A worker cooperative is a
cooperative owned and
self-managed by its workers. This control may mean a firm where every worker-owner participates in
decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
in a democratic fashion, or it may refer to one in which management is elected by every worker-owner who each have one vote.
History
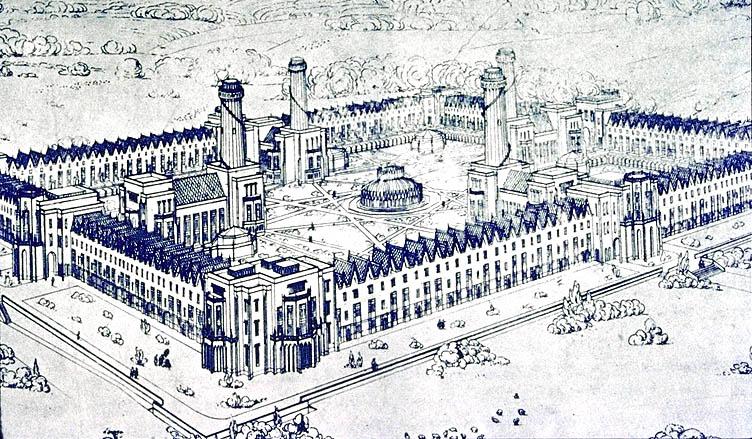
Worker cooperatives rose to prominence during the
Industrial Revolution as part of the
labour movement. As employment moved to industrial areas and job sectors declined, workers began organizing and controlling businesses for themselves. Worker cooperatives were originally sparked by "critical reaction to industrial capitalism and the excesses of the industrial revolution." Some worker cooperatives were designed to "cope with the evils of unbridled capitalism and the insecurities of wage labor".
The philosophy that underpinned the cooperative movement stemmed from the
socialist writings of thinkers including
Robert Owen
Robert Owen (; 14 May 1771 – 17 November 1858) was a Welsh textile manufacturer, philanthropist and social reformer, and a founder of utopian socialism and the cooperative movement. He strove to improve factory working conditions, promoted e ...
and
Charles Fourier. Robert Owen, considered by many as the father of the cooperative movement, made his fortune in the cotton trade but believed in putting his workers in a good environment with access to education for themselves and their children. These ideas were put into effect successfully in the
cotton mills of
New Lanark,
Scotland. It was here that the first co-operative store was opened. Spurred on by the success of this, he had the idea of forming "villages of co-operation" where workers would drag themselves out of poverty by growing their own food, making their own clothes and ultimately becoming self-governing. He tried to form such communities in
Orbiston
Orbiston is an unincorporated community in Hocking County, Ohio, United States. Orbiston is located along Ohio State Route 78
State Route 78 (SR 78) is a state highway that runs for 105 miles (169 km) from Nelsonville to Clarington in the ...
in Scotland and in
New Harmony, Indiana in the
United States of America, but both communities failed.
Similar early experiments were made in the early 19th century and by 1830 there were several hundred co-operatives.
Dr William King made Owen's ideas more workable and practical. He believed in starting small and realized that the
working classes would need to set up co-operatives for themselves, so he saw his role as one of instruction. He founded a monthly periodical called ''The Co-operator'', the first edition of which appeared on 1 May 1828. This gave a mixture of co-operative philosophy and practical advice about running a shop using cooperative principles.
Modern movement
The first successful cooperative organization was the consumer-owned
Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers
The Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers, founded in 1844, was an early consumers' co-operative, and one of the first to pay a patronage dividend, forming the basis for the modern co-operative movement.
Although other co-operatives preceded it, ...
, established in England in 1844. The Rochdale Pioneers established the ‘
Rochdale Principles
The Rochdale Principles are a set of ideals for the operation of cooperatives. They were first set out in 1844 by the Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers in Rochdale, England and have formed the basis for the principles on which co-operativ ...
’ on which they ran their cooperative. This became the basis for the development and growth of the modern cooperative movement. As the mechanization of the Industrial Revolution was forcing more and more skilled workers into poverty, these tradesmen decided to band together to open their own store selling food items they could not otherwise afford.
With lessons from prior failed attempts at co-operation in mind, they designed the now famous
Rochdale Principles
The Rochdale Principles are a set of ideals for the operation of cooperatives. They were first set out in 1844 by the Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers in Rochdale, England and have formed the basis for the principles on which co-operativ ...
, and over a period of four months, they struggled to pool one
pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
per person for a total of 28 pounds of capital. On 21 December 1844, they opened their store with a very meager selection of butter, sugar, flour, oatmeal, and a few candles. Within three months, they expanded their selection to include tea and tobacco, and they were soon known for providing high quality, unadulterated goods.
The International organization representing worker cooperatives is
CICOPA
CICOPA (''International Organisation of Cooperatives in Industry and Services'') is a branch of the International Cooperative Alliance. Founded in 1947, CICOPA has a membership of 46 national and regional cooperative federations or support organi ...
. CICOPA has two regional organizations: CECOP- CICOPA Europe and CICOPA Americas.
Today

When the current cooperative movement resurfaced in the 1960s, it developed mostly on a new system of "collective ownership" where par value shares were issued as symbols of egalitarian voting rights. Typically, a member may only own one share to maintain the egalitarian ethos. Once brought in as a member and after a period of time on probation usually so the new candidate can be evaluated, they would be given the power to manage the coop without "ownership" in the traditional sense. In the UK, this system is known as
common ownership
Common ownership refers to holding the assets of an organization, enterprise or community indivisibly rather than in the names of the individual members or groups of members as common property.
Forms of common ownership exist in every economi ...
.
Some of these early cooperatives still exist, and most new worker cooperatives follow their lead and develop a relationship to capital that is more radical than the previous system of equity share ownership.
In the United States, there is no coherent legislation regarding worker cooperatives nationally, much less Federal laws, so most worker cooperatives make use of traditional consumer cooperative law and try to fine-tune it for their purposes. In some cases, the members (workers) of the cooperative in fact "own" the enterprise by buying a share that represents a fraction of the market value of the cooperative.
In Britain, this type of cooperative was traditionally known as a ''producer cooperative''; and while it was overshadowed by the consumer and agricultural types, it also made up a small section of its own within the national apex body, the Cooperative Union. The 'new wave' of worker cooperatives that took off in Britain in the mid-1970s joined the
Industrial Common Ownership Movement Industrial Common Ownership Movement (ICOM) was a UK national umbrella organisation for worker cooperatives, set up in 1971. It worked to increase the number of worker co-ops in the country. ICOM's model rules for cooperatives, published in 1976, we ...
(ICOM) as a separate federation. Buoyed up by the alternative and ecological movements and by the political drive to create jobs, the sector peaked at around 2,000 enterprises. However, the growth rate slowed, the sector contracted, and in 2001 ICOM merged with the Co-operative Union (which was the federal body for consumer cooperatives) to create
Co-operatives UK
Co-operatives UK is a British co-operative federation described as "the central membership organisation for co-operative enterprise throughout the UK". It was founded in 1870 as the Co-operative Central Board, changing its name to the Co-opera ...
, thus reunifying the cooperative sector.
Since 2006, Co-operatives UK's Worker Cooperative Council wrote and updated a worker co-operative code, the booklet that "sets out what anyone should expect and should work together to achieve, as a member of a worker co-operative".
