Wabenaki on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Wabanaki Confederacy (''Wabenaki, Wobanaki'', translated to "People of the Dawn" or "Easterner") is a
"Sacred fire lights the Wabanaki Confederacy"
''Indian Country Today'' (June 27, 2008), ICT Media Network
 Small-scale confederacies in and around what would become the Wabanaki Confederacy were common at the time of post-
Small-scale confederacies in and around what would become the Wabanaki Confederacy were common at the time of post-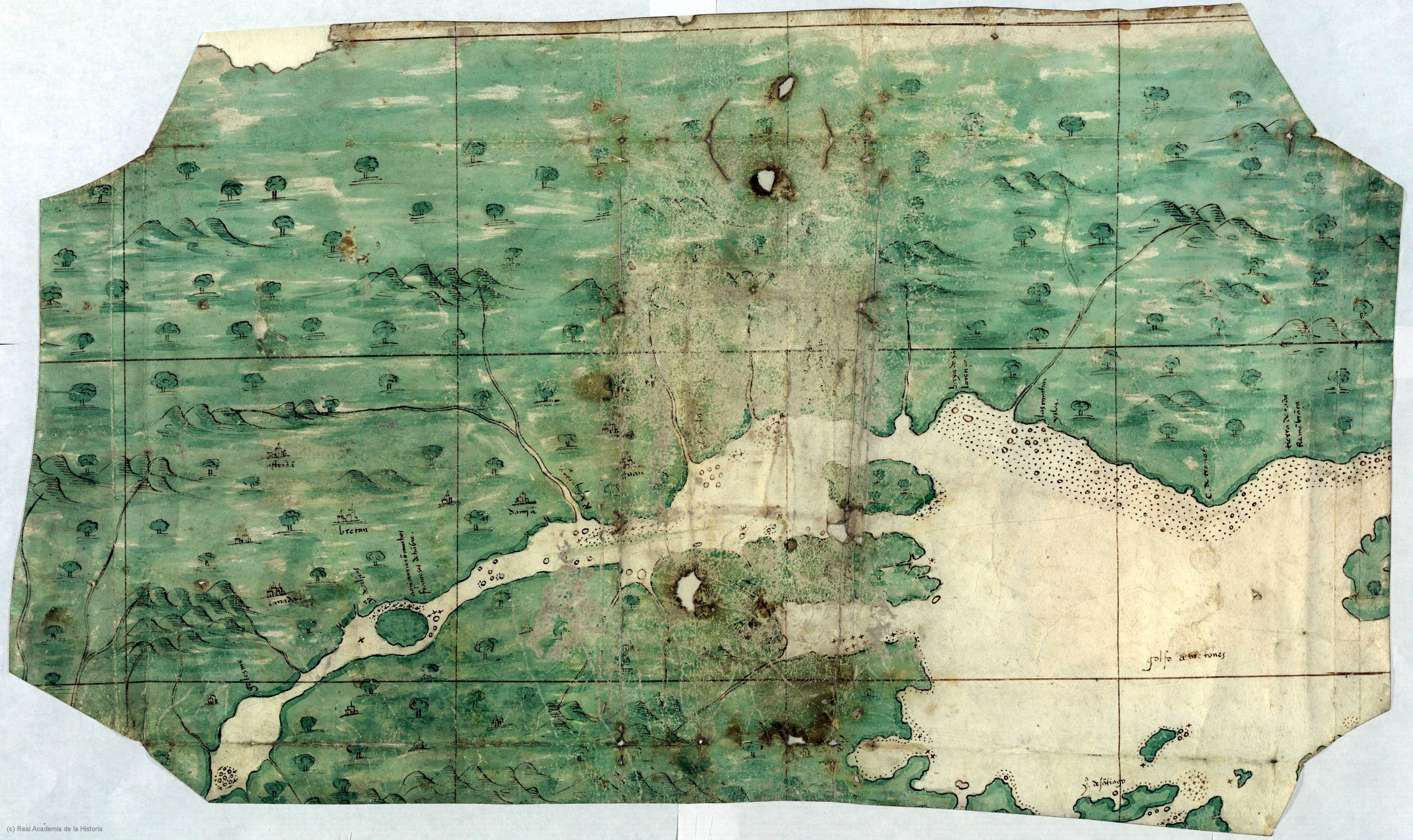 Throughout the 1500s, Wabanaki people encountered many European fishermen along with explorers looking for the Northwest Passage. They were at risk of being captured and enslaved. For instance, Portuguese explorer Estevan Gomez reached Wabanaki lands in 1525, kidnapping a few dozen people and taking them back to Spain, where he was forced to release them. The Crown did not arrange their passage back.
Italian explorer, Giovanni da Verrazano also reached Wabanaki lands. He was documented about 1525 as capturing a native boy to bring back to France, whom he was sailing for. Around 1534 French explorer
Throughout the 1500s, Wabanaki people encountered many European fishermen along with explorers looking for the Northwest Passage. They were at risk of being captured and enslaved. For instance, Portuguese explorer Estevan Gomez reached Wabanaki lands in 1525, kidnapping a few dozen people and taking them back to Spain, where he was forced to release them. The Crown did not arrange their passage back.
Italian explorer, Giovanni da Verrazano also reached Wabanaki lands. He was documented about 1525 as capturing a native boy to bring back to France, whom he was sailing for. Around 1534 French explorer  Champlain forged strong French relations with Algonquin tribes up until his death in 1635. Somewhere in the area near Ticonderoga and Crown Point, New York (historians dispute the site), Champlain and his party encountered a group of
Champlain forged strong French relations with Algonquin tribes up until his death in 1635. Somewhere in the area near Ticonderoga and Crown Point, New York (historians dispute the site), Champlain and his party encountered a group of
 The Caughnawaga Council was a large neutral political gathering in the Mohawk territory that occurred every three years for tribes and tribal confederacies within and around the Great Lakes, East Coast, and Saint Lawrence River. At one of these councils in the 1680s, the Eastern Algonquians came together to form their own confederation with the aid of an Ottawa " sakom." The Mawooshen Confederacy, of which Madockawando was part, was put in a situation where it would be absorbed into a larger confederacy that incorporated the tribes into each other's internal politics and would start to hold their own councils as a new political union. In this new union, the tribes would see each other as brothers, as family. The union helped challenge Iroquois hostilities along the
The Caughnawaga Council was a large neutral political gathering in the Mohawk territory that occurred every three years for tribes and tribal confederacies within and around the Great Lakes, East Coast, and Saint Lawrence River. At one of these councils in the 1680s, the Eastern Algonquians came together to form their own confederation with the aid of an Ottawa " sakom." The Mawooshen Confederacy, of which Madockawando was part, was put in a situation where it would be absorbed into a larger confederacy that incorporated the tribes into each other's internal politics and would start to hold their own councils as a new political union. In this new union, the tribes would see each other as brothers, as family. The union helped challenge Iroquois hostilities along the
 Probably influenced by diplomatic exchanges with Huron allies and Iroquois enemies (especially since the 1640s), the Wabanaki began using wampum belts in their diplomacy in the course of the 17th century, when envoys took such belts to send messages to allied tribes in the confederacy. Wampum belts called ''gelusewa'ngan'', meaning "speech", played an important role in maintaining Wabanaki political institutions. One of the last keepers of the "Wampum Record" and one of the last Wabanaki/Passamaquoddy delegates to go to Caughnawaga was Sepiel Selmo. Keepers of the wampum record were called ''putuwosuwin'' which involved a mix of oral history with understanding the context behind the placement of wampum on the belts.
Probably influenced by diplomatic exchanges with Huron allies and Iroquois enemies (especially since the 1640s), the Wabanaki began using wampum belts in their diplomacy in the course of the 17th century, when envoys took such belts to send messages to allied tribes in the confederacy. Wampum belts called ''gelusewa'ngan'', meaning "speech", played an important role in maintaining Wabanaki political institutions. One of the last keepers of the "Wampum Record" and one of the last Wabanaki/Passamaquoddy delegates to go to Caughnawaga was Sepiel Selmo. Keepers of the wampum record were called ''putuwosuwin'' which involved a mix of oral history with understanding the context behind the placement of wampum on the belts.
