Wind power in Germany on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wind power in Germany is a growing industry. The installed capacity was 55.6
 Offshore wind energy also has great potential in Germany. Wind speed at sea is 70 to 100% higher than onshore and much more constant. As of 2007, a new generation of 5 MW or larger wind turbines which are capable of making full use of the potential of wind power at sea had been developed. This made it possible to operate offshore wind farms in a cost-effective way.
On 15 July 2009, the first offshore German windturbine completed construction. This turbine is the first of a total of 12 wind turbines for the alpha ventus offshore wind farm in the North Sea.
Following the
Offshore wind energy also has great potential in Germany. Wind speed at sea is 70 to 100% higher than onshore and much more constant. As of 2007, a new generation of 5 MW or larger wind turbines which are capable of making full use of the potential of wind power at sea had been developed. This made it possible to operate offshore wind farms in a cost-effective way.
On 15 July 2009, the first offshore German windturbine completed construction. This turbine is the first of a total of 12 wind turbines for the alpha ventus offshore wind farm in the North Sea.
Following the
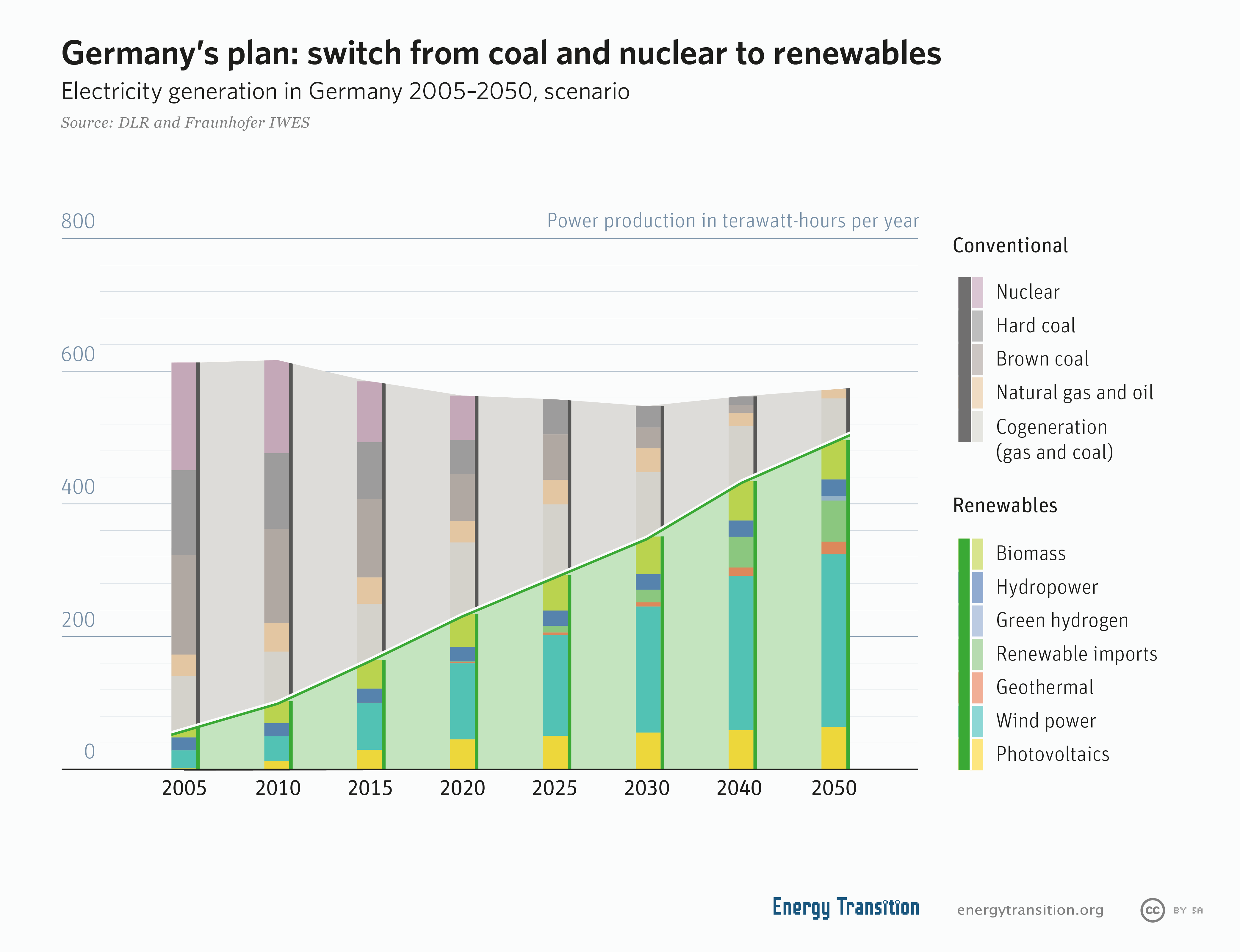 The 2010 " Energiewende" policy has been embraced by the German federal government and has resulted in a huge expansion of renewables, particularly wind power. Germany's share of renewables has increased from around 5% in 1999 to 17% in 2010, reaching close to the OECD average of 18% usage of renewables. Producers have been guaranteed a fixed feed-in tariff for 20 years, guaranteeing a fixed income. Energy co-operatives have been created, and efforts were made to decentralize control and profits. The large energy companies have a disproportionately small share of the renewables market. Nuclear power plants were closed, and the existing 9 plants will close earlier than necessary, in 2022.
The reduction of reliance on nuclear plants has so far had the consequence of increased reliance on fossil fuels and on electricity imports from France. However, in good wind Germany exports to France; in January 2015 the average price was €29/MWh in Germany, and €39/MWh in France. One factor that has inhibited efficient employment of new renewable energy has been the lack of an accompanying investment in power infrastructure (SüdLink) to bring the power to market. The transmission constraint sometimes causes Germany to pay Danish wind power to stop producing; in October/November 2015 this amounted to 96 GWh costing 1.8 million euros.