In 2018, Google announced a $1 million grant to a
platform cooperative
A platform cooperative, or platform co-op, is a cooperatively owned, democratically governed business that establishes a computing platform, and uses a website, mobile app or a protocol to facilitate the sale of goods and services. Platform coopera ...
development kit in collaboration with 5 pilot cooperatives, which are all worker-owned.
Research on worker cooperatives
Longevity and resilience
According to an analysis of all businesses in Uruguay between 1997 and 2009, worker cooperatives have a 29% smaller chance of closure after controlling for variables such as industry. In Italy, worker owned cooperatives that have been created by workers buying a business when it is facing a closure or put up to sale have a 3-year survival rate of 87%, compared to 48% of all Italian businesses. A 2012 study of Spanish and French worker cooperatives found that they “have been more resilient than conventional enterprises during the economic crisis."
In France, the three year survival rate of worker cooperatives is 80%-90%, compared to the 66% overall survival rate for all businesses. During the 2008 economic crisis, the number of workers in worker owned cooperatives in France increased by 4.2%, while employment in other businesses decreased by 0.7%.
Pay and employment stability
A 2006 study found that wages on co-ops pay in Italy were 15 to 16 percent lower than those that capitalist firms paid on average, and were more volatile, while employment was more stable. After controlling for variables, such as schooling, age, gender, occupation, industry, location, firm-size, user cost of capital, fixed costs, and deviations in its real sales, this changed to 14 percent. The authors suggest this might be due to worker cooperatives being more likely than capitalist firms to cut wages instead of laying off employees during periods of economic difficulty, or because co-op
workers may be willing to accept lower wages than workers in capitalist firms.
A study looking at all firms in Uruguay concluded that when controlling for variables such as industry, firm size, gender, age and tenure, workers employed in a worker-managed firm earn 3 percent higher wages compared with similar workers employed in the conventional firms. However, this wage premium declines significantly with increasing pay and becomes negative for top earners. According to research by Virginie Pérotin, which looked at two decades worth of international data, the tendency for greater wage flexibility and employment stability helps explain why some research observes higher and others lower pay in worker cooperatives relative to conventional businesses.
A study by ''The Democracy Collaborative'' found that in the US, worker cooperatives can increase worker incomes by 70 to 80 percent.
Pay inequality
In the
Mondragon Corporation
The Mondragon Corporation is a corporation and federation of worker cooperatives based in the Basque region of Spain.
It was founded in the town of Mondragon in 1956 by José María Arizmendiarrieta and a group of his students at a technical ...
, the world's largest worker cooperative, the pay ratio between the lowest and the highest earner was 1:9 in 2018. The ratio is decided by a democratic vote by the worker-members.
In France, the pay ratio between the highest and lowest paid 10% of the employees is 14% lower in worker cooperatives than in otherwise similar conventional firms.
Productivity
According to Virginie Pérotin's research which looked at two decades worth of international data, worker cooperatives are more productive than conventional businesses.
Another 1987 study of worker cooperatives in Italy, the UK, and France found “positive” relationships with productivity. It also found that worker cooperatives do not become less productive as they get larger. A 1995 study of worker cooperatives in the timber industry in Washington, USA found that “co-ops are more efficient than the principal conventional firms by between 6 and 14 percent”.
Worker satisfaction, trust, health and commitment
According to a study drawing on a questionnaire from the population of the Italian province of
Trento, worker cooperatives are the only form of enterprise that fosters social trust between employees. A survey conducted in Seoul suggests that in conventional firms, employees become less committed to their job as their work becomes more demanding; however, this was not the case in worker cooperatives. In the US, home health aides in worker cooperatives were significantly more satisfied with their jobs than in other agencies. A study from 2013 about home aid workers found that "Home health aides at the worker-owned, participative decision-making organization were significantly more satisfied with their jobs than those at other agencies." One 1995 study from the US also indicates that “employees who embrace an increased influence and participation in workplace decisions also reported greater job satisfaction” and a 2011 study in France found that worker-owned businesses “had a positive effect on workers’ job satisfaction.” One 2019 study indicates that “the impact on the happiness of workers is generally positive”.
Environment
A 1995 analysis published in
Ecological Economics suggests that "cooperatives will tend to use natural resource inputs more efficiently and will be less growth oriented than corporations."
Definition of worker cooperative
Many definitions exist as to what qualifies as a workers' cooperative.
CICOPA
CICOPA (''International Organisation of Cooperatives in Industry and Services'') is a branch of the International Cooperative Alliance. Founded in 1947, CICOPA has a membership of 46 national and regional cooperative federations or support organi ...
, the International Organisation of Industrial, Artisanal and Service Producers’ Cooperatives, gives an 8-page definition in their World Declaration on Workers' Cooperatives, which was approved by the
International Co-operative Alliance
The International Co-operative Alliance (ICA) is a non-governmental co-operative federation or, more precisely, a co-operative union representing co-operatives and the co-operative movement worldwide. It was founded in 1895 to unite, represent an ...
General Assembly in September 2005. Below is the section on the basic characteristics of workers' cooperatives:
# They have the objective of creating and maintaining sustainable jobs and generating wealth, to improve the quality of life of the worker-members, dignify human work, allow workers’ democratic self-management and promote community and local development.
# The free and voluntary membership of their members, in order to contribute with their personal work and economic resources, is conditioned by the existence of workplaces.
# As a general rule, work shall be carried out by the members. This implies that the majority of the workers in a given worker cooperative enterprise are members and vice versa.
# The worker-members’ relation with their cooperative shall be considered as different from that of conventional wage-based labor and to that of autonomous individual work.
# Their internal regulation is formally defined by regimes that are democratically agreed upon and accepted by the worker-members.
# They shall be autonomous and independent, before the State and third parties, in their labor relations and management, and in the usage and management of the means of production.
[ICA (2005) World Declaration on Worker Cooperatives, Approved by the ICA General Assembly in Cartagena, Colombia, 23 September 2005](_blank)
.
Workers' cooperatives also follow the
Rochdale Principles
The Rochdale Principles are a set of ideals for the operation of cooperatives. They were first set out in 1844 by the Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers in Rochdale, England and have formed the basis for the principles on which co-operativ ...
and values, which are a set of core principles for the operation of cooperatives. They were first set out by the
Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers
The Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers, founded in 1844, was an early consumers' co-operative, and one of the first to pay a patronage dividend, forming the basis for the modern co-operative movement.
Although other co-operatives preceded it, ...
in Rochdale, England, in 1844 and have formed the basis for the principles on which co-operatives around the world operate to this day.
Even though there is no universally accepted definition of a workers' cooperative, they can be considered to be businesses that make a product or offer a service to sell for profit where the workers are members or worker-owners. Worker-owners work in the business, govern it and manage it. Unlike with conventional firms, ownership and decision-making power of a worker cooperative should be vested solely with the worker-owners and ultimate authority rests with the worker-owners as a whole. Worker-owners control the resources of the cooperative and the work process, such as wages or hours of work.
[Adams, Frank and Gary Hansen (1993) Putting Democracy To Work: A Practical Guide for Starting and Managing Worker-Owned Businesses, Berrett-Koehler Publishers, Inc, San Francisco]
As mentioned above, the majority—if not all—of the workers in a given worker cooperative enterprise are worker-owners, although some casual or wage workers may be employed with whom profits and decision making are not necessarily shared equally. Workers also often undergo a trial or screening period (such as three or six months) before being allowed to have full voting rights.
