Wyoming Cowboys Football Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wyoming () is a
Bills for
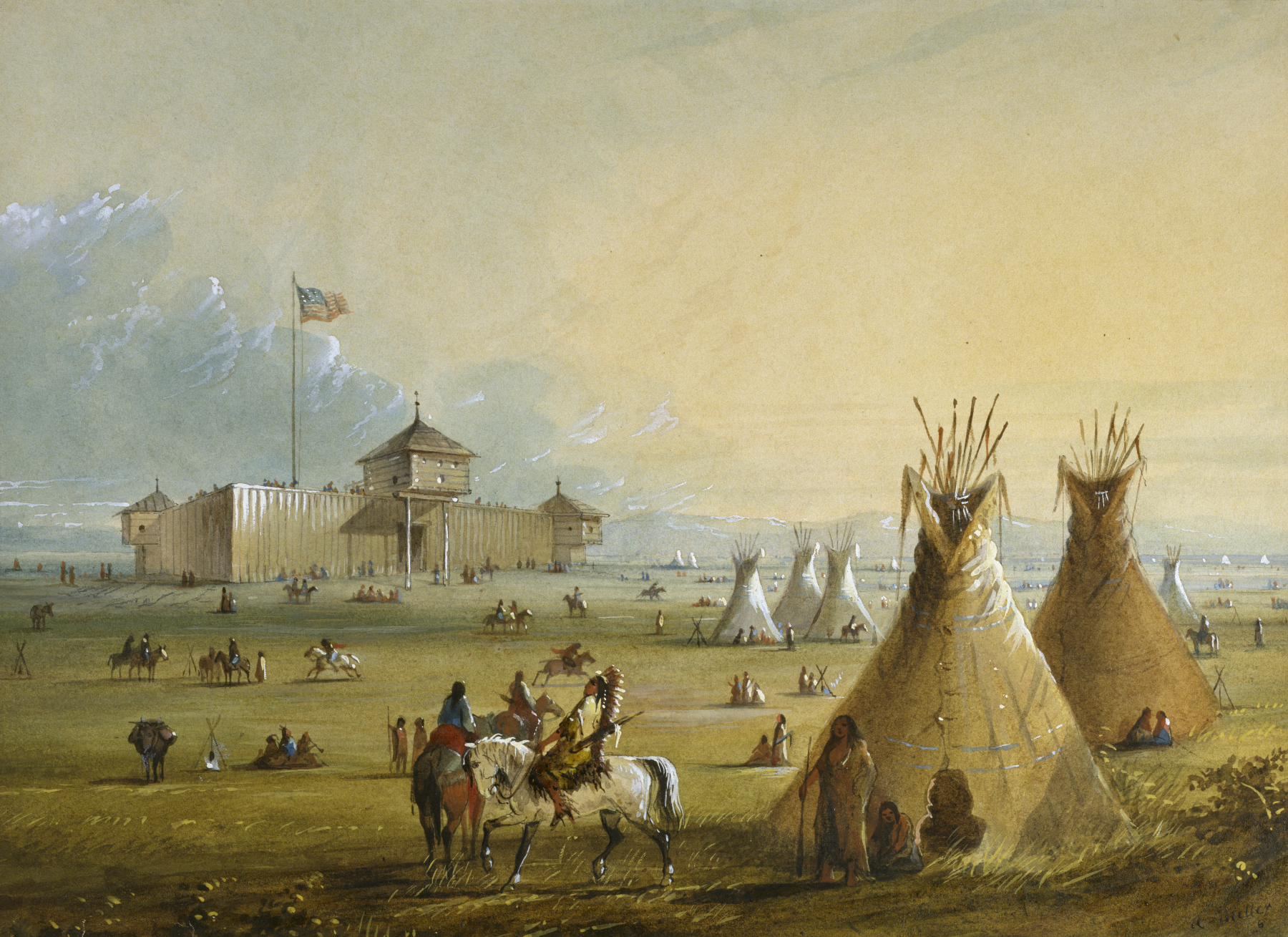 Several Native American groups originally inhabited the region today known as Wyoming. The
Several Native American groups originally inhabited the region today known as Wyoming. The  After the Union Pacific Railroad reached
After the Union Pacific Railroad reached
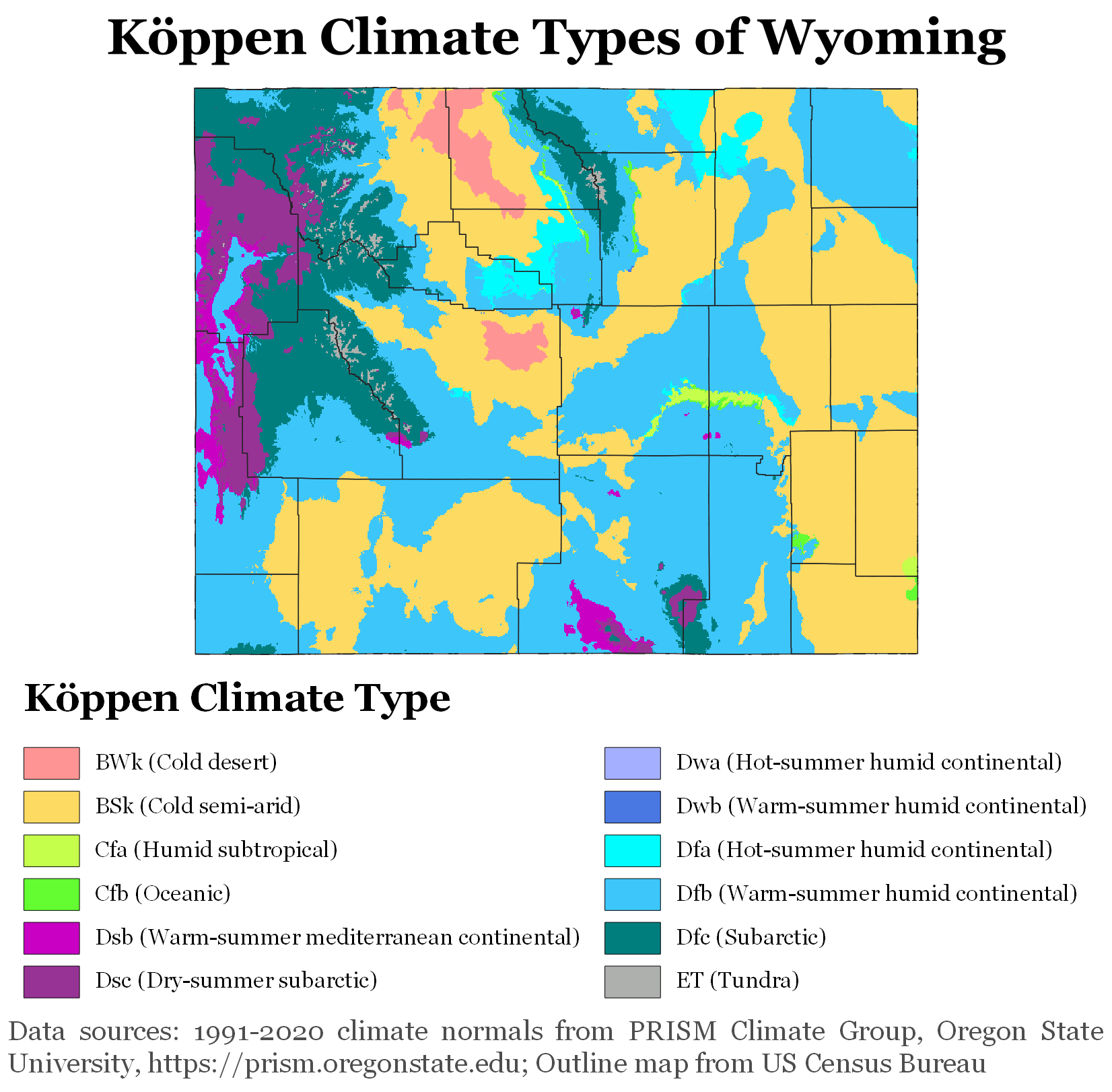
 Wyoming's climate is generally
Wyoming's climate is generally
 The
The
 The state of Wyoming has 23 county (United States), counties.
The state of Wyoming has 23 county (United States), counties.
 Vehicle registration plates of Wyoming, Wyoming license plates have a number on the left that indicates the county where the vehicle is registered, ranked by an earlier census. Specifically, the numbers are representative of the property values of the counties in 1930. The county license plate numbers are:
Vehicle registration plates of Wyoming, Wyoming license plates have a number on the left that indicates the county where the vehicle is registered, ranked by an earlier census. Specifically, the numbers are representative of the property values of the counties in 1930. The county license plate numbers are:
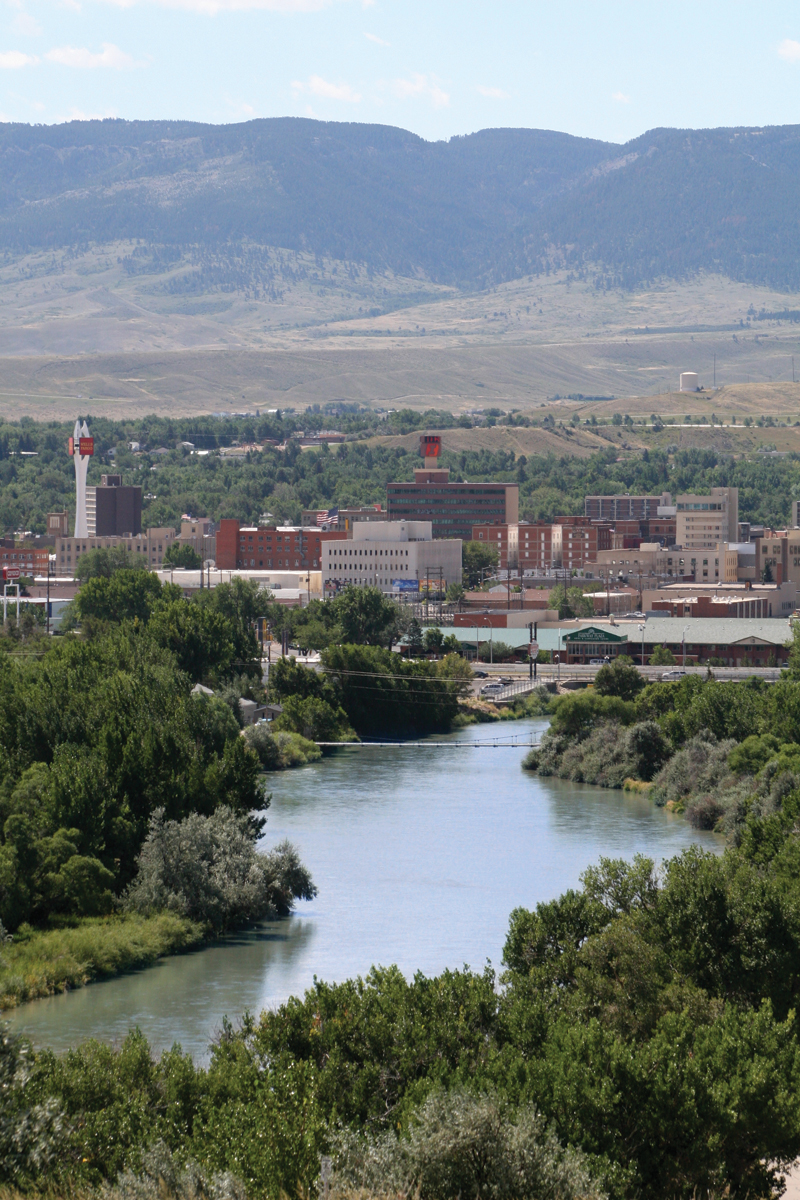





 The State of Wyoming has 99 List of municipalities in Wyoming, incorporated municipalities.
