (unknowingly) produced X-rays was William Morgan. In 1785, he presented a paper to the Royal Society of London
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
describing the effects of passing electrical currents through a partially evacuated glass tube, producing a glow created by X-rays. This work was further explored by Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for t ...
and his assistant Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
.
When Stanford University physics professor Fernando Sanford
Fernando Sanford (February 12, 1854 – May 21, 1948) was an American physicist and university professor. He was one of the 22 "pioneer professors" (founding faculty) for Stanford University.
Sanford was born on a farm near Franklin Grove in Lee ...
created his "electric photography", he also unknowingly generated and detected X-rays. From 1886 to 1888, he had studied in the Hermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Associatio ...
laboratory in Berlin, where he became familiar with the cathode rays generated in vacuum tubes when a voltage was applied across separate electrodes, as previously studied by Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz ( ; ; 22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) was a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves predicted by James Clerk Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. The unit ...
and Philipp Lenard
Philipp Eduard Anton von Lenard (; hu, Lénárd Fülöp Eduárd Antal; 7 June 1862 – 20 May 1947) was a Hungarian-born German physicist and the winner of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1905 for his work on cathode rays and the discovery of ...
. His letter of January 6, 1893 (describing his discovery as "electric photography") to the '' Physical Review'' was duly published and an article entitled ''Without Lens or Light, Photographs Taken With Plate and Object in Darkness'' appeared in the '' San Francisco Examiner''.
Starting in 1888, Philipp Lenard conducted experiments to see whether cathode rays could pass out of the Crookes tube into the air. He built a Crookes tube with a "window" at the end made of thin aluminium, facing the cathode so the cathode rays would strike it (later called a "Lenard tube"). He found that something came through, that would expose photographic plates and cause fluorescence. He measured the penetrating power of these rays through various materials. It has been suggested that at least some of these "Lenard rays" were actually X-rays.
In 1889, Ukrainian-born Ivan Puluj, a lecturer in experimental physics at the Prague Polytechnic who since 1877 had been constructing various designs of gas-filled tube
A gas-filled tube, also commonly known as a discharge tube or formerly as a Plücker tube, is an arrangement of electrodes in a gas within an insulating, temperature-resistant envelope. Gas-filled tubes exploit phenomena related to electric ...
s to investigate their properties, published a paper on how sealed photographic plates became dark when exposed to the emanations from the tubes.
Helmholtz formulated mathematical equations for X-rays. He postulated a dispersion theory before Röntgen made his discovery and announcement. He based it on the electromagnetic theory of light. However, he did not work with actual X-rays.
In 1894, Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla ( ; ,"Tesla"
''
 On November 8, 1895, German physics professor Wilhelm Röntgen stumbled on X-rays while experimenting with Lenard tubes and
On November 8, 1895, German physics professor Wilhelm Röntgen stumbled on X-rays while experimenting with Lenard tubes and 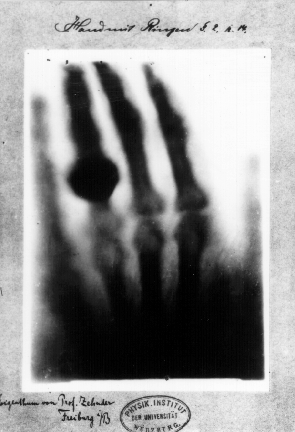 Röntgen discovered their medical use when he made a picture of his wife's hand on a photographic plate formed due to X-rays. The photograph of his wife's hand was the first photograph of a human body part using X-rays. When she saw the picture, she said "I have seen my death."
The discovery of X-rays stimulated a veritable sensation. Röntgen's biographer Otto Glasser estimated that, in 1896 alone, as many as 49 essays and 1044 articles about the new rays were published. This was probably a conservative estimate, if one considers that nearly every paper around the world extensively reported about the new discovery, with a magazine such as ''
Röntgen discovered their medical use when he made a picture of his wife's hand on a photographic plate formed due to X-rays. The photograph of his wife's hand was the first photograph of a human body part using X-rays. When she saw the picture, she said "I have seen my death."
The discovery of X-rays stimulated a veritable sensation. Röntgen's biographer Otto Glasser estimated that, in 1896 alone, as many as 49 essays and 1044 articles about the new rays were published. This was probably a conservative estimate, if one considers that nearly every paper around the world extensively reported about the new discovery, with a magazine such as ''
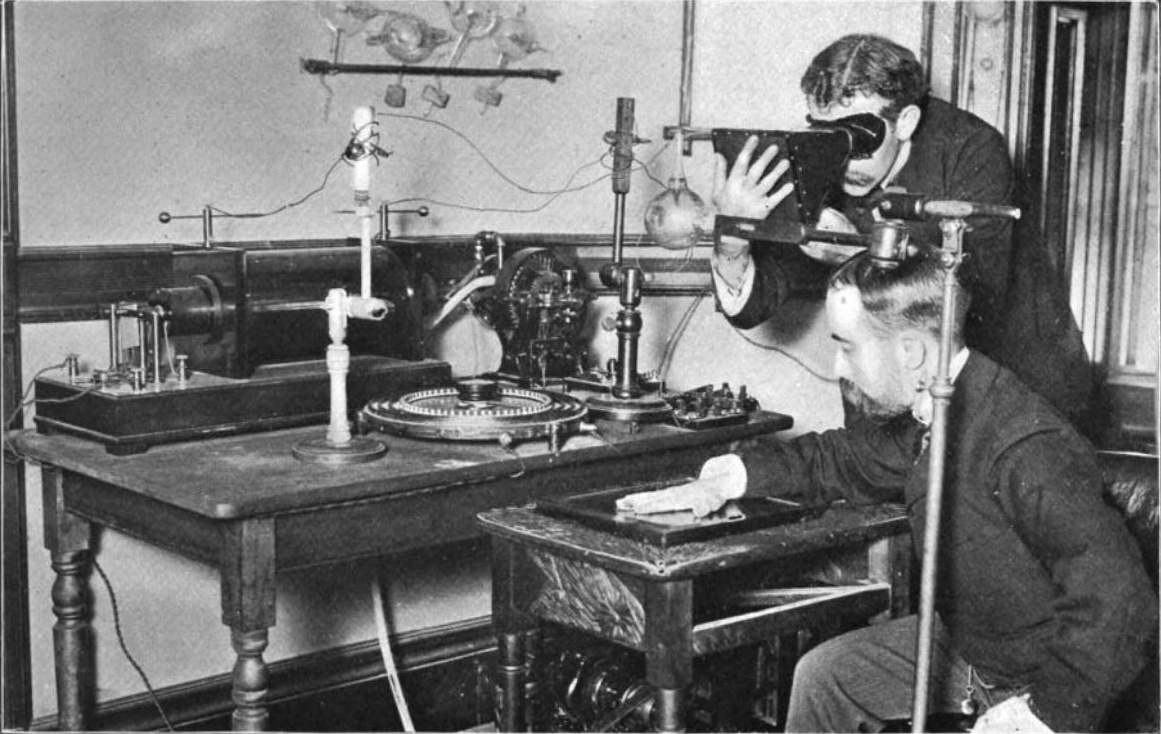 Röntgen immediately noticed X-rays could have medical applications. Along with his 28 December Physical-Medical Society submission, he sent a letter to physicians he knew around Europe (January 1, 1896). News (and the creation of "shadowgrams") spread rapidly with Scottish electrical engineer
Röntgen immediately noticed X-rays could have medical applications. Along with his 28 December Physical-Medical Society submission, he sent a letter to physicians he knew around Europe (January 1, 1896). News (and the creation of "shadowgrams") spread rapidly with Scottish electrical engineer  Many experimenters, including Röntgen himself in his original experiments, came up with methods to view X-ray images "live" using some form of luminescent screen. Röntgen used a screen coated with barium
Many experimenters, including Röntgen himself in his original experiments, came up with methods to view X-ray images "live" using some form of luminescent screen. Röntgen used a screen coated with barium
''
radiant energy
Radiant may refer to:
Computers, software, and video games
* Radiant (software), a content management system
* GtkRadiant, a level editor created by id Software for their games
* Radiant AI, a technology developed by Bethesda Softworks for '' ...