 Members of the Wabanaki Confederacy were the:
* ''(Eastern)
Members of the Wabanaki Confederacy were the:
* ''(Eastern)
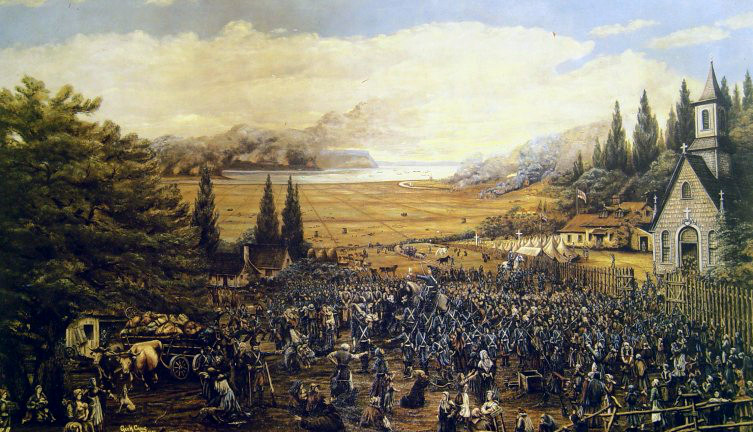 Prior to the
Prior to the
Image:The_Mi'kmaq.png,
Indian Treaties"Wabanaki People—A Story of Cultural Continuity"
, timeline curriculum by Abbe Museum
Dr. Harald E. L. Prins, "Storm Clouds over Wabanakiak Confederacy Diplomacy Until Dummer's Treaty (1727)"
Wabanaki Confederacy website
Miingignoti-Keteaoag
a partnership for the way of life of the Wabanaki Nations
{{DEFAULTSORT:Wabanaki Confederacy States and territories established in the 1680s States and territories disestablished in 1862 Algonquian peoples Historical regions First Nations history Abenaki Penobscot Passamaquoddy Maliseet Mi'kmaq Native American history of Massachusetts Native American history of Maine First Nations in Atlantic Canada Military history of Acadia Military history of Nova Scotia Military history of New England Former countries of the United States
North American
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the ...
First Nations and Native American confederation of four principal Eastern Algonquian nations: the Miꞌkmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the n ...
, Maliseet (''Wolastoqey''), Passamaquoddy
The Passamaquoddy ( Maliseet-Passamaquoddy: ''Peskotomuhkati'') are a Native American/First Nations people who live in northeastern North America. Their traditional homeland, Peskotomuhkatik'','' straddles the Canadian province of New Brunswick ...
(''Peskotomahkati'') and Penobscot
The Penobscot ( Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewi'') are an Indigenous people in North America from the Northeastern Woodlands region. They are organized as a federally recognized tribe in Maine and as a First Nations band government in the Atlantic ...
. The Western Abenaki are also considered members, being a loose identity for a number of allied tribal peoples such as the Sokoki, Cowasuck, Missiquoi, and Arsigantegok
The Androscoggin (Arosaguntacook, etc., see names) were an Abenaki people from what are now the U.S. states of Maine and New Hampshire. By the 18th century, they were absorbed by neighboring tribes.
Name
Arosaguntacook or Arossagunticook, the t ...
, among others.
There were more tribes, along with many bands, that were once part of the Confederation. Native tribes such as the Norridgewock
Norridgewock was the name of both an Indigenous village and a band of the Abenaki ("People of the Dawn") Native Americans/ First Nations, an Eastern Algonquian tribe of the United States and Canada. The French of New France called the village ...
, Etchemin, Alemousiski, and Canibas, through massacres, tribal consolidation, and ethnic label shifting were absorbed into the five larger national identities.
Members of the Wabanaki Confederacy, the Wabanaki, are located in and named for the area which they call ''Wabanakik'' ("Dawnland"), roughly the area that became the French colony of Acadia
Acadia (french: link=no, Acadie) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17th and earl ...
. It is made up of most of present-day Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
in the United States, and New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
, mainland Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
, Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (french: link=no, île du Cap-Breton, formerly '; gd, Ceap Breatainn or '; mic, Unamaꞌki) is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18. ...
, Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
and some of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
south of the St. Lawrence River, Anticosti, and Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
in Canada. The Western Abenaki live on lands in Quebec as well as in Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provin ...
, and New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
within the United States.Toensing, Gale Courey"Sacred fire lights the Wabanaki Confederacy"
''Indian Country Today'' (June 27, 2008), ICT Media Network
Name and etymology
The word Wabanaki is derived from the Algonquian root word ''"wab"'', combined with the word for "land", being ''"aki."'' "Wab" is a root that is used for the following concepts: Waban-aki can be translated into a number of ways but is most often translated into "Dawnland." The political union of the Wabanaki Confederacy was known by many names, but it is remembered as ''"Wabanaki"'', which shares a common etymological origin with the name of the "Abenaki" people. All Abenaki are Wabanaki, but not all Wabanaki are Abenaki. The name of the political union during the time it existed had gone by other names both shared and unique to its members. The Mi'kmaq, Passamaquoddy, and Wolastoqey called it ''Buduswagan'' which translates into "convention council." The Passamaquoddy also had their own unique name being ''Tolakutinaya'' which translates into "be related to one another." Finally, the Penobscot would interchangeably call it either ''Bezegowak'' or ''Gizangowak'' which can be translated into "those united into one" and "completely united" respectively.Early contact period (1497–1680s)
 Small-scale confederacies in and around what would become the Wabanaki Confederacy were common at the time of post-
Small-scale confederacies in and around what would become the Wabanaki Confederacy were common at the time of post-Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
European contact. The earliest known confederacy was the Mawooshen Confederacy located within the historic Eastern Penobscot cultural region. Its capital, ''Kadesquit'', located around modern Bangor, Maine
Bangor ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Maine and the county seat of Penobscot County. The city proper has a population of 31,753, making it the state's 3rd-largest settlement, behind Portland (68,408) and Lewiston (37,121).
Modern Bangor ...
, would play a significant role as a political hub - for the future Wabanaki Confederacy, for example.
In 1500, Portuguese explorer Gaspar Corte Real
Gaspar Corte-Real (1450–1501) was a Portuguese people, Portuguese Exploration, explorer who, alongside his father João Vaz Corte-Real and brother Miguel Corte-Real, Miguel, participated in various exploratory voyages sponsored by the Portuguese ...
reached Wabanaki lands. He captured and enslaved at least 57 people from modern-day Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
and Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
, selling them in Europe to help finance his trip. The rich fishing waters full of cod in and around the Gulf of Saint Lawrence attracted many Europeans to this area. By 1504 French Bretons were fishing off the coast of Nova Scotia. Norman fishermen began to arrive around 1507, and they too would start kidnapping people from the surrounding land. This would hurt relations with some tribes. But the fishermen also started slowly introducing European trade goods to the Wabanaki, returning to Europe with North American trade goods.
After the establishment of the Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Em ...
by which Catholic Europe established spheres of influence for exploration, Portuguese explorers commonly believed that Newfoundland and Wabanaki lands were on the Portuguese side of the '' Inter caetera'', entitling them to the land. Portuguese explorer João Álvares Fagundes attempted to establish the first European colony in Wabanaki lands in 1525. He brought families totaling almost 200 people, mostly from the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
, and founded a fishing settlement in Cape Breton, within Mi'kmaq territory. The settlement lasted at least until 1570, as fishing ships brought news of them back to Europe. The fate of the settlement is unknown, but the people would have interacted with the local Mi'kmaq.
 Throughout the 1500s, Wabanaki people encountered many European fishermen along with explorers looking for the Northwest Passage. They were at risk of being captured and enslaved. For instance, Portuguese explorer Estevan Gomez reached Wabanaki lands in 1525, kidnapping a few dozen people and taking them back to Spain, where he was forced to release them. The Crown did not arrange their passage back.