In 2005, 50.6% of Wyomingites lived in one of the 13 most populous Wyoming municipalities.
The State of Wyoming has 99 List of municipalities in Wyoming, incorporated municipalities.
In 2005, 50.6% of Wyomingites lived in one of the 13 most populous Wyoming municipalities.
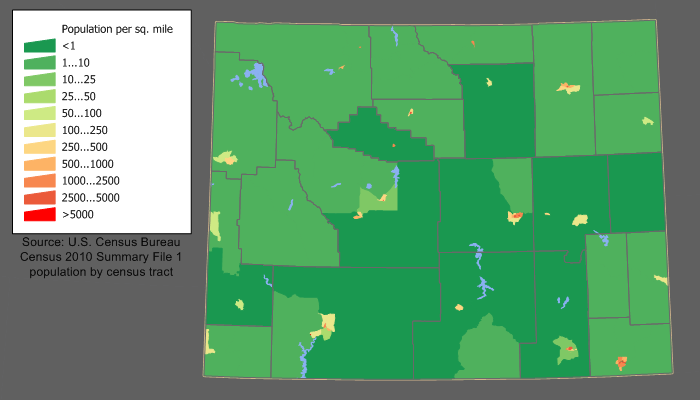 The United States Census Bureau estimated the population of Wyoming was 578,759 in 2019; in 2020, it had a 2020 census population of 576,851. The center of population of Wyoming is in Natrona County, Wyoming, Natrona County.
In 2014, the United States Census Bureau estimated the population's racial composition was 92.7% White American, white (82.9% non-Hispanic white), 2.7% American Indian and Alaska Native, 1.6% Black or African American, 1.0% Asian American, and 0.1% Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander. As of 2011, 24.9% of Wyoming's population younger than age1 were minorities. According to data from the American Community Survey, as of 2018, Wyoming was the only U.S. state where African Americans earn a higher median income than white workers.
According to the 2010 census, the racial composition of the population was 90.7% white, 0.8% black or African American, 2.4% American Indian and Alaska Native, 0.8% Asian American, 0.1% Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander, 2.2% from two or more races, and 3.0% from some other race. Ethnically, 8.9% of the total population was of Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic or Latino origin (they may be of any race) and 91.1% Non-Hispanic, with non-Hispanic whites constituting the largest non-Hispanic group at 85.9%.
As of 2015, Wyoming had an estimated population of 586,107, which was an increase of 1,954, or 0.29%, from the prior year and an increase of 22,481, or 3.99%, since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 12,165 (33,704 births minus 21,539 deaths) and an increase from net migration of 4,035 into the state. Immigration resulted in a net increase of 2,264 and migration within the country produced a net increase of 1,771. In 2004, the foreign-born population was 11,000 (2.2%). In 2005, total births in Wyoming were 7,231 (birth rate of 14.04 per thousand). Sparsely populated, Wyoming is the least populous state of the United States. Wyoming has the second-lowest population density in the country (behind
The United States Census Bureau estimated the population of Wyoming was 578,759 in 2019; in 2020, it had a 2020 census population of 576,851. The center of population of Wyoming is in Natrona County, Wyoming, Natrona County.
In 2014, the United States Census Bureau estimated the population's racial composition was 92.7% White American, white (82.9% non-Hispanic white), 2.7% American Indian and Alaska Native, 1.6% Black or African American, 1.0% Asian American, and 0.1% Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander. As of 2011, 24.9% of Wyoming's population younger than age1 were minorities. According to data from the American Community Survey, as of 2018, Wyoming was the only U.S. state where African Americans earn a higher median income than white workers.
According to the 2010 census, the racial composition of the population was 90.7% white, 0.8% black or African American, 2.4% American Indian and Alaska Native, 0.8% Asian American, 0.1% Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander, 2.2% from two or more races, and 3.0% from some other race. Ethnically, 8.9% of the total population was of Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic or Latino origin (they may be of any race) and 91.1% Non-Hispanic, with non-Hispanic whites constituting the largest non-Hispanic group at 85.9%.
As of 2015, Wyoming had an estimated population of 586,107, which was an increase of 1,954, or 0.29%, from the prior year and an increase of 22,481, or 3.99%, since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 12,165 (33,704 births minus 21,539 deaths) and an increase from net migration of 4,035 into the state. Immigration resulted in a net increase of 2,264 and migration within the country produced a net increase of 1,771. In 2004, the foreign-born population was 11,000 (2.2%). In 2005, total births in Wyoming were 7,231 (birth rate of 14.04 per thousand). Sparsely populated, Wyoming is the least populous state of the United States. Wyoming has the second-lowest population density in the country (behind
 ''Note: Births in table don't add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
* Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic and Latino Americans, White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
''Note: Births in table don't add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
* Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic and Latino Americans, White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
 According to a 2012 United States Bureau of Economic Analysis report, Wyoming's Gross regional domestic product, gross state product was $38.4 billion. As of 2014, the population was growing slightly with the most growth in tourist-oriented areas such as Teton County, Wyoming, Teton County. Boom conditions in neighboring states such as North Dakota were drawing energy workers away. About half of Wyoming's counties showed population loss. The state makes active efforts through Wyoming Grown, an internet-based recruitment program, to find jobs for young people educated in Wyoming who have emigrated but may wish to return.
The mineral extraction industry and travel and tourism sector are the main drivers of Wyoming's economy. The federal government owns about 50% of its landmass, while the state controls 6%. The total taxable value of mining production in Wyoming in 2001 was over $6.7 billion. The Tourism, tourism industry accounts for over $2 billion in revenue.
In 2002, more than six million people visited Wyoming's national parks and monuments. Wyoming's main tourist attractions include
According to a 2012 United States Bureau of Economic Analysis report, Wyoming's Gross regional domestic product, gross state product was $38.4 billion. As of 2014, the population was growing slightly with the most growth in tourist-oriented areas such as Teton County, Wyoming, Teton County. Boom conditions in neighboring states such as North Dakota were drawing energy workers away. About half of Wyoming's counties showed population loss. The state makes active efforts through Wyoming Grown, an internet-based recruitment program, to find jobs for young people educated in Wyoming who have emigrated but may wish to return.
The mineral extraction industry and travel and tourism sector are the main drivers of Wyoming's economy. The federal government owns about 50% of its landmass, while the state controls 6%. The total taxable value of mining production in Wyoming in 2001 was over $6.7 billion. The Tourism, tourism industry accounts for over $2 billion in revenue.
In 2002, more than six million people visited Wyoming's national parks and monuments. Wyoming's main tourist attractions include
 Wyoming's mineral commodities include coal, natural gas, coalbed methane, crude oil, uranium, and
Wyoming's mineral commodities include coal, natural gas, coalbed methane, crude oil, uranium, and
 Wyoming's largest airport is Jackson Hole Airport, with more than 500 employees. Three interstate highways and 13 U.S. highways pass through Wyoming. The State highways in Wyoming, Wyoming state highway system also serves the state.
Interstate 25 in Wyoming, Interstate 25 enters Wyoming south of Cheyenne and runs north, intersecting Interstate 80 immediately west of Cheyenne. It passes through Casper and ends at Interstate 90, near Buffalo, Wyoming, Buffalo.
Wyoming's largest airport is Jackson Hole Airport, with more than 500 employees. Three interstate highways and 13 U.S. highways pass through Wyoming. The State highways in Wyoming, Wyoming state highway system also serves the state.
Interstate 25 in Wyoming, Interstate 25 enters Wyoming south of Cheyenne and runs north, intersecting Interstate 80 immediately west of Cheyenne. It passes through Casper and ends at Interstate 90, near Buffalo, Wyoming, Buffalo.
 The Shoshone, Eastern Shoshone and Arapaho, Northern Arapaho tribes share the Wind River Indian Reservation in central western Wyoming, near Lander, Wyoming, Lander. The reservation is home to 2,500 Eastern Shoshone and 5,000 Northern Arapaho.
Chief Washakie established the reservation in 1868Background of Wind River Reservation
The Shoshone, Eastern Shoshone and Arapaho, Northern Arapaho tribes share the Wind River Indian Reservation in central western Wyoming, near Lander, Wyoming, Lander. The reservation is home to 2,500 Eastern Shoshone and 5,000 Northern Arapaho.
Chief Washakie established the reservation in 1868Background of Wind River Reservation
as the result of negotiations with the federal government in the Fort Bridger Treaty, PBS. Independent Lens but the federal government forced the Northern Arapaho onto the Shoshone reservation in 1876 after it failed to provide a promised separate reservation. Today the Wind River Indian Reservation is jointly owned, with each tribe having a 50% interest in the land, water, and other natural resources. It is a sovereign, self-governed land with two independent governing bodies: the Eastern Shoshone Tribe and the Northern Arapaho Tribe. Until 2014, the Shoshone Business Council and Northern Arapaho Business Council met jointly as the Joint Business Council to decide matters that affect both tribes. Six elected council members from each tribe served on the joint council.
 The federal government owns nearly half of Wyoming's land (about ); the state owns another .MainEnvironment.org
The federal government owns nearly half of Wyoming's land (about ); the state owns another .MainEnvironment.org
Public Land Ownership by State, 1995 Main Environment.org Most of it is administered by the Bureau of Land Management and United States Forest Service, U.S. Forest Service in numerous United States National Forest, national forests and a United States National Grassland, national grassland, not to mention vast swaths of "public" land and an Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, air force base near Cheyenne.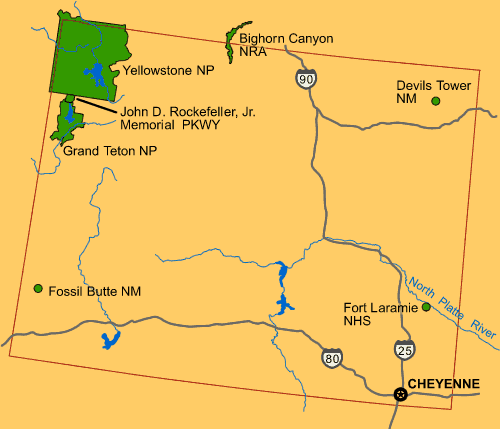 There are also areas managed by the National Park Service and agencies such as the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
:National parks
*
There are also areas managed by the National Park Service and agencies such as the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
:National parks
*
File:Castle Geyser (3678669019).jpg,
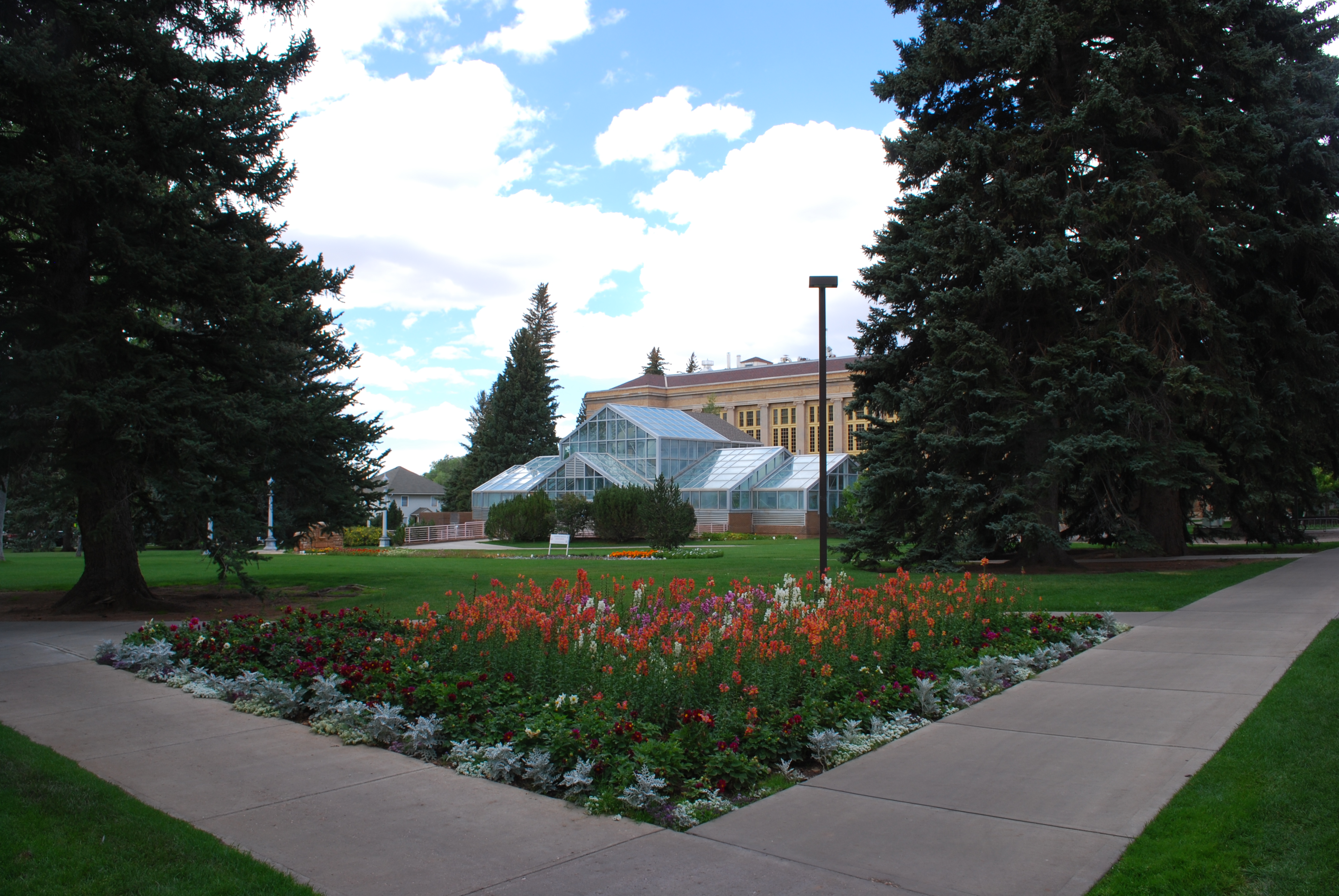 The state superintendent of public instruction, an elected state official, directs public education. The State Board of Education, a nine-member board appointed by the governor, sets educational policy. The constitution prohibits the state from establishing curriculum and textbook selections; these are the prerogative of local school boards. The Wyoming School for the Deaf was the only in-state school dedicated to supporting deaf students before it closed in the summer of 2000.
