Winter Olympics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Winter Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'hiver) is a major international multi-sport event held once every four years for sports practiced on snow and ice. The first Winter Olympic Games, the 1924 Winter Olympics, were held in Chamonix, France. The modern Olympic Games were inspired by the
 A predecessor, the Nordic Games, were organized by General Viktor Gustaf Balck in
A predecessor, the Nordic Games, were organized by General Viktor Gustaf Balck in
 The first Olympics after the war, the
The first Olympics after the war, the
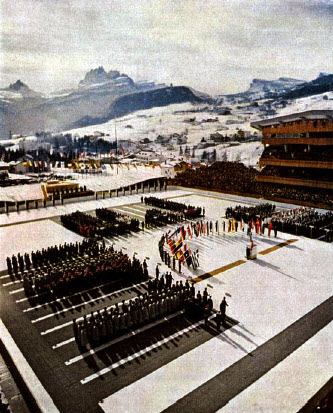 St. Moritz was selected to host the first post-war games, in 1948. Switzerland's neutrality had protected the town during World War II, and most venues from the 1928 games remained in place, which made St. Moritz a logical choice. It became the first city to host a Winter Olympics twice. Twenty-eight countries competed in Switzerland, but athletes from Germany and Japan were not invited. Controversy erupted when two hockey teams from the
St. Moritz was selected to host the first post-war games, in 1948. Switzerland's neutrality had protected the town during World War II, and most venues from the 1928 games remained in place, which made St. Moritz a logical choice. It became the first city to host a Winter Olympics twice. Twenty-eight countries competed in Switzerland, but athletes from Germany and Japan were not invited. Controversy erupted when two hockey teams from the
 The Austrian city of Innsbruck was the host in 1964. Although Innsbruck was a traditional winter sports resort, warm weather caused a lack of snow during the games and the Austrian army was enlisted to transport snow and ice to the sports venues. Soviet Union at the 1964 Winter Olympics, Soviet speed-skater Lidia Skoblikova made history by winning all four-speed skating events. Her career total of six gold medals set a record for Winter Olympics athletes. Luge was first contested in 1964, but the sport received bad publicity when a competitor was killed in a pre-Olympic training run.
Held in the French town of Grenoble, the 1968 Winter Olympics were the first Olympic Games to be broadcast in colour. There were 1,158 athletes from 37 nations competing in 35 events. France at the 1968 Winter Olympics, French alpine ski racer Jean-Claude Killy became only the second person to win all the men's alpine skiing events. The organising committee sold television rights for US$2 million, which was more than twice the cost of the broadcast rights for the Innsbruck Games.Findling and Pelle (2004), p. 277 Venues were spread over long distances requiring three athletes' villages. The organisers claimed that this was necessary to accommodate technological advances, however, critics disputed this, alleging that the layout would incorporate the best possible venues for television broadcasts at the athletes' expense.
The 1972 Winter Olympics, 1972 Winter Games, held in
The Austrian city of Innsbruck was the host in 1964. Although Innsbruck was a traditional winter sports resort, warm weather caused a lack of snow during the games and the Austrian army was enlisted to transport snow and ice to the sports venues. Soviet Union at the 1964 Winter Olympics, Soviet speed-skater Lidia Skoblikova made history by winning all four-speed skating events. Her career total of six gold medals set a record for Winter Olympics athletes. Luge was first contested in 1964, but the sport received bad publicity when a competitor was killed in a pre-Olympic training run.
Held in the French town of Grenoble, the 1968 Winter Olympics were the first Olympic Games to be broadcast in colour. There were 1,158 athletes from 37 nations competing in 35 events. France at the 1968 Winter Olympics, French alpine ski racer Jean-Claude Killy became only the second person to win all the men's alpine skiing events. The organising committee sold television rights for US$2 million, which was more than twice the cost of the broadcast rights for the Innsbruck Games.Findling and Pelle (2004), p. 277 Venues were spread over long distances requiring three athletes' villages. The organisers claimed that this was necessary to accommodate technological advances, however, critics disputed this, alleging that the layout would incorporate the best possible venues for television broadcasts at the athletes' expense.
The 1972 Winter Olympics, 1972 Winter Games, held in

 In 1988, the Canadian city of Calgary hosted the 1988 Winter Olympics, first Winter Olympics to span three weekends, lasting for a total of 16 days. New events were added in ski-jumping and speed skating, while future Olympic sports curling, short track speed skating and freestyle skiing made their debut appearance as demonstration sports. The speed skating events were held indoors for the first time, on the Olympic Oval. Dutch skater Yvonne van Gennip won three gold medals and set two world records, beating skaters from the favoured East Germany at the 1988 Winter Olympics, East German team in every race.
Her medal total was equalled by Finland at the 1988 Winter Olympics, Finnish ski jumper Matti Nykänen, who won all three events in his sport. Alberto Tomba, Italy at the 1988 Winter Olympics, an Italian skier, made his Olympic debut by winning both the giant slalom and slalom. Ski jumper Eddie the Eagle competed in the 70m and 90m in finishing last with a British ski jumping records, British record of 73.5 metres. East German Christa Luding-Rothenburger, Christa Rothenburger won the women's 1,000 metre speed skating event. Seven months later she would earn a silver in track cycling at the 1988 Summer Olympics, Summer Games in Seoul, to become the only athlete to win medals in both a Summer and Winter Olympics in the same year.
The 1992 Winter Olympics, 1992 Winter Games were the last to be held in the same year as the 1992 Summer Olympics, Summer Games. They were hosted in the French Savoie region, with 18 events held in the city of Albertville and the remaining events spread out over the Savoie. Political changes of the time were reflected in the composition of the Olympic teams competing in France: this was the first Games to be held after the fall of Communism and the fall of the Berlin Wall, and Germany competed as a single nation for the first time since the 1964 Games.Findling and Pelle (2004), p. 400
Former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavian republics Croatia at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Croatia and Slovenia at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Slovenia made their debuts as independent nations; most of the former Soviet Union, Soviet republics still competed as a single team known as the Unified Team at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Unified Team, but the Baltic States made independent appearances for the first time since before World War II. At 16 years old, Finland at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Finnish ski jumper Toni Nieminen made history by becoming the youngest male Winter Olympic champion. New Zealand at the 1992 Winter Olympics, New Zealand skier Annelise Coberger became the first Winter Olympic medallist from the southern hemisphere when she won a silver medal in the women's slalom.
The 1994 Winter Olympics, held in Lillehammer, Norway, were the first Winter Games to be held in a different year from the Summer Games. This change resulted from the decision reached in the List of IOC meetings#IOC Sessions, 91st IOC Session (1986) to separate the Summer and Winter Games and place them in alternating even-numbered years. Lillehammer is the northernmost city to ever host the Winter Games. It was the second time the Games were held in Norway, after the 1952 Winter Olympics in
In 1988, the Canadian city of Calgary hosted the 1988 Winter Olympics, first Winter Olympics to span three weekends, lasting for a total of 16 days. New events were added in ski-jumping and speed skating, while future Olympic sports curling, short track speed skating and freestyle skiing made their debut appearance as demonstration sports. The speed skating events were held indoors for the first time, on the Olympic Oval. Dutch skater Yvonne van Gennip won three gold medals and set two world records, beating skaters from the favoured East Germany at the 1988 Winter Olympics, East German team in every race.
Her medal total was equalled by Finland at the 1988 Winter Olympics, Finnish ski jumper Matti Nykänen, who won all three events in his sport. Alberto Tomba, Italy at the 1988 Winter Olympics, an Italian skier, made his Olympic debut by winning both the giant slalom and slalom. Ski jumper Eddie the Eagle competed in the 70m and 90m in finishing last with a British ski jumping records, British record of 73.5 metres. East German Christa Luding-Rothenburger, Christa Rothenburger won the women's 1,000 metre speed skating event. Seven months later she would earn a silver in track cycling at the 1988 Summer Olympics, Summer Games in Seoul, to become the only athlete to win medals in both a Summer and Winter Olympics in the same year.
The 1992 Winter Olympics, 1992 Winter Games were the last to be held in the same year as the 1992 Summer Olympics, Summer Games. They were hosted in the French Savoie region, with 18 events held in the city of Albertville and the remaining events spread out over the Savoie. Political changes of the time were reflected in the composition of the Olympic teams competing in France: this was the first Games to be held after the fall of Communism and the fall of the Berlin Wall, and Germany competed as a single nation for the first time since the 1964 Games.Findling and Pelle (2004), p. 400
Former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavian republics Croatia at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Croatia and Slovenia at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Slovenia made their debuts as independent nations; most of the former Soviet Union, Soviet republics still competed as a single team known as the Unified Team at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Unified Team, but the Baltic States made independent appearances for the first time since before World War II. At 16 years old, Finland at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Finnish ski jumper Toni Nieminen made history by becoming the youngest male Winter Olympic champion. New Zealand at the 1992 Winter Olympics, New Zealand skier Annelise Coberger became the first Winter Olympic medallist from the southern hemisphere when she won a silver medal in the women's slalom.
The 1994 Winter Olympics, held in Lillehammer, Norway, were the first Winter Games to be held in a different year from the Summer Games. This change resulted from the decision reached in the List of IOC meetings#IOC Sessions, 91st IOC Session (1986) to separate the Summer and Winter Games and place them in alternating even-numbered years. Lillehammer is the northernmost city to ever host the Winter Games. It was the second time the Games were held in Norway, after the 1952 Winter Olympics in
 2002 Winter Olympic bid scandal, After a tumultuous host city process, the 2002 Winter Olympics were held in Salt Lake City, Utah, Salt Lake City, United States. 2,399 athletes from 77 National Olympic Committees participated at 78 events in 7 sports. These Games were the first to take place since the September 11 attacks of 2001, which meant a higher degree of security to avoid a terrorist attack. The opening ceremony saw signs of the Aftermath of the September 11 attacks, aftermath of the events of that day, including the flag that flew at World Trade Center site, Ground Zero, and honour guards of NYPD and New York City Fire Department, FDNY members.
Germany at the 2002 Winter Olympics, German Georg Hackl won a silver in the singles luge, becoming the first athlete in Olympic history to win medals in the same individual event in five consecutive Olympics. Canada at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Canada achieved an unprecedented double by winning both the men's and women's Ice hockey at the 2002 Winter Olympics, ice hockey gold medals. Canada became embroiled with Russia at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Russia in a 2002 Olympic Winter Games figure skating scandal, controversy that involved the judging of the Figure skating at the 2002 Winter Olympics, pairs figure skating competition. The Russian pair of Yelena Berezhnaya and Anton Sikharulidze competed against the Canadian pair of Jamie Salé and David Pelletier for the gold medal.
The Canadians appeared to have skated well enough to win the competition, yet the Russians were awarded the gold. The France at the 2002 Winter Olympics, French judge, Marie-Reine Le Gougne, awarded the gold to the Russians. An investigation revealed that she had been pressured to give the gold to the Russian pair regardless of how they skated; in return, the Russian judge would look favourably on the French entrants in the ice dancing competition.
The IOC decided to award both pairs the gold medal in a second Olympic Games ceremony, medal ceremony held later in the Games. Australia at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Australian Steven Bradbury (speed skater), Steven Bradbury became the first gold medallist from the southern hemisphere when he won the 1,000 metre short-track speed skating event.