Italian explorer, Giovanni da Verrazano also reached Wabanaki lands. He was documented about 1525 as capturing a native boy to bring back to France, whom he was sailing for. Around 1534 French explorer
Throughout the 1500s, Wabanaki people encountered many European fishermen along with explorers looking for the Northwest Passage. They were at risk of being captured and enslaved. For instance, Portuguese explorer Estevan Gomez reached Wabanaki lands in 1525, kidnapping a few dozen people and taking them back to Spain, where he was forced to release them. The Crown did not arrange their passage back.
Italian explorer, Giovanni da Verrazano also reached Wabanaki lands. He was documented about 1525 as capturing a native boy to bring back to France, whom he was sailing for. Around 1534 French explorer Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier ( , also , , ; br, Jakez Karter; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French- Breton maritime explorer for France. Jacques Cartier was the first European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of ...
would explore the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and traded with Mi'kmaq people living in Chaleur Bay
frame, Satellite image of Chaleur Bay (NASA). Chaleur Bay is the large bay in the centre of the image; the Gaspé Peninsula is to the north and the Gulf of St. Lawrence is seen to the east.">Gulf_of_St._Lawrence.html" ;"title="Gaspé Peninsula ...
. He encountered people now known as St. Lawrence Iroquoians on the Gaspé Bay
Gaspé Bay () is a bay located on the northeast coast of the Gaspé Peninsula, Quebec, in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. The town of Gaspé, Quebec lies on a part of its southern shore, while most of its northern shore is in the Forillon National Park ...
. These are now believed to have been independent of the Five Nations of Iroquois that developed the Iroquois League further south. By the early 1600s, the St. Lawrence Iroquoian villages were abandoned. Historians now believe they may have been defeated by the Mohawk in competition over hunting. They may also have been defeated by Algonquins from further east in the St. Lawrence Valley.
Cartier traded with the Mi'kmaq, and returned to France with furs of North American animals such as beaver, which became high-demand items. Cartier brought back numerous goods from the First Nations from his three trips to the St. Lawrence, but the furs had the greatest demand. French colonists went to the area to work in what became the North American fur trade
The North American fur trade is the commercial trade in furs in North America. Various Indigenous peoples of the Americas traded furs with other tribes during the pre-Columbian era. Europeans started their participation in the North American fur ...
.
More Europeans entered Wabanaki lands over the coming decades, where they started as traders to meet the growing fur demand in Europe. The French established permanent trading operations with the Wabanaki around 1581 to obtain furs. Henry III of France
Henry III (french: Henri III, né Alexandre Édouard; pl, Henryk Walezy; lt, Henrikas Valua; 19 September 1551 – 2 August 1589) was King of France from 1574 until his assassination in 1589, as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Li ...
granted a fur monopoly to French merchants in 1588. This would lead to the desire for the French to establish permanent trade posts in and around Wabanaki lands for furs. French fur traders like François Gravé Du Pont
François Gravé (Saint-Malo, November 1560 – 1629 or soon after), said ''Du Pont'' (or ''Le Pont'', ''Pontgravé''...), was a Breton navigator (captain on the sea and on the "Big River of Canada"), an early fur trader and explorer in the N ...
would often travel to Wabanaki lands to obtain furs, establishing the French fur trading site of Tadoussac
Tadoussac () is a village in Quebec, Canada, at the confluence of the Saguenay and Saint Lawrence rivers. The indigenous Innu call the place ''Totouskak'' (plural for ''totouswk'' or ''totochak'') meaning "bosom", probably in reference to the tw ...
in 1599. During one of his trips back in 1603 he would bring Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; Fichier OrigineFor a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December 1635) was a Fr ...
with him, and he would lead to a new era of Wabanaki/French relationships.
When Champlain established contact during an expedition to the Mawooshen in Pesamkuk (present-day Mount Desert Island, Maine) in 1604, he noted that the people had quite a few European goods. Champlain had a positive encounter on Pemetic, meeting with sakom (title for community leaders) Asticou in his and his people's summer village. Asticou was a sakom with regional power over the eastern door of Mawooshen. He was subsidiary to sakom Bashaba, who led the entire Mawooshen Confederacy. Champlain went upriver to the Passamaquoddy, where he established another post at present-day St. Croix, Maine. The French colonial region known as Acadia
Acadia (french: link=no, Acadie) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17th and earl ...
developed on existing tribal territory. The ethnic French of Acadia
Acadia (french: link=no, Acadie) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17th and earl ...
and the peoples of Wabanaki coexisted in the same territory with independent, yet allied governments.
Champlain continued to establish settlements throughout Wabanaki territory, including Saint John (1604) and Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is t ...
(1608), among others. The trade and military relations between the French and the local Algonquin tribes, including the Mawooshen and later Wabanaki, lasted until the end of the French and Indian/Seven Years' War. Asticou approved the founding of a Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
mission in 1613.
The following year the mission village was destroyed by a group of English colonists led John Smith, who stopped there while on a return voyage to Europe. French and English colonists would long compete for territory in North America. To make more money, Smith invited 20 Algonquin people in modern-day Massachusetts to board his ship to trade, but he enslaved them all to sell in Spain. The famous Tisquantum was among the captives. According to an early 20th-century account, he returned to the area just before the Pilgrims landed in 1620.
English colonists established contacts with the Mawooshen in 1605. Captain George Weymouth
George Weymouth (Waymouth) () was an English explorer of the area now occupied by the state of Maine.
Voyages
George Weymouth was a native of Cockington, Devon, who spent his youth studying shipbuilding and mathematics.
In 1602 Weymouth was ...
met with them in a large village on the Kennebec River
The Kennebec River (Abenaki: ''Kinəpékʷihtəkʷ'') is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed June 30, 2011 river within the U.S. state of Maine. It rises in Moosehead ...
. He took five people as captives to take back to England, where they were questioned about settlements by Sir Ferdinando Gorges
Sir Ferdinando Gorges ( – 24 May 1647) was a naval and military commander and governor of the important port of Plymouth in England. He was involved in Essex's Rebellion against the Queen, but escaped punishment by testifying against the mai ...
. Sakom Tahánedo was the only one of those captives known to have returned home. He accompanied settlers of the short-lived Popham Colony (1607-1608), who hoped to establish good relations with the local peoples be returning Tahánedo, but local tribes were uneasy about the English colony.
In 2020 journalist Avery Yale Kamila
Avery Yale Kamila is an American journalist, vegan columnist and community organizer in the state of Maine.
Biography
Kamila was born in Westminster, Massachusetts in the 1970s and grew up on an organic farm in Litchfield, Maine. Kamila adopte ...
wrote that the account of the Weymouth voyage has culinary significance because it "is the first time a European recorded the Native American use of nut milks and nut butters."
 Champlain forged strong French relations with Algonquin tribes up until his death in 1635. Somewhere in the area near Ticonderoga and Crown Point, New York (historians dispute the site), Champlain and his party encountered a group of
Champlain forged strong French relations with Algonquin tribes up until his death in 1635. Somewhere in the area near Ticonderoga and Crown Point, New York (historians dispute the site), Champlain and his party encountered a group of Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
(likely mostly Mohawk, the easternmost nation). In a battle that began the next day, 250 Iroquois advanced on Champlain's position, and one of his guides pointed out the three chiefs. In his account of the battle, Champlain recounts firing his arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus ...
and killing two of them with a single shot, after which one of his men killed the third. The Iroquois turned and fled. This action set the tone for poor French-Iroquois relations for the rest of the century, with conflicts arising over territory and the beaver trade.
The next year the Battle of Sorel started on 19 June 1610. Champlain was aided by warriors of allies among the Wendat, Algonquin and Innu
The Innu / Ilnu ("man", "person") or Innut / Innuat / Ilnuatsh ("people"), formerly called Montagnais from the French colonial period ( French for "mountain people", English pronunciation: ), are the Indigenous inhabitants of territory in the ...
peoples, with some French regulars. They fought against the Mohawk people
The Mohawk people ( moh, Kanienʼkehá꞉ka) are the most easterly section of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy. They are an Iroquoian-speaking Indigenous people of North America, with communities in southeastern Canada and northern Ne ...
at present-day Sorel-Tracy, Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
. Champlain's forces were armed with the arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus ...