. After Röntgen identified the X-ray, Tesla began making X-ray images of his own using high voltages and tubes of his own design, as well as Crookes tubes.
Discovery by Röntgen
Crookes tube
A Crookes tube (also Crookes–Hittorf tube) is an early experimental electrical discharge tube, with partial vacuum, invented by English physicist William Crookes and others around 1869-1875, in which cathode rays, streams of electrons, were ...
s and began studying them. He wrote an initial report "On a new kind of ray: A preliminary communication" and on December 28, 1895, submitted it to Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is a city in the region of Franconia in the north of the German state of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the ''Regierungsbezirk'' Lower Franconia. It spans the banks of the Main River.
Würzburg ...
's Physical-Medical Society journal. This was the first paper written on X-rays. Röntgen referred to the radiation as "X", to indicate that it was an unknown type of radiation. Some early texts refer to them as Chi-rays having interpreted "X" as the uppercase Greek letter Chi, Χ. The name X-rays stuck, although (over Röntgen's great objections) many of his colleagues suggested calling them Röntgen rays. They are still referred to as such in many languages, including German, Hungarian, Ukrainian, Danish, Polish, Bulgarian, Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
, Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
, Estonian, Slovenian, Turkish, Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
, Latvian, Lithuanian, Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
, Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, Georgian, Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
, and Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
. Röntgen received the first Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
for his discovery.
There are conflicting accounts of his discovery because Röntgen had his lab notes burned after his death, but this is a likely reconstruction by his biographers: Röntgen was investigating cathode rays from a Crookes tube which he had wrapped in black cardboard so that the visible light from the tube would not interfere, using a fluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, ...
screen painted with barium platinocyanide Platinocyanide, also known as tetracyanoplatinate (IUPAC), cyanoplatinate, or platinocyanate, is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula t(CN)4sup>2−. The name also applies to compounds containing this ion, which are salts of the hypothetical ...
. He noticed a faint green glow from the screen, about away. Röntgen realized some invisible rays coming from the tube were passing through the cardboard to make the screen glow. He found they could also pass through books and papers on his desk. Röntgen threw himself into investigating these unknown rays systematically. Two months after his initial discovery, he published his paper.
 Röntgen discovered their medical use when he made a picture of his wife's hand on a photographic plate formed due to X-rays. The photograph of his wife's hand was the first photograph of a human body part using X-rays. When she saw the picture, she said "I have seen my death."
The discovery of X-rays stimulated a veritable sensation. Röntgen's biographer Otto Glasser estimated that, in 1896 alone, as many as 49 essays and 1044 articles about the new rays were published. This was probably a conservative estimate, if one considers that nearly every paper around the world extensively reported about the new discovery, with a magazine such as ''
Röntgen discovered their medical use when he made a picture of his wife's hand on a photographic plate formed due to X-rays. The photograph of his wife's hand was the first photograph of a human body part using X-rays. When she saw the picture, she said "I have seen my death."
The discovery of X-rays stimulated a veritable sensation. Röntgen's biographer Otto Glasser estimated that, in 1896 alone, as many as 49 essays and 1044 articles about the new rays were published. This was probably a conservative estimate, if one considers that nearly every paper around the world extensively reported about the new discovery, with a magazine such as ''Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
'' dedicating as many as 23 articles to it in that year alone. Sensationalist reactions to the new discovery included publications linking the new kind of rays to occult and paranormal theories, such as telepathy.
Advances in radiology
 Röntgen immediately noticed X-rays could have medical applications. Along with his 28 December Physical-Medical Society submission, he sent a letter to physicians he knew around Europe (January 1, 1896). News (and the creation of "shadowgrams") spread rapidly with Scottish electrical engineer
Röntgen immediately noticed X-rays could have medical applications. Along with his 28 December Physical-Medical Society submission, he sent a letter to physicians he knew around Europe (January 1, 1896). News (and the creation of "shadowgrams") spread rapidly with Scottish electrical engineer Alan Archibald Campbell-Swinton
Alan Archibald Campbell-Swinton FRS (18 October 1863 – 19 February 1930) was a Scottish consulting electrical engineer, who provided the theoretical basis for the electronic television, two decades before the technology existed to implement ...
being the first after Röntgen to create an X-ray (of a hand). Through February, there were 46 experimenters taking up the technique in North America alone.
The first use of X-rays under clinical conditions was by John Hall-Edwards in Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1. ...
, England on 11 January 1896, when he radiographed a needle stuck in the hand of an associate. On February 14, 1896, Hall-Edwards was also the first to use X-rays in a surgical operation.
In early 1896, several weeks after Röntgen's discovery, Ivan Romanovich Tarkhanov
Ivan Romanovich Tarkhanov (russian: Иван Романович Тарханов) or Ivane Tarkhnishvili ( ka, ივანე რამაზის–ძე თარხნიშვილი, თარხან-მოურავი; June 1846 – ...
irradiated frogs and insects with X-rays, concluding that the rays "not only photograph, but also affect the living function". At around the same time, the zoological illustrator James Green began to use X-rays to examine fragile specimens. George Albert Boulenger first mentioned this work in a paper he delivered before the Zoological Society of London in May 1896. The book ''Sciagraphs of British Batrachians and Reptiles'' (sciagraph is an obsolete name for an X-ray photograph), by Green and James H. Gardiner, with a foreword by Boulenger, was published in 1897.