The state superintendent of public instruction, an elected state official, directs public education. The State Board of Education, a nine-member board appointed by the governor, sets educational policy. The constitution prohibits the state from establishing curriculum and textbook selections; these are the prerogative of local school boards. The Wyoming School for the Deaf was the only in-state school dedicated to supporting deaf students before it closed in the summer of 2000.
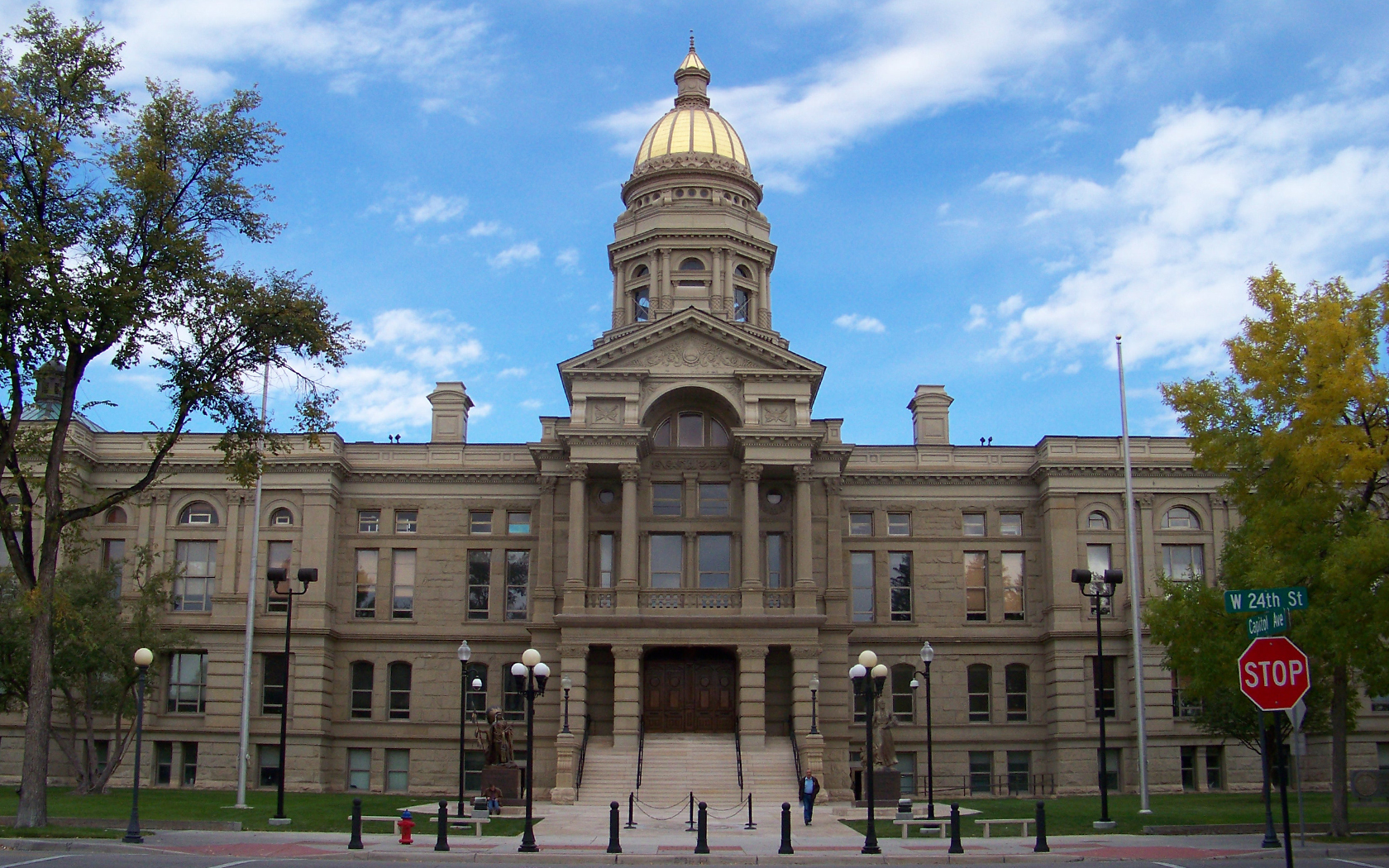

 Wyoming's political history defies easy classification. The state was the first to grant women the right to vote and to elect a woman governor. On December 10, 1869, John Allen Campbell, the first Governor of the Wyoming Territory, approved the first law in United States history explicitly granting women the right to vote. This day was later commemorated as Wyoming Day. On November 5, 1889, voters approved the first constitution in the world granting full voting rights to women.
While the state elected notable Democratic Party (United States), Democrats to federal office in the 1960s and 1970s, politics have become decidedly more conservative since the 1980s as the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party came to dominate the state's congressional delegation. Today, Wyoming is represented in Washington by its two Senators, John Barrasso and Cynthia Lummis, and its one member of the House of Representatives, Congresswoman Liz Cheney. All three are Republicans; a Democrat has not represented Wyoming in the Senate since 1977 or in the House since 1978. The state has not voted for a Democrat for president since 1964, one of only eight times since statehood. At present, there is only one relatively reliably Democratic county, affluent Teton County, Wyoming, Teton, and one swing county, college county Albany County, Wyoming, Albany. In the 2004 presidential election, George W. Bush won his second-largest victory, with 69% of the vote. Former Vice President Dick Cheney is a Wyoming resident and represented the state in Congress from 1979 to 1989.
Republicans are no less dominant at the state level. They have held a majority in the state senate continuously since 1936 and in the state house since 1964, though Democrats held the governor of Wyoming, governorship for all but eight years between 1975 and 2011. Uniquely, Wyoming elected Democrat Nellie Tayloe Ross as the first woman in United States history to serve as state governor. She served from 1925 to 1927, winning a special election after her husband, William Bradford Ross, unexpectedly died a little more than a year into his term.
In a 2020 study, Wyoming was ranked as the 25th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
Wyoming's political history defies easy classification. The state was the first to grant women the right to vote and to elect a woman governor. On December 10, 1869, John Allen Campbell, the first Governor of the Wyoming Territory, approved the first law in United States history explicitly granting women the right to vote. This day was later commemorated as Wyoming Day. On November 5, 1889, voters approved the first constitution in the world granting full voting rights to women.
While the state elected notable Democratic Party (United States), Democrats to federal office in the 1960s and 1970s, politics have become decidedly more conservative since the 1980s as the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party came to dominate the state's congressional delegation. Today, Wyoming is represented in Washington by its two Senators, John Barrasso and Cynthia Lummis, and its one member of the House of Representatives, Congresswoman Liz Cheney. All three are Republicans; a Democrat has not represented Wyoming in the Senate since 1977 or in the House since 1978. The state has not voted for a Democrat for president since 1964, one of only eight times since statehood. At present, there is only one relatively reliably Democratic county, affluent Teton County, Wyoming, Teton, and one swing county, college county Albany County, Wyoming, Albany. In the 2004 presidential election, George W. Bush won his second-largest victory, with 69% of the vote. Former Vice President Dick Cheney is a Wyoming resident and represented the state in Congress from 1979 to 1989.
Republicans are no less dominant at the state level. They have held a majority in the state senate continuously since 1936 and in the state house since 1964, though Democrats held the governor of Wyoming, governorship for all but eight years between 1975 and 2011. Uniquely, Wyoming elected Democrat Nellie Tayloe Ross as the first woman in United States history to serve as state governor. She served from 1925 to 1927, winning a special election after her husband, William Bradford Ross, unexpectedly died a little more than a year into his term.