2002 Winter Olympic bid scandal, After a tumultuous host city process, the 2002 Winter Olympics were held in Salt Lake City, Utah, Salt Lake City, United States. 2,399 athletes from 77 National Olympic Committees participated at 78 events in 7 sports. These Games were the first to take place since the September 11 attacks of 2001, which meant a higher degree of security to avoid a terrorist attack. The opening ceremony saw signs of the Aftermath of the September 11 attacks, aftermath of the events of that day, including the flag that flew at World Trade Center site, Ground Zero, and honour guards of NYPD and New York City Fire Department, FDNY members.
Germany at the 2002 Winter Olympics, German Georg Hackl won a silver in the singles luge, becoming the first athlete in Olympic history to win medals in the same individual event in five consecutive Olympics. Canada at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Canada achieved an unprecedented double by winning both the men's and women's Ice hockey at the 2002 Winter Olympics, ice hockey gold medals. Canada became embroiled with Russia at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Russia in a 2002 Olympic Winter Games figure skating scandal, controversy that involved the judging of the Figure skating at the 2002 Winter Olympics, pairs figure skating competition. The Russian pair of Yelena Berezhnaya and Anton Sikharulidze competed against the Canadian pair of Jamie Salé and David Pelletier for the gold medal.
The Canadians appeared to have skated well enough to win the competition, yet the Russians were awarded the gold. The France at the 2002 Winter Olympics, French judge, Marie-Reine Le Gougne, awarded the gold to the Russians. An investigation revealed that she had been pressured to give the gold to the Russian pair regardless of how they skated; in return, the Russian judge would look favourably on the French entrants in the ice dancing competition.
The IOC decided to award both pairs the gold medal in a second Olympic Games ceremony, medal ceremony held later in the Games. Australia at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Australian Steven Bradbury (speed skater), Steven Bradbury became the first gold medallist from the southern hemisphere when he won the 1,000 metre short-track speed skating event.
 The Italian city of Turin hosted the 2006 Winter Olympics. It was the second time that Italy had hosted the Winter Olympic Games. South Korea at the 2006 Winter Olympics, South Korean athletes won 10 medals, including 6 gold in the short-track speed skating events. Jin Sun-Yu, Sun-Yu Jin won three gold medals while her teammate Hyun-Soo Ahn won three gold medals and a bronze. In the women's Cross-country skiing at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Cross-Country team pursuit Canada at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Canadian Sara Renner broke one of her poles and, when he saw her dilemma, Norway at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Norwegian coach Bjørnar Håkensmoen decided to lend her a pole. In so doing she was able to help her team win a silver medal in the event at the expense of the Norwegian team, who finished fourth.
On winning the Super-G, Kjetil-Andre Aamodt of Norway became the most decorated ski racer of all time with 4 gold and 8 overall medals. He is also the only ski racer to have won the same event at three Olympics, winning the Super-G in
The Italian city of Turin hosted the 2006 Winter Olympics. It was the second time that Italy had hosted the Winter Olympic Games. South Korea at the 2006 Winter Olympics, South Korean athletes won 10 medals, including 6 gold in the short-track speed skating events. Jin Sun-Yu, Sun-Yu Jin won three gold medals while her teammate Hyun-Soo Ahn won three gold medals and a bronze. In the women's Cross-country skiing at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Cross-Country team pursuit Canada at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Canadian Sara Renner broke one of her poles and, when he saw her dilemma, Norway at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Norwegian coach Bjørnar Håkensmoen decided to lend her a pole. In so doing she was able to help her team win a silver medal in the event at the expense of the Norwegian team, who finished fourth.
On winning the Super-G, Kjetil-Andre Aamodt of Norway became the most decorated ski racer of all time with 4 gold and 8 overall medals. He is also the only ski racer to have won the same event at three Olympics, winning the Super-G in
 The process for awarding host city honours came under intense scrutiny after Salt Lake City had been awarded the right to host the 2002 Games. Soon after the host city had been announced it was discovered that the organisers had engaged in an elaborate bribery 2002 Winter Olympic bid scandal, scheme to curry favour with IOC officials. Gifts and other financial considerations were given to those who would evaluate and vote on Salt Lake City's bid. These gifts included medical treatment for relatives, a college scholarship for one member's son and a land deal in Utah. Even IOC president Juan Antonio Samaranch received two rifles valued at $2,000. Samaranch defended the gift as inconsequential since, as president, he was a non-voting member.Cashmore (2005), p. 444
The subsequent investigation uncovered inconsistencies in the bids for every Olympics (both Summer and Winter) since 1988. For example, the gifts received by IOC members from the Japanese Organising Committee for Nagano's bid for the 1998 Winter Olympics were described by the investigation committee as "astronomical". Although nothing strictly illegal had been done, the IOC feared that corporate sponsors would lose faith in the integrity of the process and that the Olympic brand would be tarnished to such an extent that advertisers would begin to pull their support.
The investigation resulted in the expulsion of 10 IOC members and the sanctioning of another 10. New terms and age limits were established for IOC membership, and 15 former Olympic athletes were added to the committee. Stricter rules for future bids were imposed, with ceilings imposed on the value of gifts IOC members could accept from bid cities.
The process for awarding host city honours came under intense scrutiny after Salt Lake City had been awarded the right to host the 2002 Games. Soon after the host city had been announced it was discovered that the organisers had engaged in an elaborate bribery 2002 Winter Olympic bid scandal, scheme to curry favour with IOC officials. Gifts and other financial considerations were given to those who would evaluate and vote on Salt Lake City's bid. These gifts included medical treatment for relatives, a college scholarship for one member's son and a land deal in Utah. Even IOC president Juan Antonio Samaranch received two rifles valued at $2,000. Samaranch defended the gift as inconsequential since, as president, he was a non-voting member.Cashmore (2005), p. 444
The subsequent investigation uncovered inconsistencies in the bids for every Olympics (both Summer and Winter) since 1988. For example, the gifts received by IOC members from the Japanese Organising Committee for Nagano's bid for the 1998 Winter Olympics were described by the investigation committee as "astronomical". Although nothing strictly illegal had been done, the IOC feared that corporate sponsors would lose faith in the integrity of the process and that the Olympic brand would be tarnished to such an extent that advertisers would begin to pull their support.
The investigation resulted in the expulsion of 10 IOC members and the sanctioning of another 10. New terms and age limits were established for IOC membership, and 15 former Olympic athletes were added to the committee. Stricter rules for future bids were imposed, with ceilings imposed on the value of gifts IOC members could accept from bid cities.
 The Winter Olympics have been an ideological front in the Cold War since the
The Winter Olympics have been an ideological front in the Cold War since the
 * This office is technically not head of state in and of itself, but is the presiding officer of the Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council which collectively acts as head of state.
* IOC records state Hitler opened these Games as "Chancellor" (head of government), but in 1934 that office was consolidated with "President" (head of state) into "''Führer und Reichskanzler''", or "Führer".
* Unlike the Summer Olympics, the cancelled 1940 Winter Olympics and 1944 Winter Olympics are ''not'' included in the official Roman numeral counts for the Winter Games. While the official titles of the Summer Games count Olympiads, the titles of the Winter Games only count the Games themselves.
* Th
* This office is technically not head of state in and of itself, but is the presiding officer of the Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council which collectively acts as head of state.
* IOC records state Hitler opened these Games as "Chancellor" (head of government), but in 1934 that office was consolidated with "President" (head of state) into "''Führer und Reichskanzler''", or "Führer".
* Unlike the Summer Olympics, the cancelled 1940 Winter Olympics and 1944 Winter Olympics are ''not'' included in the official Roman numeral counts for the Winter Games. While the official titles of the Summer Games count Olympiads, the titles of the Winter Games only count the Games themselves.
* Th
IOC site for the 2002 Winter Olympic Games
gives an erroneous figure of 77 participated teams; however, one can count 78 participated nations looking throug
Official Report of the XIX Olympic Winter Games
This error probably resulted from the fact that Costa Rica's delegation of one athlete joined the Games after the Opening Ceremony, so 77 nations participated in Opening Ceremony and 78 nations participated in the Games. * The IOC site for th
2018 Winter Olympic Games
does not include Korea at the 2018 Winter Olympics, United Korean (COR) women's ice hockey team as separate "nation" when counting participating nations. Nevertheless the IOC shows the Korean team in th
Pyeongchang 2018 Ice Hockey Women's Tournament Results
Thus, 92 national teams plus 1 team composed of athletes from both South Korea and North Korea participated in the Games. * Xi Jinping is the "President of the People's Republic of China, Chinese President", ''de jure'' head of state. Xi is also ''de facto'' Paramount leader, ruler as General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party.
Olympic Games
IOC official website
Winter Olympic Sports
IOC official website {{Authority control Winter Olympic Games, Recurring sporting events established in 1924 Winter multi-sport events Quadrennial sporting events February sporting events
ancient Olympic Games
The ancient Olympic Games (Ὀλυμπιακοὶ ἀγῶνες; la, Olympia, neuter plural: "the Olympics") were a series of athletic competitions among representatives of city-states and were one of the Panhellenic Games of Ancient Greece ...
, which were held in Olympia, Greece, from the 8th century BC to the 4th century AD. Baron Pierre de Coubertin
Charles Pierre de Frédy, Baron de Coubertin (; born Pierre de Frédy; ...
founded the International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swis ...
(IOC) in 1894, leading to the first modern Summer Olympic Games
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The ina ...
in Athens, Greece in 1896. The IOC is the governing body of the Olympic Movement, with the Olympic Charter
The Olympic Charter is a set of rules and guidelines for the organisation of the Olympic Games, and for governing the Olympic movement. Its last revision was on the 17th of July 2020 during the 136th IOC Session, held by video conference. Ado ...
defining its structure and authority.
The original five Winter Olympic Sports (consisting of nine disciplines) were bobsleigh
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a team winter sport that involves making timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. International bobsleigh competitions are governed by the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Fede ...
, curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
, ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
, Nordic skiing
Nordic skiing encompasses the various types of skiing in which the toe of the ski boot is fixed to the binding in a manner that allows the heel to rise off the ski, unlike alpine skiing, where the boot is attached to the ski from toe to heel. ...
(consisting of the disciplines military patrol, cross-country skiing
Cross-country skiing is a form of skiing where skiers rely on their own locomotion to move across snow-covered terrain, rather than using ski lifts or other forms of assistance. Cross-country skiing is widely practiced as a sport and recreatio ...
, Nordic combined, and ski jumping), and skating (consisting of the disciplines figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, when contested at the 1908 Olympics in London. The Olympic disciplines are me ...
and speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
). The Games were held every four years from 1924 to 1936, interrupted in 1940 and 1944 by World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, and resumed in 1948
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
. Until 1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment building in Amsterdam after two of its engin ...
, the Summer Olympic Games
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The ina ...
and the Winter Olympic Games were held in the same year, and in accordance with the 1986 decision by the IOC to place the Summer Olympic Games and the Winter Olympic Games on separate four-year cycles in alternating even-numbered years, the next Winter Olympic Games after 1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment building in Amsterdam after two of its engin ...
were held in 1994
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which sank in the Baltic Sea; Nels ...
.