The first medical X-ray made in the United States was obtained using a discharge tube of Pului's design. In January 1896, on reading of Röntgen's discovery, Frank Austin of Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College (; ) is a private research university in Hanover, New Hampshire. Established in 1769 by Eleazar Wheelock, it is one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Although founded to educate Native ...
tested all of the discharge tubes in the physics laboratory and found that only the Pului tube produced X-rays. This was a result of Pului's inclusion of an oblique "target" of mica, used for holding samples of fluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, ...
material, within the tube. On 3 February 1896, Gilman Frost, professor of medicine at the college, and his brother Edwin Frost, professor of physics, exposed the wrist of Eddie McCarthy, whom Gilman had treated some weeks earlier for a fracture, to the X-rays and collected the resulting image of the broken bone on gelatin photographic plates obtained from Howard Langill, a local photographer also interested in Röntgen's work.
platinocyanide Platinocyanide, also known as tetracyanoplatinate (IUPAC), cyanoplatinate, or platinocyanate, is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula t(CN)4sup>2−. The name also applies to compounds containing this ion, which are salts of the hypothetical ...
. On February 5, 1896, live imaging devices were developed by both Italian scientist Enrico Salvioni (his "cryptoscope") and Professor McGie of Princeton University
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the ...
(his "Skiascope"), both using barium platinocyanide. American inventor Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February 11, 1847October 18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventi ...
started research soon after Röntgen's discovery and investigated materials' ability to fluoresce when exposed to X-rays, finding that calcium tungstate
Scheelite is a calcium tungstate mineral with the chemical formula Ca W O4. It is an important ore of tungsten (wolfram). Scheelite is originally named after Swedish chemist K. Scheele (1742-1786). Well-formed crystals are sought by collectors ...
was the most effective substance. In May 1896, he developed the first mass-produced live imaging device, his "Vitascope", later called the fluoroscope
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a ...
, which became the standard for medical X-ray examinations. Edison dropped X-ray research around 1903, before the death of Clarence Madison Dally, one of his glassblowers. Dally had a habit of testing X-ray tubes on his own hands, developing a cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
in them so tenacious that both arms were amputated
Amputation is the removal of a limb by trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as malignancy or gangrene. In some cases, it is carried out on indiv ...
in a futile attempt to save his life; in 1904, he became the first known death attributed to X-ray exposure. During the time the fluoroscope was being developed, Serbian American physicist Mihajlo Pupin
Mihajlo Idvorski Pupin ( sr-Cyrl, Михајло Идворски Пупин, ; 4 October 1858Although Pupin's birth year is sometimes given as 1854 (and Serbia and Montenegro issued a postage stamp in 2004 to commemorate the 150th anniversary o ...
, using a calcium tungstate screen developed by Edison, found that using a fluorescent screen decreased the exposure time it took to create an X-ray for medical imaging from an hour to a few minutes.
In 1901, U.S. President William McKinley was shot twice in an assassination attempt. While one bullet only grazed his sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Sha ...
, another had lodged somewhere deep inside his abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the to ...
and could not be found. A worried McKinley aide sent word to inventor Thomas Edison to rush an X-ray machine
An X-ray machine is any machine that involves X-rays. It may consist of an X-ray generator and an X-ray detector.
Examples include:
*Machines for medical projectional radiography
*Machines for computed tomography
*Backscatter X-ray machines, used ...
to Buffalo to find the stray bullet. It arrived but was not used. While the shooting itself had not been lethal, gangrene had developed along the path of the bullet, and McKinley died of septic shock due to bacterial infection six days later.
Hazards discovered
With the widespread experimentation with X‑rays after their discovery in 1895 by scientists, physicians, and inventors came many stories of burns, hair loss, and worse in technical journals of the time. In February 1896, Professor John Daniel and Dr.William Lofland Dudley
William Lofland Dudley (April 16, 1859 – September 8, 1914) was an American chemistry professor at both the University of Cincinnati and Vanderbilt University and an athletics pioneer during the Progressive Era. At Vanderbilt, he was appoint ...
of Vanderbilt University
Vanderbilt University (informally Vandy or VU) is a private research university in Nashville, Tennessee. Founded in 1873, it was named in honor of shipping and rail magnate Cornelius Vanderbilt, who provided the school its initial $1-million ...
reported hair loss after Dr. Dudley was X-rayed. A child who had been shot in the head was brought to the Vanderbilt laboratory in 1896. Before trying to find the bullet, an experiment was attempted, for which Dudley "with his characteristic devotion to science" volunteered. Daniel reported that 21 days after taking a picture of Dudley's skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
(with an exposure time of one hour), he noticed a bald spot in diameter on the part of his head nearest the X-ray tube: "A plate holder with the plates towards the side of the skull was fastened and a coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order t ...
placed between the skull and the head. The tube was fastened at the other side at a distance of one-half inch [] from the hair."
In August 1896, Dr. HD. Hawks, a graduate of Columbia College, suffered severe hand and chest burns from an X-ray demonstration. It was reported in ''Electrical Review'' and led to many other reports of problems associated with X-rays being sent in to the publication. Many experimenters including Elihu Thomson
Elihu Thomson (March 29, 1853 – March 13, 1937) was an English-born American engineer and inventor who was instrumental in the founding of major electrical companies in the United States, the United Kingdom and France.
Early life
He was bor ...
at Edison's lab, William J. Morton, and Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla ( ; ,"Tesla"
''
''
Other effects were sometimes blamed for the damage including ultraviolet rays and (according to Tesla) ozone. Many physicians claimed there were no effects from X-ray exposure at all. On August 3, 1905, in
 The many applications of X-rays immediately generated enormous interest. Workshops began making specialized versions of Crookes tubes for generating X-rays and these first-generation
The many applications of X-rays immediately generated enormous interest. Workshops began making specialized versions of Crookes tubes for generating X-rays and these first-generation  The use of X-rays for medical purposes (which developed into the field of
The use of X-rays for medical purposes (which developed into the field of  An
An

 X-ray
X-ray
 X-rays interact with matter in three main ways, through photoabsorption,
X-rays interact with matter in three main ways, through photoabsorption,
 X-rays can be generated by an
X-rays can be generated by an

 Since Röntgen's discovery that X-rays can identify bone structures, X-rays have been used for medical imaging. The first medical use was less than a month after his paper on the subject. Up to 2010, five billion medical imaging examinations had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.
