

The Allies, formally referred to as the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
from 1942, were an international
military coalition formed during the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
(1939–1945) to oppose the
Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
, led by
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
,
Imperial Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
, and
Fascist Italy. Its principal members by 1941 were the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
,
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
,
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, and
China.
Membership in the Allies varied during the course of the war. When the conflict broke out on 1 September 1939, the Allied coalition consisted of the United Kingdom,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, and
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, as well as their respective
dependencies, such as
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
. They were soon joined by the independent
dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 192 ...
s of the
British Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
:
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
,
Australia,
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
and
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
. Consequently, the initial alliance resembled
that of the First World War.
As Axis forces began
invading northern Europe and the
Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, the Allies added the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
,
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
,
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
,
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
, and
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
. The Soviet Union, which initially had a
nonaggression pact with Germany and participated in its
invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week aft ...
, joined the Allies in June 1941 after
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
, the German invasion of the Soviet Union. The United States, while providing some
materiel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context.
In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the specif ...
support to European Allies since September 1940, remained formally neutral until the Japanese
bombing of Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Haw ...
in December 1941, after which it
declared war and officially joined the Allies. China had already been
at war with Japan
since 1937, and formally joined the Allies in December 1941.
The Allies were led by the so-called "Big Three"—the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States—which were the principal contributors of manpower, resources, and strategy, each playing a key role in achieving victory.
A series of conferences between Allied leaders, diplomats, and military officials gradually shaped the makeup of the alliance, the direction of the war, and ultimately the postwar international order. Relations between the United Kingdom and the United States were
especially close, with their bilateral
Atlantic Charter forming the groundwork of their alliance.
The Allies became a formalized group upon the
Declaration by United Nations
The Declaration by United Nations was the main treaty that formalized the Allies of World War II and was signed by 47 national governments between 1942 and 1945. On 1 January 1942, during the Arcadia Conference, the Allied " Big Four"—the Unite ...
on 1 January 1942, which was signed by 26 nations around the world; these ranged from
governments in exile
A government in exile (abbreviated as GiE) is a political group that claims to be a country or semi-sovereign state's legitimate government, but is unable to exercise legal power and instead resides in a foreign country. Governments in exile u ...
from the Axis occupation to small nations far removed from the war. The Declaration officially recognized the Big Three and China as the "Four Powers", acknowledging their central role in prosecuting the war; they were also referred to as the "
trustee
Trustee (or the holding of a trusteeship) is a legal term which, in its broadest sense, is a synonym for anyone in a position of trust and so can refer to any individual who holds property, authority, or a position of trust or responsibility to ...
ship of the powerful", and later as the "
Four Policemen" of the United Nations.
Many more countries joined through to the final days of the war, including colonies and former Axis nations.
After the war ended, the Allies, and the Declaration that bound them, would become the basis of the modern
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
; one enduring legacy of the alliance is the
permanent membership of the U.N. Security Council, which is made up exclusively of the principal Allied powers that won the war.
Origins
The victorious
Allies of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente (alliance), Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by French Third Republic, France, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, Russian Empire, Russia, King ...
—which included what would become the Allied powers of the Second World War—had imposed harsh terms on the opposing
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
in the
Paris Peace Conference of 1919-1920.
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
resented signing the
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
, which required that it take full responsibility for the war, lose a significant portion of territory, and pay costly reparations, among other penalties. The
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is ...
, which formed at the end of the war and subsequently negotiated the treaty, saw its legitimacy shaken, particularly as it struggled to govern a greatly weakened economy and humiliated populace.
The
Wall Street Crash of 1929
The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Great Crash, was a major American stock market crash that occurred in the autumn of 1929. It started in September and ended late in October, when share prices on the New York Stock Exchange coll ...
, and the ensuing
Great Depression, led to political unrest across Europe, especially in Germany, where
revanchist
Revanchism (french: revanchisme, from ''revanche'', " revenge") is the political manifestation of the will to reverse territorial losses incurred by a country, often following a war or social movement. As a term, revanchism originated in 1870s F ...
nationalists blamed the severity of the economic crisis on the Treaty of Versailles. The far-right
Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
led by
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
, which had formed shortly after the peace treaty, exploited growing popular resentment and desperation to become the dominant political movement in Germany; by 1933, they
gained power and rapidly established a
totalitarian
Totalitarianism is a form of government and a political system that prohibits all opposition parties, outlaws individual and group opposition to the state and its claims, and exercises an extremely high if not complete degree of control and reg ...
regime known as
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. The Nazi regime demanded the immediate cancellation of the Treaty of Versailles and made claims over German-populated Austria and the
German-populated territories of Czechoslovakia. The likelihood of war was high, but none of the major powers had the appetite for another conflict; many governments sought to ease tensions through nonmilitary strategies such as
appeasement.
Japan, which was a principal allied power in the First World War, had since become increasingly militaristic and imperialistic; parallel to Germany, nationalist sentiment increased throughout the 1920s, culminating in the
invasion of Manchuria in 1931. The
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
strongly condemned the attack as an act of aggression against China; Japan responded by leaving the League in 1933. The second
Sino-Japanese War erupted in 1937 with Japan's full-scale invasion of China. The League of Nations condemned Japan's actions and initiated sanctions; the United States, which had attempted to peacefully negotiate for peace in Asia, was especially angered by the invasion and sought to support China.
In March 1939,
Germany took over Czechoslovakia, just six months after signing the
Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
, which sought to appease Hitler by
ceding the
mainly ethnic German Czechoslovak borderlands; while most of Europe had celebrated the agreement as a major victory for peace, the open flaunting of its terms demonstrated the failure of appeasement. Britain and France, which had been the main advocates of appeasement, decided that Hitler had no intention to uphold diplomatic agreements and responded by preparing for war. On 31 March 1939, Britain formed the
Anglo-Polish military alliance
The military alliance between the United Kingdom and Poland was formalised by the Anglo-Polish Agreement in 1939, with subsequent addenda of 1940 and 1944, for mutual assistance in case of a military invasion from Nazi Germany, as specified in a ...
in an effort to avert an imminent German attack on Poland; the French likewise had a long-standing
alliance with Poland since 1921. The
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, which had been diplomatically and economically isolated by much of the world, had sought an alliance with the western powers, but Hitler preempted a potential war with Stalin by signing the
Nazi–Soviet non-aggression pact in August 1939. In addition to preventing a two-front war that had battered its forces in the last world war, the agreement secretly divided the independent states of Central and Eastern Europe between the two powers and assured adequate oil supplies for the German war machine.
On 1 September 1939,
Germany invaded Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week afte ...
; two days later Britain and France declared war on Germany. Roughly two weeks after Germany's attack, the
Soviet Union invaded Poland from the east. Britain and France established the
Anglo-French Supreme War Council
The Anglo-French Supreme War Council (SWC) was established to oversee joint military strategy at the start of the Second World War. Most of its deliberations took place during the period of the Phoney War, with its first meeting at Abbeville on ...
to coordinate military decisions. A
Polish government-in-exile
The Polish government-in-exile, officially known as the Government of the Republic of Poland in exile ( pl, Rząd Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej na uchodźstwie), was the government in exile of Poland formed in the aftermath of the Invasion of Pola ...
was set up in London, joined by hundreds of thousands of Polish soldiers, which would remain an Allied nation until the end. After a quiet winter, Germany began its invasion of Western Europe in April 1940, quickly defeating Denmark, Norway, Belgium, the Netherlands, and France; all the occupied nations would subsequently establish a government-in-exile in London, with each contributing a contingent of escaped troops. Nevertheless, by roughly one year since Germany's violation of the Munich Agreement, Britain and its Empire stood alone against Hitler and Mussolini.
Formation of the "Grand Alliance"
Before they were formally allied, the United Kingdom and the United States had cooperated in a number of ways,
notably through the
destroyers-for-bases deal
The destroyers-for-bases deal was an agreement between the United States and the United Kingdom on September 2, 1940, according to which 50 , , and US Navy destroyers were transferred to the Royal Navy from the US Navy in exchange for land rights ...
in September 1940 and the American
Lend-Lease program, which provided Britain and the Soviet Union with war materiel beginning in October 1941. The
British Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
and, to a lesser extent, the Soviet Union reciprocated with a smaller
Reverse Lend-Lease
Lend-Lease, formally the Lend-Lease Act and introduced as An Act to Promote the Defense of the United States (), was a policy under which the United States supplied the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union and other Allied nations with food, oil, ...
program.
The
First Inter-Allied Meeting took place in London in early June 1941 between the United Kingdom, the four co-belligerent British Dominions (Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa), the eight
governments in exile
A government in exile (abbreviated as GiE) is a political group that claims to be a country or semi-sovereign state's legitimate government, but is unable to exercise legal power and instead resides in a foreign country. Governments in exile u ...
(
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
,
Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
,
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
,
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
,
the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
,
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
,
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
,
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
) and
Free France
Free France (french: France Libre) was a political entity that claimed to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third Republic. Led by French general , Free France was established as a government-in-exile ...
. The meeting culminated with the
Declaration of St James's Palace
The Declaration of St James's Palace, or London Declaration, was the first joint statement of goals and principles by the Allied Powers during World War II. The declaration was issued after the first Inter-Allied Meeting at St James's Palace in ...
, which set out a first vision for the postwar world.
In June 1941, Hitler broke the non-aggression agreement with Stalin and Axis forces
invaded the Soviet Union, which consequently declared war on Germany and its allies. Britain agreed to an
alliance with the Soviet Union in July, with both nations committing to assisting one another by any means, and to never negotiate a separate peace. The following August saw the
Atlantic Conference
The Atlantic Charter was a statement issued on 14 August 1941 that set out American and British goals for the world after the end of World War II. The joint statement, later dubbed the Atlantic Charter, outlined the aims of the United States and ...
between American President
Franklin Roosevelt and British Prime Minister
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
, which defined a common Anglo-American vision of the postwar world, as formalized by the
Atlantic Charter.
At the
Second Inter-Allied Meeting in London in September 1941, the eight European governments in exile, together with the Soviet Union and representatives of the Free French Forces, unanimously adopted adherence to the common principles of policy set forth in the Atlantic Charter. In December, Japan attacked American and British territories in Asia and the Pacific, resulting in the U.S. formally entering the war as an Allied power. Still reeling from Japanese aggression, China declared war on all the Axis powers shortly thereafter.
By the end of 1941, the main lines of World War II had formed. Churchill referred to the "Grand Alliance" of the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union,
which together played the largest role in prosecuting the war. The alliance was largely one of convenience for each member: the U.K. realized that the Axis powers threatened not only
its colonies in North Africa and Asia but also the
homeland
A homeland is a place where a cultural, national, or racial identity has formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethn ...
. The United States felt that the Japanese and German expansion should be contained, but ruled out force until Japan's attack. The Soviet Union, having been betrayed by
the Axis attack in 1941, greatly despised German belligerence and the unchallenged Japanese expansion in the East, particularly considering their defeat in previous wars with Japan; the Soviets also recognized, as the U.S. and Britain had suggested, the advantages of a
two-front war
According to military terminology, a two-front war occurs when opposing forces encounter on two geographically separate fronts. The forces of two or more allied parties usually simultaneously engage an opponent in order to increase their chance ...
.
The Big Three
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
,
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
, and
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
were The Big Three leaders. They were in frequent contact through ambassadors, top generals, foreign ministers and special emissaries such as the American
Harry Hopkins. It is also often called the "Strange Alliance", because it united the leaders of the world's greatest
capitalist state
The capitalist state is the state, its functions and the form of organization it takes within capitalist socioeconomic systems.Jessop, Bob (January 1977). "Recent Theories of the Capitalist State". ''Soviet Studies''. 1: 4. pp. 353–373. This ...
(the United States), the greatest
socialist state
A socialist state, socialist republic, or socialist country, sometimes referred to as a workers' state or workers' republic, is a sovereign state constitutionally dedicated to the establishment of socialism. The term '' communist state'' is of ...
(the Soviet Union) and the greatest
colonial power
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
(the United Kingdom).
Relations between them resulted in the major decisions that shaped the war effort and planned for the postwar world.
Cooperation between the United Kingdom and the United States was
especially close and included forming a
Combined Chiefs of Staff.
There were numerous
high-level conferences; in total Churchill attended 14 meetings, Roosevelt 12, and Stalin 5. Most visible were the three summit conferences that brought together the three top leaders. The Allied policy toward Germany and Japan evolved and developed at these three conferences.
*
Tehran Conference
The Tehran Conference ( codenamed Eureka) was a strategy meeting of Joseph Stalin, Franklin Roosevelt, and Winston Churchill from 28 November to 1 December 1943, after the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran. It was held in the Soviet Union's embass ...
(codename "Eureka") – first meeting of The Big Three (28 November 1943
– 1 December 1943)
*
Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (codenamed Argonaut), also known as the Crimea Conference, held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the post ...
(codename "Argonaut") – second meeting of The Big Three (4–11 February 1945)
*
Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
(codename "Terminal") – third and final meeting of The Big Three (Truman having taken over for Roosevelt, 17 July – 2 August 1945)
Tensions
There were many tensions among the Big Three leaders, although they were not enough to break the alliance during wartime.
In 1942 Roosevelt proposed becoming, with China, the
Four Policemen of world peace. Although the 'Four Powers' were reflected in the wording of the
Declaration by United Nations
The Declaration by United Nations was the main treaty that formalized the Allies of World War II and was signed by 47 national governments between 1942 and 1945. On 1 January 1942, during the Arcadia Conference, the Allied " Big Four"—the Unite ...
, Roosevelt's proposal was not initially supported by Churchill or Stalin.
Division emerged over the length of time taken by the Western Allies to establish a
second front
The Western Front was a military theatre of World War II encompassing Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, Belgium, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, France, and Germany. The Italian front is considered a separate but related theater. The Wester ...
in Europe.
Stalin and the Soviets used the potential employment of the second front as an 'acid test' for their relations with the Anglo-American powers.
The Soviets were forced to use as much manpower as possible in the fight against the Germans, whereas the United States had the luxury of flexing industrial power, but with the "minimum possible expenditure of American lives."
Roosevelt and Churchill opened ground fronts in North Africa in 1942 and in Italy in 1943, and launched a massive air attack on Germany, but Stalin kept wanting more.
Although the U.S. had a strained relationship with the USSR in the 1920s, relations were normalized in 1933. The original terms of the
Lend-Lease loan were amended towards the Soviets, to be put in line with British terms. The United States would now expect interest with the repayment from the Soviets, following the initiation of the
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
, at the end of the war—the United States were not looking to support any "postwar Soviet reconstruction efforts", which eventually manifested into the
Molotov Plan. At the
Tehran conference
The Tehran Conference ( codenamed Eureka) was a strategy meeting of Joseph Stalin, Franklin Roosevelt, and Winston Churchill from 28 November to 1 December 1943, after the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran. It was held in the Soviet Union's embass ...
, Stalin judged Roosevelt to be a "lightweight compared to the more formidable Churchill". During the meetings from 1943 to 1945, there were disputes over the growing list of demands from the USSR.
Tensions increased further when Roosevelt died and his successor
Harry Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
rejected demands put forth by Stalin.
Roosevelt wanted to play down these ideological tensions. Roosevelt felt he "understood Stalin's psychology", stating "Stalin was too anxious to prove a point... he suffered from an inferiority complex."
United Nations