Participation is based on one vote per worker-owner, regardless of the number of shares or equity owned by each worker-owner. Voting rights are not tied to investment or patronage in the workers' co-operative, and only worker-owners can vote on decisions that affect them. In practice, worker co-operatives have to accommodate a range of interests to survive and have experimented with different voice and voting arrangements to accommodate the interests of trade unions, local authorities,
[Paton, R. (1989) ''Reluctant Entrepreneurs'', Milton Keynes: Open University Press] those who have invested proportionately more labor, or through attempts to mix individual and collective forms of worker-ownership and control.
As noted by theorists and practitioners alike, the importance of capital should be subordinated to labor in workers' cooperatives. Indeed, Adams et al. see workers' cooperatives as "labor-ist" rather than "capital-ist":
"Labor is the hiring factor, therefore the voting and property rights are assigned to the people who do the work and not to capital, even though the worker-members supply capital through membership fees and retained earnings...Any profit or loss after normal operating expenses is assigned to members on the basis of their labor contribution."
Nevertheless, recent developments in the co-operative movement have started to shift thinking more clearly towards multi-stakeholder perspectives. This has resulted in repeated attempts to develop model rules that differentiate control rights from investment and profit-sharing rights. Workers' co-operatives have often been seen as an alternative or "third way" to the domination of labor by either capital or the state (see below for a comparison). Co-operatives traditionally combine social benefit interests with capitalistic property-right interests. Co-operatives achieve a mix of social and capital purposes by democratically governing distribution questions by and between equal controlling members. Democratic oversight of decisions to equitably distribute assets and other benefits means capital ownership is arranged in a way for social benefit inside the organization. External societal benefit is also encouraged by incorporating the operating-principle of cooperation between co-operatives.
In short, workers' co-operatives are organized to serve the needs of worker-owners by generating benefits (which may or may not be profits) for the worker-owners rather than external investors. This worker-driven orientation makes them fundamentally different from other corporations. Additional cooperative structural characteristics and guiding principles further distinguish them from other business models. For example, worker-owners may not believe that
profit maximization
In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that will lead to the highest possible total profit (or just profit in short). In neoclassical economics, w ...
is the best or only goal for their co-operative or they may follow the Rochdale Principles. As another example, worker cooperatives’ flattened management structure and more egalitarian ideology often give workers more options and greater freedom in resolving work-place problems.
Profits (or losses) earned by the worker's cooperative are shared by worker-owners. Salaries generally have a low ratio difference which ideally should be "guided by principles of proportionality, external solidarity and internal solidarity"
(such as a two to one ratio between lowest and highest earner), and often are equal for all workers. Salaries can be calculated according to skill, seniority or time worked and can be raised or lowered in good times or bad to ensure job security.
Internal structure
Worker cooperatives have a wide variety of internal structures. Worker control can be exercised directly or indirectly by worker-owners. If exercised indirectly, members of representative decision-making bodies (e.g. a board of directors) must be elected by the worker-owners (who in turn hire the management) and be subject to removal by the worker-owners. This is a hierarchical structure similar to that of a conventional business, with a board of directors and various grades of manager, with the difference being that the board of directors is elected.
If exercised directly, all members meet regularly to make—and vote on—decisions on how the co-operative is run. Direct workers' cooperatives sometimes use
consensus decision-making to make decisions.
[How to set up a Workers' Co-op](_blank)
by Radical Routes Direct worker control ensures a formally flat management structure instead of a
hierarchical
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
one. This structure is influenced by activist collectives and civic organizations, with all members allowed and expected to play a managerial role. Such structures may be associated with political aims such as
anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not necessa ...
,
libertarian socialism,
distributism, and
participatory economics.
Some workers' cooperatives also practice
job rotation or
balanced job complexes to overcome inequalities of
power as well as to give workers a wider range of experiences and exposure to the different jobs in a workplace so that they are better able to make decisions about the whole workplace. The
Mondragon Bookstore & Coffeehouse
The Mondragon Bookstore & Coffeehouse was a political bookstore and vegan cafe located in The Old Market Autonomous Zone at 91 Albert Street in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The name comes from the Mondragón Cooperative Corporation and other organi ...
(now defunct) is a good example of a workplace that used this practice.
Worker collectives
The term 'worker collective' is sometimes used to describe worker cooperatives which are also collectives: that is, managed without hierarchies such as permanent manager roles.
Common ownership is practiced by large numbers of voluntary associations and non-profit organizations as well as implicitly by all public bodies. Most co-operatives have some elements of common ownership, but some parts of their capital may be individually owned.
Common ownership worker co-operatives
= Definition
=
The principle of common ownership was codified in UK law in th
Industrial Common Ownership Act 1976which defines a "common ownership enterprise" as:
a body as to which the registrar has given, and has not revoked, a certificate stating that he is satisfied—
:(a) that the body is—
::(i) a company which has no share capital, is limited by guarantee and is a bona fide co-operative society; or
::(ii) a registered society within the meaning of the Co-operative and Community Benefit Societies Act 2014; and
:(b) that the articles of association or rules of the body include provisions which secure—
::(i) that only persons who are employed by, or by a subsidiary of, the body may be members of it, that (subject to any provision about qualifications for membership which is from time to time made by the members of the body by reference to age, length of service or other factors of any description which do not discriminate between persons by reference to politics or religion) all such persons may be members of the body and that members have equal voting rights at meetings of the body,
::(ii) that the assets of the body are applied only for the purposes of objects of the body which do not include the making over of assets to any member of the body except for value and except in pursuance of arrangements for sharing the profits of the body among its members, and
::(iii) that, if on the winding up or dissolution of the body any of its assets remain to be disposed of after its liabilities are satisfied, the assets are not distributed among its members but are transferred to such a common ownership enterprise or such a central fund maintained for the benefit of common ownership enterprises as may be determined by the members at or before the time of the winding-up or dissolution or, in so far as the assets are not so transferred, are held for charitable purposes; and
:(c) that the body is controlled by a majority of the people working for the body and of the people working for the subsidiaries, if any, of the body.
The principle is typically implemented through inserting two clauses in a company's
memorandum of association, or an
industrial and provident society's rules:
* The first provides that the company's assets shall be applied solely in furtherance of its objectives and may not be divided among the members or trustees.
* The second provides for "
altruistic dissolution", an "asset lock", whereby if the enterprise is wound up, remaining assets exceeding liabilities shall not be divided among the members but shall be transferred to another enterprise with similar aims or to charity.
British law has been reluctant to entrench common ownership, insisting that a three-quarters majority of a company's members, by passing a "special resolution", have the right to amend a company's memorandum of association. This three-quarters majority above applies to most limited companies, except that it is possible since 2006 to entrench altruistic dissolution in an industrial and provident society registered as a "community benefit society" ("bencom"). This statutory asset lock is not available to societies registered as 'bona fide' co-operatives. However, such entrenchment has also been written into the
community interest company
A community interest company (CIC, colloquially pronounced "kick") is a type of company introduced by the United Kingdom government in 2005 under the Companies (Audit, Investigations and Community Enterprise) Act 2004, designed for social ente ...
(CIC), a new legal status that was introduced in 2005.