The Winter Olympic Games have evolved since their inception. Sports and disciplines have been added and some of them, such as alpine skiing
Alpine skiing, or downhill skiing, is the pastime of sliding down snow-covered slopes on skis with fixed-heel bindings, unlike other types of skiing ( cross-country, Telemark, or ski jumping), which use skis with free-heel bindings. Whether ...
, luge
A luge is a small one- or two-person sled on which one sleds supine (face up) and feet-first. A luger steers by using the calf muscles to flex the sled's runners or by exerting opposite shoulder pressure to the seat. Racing sleds weigh for ...
, short track speed skating
Short-track speed skating is a form of competitive ice speed skating. In competitions, multiple skaters (typically between four and six) skate on an oval ice track with a length of . The rink itself is long by wide, which is the same size as ...
, freestyle skiing
Freestyle skiing is a skiing discipline comprising aerials, moguls, cross, half-pipe, slopestyle and big air as part of the Winter Olympics. It can consist of a skier performing aerial flips and spins and can include skiers sliding rails an ...
, skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
, and snowboarding
Snowboarding is a recreational and competitive activity that involves descending a snow-covered surface while standing on a snowboard that is almost always attached to a rider's feet. It features in the Winter Olympic Games and Winter Paralympic ...
, have earned a permanent spot on the Olympic program. Some others, including curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
and bobsleigh
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a team winter sport that involves making timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. International bobsleigh competitions are governed by the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Fede ...
, have been discontinued and later reintroduced; others have been permanently discontinued, such as military patrol, though the modern Winter Olympic sport of biathlon is descended from it. Still others, such as speed skiing, bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two teams wearing ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal. The international governing body for bandy is ...
and skijoring
Skijoring (pronounced ) (Skijouring in British English) is a winter sport in which a person on skis is pulled by a horse, a dog (or dogs), another animal, or a motor vehicle. The name is derived from the Norwegian word ''skikjøring'', meaning ...
, were demonstration sports
A demonstration sport, or exhibition sport, is a sport which is played to promote it, rather than as part of standard medal competition. This occurs commonly during the Olympic Games, but may also occur at other sporting events.
Demonstration spor ...
but never incorporated as Olympic sports. The rise of television as a global medium for communication enhanced the profile of the Games. It generated income via the sale of broadcast rights and advertising, which has become lucrative for the IOC. This allowed outside interests, such as television companies and corporate sponsors, to exert influence. The IOC has had to address numerous criticisms over the decades like internal scandals, the use of performance-enhancing drugs by Winter Olympians, as well as a political boycott
A boycott is an act of nonviolent, voluntary abstention from a product, person, organization, or country as an expression of protest. It is usually for moral, social, political, or environmental reasons. The purpose of a boycott is to inflict so ...
of the Winter Olympic Games. Countries have used the Winter Olympic Games as well as the Summer Olympic Games to proclaim the superiority of their political systems.
The Winter Olympic Games have been hosted on three continents by thirteen countries. They have been held four times in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
(1932
Events January
* January 4 – The British authorities in India arrest and intern Mahatma Gandhi and Vallabhbhai Patel.
* January 9 – Sakuradamon Incident: Korean nationalist Lee Bong-chang fails in his effort to assassinate Emperor Hir ...
, 1960
It is also known as the "Year of Africa" because of major events—particularly the independence of seventeen African nations—that focused global attention on the continent and intensified feelings of Pan-Africanism.
Events
January
* Ja ...
, 1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning System time epoch begins at 00:00 UTC.
* January 9 – In ...
, and 2002
File:2002 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 2002 Winter Olympics are held in Salt Lake City; Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother and her daughter Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon die; East Timor gains East Timor independence, indepe ...
), three times in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
(1924
Events
January
* January 12 – Gopinath Saha shoots Ernest Day, whom he has mistaken for Sir Charles Tegart, the police commissioner of Calcutta, and is arrested soon after.
* January 20– 30 – Kuomintang in China hold ...
, 1968
The year was highlighted by protests and other unrests that occurred worldwide.
Events January–February
* January 5 – " Prague Spring": Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia.
* J ...
, and 1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment building in Amsterdam after two of its engin ...
) and twice each in Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
( 1964 and 1976), Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
( 1988 and 2010
File:2010 Events Collage New.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2010 Chile earthquake was one of the strongest recorded in history; The Eruption of Eyjafjallajökull in Iceland disrupts air travel in Europe; A scene from the opening ceremony of ...
), Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
( 1972 and 1998), Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
(1956
Events
January
* January 1 – The Anglo-Egyptian Condominium ends in Sudan.
* January 8 – Operation Auca: Five U.S. evangelical Christian missionaries, Nate Saint, Roger Youderian, Ed McCully, Jim Elliot and Pete Fleming, are kille ...
and 2006
File:2006 Events Collage V1.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2006 Winter Olympics open in Turin; Twitter is founded and launched by Jack Dorsey; The Nintendo Wii is released; Montenegro votes to declare independence from Serbia; The 2006 ...
), Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
( 1952 and 1994
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which sank in the Baltic Sea; Nels ...
) and Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
(1928
Events January
* January – British bacteriologist Frederick Griffith reports the results of Griffith's experiment, indirectly proving the existence of DNA.
* January 1 – Eastern Bloc emigration and defection: Boris Bazhano ...
and 1948
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
). Also, the Winter Olympic Games have been held just once each in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
( 1936), Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
(1984
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeas ...
), Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
(2014
File:2014 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Stocking up supplies and personal protective equipment (PPE) for the Western African Ebola virus epidemic; Citizens examining the ruins after the Chibok schoolgirls kidnapping; Bundles of wa ...
), South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
(2018
File:2018 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2018 Winter Olympics opening ceremony in PyeongChang, South Korea; Protests erupt following the Assassination of Jamal Khashoggi; March for Our Lives protests take place across the United ...
), and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
( 2022). The IOC has selected Italian cities of Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
and Cortina d'Ampezzo
Cortina d'Ampezzo (; lld, Anpezo, ; historical de-AT, Hayden) is a town and ''comune'' in the heart of the southern (Dolomites, Dolomitic) Alps in the Province of Belluno, in the Veneto region of Northern Italy. Situated on the Boite (river), ...
to host the 2026 Winter Olympics
The 2026 Winter Olympics, officially the XXV Olympic Winter Games ( it, XXV Giochi olimpici invernali) and also known as Milano Cortina 2026 ( lld, Milano-Anpezo 2026 or ), is an upcoming international multi-sport event scheduled to take place fr ...
. , no city in the Southern Hemisphere has applied to host the cold-weather-dependent Winter Olympic Games, which are held in February.
, twelve countries have participated in every Winter Olympic GamesAustria, Canada, Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bot ...
, France, Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
, Italy, Norway, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
, Switzerland and the United States. Also, Czechoslovakia participated in all Winter Olympic Games before its dissolution and its successors, Czech Republic and Slovakia have participated in all Winter Games thereafter. Six of these countries have won medals at every Winter Olympic GamesAustria, Canada, Finland, Norway, Sweden, and the United States. The only country to have won a gold medal at every Winter Olympic Games is the United States. Norway leads the all-time Olympic Games medal table
The all-time medal table for all Olympic Games from 1896 to 2022, including Summer Olympic Games, Winter Olympic Games, and a combined total of both, is tabulated below. These Olympic medal counts do not include the 1906 Intercalated Games whic ...
for the Winter Olympic Games. When including defunct states, Germany (comprising the former countries of West Germany and East Germany) leads, followed by Norway, Russia (including the former Soviet Union), and the United States.
History
Early years
 A predecessor, the Nordic Games, were organized by General Viktor Gustaf Balck in
A predecessor, the Nordic Games, were organized by General Viktor Gustaf Balck in Stockholm
Stockholm () is the capital and largest city of Sweden as well as the largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people live in the municipality, with 1.6 million in the urban area, and 2.4 million in the metropo ...
, Sweden, in 1901 and were held again in 1903 and 1905 and then every fourth year thereafter until 1926. Balck was a charter member of the IOC and a close friend of Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a multi ...
founder Pierre de Coubertin
Charles Pierre de Frédy, Baron de Coubertin (; born Pierre de Frédy; ...
. He attempted to have winter sports, specifically figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, when contested at the 1908 Olympics in London. The Olympic disciplines are me ...
, added to the Olympic programme but was unsuccessful until the 1908 Summer Olympics
The 1908 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the IV Olympiad and also known as London 1908) were an international multi-sport event held in London, England, United Kingdom, from 27 April to 31 October 1908. The 1908 Games were o ...
in London. Four figure skating events were contested, at which Ulrich Salchow (10-time world champion) and Madge Syers won the individual titles.
Three years later, Italian count Eugenio Brunetta d'Usseaux
Count Eugenio Brunetta d'Usseaux (14 December 1857 – 8 January 1919) was an Italian nobleman.
His father, the count Carlo Augusto Brunetta of Usseaux was a high-degree official of the Royal Sardinian Army, headquartered in the same city. The m ...
proposed that the IOC stage a week of winter sports included as part of the 1912 Summer Olympics
The 1912 Summer Olympics ( sv, Olympiska sommarspelen 1912), officially known as the Games of the V Olympiad ( sv, Den V olympiadens spel) and commonly known as Stockholm 1912, were an international multi-sport event held in Stockholm, Sweden, b ...
in Stockholm, Sweden. The organisers opposed this idea because they desired to protect the integrity of the Nordic Games and were concerned about a lack of facilities for winter sports.
The idea was resurrected for the 1916 Games, which were to be held in Berlin, Germany. A winter sports week with speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
, figure skating, ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
and Nordic skiing
Nordic skiing encompasses the various types of skiing in which the toe of the ski boot is fixed to the binding in a manner that allows the heel to rise off the ski, unlike alpine skiing, where the boot is attached to the ski from toe to heel. ...
was planned, but the 1916 Olympics was cancelled after the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
.
1920 to 1936
 The first Olympics after the war, the
The first Olympics after the war, the 1920 Summer Olympics
The 1920 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1920; nl, Olympische Zomerspelen van 1920; german: Olympische Sommerspiele 1920), officially known as the Games of the VII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIe olympiade; nl, Spelen van ...
, were held in Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, Belgium, and featured figure skating and an ice hockey tournament. Germany, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria and Turkey were banned from competing in the games. At the IOC Congress held the following year it was decided that the host nation of the 1924 Summer Olympics
The 1924 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1924), officially the Games of the VIII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIIe olympiade) and also known as Paris 1924, were an international multi-sport event held in Paris, France. The o ...
, France, would host a separate "International Winter Sports Week" under the patronage of the IOC. Chamonix was chosen to host this week (actually 11 days) of events.
The 1924 games in Chamonix proved to be a success when more than 250 athletes from 16 nations competed in 16 events. Athletes from Finland and Norway won 28 medals, more than the rest of the participating nations combined. The first gold medal awarded was won by Charles Jewtraw of the United States in the 500-meter speed skate. Sonja Henie
Sonja Henie (8 April 1912 – 12 October 1969) was a Norwegian figure skater and film star. She was a three-time Olympic champion (1928, 1932, 1936) in women's singles, a ten-time World champion (1927–1936) and a six-time European champio ...
of Norway, at just 11 years old, competed in the ladies' figure skating and, although finishing last, became popular with fans. Gillis Grafström of Sweden defended his 1920 gold medal in men's figure skating, becoming the first Olympian to win gold medals in both Summer and Winter Olympics.