Since Röntgen's discovery that X-rays can identify bone structures, X-rays have been used for medical imaging. The first medical use was less than a month after his paper on the subject. Up to 2010, five billion medical imaging examinations had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.

 Computed tomography (CT scanning) is a medical imaging modality where tomographic images or slices of specific areas of the body are obtained from a large series of two-dimensional X-ray images taken in different directions. These cross-sectional images can be combined into a
Computed tomography (CT scanning) is a medical imaging modality where tomographic images or slices of specific areas of the body are obtained from a large series of two-dimensional X-ray images taken in different directions. These cross-sectional images can be combined into a
San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, Elizabeth Fleischman
Elizabeth Fleischman-Aschheim (née Fleischman 5 March 1867 – 3 August 1905) was an American radiographer who is considered an X-ray pioneer. Fleischman was the first woman to die as a result of X-ray radiation exposure.
Early years
Elizabeth ...
, an American X-ray pioneer, died from complications as a result of her work with X-rays.
Hall-Edwards developed a cancer (then called X-ray dermatitis) sufficiently advanced by 1904 to cause him to write papers and give public addresses on the dangers of X-rays. His left arm had to be amputated at the elbow in 1908, and four fingers on his right arm soon thereafter, leaving only a thumb. He died of cancer in 1926. His left hand is kept at Birmingham University
, mottoeng = Through efforts to heights
, established = 1825 – Birmingham School of Medicine and Surgery1836 – Birmingham Royal School of Medicine and Surgery1843 – Queen's College1875 – Mason Science College1898 – Mason Univers ...
.
20th century and beyond
 The many applications of X-rays immediately generated enormous interest. Workshops began making specialized versions of Crookes tubes for generating X-rays and these first-generation
The many applications of X-rays immediately generated enormous interest. Workshops began making specialized versions of Crookes tubes for generating X-rays and these first-generation cold cathode
A cold cathode is a cathode that is not electrically heated by a filament.A negatively charged electrode emits electrons or is the positively charged terminal. For more, see field emission. A cathode may be considered "cold" if it emits more el ...
or Crookes X-ray tubes were used until about 1920.
A typical early 20th century medical X-ray system consisted of a Ruhmkorff coil connected to a cold cathode Crookes X-ray tube. A spark gap was typically connected to the high voltage side in parallel to the tube and used for diagnostic purposes. The spark gap allowed detecting the polarity of the sparks, measuring voltage by the length of the sparks thus determining the "hardness" of the vacuum of the tube, and it provided a load in the event the X-ray tube was disconnected. To detect the hardness of the tube, the spark gap was initially opened to the widest setting. While the coil was operating, the operator reduced the gap until sparks began to appear. A tube in which the spark gap began to spark at around was considered soft (low vacuum) and suitable for thin body parts such as hands and arms. A spark indicated the tube was suitable for shoulders and knees. An spark would indicate a higher vacuum suitable for imaging the abdomen of larger individuals. Since the spark gap was connected in parallel to the tube, the spark gap had to be opened until the sparking ceased in order to operate the tube for imaging. Exposure time for photographic plates was around half a minute for a hand to a couple of minutes for a thorax. The plates may have a small addition of fluorescent salt to reduce exposure times.
Crookes tubes were unreliable. They had to contain a small quantity of gas (invariably air) as a current will not flow in such a tube if they are fully evacuated. However, as time passed, the X-rays caused the glass to absorb the gas, causing the tube to generate "harder" X-rays until it soon stopped operating. Larger and more frequently used tubes were provided with devices for restoring the air, known as "softeners". These often took the form of a small side tube that contained a small piece of mica, a mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
that traps relatively large quantities of air within its structure. A small electrical heater heated the mica, causing it to release a small amount of air, thus restoring the tube's efficiency. However, the mica had a limited life, and the restoration process was difficult to control.
In 1904, John Ambrose Fleming invented the thermionic diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diode ...
, the first kind of vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
. This used a hot cathode
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating elemen ...
that caused an electric current to flow in a vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often di ...
. This idea was quickly applied to X-ray tubes, and hence heated-cathode X-ray tubes, called "Coolidge tubes", completely replaced the troublesome cold cathode tubes by about 1920.
In about 1906, the physicist Charles Barkla
Charles Glover Barkla FRS FRSE (7 June 1877 – 23 October 1944) was a British physicist, and the winner of the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1917 for his work in X-ray spectroscopy and related areas in the study of X-rays ( Roentgen rays).
Lif ...
discovered that X-rays could be scattered by gases, and that each element had a characteristic X-ray spectrum
X-ray spectroscopy is a general term for several spectroscopic techniques for characterization of materials by using x-ray radiation.
Characteristic X-ray spectroscopy
When an electron from the inner shell of an atom is excited by the energy o ...
. He won the 1917 Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
for this discovery.
In 1912, Max von Laue, Paul Knipping, and Walter Friedrich first observed the diffraction of X-rays by crystals. This discovery, along with the early work of Paul Peter Ewald, William Henry Bragg
Sir William Henry Bragg (2 July 1862 – 12 March 1942) was an English physicist, chemist, mathematician, and active sportsman who uniquelyThis is still a unique accomplishment, because no other parent-child combination has yet shared a Nob ...
, and William Lawrence Bragg
Sir William Lawrence Bragg, (31 March 1890 – 1 July 1971) was an Australian-born British physicist and X-ray crystallographer, discoverer (1912) of Bragg's law of X-ray diffraction, which is basic for the determination of crystal structu ...
, gave birth to the field of X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
.
In 1913, Henry Moseley performed crystallography experiments with X-rays emanating from various metals and formulated Moseley's law
Moseley's law is an empirical law concerning the characteristic x-rays emitted by atoms. The law had been discovered and published by the English physicist Henry Moseley in 1913-1914. Until Moseley's work, "atomic number" was merely an element's ...
which relates the frequency of the X-rays to the atomic number of the metal.
The Coolidge X-ray tube was invented the same year by William D. Coolidge. It made possible the continuous emissions of X-rays. Modern X-ray tubes are based on this design, often employing the use of rotating targets which allow for significantly higher heat dissipation than static targets, further allowing higher quantity X-ray output for use in high powered applications such as rotational CT scanners.
 The use of X-rays for medical purposes (which developed into the field of
The use of X-rays for medical purposes (which developed into the field of radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radi ...
) was pioneered by Major John Hall-Edwards in Birmingham, England
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
. Then in 1908, he had to have his left arm amputated because of the spread of X-ray dermatitis on his arm.