. After engaging their opponent, they slaughtered or captured nearly all of the Mohawk. The battle ended major hostilities with the Mohawk for twenty years.
In and around this time, more French arrived as traders in Nova Scotia. The French migrants formed settlements such as Port-Royal Port Royal is the former capital city of Jamaica.
Port Royal or Port Royale may also refer to:
Institutions
* Port-Royal-des-Champs, an abbey near Paris, France, which spawned influential schools and writers of the 17th century
** Port-Royal Ab ...
. At many of these settlements, the French traded weapon
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, s ...
s and other European goods
In economics, goods are items that satisfy human wants
and provide utility, for example, to a consumer making a purchase of a satisfying product. A common distinction is made between goods which are transferable, and services, which are not ...
to the local Mi'kmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the no ...
. The influx of European goods changed the social and economic landscape, as local tribes became more dependent on European goods. This new economic reality harmed their existing kinship
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that ...
ties among clans and reduced the reciprocal exchange that had supported the local economy. Subsistence
A subsistence economy is an economy directed to basic subsistence (the provision of food, clothing, shelter) rather than to the market. Henceforth, "subsistence" is understood as supporting oneself at a minimum level. Often, the subsistence econo ...
hunting shifted into a competition for animals like beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers a ...
and for access to European settlements. Population movements, and intraband and interband disputes were affected.
Allied with the Maliseet and Passamaquoddy, the Mi'kmaq fought with their Western Mawooshen (Western Abenaki/Penobscot) neighbors for goods as trading relations broke down. This power imbalance resulted in war starting around 1607. In 1615 the Mi'kmaq and their allies killed the Mawooshen Grand Chief Bashabas in his village. War was costly for the Mi'kmaq and their allies, but especially for their southern Abenaki/Penobscot adversaries. Many Abenaki villages faced great losses from the war. The war was then followed by a pandemic
A pandemic () is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. A widespread endemic disease with a stable number of in ...
known as "The Great Dying" (1616-1619), which killed around 70-95% of the local Algonquin population left after the war.
Not long after this widespread local depopulation, Pilgrim settlers from England arrived in November 1620. Algonquin peoples throughout what would become New England began to see Pilgrim settlers settling in their ancestral lands. Southern Abenaki people such as the Alemousiski would soon come into permanent contact with English settlers moving into Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
, as well as their lands in southern Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
under the colonizing efforts of people directed by Ferdinando Gorges
Sir Ferdinando Gorges ( – 24 May 1647) was a naval and military commander and governor of the important port of Plymouth in England. He was involved in Essex's Rebellion against the Queen, but escaped punishment by testifying against the mai ...
and John Mason, respectively. Pannaway Plantation near modern-day Kittery, Maine
Kittery is a town in York County, Maine, United States. Home to the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard on Seavey's Island, Kittery includes Badger's Island, the seaside district of Kittery Point, and part of the Isles of Shoals. The southernmost tow ...
would both be founded in 1623. Originally founded as fishing and lumber villages, over the decades they developed larger economies and became major population centers in the fledgling economy.
By the 1640s, internal conflicts within the region started to make Iroquois advances harder to combat for what would become the Wabanaki peoples, but also the Algonquian (tribe west of Quebec City), the Innu
The Innu / Ilnu ("man", "person") or Innut / Innuat / Ilnuatsh ("people"), formerly called Montagnais from the French colonial period ( French for "mountain people", English pronunciation: ), are the Indigenous inhabitants of territory in the ...
, and French to manage separately. Aided by French Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
, this led to the formation of a large Algonquian league against the Iroquois, who were making significant territorial land gains around the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
and Saint Lawrence River region. By the 1660s, tribes of Western Abenaki peoples as far south as Massachusetts had joined the league. This defensive alliance would not only prove to be successful, but it helped repair the relationship among the Eastern Algonquians, promoting greater political cooperation
Cooperation (written as co-operation in British English) is the process of groups of organisms working or acting together for common, mutual, or some underlying benefit, as opposed to working in competition for selfish benefit. Many animal a ...
in the coming decades.
This growing tension with two large and organized political adversaries, the Iroquois and especially English colonists, over the next 20 years would lead to an Algonquian uprising during King Philip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1676 between indigenous inhabitants of New England and New England coloni ...
(1675-1676), followed by the First Abenaki War
The First Abenaki War (also known as the northern theatre of King Philip's War) was fought along the New England/Acadia border primarily in present-day Maine. Richard Waldron and Charles Frost led the forces in the northern region, while Jean-Vin ...
(1675-1678). Soon after the many Algonquian tribes fought together in an effort to strengthen both defensive and diplomatic
Diplomatics (in American English, and in most anglophone countries), or diplomatic (in British English), is a scholarly discipline centred on the critical analysis of documents: especially, historical documents. It focuses on the conventions, p ...
power, a push to make a formal political union would take place leading to the development of the Wabanaki Confederacy.
Formation of the Wabanaki Confederacy (1680s)
TheFirst Abenaki War
The First Abenaki War (also known as the northern theatre of King Philip's War) was fought along the New England/Acadia border primarily in present-day Maine. Richard Waldron and Charles Frost led the forces in the northern region, while Jean-Vin ...
saw native peoples throughout the Eastern Algonquian lands face a common and powerful enemy, encroaching English colonists. The fighting led to large-scale depopulation
A population decline (also sometimes called underpopulation, depopulation, or population collapse) in humans is a reduction in a human population size. Over the long term, stretching from prehistory to the present, Earth's total human population ...
of English colonial settlements north of the Saco River in the district of Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
, while Wabanaki people south of the river like the Armouchiquois, would be forced from their ancestral lands. The political situation was complicated, when the Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as th ...
was forced to relinquish control of Maine to the heirs of Ferdinando Gorges
Sir Ferdinando Gorges ( – 24 May 1647) was a naval and military commander and governor of the important port of Plymouth in England. He was involved in Essex's Rebellion against the Queen, but escaped punishment by testifying against the mai ...
in 1676. This required them to find the heirs to buy back the land making up Maine, and then to issue grants for people to settle once again. This conflict as a whole was not without significant losses for the soon-to-be Wabanaki peoples, and it became clear that the tribes would have to work together. The First Abenaki War ended with the Treaty of Casco, which forced all the tribes to recognize the property rights of English colonists in southern Maine. In return, English colonists recognized "Wabanaki" sovereignty by committing themselves to pay Madockawando, as a "grandchief" of the Wabanaki alliance, a symbolic annual fee of "a peck of corn for every English Family." They also recognized the Saco River as the border.
 The Caughnawaga Council was a large neutral political gathering in the Mohawk territory that occurred every three years for tribes and tribal confederacies within and around the Great Lakes, East Coast, and Saint Lawrence River. At one of these councils in the 1680s, the Eastern Algonquians came together to form their own confederation with the aid of an Ottawa " sakom." The Mawooshen Confederacy, of which Madockawando was part, was put in a situation where it would be absorbed into a larger confederacy that incorporated the tribes into each other's internal politics and would start to hold their own councils as a new political union. In this new union, the tribes would see each other as brothers, as family. The union helped challenge Iroquois hostilities along the
The Caughnawaga Council was a large neutral political gathering in the Mohawk territory that occurred every three years for tribes and tribal confederacies within and around the Great Lakes, East Coast, and Saint Lawrence River. At one of these councils in the 1680s, the Eastern Algonquians came together to form their own confederation with the aid of an Ottawa " sakom." The Mawooshen Confederacy, of which Madockawando was part, was put in a situation where it would be absorbed into a larger confederacy that incorporated the tribes into each other's internal politics and would start to hold their own councils as a new political union. In this new union, the tribes would see each other as brothers, as family. The union helped challenge Iroquois hostilities along the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
over land and resources which was becoming a bigger problem for almost all the Eastern Algonquians to manage separately, but also provided political organization and might to push back collectively against growing English colonial expansionism, as well as mitigating large losses in the recent three-year war with them.