Four Policemen
During December 1941, Roosevelt devised the name "United Nations" for the Allies and Churchill agreed.
He referred to the Big Three and China as the "
Four Policemen" repeatedly from 1942.
Declaration by United Nations

The alliance was formalised in the
Declaration by United Nations
The Declaration by United Nations was the main treaty that formalized the Allies of World War II and was signed by 47 national governments between 1942 and 1945. On 1 January 1942, during the Arcadia Conference, the Allied " Big Four"—the Unite ...
signed on 1 January 1942. There were the 26 original signatories of the declaration; the Big Four were listed first:
*
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
*
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
*
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
*
China
*
Australia
*
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
*
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
*
Costa Rica
*
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
*
Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
*
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
*
El Salvador
*
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
*
Guatemala
*
Haiti
*
Honduras
*
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
*
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
*
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
*
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
*
Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the countr ...
*
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
*
Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
*
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
*
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
*
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
Alliance growing
The United Nations began growing immediately after its formation. In 1942, Mexico, the Philippines and Ethiopia adhered to the declaration. Ethiopia had been restored to independence by British forces after the Italian defeat in 1941. The Philippines, still owned by Washington but granted international diplomatic recognition, was allowed to join on 10 June despite its occupation by Japan.
In 1943, the Declaration was signed by Iraq, Iran, Brazil, Bolivia and Colombia.
A Tripartite Treaty of Alliance with Britain and the USSR formalised Iran's assistance to the Allies. In
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a ...
, Brazilian dictator
Getúlio Vargas
Getúlio Dornelles Vargas (; 19 April 1882 – 24 August 1954) was a Brazilian lawyer and politician who served as the 14th and 17th president of Brazil, from 1930 to 1945 and from 1951 to 1954. Due to his long and controversial tenure as Brazi ...
was considered near to fascist ideas, but realistically joined the United Nations after their evident successes.
In 1944, Liberia and France signed. The French situation was very confused.
Free French
Free France (french: France Libre) was a political entity that claimed to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third Republic. Led by French general , Free France was established as a government-in-exile ...
forces were recognized only by Britain, while the United States considered
Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its te ...
to be the legal government of the country until
Operation Overlord, while also preparing
U.S. occupation francs. Winston Churchill urged Roosevelt to restore France to its status of a major power after the liberation of Paris in August 1944; the Prime Minister feared that after the war, Britain could remain the sole great power in Europe facing the Communist threat, as it was in 1940 and 1941 against Nazism.
During the early part of 1945, Peru, Chile, Paraguay, Venezuela, Uruguay, Turkey, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, Syria (these latter two French colonies had been declared independent states by British occupation troops, despite protests by Pétain and later De Gaulle) and Ecuador became signatories.
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and
Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, which were not independent states but parts of the Soviet Union, were accepted as members of the United Nations as a way to provide greater influence to Stalin, who had only Yugoslavia as a communist partner in the alliance.
Major affiliated state combatants
United Kingdom




British Prime Minister,
Neville Chamberlain delivered his ''Ultimatum Speech'' on 3 September 1939 which
declared war on Germany, a few hours before France. As the
Statute of Westminster 1931 was not yet ratified by the parliaments of Australia and New Zealand, the British declaration of war on Germany also applied to those
dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 192 ...
s. The other dominions and members of the
British Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
declared war from 3 September 1939, all within one week of each other; they were
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
,
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
and
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
.
During the war, Churchill attended seventeen
Allied conferences at which key decisions and agreements were made. He was "the most important of the Allied leaders during the first half of World War II".
Africa colonies and dependencies
British West Africa and the British colonies in East and Southern Africa participated, mainly in the North African, East African and Middle-Eastern theatres. Two West African and one East African division served in the
Burma Campaign.
Southern Rhodesia
Southern Rhodesia was a landlocked self-governing British Crown colony in southern Africa, established in 1923 and consisting of British South Africa Company (BSAC) territories lying south of the Zambezi River. The region was informally kno ...
was a self-governing colony, having received
responsible government in 1923. It was not a sovereign dominion. It governed itself internally and controlled its own armed forces, but had no diplomatic autonomy, and, therefore, was officially at war as soon as Britain was at war. The Southern Rhodesian colonial government issued a symbolic declaration of war nevertheless on 3 September 1939, which made no difference diplomatically but preceded the declarations of war made by all other British dominions and colonies.
American colonies and dependencies
These included: the
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grena ...
,
British Honduras
British Honduras was a British Crown colony on the east coast of Central America, south of Mexico, from 1783 to 1964, then a self-governing colony, renamed Belize in June 1973, ,
British Guiana and the
Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouze ...
. The
Dominion of Newfoundland was directly ruled as a royal colony from 1933 to 1949, run by a governor appointed by London who made the decisions regarding Newfoundland.
Asia
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
included the areas and peoples covered by later
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
,
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
,
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
and (until 1937)
Burma/Myanmar, which later became a separate colony.
British Malaya covers the areas of
Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia ( ms, Semenanjung Malaysia; Jawi: سمننجڠ مليسيا), or the States of Malaya ( ms, Negeri-negeri Tanah Melayu; Jawi: نڬري-نڬري تانه ملايو), also known as West Malaysia or the Malaysian Peninsula, ...
and
Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, while
British Borneo covers the area of
Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely surrounded by t ...
, including
Sabah
Sabah () is a state of Malaysia located in northern Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah borders the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and the North Kalimantan province of Indonesia to the south. The Federal Territory o ...
and
Sarawak
Sarawak (; ) is a state of Malaysia. The largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak is located in northwest Borneo Island, and is bordered by the Malaysian state of Sabah to the northeast, ...
of Malaysia.
British Hong Kong consisted of
Hong Kong Island, the
Kowloon Peninsula, and the
New Territories
The New Territories is one of the three main regions of Hong Kong, alongside Hong Kong Island and the Kowloon Peninsula. It makes up 86.2% of Hong Kong's territory, and contains around half of the population of Hong Kong. Historically, it ...
.
Territories controlled by the
Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created to deal with the colonial affairs of British North America but required also to oversee the increasing number of c ...
, namely the
Crown Colonies
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Council ...
, were controlled politically by the UK and therefore also entered hostilities with Britain's declaration of war. At the outbreak of World War II, the
British Indian Army numbered 205,000 men. Later during World War II, the
British Indian Army became the largest all-volunteer force in history, rising to over 2.5 million men in size.
Indian soldiers earned 30
Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously ...
es during the Second World War. It suffered 87,000 military casualties (more than any Crown colony but fewer than the United Kingdom). The UK suffered 382,000 military casualties.
Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the nort ...
was a protectorate of the United Kingdom formally established in 1899. The
Trucial States
The Trucial States ( '), also known as the Trucial Coast ( '), the Trucial Sheikhdoms ( '), Trucial Arabia or Trucial Oman, was the name the British government gave to a group of tribal confederations in southeastern Arabia whose leaders had s ...
were British protectorates in the Persian Gulf.
Palestine was a mandate dependency created in the peace agreements after
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
from the former territory of the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
,
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
.
Europe
The
Cyprus Regiment was formed by the British Government during the Second World War and made part of the British Army structure. It was mostly
Greek Cypriot
Greek Cypriots or Cypriot Greeks ( el, Ελληνοκύπριοι, Ellinokýprioi, tr, Kıbrıs Rumları) are the ethnic Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2011 census, 659,115 r ...
volunteers and Turkish-speaking Cypriot inhabitants of Cyprus but also included other Commonwealth nationalities. On a brief visit to Cyprus in 1943, Winston Churchill praised the "soldiers of the Cyprus Regiment who have served honourably on many fields from Libya to Dunkirk". About 30,000 Cypriots served in the Cyprus Regiment. The regiment was involved in action from the very start and served at
Dunkirk, in the
Greek Campaign
The German invasion of Greece, also known as the Battle of Greece or Operation Marita ( de , Unternehmen Marita, links = no), was the attack of Greece by Italy and Germany during World War II. The Italian invasion in October 1940, which is usu ...
(about 600 soldiers were captured in
Kalamata
Kalamáta ( el, Καλαμάτα ) is the second most populous city of the Peloponnese peninsula, after Patras, in southern Greece and the largest city of the homonymous administrative region. As the capital and chief port of the Messenia regi ...
in 1941), North Africa (
Operation Compass
Operation Compass (also it, Battaglia della Marmarica) was the first large British military operation of the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) during the Second World War. British, Empire and Commonwealth forces attacked Italian forces of ...
), France, the Middle East and Italy. Many soldiers were taken prisoner especially at the beginning of the war and were interned in various PoW camps (
Stalag) including Lamsdorf (
Stalag VIII-B
Stalag VIII-B was a German Army prisoner-of-war camp during World War II, later renumbered Stalag-344, located near the village of Lamsdorf (now Łambinowice) in Silesia. The camp initially occupied barracks built to house British and French pri ...
), Stalag IVC at Wistritz bei Teplitz and Stalag 4b near Most in the Czech Republic. The soldiers captured in Kalamata were transported by train to prisoner of war camps.
France