In a 2020 study, Wyoming was ranked as the 25th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
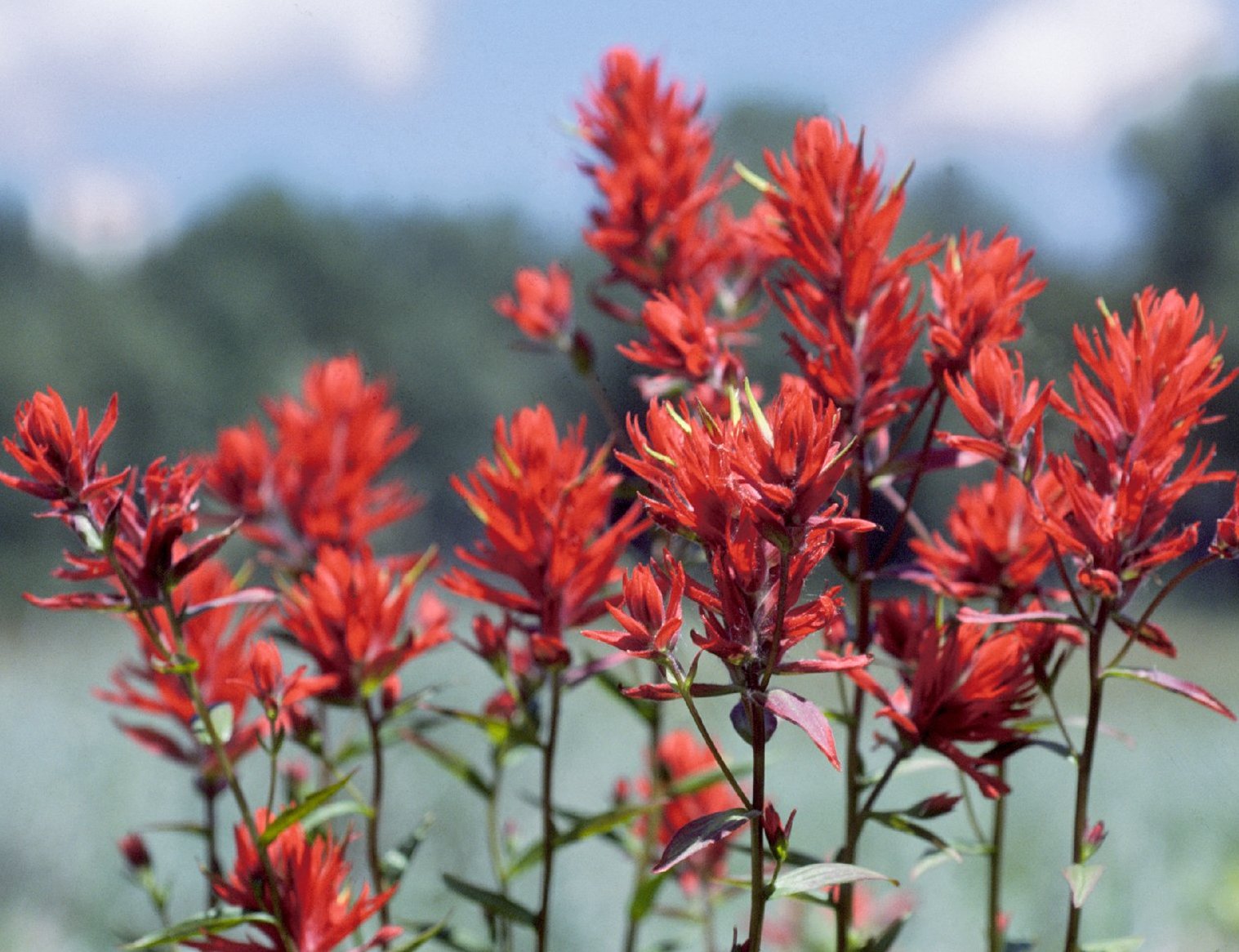 List of all Wyoming state symbols:
* List of U.S. state birds, State bird: western meadowlark (''Sturnella neglecta'')
* State coin: Sacagawea dollar
* State dinosaur: ''Triceratops''
* State emblem: Bucking Horse and Rider
* State fish: cutthroat trout (''Oncorhynchus clarki'')
* Flags of the U.S. states, State flag: Flag of the State of Wyoming
* List of U.S. state flowers, State flower: Castilleja linariifolia, Wyoming Indian paintbrush (''Castilleja linariifolia'')
* State fossil: ''Knightia''
* List of U.S. state minerals, rocks, stones and gemstones, State gemstone: Nephrite, Wyoming nephrite jade
* List of U.S. state grasses, State grass: Pascopyrum, western wheatgrass (''Pascopyrum smithii'')
* List of U.S. state insects, State insect: Callophrys sheridanii, Sheridan's green hairstreak butterfly (''Callophrys sheridanii'')
* List of U.S. state mammals, State mammal: American bison (''Bison bison'')
* List of U.S. state mottos, State motto: ''Equal Rights (motto), Equal Rights''
* List of U.S. state nicknames, State nicknames: Equality State; Cowboy State; Big Wyoming
* State reptile: horned lizard (''Phrynosoma douglassi brevirostre'')
* Seals of the U.S. states, State seal: Great Seal of the State of Wyoming
* List of U.S. state songs, State song: "Wyoming (song), Wyoming" by Charles E. Winter & George E. Knapp
* List of U.S. state sports, State sport: rodeo
* List of U.S. state trees, State tree: plains cottonwood (''Populus sargentii'')
List of all Wyoming state symbols:
* List of U.S. state birds, State bird: western meadowlark (''Sturnella neglecta'')
* State coin: Sacagawea dollar
* State dinosaur: ''Triceratops''
* State emblem: Bucking Horse and Rider
* State fish: cutthroat trout (''Oncorhynchus clarki'')
* Flags of the U.S. states, State flag: Flag of the State of Wyoming
* List of U.S. state flowers, State flower: Castilleja linariifolia, Wyoming Indian paintbrush (''Castilleja linariifolia'')
* State fossil: ''Knightia''
* List of U.S. state minerals, rocks, stones and gemstones, State gemstone: Nephrite, Wyoming nephrite jade
* List of U.S. state grasses, State grass: Pascopyrum, western wheatgrass (''Pascopyrum smithii'')
* List of U.S. state insects, State insect: Callophrys sheridanii, Sheridan's green hairstreak butterfly (''Callophrys sheridanii'')
* List of U.S. state mammals, State mammal: American bison (''Bison bison'')
* List of U.S. state mottos, State motto: ''Equal Rights (motto), Equal Rights''
* List of U.S. state nicknames, State nicknames: Equality State; Cowboy State; Big Wyoming
* State reptile: horned lizard (''Phrynosoma douglassi brevirostre'')
* Seals of the U.S. states, State seal: Great Seal of the State of Wyoming
* List of U.S. state songs, State song: "Wyoming (song), Wyoming" by Charles E. Winter & George E. Knapp
* List of U.S. state sports, State sport: rodeo
* List of U.S. state trees, State tree: plains cottonwood (''Populus sargentii'')
State of Wyoming government official website
Official Wyoming State Travel Website
Wyoming State Facts from USDA
* * {{coord, 43, -107, dim:300000_region:US-WY_type:adm1st, name=State of Wyoming, display=title Wyoming, 1890 establishments in the United States States and territories established in 1890 States of the United States Western United States Contiguous United States
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the Mountain West
The Mountain West Conference (MW) is one of the collegiate athletic conferences affiliated with the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) (formerly I-A). The MW officially began operations o ...
subregion of the Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ...
. It is bordered by Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
to the north and northwest, South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota people, Lakota and Dakota peo ...
and Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwe ...
to the east, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyom ...
to the west, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
to the southwest, and Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
to the south. With a population of 576,851 in the 2020 United States census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to of ...
, Wyoming is the least populous state despite being the 10th largest by area, with the second-lowest population density after Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
. The state capital
Below is an index of pages containing lists of capital cities.
National capitals
*List of national capitals
* List of national capitals by latitude
*List of national capitals by population
* List of national capitals by area
* List of capital c ...
and most populous city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the city proper, cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or th ...
is Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enroll ...
, which had an estimated population of 63,957 in 2018.
Wyoming's western half is covered mostly by the ranges and rangelands of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
, while the eastern half of the state is high-elevation prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
called the High Plains High Plains refers to one of two distinct land regions:
* High Plains (United States), land region of the western Great Plains
*High Plains (Australia)
The High Plains of south-eastern Australia are a sub-region, or more strictly a string of adja ...
. It is drier and windier than the rest of the country, being split between semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
and continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
climates with greater temperature extremes. Almost half of the land in Wyoming is owned by the federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
, generally protected for public uses. The state ranks 6th by area and fifth by proportion of a state's land owned by the federal government. Federal lands include two national parks (Grand Teton
Grand Teton is the highest mountain in Grand Teton National Park, in Northwest Wyoming, and a classic destination in American mountaineering.
Geography
Grand Teton, at , is the highest point of the Teton Range, and the second highest peak in t ...
and Yellowstone
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
), two national recreation areas, two national monuments, several national forests, historic sites, fish hatcheries, and wildlife refuges.
Indigenous peoples inhabited the region for thousands of years. Historic and current federally recognized tribes include the Arapaho
The Arapaho (; french: Arapahos, ) are a Native American people historically living on the plains of Colorado and Wyoming. They were close allies of the Cheyenne tribe and loosely aligned with the Lakota and Dakota.
By the 1850s, Arapaho band ...
, Crow
A crow is a bird of the genus '' Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifica ...
, Lakota
Lakota may refer to:
* Lakota people, a confederation of seven related Native American tribes
*Lakota language, the language of the Lakota peoples
Place names
In the United States:
* Lakota, Iowa
* Lakota, North Dakota, seat of Nelson County
* La ...
, and Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ) are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:
* Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming
* Northern Shoshone: southern Idaho
* Western Shoshone: Nevada, northern Utah
* Goshute: western Utah, easter ...
. During European exploration, the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
was the first to "claim" southern Wyoming. With Mexican independence, it became part of that republic. After defeat in the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, Mexico ceded this territory to the U.S. in 1848.
The region was named "Wyoming" in a bill introduced to Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
in 1865 to provide a temporary government for the territory of Wyoming. It had been used earlier by colonists for the Wyoming Valley
The Wyoming Valley is a historic industrialized region of Northeastern Pennsylvania. The region is historically notable for its influence in helping fuel the American Industrial Revolution with its many anthracite coal-mines. As a metropolitan are ...
in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, and is derived from the Lenape language
The Delaware languages, also known as the Lenape languages ( del, Lënapei èlixsuwakàn), are Munsee language, Munsee and Unami language, Unami, two closely related languages of the Eastern Algonquian languages, Eastern Algonquian subgroup of ...
Munsee
The Munsee (or Minsi or Muncee) or mə́n'si·w ( del, Monsiyok)Online Lenape Talking Dictionary, "Munsee Indians"Link/ref> are a subtribe of the Lenape, originally constituting one of the three great divisions of that nation and dwelling along t ...
word , meaning "at the big river flat".Bright, William (2004). ''Native American Place Names of the United States''. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, pg. 576State of Wyoming—NarrativeBills for
Wyoming Territory
The Territory of Wyoming was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 25, 1868, until July 10, 1890, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Wyoming. Cheyenne was the territorial capital. The bou ...
's admission to the union were introduced in both the U.S. Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and powe ...
and U.S. House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
in December 1889. On March 27, 1890, the House passed the bill and President Benjamin Harrison
Benjamin Harrison (August 20, 1833March 13, 1901) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 23rd president of the United States from 1889 to 1893. He was a member of the Harrison family of Virginia–a grandson of the ninth pr ...
signed Wyoming's statehood bill; Wyoming became the 44th state in the union.
Historically, European Americans farmed and ranched here, with shepherds and cattle ranchers in conflict over lands. Today Wyoming's economy is largely based on tourism and the extraction of minerals such as coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
, and trona
Trona (trisodium hydrogendicarbonate dihydrate, also sodium sesquicarbonate dihydrate, Na2CO3•2NaHCO3•3H2O) is a non-marine evaporite mineral. It is mined as the primary source of sodium carbonate in the United States, where it has replaced ...
. Agricultural commodities include barley, hay, livestock, sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together wi ...
s, wheat, and wool. It was the first state to allow women the right to vote
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to v ...
and the right to assume elected office, as well as the first state to elect a female governor. Due to this part of its history, its main nickname is "The Equality State" and its official state motto is "Equal Rights". It has been a politically conservative state since the 1950s. The Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
presidential nominee has carried the state in every election since 1968.
History
 Several Native American groups originally inhabited the region today known as Wyoming. The
Several Native American groups originally inhabited the region today known as Wyoming. The Crow
A crow is a bird of the genus '' Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifica ...
, Arapaho
The Arapaho (; french: Arapahos, ) are a Native American people historically living on the plains of Colorado and Wyoming. They were close allies of the Cheyenne tribe and loosely aligned with the Lakota and Dakota.
By the 1850s, Arapaho band ...
, Lakota
Lakota may refer to:
* Lakota people, a confederation of seven related Native American tribes
*Lakota language, the language of the Lakota peoples
Place names
In the United States:
* Lakota, Iowa
* Lakota, North Dakota, seat of Nelson County
* La ...
, and Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ) are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:
* Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming
* Northern Shoshone: southern Idaho
* Western Shoshone: Nevada, northern Utah
* Goshute: western Utah, easter ...
were but a few of the original inhabitants European explorers encountered when they first visited the region. What is now southwestern Wyoming was claimed by the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
, which extended through the Southwest and Mexico. With Mexican independence in 1821, it was considered part of Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
. U.S. expansion brought settlers who fought for control. Mexico ceded these territories after its defeat in 1848 in the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
.