The political union incorporated many political elements from other local confederacies like the Iroquois and Huron
Huron may refer to:
People
* Wyandot people (or Wendat), indigenous to North America
* Wyandot language, spoken by them
* Huron-Wendat Nation, a Huron-Wendat First Nation with a community in Wendake, Quebec
* Nottawaseppi Huron Band of Potawato ...
, the role of wampum council conduct being a major example. This political unit allowed for the safe passage of people through each of their territories (including camping and subsisting on the land), safer trade networks from the western agricultural centers to the eastern gathering economies (copper/pelts) through non-aggression pacts and sharing natural resources from their respected habitats, freedom to move to each and any of the other's villages along with organizing inter-tribal marriages, and a large-scale defensive alliance to fend off attacks in their now shared territory. Madockawando for instance would later move from Penobscot lands to Maliseet lands, living in their political hub of Meductic until his death. These events would lead to the formal creation of what is now called the Wabanaki Confederacy.
The Passamaquoddy wampum record or ''Wapapi Akonutomakonol'' tells about the event that took place at the Caughnawaga Council that led to the formation of the Wabanaki Confederacy.Silently they sat for seven days. Everyday, no one spoke. That was called, "The Wigwam is Silent." Every councilor had to think about what he was going to say when they made the laws. All of them thought about how the fighting could be stopped. Next they opened up the wigwam. It was now called "Every One of Them Talks." And during that time they began their council....When all had finished talking, they decided to make a great fence; and in addition they put in the center a great wigwam within the fence; and also they made a whip and placed it with their father. Then whoever disobeyed him would be whipped. Whichever of his children was within the fence - all of them had to obey him. And he always had to kindle their great fire, so that it would not burn out. This is where the Wampum Laws originated. That fence was the confederacy agreement....There would be no arguing with one another again. They had to live like brothers and sisters who had the same parent....And their parent, he was the great chief at Caughnawaga. And the fence and the whip were the Wampum Laws. Whoever disobeyed them, the tribes together had to watch him.
Governance
The Wabanaki Confederacy were governed by a council of elected sakoms, tribal leaders who were frequently also the governors of thedrainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
their village was built on. Sakoms themselves were more of respected listeners and debaters than simply rulers.
Wabanaki politics was fundamentally rooted on reaching a consensus on issues, often after much debate. Sakoms frequently used stylized metaphorical speech at council fires, trying to win over others sakoms. Sakoms who were skilled at debate often became quite influential in the Confederacy, often being older men who were called ''nebáulinowak'' or "riddle men." "They have reproached me a hundred times because we fear our Captains, while they laugh at and make sport of theirs. All the authority of their chief is in his tongue's end; for he is powerful in so far as he is eloquent; and even if he kills himself talking and haranguing he will not be obeyed unless he please the ndians"Wabanaki sakoms held regular conventions at their various "council fires" (seats of government) whenever there was a need to call each other together. In a council fire, they would sit in a large rectangle with all members facing each other. Each sakom member would have a chance to speak and be listened to, with the understanding that they would do the same for the others. Each tribe a sakom was part of also had a "kinship" status, being that they are brothers some members were older and younger. The lack of a single centralized capital complemented the Wabanaki government style, as sakoms were able to shift their political influence to any part of the nation that needed it. This could mean bringing leadership near or away from conflict zones. When a formal internal agreement was reached, not one but often at least five representatives speaking on behalf of their respective tribe and nation as a whole would set off to negotiate.
 Probably influenced by diplomatic exchanges with Huron allies and Iroquois enemies (especially since the 1640s), the Wabanaki began using wampum belts in their diplomacy in the course of the 17th century, when envoys took such belts to send messages to allied tribes in the confederacy. Wampum belts called ''gelusewa'ngan'', meaning "speech", played an important role in maintaining Wabanaki political institutions. One of the last keepers of the "Wampum Record" and one of the last Wabanaki/Passamaquoddy delegates to go to Caughnawaga was Sepiel Selmo. Keepers of the wampum record were called ''putuwosuwin'' which involved a mix of oral history with understanding the context behind the placement of wampum on the belts.
Probably influenced by diplomatic exchanges with Huron allies and Iroquois enemies (especially since the 1640s), the Wabanaki began using wampum belts in their diplomacy in the course of the 17th century, when envoys took such belts to send messages to allied tribes in the confederacy. Wampum belts called ''gelusewa'ngan'', meaning "speech", played an important role in maintaining Wabanaki political institutions. One of the last keepers of the "Wampum Record" and one of the last Wabanaki/Passamaquoddy delegates to go to Caughnawaga was Sepiel Selmo. Keepers of the wampum record were called ''putuwosuwin'' which involved a mix of oral history with understanding the context behind the placement of wampum on the belts.Wampum shells arranged on strings in such a manner, that certain combinations suggested certain sentences or certain ideas to the narrator, who, of course, knew his record by heart and was merely aided by the association of the shell combinations in his mind with incidents of the tale or record which he was rendering.What was not recorded through wampum was remembered in a long chain of oral record-keeping which village elders were in charge of, with multiple elders being able to double check each other. In the 1726 treaty following Dummer's War, the Wabanaki had to challenge a claim that land was sold to English settlers, of which not a single elder had a memory of. After much challenge with New England Lt. Governor William Dummer, Wabanaki leadership was very careful and took their time to make sure there was as little misunderstanding of the terms of the land and peace as possible. The terms were worked out little by little each day, from August 1 through 5th. When an impasse was found, leadership would withdraw to talk about the matter thoroughly among themselves before reconvening to debate once more, with all representatives debating on the same page, with their most well thought-out arguments. The Wabanaki never had a formal "grandchief" or single leader of the whole confederacy, and thus never had a single
seat of government
The seat of government is (as defined by ''Brewer's Politics'') "the building, complex of buildings or the city from which a government exercises its authority".
In most countries, the nation’s capital is also seat of its government, thus that ...
. Though Madockawando was treated as such in the Treaty of Casco, and his descendants such as Wabanaki Lieutenant-Governor John Neptune would maintain an elevated status in the confederacy, both officially had the same amount of power as any other sakom. This would continue throughout the entire history of the Wabanaki, as the confederacy remained decentralized so as to never give more power to any of the member tribes. This meant that all major decisions had to be thoroughly debated by sakoms at council fires, which created a strong political culture empowering the best debaters.
The four/fourteen tribes were not completely independent from each other. Not only was it possible for sanctions to be placed on each other for creating problems, but also when a sakom died, newly elected sakoms would be confirmed by allied Wabanaki tribes who would visit following a year of mourning in the village. An event to appoint a new sakom, known as a ''Nská'wehadin'' or "assembly", could last several weeks. Tribes had a lot of autonomy, but they built a culture which normalized being involved in each other's political affairs to help maintain unity and cooperation. This event would continue until 1861 when the last Nská'wehadin was held in Old Town, Maine
Old Town is a city in Penobscot County, Maine, United States. The population was 7,431 at the 2020 census. The city's developed area is chiefly located on the relatively large Marsh Island, though its boundaries extend beyond that. The island i ...
, shortly before the end of the confederacy. Occasionally some sakoms were known to ignore the will of the confederacy, most often the case for tribes on the border of European powers who had the most to lose during peace after war. Gray Lock
Gray Lock (or Greylock, born Wawanotewat, Wawanolet, or Wawanolewat), was a Western Abenaki warrior chieftain of Woronoco/Pocumtuck ancestry who came to lead the Missisquoi Abenaki band, and whose direct descendants have led the Missisquoi Aben ...
, who was among the most successful wartime Wabanaki sakoms, refused to make peace after the 1722-1726 Dummer's War
Dummer's War (1722–1725) is also known as Father Rale's War, Lovewell's War, Greylock's War, the Three Years War, the Wabanaki-New England War, or the Fourth Anglo-Abenaki War. It was a series of battles between the New England Colonies and the ...