War declared
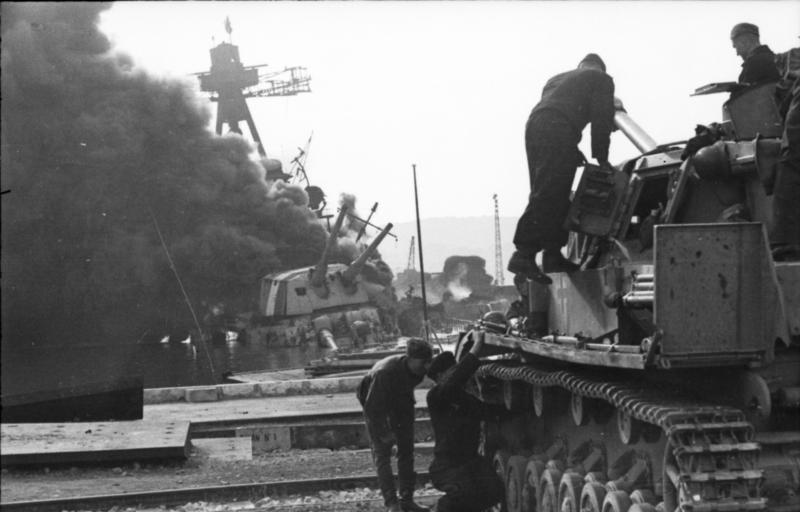


After Germany invaded Poland, France
declared war on Germany on 3 September 1939.
[Speeches that Reshaped the World.] In January 1940, French Prime Minister
Édouard Daladier
Édouard Daladier (; 18 June 1884 – 10 October 1970) was a French Radical-Socialist (centre-left) politician, and the Prime Minister of France who signed the Munich Agreement before the outbreak of World War II.
Daladier was born in Carpe ...
made a major speech denouncing the actions of Germany:
France experienced several major phases of action during World War II:
* The "
Phoney War
The Phoney War (french: Drôle de guerre; german: Sitzkrieg) was an eight-month period at the start of World War II, during which there was only one limited military land operation on the Western Front, when French troops invaded Germa ...
" of 1939–1940, also called ''drôle de guerre'' in France, ''dziwna wojna'' in Poland (both meaning "Strange War"), or the ''"Sitzkrieg"'' ("Sitting War") in Germany.
* The
Battle of France in May–June 1940, which resulted in the defeat of the Allies, the fall of the
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic (french: Troisième République, sometimes written as ) was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 19 ...
, the
German occupation of northern and western France, and the creation of the rump state
Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its te ...
, which received diplomatic recognition from the Axis and most neutral countries including the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
.
* The period of
resistance against the occupation and Franco-French struggle for control of the colonies between the Vichy regime and the
Free French
Free France (french: France Libre) was a political entity that claimed to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third Republic. Led by French general , Free France was established as a government-in-exile ...
, who continued the fight on the Allies' side after the
Appeal of 18 June
The Appeal of 18 June (french: L'Appel du 18 juin) was the first speech made by Charles de Gaulle after his arrival in London in 1940 following the Battle of France. Broadcast to Vichy France by the radio services of the British Broadcasting Cor ...
by General
Charles de Gaulle, recognized by the United Kingdom as France's government-in-exile. It culminated in the
Allied landings in North Africa
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – 16 November 1942) was an Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while al ...
on 11 November 1942, when Vichy ceased to exist as an independent entity after having been invaded
by both the Axis and the Allies simultaneously, being thereafter only the nominal government in charge during the occupation of France. Vichy forces in French North Africa switched allegiance and
merged with the Free French to participate in the campaigns
of Tunisia and
of Italy and the invasion
of Corsica in 1943–44.
* The
liberation of mainland France beginning with
D-Day on 6 June 1944 and
operation Overlord, and then with
operation Dragoon on 15 August 1944, leading to the
Liberation of Paris on 25 August 1944 by the Free French
2e Division Blindée
The French 2nd Armored Division (french: link=no, 2e Division Blindée, 2e DB), commanded by General Philippe Leclerc, fought during the final phases of World War II in the Western Front for the liberation of France. The division was formed aro ...
and the installation of the
Provisional Government of the French Republic in the newly liberated capital.
* Participation of the re-established provisional French Republic's
First Army in the
Allied advance from Paris to the Rhine
The Allied advance from Paris to the Rhine, also known as the Siegfried Line campaign, was a phase in the Western European campaign of World War II.
This phase spans from the end of the Battle of Normandy, or Operation Overlord, (25 August 194 ...
and the
Western Allied invasion of Germany
The Western Allied invasion of Germany was coordinated by the Western Allies during the final months of hostilities in the European theatre of World War II. In preparation for the Allied invasion of Germany east of the Rhine, a series of offensi ...
until
V-E Day
Victory in Europe Day is the day celebrating the formal acceptance by the Allies of World War II of Germany's unconditional surrender of its armed forces on Tuesday, 8 May 1945, marking the official end of World War II in Europe in the Easte ...
on 8 May 1945.
Colonies and dependencies
= Africa
=
In Africa these included:
French West Africa,
French Equatorial Africa
French Equatorial Africa (french: link=no, Afrique-Équatoriale française), or the AEF, was the federation of French colonial possessions in Equatorial Africa, extending northwards from the Congo River into the Sahel, and comprising what are ...
, the League of Nations mandates of
French Cameroun and
French Togoland
French Togoland (French: '' Togo français'') was a French colonial empires, French colonial League of Nations mandate from 1916 to 1960 in French West Africa. In 1960 it became the independent Togolese Republic, and the present day nation of T ...
,
French Madagascar,
French Somaliland, and the protectorates of
French Tunisia
The French protectorate of Tunisia (french: Protectorat français de Tunisie; ar, الحماية الفرنسية في تونس '), commonly referred to as simply French Tunisia, was established in 1881, during the French colonial Empire era, ...
and
French Morocco.
French Algeria was then not a colony or dependency but a fully-fledged part of
metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European ...
.
= Asia and Oceania
=

In Asia and Oceania France has several territories:
French Polynesia,
Wallis and Futuna
Wallis and Futuna, officially the Territory of the Wallis and Futuna Islands (; french: Wallis-et-Futuna or ', Fakauvea and Fakafutuna: '), is a French island collectivity in the South Pacific, situated between Tuvalu to the northwest, Fiji ...
,
New Caledonia, the
New Hebrides
New Hebrides, officially the New Hebrides Condominium (french: link=no, Condominium des Nouvelles-Hébrides, "Condominium of the New Hebrides") and named after the Hebrides Scottish archipelago, was the colonial name for the island group ...
,
French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China),; vi, Đông Dương thuộc Pháp, , lit. 'East Ocean under French Control; km, ឥណ្ឌូចិនបារាំង, ; th, อินโดจีนฝรั่งเศส, ...
,
French India,
Guangzhouwan
The Leased Territory of Guangzhouwan, officially the , was a territory on the coast of Zhanjiang in China leased to France and administered by French Indochina. The capital of the territory was Fort-Bayard, present-day Zhanjiang.
The Japan ...
, the mandates of
Greater Lebanon
The State of Greater Lebanon ( ar, دولة لبنان الكبير, Dawlat Lubnān al-Kabīr; french: État du Grand Liban), informally known as French Lebanon, was a state declared on 1 September 1920, which became the Lebanese Republic ( ar, ...
and
French Syria. The French government in 1936 attempted to grant independence to its mandate of
Syria in the
Franco-Syrian Treaty of Independence of 1936 signed by France and Syria. However, opposition to the treaty grew in France and the treaty was not ratified. Syria had become an official republic in 1930 and was largely self-governing. In 1941, a British-led invasion supported by Free French forces expelled Vichy French forces in
Operation Exporter
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Man ...
.
= Americas
=
France had several colonies in America, namely
Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in ...
,
Guadeloupe,
French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
and
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon (), officially the Territorial Collectivity of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon (french: link=no, Collectivité territoriale de Saint-Pierre et Miquelon ), is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France in t ...
.
Soviet Union
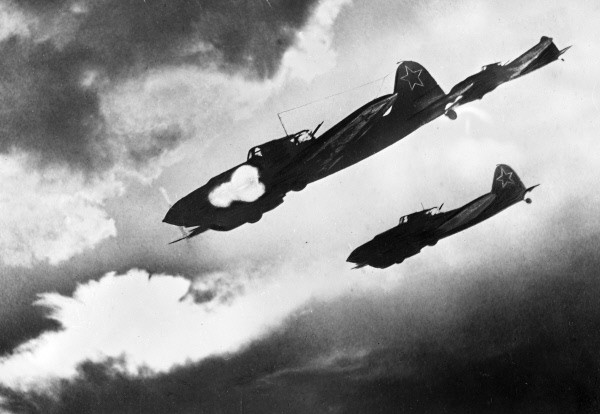



History
In the lead-up to the war between the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany, relations between the two states underwent several stages.
General Secretary Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
and the government of the Soviet Union had supported so-called
popular front
A popular front is "any coalition of working-class and middle-class parties", including liberal and social democratic ones, "united for the defense of democratic forms" against "a presumed Fascist assault".
More generally, it is "a coalition ...
movements of
anti-fascists
Anti-fascism is a political movement in opposition to fascist ideologies, groups and individuals. Beginning in European countries in the 1920s, it was at its most significant shortly before and during World War II, where the Axis powers were ...
including communists and non-communists from 1935 to 1939.
[Paul Bushkovitch. ''A Concise History of Russia''. Cambridge, England, UK; New York, New York, US: Cambridge University Press, 2012. P. 390–391.] The popular front strategy was terminated from 1939 to 1941, when the Soviet Union cooperated with Germany in 1939 in the occupation and partitioning of Poland. The Soviet leadership refused to endorse either the Allies or the Axis from 1939 to 1941, as it called the Allied-Axis conflict an "imperialist war".
Stalin had studied Hitler, including reading ''
Mein Kampf'', and from it knew of Hitler's motives for destroying the Soviet Union. As early as in 1933, the Soviet leadership voiced its concerns with the alleged threat of a potential German invasion of the country should Germany attempt a conquest of
Lithuania,
Latvia, or
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
, and in December 1933 negotiations began for the issuing of a joint Polish-Soviet declaration guaranteeing the sovereignty of the three Baltic countries.
[David L. Ransel, Bozena Shallcross. Polish Encounters, Russian Identity. Indiana University Press, 2005. P184.] However, Poland withdrew from the negotiations following German and Finnish objections.
The Soviet Union and Germany at this time competed with each other for influence in Poland. The Soviet government also was concerned with the anti-Soviet sentiment in Poland and particularly
Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was ...
's proposed Polish federation that would include the territories of Poland, Lithuania, Belarus, and Ukraine within it that threatened the territorial integrity of the Soviet Union.
On 20 August 1939, forces of the
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
under General
Georgy Zhukov
Georgy Konstantinovich Zhukov ( rus, Георгий Константинович Жуков, p=ɡʲɪˈorɡʲɪj kənstɐnʲˈtʲinəvʲɪtɕ ˈʐukəf, a=Ru-Георгий_Константинович_Жуков.ogg; 1 December 1896 – ...
, together with the
People's Republic of Mongolia
The Mongolian People's Republic ( mn, Бүгд Найрамдах Монгол Ард Улс, БНМАУ; , ''BNMAU''; ) was a socialist state which existed from 1924 to 1992, located in the historical region of Outer Mongolia in East Asia. It ...
eliminated the threat of conflict in the east with a victory over Imperial Japan at the
Battle of Khalkhin Gol
The Battles of Khalkhin Gol (russian: Бои на Халхин-Голе; mn, Халхын голын байлдаан) were the decisive engagements of the undeclared Soviet–Japanese border conflicts involving the Soviet Union, Mongolia, ...
in eastern Mongolia.
On the same day, Soviet party leader
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
received a telegram from German Chancellor
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
, suggesting that German Foreign Minister
Joachim von Ribbentrop fly to Moscow for diplomatic talks. (After receiving a lukewarm response throughout the spring and summer, Stalin abandoned attempts for a better diplomatic relationship with France and the United Kingdom.)
On 23 August, Ribbentrop and Soviet Foreign Minister
Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov. ; (;. 9 March Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">O._S._25_February.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O. S. 25 February">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dat ...
signed
the non-aggression pact including secret protocols dividing Eastern Europe into defined "spheres of influence" for the two regimes, and specifically concerning the partition of the Polish state in the event of its "territorial and political rearrangement".
On 15 September 1939, Stalin concluded a durable ceasefire with Japan, to take effect the following day (it would be upgraded to
a non-aggression pact in April 1941). The day after that, 17 September, Soviet forces
invaded Poland from the east. Although some fighting continued until 5 October, the two invading armies held at least one joint
military parade on 25 September, and reinforced their non-military partnership with the
German–Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Demarcation on 28 September. German and Soviet cooperation against Poland in 1939 has been described as
co-belligerence
Co-belligerence is the waging of a war in cooperation against a common enemy with or without a formal treaty of military alliance. Generally, the term is used for cases where no alliance exists. Likewise, allies may not become co-belligerents in a ...
.
On 30 November, the Soviet Union
attacked Finland, for which it was expelled from the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
. In the following year of 1940, while the world's attention was focused upon the German invasion of France and Norway, the USSR militarily
occupied and annexed Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania as well as parts of
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
.
German-Soviet treaties were brought to an end by the
German surprise attack on the USSR on 22 June 1941. After the invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, Stalin endorsed the Western Allies as part of a renewed popular front strategy against Germany and called for the international communist movement to make a coalition with all those who opposed the Nazis.
The Soviet Union soon entered in alliance with the United Kingdom. Following the USSR, a number of other
communist, pro-Soviet or Soviet-controlled forces fought against the
Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
powers during the Second World War. They were as follows: the
Albanian National Liberation Front
The National Liberation Movement ( sq, Lëvizja Nacional-Çlirimtare; or ''Lëvizja Antifashiste Nacional-Çlirimtare'' (LANÇ)), also translated as National Liberation Front, was an Albanian communist resistance organization that fought in World ...
, the
Chinese Red Army
The Chinese Workers' and Peasants' Red Army or Chinese Workers' and Peasants' Revolutionary Army, commonly known as the Chinese Red Army or simply the Red Army, are the armed forces of the Chinese Communist Party. It was formed when Communis ...
, the
Greek National Liberation Front, the
Hukbalahap
The Hukbong Bayan Laban sa Hapon (), better known by the acronym Hukbalahap, was a communist guerrilla movement formed by the farmers of Central Luzon. They were originally formed to fight the Japanese, but extended their fight into a rebelli ...
, the
Malayan Communist Party
The Malayan Communist Party (MCP), officially the Communist Party of Malaya (CPM), was a Marxist–Leninist and anti-imperialist communist party which was active in British Malaya and later, the modern states of Malaysia and Singapore from ...
, the
People's Republic of Mongolia
The Mongolian People's Republic ( mn, Бүгд Найрамдах Монгол Ард Улс, БНМАУ; , ''BNMAU''; ) was a socialist state which existed from 1924 to 1992, located in the historical region of Outer Mongolia in East Asia. It ...
, the
Polish People's Army
The Polish People's Army ( pl, Ludowe Wojsko Polskie , LWP) constituted the second formation of the Polish Armed Forces in the East in 1943–1945, and in 1945–1989 the armed forces of the Polish communist state ( from 1952, the Polish Pe ...
, the
Tuvan People's Republic
The Tuvan People's Republic (TPR; tyv, Тыва Арат Республик, translit=Tywa Arat Respublik; Yanalif: ''Tьʙа Arat Respuʙlik'', ),) and abbreviated TAR. known as the Tannu Tuva People's Republic until 1926, was a partially rec ...
(annexed by the Soviet Union in 1944),
[Toomas Alatalu. Tuva. A State Reawakens. ''Soviet Studies'', Vol. 44, No. 5 (1992), pp. 881–895] the
Viet Minh
The Việt Minh (; abbreviated from , chữ Nôm and Hán tự: ; french: Ligue pour l'indépendance du Viêt Nam, ) was a national independence coalition formed at Pác Bó by Hồ Chí Minh on 19 May 1941. Also known as the Việt Minh Fro ...
and the
Yugoslav Partisans
The Yugoslav Partisans,Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, Slovene: , or the National Liberation Army, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska (NOV), Народноослободилачка војска (НОВ); mk, Народноослобод� ...
.
The Soviet Union intervened against Japan and its
client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
in
Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
in 1945, cooperating with the
Nationalist Government of China and the
Nationalist Party led by
Chiang Kai-shek; though also cooperating, preferring, and encouraging the
Chinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Civil ...
led by
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
to take effective control of Manchuria after expelling Japanese forces.
United States