From the late 18th century, French-Canadian
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to Fr ...
trappers from Québec and Montréal regularly entered the area for trade with the tribes. French toponyms such as Téton and La Ramie are marks of that history.
American John Colter
John Colter (c.1770–1775 – May 7, 1812 or November 22, 1813) was a member of the Lewis and Clark Expedition (1804–1806). Though party to one of the more famous expeditions in history, Colter is best remembered for explorations he made ...
first recorded a description in English of the region in 1807. He was a member of the Lewis and Clark Expedition
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select gro ...
, which was guided by French Canadian Toussaint Charbonneau
Toussaint Charbonneau (March 20, 1767 – August 12, 1843) was a French-Canadian explorer, trader and a member of the Lewis and Clark Expedition. He is also known as the husband of Sacagawea.
Early years
Charbonneau was born in Boucherv ...
and his young Shoshone wife, Sacagawea
Sacagawea ( or ; also spelled Sakakawea or Sacajawea; May – December 20, 1812 or April 9, 1884)Sacagawea
...
. At the time, Colter's reports of the ...
Yellowstone
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
area were considered fictional. On a return from Astoria, Robert Stuart and a party of five men discovered South Pass in 1812.
The Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and Westward Expansion Trails, emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what ...
later followed that route as emigrants moved to the west coast. In 1850, mountain man Jim Bridger
James Felix "Jim" Bridger (March 17, 1804 – July 17, 1881) was an American mountain man, trapper, Army scout, and wilderness guide who explored and trapped in the Western United States in the first half of the 19th century. He was known as Old ...
found what is now known as Bridger Pass
Bridger Pass is a mountain pass in Carbon County, Wyoming on the Continental Divide of the Americas near the south Great Divide Basin bifurcation point, i.e., the point at which the divide appears to split and envelop the basin.
The first docu ...
. Bridger also explored Yellowstone, and filed reports on the region that, like Colter's, were largely regarded at the time as tall tale
A tall tale is a story with unbelievable elements, related as if it were true and factual. Some tall tales are exaggerations of actual events, for example fish stories ("the fish that got away") such as, "That fish was so big, why I tell ya', it n ...
s. The Union Pacific Railroad
The Union Pacific Railroad , legally Union Pacific Railroad Company and often called simply Union Pacific, is a freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Paci ...
constructed track through Bridger Pass in 1868. It was used as the route for construction of Interstate 80
Interstate 80 (I-80) is an east–west transcontinental freeway that crosses the United States from downtown San Francisco, California, to Teaneck, New Jersey, in the New York metropolitan area. The highway was designated in 1956 as one o ...
through the mountains 90 years later.
The region acquired the name ''Wyoming'' by 1865, when Representative James Mitchell Ashley
James Mitchell Ashley (November 14, 1824September 16, 1896) was an American politician and abolitionist. A member of the Republican Party, Ashley served as a member of the United States House of Representatives from Ohio during the American Civ ...
of Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
introduced a bill to Congress to provide a "temporary government for the territory of Wyoming". The territory was named after the Wyoming Valley
The Wyoming Valley is a historic industrialized region of Northeastern Pennsylvania. The region is historically notable for its influence in helping fuel the American Industrial Revolution with its many anthracite coal-mines. As a metropolitan are ...
in Pennsylvania. Thomas Campbell Thomas Campbell may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Thomas Campbell (poet) (1777–1844), Scottish poet
* Thomas Campbell (sculptor) (1790–1858), Scottish sculptor
* Thomas Campbell (visual artist) (born 1969), California-based visual artist ...
wrote his 1809 poem "Gertrude of Wyoming
''Gertrude of Wyoming: A Pennsylvanian Tale'' (1809) is a romantic epic in Spenserian stanza composed by Scottish poet Thomas Campbell (1777–1844). The poem was well received, but not a financial success for its author. The poem was written in ...
", inspired by the Battle of Wyoming
The Battle of Wyoming, also known as the Wyoming Massacre, was a military engagement during the American Revolutionary War between Patriot militiamen and a mixed force of Loyalist soldiers and Iroquois raiders. The clash took place in the Wyom ...
in the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
. The name ultimately derives from the Lenape Munsee
The Munsee (or Minsi or Muncee) or mə́n'si·w ( del, Monsiyok)Online Lenape Talking Dictionary, "Munsee Indians"Link/ref> are a subtribe of the Lenape, originally constituting one of the three great divisions of that nation and dwelling along t ...
word ("at the big river flat").
Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enroll ...
in 1867, population growth was stimulated. The federal government established the Wyoming Territory
The Territory of Wyoming was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 25, 1868, until July 10, 1890, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Wyoming. Cheyenne was the territorial capital. The bou ...
on July 25, 1868. Lacking significant deposits of gold and silver, unlike mineral-rich Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
, Wyoming did not have such a population boom. But South Pass City had a short-lived boom after the Carissa Mine began producing gold in 1867. Copper was mined in some areas between the Sierra Madre Mountains and the Snowy Range near Grand Encampment.
Once government-sponsored expeditions to the Yellowstone country began, Colter's and Bridger's descriptions of the region's landscape were confirmed. In 1872, Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
was created as the world's first, to protect this area. Nearly all of the park lies within the northwestern corner of Wyoming.
On December 10, 1869, territorial Governor John Allen Campbell extended the right to vote to women, making Wyoming the first territory to do so. It kept that franchise when it established its state constitution. Women first served on juries in Wyoming ( Laramie in 1870).
Wyoming was also a pioneer in welcoming women into electoral politics. It had the first female court bailiff ( Mary Atkinson, Laramie, in 1870), and the first female justice of the peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or ''puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission ( letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the sa ...
in the country ( Esther Hobart Morris, South Pass City, in 1870). In 1924, Wyoming was the first state to elect a female governor, Nellie Tayloe Ross, who took office in January 1925. Due to its civil-rights history, one of Wyoming's state nicknames is "The Equality State", and the official state motto is "Equal Rights".
Wyoming's constitution included women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the right of women to vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to grant women the right to vot ...
and a pioneering article on water right
Water right in water law refers to the right of a user to use water from a water source, e.g., a river, stream, pond or source of groundwater. In areas with plentiful water and few users, such systems are generally not complicated or contentious ...
s. Congress admitted Wyoming into the Union as the 44th state on July 10, 1890.
Wyoming was the location of the Johnson County War
The Johnson County War, also known as the War on Powder River and the Wyoming Range War, was a range conflict that took place in Johnson County, Wyoming from 1889 to 1893. The conflict began when cattle companies started ruthlessly persecuting ...
of 1892, which erupted between competing groups of cattle ranchers. The passage of the Homestead Act
The Homestead Acts were several laws in the United States by which an applicant could acquire ownership of government land or the public domain, typically called a homestead. In all, more than of public land, or nearly 10 percent of th ...
led to an influx of small ranchers. A range war
A range war or range conflict is a type of usually violent conflict, most commonly in the 19th and early 20th centuries in the American West. The subject of these conflicts was control of "open range", or range land freely used for cattle grazing, ...
broke out when either or both of the groups chose violent conflict over commercial competition in the use of the public land.
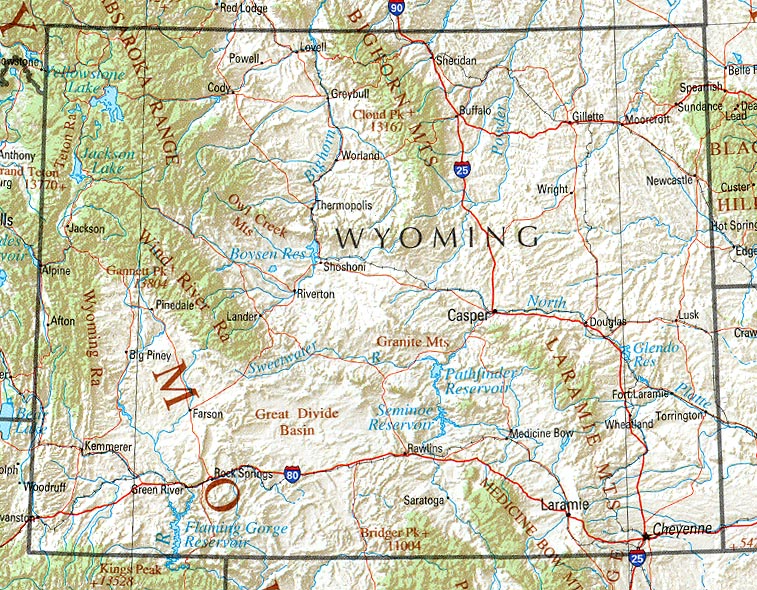
Geography
Climate


semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
and continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
'' ''BSk'''') and is drier and windier in comparison to most of the United States with greater temperature extremes. Much of this is due to the topography of the state. Summers in Wyoming are warm with July high temperatures averaging between in most of the state. With increasing elevation, however, this average drops rapidly with locations above averaging around . Summer nights throughout the state are characterized by a rapid cooldown with even the hottest locations averaging in the range at night. In most of the state, most of the precipitation tends to fall in the late spring and early summer. Winters are cold, but are variable with periods of sometimes extreme cold interspersed between generally mild periods, with Chinook winds
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from ...
providing unusually warm temperatures in some locations.
Wyoming is a dry state with much of the land receiving less than of rainfall per year. Precipitation depends on elevation with lower areas in the Big Horn Basin
The Bighorn Basin is a plateau region and intermontane basin, approximately 100 miles (160 km) wide, in north-central Wyoming in the United States. It is bounded by the Absaroka Range on the west, the Pryor Mountains on the north, the Bighor ...
averaging , making the area nearly a true desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
. The lower areas in the North and on the eastern plains typically average around , making the climate there semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
. Some mountain areas do receive a good amount of precipitation, or more, much of it as snow, sometimes or more annually. The state's highest recorded temperature is at Basin on July 12, 1900, and the lowest recorded temperature is at Riverside
Riverside may refer to:
Places Australia
* Riverside, Tasmania, a suburb of Launceston, Tasmania
Canada
* Riverside (electoral district), in the Yukon
* Riverside, Calgary, a neighbourhood in Alberta
* Riverside, Manitoba, a former rural m ...
on February 9, 1933.
The number of thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are someti ...
days vary across the state with the southeastern plains of the state having the most days of thunderstorm activity. Thunderstorm activity in the state is highest during the late spring and early summer. The southeastern corner of the state is the most vulnerable part of the state to tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, altho ...
activity. Moving away from that point and westwards, the incidence of tornadoes drops dramatically with the west part of the state showing little vulnerability. Tornadoes, where they occur, tend to be small and brief, unlike some of those that occur farther east.
Location and size
As specified in the designating legislation for theTerritory of Wyoming
The Territory of Wyoming was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 25, 1868, until July 10, 1890, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Wyoming. Cheyenne was the territorial capital. The bo ...
, Wyoming's borders are lines of latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
41°N and 45°N, and longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east–west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter l ...
104°3'W and 111°3'W (27 and 34 west of the Washington Meridian
The Washington meridians are four meridians that were used as prime meridians in the United States and pass through Washington, D.C. The four which have been specified are:
# through the Capitol
# through the White House
# through the old Naval Ob ...
)—a geodesic
In geometry, a geodesic () is a curve representing in some sense the shortest path ( arc) between two points in a surface, or more generally in a Riemannian manifold. The term also has meaning in any differentiable manifold with a connection. ...
quadrangle. Wyoming is one of only three states (the others being Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
and Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
) to have borders defined by ''only'' "straight" lines. Due to surveying inaccuracies during the 19th century, Wyoming's legal border deviates from the true latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
and longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east–west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter l ...
lines by up to half of a mile (0.8 km) in some spots, especially in the mountainous region along the 45th parallel. Wyoming is bordered on the north by Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
, on the east by South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota people, Lakota and Dakota peo ...
and Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwe ...