Germany remained banned until 1925, and instead hosted a series of games called Deutsche Kampfspiele, starting with the winter edition of 1922 (which predated the first Winter Olympics). In 1925 the IOC decided to create a separate winter event and the 1924 games in Chamonix was retroactively designated as the first Winter Olympics.
St. Moritz, Switzerland, was appointed by the IOC to host the second Winter Games in 1928. Fluctuating weather conditions challenged the hosts. The opening ceremony
An opening ceremony, grand opening, or ribbon-cutting ceremony marks the official opening of a newly-constructed location or the start of an event.
was held in a blizzard while warm weather conditions plagued sporting events throughout the rest of the games. Because of the weather the 10,000 metre speed-skating event had to be abandoned and officially cancelled. The weather was not the only noteworthy aspect of the 1928 games: Sonja Henie
Sonja Henie (8 April 1912 – 12 October 1969) was a Norwegian figure skater and film star. She was a three-time Olympic champion (1928, 1932, 1936) in women's singles, a ten-time World champion (1927–1936) and a six-time European champio ...
of Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
returned to the Winter Olympics to make history when she won the ladies' figure skating at the age of 15. She became the youngest Olympic champion in history, a distinction she held for 70 years, and went on to defend her title at the next two Winter Olympics. Gillis Grafström won his third consecutive figure skating gold and went on to win silver in 1932, becoming the most decorated men's figure skater to date.
The next Winter Olympics, held in Lake Placid, New York, United States was the first to be hosted outside of Europe. Seventeen nations and 252 athletes participated. This was less than in 1928, as the journey to Lake Placid was too long and expensive for some European nations that encountered financial problems in the midst of the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
. The athletes competed in fourteen events in four sports. Virtually no snow fell for two months before the Games, and there was not enough snow to hold all the events until mid-January. Sonja Henie defended her Olympic title, and Eddie Eagan
Edward Patrick Francis Eagan (April 26, 1897 – June 14, 1967) was an American boxer and bobsledder who is notable as being the only person to win a gold medal at both the Summer and Winter Olympic Games in different disciplines. Gillis Grafst ...
of the United States, who had been an Olympic champion in boxing in 1920, won the gold medal in the men's bobsleigh event to join Gillis Grafström as the only athletes to have won gold medals in both the Summer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, wit ...
and Winter Olympics. Eagan has the distinction as the only Olympian as of 2020 to accomplish this feat in different sports.
The German towns of Garmisch and Partenkirchen joined to organise the 1936 edition of the Winter Games, held from 6–16 February. This was the last time the Summer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, wit ...
and Winter Olympics were held in the same country in the same year. Alpine skiing
Alpine skiing, or downhill skiing, is the pastime of sliding down snow-covered slopes on skis with fixed-heel bindings, unlike other types of skiing ( cross-country, Telemark, or ski jumping), which use skis with free-heel bindings. Whether ...
made its Olympic debut, but skiing teachers were barred from entering because they were considered to be professionals. Because of this decision the Swiss and Austrian skiers refused to compete at the games.
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
interrupted the Winter Olympics. The 1940 games had been awarded to Sapporo
( ain, サッ・ポロ・ペッ, Satporopet, lit=Dry, Great River) is a city in Japan. It is the largest city north of Tokyo and the largest city on Hokkaido, the northernmost main island of the country. It ranks as the fifth most populous city ...
, Japan, but the decision was rescinded in 1938 because of the Japanese invasion
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing ...
of China. The games were then to be held at Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany, but the 1940 games were cancelled following the German invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week af ...
in 1939. Due to the ongoing war, the 1944 games, originally scheduled for Cortina D'Ampezzo
Cortina d'Ampezzo (; lld, Anpezo, ; historical de-AT, Hayden) is a town and ''comune'' in the heart of the southern (Dolomites, Dolomitic) Alps in the Province of Belluno, in the Veneto region of Northern Italy. Situated on the Boite (river), ...
, Italy, were cancelled.
1948 to 1960
 St. Moritz was selected to host the first post-war games, in 1948. Switzerland's neutrality had protected the town during World War II, and most venues from the 1928 games remained in place, which made St. Moritz a logical choice. It became the first city to host a Winter Olympics twice. Twenty-eight countries competed in Switzerland, but athletes from Germany and Japan were not invited. Controversy erupted when two hockey teams from the
St. Moritz was selected to host the first post-war games, in 1948. Switzerland's neutrality had protected the town during World War II, and most venues from the 1928 games remained in place, which made St. Moritz a logical choice. It became the first city to host a Winter Olympics twice. Twenty-eight countries competed in Switzerland, but athletes from Germany and Japan were not invited. Controversy erupted when two hockey teams from the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
arrived, both claiming to be the legitimate U.S. Olympic hockey representative. The Olympic flag
The International Olympic Committee (IOC) uses icons, flags and symbols to elevate the Olympic Games. These symbols include those commonly used during Olympic competition—such as the flame, fanfare and theme—as well as those used througho ...
presented at the 1920 Summer Olympics
The 1920 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1920; nl, Olympische Zomerspelen van 1920; german: Olympische Sommerspiele 1920), officially known as the Games of the VII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIe olympiade; nl, Spelen van ...
in Antwerp was stolen, as was its replacement. There was unprecedented parity at these games, during which 10 countries won gold medals—more than any games to that point.
The Olympic Flame for the 1952 games in Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
, was lit in the fireplace by Norwegian skiing pioneer Sondre Nordheim
Sondre Norheim, born Sondre Auverson, (10 June 1825 – 9 March 1897) was a Norwegian skier and pioneer of modern skiing. Sondre Norheim is known as the father of Telemark skiing.
Background
Sondre Auverson was born at Øverbø, a little ...
, and the torch relay was conducted by 94 participants entirely on skis. Bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two teams wearing ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal. The international governing body for bandy is ...
, a popular sport in the Nordic countries, was featured as a demonstration sport, though only Norway, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
, and Finland fielded teams. Norwegian athletes won 17 medals, which outpaced all the other nations. They were led by Hjalmar Andersen who won three gold medals in four events in the speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
competition.
After not being able to host the games in 1944, Cortina d'Ampezzo was selected to organise the 1956 Winter Olympics
The 1956 Winter Olympics, officially known as the VII Olympic Winter Games ( it, VII Giochi Olimpici invernali) and commonly known as Cortina d'Ampezzo 1956 ( lld, Anpezo 1956 or ), was a multi-sport event held in Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy, fro ...
. At the opening ceremonies the final torchbearer, Guido Caroli, entered the Olympic Stadium
''Olympic Stadium'' is the name usually given to the main stadium of an Olympic Games. An Olympic stadium is the site of the opening and closing ceremonies. Many, though not all, of these venues actually contain the words ''Olympic Stadium'' as ...
on ice skates. As he skated around the stadium his skate caught on a cable and he fell, nearly extinguishing the flame. He was able to recover and light the cauldron. These were the first Winter Games to be televised, and the first Olympics ever broadcast to an international audience, though no television rights were sold until the 1960 Summer Olympics
The 1960 Summer Olympics ( it, Giochi Olimpici estivi del 1960), officially known as the Games of the XVII Olympiad ( it, Giochi della XVII Olimpiade) and commonly known as Rome 1960 ( it, Roma 1960), were an international multi-sport event held ...
in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
.Guttman (1986), p. 135 The Cortina games were used to test the feasibility of televising large sporting events.
The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
made its Olympic debut and had an immediate impact, winning more medals than any other nation. The Soviets' immediate success might be explained by the advent of the state-sponsored "full-time amateur athlete". The USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
entered teams of athletes who were all nominally students, soldiers, or working in a profession, but many of whom were in reality paid by the state to train full-time. Chiharu Igaya
is a former Olympic games, Olympic Alpine skiing, alpine ski racer and Alpine skiing at the 1956 Winter Olympics – Men's slalom, silver medalist from Japan. He competed in three Alpine skiing at the Winter Olympics, Winter Olympics (Japan at ...
won the first Winter Olympics medal for Japan and the continent of Asia when he placed second in the slalom.
The IOC awarded the 1960 Olympics to Squaw Valley, United States. It was an undeveloped resort in 1955, so from 1956 to 1960 the infrastructure and all of the venues were built at a cost of US$80,000,000.Judd (2008), pp. 27–28 The opening and closing ceremonies were produced by Walt Disney.Judd (2008), p. 28 The Squaw Valley Olympics was the first Winter Games to have a dedicated athletes' village, the first to use a computer (courtesy of IBM) to tabulate results, and the first to feature female speed skating events. The bobsleigh events were absent for the only time due to a minimal number of nations expressing interest in competing and the cost of building a bobsleigh run.
1964 to 1980
 The Austrian city of Innsbruck was the host in 1964. Although Innsbruck was a traditional winter sports resort, warm weather caused a lack of snow during the games and the Austrian army was enlisted to transport snow and ice to the sports venues. Soviet Union at the 1964 Winter Olympics, Soviet speed-skater Lidia Skoblikova made history by winning all four-speed skating events. Her career total of six gold medals set a record for Winter Olympics athletes. Luge was first contested in 1964, but the sport received bad publicity when a competitor was killed in a pre-Olympic training run.
Held in the French town of Grenoble, the 1968 Winter Olympics were the first Olympic Games to be broadcast in colour. There were 1,158 athletes from 37 nations competing in 35 events. France at the 1968 Winter Olympics, French alpine ski racer Jean-Claude Killy became only the second person to win all the men's alpine skiing events. The organising committee sold television rights for US$2 million, which was more than twice the cost of the broadcast rights for the Innsbruck Games.Findling and Pelle (2004), p. 277 Venues were spread over long distances requiring three athletes' villages. The organisers claimed that this was necessary to accommodate technological advances, however, critics disputed this, alleging that the layout would incorporate the best possible venues for television broadcasts at the athletes' expense.
The 1972 Winter Olympics, 1972 Winter Games, held in
The Austrian city of Innsbruck was the host in 1964. Although Innsbruck was a traditional winter sports resort, warm weather caused a lack of snow during the games and the Austrian army was enlisted to transport snow and ice to the sports venues. Soviet Union at the 1964 Winter Olympics, Soviet speed-skater Lidia Skoblikova made history by winning all four-speed skating events. Her career total of six gold medals set a record for Winter Olympics athletes. Luge was first contested in 1964, but the sport received bad publicity when a competitor was killed in a pre-Olympic training run.
Held in the French town of Grenoble, the 1968 Winter Olympics were the first Olympic Games to be broadcast in colour. There were 1,158 athletes from 37 nations competing in 35 events. France at the 1968 Winter Olympics, French alpine ski racer Jean-Claude Killy became only the second person to win all the men's alpine skiing events. The organising committee sold television rights for US$2 million, which was more than twice the cost of the broadcast rights for the Innsbruck Games.Findling and Pelle (2004), p. 277 Venues were spread over long distances requiring three athletes' villages. The organisers claimed that this was necessary to accommodate technological advances, however, critics disputed this, alleging that the layout would incorporate the best possible venues for television broadcasts at the athletes' expense.
The 1972 Winter Olympics, 1972 Winter Games, held in Sapporo
( ain, サッ・ポロ・ペッ, Satporopet, lit=Dry, Great River) is a city in Japan. It is the largest city north of Tokyo and the largest city on Hokkaido, the northernmost main island of the country. It ranks as the fifth most populous city ...