War justifications
The United States had indirectly supported Britain's war effort against Germany up to 1941 and declared its opposition to territorial aggrandizement. Materiel support to Britain was provided while the U.S. was officially neutral via the
Lend-Lease Act starting in 1941.
President
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
and Prime Minister
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
in August 1941 promulgated the
Atlantic Charter that pledged commitment to achieving "the final destruction of Nazi tyranny". Signing the Atlantic Charter, and thereby joining the "United Nations" was the way a state joined the Allies, and also became eligible for membership in the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
world body that formed in 1945.
The US strongly supported the Nationalist Government in China in its war with Japan, and provided military equipment, supplies, and volunteers to the Nationalist Government of China to assist in its war effort. In December 1941 Japan opened the war with its
attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii ...
, the US declared war on Japan, and Japan's allies Germany and Italy declared war on the US, bringing the US into World War II.
The US played a central role in liaising among the Allies and especially among the Big Four. At the
Arcadia Conference The First Washington Conference, also known as the Arcadia Conference (ARCADIA was the code name used for the conference), was held in Washington, D.C., from December 22, 1941, to January 14, 1942. President Roosevelt of the United States and Prime ...
in December 1941, shortly after the US entered the war, the US and Britain established a
Combined Chiefs of Staff, based in Washington, which deliberated the military decisions of both the US and Britain.
History
On 8 December 1941, following the attack on Pearl Harbor, the United States Congress declared war on Japan at the request of President
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
. This was followed by Germany and Italy declaring war on the United States on 11 December, bringing the country into the European theatre.
The US-led Allied forces in the Pacific theatre against Japanese forces from 1941 to 1945. From 1943 to 1945, the US led and coordinated the Western Allies' war effort in Europe under the leadership of General
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
.
The surprise attack on Pearl Harbor followed by Japan's swift attacks on Allied locations throughout the Pacific, resulted in major US losses in the first several months in the war, including losing control of the
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
,
Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
,
Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of T ...
and several Aleutian islands including
Attu and
Kiska
Kiska ( ale, Qisxa, russian: Кыска) is one of the Rat Islands, a group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. It is about long and varies in width from . It is part of Aleutian Islands Wilderness and as such, special permission is require ...
to Japanese forces. American naval forces attained some early successes against Japan. One was the bombing of Japanese industrial centres in the
Doolittle Raid
The Doolittle Raid, also known as the Tokyo Raid, was an air raid on 18 April 1942 by the United States on the Japanese capital Tokyo and other places on Honshu during World War II. It was the first American air operation to strike the Japa ...
. Another was repelling a Japanese invasion of
Port Moresby
(; Tok Pisin: ''Pot Mosbi''), also referred to as Pom City or simply Moresby, is the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea. It is one of the largest cities in the southwestern Pacific (along with Jayapura) outside of Australia and New ...
in
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
during the
Battle of the Coral Sea. A major turning point in the Pacific War was the
Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II that took place on 4–7 June 1942, six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor and one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea. The U.S. Navy under ...
where American naval forces were outnumbered by Japanese forces that had been sent to Midway to draw out and destroy American aircraft carriers in the Pacific and seize control of Midway that would place Japanese forces in proximity to Hawaii. However American forces managed to sink four of Japan's six large aircraft carriers that had initiated the attack on Pearl Harbor along with other attacks on Allied forces. Afterwards, the US began an offensive against Japanese-captured positions. The
Guadalcanal Campaign from 1942 to 1943 was a major contention point where Allied and Japanese forces struggled to gain control of
Guadalcanal.
Colonies and dependencies
=In the Americas and the Pacific
=
The United States held multiple dependencies in the Americas, such as
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
, the
Panama Canal Zone,
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, and the
U.S. Virgin Islands.
In the Pacific it held multiple island dependencies such as
American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internationa ...
,
Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
,
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
,
Midway Islands
Midway Atoll (colloquial: Midway Islands; haw, Kauihelani, translation=the backbone of heaven; haw, Pihemanu, translation=the loud din of birds, label=none) is a atoll in the North Pacific Ocean. Midway Atoll is an insular area of the Unit ...
,
Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of T ...
and others. These dependencies were directly involved in the Pacific campaign of the war.
=In Asia
=
The
Commonwealth of the Philippines was a sovereign protectorate referred to as an "associated state" of the United States. From late 1941 to 1944, the Philippines was
occupied by Japanese forces, who established the
Second Philippine Republic
The Second Philippine Republic, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines ( tl, Repúbliká ng Pilipinas; es, República de Filipinas; ja, フィリピン共和国, ''Firipin-kyōwakoku'') and also known as the Japanese-sponsored Phi ...
as a client state that had nominal control over the country.
China
In the 1920s the Soviet Union provided military assistance to the
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
, or the Nationalists, and helped reorganize their party along
Leninist
Leninism is a political ideology developed by Russian Marxist revolutionary Vladimir Lenin that proposes the establishment of the dictatorship of the proletariat led by a revolutionary vanguard party as the political prelude to the establishm ...
lines: a unification of party, state, and army. In exchange the Nationalists agreed to let members of the
Chinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Civil ...
join the Nationalists on an individual basis. However, following the nominal unification of China at the end of the
Northern Expedition
The Northern Expedition was a military campaign launched by the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) of the Kuomintang (KMT), also known as the "Chinese Nationalist Party", against the Beiyang government and other regional warlords in 1926. The ...
in 1928,
Generalissimo
''Generalissimo'' ( ) is a military rank of the highest degree, superior to field marshal and other five-star ranks in the states where they are used.
Usage
The word (), an Italian term, is the absolute superlative of ('general') thus me ...
Chiang Kai-shek purged leftists from his party and fought against the revolting Chinese Communist Party, former
warlord
A warlord is a person who exercises military, economic, and political control over a region in a country without a strong national government; largely because of coercive control over the armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of h ...
s, and other militarist factions. A fragmented China provided easy opportunities for Japan to gain territories piece by piece without engaging in
total war
Total war is a type of warfare that includes any and all civilian-associated resources and infrastructure as legitimate military targets, mobilizes all of the resources of society to fight the war, and gives priority to warfare over non-combata ...
. Following the 1931
Mukden Incident, the puppet state of
Manchukuo was established. Throughout the early to mid-1930s, Chiang's anti-communist and anti-militarist campaigns continued while he fought small, incessant conflicts against Japan, usually followed by unfavorable settlements and concessions after military defeats.
In 1936 Chiang was forced to cease his
anti-communist military campaigns after
his kidnap and release by
Zhang Xueliang
Chang Hsüeh-liang (, June 3, 1901 – October 15, 2001), also romanized as Zhang Xueliang, nicknamed the "Young Marshal" (少帥), known in his later life as Peter H. L. Chang, was the effective ruler of Northeast China and much of northern ...
, and reluctantly formed
a nominal alliance with the Communists, while the Communists agreed to fight under the nominal command of the Nationalists against the Japanese. Following the
Marco Polo Bridge Incident of 7 July 1937, China and Japan became embroiled in a full-scale war. The Soviet Union, wishing to keep China in the fight against Japan, supplied China with military assistance until 1941, when it
signed a non-aggression pact with Japan. China formally declared war on Japan, as well as Germany and Italy, in December 1941, after the attack on Pearl Harbor.
Continuous clashes between the Communists and Nationalists behind enemy lines cumulated in
a major military conflict between these two former allies that effectively ended their cooperation against the Japanese, and China had been divided between the internationally recognized
Nationalist China under the leadership of Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek and
Communist China under the leadership of
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
until the Japanese surrendered in 1945.
Factions
=Nationalists
=
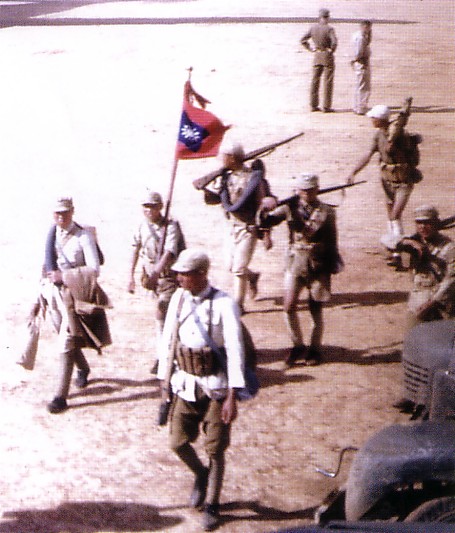

Prior to the alliance of Germany and Italy to Japan, the Nationalist Government held close relations with both Germany and Italy. In the early 1930s,
Sino-German cooperation existed between the Nationalist Government and Germany in military and industrial matters. Nazi Germany provided the largest proportion of Chinese arms imports and technical expertise. Relations between the Nationalist Government and Italy during the 1930s varied, however even after the Nationalist Government followed League of Nations sanctions against Italy for
its invasion of
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, the international sanctions proved unsuccessful, and relations between the Fascist government in Italy and the Nationalist Government in China returned to normal shortly afterwards.
[G. Bruce Strang. On the fiery march: Mussolini prepares for war. Westport, Connecticut, US: Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc., 2003. Pp. 58–59.] Up until 1936, Mussolini had provided the Nationalists with Italian military air and naval missions to help the Nationalists fight against Japanese incursions and communist insurgents.
Italy also held strong commercial interests and a strong commercial position in China supported by the
Italian concession in Tianjin.
However, after 1936 the relationship between the Nationalist Government and Italy changed due to a Japanese diplomatic proposal to recognize the
Italian Empire
The Italian colonial empire ( it, Impero coloniale italiano), known as the Italian Empire (''Impero Italiano'') between 1936 and 1943, began in Africa in the 19th century and comprised the colonies, protectorates, concessions and dependenci ...
that included occupied Ethiopia within it in exchange for Italian recognition of
Manchukuo, Italian Foreign Minister
Galeazzo Ciano
Gian Galeazzo Ciano, 2nd Count of Cortellazzo and Buccari ( , ; 18 March 1903 – 11 January 1944) was an Italian diplomat and politician who served as Foreign Minister in the government of his father-in-law, Benito Mussolini, from 1936 until 1 ...
accepted this offer by Japan, and on 23 October 1936 Japan recognized the Italian Empire and Italy recognized Manchukuo, as well as discussing increasing commercial links between Italy and Japan.
The Nationalist Government held close relations with the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. The United States opposed Japan's invasion of China in 1937 that it considered an illegal violation of China's
sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
, and offered the Nationalist Government diplomatic, economic, and military assistance during its war against Japan. In particular, the United States sought to bring the Japanese war effort to a complete halt by imposing a full embargo on all trade between the United States to Japan, Japan was dependent on the United States for 80 per cent of its
petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
, resulting in an economic and military crisis for Japan that could not continue its war effort with China without access to petroleum. In November 1940, American military aviator
Claire Lee Chennault
Claire Lee Chennault (September 6, 1893 – July 27, 1958) was an American military aviator best known for his leadership of the "Flying Tigers" and the Chinese Air Force in World War II.
Chennault was a fierce advocate of "pursuit" or fighte ...
upon observing the dire situation in the air war between China and Japan, set out to organize a volunteer squadron of American fighter pilots to fight alongside the Chinese against Japan, known as the
Flying Tigers
The First American Volunteer Group (AVG) of the Republic of China Air Force, nicknamed the Flying Tigers, was formed to help oppose the Japanese invasion of China. Operating in 1941–1942, it was composed of pilots from the United States ...
.
[Guo wu yuan. Xin wen ban gong shi. Col. C.L. Chennault and Flying Tigers. English translation. State Council Information Office of the People's Republic of China. Pp. 16.] US President
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
accepted dispatching them to China in early 1941.
However, they only became operational shortly after the attack on Pearl Harbor.
The
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
recognised the
Republic of China but urged reconciliation with the Chinese Communist Party and inclusion of Communists in the government.
[Frederic J. Fleron, Erik P. Hoffmann, Robbin Frederick Laird. ''Soviet Foreign Policy: Classic and Contemporary Issues.'' Third paperback edition. New Brunswick, New Jersey, US: Transaction Publishers, 2009. Pp. 236.] The Soviet Union also urged military and cooperation between Nationalist China and Communist China during the war.
Even though China had been fighting the longest among all the Allied powers, it only officially joined the Allies after the attack on Pearl Harbor, on 7 December 1941. China fought the Japanese Empire before joining the Allies in the
Pacific War. Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek thought Allied victory was assured with the entrance of the United States into the war, and he declared war on Germany and the other Axis states. However, Allied aid remained low because the
Burma Road
The Burma Road () was a road linking Burma (now known as Myanmar) with southwest China. Its terminals were Kunming, Yunnan, and Lashio, Burma. It was built while Burma was a British colony to convey supplies to China during the Second Sino ...
was closed and the Allies suffered a series of military defeats against Japan early on in the campaign. General
Sun Li-jen
Sun Li-jen (; December 8, 1900November 19, 1990) was a Chinese Nationalist (KMT) general, a graduate of Virginia Military Institute, best known for his leadership in the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Chinese Civil War. His military achiev ...
led the R.O.C. forces to the relief of 7,000 British forces trapped by the Japanese in the
Battle of Yenangyaung
The Battle of Yenangyaung () was fought in Burma, now Myanmar, during the Burma Campaign in World War II. The battle of Yenaungyaung was fought in the vicinity of Yenangyaung and its oil fields.
Background
After the Japanese captured Rangoon in ...
. He then reconquered North Burma and re-established the land route to China by the
Ledo Road
The Ledo Road (from Ledo, Assam, India to Kunming, Yunnan, China) was an overland connection between India and China, built during World War II to enable the Western Allies to deliver supplies to China and aid the war effort against Japan ...
. But the bulk of military aid did not arrive until the spring of 1945. More than 1.5 million Japanese troops were trapped in the China Theatre, troops that otherwise could have been deployed elsewhere if China had collapsed and made a separate peace.
=Communists
=