Medical science also used the motion picture to study human physiology. In 1913, a motion picture was made in Detroit showing a hard-boiled egg inside a human stomach. This early X-ray movie was recorded at a rate of one still image every four seconds. Dr Lewis Gregory Cole of New York was a pioneer of the technique, which he called "serial radiography". In 1918, X-rays were used in association with motion picture cameras to capture the human skeleton in motion. In 1920, it was used to record the movements of tongue and teeth in the study of languages by the Institute of Phonetics in England.
In 1914, Marie Curie
Marie Salomea Skłodowska–Curie ( , , ; born Maria Salomea Skłodowska, ; 7 November 1867 – 4 July 1934) was a Polish and naturalized-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity. She was the first ...
developed radiological cars to support soldiers injured in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The cars would allow for rapid X-ray imaging of wounded soldiers so battlefield surgeons could quickly and more accurately operate.
From the early 1920s through to the 1950s, X-ray machines were developed to assist in the fitting of shoes and were sold to commercial shoe stores. Concerns regarding the impact of frequent or poorly controlled use were expressed in the 1950s, leading to the practice's eventual end that decade.
The X-ray microscope was developed during the 1950s.
The Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources 1 ...
, launched on July 23, 1999, has been allowing the exploration of the very violent processes in the universe which produce X-rays. Unlike visible light, which gives a relatively stable view of the universe, the X-ray universe is unstable. It features stars being torn apart by black holes, galactic collisions, and novae, and neutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. w ...
s that build up layers of plasma that then explode into space.
 An
An X-ray laser
An X-ray laser is a device that uses stimulated emission to generate or amplify electromagnetic radiation in the near X-ray or extreme ultraviolet region of the spectrum, that is, usually on the order of several tens of nanometers (nm) wavelength ...
device was proposed as part of the Reagan Administration
Ronald Reagan's tenure as the 40th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1981, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Republican from California, took office following a landslide victory over ...
's Strategic Defense Initiative in the 1980s, but the only test of the device (a sort of laser "blaster" or death ray, powered by a thermonuclear explosion) gave inconclusive results. For technical and political reasons, the overall project (including the X-ray laser) was defunded (though was later revived by the second Bush Administration as National Missile Defense
National missile defense (NMD) is a generic term for a type of missile defense intended to shield an entire country against incoming missiles, such as intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBMs) or other ballistic missiles.
This is also used ...
using different technologies).
Phase-contrast X-ray imaging
Phase-contrast X-ray imaging or phase-sensitive X-ray imaging is a general term for different technical methods that use information concerning changes in the phase of an X-ray beam that passes through an object in order to create its images. St ...
refers to a variety of techniques that use phase information of an X-ray beam to form the image. Due to its good sensitivity to density differences, it is especially useful for imaging soft tissues. It has become an important method for visualizing cellular and histological structures in a wide range of biological and medical studies. There are several technologies being used for X-ray phase-contrast imaging, all utilizing different principles to convert phase variations in the X-rays emerging from an object into intensity variations. These include propagation-based phase contrast, Talbot interferometry, refraction-enhanced imaging, and X-ray interferometry. These methods provide higher contrast compared to normal absorption-based X-ray imaging, making it possible to distinguish from each other details that have almost similar density. A disadvantage is that these methods require more sophisticated equipment, such as synchrotron or microfocus X-ray sources, X-ray optics X-ray optics is the branch of optics that manipulates X-rays instead of visible light. It deals with focusing and other ways of manipulating the X-ray beams for research techniques such as X-ray crystallography, X-ray fluorescence, small-angle X-ray ...
, and high resolution X-ray detectors.
Energy ranges
Soft and hard X-rays
X-rays with high photon energies above 5–10 keV (below 0.2–0.1 nm wavelength) are called ''hard X-rays'', while those with lower energy (and longer wavelength) are called ''soft X-rays''. The intermediate range with photon energies of several keV is often referred to as ''tender X-rays''. Due to their penetrating ability, hard X-rays are widely used to image the inside of objects, e.g., in medical radiography andairport security
Airport security includes the techniques and methods used in an attempt to protect passengers, staff, aircraft, and airport property from malicious harm, crime, terrorism, and other threats.
Aviation security is a combination of measures and hum ...
. The term ''X-ray'' is metonymically used to refer to a radiographic
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeut ...
image produced using this method, in addition to the method itself. Since the wavelengths of hard X-rays are similar to the size of atoms, they are also useful for determining crystal structures by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
. By contrast, soft X-rays are easily absorbed in air; the attenuation length
In physics, the attenuation length or absorption length is the distance \lambda into a material when the probability has dropped to 1/e that a particle has ''not'' been absorbed. Alternatively, if there is a beam of particles incident on the mate ...
of 600 eV (~2 nm) X-rays in water is less than 1 micrometer.
Gamma rays
There is no consensus for a definition distinguishing between X-rays andgamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
s. One common practice is to distinguish between the two types of radiation based on their source: X-rays are emitted by electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s, while gamma rays are emitted by the atomic nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron ...
. This definition has several problems: other processes can also generate these high-energy photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
s, or sometimes the method of generation is not known. One common alternative is to distinguish X- and gamma radiation on the basis of wavelength (or, equivalently, frequency or photon energy), with radiation shorter than some arbitrary wavelength, such as 10−11 m (0.1 Å), defined as gamma radiation. This criterion assigns a photon to an unambiguous category, but is only possible if wavelength is known. (Some measurement techniques do not distinguish between detected wavelengths.) However, these two definitions often coincide since the electromagnetic radiation emitted by X-ray tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contrast ...
s generally has a longer wavelength and lower photon energy than the radiation emitted by radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consi ...
nuclei. Occasionally, one term or the other is used in specific contexts due to historical precedent, based on measurement (detection) technique, or based on their intended use rather than their wavelength or source.
Thus, gamma-rays generated for medical and industrial uses, for example radiotherapy, in the ranges of 6–20 MeV
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV, also written electron-volt and electron volt) is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating from rest through an electric potential difference of one volt in vacu ...
, can in this context also be referred to as X-rays.
Properties
photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
s carry enough energy to ionize
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule ...
atoms and disrupt molecular bonds. This makes it a type of ionizing radiation, and therefore harmful to living tissue. A very high radiation dose over a short period of time causes radiation sickness, while lower doses can give an increased risk of radiation-induced cancer
Exposure to ionizing radiation is known to increase the future incidence of cancer, particularly leukemia. The mechanism by which this occurs is well understood, but quantitative models predicting the level of risk remain controversial. The most wi ...