Promotion and finance
In a world of predominately traditional businesses, Worker Cooperatives have developed a wide variety of financing methods over time in order to survive and thrive in the market. Cooperative businesses often employ multiple forms of financing together as each technique tends to be unsustainable on its own.
= ''Internal Capital Accounts/Member Buy-Ins''
=
Internal Capital Accounts (ICA's), also known as Member Buy-Ins, are shares of capital distributed equally and exclusively to workers.
They act as a mandated buy-in loan to the cooperative that generates financial return over time in the form of interest.
ICA's are typically equal to a specific term's wages, like an annual salary, that is given a fixed rate of return that is not directly tied to the cooperative's losses or profits.
Cooperatives in low-income communities often raise donations to assist workers in meeting the ICA Buy-In requirement, as in the case of the Mariposa Food Coop.
This method of financing is one of the most prominent due to its high rates of success in maintaining financial stability for cooperatives.
When the cooperative allocates profits, a significant portion are paid back to the workers through these capital accounts. The
Mondragon Corporation
The Mondragon Corporation is a corporation and federation of worker cooperatives based in the Basque region of Spain.
It was founded in the town of Mondragon in 1956 by José María Arizmendiarrieta and a group of his students at a technical ...
utilizes a 10-20-70 system, in which 10% of profits are placed into community development and infrastructure programs, 20% back into corporate reserves, and 70% into individual capital accounts.
In certain cases, like the Mumbai Tiffin Box Supplier's Association in India, Member Buy-In's allow cooperatives to become completely financially independent from other sources of investment.
= ''Committed Capital/Preferred Stock''
=
Committed Capital, also known as
Preferred Stock, are shares of capital offered to external accredited investors that are not a part of the cooperative.
In order to maintain workers' ownership over the firm's decisions, these external investors have limited to no voting rights within the cooperative.
Committed Capital often have non-guaranteed rates of return.
However,
Equal Exchange
Equal Exchange is a for-profit, Fairtrade certification, Fairtrade Worker cooperative, worker-owned cooperative headquartered in West Bridgewater, Massachusetts. Equal Exchange distributes Organic food, organic, gourmet coffee, tea, sugar, banan ...
, a U.S.-based worker cooperative, offers preferred stock that still ensures at least a 5% return rate even during periods of economic recession.
Because the communal ownership model of cooperatives makes it difficult for investors to determine the credit and reliability of their investments, they often rely on close analysis of the structure, management, and experience of each cooperative in order to decide in which one to acquire stock.
= ''State Financing''
=
In many countries, the state provides loans or direct funding for worker cooperatives' production, community programs, and investments. Government funding is especially important in assisting newly developing cooperatives in securing finances for the initial stages of business.
In Spain, the
Basque Government assists in financing cooperatives within the
Mondragon Corporation
The Mondragon Corporation is a corporation and federation of worker cooperatives based in the Basque region of Spain.
It was founded in the town of Mondragon in 1956 by José María Arizmendiarrieta and a group of his students at a technical ...
and for many of Mondragon's education and healthcare programs.
Additionally, the
Basque Government financially assists Mondragon in acquiring declining capitalist businesses and transitioning them into worker cooperatives.
The
Indian government provides financing, often in the form of loans, to new cooperatives. The
government of Kerala and the
Khadi Development and Village Industries Commission in India often provide initial loans for cooperatives in order to help them eventually transition into relying primarily on Internal Capital Accounts.
In 1978, the
UK government set up the National Cooperative Development Agency and in subsequent years common ownership was promoted as a model to create employment, leading approximately 100 local authorities to establish cooperative development agencies. The Industrial Common Ownership Act authorized the Secretary of State for Industry to make grants and loans to organizations that assisted common ownership and cooperative enterprises. Grants were made to the
Industrial Common Ownership Movement Industrial Common Ownership Movement (ICOM) was a UK national umbrella organisation for worker cooperatives, set up in 1971. It worked to increase the number of worker co-ops in the country. ICOM's model rules for cooperatives, published in 1976, we ...
and the Scottish Co-operatives Development Committee, while loans were administered through Common Ownership Finance Ltd. However, this section was repealed in 2004.
The
Italian Government, through the
Legge Marcora (Marcora Law) provisions of 1985, reformed in 2001, has established a financing mechanism of patient capital for creating worker cooperatives, social cooperatives, and for worker buyouts of firms that are in trouble or that have retiring owners, especially for traditional businesses that require extra financial assistance while transitioning or converting into cooperatives.
Originally, this state investment was equivalent to three times the collective internal capital account investment from workers.
As of 2001, the state investment is on a 1:1 ratio with workers' capital contributions.
Canadian worker cooperatives also rely on government funding to finance their early development.
State sources of finance, which often come in the form of grants, include the Quebec Local Development Centre, the Co-op Development Initiative, and the Young Entrepreneurs program.
= ''Financing via Traditional Business Transitions''
=
When the owner of a traditional business decides to resign and transition the ownership of the firm into a workers' cooperative, they often provide initial financial investment.
However, this typically is not a sustainable form of capital investment and cooperatives often use it to begin business and then transition to depend on other forms of finance.
Examples of this method of financing include Select Machines, Inc., Metis Construction, A Slice of New York, and Rock City Roasters.
The transition process often takes several years and is executed in 5 stages. First, the selling owners must evaluate if a transition is an appropriate step for the business and must consult with advisors and employees regarding new leadership changes. Second, the selling owner must employ specialists to determine the legal and financial logistics of the transition. Third, a transition group or the selling owner must organize the new managerial structure, business practices, and ownership policies. Fourth, legal contracts are signed to establish the new management while methods of finance are drawn upon to jumpstart the newfound cooperative. Fifth, an adjustment period occurs in which training is provided for workers regarding new business policies.
= ''External Finance Firm Investment''
=
Most finance firms that specialize in providing capital for worker cooperatives are Cooperative Funds and
Community Development Financial Institutions
A community is a social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place, norms, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, village, town ...
(CDFI's).
CDFI's often do not supply the majority of finance for cooperatives, but act as collateral for other forms of investment and/or as support for another form of finance. Additionally, many cooperatives utilize external finance for improvements to their physical capital in order to improve productivity.
Several U.S. CDFIs include the Cooperative Fund of New England, the Common Wealth Revolving Loan Fund, the Shared Capital Cooperative of Minneapolis, and
Capital Impact Partners.
In France, worker cooperatives contribute funds to the SOCODEN (Société coopérative de développement et d’entraide), a cooperative financial institution that finances developing and struggling cooperatives. Additionally, this fund provides collateral for other sources of funding and subsidies for interests on loans for these cooperatives.
= ''Direct Public Offerings''
=
Direct Public Offerings (DPO's) are loans or donations generated either socially by communities or individually by both accredited and non-accredited investors.
The voting rights that this investment produces for the community or investor varies depending on the cooperative and offering type.
This form of financing is especially popular with cooperatives that provide services to local communities.
One of the primary attributes of DPO's that attract cooperatives is that by advertising investment opportunities to local communities, the firm not only generates financial capital but it also employs an efficient method of advertising that keeps the community engaged in the firm's products and success.
For cooperatives undergoing an ownership transition, DPO's are often a source of financial support to the initial loan of the retiring owner.
Examples of firms that have utilized Direct Public Offerings for financial support are Real Pickles and the CERO Cooperative.
= ''Peer Financing''
=
Many worker cooperatives utilize surplus profits to provide loans or establish offering funds in order to support other developing or struggling cooperatives.