, Japan, were the first to be hosted on a continent other than North America or Europe. The issue of professionalism was disputed during these Games when a number of alpine skiers were found to have participated in a ski camp at Mammoth Mountain in the United States; three days before the opening ceremony, IOC president Avery Brundage threatened to bar the skiers from competing in the Games as he insisted that they were no longer amateurs having benefited financially from their status as athletes. Eventually only Austria at the 1972 Winter Olympics, Austrian Karl Schranz, who earned more than the other skiers, was excluded from the competition. Canada did not send teams to the Ice hockey at the 1972 Winter Olympics, 1972 or Ice hockey at the 1976 Winter Olympics, 1976 ice hockey tournaments in protest at not being able to use players from professional leagues. It also accused the Soviet Union of using state-sponsored athletes, who were de facto professionals. Francisco Fernández Ochoa became the first and, as of 2018, only Spain at the 1972 Winter Olympics, Spaniard to win a Winter Olympic gold medal when he triumphed in the Alpine skiing at the 1972 Winter Olympics, slalom.
The 1976 Winter Olympics had initially been awarded in 1970 to Denver, Colorado in the United States. These Games would have coincided with the year of Colorado's centennial and the United States Bicentennial. However, in November 1972 the people of Colorado voted against public funding of the Games by a 3:2 margin. The IOC responded by offering the Games to Vancouver-Garibaldi Ranges, Garibaldi, British Columbia, which had previously been an official candidate for the 1976 Games. However, a change in the provincial government resulted in an administration that did not support the Olympic bid, so the IOC's offer was rejected.
Salt Lake City, previously a candidate for the 1972 Winter Olympics, then put itself forward, but the IOC opted instead to invite Innsbruck to host the 1976 Games, as most of the infrastructure from the 1964 Games had been maintained. Despite only having half the usual time to prepare for the Games, Innsbruck accepted the invitation to replace Denver in February 1973. Two Olympic flames were lit because it was the second time that the Austrian town had hosted the Winter Games. The 1976 Games featured the first Igls bobsleigh, luge, and skeleton track, combination bobsleigh and luge track, in neighbouring Igls. The Soviet Union at the 1976 Winter Olympics, Soviet Union won its fourth consecutive ice hockey gold medal.
1980 Winter Olympics, In 1980 the Winter Olympics returned to Lake Placid, which had hosted the 1932 Games. Cyprus made their Olympic debut at the games. The People's Republic of China and Costa Rica both made their Winter Olympic debut. The Republic of China refused to attend the Games over the IOC's recognition of the People's Republic of China as "China", and its request for the Republic of China to compete as "Chinese Taipei". The PRC, on the other hand, returned to the Olympics for the first time since 1952 and made its Winter Olympic debut.Findling and Pelle (1996), p. 299
United States at the 1980 Winter Olympics, American speed-skater Eric Heiden set either an Olympic or World record in every one of the five Speed skating at the 1980 Winter Olympics, events in which he competed, winning a total of five individual gold medals and breaking the record for most individual golds in a single Olympics (both Summer and Winter). Hanni Wenzel won both the slalom and giant slalom and her country, Liechtenstein at the 1980 Winter Olympics, Liechtenstein, became the smallest nation to produce an Olympic gold medallist. In the "Miracle on Ice", the United States men's national ice hockey team, American hockey team composed of college players beat the favoured seasoned professionals from the Soviet Union national ice hockey team, Soviet Union, and progressed to eventually win the gold medal.
1984 to 1998

Sapporo
( ain, サッ・ポロ・ペッ, Satporopet, lit=Dry, Great River) is a city in Japan. It is the largest city north of Tokyo and the largest city on Hokkaido, the northernmost main island of the country. It ranks as the fifth most populous city ...
, Japan, and Gothenburg, Sweden, were front-runners to host the 1984 Winter Olympics. It was therefore a surprise when Sarajevo, Yugoslavia, was selected as host. The Games were well-organised and not affected by the run-up to the Bosnian War, war that engulfed the country eight years later. A total of 49 nations and 1,272 athletes participated in 39 events. Host nation Yugoslavia won its first Olympic medal when alpine skier Jure Franko won silver in the giant slalom. Another sporting highlight was the free dance performance of Great Britain at the 1984 Winter Olympics, British ice dancers Jayne Torvill and Christopher Dean; their ''Boléro'' routine received unanimous perfect scores for artistic impression, earning them the gold medal.
 In 1988, the Canadian city of Calgary hosted the 1988 Winter Olympics, first Winter Olympics to span three weekends, lasting for a total of 16 days. New events were added in ski-jumping and speed skating, while future Olympic sports curling, short track speed skating and freestyle skiing made their debut appearance as demonstration sports. The speed skating events were held indoors for the first time, on the Olympic Oval. Dutch skater Yvonne van Gennip won three gold medals and set two world records, beating skaters from the favoured East Germany at the 1988 Winter Olympics, East German team in every race.
Her medal total was equalled by Finland at the 1988 Winter Olympics, Finnish ski jumper Matti Nykänen, who won all three events in his sport. Alberto Tomba, Italy at the 1988 Winter Olympics, an Italian skier, made his Olympic debut by winning both the giant slalom and slalom. Ski jumper Eddie the Eagle competed in the 70m and 90m in finishing last with a British ski jumping records, British record of 73.5 metres. East German Christa Luding-Rothenburger, Christa Rothenburger won the women's 1,000 metre speed skating event. Seven months later she would earn a silver in track cycling at the 1988 Summer Olympics, Summer Games in Seoul, to become the only athlete to win medals in both a Summer and Winter Olympics in the same year.
The 1992 Winter Olympics, 1992 Winter Games were the last to be held in the same year as the 1992 Summer Olympics, Summer Games. They were hosted in the French Savoie region, with 18 events held in the city of Albertville and the remaining events spread out over the Savoie. Political changes of the time were reflected in the composition of the Olympic teams competing in France: this was the first Games to be held after the fall of Communism and the fall of the Berlin Wall, and Germany competed as a single nation for the first time since the 1964 Games.Findling and Pelle (2004), p. 400
Former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavian republics Croatia at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Croatia and Slovenia at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Slovenia made their debuts as independent nations; most of the former Soviet Union, Soviet republics still competed as a single team known as the Unified Team at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Unified Team, but the Baltic States made independent appearances for the first time since before World War II. At 16 years old, Finland at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Finnish ski jumper Toni Nieminen made history by becoming the youngest male Winter Olympic champion. New Zealand at the 1992 Winter Olympics, New Zealand skier Annelise Coberger became the first Winter Olympic medallist from the southern hemisphere when she won a silver medal in the women's slalom.
The 1994 Winter Olympics, held in Lillehammer, Norway, were the first Winter Games to be held in a different year from the Summer Games. This change resulted from the decision reached in the List of IOC meetings#IOC Sessions, 91st IOC Session (1986) to separate the Summer and Winter Games and place them in alternating even-numbered years. Lillehammer is the northernmost city to ever host the Winter Games. It was the second time the Games were held in Norway, after the 1952 Winter Olympics in
In 1988, the Canadian city of Calgary hosted the 1988 Winter Olympics, first Winter Olympics to span three weekends, lasting for a total of 16 days. New events were added in ski-jumping and speed skating, while future Olympic sports curling, short track speed skating and freestyle skiing made their debut appearance as demonstration sports. The speed skating events were held indoors for the first time, on the Olympic Oval. Dutch skater Yvonne van Gennip won three gold medals and set two world records, beating skaters from the favoured East Germany at the 1988 Winter Olympics, East German team in every race.
Her medal total was equalled by Finland at the 1988 Winter Olympics, Finnish ski jumper Matti Nykänen, who won all three events in his sport. Alberto Tomba, Italy at the 1988 Winter Olympics, an Italian skier, made his Olympic debut by winning both the giant slalom and slalom. Ski jumper Eddie the Eagle competed in the 70m and 90m in finishing last with a British ski jumping records, British record of 73.5 metres. East German Christa Luding-Rothenburger, Christa Rothenburger won the women's 1,000 metre speed skating event. Seven months later she would earn a silver in track cycling at the 1988 Summer Olympics, Summer Games in Seoul, to become the only athlete to win medals in both a Summer and Winter Olympics in the same year.
The 1992 Winter Olympics, 1992 Winter Games were the last to be held in the same year as the 1992 Summer Olympics, Summer Games. They were hosted in the French Savoie region, with 18 events held in the city of Albertville and the remaining events spread out over the Savoie. Political changes of the time were reflected in the composition of the Olympic teams competing in France: this was the first Games to be held after the fall of Communism and the fall of the Berlin Wall, and Germany competed as a single nation for the first time since the 1964 Games.Findling and Pelle (2004), p. 400
Former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavian republics Croatia at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Croatia and Slovenia at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Slovenia made their debuts as independent nations; most of the former Soviet Union, Soviet republics still competed as a single team known as the Unified Team at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Unified Team, but the Baltic States made independent appearances for the first time since before World War II. At 16 years old, Finland at the 1992 Winter Olympics, Finnish ski jumper Toni Nieminen made history by becoming the youngest male Winter Olympic champion. New Zealand at the 1992 Winter Olympics, New Zealand skier Annelise Coberger became the first Winter Olympic medallist from the southern hemisphere when she won a silver medal in the women's slalom.
The 1994 Winter Olympics, held in Lillehammer, Norway, were the first Winter Games to be held in a different year from the Summer Games. This change resulted from the decision reached in the List of IOC meetings#IOC Sessions, 91st IOC Session (1986) to separate the Summer and Winter Games and place them in alternating even-numbered years. Lillehammer is the northernmost city to ever host the Winter Games. It was the second time the Games were held in Norway, after the 1952 Winter Olympics in Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
, and the first time the Olympic Truce was observed. As a result, after the dissolution of Czechoslovakia in 1993, the Czech Republic at the 1994 Winter Olympics, Czech Republic and Slovakia at the 1994 Winter Olympics, Slovakia made their Olympic debuts.
The women's figure skating competition drew media attention when United States at the 1994 Winter Olympics, American skater Nancy Kerrigan was injured on 6 January 1994, in an assault planned by the ex-husband of opponent Tonya Harding. Both skaters competed in the Games, but the gold medal was controversially won by Oksana Baiul who became Ukraine at the 1994 Winter Olympics, Ukraine's first Olympic champion, while Kerrigan won the silver medal. Johann Olav Koss of Norway at the 1994 Winter Olympics, Norway won three gold medals, coming first in all of the distance speed skating events.
13-year-old Kim Yun-Mi (speed skater), Kim Yoon-Mi became the youngest-ever Olympic gold medallist when South Korea won the women's 3,000-metre speed skating relay. Bjørn Dæhli of Norway won a medal in four out of five cross-country events, becoming the most decorated Winter Olympian until then. Russia at the 1994 Winter Olympics, Russia won the most events, with eleven gold medals, while Norway achieved 26 podium finishes, collecting the most medals overall on home ground. Juan Antonio Samaranch described Lillehammer as "the best Olympic Winter Games ever" in his closing ceremony speech.