Communist China had been tacitly supported by the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
since the 1920s, though the Soviet Union diplomatically recognised the Republic of China,
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
supported cooperation between the Nationalists and the Communists—including pressuring the Nationalist Government to grant the Communists state and military positions in the government.
This was continued into the 1930s that fell in line with the Soviet Union's subversion policy of
popular front
A popular front is "any coalition of working-class and middle-class parties", including liberal and social democratic ones, "united for the defense of democratic forms" against "a presumed Fascist assault".
More generally, it is "a coalition ...
s to increase communists' influence in governments.
The Soviet Union urged military and cooperation between Soviet China and Nationalist China during China's war against Japan.
Initially
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
accepted the demands of the Soviet Union and in 1938 had recognized Chiang Kai-shek as the "leader" of the "Chinese people".
[Dieter Heinzig. The Soviet Union and communist China, 1945–1950: the arduous road to the alliance. M.E. Sharpe, 2004. Pp. 9.] In turn, the Soviet Union accepted Mao's tactic of "continuous guerilla warfare" in the countryside that involved a goal of extending the Communist bases, even if it would result in increased tensions with the Nationalists.
After the breakdown of their cooperation with the Nationalists in 1941, the Communists prospered and grew as the war against Japan dragged on, building up their sphere of influence wherever opportunities were presented, mainly through rural mass organizations, administrative, land and tax reform measures favoring poor peasants; while the Nationalists attempted to neutralize the spread of Communist influence by military blockade and fighting the Japanese at the same time.
The Communist Party's position in China was boosted further upon the
Soviet invasion of Manchuria
The Soviet invasion of Manchuria, formally known as the Manchurian strategic offensive operation (russian: Манчжурская стратегическая наступательная операция, Manchzhurskaya Strategicheskaya Nastu ...
in August 1945 against the Japanese puppet state of
Manchukuo and the Japanese
Kwantung Army
''Kantō-gun''
, image = Kwantung Army Headquarters.JPG
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Kwantung Army headquarters in Hsinking, Manchukuo
, dates = April ...
in China and
Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
. Upon the intervention of the Soviet Union against Japan in World War II in 1945, Mao Zedong in April and May 1945 had planned to mobilize 150,000 to 250,000 soldiers from across China to work with forces of the Soviet Union in capturing Manchuria.
Other affiliated state combatants
Albania
Albania was retroactively recognized as an "Associated Power" at the 1946 Paris conference and officially signed the treaty ending WWII between the "Allied and Associated Powers" and Italy in Paris, on 10 February 1947.
Australia
Australia was a sovereign Dominion under the
Australian monarchy, as per the
Statute of Westminster 1931. At the start of the war Australia followed Britain's foreign policies and accordingly declared war against Germany on 3 September 1939. Australian foreign policy became more independent after the
Australian Labor Party
The Australian Labor Party (ALP), also simply known as Labor, is the major centre-left political party in Australia, one of two major parties in Australian politics, along with the centre-right Liberal Party of Australia. The party forms t ...
formed government in October 1941, and Australia separately declared war against Finland, Hungary and Romania on 8 December 1941 and against Japan the next day.
Belgium