These funds are also used as collateral for other forms of finance by cooperatives in need.
Examples of Peer Financing in the U.S. include the
Evergreen Cooperatives, the Share Capital Cooperative, and the Valley Alliance of Worker Cooperatives.
In Italy, large cooperative federations utilize excess profits to develop peer financing funds that not only financially assist other cooperatives, but are also used for workers' training programs and for research into cooperatives.
France's worker cooperatives, otherwise known as Société coopérative et participative (SCOPs), are required to allocate a small portion of profits to a financial fund for other French worker cooperatives in
cooperative federations.
Examples
A very significant early influence on the movement has been the
Scott Bader Commonwealth
Ernest Bader (24 November 1890 – 5 February 1982) and his wife, Dora Scott, founded a chemical company, Scott Bader, and gave it to the employees under terms of Common ownership, forming the Scott Bader Commonwealth in 1951.
Scott Bader Ltd. w ...
, a composites and specialty polymer plastics manufacturing company in Wellingborough, Northamptonshire, which its owner Ernest Bader gave to the workforce in installments through the late 1950s to early 1960s. Contrary to the popular concept of common ownership organizations as being small organizations, this is a high-technology chemical manufacturer whose turnover has exceeded £100 million per annum since the early 1990s with a workforce of hundreds. In London, Calverts is an example of an established worker co-operative with a policy of pay parity. From the collective movement, one of the most successful ventures is probably
Suma Wholefoods
Suma is the trading name of the Triangle Wholefoods Collective Limited, a worker co-operative wholefoods wholesaler. It was founded in Leeds in 1977 and is now based in Elland, West Yorkshire. It is the largest independent wholefood wholesaler ...
in Elland, West Yorkshire.
Political philosophy of workers' cooperatives
The advocacy of
workplace democracy, especially with the fullest expression of
worker self-management
Workers' self-management, also referred to as labor management and organizational self-management, is a form of organizational management based on self-directed work processes on the part of an organization's workforce. Self-management is a def ...
such as within workers' cooperatives, is rooted within several intellectual or political traditions:
* The alleviation of
alienation in the workplace, especially in regard to
Marxist
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
thought
* The encouragement of
participatory
Citizen Participation or Public Participation in social science refers to different mechanisms for the public to express opinions—and ideally exert influence—regarding political, economic, management or other social decisions. Participato ...
or
direct democracy
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the Election#Electorate, electorate decides on policy initiatives without legislator, elected representatives as proxies. This differs from the majority of currently establishe ...
* Radical but popular-democratic strategies for the overthrow of
capitalism, for example, several strains of
socialist and
anarchist
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not neces ...
thought
* Autonomy and self-control, especially within anarchist thought
* Cooperating with other worker cooperatives
Workers' cooperatives are also central to ideas of
autonomism,
distributism,
mutualism,
syndicalism,
participatory economics,
guild socialism,
market socialism and
libertarian socialism, among others.
The idea of achieving economic democracy through worker ownership on a national scale has been argued by economist Tom Winters, who states that "building a cooperative economy is one small step on the journey to reclaiming the wealth we all collectively create."
An economic model: the labor-managed firm
Economists have modeled the worker cooperative as a firm in which labor hires capital, rather than capital hiring labor as in a conventional firm. The classic theoretical contributions of such a "labor managed firm" (LMF) model are due to Benjamin Ward and
Jaroslav Vanek
Jaroslav (also written as Yaroslav or Jarosław in other Slavic languages) is a Czech and Slovak first name, pagan in origin.
There are several possible origins of the name Jaroslav. It is very likely that originally the two elements of the nam ...
.
In the neoclassical version, the objective of the LMF is to maximize not total profit, but rather income per worker. But such a scenario implies "perverse" behavior, such as laying off workers when output price rises so as to divide increased profits among fewer members. Evidence supporting such behavior is lacking, however; a review of the empirical economics literature is found in Bonin, Jones, and Putterman. But alternative behavioral models have been proposed. Peter Law examined LMFs that value employment and income. Nobel Laureate
Amartya Sen examined pay according to work and according to need. Nobel Laureate
James Meade examined behavior of an "inegalitarian" LMF. Worker cooperatives tend to have a more compressed wage distribution, which can potentially turn off high-ability workers, potentially causing the cooperative to suffer a "brain drain" as they leave to seek higher wages elsewhere, though this effect is less of an issue in a cooperative with a less compressed wage distribution.
Hiring managers from capitalist firms can be very difficult because of the lower wages.
Generally, the evidence indicates that worker cooperatives have higher productivity than conventional companies although this difference may be modest in size. Research indicates that employee ownership can improve company performance, increase firm stability, increase survival rates and reduce layoffs during a crisis, though the effect is small and only an average, meaning it is not necessarily guaranteed to bring benefits. A 2016 metanalysis concluded that employee ownership had a small positive effect on firm performance but no effects on efficiency or growth-related outcomes. However some researchers have argued that while cooperatives can have higher performance in some circumstances, there is generally little difference in performance between cooperatives and conventional firms and that ultimately they are, on average, just as productive as each other. Economists have explained the clustering of worker coops through leagues or "supporting structures" Regions where large clusters of worker cooperatives are found supported by leagues include
Mondragón, in the
Basque region of Spain, home of
Mondragón Cooperative Corporation
The Mondragon Corporation is a corporation and federation of worker cooperatives based in the Basque region of Spain.
It was founded in the town of Mondragon in 1956 by José María Arizmendiarrieta and a group of his students at a technical ...
and in Italy, particularly
Emilia-Romagna. Leagues provide various kinds of scale economies to make coops viable. But as leagues need coops to start them the result is a
chicken or egg
The chicken or the egg causality dilemma is commonly stated as the question, "which came first: the chicken or the egg?" The dilemma stems from the observation that all chickens hatch from eggs and all chicken eggs are laid by chickens. "Chic ...
problem that helps explain why few coops get started. Research has suggested that the primary appeal of a cooperative for its members is in security of employment, as workers can actually become decoupled from a cooperative's ostensible worker ownership (due to a mixture of interests and the more individualistic values of more recent workers), making secure employment, particularly in economically precarious times, a major draw. While it has been suggested that cooperatives could be a solution to unemployment, research indicates that this is unlikely to be the case.
Worker cooperatives do not seem to differ in innovation or management capabilities from conventional firms. Workers at cooperatives tend to report higher levels of involvement in their tasks, more positive evaluations of supervisors and greater fairness in their perception of the amount of wages they received and methods of payment. Employment in worker-owned firms tends to be more stable than conventional firms, which fluctuate more. This was attributed to conventional firms fixing wages and having to lay off employees during times of economic difficulty, as workers would not accept a wage cut since they could not guarantee restoration of their original wages at a later date, requiring workers to be laid off instead. In a cooperative, workers can accept a wage cut since they know they can restore it at a later date. Cooperatives have a higher survival rate than traditional firms, which seems to be down to greater employment stability and willingness of workers to make adjustments to allow the firm to survive, rather than other possible explanations like greater productivity or financial strength. Worker cooperatives and conventional firms tend to have similar wages after controlling for other possible variables, with any wage differentiation being due to other characteristics aside from firm organization.
If the workers are not satisfied with their work and participation, they can express their disengagement with higher rates of
absenteeism.