The German states have varying attitudes to the construction of new power lines. Industry has had their rates frozen and so the increased costs of the Energiewende have been passed on to consumers, who have had rising electricity bills. Germans in 2013 had some of the highest electricity costs in Europe.
The 2010 " Energiewende" policy has been embraced by the German federal government and has resulted in a huge expansion of renewables, particularly wind power. Germany's share of renewables has increased from around 5% in 1999 to 17% in 2010, reaching close to the OECD average of 18% usage of renewables. Producers have been guaranteed a fixed feed-in tariff for 20 years, guaranteeing a fixed income. Energy co-operatives have been created, and efforts were made to decentralize control and profits. The large energy companies have a disproportionately small share of the renewables market. Nuclear power plants were closed, and the existing 9 plants will close earlier than necessary, in 2022.
The reduction of reliance on nuclear plants has so far had the consequence of increased reliance on fossil fuels and on electricity imports from France. However, in good wind Germany exports to France; in January 2015 the average price was €29/MWh in Germany, and €39/MWh in France. One factor that has inhibited efficient employment of new renewable energy has been the lack of an accompanying investment in power infrastructure (SüdLink) to bring the power to market. The transmission constraint sometimes causes Germany to pay Danish wind power to stop producing; in October/November 2015 this amounted to 96 GWh costing 1.8 million euros.
The German states have varying attitudes to the construction of new power lines. Industry has had their rates frozen and so the increased costs of the Energiewende have been passed on to consumers, who have had rising electricity bills. Germans in 2013 had some of the highest electricity costs in Europe.
 In Germany, hundreds of thousands of people have invested in citizens' wind farms across the country and thousands of small and medium-sized enterprises are running successful businesses in a new sector that in 2015 employed 142,900 people and generated 12.3 percent of Germany's electricity in 2016.
However, more recently, there has been increasing local resistance to the expansion of wind power in Germany, due to its impact on the landscape, incidences of removal of forests to build wind turbines, the emission of low frequency noise, and the negative impact on wildlife, such as birds of prey and bats.