, on the south by Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
, on the southwest by Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, and on the west by Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyom ...
. It is the tenth largest state in the United States in total area, containing and is made up of 23 counties. From the north border to the south border it is ; and from the east to the west border is at its south end and at the north end.
Natural landforms
Mountain ranges

 The
The Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
meet the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
in Wyoming. The state is a great plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ha ...
broken by many mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
s. Surface elevations range from the summit of Gannett Peak
Gannett Peak is the highest mountain peak in the U.S. state of Wyoming at . It lies in the Wind River Range within the Bridger Wilderness of the Bridger-Teton National Forest. Straddling the Continental Divide along the boundary between Frem ...
in the Wind River Mountain Range, at , to the Belle Fourche River
The Belle Fourche River (pronounced ''bel FOOSH''; lkt, Šahíyela Wakpá) is a tributary of the Cheyenne River, approximately long, in the U.S. states of Wyoming and South Dakota. It is part of the Mississippi River watershed via the Cheyenn ...
valley in the state's northeast corner, at . In the northwest are the Absaroka, Owl Creek, Gros Ventre
The Gros Ventre ( , ; meaning "big belly"), also known as the Aaniiih, A'aninin, Haaninin, Atsina, and White Clay, are a historically Algonquian-speaking Native American tribe located in north central Montana. Today the Gros Ventre people are ...
, Wind River, and the Teton ranges. In the north central are the Big Horn Mountains
The Bighorn Mountains ( cro, Basawaxaawúua, lit=our mountains or cro, Iisaxpúatahchee Isawaxaawúua, label=none, lit=bighorn sheep's mountains) are a mountain range in northern Wyoming and southern Montana in the United States, forming a nort ...
; in the northeast, the Black Hills
The Black Hills ( lkt, Ȟe Sápa; chy, Moʼȯhta-voʼhonáaeva; hid, awaxaawi shiibisha) is an isolated mountain range rising from the Great Plains of North America in western South Dakota and extending into Wyoming, United States. Black Elk P ...
; and in the southern region the Laramie, Snowy, and Sierra Madre
Sierra Madre (Spanish, 'mother mountain range') may refer to:
Places and mountains Mexico
*Sierra Madre Occidental, a mountain range in northwestern Mexico and southern Arizona
*Sierra Madre Oriental, a mountain range in northeastern Mexico
*S ...
ranges.
The Snowy Range in the south central part of the state is an extension of the Colorado Rockies
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
both in geology and in appearance. The Wind River Range in the west central part of the state is remote and includes more than 40 mountain peaks in excess of tall in addition to Gannett Peak
Gannett Peak is the highest mountain peak in the U.S. state of Wyoming at . It lies in the Wind River Range within the Bridger Wilderness of the Bridger-Teton National Forest. Straddling the Continental Divide along the boundary between Frem ...
, the highest peak in the state. The Bighorn Mountains in the north central portion are somewhat isolated from the bulk of the Rocky Mountains.
The Teton Range in the northwest extends for , part of which is included in Grand Teton National Park
Grand Teton National Park is an American national park in northwestern Wyoming. At approximately , the park includes the major peaks of the Teton Range as well as most of the northern sections of the valley known as Jackson Hole. Grand Teton Na ...
. The park includes the Grand Teton
Grand Teton is the highest mountain in Grand Teton National Park, in Northwest Wyoming, and a classic destination in American mountaineering.
Geography
Grand Teton, at , is the highest point of the Teton Range, and the second highest peak in t ...
, the second-highest peak in the state.
The Continental Divide
A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, not ...
spans north–south across the central portion of the state. Rivers east of the divide drain into the Missouri River Basin
The Missouri River Valley outlines the journey of the Missouri River from its headwaters where the Madison, Jefferson and Gallatin Rivers flow together in Montana to its confluence with the Mississippi River in the State of Missouri. At long th ...
and eventually the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
. They are the North Platte
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' is ...
, Wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
, Bighorn
The bighorn sheep (''Ovis canadensis'') is a species of sheep native to North America. It is named for its large horns. A pair of horns might weigh up to ; the sheep typically weigh up to . Recent genetic testing indicates three distinct subspec ...
, and Yellowstone
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
rivers. The Snake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake ...
in northwest Wyoming eventually drains into the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
and the Pacific Ocean, as does the Green River Green River may refer to:
Rivers
Canada
* Green River (British Columbia), a tributary of the Lillooet River
*Green River, a tributary of the Saint John River, also known by its French name of Rivière Verte
*Green River (Ontario), a tributary of ...
through the Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid drainage basin, watershed that encompasses parts of ...
Basin.
The Continental Divide forks in the south central part of the state in an area known as the Great Divide Basin where water that precipitates onto or flows into it cannot reach an ocean—it ''all'' sinks into the soil and eventually evaporates.
Several rivers begin in or flow through the state, including the Yellowstone River, Bighorn River, Green River, and the Snake River.
Basins
Much of Wyoming is covered with large basins containing different eco-regions, from shrublands to smaller patches of desert. Regions of the state classified as basins contain everything from large geologic formations to sand dunes and vast unpopulated spaces. Basin landscapes are typically at lower elevations and include rolling hills, valleys, mesas, terraces and other rugged terrain, but also include natural springs as well as rivers and artificial reservoirs. They have common plant species such as various subspecies of Artemisia tridentata, sagebrush, juniper and grasses such as Agropyron, wheatgrass, but basins are known for their diversity of plant and animal species.Islands
Wyoming has 32 named islands; the majority are in Jackson Lake (Wyoming), Jackson Lake and Yellowstone Lake, withinYellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
in the northwest portion of the state. The Green River Green River may refer to:
Rivers
Canada
* Green River (British Columbia), a tributary of the Lillooet River
*Green River, a tributary of the Saint John River, also known by its French name of Rivière Verte
*Green River (Ontario), a tributary of ...
in the southwest also contains a number of islands.
Regions and administrative divisions
Counties
 The state of Wyoming has 23 county (United States), counties.
The state of Wyoming has 23 county (United States), counties.
 Vehicle registration plates of Wyoming, Wyoming license plates have a number on the left that indicates the county where the vehicle is registered, ranked by an earlier census. Specifically, the numbers are representative of the property values of the counties in 1930. The county license plate numbers are:
Vehicle registration plates of Wyoming, Wyoming license plates have a number on the left that indicates the county where the vehicle is registered, ranked by an earlier census. Specifically, the numbers are representative of the property values of the counties in 1930. The county license plate numbers are:
Cities and towns





 The State of Wyoming has 99 List of municipalities in Wyoming, incorporated municipalities.
In 2005, 50.6% of Wyomingites lived in one of the 13 most populous Wyoming municipalities.
The State of Wyoming has 99 List of municipalities in Wyoming, incorporated municipalities.
In 2005, 50.6% of Wyomingites lived in one of the 13 most populous Wyoming municipalities.
Metropolitan areas
The United States Census Bureau has defined two United States metropolitan area, metropolitan statistical areas (MSA) and seven United States micropolitan area, micropolitan statistical areas (MiSA) for the state. In 2008, 30.4% of Wyomingites lived in either of the metropolitan statistical areas, and 73% lived in either a metropolitan or a micropolitan area.Demographics
Population
 The United States Census Bureau estimated the population of Wyoming was 578,759 in 2019; in 2020, it had a 2020 census population of 576,851. The center of population of Wyoming is in Natrona County, Wyoming, Natrona County.
In 2014, the United States Census Bureau estimated the population's racial composition was 92.7% White American, white (82.9% non-Hispanic white), 2.7% American Indian and Alaska Native, 1.6% Black or African American, 1.0% Asian American, and 0.1% Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander. As of 2011, 24.9% of Wyoming's population younger than age1 were minorities. According to data from the American Community Survey, as of 2018, Wyoming was the only U.S. state where African Americans earn a higher median income than white workers.
According to the 2010 census, the racial composition of the population was 90.7% white, 0.8% black or African American, 2.4% American Indian and Alaska Native, 0.8% Asian American, 0.1% Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander, 2.2% from two or more races, and 3.0% from some other race. Ethnically, 8.9% of the total population was of Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic or Latino origin (they may be of any race) and 91.1% Non-Hispanic, with non-Hispanic whites constituting the largest non-Hispanic group at 85.9%.
As of 2015, Wyoming had an estimated population of 586,107, which was an increase of 1,954, or 0.29%, from the prior year and an increase of 22,481, or 3.99%, since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 12,165 (33,704 births minus 21,539 deaths) and an increase from net migration of 4,035 into the state. Immigration resulted in a net increase of 2,264 and migration within the country produced a net increase of 1,771. In 2004, the foreign-born population was 11,000 (2.2%). In 2005, total births in Wyoming were 7,231 (birth rate of 14.04 per thousand). Sparsely populated, Wyoming is the least populous state of the United States. Wyoming has the second-lowest population density in the country (behind
The United States Census Bureau estimated the population of Wyoming was 578,759 in 2019; in 2020, it had a 2020 census population of 576,851. The center of population of Wyoming is in Natrona County, Wyoming, Natrona County.
In 2014, the United States Census Bureau estimated the population's racial composition was 92.7% White American, white (82.9% non-Hispanic white), 2.7% American Indian and Alaska Native, 1.6% Black or African American, 1.0% Asian American, and 0.1% Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander. As of 2011, 24.9% of Wyoming's population younger than age1 were minorities. According to data from the American Community Survey, as of 2018, Wyoming was the only U.S. state where African Americans earn a higher median income than white workers.
According to the 2010 census, the racial composition of the population was 90.7% white, 0.8% black or African American, 2.4% American Indian and Alaska Native, 0.8% Asian American, 0.1% Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander, 2.2% from two or more races, and 3.0% from some other race. Ethnically, 8.9% of the total population was of Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic or Latino origin (they may be of any race) and 91.1% Non-Hispanic, with non-Hispanic whites constituting the largest non-Hispanic group at 85.9%.
As of 2015, Wyoming had an estimated population of 586,107, which was an increase of 1,954, or 0.29%, from the prior year and an increase of 22,481, or 3.99%, since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 12,165 (33,704 births minus 21,539 deaths) and an increase from net migration of 4,035 into the state. Immigration resulted in a net increase of 2,264 and migration within the country produced a net increase of 1,771. In 2004, the foreign-born population was 11,000 (2.2%). In 2005, total births in Wyoming were 7,231 (birth rate of 14.04 per thousand). Sparsely populated, Wyoming is the least populous state of the United States. Wyoming has the second-lowest population density in the country (behind Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
) and is the sparsest-populated of the 48 contiguous states. It is one of only two states (Vermont) with a population smaller than that of the nation's capital.
According to the 2000 census, the largest ancestry groups in Wyoming were: German-American, German (26.0%), English American, English (16.0%), Irish American, Irish (13.3%), Norwegian-American, Norwegian (4.3%), and Swedish Americans, Swedish (3.5%).