Before the war, Belgium had pursued a policy of
neutrality and only became an Allied member after
being invaded by Germany on 10 May 1940. During the ensuing fighting, Belgian forces fought alongside French and British forces against the invaders. While the British and French were struggling against
the fast German advance elsewhere on the front, the Belgian forces were pushed into a pocket to the north. Finally, on 28 May, the
King Leopold III
Leopold III (3 November 1901 – 25 September 1983) was King of the Belgians from 23 February 1934 until his abdication on 16 July 1951. At the outbreak of World War II, Leopold tried to maintain Belgian neutrality, but after the German invasi ...
surrendered himself and his military to the Germans, having decided the Allied cause was lost. The legal Belgian government was reformed as
a government in exile in London. Belgian troops and pilots continued to fight on the Allied side as the
Free Belgian Forces. Belgium itself was occupied, but a sizeable
Resistance was formed and was loosely coordinated by the government in exile and other Allied powers.
British and Canadian troops arrived in Belgium in September 1944 and the capital,
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
, was liberated on 6 September. Because of the
Ardennes Offensive
The Battle of the Bulge, also known as the Ardennes Offensive, was the last major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II. The battle lasted from 16 December 1944 to 28 January 1945, towards the end of the war in ...
, the country was only fully liberated in early 1945.
Colonies and dependencies
Belgium held the colony of the
Belgian Congo
The Belgian Congo (french: Congo belge, ; nl, Belgisch-Congo) was a Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960. The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), in 1964.
Colo ...
and the League of Nations mandate of
Ruanda-Urundi. The Belgian Congo was not occupied and remained loyal to the Allies as an important economic asset while its deposits of uranium were useful to the Allied efforts to develop the atomic bomb. Troops from the Belgian Congo participated in the
East African Campaign against the Italians. The colonial ''
Force Publique
The ''Force Publique'' (, "Public Force"; nl, Openbare Weermacht) was a gendarmerie and military force in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo from 1885 (when the territory was known as the Congo Free State), through the period of ...
'' also served in other theatres including Madagascar, the Middle-East, India and Burma within British units.
Brazil
Initially,
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
maintained a position of neutrality, trading with both the Allies and the
Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
, while Brazilian president
Getúlio Vargas
Getúlio Dornelles Vargas (; 19 April 1882 – 24 August 1954) was a Brazilian lawyer and politician who served as the 14th and 17th president of Brazil, from 1930 to 1945 and from 1951 to 1954. Due to his long and controversial tenure as Brazi ...
's quasi-
Fascist policies indicated a leaning toward the Axis powers. However, as the war progressed, trade with the Axis countries became almost impossible and the United States initiated forceful diplomatic and economic efforts to bring Brazil onto the Allied side.
At the beginning of 1942, Brazil permitted the United States to set up air bases on its territory, especially in
Natal
NATAL or Natal may refer to:
Places
* Natal, Rio Grande do Norte, a city in Brazil
* Natal, South Africa (disambiguation), a region in South Africa
** Natalia Republic, a former country (1839–1843)
** Colony of Natal, a former British colony ( ...
, strategically located at the easternmost corner of the
South American
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southe ...
continent, and on 28 January the country severed diplomatic relations with Germany, Japan and Italy. After that, 36 Brazilian merchant ships were sunk by the German and Italian navies, which led the Brazilian government to declare war against Germany and Italy on 22 August 1942.
Brazil then sent a 25,700 strong
Expeditionary Force to Europe that fought mainly on the
Italian front, from September 1944 to May 1945. Also, the
Brazilian Navy
)
, colors= Blue and white
, colors_label= Colors
, march= "Cisne Branco" ( en, "White Swan") (same name as training ship ''Cisne Branco''
, mascot=
, equipment= 1 multipurpose aircraft carrier7 submarines6 frigates2 corvettes4 amphibious war ...
and
Air Force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ...
acted in the
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
from the middle of 1942 until the end of the war. Brazil was the only South American country to send troops to fight in the European theatre in the Second World War.
Canada
Canada was a sovereign Dominion under the
Canadian monarchy
The monarchy of Canada is Canada's form of government embodied by the Canadian sovereign and head of state. It is at the core of Canada's constitutional federal structure and Westminster-style parliamentary democracy. The monarchy is the founda ...
, as per the Statute of Westminster 1931. In a symbolic statement of autonomous foreign policy Prime Minister
William Lyon Mackenzie King
William Lyon Mackenzie King (December 17, 1874 – July 22, 1950) was a Canadian statesman and politician who served as the tenth prime minister of Canada for three non-consecutive terms from 1921 to 1926, 1926 to 1930, and 1935 to 1948. A L ...
delayed parliament's vote on a declaration of war for seven days after Britain had declared war. Canada was the last member of the Commonwealth to declare war on Germany on 10 September 1939.
Cuba
Because of
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
's geographical position at the entrance of the
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
,
Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center. 's role as the principal trading port in the
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
, and the country's natural resources, Cuba was an important participant in the
American Theater of World War II, and subsequently one of the greatest beneficiaries of the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
'
Lend-Lease program. Cuba declared war on the
Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
in December 1941,
making it one of the first
Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
n countries to enter the conflict, and by the war's end in 1945 its military had developed a reputation as being the most efficient and cooperative of all the Caribbean states.
On 15 May 1943, the Cuban patrol boat CS-13 sank the German submarine ''
U-176''.
Czechoslovakia
In 1938, with the
Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
, Czechoslovakia, the United Kingdom, and France sought to resolve German irredentist claims to the
Sudetenland region. As a result, the incorporation of the Sudetenland into Germany began on 1 October 1938. Additionally, a small northeastern part of the border region known as
Zaolzie
Trans-Olza ( pl, Zaolzie, ; cs, Záolží, ''Záolší''; german: Olsa-Gebiet; Cieszyn Silesian: ''Zaolzi''), also known as Trans-Olza Silesia ( Polish: ''Śląsk Zaolziański''), is a territory in the Czech Republic, which was disputed betwe ...
was occupied by and annexed to
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. Further, by the
First Vienna Award
The First Vienna Award was a treaty signed on 2 November 1938 pursuant to the Vienna Arbitration, which took place at Vienna's Belvedere Palace. The arbitration and award were direct consequences of the previous month's Munich Agreement, which ...
,
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
received southern territories of Slovakia and
Carpathian Ruthenia
Carpathian Ruthenia ( rue, Карпатьска Русь, Karpat'ska Rus'; uk, Закарпаття, Zakarpattia; sk, Podkarpatská Rus; hu, Kárpátalja; ro, Transcarpatia; pl, Zakarpacie); cz, Podkarpatská Rus; german: Karpatenukrai ...
.
A
Slovak State
Slovak may refer to:
* Something from, related to, or belonging to Slovakia (''Slovenská republika'')
* Slovaks, a Western Slavic ethnic group
* Slovak language, an Indo-European language that belongs to the West Slavic languages
* Slovak, Arka ...
was proclaimed on 14 March 1939, and the next day Hungary occupied and annexed the remainder of Carpathian Ruthenia, and the German ''
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
'' moved into the remainder of the Czech Lands. On 16 March 1939 the
Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
The Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia; cs, Protektorát Čechy a Morava; its territory was called by the Nazis ("the rest of Czechia"). was a partially annexed territory of Nazi Germany established on 16 March 1939 following the German oc ...
was proclaimed after negotiations with
Emil Hácha
Emil Dominik Josef Hácha (12 July 1872 – 27 June 1945) was a Czech lawyer, the president of Czechoslovakia from November 1938 to March 1939. In March 1939, after the breakup of Czechoslovakia, Hácha was the nominal president of the newly pro ...
, who remained technically head of state with the title of State President. After a few months, former Czechoslovak President Beneš organized a committee in exile and sought diplomatic recognition as the legitimate government of the
First Czechoslovak Republic
The First Czechoslovak Republic ( cs, První československá republika, sk, Prvá česko-slovenská republika), often colloquially referred to as the First Republic ( cs, První republika, Slovak: ''Prvá republika''), was the first Czechoslo ...
. The committee's success in obtaining intelligence and coordinating actions by the
Czechoslovak resistance led first Britain and then the other Allies to recognize it in 1941. In December 1941 the
Czechoslovak government-in-exile
The Czechoslovak government-in-exile, sometimes styled officially as the Provisional Government of Czechoslovakia ( cz, Prozatímní vláda Československa, sk, Dočasná vláda Československa), was an informal title conferred upon the Czechos ...
declared war on the Axis powers. Czechoslovakian military units took part in the war.
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic was one of the very few countries willing to accept mass Jewish immigration during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. At the
Évian Conference
The Évian Conference was convened 6–15 July 1938 at Évian-les-Bains, France, to address the problem of German and Austrian Jewish refugees wishing to flee persecution by Nazi Germany. It was the initiative of United States President Franklin ...
, it offered to accept up to 100,000 Jewish refugees. The DORSA (Dominican Republic Settlement Association) was formed with the assistance of the JDC, and helped settle Jews in
Sosúa
Sosúa is a beach town in the Puerto Plata province of the Dominican Republic. Located approximately from the Gregorio Luperón International Airport in San Felipe de Puerto Plata.
The town is divided into three sectors: ''El Batey'', which i ...
, on the northern coast. About 700 European Jews of
Ashkenazi Jewish descent reached the settlement where each family received of land, 10 cows (plus 2 additional cows per children), a mule and a horse, and a
US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
10,000 loan (about dollars at prices) at 1% interest.
The Dominican Republic officially declared war on the Axis powers on 11 December 1941, after the
attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii ...
. However, the Caribbean state had already been engaged in war actions since before the formal declaration of war. Dominican sailboats and schooners had been attacked on previous occasions by German submarines as, highlighting the case of the 1,993-ton merchant ship, ''"San Rafael"'', which was making a trip from
Tampa, Florida
Tampa () is a city on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The city's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and ...
to
Kingston, Jamaica, when 80 miles away from its final destination, it was torpedoed by the
German submarine U-125, causing the command to abandon the ship by the commander. Although the crew of ''San Rafael'' managed to escape the event, it would be remembered by the Dominican press as a sign of the ''infamy of the German submarines and the danger they represented in the Caribbean.''
Recently, due to a research work carried out by the Embassy of the United States of America in Santo Domingo and the
Institute of Dominican Studies of the City of New York (CUNY), documents of the
Department of Defense Department of Defence or Department of Defense may refer to:
Current departments of defence
* Department of Defence (Australia)
* Department of National Defence (Canada)
* Department of Defence (Ireland)
* Department of National Defense (Philipp ...
were discovered in which it was confirmed that around 340 men and women of Dominican origin were part of the US Armed Forces during the World War II. Many of them received medals and other recognitions for their outstanding actions in combat.
Ethiopia
The Ethiopian Empire was
invaded by
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
on 3 October 1935. On 2 May 1936, Emperor
Haile Selassie I
Haile Selassie I ( gez, ቀዳማዊ ኀይለ ሥላሴ, Qädamawi Häylä Səllasé, ; born Tafari Makonnen; 23 July 189227 August 1975) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as Regent Plenipotentiary of Ethiopia ('' ...
fled into exile, just before the Italian occupation on 7 May. After the outbreak of World War II, the Ethiopian government-in-exile cooperated with the British during the
British Invasion of Italian East Africa beginning in June 1940. Haile Selassie returned to his rule on 18 January 1941. Ethiopia declared war on Germany, Italy and Japan in December 1942.
Greece
Greece was
invaded by Italy on 28 October 1940 and subsequently joined the Allies. The Greek Army managed to stop the Italian offensive from Italy's protectorate of Albania, and Greek forces pushed Italian forces back into Albania. However, after the
German invasion of Greece
The German invasion of Greece, also known as the Battle of Greece or Operation Marita ( de , Unternehmen Marita, links = no), was the attack of Greece by Italy and Germany during World War II. The Italian invasion in October 1940, which is usu ...
in April 1941, German forces managed to occupy mainland Greece and, a month later,
the island of Crete. The Greek government
went into exile, while the country was placed under
a puppet government and divided into occupation zones run by Italy, Germany and Bulgaria. From 1941, a strong resistance movement appeared, chiefly in the mountainous interior, where it established a "Free Greece" by mid-1943. Following the Italian capitulation in September 1943, the Italian zone was taken over by the Germans. Axis forces left mainland Greece in October 1944, although some Aegean islands, notably Crete, remained under German occupation until the end of the war.
Luxembourg
Before the war, Luxembourg had pursued a policy of
neutrality and only became an Allied member after
being invaded by Germany on 10 May 1940. The government in exile fled, winding up in England. It made Luxembourgish language broadcasts to the occupied country on
BBC radio
BBC Radio is an operational business division and service of the British Broadcasting Corporation (which has operated in the United Kingdom under the terms of a royal charter since 1927). The service provides national radio stations covering ...
.
In 1944, the government in exile signed
a treaty with the Belgian and Dutch governments, creating the
Benelux
The Benelux Union ( nl, Benelux Unie; french: Union Benelux; lb, Benelux-Unioun), also known as simply Benelux, is a politico- economic union and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in western Europe: ...
Economic Union and also signed into the
Bretton Woods system.
Mexico
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
declared war on Germany in 1942 after German submarines attacked the Mexican oil tankers ''
Potrero del Llano'' and ''
Faja de Oro
SS ''Faja de Oro'' ("Strip of Gold", which is a petroleum rich area in Mexico) was an oil tanker built in 1914. She sailed for a number of companies, and survived service in the First World War, only to be torpedoed and sunk by a German submarine ...
'' that were transporting crude oil to the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. These attacks prompted
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
Manuel Ávila Camacho
Manuel Ávila Camacho (; 24 April 1897 – 13 October 1955) was a Mexican politician and military leader who served as the President of Mexico from 1940 to 1946. Despite participating in the Mexican Revolution and achieving a high rank, he cam ...
to declare war on the Axis powers.
Mexico formed
Escuadrón 201
The 201st Fighter Squadron ( es, Escuadrón Aéreo de Pelea 201) is a fighter squadron of the Mexican Air Force, part of the Mexican Expeditionary Air Force that aided the Allied war effort during World War II. The squadron was known by the n ...
fighter squadron as part of the
Fuerza Aérea Expedicionaria Mexicana (FAEM—"Mexican Expeditionary Air Force"). The squadron was attached to the
58th Fighter Group of the
United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
and carried out tactical air support missions during the liberation of the main Philippine island of
Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as ...
in the summer of 1945.
Some 300,000 Mexican citizens went to the United States to work on farms and factories. Some 15,000 U.S. nationals of Mexican origin and Mexican residents in the US enrolled in the US Armed Forces and fought in various fronts around the world.
Netherlands
The Netherlands became an Allied member after being invaded on 10 May 1940 by Germany. During the
ensuing campaign, the Netherlands were defeated and occupied by Germany. The Netherlands was liberated by Canadian, British, American and other allied forces during the campaigns of 1944 and 1945. The
Princess Irene Brigade
During the Second World War, the Royal Netherlands Motorized Infantry Brigade, later known as the Princess Irene Brigade ( nl, Prinses Irene Brigade) was a Dutch military unit initially formed from approximately 1,500 troops, including a small gro ...
, formed from escapees from the German invasion, took part in several actions in 1944 in Arromanches and in 1945 in the Netherlands. Navy vessels saw action in the British Channel, the North Sea and the Mediterranean, generally as part of Royal Navy units. Dutch airmen flying British aircraft participated in the air war over Germany.
Colonies and dependencies
The
Dutch East Indies (modern-day
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
) was the principal Dutch colony in Asia, and was seized by Japan in 1942. During the
Dutch East Indies Campaign, the Netherlands played a significant role in the Allied effort to halt the Japanese advance as part of the
American-British-Dutch-Australian (ABDA) Command. The ABDA fleet finally encountered the Japanese surface fleet at the
Battle of Java Sea
The Battle of the Java Sea ( id, Pertempuran Laut Jawa, ja, スラバヤ沖海戦, Surabaya oki kaisen, Surabaya open-sea battle, Javanese : ꦥꦼꦫꦁꦱꦼꦒꦫꦗꦮ, romanized: ''Perang Segara Jawa'') was a decisive naval battle o ...
, at which Doorman gave the order to engage. During the ensuing battle the ABDA fleet suffered heavy losses, and was mostly destroyed after several naval battles around
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mos ...
; the ABDA Command was later dissolved. The Japanese
finally occupied the Dutch East Indies in February–March 1942. Dutch troops, aircraft and escaped ships continued to fight on the Allied side and also mounted a
guerrilla campaign in Timor.
New Zealand
New Zealand was a sovereign Dominion under the
New Zealand monarchy, as per the Statute of Westminster 1931. It quickly entered World War II, officially declaring war on Germany on 3 September 1939, just hours after Britain. Unlike Australia, which had felt obligated to declare war, as it also had not ratified the Statute of Westminster, New Zealand did so as a sign of allegiance to Britain, and in recognition of Britain's abandonment of its
former appeasement policy, which New Zealand had long opposed. This led to then Prime Minister
Michael Joseph Savage
Michael Joseph Savage (23 March 1872 – 27 March 1940) was a New Zealand politician who served as the 23rd prime minister of New Zealand, heading the First Labour Government from 1935 until his death in 1940.
Savage was born in the Colon ...
declaring two days later:
''"With gratitude for the past and confidence in the future we range ourselves without fear beside Britain. Where she goes, we go; where she stands, we stand. We are only a small and young nation, but we march with a union of hearts and souls to a common destiny."''
Norway

Because of its strategic location for control of the sea lanes in the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
and the
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
, both the Allies and Germany worried about the other side gaining control of the neutral country. Germany ultimately struck first with
Operation Weserübung
Operation Weserübung (german: Unternehmen Weserübung , , 9 April – 10 June 1940) was Germany's assault on Denmark and Norway during the Second World War and the opening operation of the Norwegian Campaign.
In the early morning of 9 Ap ...
on 9 April 1940, resulting in the two-month-long
Norwegian Campaign, which ended in a German victory and their war-long
occupation of Norway
The occupation of Norway by Nazi Germany during the Second World War began on 9 April 1940 after Operation Weserübung. Conventional armed resistance to the German invasion ended on 10 June 1940, and Nazi Germany controlled Norway until th ...
.
Units of the Norwegian Armed Forces evacuated from Norway or raised abroad continued participating in the war Norwegian Armed Forces in exile, from exile.
The Norwegian merchant fleet, then the fourth largest in the world, was organized into Nortraship to support the Allied cause. Nortraship was the world's largest shipping company, and at its height operated more than 1000 ships.
Norway was neutral when Germany invaded, and it is not clear when Norway became an Allied country. Great Britain, France and Polish Armed Forces in the West, Polish forces in exile supported Norwegian forces against the invaders but without a specific agreement. Norway's cabinet signed a military agreement with Britain on 28 May 1941. This agreement allowed all Norwegian forces in exile to operate under UK command. Norwegian troops in exile should primarily be prepared for the liberation of Norway, but could also be used to defend Britain. At the end of the war German forces in Norway surrendered to British officers on 8 May and Operation Doomsday, allied troops occupied Norway until 7 June.
[Skodvin, Magne (red.) (1984): ''Norge i krig.'' Bind 7. Oslo: Aschehoug.]
Poland
The Invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939, started the war in Europe, and the United Kingdom and France declared war on Germany on 3 September. Poland fielded the third biggest army among the European Allies, after the Soviet Union and United Kingdom, but before France.
Polish Army suffered a series of defeats in the first days of the invasion. The Soviet Union unilaterally considered the flight to Romania of President Ignacy Mościcki and Marshal Edward Rydz-Śmigły on 17 September as evidence of ''debellatio'' causing the extinction of the Polish state, and consequently declared itself allowed to invade (according to the Soviet position: "to protect") Eastern Poland starting from the same day. However, the Red Army had invaded the Second Polish Republic several hours before the Polish president fled to Romania. The Soviets invaded on 17 September at 3 a.m., while president Mościcki crossed the Polish-Romanian border at 21:45 on the same day. The Polish military continued to fight against both the Germans and the Soviets, and the last major battle of the war, the Battle of Kock (1939), Battle of Kock, ended at 1 a.m. on 6 October 1939 with the Independent Operational Group "Polesie," a field army, surrendering due to lack of ammunition. The country never officially surrendered to
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, nor to the Soviet Union, primarily because neither of the totalitarian powers requested an official surrender, and continued the war effort under the Polish government in exile.