. In medical imaging, this increased cancer risk is generally greatly outweighed by the benefits of the examination. The ionizing capability of X-rays can be utilized in cancer treatment
Cancer can be treated by surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy (including immunotherapy such as monoclonal antibody therapy) and synthetic lethality, most commonly as a series of separate treatments (e.g. ...
to kill malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
cells using radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radi ...
. It is also used for material characterization using X-ray spectroscopy
X-ray spectroscopy is a general term for several spectroscopic techniques for characterization of materials by using x-ray radiation.
Characteristic X-ray spectroscopy
When an electron from the inner shell of an atom is excited by the energy o ...
.
Hard X-rays can traverse relatively thick objects without being much absorbed or scattered. For this reason, X-rays are widely used to image the inside of visually opaque objects. The most often seen applications are in medical radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeu ...
and airport security
Airport security includes the techniques and methods used in an attempt to protect passengers, staff, aircraft, and airport property from malicious harm, crime, terrorism, and other threats.
Aviation security is a combination of measures and hum ...
scanners, but similar techniques are also important in industry (e.g., industrial radiography
Industrial radiography is a modality of non-destructive testing that uses ionizing radiation to inspect materials and components with the objective of locating and quantifying defects and degradation in material properties that would lead to the ...
and industrial CT scanning) and research (e.g., small animal CT). The penetration depth
Penetration depth is a measure of how deep light or any electromagnetic radiation can penetrate into a material. It is defined as the depth at which the intensity of the radiation inside the material falls to 1/e (about 37%) of its original valu ...
varies with several orders of magnitude
An order of magnitude is an approximation of the logarithm of a value relative to some contextually understood reference value, usually 10, interpreted as the base of the logarithm and the representative of values of magnitude one. Logarithmic dis ...
over the X-ray spectrum. This allows the photon energy to be adjusted for the application so as to give sufficient transmission through the object and at the same time provide good contrast in the image.
X-rays have much shorter wavelengths than visible light, which makes it possible to probe structures much smaller than can be seen using a normal microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
. This property is used in X-ray microscopy to acquire high-resolution images, and also in X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
to determine the positions of atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, ...
s in crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
s.
Interaction with matter
Compton scattering
Compton scattering, discovered by Arthur Holly Compton, is the scattering of a high frequency photon after an interaction with a charged particle, usually an electron. If it results in a decrease in energy (increase in wavelength) of the photon ...
, and Rayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scattering ( ), named after the 19th-century British physicist Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt), is the predominantly elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of th ...
. The strength of these interactions depends on the energy of the X-rays and the elemental composition of the material, but not much on chemical properties, since the X-ray photon energy is much higher than chemical binding energies. Photoabsorption or photoelectric absorption is the dominant interaction mechanism in the soft X-ray regime and for the lower hard X-ray energies. At higher energies, Compton scattering dominates.
Photoelectric absorption
The probability of a photoelectric absorption per unit mass is approximately proportional to ''Z''3/''E''3, where ''Z'' is theatomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
and ''E'' is the energy of the incident photon. This rule is not valid close to inner shell electron binding energies where there are abrupt changes in interaction probability, so called absorption edges. However, the general trend of high absorption coefficient
The linear attenuation coefficient, attenuation coefficient, or narrow-beam attenuation coefficient characterizes how easily a volume of material can be penetrated by a beam of light, sound, particles, or other energy or matter. A coefficient valu ...
s and thus short penetration depth
Penetration depth is a measure of how deep light or any electromagnetic radiation can penetrate into a material. It is defined as the depth at which the intensity of the radiation inside the material falls to 1/e (about 37%) of its original valu ...
s for low photon energies and high atomic numbers is very strong. For soft tissue, photoabsorption dominates up to about 26 keV photon energy where Compton scattering takes over. For higher atomic number substances, this limit is higher. The high amount of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
(''Z'' = 20) in bones, together with their high density, is what makes them show up so clearly on medical radiographs.
A photoabsorbed photon transfers all its energy to the electron with which it interacts, thus ionizing the atom to which the electron was bound and producing a photoelectron that is likely to ionize more atoms in its path. An outer electron will fill the vacant electron position and produce either a characteristic X-ray or an Auger electron
The Auger effect or Auger−Meitner effect is a physical phenomenon in which the filling of an inner-shell vacancy of an atom is accompanied by the emission of an electron from the same atom. When a core electron is removed, leaving a vacancy, ...
. These effects can be used for elemental detection through X-ray spectroscopy
X-ray spectroscopy is a general term for several spectroscopic techniques for characterization of materials by using x-ray radiation.
Characteristic X-ray spectroscopy
When an electron from the inner shell of an atom is excited by the energy o ...
or Auger electron spectroscopy.
Compton scattering
Compton scattering is the predominant interaction between X-rays and soft tissue in medical imaging. Compton scattering is aninelastic scattering In chemistry, nuclear physics, and particle physics, inelastic scattering is a fundamental scattering process in which the kinetic energy of an incident particle is not conserved (in contrast to elastic scattering). In an inelastic scattering proces ...
of the X-ray photon by an outer shell electron. Part of the energy of the photon is transferred to the scattering electron, thereby ionizing the atom and increasing the wavelength of the X-ray. The scattered photon can go in any direction, but a direction similar to the original direction is more likely, especially for high-energy X-rays. The probability for different scattering angles is described by the Klein–Nishina formula
In particle physics, the Klein–Nishina formula gives the differential cross section (i.e. the "likelihood" and angular distribution) of photons scattered from a single free electron, calculated in the lowest order of quantum electrodynamics. I ...
. The transferred energy can be directly obtained from the scattering angle from the conservation of energy and momentum.
Rayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scattering is the dominantelastic scattering
Elastic scattering is a form of particle scattering in scattering theory, nuclear physics and particle physics. In this process, the kinetic energy of a particle is conserved in the center-of-mass frame, but its direction of propagation is modif ...
mechanism in the X-ray regime. Inelastic forward scattering gives rise to the refractive index, which for X-rays is only slightly below 1.
Production
Whenever charged particles (electrons or ions) of sufficient energy hit a material, X-rays are produced.Production by electrons
 X-rays can be generated by an
X-rays can be generated by an X-ray tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contrast ...
, a vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
that uses a high voltage to accelerate the electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s released by a hot cathode
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating elemen ...
to a high velocity. The high velocity electrons collide with a metal target, the anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic ...
, creating the X-rays. In medical X-ray tubes the target is usually tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
or a more crack-resistant alloy of rhenium
Rhenium is a chemical element with the symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-gray, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an estimated average concentration of 1 part per billion (ppb), rhenium is one ...