, given that his Vermont lands were being settled by English colonists. He would hold a successful guerrilla war
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tactics ...
for the following two decades, never being caught, and successfully deterring settlers entering his lands.
Kinship metaphors like "Brother", "Father", or "Uncle" in their original linguistic context were much more complex than when they were when translated into English or French. Such terms were used to understand the status and role of a diplomatic relationship. For instance, for the other tribes in the Wabanaki the Penobscot were called the ''ksés'i'zena'' or "our elder brother". The Passamaquoddy, Maliseet, and Mi'kmaq in this order of "age" were called ''ndo'kani'mi'zena'' or "our younger brother". The Maliseet referred to the Penobscot and Passamaquoddy as ''ksés'i'zena'' and the Mi'kmaq as ''ndo'kani'mi'zena''. Concepts like this were also found in other confederacies like the Iroquois. In the Wabanaki context, such terms indicated concepts like the Penobscot looking out for the well-being of the younger brothers, while younger brothers would support and respect the wisdom of an older brother. The idea of being related helped establish unity and cooperation in Wabanaki culture, using family as a metaphor to overcome factionalism and to quell internal conflicts like a family would. The age rank was based on the tribes proximity to the Caughnawaga Council, with the Penobscots being the closest. Before the massacre of the Norridgewock and the slow abandonment of their settlements and integration into their neighbor tribes, they were once seen as an older brother to the Penobscot.
This system was not seen as something indicating superiority per se, but rather a way to perceive a relationship in a manner that reflected the cultural norms of the Wabanaki. When the Wabanaki called the French Canadian governor and King of France "our father", it was a relationship built upon a sense of respect and protective care that reflected a Wabanaki father-son relationship. This was not well understood by diplomats from France and England who did not live with the peoples, seeing such terms as acknowledgment of subservience. Miscommunication over these terms was one of the biggest challenges in Wabanaki and European diplomacy. The culture and government style of Wabanaki would strongly push for a clear and mutual understanding of political matters, both internally and externally.
The Wabanaki saw and called the Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the c ...
"our father" for both their role as a leader in the Caughnawaga Council and in being a tribe that helped found Wabanaki and issued binding judgments that help maintain order. This did not mean the Wabanaki ever saw themselves as subservient to the Ottawa in any way, this was the same with the French. The Ottawa were largely seen as a form of third party political oversight.
Military
Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pre ...
'' or ''Panuwapskek'' (Penobscot
The Penobscot ( Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewi'') are an Indigenous people in North America from the Northeastern Woodlands region. They are organized as a federally recognized tribe in Maine and as a First Nations band government in the Atlantic ...
)
* ''(Western) Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pre ...
''
* ''Míkmaq'' (Miꞌkmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the n ...
, L'nu)
* ''Peskotomuhkati'' (Passamaquoddy
The Passamaquoddy ( Maliseet-Passamaquoddy: ''Peskotomuhkati'') are a Native American/First Nations people who live in northeastern North America. Their traditional homeland, Peskotomuhkatik'','' straddles the Canadian province of New Brunswick ...
)
* ''Wolastoqew'', ''Wolastoq'' (Maliseet
The Wəlastəkwewiyik, or Maliseet (, also spelled Malecite), are an Algonquian-speaking First Nation of the Wabanaki Confederacy. They are the indigenous people of the Wolastoq ( Saint John River) valley and its tributaries. Their territory ...
or Malicite)
Nations in the Confederacy also allied with the Innu
The Innu / Ilnu ("man", "person") or Innut / Innuat / Ilnuatsh ("people"), formerly called Montagnais from the French colonial period ( French for "mountain people", English pronunciation: ), are the Indigenous inhabitants of territory in the ...
of Nitassinan, the Algonquin people
The Algonquin people are an Indigenous people who now live in Eastern Canada. They speak the Algonquin language, which is part of the Algonquian language family. Culturally and linguistically, they are closely related to the Odawa, Potawatomi ...
and with the Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoia ...
-speaking Wyandot people
The Wyandot people, or Wyandotte and Waⁿdát, are Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands. The Wyandot are Iroquoian Indigenous peoples of North America who emerged as a confederacy of tribes around the north shore of Lake Ontario ...
. The homeland of the Wabanaki Confederacy stretches from Newfoundland, Canada to Massachusetts, United States. Members of the Wabanaki Confederacy participated in seven major wars.
*King Phillip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1676 between indigenous inhabitants of New England and New England colon ...
(1675–1678)
*King William's War
King William's War (also known as the Second Indian War, Father Baudoin's War, Castin's War, or the First Intercolonial War in French) was the North American theater of the Nine Years' War (1688–1697), also known as the War of the Grand Alli ...
(1688–1697)
*Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In E ...
(1702–1713)
*Dummer's War
Dummer's War (1722–1725) is also known as Father Rale's War, Lovewell's War, Greylock's War, the Three Years War, the Wabanaki-New England War, or the Fourth Anglo-Abenaki War. It was a series of battles between the New England Colonies and the ...
(1722–1725)
*King George's War
King George's War (1744–1748) is the name given to the military operations in North America that formed part of the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748). It was the third of the four French and Indian Wars. It took place primarily in t ...
(1744–1748)
*Father Le Loutre's War
Father Le Loutre's War (1749–1755), also known as the Indian War, the Mi'kmaq War and the Anglo-Mi'kmaq War, took place between King George's War and the French and Indian War in Acadia and Nova Scotia. On one side of the conflict, the Br ...
(1749–1755)
*French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the st ...
(1754–1763)
During this period, their population was radically decimated due to many decades of warfare, but also because of famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompan ...
s and devastating epidemics of infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
. The number of European settlers increased from about 300 in 1650 to about 6,650 in 1750. European diseases such as smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
and measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
were introduced.
British military campaign against New France
TheMiꞌkmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the n ...
were among the first tribes to establish trade with European settlers and helped to establish a barter
In trade, barter (derived from ''baretor'') is a system of exchange in which participants in a transaction directly exchange goods or services for other goods or services without using a medium of exchange, such as money. Economists disti ...
system along the coast. Settlers and natives communicated in a language that mixed French and Mikmawisimk. The Miꞌkmaq traded beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers a ...
, otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes we ...
, marten
A marten is a weasel-like mammal in the genus ''Martes'' within the subfamily Guloninae, in the family Mustelidae. They have bushy tails and large paws with partially retractile claws. The fur varies from yellowish to dark brown, depending on ...
, seal, moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
, and deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
furs with European settlers. The French missionary Chrestien Le Clercq complained, that "they ridicule and laugh at the most sumptuous and magnificent of our buildings".
In 1711 the Acadians
The Acadians (french: Acadiens , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Most Acadians live in the region of Acadia, as it is the region where the de ...
joined the Wabanaki Confederacy, when Fort Anne was besieged. The British proceeded to raid the coastal settlements, demanding an oath of allegiance from the Acadians. When British settlers encroached on the territory of the Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pre ...
, Penobscot
The Penobscot ( Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewi'') are an Indigenous people in North America from the Northeastern Woodlands region. They are organized as a federally recognized tribe in Maine and as a First Nations band government in the Atlantic ...
, and the Passamaquoddy
The Passamaquoddy ( Maliseet-Passamaquoddy: ''Peskotomuhkati'') are a Native American/First Nations people who live in northeastern North America. Their traditional homeland, Peskotomuhkatik'','' straddles the Canadian province of New Brunswick ...
, these First Nations joined the Maliseet
The Wəlastəkwewiyik, or Maliseet (, also spelled Malecite), are an Algonquian-speaking First Nation of the Wabanaki Confederacy. They are the indigenous people of the Wolastoq ( Saint John River) valley and its tributaries. Their territory ...
and the Miꞌkmaq in the Wabanaki Confederacy. In 1715 the Miꞌkmaq attacked fishing vessels off Sable Island. The Miꞌkmaq declared "the Lands are ursand ecan make War and peace when eplease". The Wabanaki Confederacy did not fight under the leadership of a commander, but nevertheless implemented a strategy that was aimed to clear their land of intruders. Between 1722 and 1724 the Penobscot attacked Fort St. George four times, the Wabanakis attacked British colonial settlements along Kennebec River
The Kennebec River (Abenaki: ''Kinəpékʷihtəkʷ'') is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed June 30, 2011 river within the U.S. state of Maine. It rises in Moosehead ...