Birth data
Languages
In 2010, 93.39% (474,343) of Wyomingites over age 5 spoke English language, English as their primary language; 4.47% (22,722) spoke Spanish language, Spanish, 0.35% (1,771) spoke German language, German, and 0.28% (1,434) spoke French language, French. Other common non-English languages included Algonquian languages, Algonquian (0.18%), Russian language, Russian (0.10%), Tagalog language, Tagalog, and Greek language, Greek (both 0.09%). In 2007, the American Community Survey reported 6.2% (30,419) of Wyoming's population over five spoke a language other than English at home. Of those, 68.1% were able to speak English very well, 16.0% spoke English well, 10.9% did not speak English well, and 5.0% did not speak English at all.Religion
In 2020, the Public Religion Research Institute determined that about 55% of Wyoming's adult population was Christianity, Christian, primarily Evangelicalism, evangelical and mainline Protestant, Catholic Church, Roman Catholic, and Mormonism, Mormon. The Public Religion Research Institute survey documented a decrease in religiosity from a 2014 separate Pew Research Center study; according to the Public Religion Research Institute, the irreligious made up 40% of the state population by 2020. According to a 2013 Gallup poll, Wyomingites' religious affiliations were 49% Protestant, 23% nonreligious or other, 18% Catholic, 9% Latter Day Saint movement, Latter-day Saint (Mormons), and less than 1% Judaism, Jewish. A 2010 ARDA report recognized as Wyoming's largest denominations the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons), with 62,804 (11%); the Catholic Church, with 61,222 (10.8%); and the Southern Baptist Convention, with 15,812 (2.8%). The report counted 59,247 evangelical Protestants (10.5%), 36,539 mainline Protestants (6.5%), 785 Eastern Orthodox Christians; 281 Black Protestants; 65,000 adhering to other traditions; and 340,552 claiming no religious tradition. In 2020, ARDA reported the state's largest individual denominations as the following: the Catholic Church (69,500); the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (67,729); and the Southern Baptist Convention (11,082). Non-denominational Protestants were 23,410 in number.Economy and infrastructure
 According to a 2012 United States Bureau of Economic Analysis report, Wyoming's Gross regional domestic product, gross state product was $38.4 billion. As of 2014, the population was growing slightly with the most growth in tourist-oriented areas such as Teton County, Wyoming, Teton County. Boom conditions in neighboring states such as North Dakota were drawing energy workers away. About half of Wyoming's counties showed population loss. The state makes active efforts through Wyoming Grown, an internet-based recruitment program, to find jobs for young people educated in Wyoming who have emigrated but may wish to return.
The mineral extraction industry and travel and tourism sector are the main drivers of Wyoming's economy. The federal government owns about 50% of its landmass, while the state controls 6%. The total taxable value of mining production in Wyoming in 2001 was over $6.7 billion. The Tourism, tourism industry accounts for over $2 billion in revenue.
In 2002, more than six million people visited Wyoming's national parks and monuments. Wyoming's main tourist attractions include
According to a 2012 United States Bureau of Economic Analysis report, Wyoming's Gross regional domestic product, gross state product was $38.4 billion. As of 2014, the population was growing slightly with the most growth in tourist-oriented areas such as Teton County, Wyoming, Teton County. Boom conditions in neighboring states such as North Dakota were drawing energy workers away. About half of Wyoming's counties showed population loss. The state makes active efforts through Wyoming Grown, an internet-based recruitment program, to find jobs for young people educated in Wyoming who have emigrated but may wish to return.
The mineral extraction industry and travel and tourism sector are the main drivers of Wyoming's economy. The federal government owns about 50% of its landmass, while the state controls 6%. The total taxable value of mining production in Wyoming in 2001 was over $6.7 billion. The Tourism, tourism industry accounts for over $2 billion in revenue.
In 2002, more than six million people visited Wyoming's national parks and monuments. Wyoming's main tourist attractions include Grand Teton National Park
Grand Teton National Park is an American national park in northwestern Wyoming. At approximately , the park includes the major peaks of the Teton Range as well as most of the northern sections of the valley known as Jackson Hole. Grand Teton Na ...
, Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
, Devils Tower National Monument, Independence Rock (Wyoming), Independence Rock and Fossil Butte National Monument. Yellowstone, the world's first national park, receives three million visitors each year.
Historically, agriculture has been an important component of Wyoming's economy. Its overall importance to the economy has waned, but it is still an essential part of Wyoming's culture and lifestyle. The main agricultural commodities Wyoming produces include livestock (beef), hay, sugar beets, grain (wheat and barley), and wool. More than 91% of Wyoming's land is classified as rural.
Wyoming is the home of only a handful of companies with a regional or national presence. Taco John's and Sierra Trading Post, both in Cheyenne, are privately held. Cloud Peak Energy in Gillette and U.S. Energy Corp. (NASDAQ: USEG) in Riverton are Wyoming's only publicly traded companies.
Mineral and energy production
 Wyoming's mineral commodities include coal, natural gas, coalbed methane, crude oil, uranium, and
Wyoming's mineral commodities include coal, natural gas, coalbed methane, crude oil, uranium, and trona
Trona (trisodium hydrogendicarbonate dihydrate, also sodium sesquicarbonate dihydrate, Na2CO3•2NaHCO3•3H2O) is a non-marine evaporite mineral. It is mined as the primary source of sodium carbonate in the United States, where it has replaced ...
.
* Wyoming produced 277 million short tons (251.29 million metric tons) of coal in 2019, a 9% drop from 2018. Wyoming's coal production peaked in 2008, when 514 million short tons (466.3 million metric tons) were produced. Wyoming has a reserve of 68.7 billion tons (62.3 billion metric tons) of coal. Major coal areas include the Powder River Basin and the Green River Basin.
* The boom for coalbed methane (CBM) began in the mid-1990s. CBM is methane gas extracted from Wyoming's coal bed seams. It is a means of natural gas production. There has been substantial CBM production in the Powder River Basin. In 2002, the CBM production yield was 327.5 billion cubic feet (9.3 km3).
* Wyoming produced of crude oil in 2007. The state ranked fifth nationwide in oil production in 2007. Petroleum is most often used as a motor fuel, but is also used in the manufacture of plastics, paints, and synthetic rubber.
* The Kelsey Lake Diamond Mine in Colorado, less than from the Wyoming border, produced gem-quality diamonds for several years. The Wyoming craton, which hosts the kimberlite volcanic pipes that were mined, underlies most of Wyoming.
* Wyoming produced 1.77 trillion cubic feet (50.0 billion m3) of natural gas in 2016, ranking the state ranked 6th nationwide in natural gas production. Major markets for natural gas include industrial, commercial, and domestic heating.
* Wyoming possesses the world's largest known reserve of trona
Trona (trisodium hydrogendicarbonate dihydrate, also sodium sesquicarbonate dihydrate, Na2CO3•2NaHCO3•3H2O) is a non-marine evaporite mineral. It is mined as the primary source of sodium carbonate in the United States, where it has replaced ...
, a mineral used in manufacturing glass, paper, soaps, baking soda, water softeners, and pharmaceuticals. In 2008, Wyoming produced 46 million short tons (41.7 million metric tons) of trona, 25% of the world's production.
* Because of its geography and altitude, the potential for wind power in Wyoming is one of the highest of any U.S. state. The Chokecherry and Sierra Madre Wind Energy Project is the largest commercial wind generation facility under development in North America. Carbon County, Wyoming, Carbon County is home to the largest proposed wind farm in the nation. Construction plans have been halted because of proposed new taxes on wind power energy production.
* Although uranium mining in Wyoming is much less active than in previous decades, recent increases in uranium's price have generated new interest in prospecting and mining.
Taxes
Unlike most other states, Wyoming levies no individual or corporate income tax. It also assesses no tax on retirement income earned and received from another state. Wyoming has a state sales tax of 4%. Counties have the option to collect an additional 1% tax for general revenue and a 1% tax for specific purposes, if approved by voters. Food for human consumption is not subject to sales tax. A county lodging tax varies from 2% to 5%. The state collects a use tax of 5% on items purchased elsewhere and brought into Wyoming. All property tax is based on the proprety's assessed value; Wyoming's Department of Revenue's Ad Valorem Tax Division supports, trains, and guides local government agencies in the uniform assessment, valuation and taxation of locally assessed property. "Assessed value" means taxable value; "taxable value" means a percentage of the fair market value of property in a particular class. Statutes limit property tax increases. For county revenue, the property tax rate cannot exceed 12 Mill (currency), mills (or 1.2%) of assessed value. For cities and towns, the rate is limited to eight Mill (currency), mills (0.8%). With very few exceptions, state law limits the property tax rate for all governmental purposes. Personal property held for personal use is tax-exempt. Inventory held for resale, pollution control equipment, cash, accounts receivable, stocks and bonds are also exempt. Other exemptions include property used for religious, educational, charitable, fraternal, benevolent and government purposes and improvements for handicapped access. Mine lands, underground mining equipment, and oil and gas extraction equipment are exempt from property tax, but companies must pay a gross products tax on minerals and a severance tax on mineral production. Wyoming does not collect inheritance taxes. There is limited estate tax related to federal estate tax collection. In 2008, the Tax Foundation reported that Wyoming had the most "business-friendly" tax climate of any U.S. state. Wyoming state and local governments in fiscal year 2007 collected $2.242 billion in taxes, levies, and royalties from the oil and gas industry. The state's mineral industry, including oil, gas,trona
Trona (trisodium hydrogendicarbonate dihydrate, also sodium sesquicarbonate dihydrate, Na2CO3•2NaHCO3•3H2O) is a non-marine evaporite mineral. It is mined as the primary source of sodium carbonate in the United States, where it has replaced ...
, and coal, provided $1.3 billion in property taxes from 2006 mineral production. As of 2017, Wyoming receives more federal tax dollars as a percentage of state general revenue than any state except Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
.
As of 2016, Wyoming does not require the beneficial owners of LLCs to be disclosed in the filing, which creates an opportunity for a tax haven, according to Clark Stith of Clark Stith & Associates.
Transportation
Interstate 80
Interstate 80 (I-80) is an east–west transcontinental freeway that crosses the United States from downtown San Francisco, California, to Teaneck, New Jersey, in the New York metropolitan area. The highway was designated in 1956 as one o ...
crosses the Utah border west of Evanston, Wyoming, Evanston and runs east through the southern third of the state, passing through Cheyenne before entering Nebraska near Pine Bluffs, Wyoming, Pine Bluffs. Interstate 90 in Wyoming, Interstate 90 comes into Wyoming near Parkman, Wyoming, Parkman and cuts through the northeastern part of the state. It serves Gillette, Wyoming, Gillette and enters South Dakota east of Sundance, Wyoming, Sundance.
U.S. Routes U.S. Route 14, 14, U.S. Route 16, 16, and U.S. Route 20#Eastern Section, the eastern section of U.S. 20 have their western terminus at the eastern entrance to Yellowstone National Park and pass through Cody, Wyoming, Cody. U.S. 14 runs eastward before joining I-90 at Gillette, Wyoming, Gillette. U.S. 14 then follows I-90 to the South Dakota border. U.S. 16 and 20 split off of U.S. 14 at Greybull, Wyoming, Greybull and U.S. 16 turns east at Worland, Wyoming, Worland while U.S. 20 continues south Shoshoni, Wyoming, Shoshoni. U.S. Route 287 runs from Fort Collins, Colorado, to Laramie, Wyoming, through a pass between the Laramie Mountains and the Medicine Bow Mountains, then merges with US 30 and I-80 until it reaches Rawlins, where it continues north, passing Lander. Outside of Moran, Wyoming, Moran, U.S. 287 is part of a large interchange with U.S. Highways 26, 191, and 89, before continuing north to Yellowstone's southern entrance. U.S. 287 continues north of Yellowstone, but the park separates the two sections.
Other United States Numbered Highways, U.S. highways that pass through Wyoming are U.S. Highway 18 (Wyoming), 18, U.S. Highway 26 (Wyoming), 26, U.S. Highway 30 (Wyoming), 30, U.S. Highway 85 (Wyoming), 85, U.S. Highway 87 (Wyoming), 87, U.S. Highway 89 (Wyoming), 89, U.S. Highway 189 (Wyoming), 189, U.S. Highway 191 (Wyoming), 191, U.S. Highway 212 (Wyoming), 212, and U.S. Highway 287 (Wyoming), 287.
Wyoming is one of only two states (the other is South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota people, Lakota and Dakota peo ...