(5%) and tungsten (95%), but sometimes molybdenum for more specialized applications, such as when softer X-rays are needed as in mammography. In crystallography, a copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
target is most common, with cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
often being used when fluorescence from iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
content in the sample might otherwise present a problem.
The maximum energy of the produced X-ray photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
is limited by the energy of the incident electron, which is equal to the voltage on the tube times the electron charge, so an 80 kV tube cannot create X-rays with an energy greater than 80 keV. When the electrons hit the target, X-rays are created by two different atomic processes:
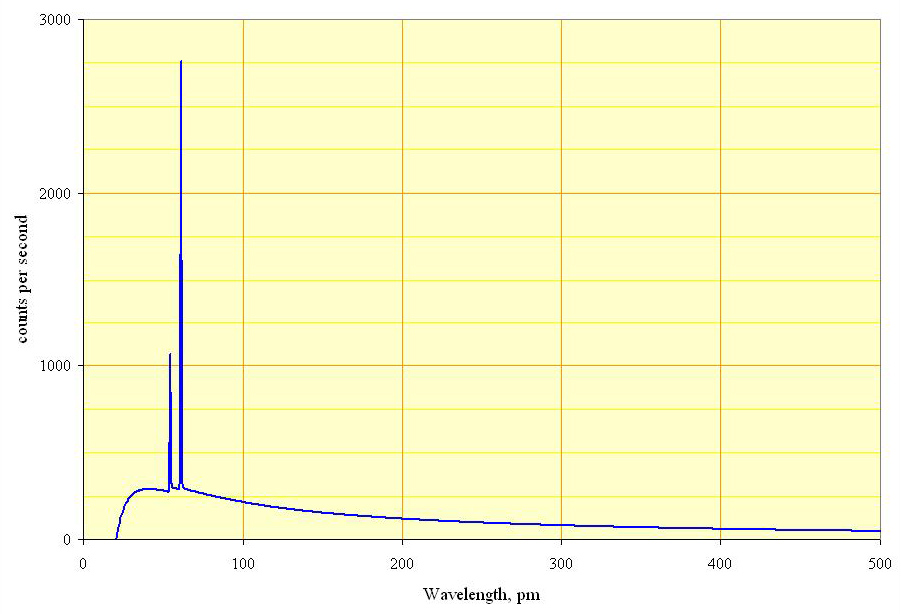
# ''Characteristic X-ray Characteristic X-rays are emitted when outer-shell electrons fill a vacancy in the inner shell of an atom, releasing X-rays in a pattern that is "characteristic" to each element. Characteristic X-rays were discovered by Charles Glover Barkla in 190 ...
emission'' (X-ray electroluminescence): If the electron has enough energy, it can knock an orbital electron out of the inner electron shell
In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell may be thought of as an orbit followed by electrons around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" (also called the "K shell"), followed by the "2 shell" (or ...
of the target atom. After that, electrons from higher energy levels fill the vacancies, and X-ray photons are emitted. This process produces an emission spectrum of X-rays at a few discrete frequencies, sometimes referred to as spectral lines. Usually, these are transitions from the upper shells to the K shell (called K lines), to the L shell (called L lines) and so on. If the transition is from 2p to 1s, it is called Kα, while if it is from 3p to 1s it is Kβ. The frequencies of these lines depend on the material of the target and are therefore called characteristic lines. The Kα line usually has greater intensity than the Kβ one and is more desirable in diffraction experiments. Thus the Kβ line is filtered out by a filter. The filter is usually made of a metal having one proton less than the anode material (e.g., Ni filter for Cu anode or Nb filter for Mo anode).
# '' Bremsstrahlung'': This is radiation given off by the electrons as they are scattered by the strong electric field near the high-''Z'' ( proton number) nuclei. These X-rays have a continuous spectrum. The frequency of bremsstrahlung is limited by the energy of incident electrons.
So, the resulting output of a tube consists of a continuous bremsstrahlung spectrum falling off to zero at the tube voltage, plus several spikes at the characteristic lines. The voltages used in diagnostic X-ray tubes range from roughly 20 kV to 150 kV and thus the highest energies of the X-ray photons range from roughly 20 keV to 150 keV.
Both of these X-ray production processes are inefficient, with only about one percent of the electrical energy used by the tube converted into X-rays, and thus most of the electric power consumed by the tube is released as waste heat. When producing a usable flux of X-rays, the X-ray tube must be designed to dissipate the excess heat.
A specialized source of X-rays which is becoming widely used in research is synchrotron radiation, which is generated by particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams.
Large accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle ...
s. Its unique features are X-ray outputs many orders of magnitude greater than those of X-ray tubes, wide X-ray spectra, excellent collimation
A collimated beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation has parallel rays, and therefore will spread minimally as it propagates. A perfectly collimated light beam, with no divergence, would not disperse with distance. However, diffraction ...
, and linear polarization
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarizati ...
.
Short nanosecond bursts of X-rays peaking at 15 keV in energy may be reliably produced by peeling pressure-sensitive adhesive tape from its backing in a moderate vacuum. This is likely to be the result of recombination of electrical charges produced by triboelectric charging. The intensity of X-ray triboluminescence is sufficient for it to be used as a source for X-ray imaging.
Production by fast positive ions
X-rays can also be produced by fast protons or other positive ions. The proton-induced X-ray emission or particle-induced X-ray emission is widely used as an analytical procedure. For high energies, the productioncross section
Cross section may refer to:
* Cross section (geometry)
** Cross-sectional views in architecture & engineering 3D
*Cross section (geology)
* Cross section (electronics)
* Radar cross section, measure of detectability
* Cross section (physics)
**Abs ...
is proportional to ''Z''12''Z''2−4, where ''Z''1 refers to the atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
of the ion, ''Z''2 refers to that of the target atom. An overview of these cross sections is given in the same reference.
Production in lightning and laboratory discharges
X-rays are also produced in lightning accompanyingterrestrial gamma-ray flash
A terrestrial gamma-ray flash (TGF), also known as dark lightning, is a burst of gamma rays produced in Earth's atmosphere. TGFs have been recorded to last 0.2 to 3.5 milliseconds, and have energies of up to 20 million electronvolts. It is spec ...
es. The underlying mechanism is the acceleration of electrons in lightning related electric fields and the subsequent production of photons through Bremsstrahlung. This produces photons with energies of some few keV Kev can refer to:
Given name
* Kev Adams, French comedian, actor, screenwriter and film producer born Kevin Smadja in 1991
* Kevin Kev Carmody (born 1946), Indigenous Australian singer-songwriter
* Kev Coghlan (born 1988), Scottish Grand Prix moto ...
and several tens of MeV. In laboratory discharges with a gap size of approximately 1 meter length and a peak voltage of 1 MV, X-rays with a characteristic energy of 160 keV are observed. A possible explanation is the encounter of two streamers and the production of high-energy run-away electrons; however, microscopic simulations have shown that the duration of electric field enhancement between two streamers is too short to produce a significant number of run-away electrons. Recently, it has been proposed that air perturbations in the vicinity of streamers can facilitate the production of run-away electrons and hence of X-rays from discharges.