Managers can refrain from proposing controversial, needed changes if they feel that they would be rejected by the workers.
Worker cooperatives by country
Europe
Worker co-operation is well established in most countries in Europe, with the largest movements being in Italy, Spain, and France.
The
European Cooperative Statute
The European Cooperative Society (SCE, for Latin ) is, in corporate law, a European cooperative type of company, established in 2006 and related to the Societas Europaea (SE). They may be established and may operate throughout the European Eco ...
, which has been in force since 2006, permits worker cooperatives to be created by individuals or corporate bodies in different EU countries. It is a loose framework that devolves much detail to the national legislation of the country in which the European Cooperative Society (ECS) is registered. It permits a minority of shares to be held by 'investor members' which are not employees.
France
Workers' associations were legalized in 1848 and again in 1864. In 1871, during the
Paris Commune, workshops abandoned by their owners were taken over by their workers. In 1884 a chamber of workers' cooperatives was founded. By 1900 France had nearly 250 workers' cooperatives and 500 by 1910. The movement was to rise and fall throughout the twentieth century, with growth in 1936, after the Second World War, between 1978 and 1982 and since 1995.
In 2004 France had 1700 workers' co-operatives, with 36,000 people working in them. The average size of a co-operative was 21 employees. More than 60% of co-operative employees were also members. French workers' co-operatives today include some large organisations such as and . Other cooperatives whose names are generally known to include the magazines ''
Alternatives économiques
''Alternatives économiques'' (; ) is a French magazine specializing in economic issues. The magazine was established in 1980 by Denis Clerc. It is published on a monthly basis. The headquarters is in Paris. During the period 2013-2014 the magazi ...
'' and ''
Les Dernières Nouvelles d'Alsace
''Les Dernières Nouvelles d'Alsace'', commonly known as ''DNA'', is a regional daily French newspaper covering the Alsace region.
History and profile
''DNA'' was created in November 1877 as ''Neueste Nachrichten'' by German Heinrich Ludwig Kays ...
'', the driving school ECF CERCA and the toy manufacturer "Moulin Roty".
Italy
Pencavel et al. (2006) found that in the north of
Italy, the area where the most co-ops are located, employing around over 4% of the labour force, actually paid their workers 14% less than capitalist firms and their wages were more volatile. This was after controlling for various variables, such as schooling, age, gender, occupation, industry, location, firm-size, user cost of capital, fixed costs, and deviations in its real sales.
The cooperative movement in Emilia-Romagna, Italy, successfully melds two divergent philosophical currents: Socialism and Catholicism. With more than a century of cooperative history, the region includes more than 8,000 cooperatives.
Spain
One of the world's best known examples of worker cooperation is the
Mondragón Cooperative Corporation
The Mondragon Corporation is a corporation and federation of worker cooperatives based in the Basque region of Spain.
It was founded in the town of Mondragon in 1956 by José María Arizmendiarrieta and a group of his students at a technical ...
in the
Basque Country
Basque Country may refer to:
* Basque Country (autonomous community), as used in Spain ( es, País Vasco, link=no), also called , an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain (shown in pink on the map)
* French Basque Country o ...
.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, the
Labour Party's enthusiasm for worker cooperatives was at its highest in the 1970s and 1980s, with
Tony Benn being a prominent advocate. The principle has also found some support from the more radical wing of the
Liberal Democrats, such as from
Michael Meadowcroft.
A small number of such co-operatives were formed during the 1974 Labour Government as worker takeovers
[Ridley-Duff, R. J. (2007) "Communitarian Perspectives on Social Enterprise", ''Corporate Governance: An International Review'', 15(2):382–392](_blank)
following the bankruptcy of a private firm in a desperate attempt to save the jobs at risk. However the change in ownership structure was usually unable to resist the underlying commercial failure.
This was true in particular of the best known, the
Meriden motor-cycle cooperative in the
West Midlands
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
which took over the assets of the ailing
Triumph company, although there were instances of successful employee buy-outs of nationalized industries in the period, notably
National Express. Meanwhile, many more worker co-operatives were founded as start-up businesses, and by the late 1980s, there were some 2,000 in existence. Since then the number has declined considerably.
Co-operatives are typically registered under either the
Companies Act 2006 or the
Co-operative and Community Benefit Societies Act 2014 (IPS), though other legal forms are available. A number of model rules have been devised to enable cooperatives to register under both acts; for workers' cooperatives, these rules restrict membership to those who are employed by the workplace. Most workers' co-operatives are incorporated bodies, which limits the liability if the co-operative fails and goes into liquidation.
The largest examples of a British worker cooperatives include,
Suma Wholefoods
Suma is the trading name of the Triangle Wholefoods Collective Limited, a worker co-operative wholefoods wholesaler. It was founded in Leeds in 1977 and is now based in Elland, West Yorkshire. It is the largest independent wholefood wholesaler ...
, Bristol-based Essential Trading Co-operative and the
Brighton
Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze A ...
-based Infinity Foods Cooperative Ltd.
Middle East
Israel
In Israel, worker cooperatives emerged in the early 20th century alongside the
Kibbutz
A kibbutz ( he, קִבּוּץ / , lit. "gathering, clustering"; plural: kibbutzim / ) is an intentional community in Israel that was traditionally based on agriculture. The first kibbutz, established in 1909, was Degania. Today, farming h ...
, the collective farming movement. The Kibbutz is a cooperative movement that was founded on
Zionist ideas, with the intention to cultivate land and increase the number of
Jewish settlements Jewish settlement may refer to:
Events
* Jewish settlement in the land of Israel
* Israeli settlement, Jewish communities currently established in the West Bank and in the Golan Heights, between 1967 and 2006 in the Gaza Strip, and between 1967 and ...
. By the 1970s, the
Histadrut
Histadrut, or the General Organization of Workers in Israel, originally ( he, ההסתדרות הכללית של העובדים בארץ ישראל, ''HaHistadrut HaKlalit shel HaOvdim B'Eretz Yisrael''), is Israel's national trade union center ...
(Israel Labour Federation) controlled a significant number of corporations, including Israel's largest bank—
Bank Hapoalim
Bank Hapoalim ( he, בנק הפועלים lit. ''The Workers' Bank'') is one of Israel's largest banks.
History
The bank was established in 1921 by the ''Histadrut'', the Israeli trade union congress (lit. "General Federation of Laborers in the ...
(literally the Worker's Bank). By the 1990s, the Histadrut had lost its power and influence and many worker cooperative corporations were sold or became
public companies. Israel's biggest
public transportation company,
Egged, is still a workers cooperative. However, Egged employs workers who are not cooperative members and are paid at a lower wage than worker-members.
In North America
United States
National organization
The
United States Federation of Worker Cooperatives
The United States Federation of Worker Cooperatives (USFWC) is a federation of worker cooperatives in the United States. USFWC was founded at the U.S. Conference of Democratic Workplaces in Minneapolis, Minnesota in May 2004.
The Federation w ...
is the only organization in the U.S. representing worker cooperative interests nationally. Offering a voice on national level, promoting the worker co-operative model, uniting co-ops at conferences and providing a base of support and technical assistance to the worker co-operative community.
Regional organizations
The Eastern Conference for Workplace Democracy and Western Worker Co-operative Conference hold conferences every other year for their respective regions. In addition, there are national and regional nonprofit organizations that focus on providing technical support and assistance to both create new worker cooperatives (start-ups) and conversions of existing businesses into worker cooperatives, usually when the business owner is retiring and wants to sell the company. These organizations include
Democracy at Work Institute
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose gov ...