) in the 48 contiguous states not served by Amtrak. It was once served by Amtrak's San Francisco Zephyr and Pioneer (Amtrak), Pioneer lines. While no passenger trains roll through Wyoming today, intercity buses continue to connect residents across the state. Intercity bus carriers in the state include Express Arrow, Greyhound Lines, and Jefferson Lines.
Major interstates
* (300.5 mi) connects Denver,Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enroll ...
, Casper, Wyoming, Casper and Buffalo, Wyoming, Buffalo. Most of the highway is connected with U.S. Route 87, US 87. Major junctions include Interstate 80
Interstate 80 (I-80) is an east–west transcontinental freeway that crosses the United States from downtown San Francisco, California, to Teaneck, New Jersey, in the New York metropolitan area. The highway was designated in 1956 as one o ...
, U.S. Route 30, US 30, U.S. Route 85, US 85, U.S. Route 26, US 26, US Routes U.S. Route 18, 18 & U.S. Route 20, 20 and U.S. Route 16, US 16 before its northern terminus at Interstate 90 in Wyoming, Interstate 90 in Buffalo.
* (402.8 mi) connects Evanston, Wyoming, Evanston, Rock Springs, Wyoming, Rock Springs, Rawlins, Wyoming, Rawlins, Laramie and Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enroll ...
. Major junctions include U.S. Route 191, US 191, U.S. Route 287, US 287, Interstate 25 in Wyoming, I-25, and U.S. Route 85, US 85 & Interstate 180 (Wyoming), I-180.
* (208.8 mi) connects Sheridan, Wyoming, Sheridan, Buffalo, Wyoming, Buffalo and Gillette, Wyoming, Gillette. Primarily in northeastern Wyoming. Major junctions include U.S. Route 14, US 14, Interstate 25 in Wyoming, I-25 and U.S. Route 16, US 16.
Wind River Indian Reservation
as the result of negotiations with the federal government in the Fort Bridger Treaty, PBS. Independent Lens but the federal government forced the Northern Arapaho onto the Shoshone reservation in 1876 after it failed to provide a promised separate reservation. Today the Wind River Indian Reservation is jointly owned, with each tribe having a 50% interest in the land, water, and other natural resources. It is a sovereign, self-governed land with two independent governing bodies: the Eastern Shoshone Tribe and the Northern Arapaho Tribe. Until 2014, the Shoshone Business Council and Northern Arapaho Business Council met jointly as the Joint Business Council to decide matters that affect both tribes. Six elected council members from each tribe served on the joint council.
Public lands
 The federal government owns nearly half of Wyoming's land (about ); the state owns another .MainEnvironment.org
The federal government owns nearly half of Wyoming's land (about ); the state owns another .MainEnvironment.orgPublic Land Ownership by State, 1995 Main Environment.org Most of it is administered by the Bureau of Land Management and United States Forest Service, U.S. Forest Service in numerous United States National Forest, national forests and a United States National Grassland, national grassland, not to mention vast swaths of "public" land and an Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, air force base near Cheyenne.
 There are also areas managed by the National Park Service and agencies such as the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
:National parks
*
There are also areas managed by the National Park Service and agencies such as the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
:National parks
* Grand Teton National Park
Grand Teton National Park is an American national park in northwestern Wyoming. At approximately , the park includes the major peaks of the Teton Range as well as most of the northern sections of the valley known as Jackson Hole. Grand Teton Na ...
* Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
—first designated national park in the world
:Memorial parkway
* The John D. Rockefeller Jr. Memorial Parkway connects Yellowstone and Grand Teton.
:National recreation areas
* Bighorn Canyon National Recreation Area
* Flaming Gorge National Recreation Area (managed by the Forest Service as part of Ashley National Forest)
:National monuments
* Devils Tower, Devils Tower National Monument—first national monument in the U.S.
* Fossil Butte National Monument
:National historic trails, landmarks and sites
* California Trail, California National Historic Trail
* Fort Laramie National Historic Site
* Independence Rock (Wyoming), Independence Rock National Historic Landmark
* Medicine Wheel/Medicine Mountain National Historic Landmark
* Mormon Trail, Mormon Pioneer National Historic Trail
* National Register of Historic Places listings in Wyoming
* Oregon Trail, Oregon National Historic Trail
* Pony Express, Pony Express National Historic Trail
:National fish hatcheries
* Jackson National Fish Hatchery
* Saratoga National Fish Hatchery
:National wildlife refuges
* National Elk Refuge
* Seedskadee National Wildlife Refuge
Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
File:A110, Devils Tower National Monument, Wyoming, USA, 2004.jpg, Devils Tower, Devils Tower National Monument
File:Thunder Basin National Grassland Douglas.jpg, Thunder Basin National Grassland
File:Seedskadee nwr sunset.jpg, Seedskadee National Wildlife Refuge
Education
Higher education
Wyoming has a public four-year institution, the University of Wyoming in Laramie, and a private four-year college, Wyoming Catholic College, in Lander, Wyoming, Lander. There are also seven two-year community colleges. Before the passing of a new law in 2006, Wyoming had hosted unaccredited institutions, many of them suspected diploma mills. The 2006 law requires unaccredited institutions to make one of three choices: move out of Wyoming, close down, or apply for accreditation. The Oregon State Office of Degree Authorization predicted in 2007 that in a few years the problem of diploma mills in Wyoming might be resolved.Media
Wyoming's media market consists of 16 broadcast TV stations, radio stations and dozens of small to medium-sized newspapers. There are also a few small independent news sources such as the nonprofit news site Wyofile.com and Oil City News.Government and politics

State government
Wyoming's Constitution established three branches of government: the List of Governors of Wyoming, executive, Wyoming Legislature, legislative, and Wyoming Supreme Court, judicial branches. The Wyoming State Legislature, state legislature comprises a Wyoming House of Representatives, House of Representatives with 60 members and a Wyoming Senate, Senate with 30 members. The executive branch is headed by the Governor of Wyoming, governor and includes a Secretary of State of Wyoming, secretary of state, Wyoming State Auditor, auditor, treasurer, and superintendent of public instruction. As Wyoming does not have a Lieutenant governor (United States)#Wyoming, lieutenant governor, the secretary of state is first in the line of succession. Wyoming's sparse population warrants the state only one at-large seat in theU.S. House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
, and hence only three votes in the Electoral College (United States), Electoral College.
The Wyoming State Liquor Association is the state's sole legal wholesale distributor of spirits, making it an alcoholic beverage control state. With the exception of wine, state law prohibits the purchase of alcoholic beverages for resale from any other source.
Judicial system
Wyoming's highest court is the Supreme Court of Wyoming, with five justices presiding over appeals from the state's lower courts. Wyoming is unusual in that it does not have an intermediate appellate court, like most states. This is largely attributable to the state's population and correspondingly lower caseload. Appeals from the state district courts go directly to the Wyoming Supreme Court. Wyoming also has state circuit courts (formerly county courts), of limited jurisdiction, which handle certain types of cases, such as civil claims with lower dollar amounts, misdemeanor criminal offenses, and felony arraignments. Circuit court judges also commonly hear small claims cases as well. Before 1972, Wyoming judges were selected by popular vote on a nonpartisan ballot. This earlier system was criticized by the state bar who called for the adoption of the Missouri Plan, a system designed to balance judiciary independence with judiciary accountability. In 1972, an amendment to Article5 of the Wyoming Constitution, which incorporated a modified version of the plan, was adopted by the voters. Since the adoption of the amendment, all state court judges in Wyoming are nominated by the Judicial Nominating Commission and appointed by the Governor. They are then subject to a retention vote by the electorate one year after appointment.Political history
Culture
Sports
Due to its sparse population, Wyoming lacks any major professional sports teams; the Wyoming Mustangs, an Indoor American football, indoor football team based in Gillette that began play in 2021, is the only professional team in the state. However, the Wyoming Cowboys and Cowgirls—particularly the football and basketball teams—are quite popular; their stadiums in Laramie are about 7,200 feet (2,200 m) above sea level, the highest in NCAA Division I, NCAA DivisionI. The Wyoming High School Activities Association also sponsors twelve sports and there are three junior ice hockey teams, all of which are members of the North American 3 Hockey League, NA3HL. Casper, Wyoming, Casper has hosted the College National Finals Rodeo since 2001.State symbols
 List of all Wyoming state symbols:
* List of U.S. state birds, State bird: western meadowlark (''Sturnella neglecta'')
* State coin: Sacagawea dollar
* State dinosaur: ''Triceratops''
* State emblem: Bucking Horse and Rider
* State fish: cutthroat trout (''Oncorhynchus clarki'')
* Flags of the U.S. states, State flag: Flag of the State of Wyoming
* List of U.S. state flowers, State flower: Castilleja linariifolia, Wyoming Indian paintbrush (''Castilleja linariifolia'')
* State fossil: ''Knightia''
* List of U.S. state minerals, rocks, stones and gemstones, State gemstone: Nephrite, Wyoming nephrite jade
* List of U.S. state grasses, State grass: Pascopyrum, western wheatgrass (''Pascopyrum smithii'')
* List of U.S. state insects, State insect: Callophrys sheridanii, Sheridan's green hairstreak butterfly (''Callophrys sheridanii'')
* List of U.S. state mammals, State mammal: American bison (''Bison bison'')
* List of U.S. state mottos, State motto: ''Equal Rights (motto), Equal Rights''
* List of U.S. state nicknames, State nicknames: Equality State; Cowboy State; Big Wyoming
* State reptile: horned lizard (''Phrynosoma douglassi brevirostre'')
* Seals of the U.S. states, State seal: Great Seal of the State of Wyoming
* List of U.S. state songs, State song: "Wyoming (song), Wyoming" by Charles E. Winter & George E. Knapp
* List of U.S. state sports, State sport: rodeo
* List of U.S. state trees, State tree: plains cottonwood (''Populus sargentii'')
List of all Wyoming state symbols:
* List of U.S. state birds, State bird: western meadowlark (''Sturnella neglecta'')
* State coin: Sacagawea dollar
* State dinosaur: ''Triceratops''
* State emblem: Bucking Horse and Rider
* State fish: cutthroat trout (''Oncorhynchus clarki'')
* Flags of the U.S. states, State flag: Flag of the State of Wyoming
* List of U.S. state flowers, State flower: Castilleja linariifolia, Wyoming Indian paintbrush (''Castilleja linariifolia'')
* State fossil: ''Knightia''
* List of U.S. state minerals, rocks, stones and gemstones, State gemstone: Nephrite, Wyoming nephrite jade
* List of U.S. state grasses, State grass: Pascopyrum, western wheatgrass (''Pascopyrum smithii'')
* List of U.S. state insects, State insect: Callophrys sheridanii, Sheridan's green hairstreak butterfly (''Callophrys sheridanii'')
* List of U.S. state mammals, State mammal: American bison (''Bison bison'')
* List of U.S. state mottos, State motto: ''Equal Rights (motto), Equal Rights''
* List of U.S. state nicknames, State nicknames: Equality State; Cowboy State; Big Wyoming
* State reptile: horned lizard (''Phrynosoma douglassi brevirostre'')
* Seals of the U.S. states, State seal: Great Seal of the State of Wyoming
* List of U.S. state songs, State song: "Wyoming (song), Wyoming" by Charles E. Winter & George E. Knapp
* List of U.S. state sports, State sport: rodeo
* List of U.S. state trees, State tree: plains cottonwood (''Populus sargentii'')
See also
*Bibliography of Wyoming history *Index of Wyoming-related articles *Outline of WyomingNotes
References
External links
State of Wyoming government official website
Official Wyoming State Travel Website
Wyoming State Facts from USDA
* * {{coord, 43, -107, dim:300000_region:US-WY_type:adm1st, name=State of Wyoming, display=title Wyoming, 1890 establishments in the United States States and territories established in 1890 States of the United States Western United States Contiguous United States