In Germany, hundreds of thousands of people have invested in citizens' wind farms across the country and thousands of small and medium-sized enterprises are running successful businesses in a new sector that in 2015 employed 142,900 people and generated 12.3 percent of Germany's electricity in 2016.
However, more recently, there has been increasing local resistance to the expansion of wind power in Germany, due to its impact on the landscape, incidences of removal of forests to build wind turbines, the emission of low frequency noise, and the negative impact on wildlife, such as birds of prey and bats.
 Installed wind power capacity and generation in recent years is shown in the tables below:
Installed wind power capacity and generation in recent years is shown in the tables below:

Germany Inaugurates 5 MW Wind Turbine Prototype5-MW BARD Near-shore Wind Turbine Erected in GermanyDeutsche Energie-Agentur (Dena), German Energy AgencyOfficial site about wind power and renewable Energy in the Emscher-Lippe-RegionCost-optimal expansion of renewables would save Germany up to two billion euros a year
{{Energy in Germany de:Windenergie#Deutschland
gigawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wat ...
s (GW) at the end of 2017, with 5.2 GW from offshore installations. In 2019, a quarter of the country's total electricity was generated using wind power, compared to an estimated 9.3% in 2010.
More than 26,772 wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. ...
s were located in the German federal area by year end 2015, and the country has plans for further expansion. As of the end of 2015, Germany was the third largest producer of wind power in the world by installations, behind China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
and the USA. Germany also has a number of turbine manufacturers, like Enercon
Enercon GmbH is a wind turbine manufacturer based in Aurich, Lower Saxony, Germany. It has been the market leader in Germany since the mid-1990s. Enercon has production facilities in Germany (Aurich, Emden and Magdeburg), Brazil, India, Canada, ...
, Nordex
Nordex SE is a European company that designs, sells and manufactures wind turbines. The company's headquarters is located in the German city of Rostock while management is situated in Hamburg. Production takes place in Rostock as well as in China ...
and Senvion.
In the first half of 2021, with 22% a contribution to German electric generation, wind was the second most important contributor, following coal, which was the top producer, with 27%. In 2020 wind was the top generator.
Onshore wind power
Since 1995, onshore wind energy has been an important and major industry in Germany. In 1995, the gross production of onshore wind power was 1,530 GWh. By 2019, gross production from onshore wind power was over 101,000 GWh, allowing Germany to power about a fifth of the country from wind. Larger onshore installations are in the works, which could possibly see a larger percentage of wind energy powering Germany. Germany is also notable for having some major wind turbine manufacturers based there, such asEnercon
Enercon GmbH is a wind turbine manufacturer based in Aurich, Lower Saxony, Germany. It has been the market leader in Germany since the mid-1990s. Enercon has production facilities in Germany (Aurich, Emden and Magdeburg), Brazil, India, Canada, ...
in Aurich
Aurich (; East Frisian Low Saxon: ''Auerk'', West Frisian: ''Auwerk'', stq, Aurk) is a town in the East Frisian region of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the capital of the district of Aurich and is the second largest City in East Frisia, both i ...
, Senvion in Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
, and Nordex
Nordex SE is a European company that designs, sells and manufactures wind turbines. The company's headquarters is located in the German city of Rostock while management is situated in Hamburg. Production takes place in Rostock as well as in China ...
in Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state ...
.
Offshore wind power
 Offshore wind energy also has great potential in Germany. Wind speed at sea is 70 to 100% higher than onshore and much more constant. As of 2007, a new generation of 5 MW or larger wind turbines which are capable of making full use of the potential of wind power at sea had been developed. This made it possible to operate offshore wind farms in a cost-effective way.
On 15 July 2009, the first offshore German windturbine completed construction. This turbine is the first of a total of 12 wind turbines for the alpha ventus offshore wind farm in the North Sea.