(created by the
U.S. Federation of Worker Cooperatives),
Cooperative Development Institute
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-control ...
,
Ohio Employee Ownership Center The Ohio Employee Ownership Center (OEOC) is an organization based at Kent State University which provides employees of businesses in Ohio with resources for establishing Employee Share Ownership Plan
Employee stock ownership, or employee share o ...
,
Vermont Employee Ownership Center
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the ...
,
Rhode Island Center for Employee Ownership,
Project Equity
A project is any undertaking, carried out individually or collaboratively and possibly involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a particular goal.
An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of even ...
, and others.
Cooperation Jackson
Cooperation Jackson is an emerging network of worker cooperatives in Jackson, Mississippi, United States. It aims to develop a series of independent but connected democratic institutions to empower workers and residents of Jackson, particularly t ...
is a federation of cooperatives based in
Jackson, Mississippi, which seeks to build worker-owned coops and other locally operated institutions.
The
Freedom Quilting Bee was a notable cooperative founded in Alabama during the midst of the Civil Rights movement, and was instrumental in helping underprivileged black workers in the area escape poverty, amassing enough success to fill orders for major department stores such as
Sears while helping to spark contemporary interest in quilting.
Canada
Worker co-ops in Canada are represented by the
Canadian Worker Co-op Federation
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
(CWCF). Members of the CWCF are found throughout English Canada.
Ontario has its own federation with well-developed standards. Quebec has a distinct worker co-operative history, and is presently organised into a number of regional federations.
Mexico
After the revolt on 1 January 1994 from
EZLN
The Zapatista Army of National Liberation (, EZLN), often referred to as the Zapatistas (Mexican ), is a far-left political and militant group that controls a substantial amount of territory in Chiapas, the southernmost state of Mexico.
Since ...
, the indigenous people in
Chiapas
Chiapas (; Tzotzil language, Tzotzil and Tzeltal language, Tzeltal: ''Chyapas'' ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas), is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, ...
started the reconstruction of their
Zapatista coffee cooperatives
Zapatista Coffee Cooperatives primarily operate in Chiapas, the southernmost state of Mexico following Zapatismo ideology.
The economic importance of coffee
Mexico is a significant coffee producer (7th place worldwide). Specifically, the climati ...
.
South America
Venezuela
Hugo Chávez
Hugo Rafael Chávez Frías (; 28 July 1954 – 5 March 2013) was a Venezuelan politician who was president of Venezuela from 1999 until his death in 2013, except for a brief period in 2002. Chávez was also leader of the Fifth Republ ...
, in his effort to democratize the workforce, established a lot of worker-owned and operated cooperatives the moment he got into office, in 1998. By 2006, there had been 100,000 worker co-ops set up, which represented around 1.5 million workers. From day one, he made sure to give them cheap start-up credit, technical training, and preferential treatment with government purchases of goods and equipment. Not even a year later, in 1999, he increased the number of co-ops that got tax incentives. A 2006 census showed that 50% of the co-ops were either functioning improperly or were simply created just to get access to public funds.
Argentina
In response to the
economic crisis in Argentina, many Argentinian workers occupied the premises of bankrupt businesses and began to run them as worker-owned cooperatives. As of 2005, there were roughly 200 worker-owned businesses in Argentina, most of which were started in response to this crisis. By 2020, around 16,000 Argentine workers were running over 400 recuperated enterprises in Argentina. The documentary film ''
The Take'' described this phenomenon journalistically, while Marcelo Vieta's book,
Workers' Self-Management in Argentina, provides and extensive academic, case study, and historical account of the phenomenon.
According to a recent statement by the International Co-operative Alliance, cooperative businesses (most of which are not worker co-ops) in Argentina have nearly 20 million members across a number of business sectors from health care to housing to factory work and beyond. These businesses are increasing in number at a drastic rate, with over 6000 having been created in 2012 alone.
Worker-owned cooperatives in Argentina have played a role in developing their surrounding communities. For example, the worker-owners of
FaSinPat voted to use excess profits to establish education programs, healthcare facilities, and recreational activities for its neighborhood.
Asia
India
India has a substantial set of laws, rules & regulations for enterprises in the co-operative sector.
The
Indian Coffee Houses in India were started by the Coffee Board in the early 1940s, during British rule. In the mid-1950s the Board closed down the Coffee Houses, due to a policy change. The thrown-out workers then took over the branches, under the leadership of
A. K. Gopalan
Ayillyath Kuttiari Gopalan (1 October 1904 – 22 March 1977), popularly known as A. K. Gopalan or AKG, was an Indian communist politician. He was one of 16 Communist Party of India members elected to the first Lok Sabha in 1952. Later he beca ...
and renamed the network as Indian Coffee House. This history is recorded in
Coffee Housinte Katha
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of th ...
, a book in
Malayalam, the mother tongue of A. K. Gopalan. The author of the book is
Nadakkal Parameswaran Pillai
N. S. Parameswaran Pillai or Nadakkal Parameswaran Pillai (1931–2010) is the co-founder of Indian Coffee Houses in Kerala with T. K. Krishnan. He is also the author of a history of Indian Coffee House, a worker cooperative.
Historian of ...
one of the leaders of the ICH movement. Another very large network of worker coops is
Kerala Dinesh Beedi, originally started by exploited beedi rollers.
[See T.M. Thomas Isaac, Richard W. Franke, and Pyaralal Raghavan, ''Democracy at Work in an Indian Industrial Cooperative. The Story of Kerala Dinesh Beedi'', Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1998.]
Comparison with other work organizations
There are significant differences between ends and means between firms where capital controls labor or firms where the state controls both labor and capital. These distinctions are easily seen when measured by essential elements of commerce: purpose, organization, ownership, control, sources of capital, distribution of profits,
dividends, operational practices, and tax treatment. The following chart compares the commercial elements of capitalism, state ownership, and cooperative worker-ownership. It is based on US rules and regulations.
See also
*
Market socialism
*
Codetermination
**
Worker representation on corporate boards of directors
*
Employee-owned corporation
*
Employee stock ownership
*
Industrial democracy
*
Social ownership
*
Workers' control
*
Economic democracy
*
Economics of participation
Economics of participation is an umbrella term spanning the economic analysis of worker cooperatives, labor-managed firms, profit sharing, gain sharing, employee ownership, employee stock ownership plans, works councils, codetermination, and o ...
*
Voluntary association
*
Collectives
*
Benefit Corporation
*
Democratic Education
*
Housing Cooperative
A housing cooperative, or housing co-op, is a legal entity, usually a cooperative or a corporation, which owns real estate, consisting of one or more residential buildings; it is one type of housing tenure. Housing cooperatives are a distinc ...
;Other workers' cooperative thinkers
*
Michael Albert
*
Hilaire Belloc
*
Kevin Carson
*
G. K. Chesterton
Gilbert Keith Chesterton (29 May 1874 – 14 June 1936) was an English writer, philosopher, Christian apologist, and literary and art critic. He has been referred to as the "prince of paradox". Of his writing style, ''Time'' observed: "Wh ...
*
G.D.H. Cole
George Douglas Howard Cole (25 September 1889 – 14 January 1959) was an English political theorist, economist, and historian. As a believer in common ownership of the means of production, he theorised guild socialism (production organised ...