, while western Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
was attacked by the Pigwacket
The Pequawket (also Pigwacket and many other spelling variants, from Eastern Abenaki ''apíkwahki'', "land of hollows") are a Native American subdivision of the Abenaki people who formerly lived near the headwaters of the Saco River in Carroll ...
and the Amarascoggin. The Wabanaki Confederacy destroyed the Brunswick settlement as well as other British colonial settlements on the banks of the Androscoggin River
The Androscoggin River (Abenaki: ''Aləssíkαntekʷ'') is a river in the U.S. states of Maine and New Hampshire, in northern New England. It is U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Ma ...
.
 Prior to the
Prior to the Expulsion of the Acadians
The Expulsion of the Acadians, also known as the Great Upheaval, the Great Expulsion, the Great Deportation, and the Deportation of the Acadians (french: Le Grand Dérangement or ), was the forced removal, by the British, of the Acadian peo ...
(1755–1764), the Acadians living in Nova Scotia largely refused to swear allegiance to the British Crown. When the Acadians in 1755 again refused to swear allegiance to the Crown, about 6,000 were deported to British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestow ...
, France and Louisiana. Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
was taken by the British in 1759 and the French government effectively lost all influence in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
.
British rule
The French were defeated by the British in 1753. The British colonial authorities marginalised Indigenous people as a matter ofpolicy
Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an orga ...
, because the Mi'kmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the no ...
had supported the French. 13,000 French settlers were evicted by the British and the land was occupied by settlers from New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
, Britain and other Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an countries, including Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
.
After 1783 and the end of the American Revolutionary War, Black Loyalist
Black Loyalists were people of African descent who sided with the Loyalists during the American Revolutionary War. In particular, the term refers to men who escaped enslavement by Patriot masters and served on the Loyalist side because of the C ...
s, freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), emancipation (granted freedom ...
from the British North American colonies, were resettled by the British in this historical territory. They had promised slave
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
s freedom if they left their Patriot masters and joined the British. Three thousand freedmen were evacuated to Nova Scotia by British ships from the colonies after the war.
Oppressive policies instituted by successive colonial and federal administrations against the Acadians
The Acadians (french: Acadiens , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Most Acadians live in the region of Acadia, as it is the region where the de ...
, Black Canadians and Mi'kmaq people tended to force these peoples together as allies of necessity. Some white and black parents left their children behind in reserves to be raised according to Wabanaki culture, even as late as the 1970s. The colonial government declared the Wabanaki Confederacy forcibly disbanded in 1862. However the five Wabanaki nations still exist, continued to meet, and the Confederacy was formally re-established in 1993.
Contemporary revival
The Wabanaki Confederacy gathering was revived in 1993. The first reconstituted confederacy conference in contemporary time was developed and proposed by Claude Aubin and Beaver Paul and hosted by the Mi'kmaq community of Listuguj under the leadership of Chief Brenda Gideon Miller. The sacred Council Fire was lit again, and embers from the fire have been kept burning continually since then. The revival of the Wabanaki Confederacy brought together the Passamaquoddy Nation, Penobscot Nation, Maliseet Nation, the Miꞌkmaq Nation, and the Abenaki Nation. Following the 2010Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples
The Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP or DOTROIP) is a legally non-binding resolution passed by the United Nations in 2007. It delineates and defines the individual and collective rights of Indigenous peoples, including th ...
(UNDRIP), the member nations began to re-assert their treaty rights, and the Wabanaki leadership emphasized the continuing role of the Confederacy in protecting natural capital
Natural capital is the world's stock of natural resources, which includes geology, soils, air, water and all living organisms. Some natural capital assets provide people with free goods and services, often called ecosystem services. All of t ...
.
There were meetings amongst allies, a "Water Convergence Ceremony" in May 2013, with Algonquin grandmothers in August 2013 supported by Kairos Canada, and with other Indigenous groups.
Alma Brooks represented the Confederacy at the June 2014 UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues
The United Nations Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues (UNPFII or PFII) is the UN's central coordinating body for matters relating to the concerns and rights of the world's indigenous peoples. There are more than 370 million indigenous pe ...
. She discussed the Wabanaki/Wolostoq position on the Energy East
The Energy East pipeline was a proposed oil pipeline in Canada. It would have delivered diluted bitumen from Western Canada and North Western United States to Eastern Canada, from receipt points in Alberta, Saskatchewan and North Dakota to ref ...
pipeline. Opposition to its construction has been a catalyst for organizing:
"On May 30015 Fifteen or 15 may refer to: *15 (number), the natural number following 14 and preceding 16 *one of the years 15 BC, AD 15, 1915, 2015 Music *Fifteen (band), a punk rock band Albums * ''15'' (Buckcherry album), 2005 * ''15'' (Ani Lorak albu ...residents of Saint John will join others inAtlantic Canada Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (french: provinces de l'Atlantique), is the region of Eastern Canada comprising the provinces located on the Atlantic coast, excluding Quebec. The four provinces are New Brunswick, Newfoundla ..., including Indigenous people from the Wolastoqiyik (Maliseet), Passamaquoddy and Mi'kmaq, to march to the end of the proposed pipeline and draw a line in the sand." This was widely publicized.
2015 Grandmothers' Declaration
These and other preparatory meetings set an agenda for the August 19–22, 2015, meeting which produced the promised Grandmothers' Declaration "adopted unanimously at N'dakinna (Shelburne, Vermont
Shelburne is a town in Chittenden County, Vermont, United States. Located along the shores of Lake Champlain, Shelburne's town center lies approximately south of the city center of Burlington, the largest city in the state of Vermont. As of th ...
) on August 21, 2015". The Declaration included mention of:
*Revitalization and maintenance of Indigenous languages
*Article 25 of the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples
The Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP or DOTROIP) is a legally non-binding resolution passed by the United Nations in 2007. It delineates and defines the individual and collective rights of Indigenous peoples, including th ...
(UNDRIP) on land, food, and water
*A commitment to "establish decolonized maps"
*The Wingspread Statement on the Precautionary Principles
*Obligation of governments to "obtain free, prior, and informed consent" before "further infringement"
*A commitment to "strive to unite the Indigenous Peoples; from coast to coast", e.g. against Tar Sands.
*Protecting food, "seeds, waters, and lands, from chemical and genetic contamination"
*Recognizes and confirms the unique decision-making structures of the Wabanaki Peoples in accordance with Article 18 of the UNDRIP Indigenous decision-making institutions:
**"Our vision is to construct a Lodge, which will serve as a living constitution and decision-making structure for the Wabanaki Confederacy."
*Recognizes the Western Abenaki living in Vermont and the United States as a "People" and member nation
*Peace and friendship with "the Seven Nations of Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
"
Position on ecological and health issues
On October 15, 2015, Alma Brooks spoke to the New Brunswick Hydrofracturing Commission, applying the Declaration to current provincial industrial practices: *She criticized the "industry of hydro-fracturing for natural gas in our territory" because "our people have not been adequately consulted ... have been abused and punished for taking a stand," and cited traditional knowledge of floods, quakes and salt lakes in New Brunswick; *Criticized Irving Forestry Companies for having "clear cut our forests ndspraying poisonous carcinogenic herbicides such as glyphosate all over 'our land', to kill hardwood trees, and other green vegetation," harming human and animal health; *Noted "Streams, brooks, and creeks are drying up; causing the dwindling ofAtlantic salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are ...
and trout. Places where our people gather medicines, hunt deer, and moose are being contaminated with poison. We were not warned about the use of these dangerous herbicides, but since then cancer rates have been on the rise in Maliseet Communities; especially breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or ...
in women and younger people are dying from cancer."
*Open pit mining
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique of extracting rock or minerals from the earth from an open-air pit, sometimes known as a borrow.