Following the
Offshore wind energy also has great potential in Germany. Wind speed at sea is 70 to 100% higher than onshore and much more constant. As of 2007, a new generation of 5 MW or larger wind turbines which are capable of making full use of the potential of wind power at sea had been developed. This made it possible to operate offshore wind farms in a cost-effective way.
On 15 July 2009, the first offshore German windturbine completed construction. This turbine is the first of a total of 12 wind turbines for the alpha ventus offshore wind farm in the North Sea.
Following the 2011 Japanese nuclear accidents
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and ...
, Germany's federal government began work on a new plan for increasing renewable energy commercialization
Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include b ...
, with a particular focus on offshore wind farm
Offshore wind power or offshore wind energy is the generation of electricity through wind farms in bodies of water, usually at sea. There are higher wind speeds offshore than on land, so offshore farms generate more electricity per amount of ...
s. Under the plan, large wind turbines were to be erected far away from the coastlines, where the wind blows more consistently than it does on land, and where the enormous turbines won't bother the inhabitants. The plan aimed to decrease Germany's dependence on energy derived from coal and nuclear power plants.
The German government wanted to see 7.6 GW installed by 2020 and as much as 26 GW by 2030.
A major challenge was the lack of sufficient network capacities for transmitting the power generated in the North Sea to the large industrial consumers in southern Germany.The Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' is an American business-focused, international daily newspaper based in New York City, with international editions also available in Chinese and Japanese. The ''Journal'', along with its Asian editions, is published ...
Online, 24 April 2012
In 2014 410 turbines with 1747 megawatts were added to Germany's offshore windparks. Due to not yet finished grid-connections, only turbines with combined 528.9 megawatts were added to the grid feed at the end of 2014. Despite this, the gigawatt offshore windpower barrier was reportedly breached by Germany around the end of 2014
During 2015 offshore windpower was tripled to over 3 gigawatts capacity, signalling the growing importance of this sector.
At the end of 2019, Germany had installed 1,469 offshore wind turbines with a total capacity of 7.52 GW. Capacity in the North Sea reached 6.44 GW, capacity in the Baltic Sea reached 1.08 GW. In total, 25.8 TWh of power were produced in German offshore wind parks in 2019.
Government support
Since 2011, Germany's federal government has been working on a new plan for increasingrenewable energy commercialization
Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include b ...
, with a particular focus on offshore wind farm
Offshore wind power or offshore wind energy is the generation of electricity through wind farms in bodies of water, usually at sea. There are higher wind speeds offshore than on land, so offshore farms generate more electricity per amount of ...
s.
In 2016, Germany decided to replace feed-in tariffs with auctions from 2017, citing the mature nature of the windpower market being best served in this way. These auctions have resulted in some future offshore wind farms to be operated at market prices and receive no subsidy.
Energy transition
 The 2010 " Energiewende" policy has been embraced by the German federal government and has resulted in a huge expansion of renewables, particularly wind power. Germany's share of renewables has increased from around 5% in 1999 to 17% in 2010, reaching close to the OECD average of 18% usage of renewables. Producers have been guaranteed a fixed feed-in tariff for 20 years, guaranteeing a fixed income. Energy co-operatives have been created, and efforts were made to decentralize control and profits. The large energy companies have a disproportionately small share of the renewables market. Nuclear power plants were closed, and the existing 9 plants will close earlier than necessary, in 2022.
The reduction of reliance on nuclear plants has so far had the consequence of increased reliance on fossil fuels and on electricity imports from France. However, in good wind Germany exports to France; in January 2015 the average price was €29/MWh in Germany, and €39/MWh in France. One factor that has inhibited efficient employment of new renewable energy has been the lack of an accompanying investment in power infrastructure (SüdLink) to bring the power to market. The transmission constraint sometimes causes Germany to pay Danish wind power to stop producing; in October/November 2015 this amounted to 96 GWh costing 1.8 million euros.
The German states have varying attitudes to the construction of new power lines. Industry has had their rates frozen and so the increased costs of the Energiewende have been passed on to consumers, who have had rising electricity bills. Germans in 2013 had some of the highest electricity costs in Europe.