The 1998 Winter Olympics were held in the Japanese city of Nagano (city), Nagano and were the first Games to host more than 2,000 athletes. The National Hockey League allowed its players to participate in the men's Ice hockey at the 1998 Winter Olympics – Men's tournament, ice hockey tournament for the first time, and the Czech Republic men's national ice hockey team, Czech Republic won the tournament. Women's ice hockey made its debut, and the United States women's national ice hockey team, United States won the gold medal. Bjørn Dæhlie of Norway at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Norway won three gold medals in Nordic skiing, becoming the most decorated Winter Olympic athlete, with eight gold medals and twelve medals overall. Austria at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Austrian Hermann Maier survived a crash during the downhill competition and returned to win gold in the Alpine skiing at the 1998 Winter Olympics – Men's super-G, super-G and the giant slalom. Tara Lipinski of the United States at the 1998 Winter Olympics, United States, aged just 15, became the youngest ever female gold medallist in an individual event when she won the Figure skating at the 1998 Winter Olympics#Ladies, Ladies' Singles, a record that had stood since Sonja Henie
Sonja Henie (8 April 1912 – 12 October 1969) was a Norwegian figure skater and film star. She was a three-time Olympic champion (1928, 1932, 1936) in women's singles, a ten-time World champion (1927–1936) and a six-time European champio ...
of Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
won the same event, also aged 15, in 1928 Winter Olympics, St. Moritz in 1928. New world records were set in Speed skating at the 1998 Winter Olympics, speed skating largely due to the introduction of the clap skate.
2002 to 2022
 2002 Winter Olympic bid scandal, After a tumultuous host city process, the 2002 Winter Olympics were held in Salt Lake City, Utah, Salt Lake City, United States. 2,399 athletes from 77 National Olympic Committees participated at 78 events in 7 sports. These Games were the first to take place since the September 11 attacks of 2001, which meant a higher degree of security to avoid a terrorist attack. The opening ceremony saw signs of the Aftermath of the September 11 attacks, aftermath of the events of that day, including the flag that flew at World Trade Center site, Ground Zero, and honour guards of NYPD and New York City Fire Department, FDNY members.
Germany at the 2002 Winter Olympics, German Georg Hackl won a silver in the singles luge, becoming the first athlete in Olympic history to win medals in the same individual event in five consecutive Olympics. Canada at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Canada achieved an unprecedented double by winning both the men's and women's Ice hockey at the 2002 Winter Olympics, ice hockey gold medals. Canada became embroiled with Russia at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Russia in a 2002 Olympic Winter Games figure skating scandal, controversy that involved the judging of the Figure skating at the 2002 Winter Olympics, pairs figure skating competition. The Russian pair of Yelena Berezhnaya and Anton Sikharulidze competed against the Canadian pair of Jamie Salé and David Pelletier for the gold medal.
The Canadians appeared to have skated well enough to win the competition, yet the Russians were awarded the gold. The France at the 2002 Winter Olympics, French judge, Marie-Reine Le Gougne, awarded the gold to the Russians. An investigation revealed that she had been pressured to give the gold to the Russian pair regardless of how they skated; in return, the Russian judge would look favourably on the French entrants in the ice dancing competition.
The IOC decided to award both pairs the gold medal in a second Olympic Games ceremony, medal ceremony held later in the Games. Australia at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Australian Steven Bradbury (speed skater), Steven Bradbury became the first gold medallist from the southern hemisphere when he won the 1,000 metre short-track speed skating event.
2002 Winter Olympic bid scandal, After a tumultuous host city process, the 2002 Winter Olympics were held in Salt Lake City, Utah, Salt Lake City, United States. 2,399 athletes from 77 National Olympic Committees participated at 78 events in 7 sports. These Games were the first to take place since the September 11 attacks of 2001, which meant a higher degree of security to avoid a terrorist attack. The opening ceremony saw signs of the Aftermath of the September 11 attacks, aftermath of the events of that day, including the flag that flew at World Trade Center site, Ground Zero, and honour guards of NYPD and New York City Fire Department, FDNY members.
Germany at the 2002 Winter Olympics, German Georg Hackl won a silver in the singles luge, becoming the first athlete in Olympic history to win medals in the same individual event in five consecutive Olympics. Canada at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Canada achieved an unprecedented double by winning both the men's and women's Ice hockey at the 2002 Winter Olympics, ice hockey gold medals. Canada became embroiled with Russia at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Russia in a 2002 Olympic Winter Games figure skating scandal, controversy that involved the judging of the Figure skating at the 2002 Winter Olympics, pairs figure skating competition. The Russian pair of Yelena Berezhnaya and Anton Sikharulidze competed against the Canadian pair of Jamie Salé and David Pelletier for the gold medal.
The Canadians appeared to have skated well enough to win the competition, yet the Russians were awarded the gold. The France at the 2002 Winter Olympics, French judge, Marie-Reine Le Gougne, awarded the gold to the Russians. An investigation revealed that she had been pressured to give the gold to the Russian pair regardless of how they skated; in return, the Russian judge would look favourably on the French entrants in the ice dancing competition.
The IOC decided to award both pairs the gold medal in a second Olympic Games ceremony, medal ceremony held later in the Games. Australia at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Australian Steven Bradbury (speed skater), Steven Bradbury became the first gold medallist from the southern hemisphere when he won the 1,000 metre short-track speed skating event.
 The Italian city of Turin hosted the 2006 Winter Olympics. It was the second time that Italy had hosted the Winter Olympic Games. South Korea at the 2006 Winter Olympics, South Korean athletes won 10 medals, including 6 gold in the short-track speed skating events. Jin Sun-Yu, Sun-Yu Jin won three gold medals while her teammate Hyun-Soo Ahn won three gold medals and a bronze. In the women's Cross-country skiing at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Cross-Country team pursuit Canada at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Canadian Sara Renner broke one of her poles and, when he saw her dilemma, Norway at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Norwegian coach Bjørnar Håkensmoen decided to lend her a pole. In so doing she was able to help her team win a silver medal in the event at the expense of the Norwegian team, who finished fourth.
On winning the Super-G, Kjetil-Andre Aamodt of Norway became the most decorated ski racer of all time with 4 gold and 8 overall medals. He is also the only ski racer to have won the same event at three Olympics, winning the Super-G in
The Italian city of Turin hosted the 2006 Winter Olympics. It was the second time that Italy had hosted the Winter Olympic Games. South Korea at the 2006 Winter Olympics, South Korean athletes won 10 medals, including 6 gold in the short-track speed skating events. Jin Sun-Yu, Sun-Yu Jin won three gold medals while her teammate Hyun-Soo Ahn won three gold medals and a bronze. In the women's Cross-country skiing at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Cross-Country team pursuit Canada at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Canadian Sara Renner broke one of her poles and, when he saw her dilemma, Norway at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Norwegian coach Bjørnar Håkensmoen decided to lend her a pole. In so doing she was able to help her team win a silver medal in the event at the expense of the Norwegian team, who finished fourth.
On winning the Super-G, Kjetil-Andre Aamodt of Norway became the most decorated ski racer of all time with 4 gold and 8 overall medals. He is also the only ski racer to have won the same event at three Olympics, winning the Super-G in 1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment building in Amsterdam after two of its engin ...
, 2002
File:2002 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 2002 Winter Olympics are held in Salt Lake City; Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother and her daughter Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon die; East Timor gains East Timor independence, indepe ...
and 2006
File:2006 Events Collage V1.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2006 Winter Olympics open in Turin; Twitter is founded and launched by Jack Dorsey; The Nintendo Wii is released; Montenegro votes to declare independence from Serbia; The 2006 ...
. Claudia Pechstein of Germany at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Germany became the first speed skater to earn nine career medals.
In February 2009, Pechstein tested positive for "blood manipulation" and received a two-year suspension, which she appealed. The Court of Arbitration for Sport upheld her suspension but a Swiss court ruled that she could compete for a spot on the Germany at the 2010 Winter Olympics, 2010 German Olympic team. This ruling was brought to the Swiss Federal Tribunal, which overturned the lower court's ruling and precluded her from competing in Vancouver.
In 2003 the IOC awarded the 2010 Winter Olympics to Vancouver, thus allowing Canada to host its second Winter Olympics. With a population of more than 2.5 million people Vancouver is the largest metropolitan area to ever host a Winter Olympic Games. Over 2,500 athletes from 82 countries participated in 86 events. The death of Georgia at the 2010 Winter Olympics, Georgian luger Nodar Kumaritashvili in a training run on the day of the opening ceremonies resulted in the Whistler Sliding Centre changing the track layout on safety grounds.
Norway at the 2010 Winter Olympics, Norwegian cross-country skier Marit Bjørgen won five medals in the six cross-country events on the women's programme. She finished the Olympics with three golds, a silver and a bronze. For the first time, Canada at the 2010 Winter Olympics, Canada won a gold medal at an Olympic Games it hosted, having failed to do so at both the 1976 Summer Olympics in Montreal and the 1988 Winter Olympics in Calgary. In contrast to the lack of gold medals at these previous Olympics, the Canadian team finished first overall in gold medal wins, and became the first host nation—since Norway at the 1952 Winter Olympics, Norway in 1952—to lead the gold medal count, with 14 medals. In doing so, it also broke the record for the most gold medals won by a NOC at a single Winter Olympics (the previous was 13, set by the Soviet Union at the 1976 Winter Olympics, Soviet Union in 1976 and matched by Norway at the 2002 Winter Olympics, Norway in 2002).
The Vancouver Games were notable for the poor performance of the Russia at the 2010 Winter Olympics, Russian athletes. From their first Winter Olympics in 1956
Events
January
* January 1 – The Anglo-Egyptian Condominium ends in Sudan.
* January 8 – Operation Auca: Five U.S. evangelical Christian missionaries, Nate Saint, Roger Youderian, Ed McCully, Jim Elliot and Pete Fleming, are kille ...
to the 2006 Games, a Soviet or Russian delegation had never been outside the top five medal-winning nations, but in 2010 they finished sixth in total medals and eleventh in gold medals. Russian President, President Dmitry Medvedev called for the resignation of top sports officials immediately after the Games. Russia's disappointing performance at Vancouver is cited as the reason behind the Doping in Russia, enhancement of an already existing doping scheme alleged to have been in operation at major events such as the 2014 Games at Sochi.
The success of Asian countries stood in stark contrast to the under-performing Russian team, with Vancouver marking a high point for medals won by Asian countries. At the Albertville Games in 1992 the Asian countries had won fifteen medals, three of which were gold. In Vancouver, the total number of medals won by athletes from Asia had increased to thirty-one, with eleven of them being gold. The rise of Asian nations in Winter Olympics sports is due in part to the growth of winter sports programmes and the interest in winter sports in nations such as Kazakhstan, South Korea, Japan and China. These results increased the chances of an Asian city hosting the 2018 Winter Olympics that would be held the following year.
Sochi, Russia, was selected as the host city for the 2014 Winter Olympics over Salzburg, Austria, and Pyeongchang County, Pyeongchang, South Korea. This was the first time that Russia had hosted a Winter Olympics. The Games took place from 7 to 23 February 2014. A record 2,800 athletes from 88 countries competed in 98 events. The Olympic Village and Olympic Stadium were located on the Black Sea coast. All of the mountain venues were away in the alpine region known as Krasnaya Polyana, Sochi, Krasnodar Krai, Krasnaya Polyana. The Games were the most expensive until the date, with a cost of £30 billion (US$51 billion).