Polish soldiers fought under their own flag but under the command of the British military. They were major contributors to the Allies in the Western Front (World War II), theatre of war west of Germany and in the theatre of Eastern Front (World War II), war east of Germany, with the Soviet Union. The Polish armed forces in the West created after the fall of Poland played minor roles in the
Battle of France, and larger ones in the Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian and North African Campaigns.
[At the siege of Tobruk] The Soviet Union recognized the London-based government at first. But it broke diplomatic relations after the Katyn massacre of Polish nationals was revealed. In 1943, the Soviet Union organized the
Polish People's Army
The Polish People's Army ( pl, Ludowe Wojsko Polskie , LWP) constituted the second formation of the Polish Armed Forces in the East in 1943–1945, and in 1945–1989 the armed forces of the Polish communist state ( from 1952, the Polish Pe ...
under Zygmunt Berling, around which it constructed the post-war successor state People's Republic of Poland. The Polish People's Army formed in USSR took part in a number of battles of the Eastern Front, including the Battle of Berlin, the closing battle of the European theater of war.
The Home Army, loyal to the London-based government and the largest underground force in Europe, as well other smaller resistance organizations in occupied Poland provided intelligence to the Allies and led to uncovering of Nazi war crimes (i.e., death camps).
South Africa
South Africa was a sovereign Dominion under the Monarchy of South Africa, South African monarchy, as per the Statute of Westminster 1931. South Africa held authority over the mandate of South-West Africa.
Yugoslavia

Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
entered the war on the Allied side after Invasion of Yugoslavia, the invasion of Axis powers on 6 April 1941. The Royal Yugoslav Army was thoroughly defeated in less than two weeks and the country was occupied starting on 18 April. The Italian-backed Croatian fascist leader Ante Pavelić declared the Independent State of Croatia before the invasion was over. Peter II of Yugoslavia, King Peter II and much of the Yugoslavian government had left the country. In the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, they joined numerous other governments in exile from Nazi-occupied Europe. Beginning with the June 1941 uprising in eastern Herzegovina, uprising in Herzegovina in June 1941, there was continuous anti-Axis resistance in Yugoslavia until the end of the war.
Resistance factions

Before the end of 1941, the anti-Axis resistance movement split between the royalist Chetniks and the communist
Yugoslav Partisans
The Yugoslav Partisans,Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, Slovene: , or the National Liberation Army, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska (NOV), Народноослободилачка војска (НОВ); mk, Народноослобод� ...
of Josip Broz Tito who fought both against each other during the war and against the occupying forces. The Yugoslav Partisans managed to put up considerable resistance to the Axis occupation, forming various liberated territories during the war. In August 1943, there were over 30 Axis divisions on the territory of Yugoslavia, not including the forces of the Independent State of Croatia, Croatian puppet state and other quisling formations. In 1944, the leading Allied powers persuaded Tito's Yugoslav Partisans and the royalist Yugoslav government led by Prime Minister Ivan Šubašić to sign the Treaty of Vis that created the Democratic Federal Yugoslavia.
=Partisans
=
The Partisans were a major Yugoslav resistance movement against the Axis occupation and partition of Yugoslavia. Initially, the Partisans were in rivalry with the Chetniks over control of the resistance movement. However, the Partisans were recognized by both the Eastern and Western Allies as the primary resistance movement in 1943. After that, their strength increased rapidly, from 100,000 at the beginning of 1943 to over 648,000 in September 1944. In 1945 they were transformed into the Yugoslav People's Army, Yugoslav army, organized in four field armies with 800,000 fighters.
=Chetniks
=

The Chetniks, the short name given to the movement titled the ''Yugoslav Army of the Fatherland'', were initially a major Allied Yugoslav resistance movement. However, due to their royalist and anti-communist views, Chetniks were considered to have begun collaborating with the Axis as a tactical move to focus on destroying their Partisan rivals. The Chetniks presented themselves as a Yugoslav movement, but were primarily a Serbs, Serb movement. They reached their peak in 1943 with 93,000 fighters. Their major contribution was Operation Halyard in 1944. In collaboration with the Office of Strategic Services, OSS, 413 Allied airmen shot down over Yugoslavia were rescued and evacuated.
Client and occupied states
British
Egypt
The Kingdom of Egypt was nominally sovereign since 1922 but effectively remained in the British sphere of influence; the British Mediterranean Fleet was stationed in Alexandria while British Army forces were based in the Suez Canal zone. Egypt was a neutral country for most of World War II, but the Anglo-Egyptian treaty of 1936 permitted British forces in Egypt to defend the Suez Canal. The United Kingdom controlled Egypt and used it as a major base for Allied operations throughout the region, especially the battles in North Africa against Italy and Germany. Its highest priorities were control of the Eastern Mediterranean, and especially keeping the Suez Canal open for merchant ships and for military connections with India and Australia.
Egypt faced an Axis campaign led by Italian and German forces during the war. British frustration over Farouk of Egypt, King Farouk's reign over Egypt resulted in the Abdeen Palace incident of 1942 where British Army forces surrounded the royal palace and demanded a new government be established, nearly forcing the abdication of Farouk until he submitted to British demands. The Kingdom of Egypt joined the United Nations on 24 February 1945.
India (British Raj)
At the outbreak of World War II, the
British Indian Army numbered 205,000 men. Later during World War II, the Indian Army became the largest all-volunteer force in history, rising to over 2.5 million men in size. These forces included tank, artillery and airborne forces.
Indian soldiers earned 30 Victoria Crosses during the Second World War. During the war, India suffered more civilian casualties than the United Kingdom, with the Bengal famine of 1943 estimated to have killed at least 23 million people. In addition, India suffered 87,000 military casualties, more than any Crown colony but fewer than the United Kingdom, which suffered 382,000 military casualties.
Burma
Burma was a British colony at the start of World War II. It was later invaded by Japanese forces and that contributed to the Bengal Famine of 1943. For the native Burmese, it was an uprising against colonial rule, so some fought on the Japanese's side, but most minorities fought on the Allies side. Burma also contributed resources such as rice and rubber.
Soviet sphere
Bulgaria
After a period of neutrality, Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgaria joined the Axis powers from 1941 to 1944. The Orthodox Church and others convinced King Boris to not allow the Bulgarian Jews to be exported to concentration camps. The king died shortly afterwards, suspected of being poisoned after a visit to Germany. Bulgaria abandoned the Axis and joined the Allies when the Soviet Union invaded, offering no resistance to the incoming forces. Bulgarian troops then fought alongside Soviet Army in Yugoslavia, Hungary and Austria. In the 1947 peace treaties, Bulgaria gained a small area near the Black Sea from Romania, making it the only former German ally to gain territory from WWII.
Central Asian and Caucasian Republics
Among the Soviet forces during World War II, millions of troops were from the Soviet Central Asian Republics. They included 1,433,230 soldiers from Uzbekistan, more than 1million from Kazakhstan, and more than 700,000 from Azerbaijan, among other Central Asian Republics.
Mongolia
Mongolian People's Republic, Mongolia fought against Japan during the Battles of Khalkhin Gol in 1939 and the Soviet–Japanese War in August 1945 to protect its independence and to liberate Southern Mongolia (region), Southern Mongolia from Japan and China. Mongolia had been in the Soviet sphere of influence since the 1920s.
Poland
By 1944, Poland entered the Soviet sphere of influence with the establishment of Władysław Gomułka's communist regime. Polish forces fought alongside Soviet forces against Germany.
Romania

Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
had initially been a member of the Axis powers but switched allegiance upon facing invasion by the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
. In a radio broadcast to the Romanian people and army on the night of 23 August 1944 Michael I of Romania, King Michael issued a cease-fire,
proclaimed Romania's loyalty to the Allies, announced the acceptance of an armistice (to be signed on 12 September) offered by the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, and declared war on Germany. The coup accelerated the Second Jassy–Kishinev Offensive, Red Army's advance into Romania, but did not avert a rapid Soviet occupation and capture of about 130,000 Romanian soldiers, who were transported to the Soviet Union where many perished in prison camps.
The armistice was signed three weeks later on 12 September 1944, on terms virtually dictated by the Soviet Union.
Under the terms of the armistice, Romania announced its unconditional surrender to the USSR and was placed under the occupation of the Allied forces with the Soviet Union as their representative, in control of the media, communication, post, and civil administration behind the front.
Romanian troops then fought alongside the Soviet Army until the end of the war, reaching as far as Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovakia and Nazi Germany, Germany.
Tuva
The
Tuvan People's Republic
The Tuvan People's Republic (TPR; tyv, Тыва Арат Республик, translit=Tywa Arat Respublik; Yanalif: ''Tьʙа Arat Respuʙlik'', ),) and abbreviated TAR. known as the Tannu Tuva People's Republic until 1926, was a partially rec ...
was a partially recognized state founded from the former Tuvan protectorate of Imperial Russia. It was a client state of the Soviet Union and was annexed into the Soviet Union in 1944.
Co-belligerent state combatants
Finland
Following the Moscow Armistice of September 1944, Finland fought on the side of the Allies against Axis forces until April 1945 in the Lapland War.
Italy

Kingdom of Italy, Italy initially had been a leading member of the Axis powers, however after facing multiple military losses including the loss of Italian Empire, all of Italy's colonies to advancing Allied forces, ''Duce'' Benito Mussolini was deposed and arrested in July 1943 by order of King of Italy, King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy in co-operation with members of the Grand Council of Fascism who viewed Mussolini as having led Italy to ruin by allying with Germany in the war. Victor Emmanuel III dismantled the remaining apparatus of the Italian Fascism, Fascist regime and appointed Field Marshal Pietro Badoglio as Prime Minister of Italy. On 8 September 1943, Italy signed the Armistice of Cassibile with the Allies, ending Italy's war with the Allies and ending Italy's participation with the Axis powers. Expecting immediate German retaliation, Victor Emmanuel III and the Italian government relocated to southern Italy under Allied control. Germany viewed the Italian government's actions as an act of betrayal, and German forces immediately occupied all Italian territories outside of Allied control, in some cases even Massacre of the Acqui Division, massacring Italian troops.
Italy became a co-belligerent of the Allies, and the Italian Co-Belligerent Army was created to fight against the German occupation of Northern Italy, where German paratroopers Gran Sasso raid, rescued Mussolini from arrest and he was placed in charge of a German puppet state known as the Italian Social Republic (RSI). Italy Italian Civil War, descended into civil war until the end of hostilities after his deposition and arrest, with Fascists loyal to him allying with German forces and helping them against the Italian armistice government and Italian resistance movement, partisans.
Legacy
Charter of the United Nations
The
Declaration by United Nations
The Declaration by United Nations was the main treaty that formalized the Allies of World War II and was signed by 47 national governments between 1942 and 1945. On 1 January 1942, during the Arcadia Conference, the Allied " Big Four"—the Unite ...
on 1 January 1942, signed by the
Four Policemen – the United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union and China – and 22 other nations laid the groundwork for the future of the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
.
At the
Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
of July–August 1945, Roosevelt's successor, Harry S. Truman, proposed that the foreign ministers of China, France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States "should draft the peace treaties and boundary settlements of Europe", which led to the creation of the Council of Foreign Ministers of the "Big Five", and soon thereafter the establishment of those states as the Permanent members of the United Nations Security Council, permanent members of the UNSC.

The Charter of the United Nations was agreed to during the war at the United Nations Conference on International Organization, held between April and July 1945. The Charter was signed by 50 states on 26 June (Poland had its place reserved and later became the 51st "original" signatory), and was History of the United Nations#Establishment, formally ratified shortly after the war on 24 October 1945. In 1944, the United Nations was formulated and negotiated among the delegations from the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, the United States and China at the Dumbarton Oaks Conference where the formation and the Permanent members of the United Nations Security Council, permanent seats (for the "Big Five", China, France, the UK, US, and USSR) of the United Nations Security Council were decided. The Security Council met for the first time in the immediate aftermath of war on 17 January 1946.
[United Nations Security Council: Official Records: First Year, First Series, First Meeting]
These are the original 51 signatories (UNSC permanent members are asterisked):
* Argentina, Argentine Republic
* Australia, Commonwealth of Australia
* Belgium, Kingdom of Belgium
* Bolivia, Republic of Bolivia
* Vargas Era, United States of Brazil
* Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic
* Canada, Dominion of Canada
* Presidential Republic (1925–73), Republic of Chile
* Republic of China (1912–49), Republic of China*
* Colombia, Republic of Colombia
* Costa Rica, Republic of Costa Rica
* Republic of Cuba (1902–59), Republic of Cuba
* Czechoslovakia, Czechoslovak Republic
* Denmark, Kingdom of Denmark
* Dominican Republic
* Ecuador, Republic of Ecuador
* Kingdom of Egypt
* El Salvador, Republic of El Salvador
* Ethiopian Empire
* Provisional Government of the French Republic, French Republic*
* Kingdom of Greece
* Guatemala, Republic of Guatemala
* Republic of Haiti (1859–1957), Republic of Haiti
* Honduras, Republic of Honduras
* British Raj, Indian Empire
* Pahlavi Iran, Imperial Kingdom of Iran
* Kingdom of Iraq
* Lebanon, Lebanese Republic
* Liberia, Republic of Liberia
* Luxembourg, Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
* Mexico, United Mexican States
* Kingdom of the Netherlands
* Dominion of New Zealand
* Nicaragua, Republic of Nicaragua
* Norway, Kingdom of Norway
* Panama, Republic of Panama
* Paraguay, Republic of Paraguay
* Peru, Republic of Peru
*
Commonwealth of the Philippines
* Provisional Government of National Unity, Republic of Poland
* Saudi Arabia, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
* Union of South Africa
* Mandatory Syrian Republic, Syrian Republic
* Turkey, Republic of Turkey
* Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
* Soviet Union, Union of Soviet Socialist Republics*
* United Kingdom, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland*
* United States, United States of America*
* Uruguay, Oriental Republic of Uruguay
* United States of Venezuela
* Democratic Federal Yugoslavia
Cold War
Despite the successful creation of the United Nations, the alliance of the Soviet Union with the United States and Anglo-Soviet Treaty of 1942, with the United Kingdom ultimately broke down and evolved into the Cold War, which took place over the following half-century.
Summary table
Timeline of allied nations entering the war
The following list denotes dates on which states declared war on the Axis powers, or on which an Axis power declared war on them. The Indian Empire had a status less independent than the Dominions.