Detectors
X-ray detectors vary in shape and function depending on their purpose. Imaging detectors such as those used forradiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeu ...
were originally based on photographic plates and later photographic film, but are now mostly replaced by various digital detector types such as image plates and flat panel detectors. For radiation protection
Radiation protection, also known as radiological protection, is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, and the means for achieving this". Expos ...
direct exposure hazard is often evaluated using ionization chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest type of gas-filled radiation detector, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of certain types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, and beta particles. Conventionally, the term ...
s, while dosimeters
A radiation dosimeter is a device that measures dose uptake of external ionizing radiation. It is worn by the person being monitored when used as a personal dosimeter, and is a record of the radiation dose received. Modern electronic personal do ...
are used to measure the radiation dose a person has been exposed to. X-ray spectra can be measured either by energy dispersive or wavelength dispersive spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the ...
s. For X-ray diffraction applications, such as X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
, hybrid photon counting detectors are widely used.
Medical uses

 Since Röntgen's discovery that X-rays can identify bone structures, X-rays have been used for medical imaging. The first medical use was less than a month after his paper on the subject. Up to 2010, five billion medical imaging examinations had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.
Since Röntgen's discovery that X-rays can identify bone structures, X-rays have been used for medical imaging. The first medical use was less than a month after his paper on the subject. Up to 2010, five billion medical imaging examinations had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.
Projectional radiographs

Projectional radiography
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by x-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images a ...
is the practice of producing two-dimensional images using X-ray radiation. Bones contain a high concentration of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
, which, due to its relatively high atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
, absorbs X-rays efficiently. This reduces the amount of X-rays reaching the detector in the shadow of the bones, making them clearly visible on the radiograph. The lungs and trapped gas also show up clearly because of lower absorption compared to tissue, while differences between tissue types are harder to see.
Projectional radiographs are useful in the detection of pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
of the skeletal system
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
as well as for detecting some disease processes in soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ...
. Some notable examples are the very common chest X-ray, which can be used to identify lung diseases such as pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
, lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
, or pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia and respiratory failure. It is due t ...
, and the abdominal x-ray
An abdominal x-ray is an Projectional radiography, x-ray of the abdomen. It is sometimes abbreviated to AXR, or kidneys, ureters, and bladder, KUB (for kidneys, ureters, and urinary bladder).
Indications
In children, abdominal x-ray is indicated ...
, which can detect bowel (or intestinal) obstruction, free air (from visceral perforations), and free fluid (in ascites
Ascites is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than one liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size, increased weight, a ...
). X-rays may also be used to detect pathology such as gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of mi ...
s (which are rarely radiopaque
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypod ...
) or kidney stone
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine s ...
s which are often (but not always) visible. Traditional plain X-rays are less useful in the imaging of soft tissues such as the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
or muscle. One area where projectional radiographs are used extensively is in evaluating how an orthopedic implant, such as a knee, hip or shoulder replacement, is situated in the body with respect to the surrounding bone. This can be assessed in two dimensions from plain radiographs, or it can be assessed in three dimensions if a technique called '2D to 3D registration' is used. This technique purportedly negates projection errors associated with evaluating implant position from plain radiographs.
Dental radiography
Dental radiographs, commonly known as X-rays, are radiographs used to diagnose hidden dental structures, malignant or benign masses, bone loss, and cavities.
A radiographic image is formed by a controlled burst of X-ray radiation which penet ...
is commonly used in the diagnoses of common oral problems, such as cavities.
In medical diagnostic applications, the low energy (soft) X-rays are unwanted, since they are totally absorbed by the body, increasing the radiation dose without contributing to the image. Hence, a thin metal sheet, often of aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
, called an X-ray filter An X-ray filter is a material placed in front of an X-ray source in order to reduce the intensity of particular wavelengths from its spectrum and selectively alter the distribution of X-ray wavelengths within a given beam.
When X-rays hit matter, p ...
, is usually placed over the window of the X-ray tube, absorbing the low energy part in the spectrum. This is called ''hardening'' the beam since it shifts the center of the spectrum towards higher energy (or harder) X-rays.
To generate an image of the cardiovascular system, including the arteries and veins (angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is perfor ...
) an initial image is taken of the anatomical region of interest. A second image is then taken of the same region after an iodinated contrast agent
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiop ...
has been injected into the blood vessels within this area. These two images are then digitally subtracted, leaving an image of only the iodinated contrast outlining the blood vessels. The radiologist
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiat ...
or surgeon then compares the image obtained to normal anatomical images to determine whether there is any damage or blockage of the vessel.
Computed tomography
 Computed tomography (CT scanning) is a medical imaging modality where tomographic images or slices of specific areas of the body are obtained from a large series of two-dimensional X-ray images taken in different directions. These cross-sectional images can be combined into a
Computed tomography (CT scanning) is a medical imaging modality where tomographic images or slices of specific areas of the body are obtained from a large series of two-dimensional X-ray images taken in different directions. These cross-sectional images can be combined into a three-dimensional
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called ''parameters'') are required to determine the position of an element (i.e., point). This is the informa ...
image of the inside of the body and used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in various medical disciplines.
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal structure and function ...
is an imaging technique commonly used by physicians or radiation therapists to obtain real-time moving images of the internal structures of a patient through the use of a fluoroscope. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, modern fluoroscopes couple the screen to an X-ray image intensifier
An X-ray image intensifier (XRII) is an image intensifier that converts X-rays into visible light at higher intensity than the more traditional fluorescent screens can. Such intensifiers are used in X-ray imaging systems (such as fluoroscopes) ...
and CCD video camera
A video camera is an optical instrument that captures videos (as opposed to a movie camera, which records images on film). Video cameras were initially developed for the television industry but have since become widely used for a variety of oth ...
allowing the images to be recorded and played on a monitor. This method may use a contrast material. Examples include cardiac catheterization (to examine for coronary artery blockages) and barium swallow (to examine for esophageal disorder Esophageal can refer to:
* The esophagus
* Esophageal arteries
* Esophageal glands
* Esophageal cancer
{{disambig