On the snow, Norwegian biathlete Ole Einar Bjørndalen took two golds to bring his total tally of Olympic medals to 13, overtaking his compatriot Bjørn Dæhlie to become the most decorated Winter Olympian of all time. Another Norwegian, cross-country skier Marit Bjørgen took three golds; her total of ten Olympic medals tied her as the female Winter Olympian with most medals, alongside Raisa Smetanina and Stefania Belmondo. Snowboarder Ayumu Hirano became the youngest medallist on snow at the Winter Games when he took a silver in the Snowboarding at the 2014 Winter Olympics – Men's halfpipe, halfpipe competition at the age of fifteen.
On the ice, the Netherlands team dominated the speed skating events, taking 23 medals, four clean sweeps of the podium places and at least one medal in each of the twelve medal events. Ireen Wüst was their most successful competitor, taking two golds and three silvers. In figure skating, Yuzuru Hanyu became the first skater to break the 100-point barrier in the short programme on the way to winning the gold medal. Among the sledding disciplines, luger Armin Zöggeler took a bronze, becoming the first Winter Olympian to secure a medal in six consecutive Games.
Following their disappointing performance at the 2010 Games, and an investment of £600 million in elite sport, Russia at the 2014 Winter Olympics, Russia initially topped the 2014 Winter Olympics medal table, medal table, taking 33 medals including thirteen golds. However Grigory Rodchenkov, the former head of the Russian national anti-doping laboratory, subsequently claimed that he had been involved in doping dozens of Russian competitors for the Games, and that he had been assisted by the Russian Federal Security Service in opening and re-sealing bottles containing urine samples so that samples with banned substances could be replaced with "clean" urine.
A subsequent McLaren Report, investigation commissioned by the World Anti-Doping Agency led by Richard McLaren (academic), Richard McLaren concluded that a state-sponsored doping programme had operated in Russia from "at least late 2011 to 2015" across the "vast majority" of Summer and Winter Olympic sports. On 5 December 2017, the IOC announced that Russian Olympic Committee, Russia would compete as the Olympic Athletes from Russia at the 2018 Winter Olympics, Olympic Athletes from Russia at the 2018 Winter Olympics and by the end of 2017 the Oswald Commission, IOC Disciplinary Commission had disqualified 43 Russian athletes, stripping thirteen medals and knocking Russia from the top of the medal table, thus putting Norway in the lead. However, nine medals were later returned, meaning that Russia reclaimed first place in the overall medal table, and joint first place with Norway in terms of gold medals.
On 6 July 2011, Pyeongchang County, Pyeongchang, South Korea, was selected to host the 2018 Winter Olympics over Munich, Germany, and Annecy, France. This was the first time that South Korea had been selected to host a Winter Olympics and it was the second time the Olympics were held in the country overall, after the 1988 Summer Olympics, 1988 Summer Olympics in Seoul. The Games took place from 9 to 25 February 2018. More than 2,900 athletes from 92 countries participated in 102 events. The main venue cluster was the Alpensia Resort in Daegwallyeong-myeon, while the ice events are held at Gangneung Olympic Park in Pyeongchang's neighbouring sea-city of Gangneung.
The lead-up to the 2018 Winter Olympics was affected by 2018 Winter Olympics#North Korean relations, the tensions between North and South Korea and the ongoing Doping in Russia, Russian doping scandal. Despite North Korea–South Korea relations, tense relations, North Korea agreed to participate in the Games, enter with South Korea during the opening ceremony as a unified Korea, and field a Korea at the 2018 Winter Olympics, unified team in Korea women's national ice hockey team, women's ice hockey. Russian athletes, who complied with the IOC's doping regulations, were given the option to compete in Pyeongchang as "Olympic Athletes from Russia" (OAR).
The Games saw the addition of Snowboarding#Big air, big air snowboarding, mass start speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors race each other in travelling a certain distance on skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skati ...
, mixed doubles curling, and mixed team alpine skiing to the programme. Like four years early, the Netherlands again dominated speed skating, winning gold medals in seven of the ten individual events. Dutch speed skater Sven Kramer won gold in the men's 5000m event, becoming the only male speed skater to win the same Olympic event three times. On the snow, Norway led the medal tally in cross-country skiing, with Marit Bjørgen winning bronze in the women's team sprint and gold in the 30-kilometre classical event, bringing her total Olympic medal haul to fifteen, the most won by any athlete (male or female) in Winter Olympics history.
Johannes Høsflot Klæbo of Norway became the youngest ever male to win an Olympic gold in cross-country skiing when he won the Cross-country skiing at the 2018 Winter Olympics – Men's sprint, men's sprint at age 21. Noriaki Kasai of Japan became the first athlete in history to participate in eight Winter Olympics when he took part in the ski jumping qualification the day before the opening of the Games. Ester Ledecká of the Czech Republic won gold in the skiing super-G event and another gold in the snowboarding parallel giant slalom, making her the first female athlete to win Olympic gold medals in two sports at a single Winter Games.
Norway led the total medal standings with 39, the highest number of medals by a nation in any Winter Olympics, followed by Germany's 31 and Canada's 29. Host nation South Korea at the 2018 Winter Olympics, South Korea won seventeen medals, five of them gold, its highest medal haul at a Winter Olympics.
Beijing, the capital of the China, People's Republic of China, was elected as the host city for the 2022 Winter Olympics on 31 July 2015 at the 128th IOC Session. Beijing became the first city ever to have hosted both the Summer and Winter Olympics. Like the Summer Olympics held six months earlier in Tokyo, the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in the implementation of strict health and safety protocols, including restrictions on public attendance at the Games. The Games included a record 109 events over 15 disciplines in seven sports with seven new medal events, including mixed team competitions in freestyle skiing aerials, ski jumping, and snowboard cross. The Games were held between 4 February and 20 February 2022 at venues in Beijing and Zhangjiakou which for the first time were run entirely on renewable energy. Several of the events were impacted by temperatures as low as minus 20 Celsius and strong wind.
The first gold medal of the Games was won by Therese Johaug of Norway at the 2022 Winter Olympics, Norway in the women's skiathlon. Johaug had been excluded from the 2018 Winter Olympics in a controversial decision after having used a banned cream for sunburned lips. She went on to also win the women's 10 km and 30 km cross-country distances. In the women's snowboard cross, Lindsey Jacobellis of the United States at the 2022 Winter Olympics, United States won the gold, having lost the gold 16 years earlier at the 2006 Winter Olympics in Torino due to a brutal fall. On the ice, the Netherlands at the 2022 Winter Olympics, Netherlands dominated with a total of six gold medals and Irene Schouten winning the women's mass start, 3,000m and 5,000m distances. Nils van der Poel of Sweden at the 2022 Winter Olympics, Sweden won the men's 5,000m and 10,000m distances, setting new Olympic records in both distances. Kamila Valieva of Russian Olympic Committee athletes at the 2022 Winter Olympics, Russia was allowed to compete in the Figure skating at the 2022 Winter Olympics – Women's singles, women's figure skating in spite of a failed doping test in December 2021. She failed, however, to win an individual medal after falling in her final routine. Russia's Figure skating at the 2022 Winter Olympics – Team event, team gold medal remains in limbo to this day, pending investigation into Valieva's positive drug test. Finland at the 2022 Winter Olympics, Finland claimed its first ice hockey gold ever, having beaten the Russian Olympic Committee in the men's final on the last day of the Games.
Norway was first in the overall medal standings, claiming 37 medals in total and 16 gold medals, the highest number of gold medals of any country in a single Winter Olympics. This was the ninth time Norway claimed the highest number of gold medals in the Winter Games.
Future
The2026 Winter Olympics
The 2026 Winter Olympics, officially the XXV Olympic Winter Games ( it, XXV Giochi olimpici invernali) and also known as Milano Cortina 2026 ( lld, Milano-Anpezo 2026 or ), is an upcoming international multi-sport event scheduled to take place fr ...
will be in Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
-Cortina d'Ampezzo
Cortina d'Ampezzo (; lld, Anpezo, ; historical de-AT, Hayden) is a town and ''comune'' in the heart of the southern (Dolomites, Dolomitic) Alps in the Province of Belluno, in the Veneto region of Northern Italy. Situated on the Boite (river), ...
, Italy and take place between 6 and 22 February 2026. The 2030 Winter Olympics will be in either Salt Lake City, United States or Sapporo
( ain, サッ・ポロ・ペッ, Satporopet, lit=Dry, Great River) is a city in Japan. It is the largest city north of Tokyo and the largest city on Hokkaido, the northernmost main island of the country. It ranks as the fifth most populous city ...
, Japan and take place between 8 and 24 February 2030.
Problems and politics
Controversy
 The process for awarding host city honours came under intense scrutiny after Salt Lake City had been awarded the right to host the 2002 Games. Soon after the host city had been announced it was discovered that the organisers had engaged in an elaborate bribery 2002 Winter Olympic bid scandal, scheme to curry favour with IOC officials. Gifts and other financial considerations were given to those who would evaluate and vote on Salt Lake City's bid. These gifts included medical treatment for relatives, a college scholarship for one member's son and a land deal in Utah. Even IOC president Juan Antonio Samaranch received two rifles valued at $2,000. Samaranch defended the gift as inconsequential since, as president, he was a non-voting member.Cashmore (2005), p. 444
The subsequent investigation uncovered inconsistencies in the bids for every Olympics (both Summer and Winter) since 1988. For example, the gifts received by IOC members from the Japanese Organising Committee for Nagano's bid for the 1998 Winter Olympics were described by the investigation committee as "astronomical". Although nothing strictly illegal had been done, the IOC feared that corporate sponsors would lose faith in the integrity of the process and that the Olympic brand would be tarnished to such an extent that advertisers would begin to pull their support.
The investigation resulted in the expulsion of 10 IOC members and the sanctioning of another 10. New terms and age limits were established for IOC membership, and 15 former Olympic athletes were added to the committee. Stricter rules for future bids were imposed, with ceilings imposed on the value of gifts IOC members could accept from bid cities.
The process for awarding host city honours came under intense scrutiny after Salt Lake City had been awarded the right to host the 2002 Games. Soon after the host city had been announced it was discovered that the organisers had engaged in an elaborate bribery 2002 Winter Olympic bid scandal, scheme to curry favour with IOC officials. Gifts and other financial considerations were given to those who would evaluate and vote on Salt Lake City's bid. These gifts included medical treatment for relatives, a college scholarship for one member's son and a land deal in Utah. Even IOC president Juan Antonio Samaranch received two rifles valued at $2,000. Samaranch defended the gift as inconsequential since, as president, he was a non-voting member.Cashmore (2005), p. 444
The subsequent investigation uncovered inconsistencies in the bids for every Olympics (both Summer and Winter) since 1988. For example, the gifts received by IOC members from the Japanese Organising Committee for Nagano's bid for the 1998 Winter Olympics were described by the investigation committee as "astronomical". Although nothing strictly illegal had been done, the IOC feared that corporate sponsors would lose faith in the integrity of the process and that the Olympic brand would be tarnished to such an extent that advertisers would begin to pull their support.