1939
*
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
: 1 September 1939
*
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
: 3 September 1939
—On 22 June 1940,
Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its te ...
under Philippe Pétain, Marshal Pétain formally capitulated to Germany, and became neutral. This capitulation was denounced by Charles de Gaulle, General de Gaulle, who established the
Free France
Free France (french: France Libre) was a political entity that claimed to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third Republic. Led by French general , Free France was established as a government-in-exile ...
government-in-exile, which continued to fight against Germany. This led to the
Provisional Government of the French Republic, which was officially recognized by the other Allies as the legitimate government of France on 23 October 1944. Pétain's 1940 surrender was also legally nullified, so France is considered an Ally throughout the war.
*
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
: 3 September 1939
** British Raj, India: 3 September 1939
*
Australia: 3 September 1939
*
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
: 3 September 1939
* Kingdom of Nepal, Nepal: 4 September 1939
*
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
: 6 September 1939
*
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
: 10 September 1939
* Sultanate of Muscat and Oman: 10 September 1939
1940
*
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
: 8 April 1940
—German invasion of a neutral country without declaration of war. The Allies supported Norway during the
Norwegian Campaign. Norway did not officially join the Allies until later.
[Tamelander, M. og N. Zetterling (2001): ''9. April.'' Oslo: Spartacus.]
* Denmark 9 April 1940—German invasion without declaration of war
*
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
: 10 May 1940
*
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
: 10 May 1940
*
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
: 10 May 1940
*
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
: 28 October 1940
1941
*
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
: 6 April 1941 (Yugoslavia signed the Tripartite Pact, becoming a nominal member of the Axis on 25 March; but was attacked by the Axis on 6 April 1941.)

*
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
: 22 June 1941; Despite membership of the Soviet Union,
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and
Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
were recognized as separate fighting states by the United Kingdom and the United States at the end of the war.
*
Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
: 7 December 1941
*
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
: 8 December 1941 (war declared on Japan)
**
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
: 8 December 1941
*
Costa Rica: 8 December 1941
* Dominican Republic: 8 December 1941
*
El Salvador: 8 December 1941
*
Haiti: 8 December 1941
*
Honduras: 8 December 1941
*
Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the countr ...
: 8 December 1941
*
China: 9 December 1941
(at war with Japan since 1937)
*
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
: 9 December 1941
*
Guatemala: 9 December 1941
*
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
: 11 December 1941 (war declared on the U.S. by Germany and Italy)
Provisional governments or governments-in exile that declared war against the Axis in 1941:
* Vietnam (
Viet Minh
The Việt Minh (; abbreviated from , chữ Nôm and Hán tự: ; french: Ligue pour l'indépendance du Viêt Nam, ) was a national independence coalition formed at Pác Bó by Hồ Chí Minh on 19 May 1941. Also known as the Việt Minh Fro ...
): 7 December 1941
* Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea: 10 December 1941
* Czechoslovak government-in-exile, Czechoslovakia (government-in-exile): 16 December 1941
1942
*
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
: 22 May 1942
*
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
: 22 August 1942
*
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
: 14 December 1942
1943
* Kingdom of Iraq, Iraq: 16 January 1943
—former Axis power
* Bolivia: 7 April 1943
* Colombia: 26 July 1943
* Pahlavi Iran, Iran: 9 September 1943
* Kingdom of Italy, Italy: 10 October 1943
—former Axis power; Italian Social Republic was founded in September 1943 and continued on the Axis side
1944
* Liberia: 27 January 1944
*
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
: 25 August 1944
—former Axis power
* Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgaria: 8 September 1944—former Axis power
* Finland: 19 September 1944—former co-belligerent on the Axis side
1945
* Ecuador: 2 February 1945
* Paraguay: 7 February 1945
* Peru: 12 February 1945
* Uruguay: 15 February 1945
* United States of Venezuela, Venezuela: 15 February 1945
* Turkey: 23 February 1945
* Kingdom of Egypt, Egypt: 24 February 1945
*
Syria: 26 February 1945
* Lebanon: 27 February 1945
* Saudi Arabia: 1 March 1945
* Finland: 3 March 1945
—former co-belligerent of Germany in the Continuation War. On 3 March 1945, Finland retroactively declared war on Germany from 15 September 1944.
* Argentina: 27 March 1945
[Decree 6945/45]
* Presidential Republic (1925–73), Chile: 11 April 1945 declared war on Japan
* Mongolian People's Republic, Mongolia: August 1945 declared war on Japan
See also
* Allied leaders of World War II
* Allied war crimes during World War II
* Free World (World War II)
* Military production during World War II
* Participants in World War II
Footnotes
Bibliography
*
* Norman Davies, Davies, Norman (2006), ''Europe at War 1939–1945: No Simple Victory''. London: Macmillan.
* Dear, Ian C. B. and Michael Foot, eds. ''The Oxford Companion to World War II'' (2005), comprehensive encyclopedia for all countries
* Holland R. (1981), ''Britain and the Commonwealth alliance, 1918–1939'', London: Macmillan.
* Leonard, T. M. (2007). ''Latin America during World War II''. Lanham Md: Rowman & Littlefield.
* Richard Overy, Overy, Richard (1997), ''Russia's War: A History of the Soviet Effort: 1941–1945''. New York: Penguin. .
* Smith, Gaddis. ''American Diplomacy During the Second World War, 1941–1945'' (1965
online* Weinberg, Gerhard L. (1994). ''A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II''. Comprehensive coverage of the war with emphasis on diplomac
excerpt and text search
Further reading
* Omnibus o
Volume I: ''The European Theater'' and Volume II: ''The Asian Theater''.
External links
The Atlantic Conference: Resolution of 24 September 1941
{{Authority control
20th-century military alliances
Military alliances involving Canada
Military alliances involving the United Kingdom
Military alliances involving the United States
Military alliances involving Australia
Military alliances involving New Zealand
Military alliances involving South Africa
Military alliances involving France
Politics of World War II
History of diplomacy

 The Allies, formally referred to as the
The Allies, formally referred to as the 
 The alliance was formalised in the
The alliance was formalised in the 


 British Prime Minister, Neville Chamberlain delivered his ''Ultimatum Speech'' on 3 September 1939 which declared war on Germany, a few hours before France. As the Statute of Westminster 1931 was not yet ratified by the parliaments of Australia and New Zealand, the British declaration of war on Germany also applied to those
British Prime Minister, Neville Chamberlain delivered his ''Ultimatum Speech'' on 3 September 1939 which declared war on Germany, a few hours before France. As the Statute of Westminster 1931 was not yet ratified by the parliaments of Australia and New Zealand, the British declaration of war on Germany also applied to those 

 After Germany invaded Poland, France declared war on Germany on 3 September 1939.Speeches that Reshaped the World. In January 1940, French Prime Minister
After Germany invaded Poland, France declared war on Germany on 3 September 1939.Speeches that Reshaped the World. In January 1940, French Prime Minister  In Asia and Oceania France has several territories: French Polynesia,
In Asia and Oceania France has several territories: French Polynesia, 






 The Commonwealth of the Philippines was a sovereign protectorate referred to as an "associated state" of the United States. From late 1941 to 1944, the Philippines was occupied by Japanese forces, who established the
The Commonwealth of the Philippines was a sovereign protectorate referred to as an "associated state" of the United States. From late 1941 to 1944, the Philippines was occupied by Japanese forces, who established the 
 Communist China had been tacitly supported by the
Communist China had been tacitly supported by the  Before the war, Belgium had pursued a policy of neutrality and only became an Allied member after being invaded by Germany on 10 May 1940. During the ensuing fighting, Belgian forces fought alongside French and British forces against the invaders. While the British and French were struggling against the fast German advance elsewhere on the front, the Belgian forces were pushed into a pocket to the north. Finally, on 28 May, the
Before the war, Belgium had pursued a policy of neutrality and only became an Allied member after being invaded by Germany on 10 May 1940. During the ensuing fighting, Belgian forces fought alongside French and British forces against the invaders. While the British and French were struggling against the fast German advance elsewhere on the front, the Belgian forces were pushed into a pocket to the north. Finally, on 28 May, the  Because of its strategic location for control of the sea lanes in the
Because of its strategic location for control of the sea lanes in the  Polish soldiers fought under their own flag but under the command of the British military. They were major contributors to the Allies in the Western Front (World War II), theatre of war west of Germany and in the theatre of Eastern Front (World War II), war east of Germany, with the Soviet Union. The Polish armed forces in the West created after the fall of Poland played minor roles in the Battle of France, and larger ones in the Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian and North African Campaigns.At the siege of Tobruk The Soviet Union recognized the London-based government at first. But it broke diplomatic relations after the Katyn massacre of Polish nationals was revealed. In 1943, the Soviet Union organized the
Polish soldiers fought under their own flag but under the command of the British military. They were major contributors to the Allies in the Western Front (World War II), theatre of war west of Germany and in the theatre of Eastern Front (World War II), war east of Germany, with the Soviet Union. The Polish armed forces in the West created after the fall of Poland played minor roles in the Battle of France, and larger ones in the Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian and North African Campaigns.At the siege of Tobruk The Soviet Union recognized the London-based government at first. But it broke diplomatic relations after the Katyn massacre of Polish nationals was revealed. In 1943, the Soviet Union organized the  Before the end of 1941, the anti-Axis resistance movement split between the royalist Chetniks and the communist
Before the end of 1941, the anti-Axis resistance movement split between the royalist Chetniks and the communist  The Chetniks, the short name given to the movement titled the ''Yugoslav Army of the Fatherland'', were initially a major Allied Yugoslav resistance movement. However, due to their royalist and anti-communist views, Chetniks were considered to have begun collaborating with the Axis as a tactical move to focus on destroying their Partisan rivals. The Chetniks presented themselves as a Yugoslav movement, but were primarily a Serbs, Serb movement. They reached their peak in 1943 with 93,000 fighters. Their major contribution was Operation Halyard in 1944. In collaboration with the Office of Strategic Services, OSS, 413 Allied airmen shot down over Yugoslavia were rescued and evacuated.
The Chetniks, the short name given to the movement titled the ''Yugoslav Army of the Fatherland'', were initially a major Allied Yugoslav resistance movement. However, due to their royalist and anti-communist views, Chetniks were considered to have begun collaborating with the Axis as a tactical move to focus on destroying their Partisan rivals. The Chetniks presented themselves as a Yugoslav movement, but were primarily a Serbs, Serb movement. They reached their peak in 1943 with 93,000 fighters. Their major contribution was Operation Halyard in 1944. In collaboration with the Office of Strategic Services, OSS, 413 Allied airmen shot down over Yugoslavia were rescued and evacuated.

 Kingdom of Italy, Italy initially had been a leading member of the Axis powers, however after facing multiple military losses including the loss of Italian Empire, all of Italy's colonies to advancing Allied forces, ''Duce'' Benito Mussolini was deposed and arrested in July 1943 by order of King of Italy, King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy in co-operation with members of the Grand Council of Fascism who viewed Mussolini as having led Italy to ruin by allying with Germany in the war. Victor Emmanuel III dismantled the remaining apparatus of the Italian Fascism, Fascist regime and appointed Field Marshal Pietro Badoglio as Prime Minister of Italy. On 8 September 1943, Italy signed the Armistice of Cassibile with the Allies, ending Italy's war with the Allies and ending Italy's participation with the Axis powers. Expecting immediate German retaliation, Victor Emmanuel III and the Italian government relocated to southern Italy under Allied control. Germany viewed the Italian government's actions as an act of betrayal, and German forces immediately occupied all Italian territories outside of Allied control, in some cases even Massacre of the Acqui Division, massacring Italian troops.
Italy became a co-belligerent of the Allies, and the Italian Co-Belligerent Army was created to fight against the German occupation of Northern Italy, where German paratroopers Gran Sasso raid, rescued Mussolini from arrest and he was placed in charge of a German puppet state known as the Italian Social Republic (RSI). Italy Italian Civil War, descended into civil war until the end of hostilities after his deposition and arrest, with Fascists loyal to him allying with German forces and helping them against the Italian armistice government and Italian resistance movement, partisans.
Kingdom of Italy, Italy initially had been a leading member of the Axis powers, however after facing multiple military losses including the loss of Italian Empire, all of Italy's colonies to advancing Allied forces, ''Duce'' Benito Mussolini was deposed and arrested in July 1943 by order of King of Italy, King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy in co-operation with members of the Grand Council of Fascism who viewed Mussolini as having led Italy to ruin by allying with Germany in the war. Victor Emmanuel III dismantled the remaining apparatus of the Italian Fascism, Fascist regime and appointed Field Marshal Pietro Badoglio as Prime Minister of Italy. On 8 September 1943, Italy signed the Armistice of Cassibile with the Allies, ending Italy's war with the Allies and ending Italy's participation with the Axis powers. Expecting immediate German retaliation, Victor Emmanuel III and the Italian government relocated to southern Italy under Allied control. Germany viewed the Italian government's actions as an act of betrayal, and German forces immediately occupied all Italian territories outside of Allied control, in some cases even Massacre of the Acqui Division, massacring Italian troops.
Italy became a co-belligerent of the Allies, and the Italian Co-Belligerent Army was created to fight against the German occupation of Northern Italy, where German paratroopers Gran Sasso raid, rescued Mussolini from arrest and he was placed in charge of a German puppet state known as the Italian Social Republic (RSI). Italy Italian Civil War, descended into civil war until the end of hostilities after his deposition and arrest, with Fascists loyal to him allying with German forces and helping them against the Italian armistice government and Italian resistance movement, partisans.

 *
*