The 2010 " Energiewende" policy has been embraced by the German federal government and has resulted in a huge expansion of renewables, particularly wind power. Germany's share of renewables has increased from around 5% in 1999 to 17% in 2010, reaching close to the OECD average of 18% usage of renewables. Producers have been guaranteed a fixed feed-in tariff for 20 years, guaranteeing a fixed income. Energy co-operatives have been created, and efforts were made to decentralize control and profits. The large energy companies have a disproportionately small share of the renewables market. Nuclear power plants were closed, and the existing 9 plants will close earlier than necessary, in 2022.
The reduction of reliance on nuclear plants has so far had the consequence of increased reliance on fossil fuels and on electricity imports from France. However, in good wind Germany exports to France; in January 2015 the average price was €29/MWh in Germany, and €39/MWh in France. One factor that has inhibited efficient employment of new renewable energy has been the lack of an accompanying investment in power infrastructure (SüdLink) to bring the power to market. The transmission constraint sometimes causes Germany to pay Danish wind power to stop producing; in October/November 2015 this amounted to 96 GWh costing 1.8 million euros.
The German states have varying attitudes to the construction of new power lines. Industry has had their rates frozen and so the increased costs of the Energiewende have been passed on to consumers, who have had rising electricity bills. Germans in 2013 had some of the highest electricity costs in Europe.
Public opinion
 In Germany, hundreds of thousands of people have invested in citizens' wind farms across the country and thousands of small and medium-sized enterprises are running successful businesses in a new sector that in 2015 employed 142,900 people and generated 12.3 percent of Germany's electricity in 2016.
However, more recently, there has been increasing local resistance to the expansion of wind power in Germany, due to its impact on the landscape, incidences of removal of forests to build wind turbines, the emission of low frequency noise, and the negative impact on wildlife, such as birds of prey and bats.
In Germany, hundreds of thousands of people have invested in citizens' wind farms across the country and thousands of small and medium-sized enterprises are running successful businesses in a new sector that in 2015 employed 142,900 people and generated 12.3 percent of Germany's electricity in 2016.
However, more recently, there has been increasing local resistance to the expansion of wind power in Germany, due to its impact on the landscape, incidences of removal of forests to build wind turbines, the emission of low frequency noise, and the negative impact on wildlife, such as birds of prey and bats.
Repowering
Repowering
Repowering is the process of replacing older power stations with newer ones that either have a greater nameplate capacity or more efficiency which results in a net increase of power generated. Repowering can happen in several different ways. It can ...
, the replacement of first-generation wind turbines with modern multi-megawatt machines, is occurring in Germany. Modern turbines make better use of available wind energy and so more wind power can come from the same area of land. Modern turbines also offer much better grid integration since they use a connection method similar to conventional power plants.
Statistics
Total
Offshore only
By State

See also
*Renewable energy in Germany
Renewable energy in Germany is mainly based on wind and biomass, plus solar and hydro. Germany had the world's largest photovoltaic installed capacity until 2014, and as of 2021 it has over 58 GW. It is also the world's third country by instal ...
*Solar power in Germany
Solar power in Germany consists almost exclusively of photovoltaics (PV) and accounted for an estimated 8.2 percent of the country's gross-electricity generation in 2019.
About 1.5 million photovoltaic systems were installed around the count ...
* Geothermal power in Germany
*Wind power in the European Union
As of December 2017, the European Union had a total installed wind Nameplate capacity, capacity of 169.3gigawatts (GW). In 2017, a total of 15,680 MW of wind power was installed, representing 55% of all new power capacity, and the wind p ...
*Renewable energy by country
This is a list of renewable energy topics by country and territory. These links can be used to compare developments in renewable energy in different countries and territories and to help and encourage new writers to participate in writing about ...
References
External links
Germany Inaugurates 5 MW Wind Turbine Prototype
{{Energy in Germany de:Windenergie#Deutschland