The investigation resulted in the expulsion of 10 IOC members and the sanctioning of another 10. New terms and age limits were established for IOC membership, and 15 former Olympic athletes were added to the committee. Stricter rules for future bids were imposed, with ceilings imposed on the value of gifts IOC members could accept from bid cities.
Host city legacy
According to the IOC, the host city for the Winter Olympics is responsible for "...establishing functions and services for all aspects of the Games, such as sports planning, venues, finance, technology, accommodation, catering, media services, etc., as well as operations during the Games." Due to the cost of hosting the Games, most host cities never realise a profit on their investment. For example, the 2006 Winter Olympics in Turin, Italy, cost $3.6 billion to host. By comparison, the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano (city), Nagano, Japan, cost $12.5 billion. The organisers of the Nagano Games claimed that the cost of extending the Shinkansen, bullet train service from Tokyo to Nagano was responsible for the large price tag. The organising committee had hoped that the exposure gained from hosting the Winter Olympics, and the improved access to Nagano from Tokyo, would benefit the local economy for years afterwards. In fact, Nagano's economy did experience a post-Olympic boom for a year or two, but the long-term effects have not materialised as anticipated. The likelihood of heavy debt is a deterrent to prospective host cities, as well as the prospect of unused sports venues and infrastructure saddling the local community with upkeep costs into the future with no appreciable post-Olympic value. The Winter Olympics has the added problem of the alpine events requiring a mountain location; the men's downhill needs an 800-meter altitude difference along a suitable course. As this is a focal event that is central to the Games, the IOC has previously not agreed to it taking place a great distance from the main host city, in contrast to the Summer Games, where sailing and horse sports have taken place more than away. The requirement for a mountain location also means that venues such as hockey arenas often have to be built in sparsely populated areas with little future need for a large arena and for the hotels and infrastructure needed for all Olympic visitors. Due to cost issues, fewer and fewer cities are willing to host. Both the 2006 Winter Olympics, Torino 2006 and 2010 Winter Olympics, Vancouver 2010 Games, which were hosted in countries where large cities are located close to suitable mountain regions, had lower costs since more venues, hotels and transport infrastructure already existed. In contrast, the 2014 Winter Olympics, Sochi 2014 games had large costs as most installations had to be built. The IOC has enacted several initiatives to mitigate these concerns. Firstly, the commission has agreed to fund part of the host city's budget for staging the Games. Secondly, the qualifying host countries are limited to those that have the resources and infrastructure to successfully host an Olympic Games without negatively impacting the region or nation; this consequently rules out a large portion of the developing world. Finally, any prospective host city planning to bid for the Games is required to add a "legacy plan" to their proposal, with a view to the long-term economic and environmental impact that hosting the Olympics will have on the region. For the 2022 Winter Olympics, 2022 Winter Games, IOC allowed a longer distance between the alpine events and other events. The Oslo bid for the 2022 Winter Olympics, Oslo bid had to the Kvitfjell downhill arena, while eventual host Beijing had venues 220 km away from the city as well. For the 2026 Winter Games, IOC allowed Stockholm to have the alpine event in Åre, away by road.Doping
In 1967 the IOC began enacting drug testing protocols. They started by randomly testing athletes at the 1968 Winter Olympics. The first Winter Games athlete to test positive for a banned substance was Alois Schloder, a West Germany at the 1972 Winter Olympics, West German hockey player, but his team was still allowed to compete. During the 1970s testing outside of competition was escalated because it was found to deter athletes from using performance-enhancing drugs.Mottram (2003), p. 313 The problem with testing during this time was a lack of standardisation of the test procedures, which undermined the credibility of the tests. It was not until the late 1980s that international sporting federations began to coordinate efforts to standardise the drug-testing protocols. The IOC took the lead in the fight against steroids when it established the independent World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) in November 1999. The 2006 Winter Olympics in Turin became notable for a scandal involving the emerging trend of blood doping, the use of blood transfusions or synthetic hormones such as Erythropoietin (EPO) to improve oxygen flow and thus reduce fatigue. The Italian police conducted a raid on the Austria at the 2006 Winter Olympics, Austrian cross-country ski team's residence during the Games where they seized blood-doping specimens and equipment. This event followed the pre-Olympics suspension of 12 cross-country skiers who tested positive for unusually high levels of hemoglobin, haemoglobin, which is evidence of blood doping. The 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi's Russian Doping Scandal has resulted in the International Olympic Committee to begin disciplinary proceedings against 28 (later increased to 46) Russian athletes who competed at the 2014 Winter Games in Sochi, Russia, acting on evidence that their urine samples were tampered with.Cold War
 The Winter Olympics have been an ideological front in the Cold War since the
The Winter Olympics have been an ideological front in the Cold War since the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
first participated at the 1956 Winter Olympics, 1956 Winter Games. It did not take long for the Cold War combatants to discover what a powerful propaganda tool the Olympic Games could be. The advent of the state-sponsored "full-time amateur athlete" of the Eastern Bloc countries further eroded the ideology of the pure amateur, as it put the self-financed amateurs of the Western countries at a disadvantage. The Soviet Union at the Olympics, Soviet Union entered teams of athletes who were all nominally students, soldiers, or working in a profession, but many of whom were in reality paid by the state to train on a full-time basis. Nevertheless, the IOC held to the traditional rules regarding amateurism until the '90s.
The Cold War created tensions amongst countries allied to the two superpowers. The strained relationship between East and West Germany created a difficult political situation for the IOC. Because of its role in World War II, Germany was not allowed to compete at the 1948 Winter Olympics. In 1950 the IOC recognised the West German Olympic Committee, and invited East and West Germany to compete as a unified team at the 1952 Winter Games.Hill (1992), p. 34 East Germany declined the invitation and instead sought international legitimacy separate from West Germany.
In 1955 the Soviet Union recognised East Germany as a sovereign state, thereby giving more credibility to East Germany's campaign to become an independent participant at the Olympics. The IOC agreed to provisionally accept the East German National Olympic Committee with the condition that East and West Germans compete on one team. The situation became tenuous when the Berlin Wall was constructed by East Germany in 1962 and Western European nations began refusing visas to East German athletes. The uneasy compromise of a unified team held until the 1968 Grenoble Games when the IOC officially split the teams and threatened to reject the host-city bids of any country that refused entry visas to East German athletes.
Boycott
The Winter Games have had only one national team boycott when Taiwan decided not to participate in the 1980 Winter Olympics held in Lake Placid. Prior to the Games, the IOC agreed to allow China to compete in the Olympics for the first time since 1952. China was given permission to compete as the "People's Republic of China" (PRC) and to use the PRC flag and anthem. Until 1980 the island of Taiwan had been competing under the name "Republic of China" (ROC) and had been using the ROC flag and anthem. The IOC attempted to have the countries compete together but when this proved to be unacceptable the IOC demanded that Taiwan cease to call itself the "Republic of China". The IOC renamed the island "Chinese Taipei" and demanded that it adopt a different flag and national anthem, stipulations to which Taiwan would not agree. Despite numerous appeals and court hearings, the IOC's decision stood. When the Taiwanese athletes arrived at the Olympic village with their Republic of China identification cards they were not admitted. They subsequently left the Olympics in protest, just before the opening ceremonies. Taiwan returned to Olympic competition at the 1984 Winter Games in Sarajevo as Chinese Taipei. The country agreed to compete under a flag bearing the emblem of their National Olympic Committee and to play the anthem of their National Olympic Committee should one of their athletes win a gold medal. The agreement remains in place to this day.Sports
TheOlympic Charter
The Olympic Charter is a set of rules and guidelines for the organisation of the Olympic Games, and for governing the Olympic movement. Its last revision was on the 17th of July 2020 during the 136th IOC Session, held by video conference. Ado ...
limits winter sports to "those sports which are practised on snow or ice." Since 1992 a number of new sports have been added to the Olympic programme; which include short track speed skating, snowboarding, freestyle and moguls skiing. The addition of these events has broadened the appeal of the Winter Olympics beyond Europe and North America. While European powers such as Norway and Germany still dominate the traditional Winter Olympic sports, countries such as South Korea, Australia and Canada are finding success in the new sports. The results are: more parity in the national medal tables; more interest in the Winter Olympics; and higher global television ratings.
Current sports
Demonstration events
Demonstration sports#Winter Olympics, Demonstration sports have historically provided a venue for host countries to attract publicity to locally popular sports by having a competition without granting medals. Demonstration sports were discontinued after1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment building in Amsterdam after two of its engin ...
. Military patrol, a precursor to the biathlon, was a medal sport in 1924 and was demonstrated in 1928, 1936 and 1948, becoming an official sport in 1960. The special figures figure skating event was only contested at the Figure skating at the 1908 Summer Olympics, 1908 Summer Olympics. Bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two teams wearing ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal. The international governing body for bandy is ...
(Russian hockey) is a sport popular in the Nordic countries and Russia. In the latter it's considered a national sport. It was demonstrated at the Oslo Games.
Ice stock sport, a German variant of curling, was demonstrated in 1936 in Germany and 1964 in Austria. The ski ballet event, later known as ski-acro, was demonstrated in 1988 and 1992. Skijöring, skiing behind dogs, was a demonstration sport in St. Moritz in 1928. A Sled dog race at the 1932 Winter Olympics, sled-dog race was held at Lake Placid in 1932. Speed skiing was demonstrated in Albertville at the 1992 Winter Olympics. Winter pentathlon, a variant of the modern pentathlon, was included as a demonstration event at the 1948 Games in Switzerland. It included cross-country skiing (sport), cross-country skiing, shooting sports, shooting, Downhill (ski competition), downhill skiing, fencing, and Equestrian at the Summer Olympics, horse riding.
All-time medal table
The table below uses official data provided by the IOC.Medal leaders by year
; Number of occurrences * — 9 times * — 7 times * — 3 times * — 2 times * — 1 time * — 1 time * — 1 time * — 1 timeList of Winter Olympic Games
IOC site for the 2002 Winter Olympic Games
gives an erroneous figure of 77 participated teams; however, one can count 78 participated nations looking throug
Official Report of the XIX Olympic Winter Games
This error probably resulted from the fact that Costa Rica's delegation of one athlete joined the Games after the Opening Ceremony, so 77 nations participated in Opening Ceremony and 78 nations participated in the Games. * The IOC site for th
2018 Winter Olympic Games
does not include Korea at the 2018 Winter Olympics, United Korean (COR) women's ice hockey team as separate "nation" when counting participating nations. Nevertheless the IOC shows the Korean team in th
Pyeongchang 2018 Ice Hockey Women's Tournament Results
Thus, 92 national teams plus 1 team composed of athletes from both South Korea and North Korea participated in the Games. * Xi Jinping is the "President of the People's Republic of China, Chinese President", ''de jure'' head of state. Xi is also ''de facto'' Paramount leader, ruler as General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party.
See also
* List of multiple Winter Olympic medallists * List of participating nations at the Winter Olympic Games * Lists of Olympic medallists * Olympic Games scandals and controversies * Winter Paralympic Games * Paralympic Games *Summer Olympic Games
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The ina ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Official Report (1924) of both Summer and Winter Games: * * * * * * * *External links
Olympic Games
IOC official website
Winter Olympic Sports
IOC official website {{Authority control Winter Olympic Games, Recurring sporting events established in 1924 Winter multi-sport events Quadrennial sporting events February sporting events