This form of minin ...
"for tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
and molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ...
hichrequire tailing ponds; this one designated to be the largest in the world hichdefinitely will seep out into the environment. A spill or leak from the Sisson Brook open-pit mine will permanently contaminate the Nashwaak River
The Nashwaak River, located in west-central New Brunswick, Canada, is a tributary of the Saint John River. It is 113 kilometres long. The river rises from Nashwaak Lake (southeast of the village of Juniper) and flows south and east through un ...
; which is a tributary of the Wolastok ( St. John River) and surrounding waterways. This is the only place left clean enough for the survival of the Atlantic salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are ...
."
*"Oil pipeline
Pipeline transport is the long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas through a system of pipes—a pipeline—typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 count ...
s and "refineries ... bent on contaminating and destroying the very last inch of (Wəlastokok) Maliseet territory."
*Rivers, lakes, streams, and lands.. contaminated "to the point that we are unable to gather our annual supply of fiddlehead
Fiddleheads or fiddlehead greens are the furled fronds of a young fern, harvested for use as a vegetable.
Left on the plant, each fiddlehead would unroll into a new frond (circinate vernation). As fiddleheads are harvested early in the sea ...
s n edible fern and medicines."
*The "duty to consult with aboriginal people ... has become a meaningless process,"..."therefore governments and/or companies do not have our consent to proceed with hydro-fracturing, open-pit mining, or the building of pipelines for gas and oil bitumen."
2016
The Passamaquoddy will host the 2016 Wabanaki Confederacy Conference.Ceremony at The Pines
Since the 1990s, members of ThePenobscot nation
The Penobscot (Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewi'') are an Indigenous people in North America from the Northeastern Woodlands region. They are organized as a federally recognized tribe in Maine and as a First Nations band government in the Atlantic pr ...
and other members of the Wabanaki Confederacy gather at The Pines on Father Ralse Road in Madison at the former Nanrantsouak village to remember and honor ancestors massacred by the British on August 22, 1724. A ceremony takes place and afterward a traditional Wabanaki meal of roasted corn, salmon, baked beans or moose stew is eaten. The tradition was begun by Barry Dana during an overnight sacred run. The ceremony began as a private Wabanaki remembrance but now the public is welcome to educate about this history.
Culture
Basket art
Members of the Wabanaki Confederacy are recognized for their fine art basket making. Well-known Wabanaki basket makers Molly Neptune Parker, Clara Neptune Keezer, and Fred Tomah have been recognized for their art. Parker's grandchild Geo Soctomah Neptune is also a nationally-recognized basket artist who istwo-spirit
Two-spirit (also two spirit, 2S or, occasionally, twospirited) is a modern, , umbrella term used by some Indigenous North Americans to describe Native people in their communities who fulfill a traditional third-gender (or other gender-varia ...
and was featured in ''Vogue
Vogue may refer to:
Business
* ''Vogue'' (magazine), a US fashion magazine
** British ''Vogue'', a British fashion magazine
** ''Vogue Arabia'', an Arab fashion magazine
** ''Vogue Australia'', an Australian fashion magazine
** ''Vogue China'', ...
'' magazine in 2022 for their style and earring collection. Gabriel Frey received the Best in Class award in the Basketry category at the 2021 Santa Fe Indian Market.
Cuisine
Wabanaki cuisine, like other Indigenous cuisine, is based on what can be grown and hunted locally.Corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
, beans, squash, fresh-water fish, salt-water fish, moose, and white tailed deer are common foods. Maple syrup, wild blueberries, ground cherries, ground nuts, and sunchokes are also incorporated into many dishes. Wabanaki people traditionally made milks, butters, and infant formula from walnuts, cornmeal, and sunflower seeds for centuries before colonizers arrived.
Wabanaki dishes include roasted parched sweet corn, hickorynut and hull corn salad, roasted groundnuts, cranberry sauce, grilled whitefish, Abenaki rose cornmeal pudding, pemmican
Pemmican (also pemican in older sources) is a mixture of tallow, dried meat, and sometimes dried berries. A calorie-rich food, it can be used as a key component in prepared meals or eaten raw. Historically, it was an important part of indigenou ...
made from ground fruits, nuts, and berries, Three Sisters soup, dandelion greens, fiddlehead
Fiddleheads or fiddlehead greens are the furled fronds of a young fern, harvested for use as a vegetable.
Left on the plant, each fiddlehead would unroll into a new frond (circinate vernation). As fiddleheads are harvested early in the sea ...
salad, creamy sorrel and fiddlehead soup, clams with sunchokes, m8wikisoak stew, hazelnut
The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus '' Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species ''Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts according ...
cakes, salmon burgers, and maple syrup
Maple syrup is a syrup made from the sap of maple trees. In cold climates, these trees store starch in their trunks and roots before winter; the starch is then converted to sugar that rises in the sap in late winter and early spring. Maple tr ...
pie.
In Indigenous languages
Maps
Maps showing the approximate locations of areas occupied by members of the Wabanaki Confederacy (from north to south):Mi'kmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the no ...
Image:Wohngebiet_Maliseet.png, Maliseet
The Wəlastəkwewiyik, or Maliseet (, also spelled Malecite), are an Algonquian-speaking First Nation of the Wabanaki Confederacy. They are the indigenous people of the Wolastoq ( Saint John River) valley and its tributaries. Their territory ...
, Passamaquoddy
The Passamaquoddy ( Maliseet-Passamaquoddy: ''Peskotomuhkati'') are a Native American/First Nations people who live in northeastern North America. Their traditional homeland, Peskotomuhkatik'','' straddles the Canadian province of New Brunswick ...
Image:Wohngebiet_Oestlicheabenaki.png, Eastern Abenaki (Penobscot
The Penobscot ( Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewi'') are an Indigenous people in North America from the Northeastern Woodlands region. They are organized as a federally recognized tribe in Maine and as a First Nations band government in the Atlantic ...
, Kennebec, Arosaguntacook, Pigwacket/Pequawket)
Image:Wohngebiet_Westlicheabenaki.png, Western Abenaki (Arsigantegok, Missisquoi, Cowasuck, Sokoki, Pennacook
The Pennacook, also known by the names Penacook and Pennacock, were an Algonquian-speaking Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands who lived in Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and southern Maine. They were not a united tribe but a n ...
References
Further reading
* McBride, Bunny (2001). ''Women of the Dawn''. * Mead, Alice (1996). ''Giants of the Dawnland: Eight Ancient Wabanaki Legends''. * Prins, Harald E. L. (2002). "The Crooked Path of Dummer's Treaty: Anglo-Wabanaki Diplomacy and the Quest for Aboriginal Rights". ''Papers of the Thirty-Third Algonquian Conference''. H.C. Wolfart, ed. Winnipeg: U Manitoba Press. pp. 360–378. * Speck, Frank G. "The Eastern Algonkian Wabanaki Confederacy". ''American Anthropologist
''American Anthropologist'' is the flagship journal of the American Anthropological Association (AAA), published quarterly by Wiley. The "New Series" began in 1899 under an editorial board that included Franz Boas, Daniel G. Brinton, and John ...
, New Series'', Vol. 17, No. 3 (July–September 1915), pp. 492–508
* Walker, Willard. "The Wabanaki Confederacy". ''Maine History'' 37 (3) (1998): 100–139.
External links
Indian Treaties
, timeline curriculum by Abbe Museum
Dr. Harald E. L. Prins, "Storm Clouds over Wabanakiak Confederacy Diplomacy Until Dummer's Treaty (1727)"
Wabanaki Confederacy website
Miingignoti-Keteaoag
a partnership for the way of life of the Wabanaki Nations
{{DEFAULTSORT:Wabanaki Confederacy States and territories established in the 1680s States and territories disestablished in 1862 Algonquian peoples Historical regions First Nations history Abenaki Penobscot Passamaquoddy Maliseet Mi'kmaq Native American history of Massachusetts Native American history of Maine First Nations in Atlantic Canada Military history of Acadia Military history of Nova Scotia Military history of New England Former countries of the United States