*
Robert A. Dahl
Robert Alan Dahl (; December 17, 1915 – February 5, 2014) was an American political theorist and Sterling Professor of Political Science at Yale University.
He established the pluralist theory of democracy—in which political outcomes are ...
*
Sam Dolgoff
*
Noam Chomsky
*
John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill (20 May 1806 – 7 May 1873) was an English philosopher, political economist, Member of Parliament (MP) and civil servant. One of the most influential thinkers in the history of classical liberalism, he contributed widely to ...
*
Gregory Dow
Gregory Keith Dow (born February 2, 1954) is an economist at Simon Fraser University who has contributed to the economics of participation and particularly to research on worker cooperatives. He received his Ph.D. from the University of Michigan ...
*
David Ellerman
David Patterson Ellerman (born 14 March 1943) is a philosopher and author who works in the fields of economics and political economy, social theory and philosophy, quantum mechanics, and in mathematics. He has written extensively on workplace dem ...
*
Charles Gide
*
David Griffiths
*
George Holyoake
*
Derek C. Jones
Derek C. Jones (born c. 1946) is the Irma M. and Robert D. Morris Professor of Economics at Hamilton College who has contributed to the economics of participation, and pioneered the econometric analysis of productivity of worker cooperatives, emp ...
*
William King William King may refer to:
Arts
*Willie King (1943–2009), American blues guitarist and singer
*William King (author) (born 1959), British science fiction author and game designer, also known as Bill King
*William King (artist) (1925–2015), Ame ...
*
Naomi Klein
*
Michael Moore
Michael Francis Moore (born April 23, 1954) is an American filmmaker, author and left-wing activist. His works frequently address the topics of globalization and capitalism.
Moore won the 2002 Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature for ' ...
*
Robert Owen
Robert Owen (; 14 May 1771 – 17 November 1858) was a Welsh textile manufacturer, philanthropist and social reformer, and a founder of utopian socialism and the cooperative movement. He strove to improve factory working conditions, promoted e ...
*
James Meade
*
Mario Bunge
*
Carole Pateman
Carole Pateman (born 11 December 1940) is a feminist and political theorist. She is known as a critic of liberal democracy and has been a member of the British Academy since 2007.
Biography
Pateman was born in Maresfield, Sussex, England. Ed ...
*
Friedrich Wilhelm Raiffeisen
*
The Rochdale Pioneers
''The Rochdale Pioneers'' is a British biographical feature film, released in 2012, that tells the story of the foundation of the first successful cooperative retail store by working class members of the Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers, i ...
*
David Schweickart
*
José María Arizmendiarrieta
Father José María Arizmendiarrieta Madariaga ( Marquina-Xemein, Bizkaia, Spain, April 22, 1915 - Mondragon, Gipuzkoa, Spain, November 29, 1976) was a Basque Catholic priest and promoter of the cooperative companies of the Mondragon Corporat ...
*
E. F. Schumacher
Ernst Friedrich Schumacher (16 August 1911 – 4 September 1977) was a German-British statistician and economist who is best known for his proposals for human-scale, decentralised and appropriate technologies.Biography on the inner dustjacket ...
*
Stephen C. Smith
*
Roger Spear
Roger Ruskin Spear (born 29 June 1943 in Hammersmith, London) is an English sculptor, multimedia artist and multi-instrumentalist (saxophones, clarinet, piano, guitars, percussion) who was a member of the Bonzo Dog Doo-Dah Band.
Career
After Sp ...
*
Leland Stanford
Amasa Leland Stanford (March 9, 1824June 21, 1893) was an American industrialist and politician. A member of the Republican Party, he served as the 8th governor of California from 1862 to 1863 and represented California in the United States Se ...
*
Jaroslav Vanek
Jaroslav (also written as Yaroslav or Jarosław in other Slavic languages) is a Czech and Slovak first name, pagan in origin.
There are several possible origins of the name Jaroslav. It is very likely that originally the two elements of the nam ...
*
Beatrice Webb
Martha Beatrice Webb, Baroness Passfield, (née Potter; 22 January 1858 – 30 April 1943) was an English sociologist, economist, socialist, labour historian and social reformer. It was Webb who coined the term ''collective bargaining''. She ...
*
Sidney Webb
Sidney James Webb, 1st Baron Passfield, (13 July 1859 – 13 October 1947) was a British socialist, economist and reformer, who co-founded the London School of Economics. He was an early member of the Fabian Society in 1884, joining, like Geo ...
*
William Foote Whyte
*
Richard D. Wolff
Richard David Wolff (born April 1, 1942) is an American Marxian economist known for his work on economic methodology and class analysis. He is professor emeritus of economics at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and a visiting professor ...
;Videos about workers' cooperatives
* ''
Anarchism in America''
* ''
Capitalism: A Love Story''
*
This Way Out: A Guide to Starting a Worker Cooperative. (and other films by Jai Jai Noire, Mighty Small Films)'
Notes
References
Further reading
* ''For All The People: Uncovering the Hidden History of Cooperation, Cooperative Movements, and Communalism in America'', PM Press, by John Curl, 2009,
* Créer en Scop, le guide de l'entreprise participative, Ed Scop Edit 2005 (disponible gratuitement su
le site de la CG SCOP)
* Histoire des Scop et de la coopération, Jean Gautier, Ed Scop Edit, 2006 (DVD)
External links
*
GEO.CoopNYCWorker.CoopUSWorker.Coop
{{DEFAULTSORT:Worker Cooperative
Business models
Market socialism
Mutualism (movement)
Socialism
Types of organization
ta:தொழிலாளர் கூட்டுறவு
 Worker cooperatives rose to prominence during the Industrial Revolution as part of the labour movement. As employment moved to industrial areas and job sectors declined, workers began organizing and controlling businesses for themselves. Worker cooperatives were originally sparked by "critical reaction to industrial capitalism and the excesses of the industrial revolution." Some worker cooperatives were designed to "cope with the evils of unbridled capitalism and the insecurities of wage labor".
The philosophy that underpinned the cooperative movement stemmed from the socialist writings of thinkers including
Worker cooperatives rose to prominence during the Industrial Revolution as part of the labour movement. As employment moved to industrial areas and job sectors declined, workers began organizing and controlling businesses for themselves. Worker cooperatives were originally sparked by "critical reaction to industrial capitalism and the excesses of the industrial revolution." Some worker cooperatives were designed to "cope with the evils of unbridled capitalism and the insecurities of wage labor".
The philosophy that underpinned the cooperative movement stemmed from the socialist writings of thinkers including  When the current cooperative movement resurfaced in the 1960s, it developed mostly on a new system of "collective ownership" where par value shares were issued as symbols of egalitarian voting rights. Typically, a member may only own one share to maintain the egalitarian ethos. Once brought in as a member and after a period of time on probation usually so the new candidate can be evaluated, they would be given the power to manage the coop without "ownership" in the traditional sense. In the UK, this system is known as
When the current cooperative movement resurfaced in the 1960s, it developed mostly on a new system of "collective ownership" where par value shares were issued as symbols of egalitarian voting rights. Typically, a member may only own one share to maintain the egalitarian ethos. Once brought in as a member and after a period of time on probation usually so the new candidate can be evaluated, they would be given the power to manage the coop without "ownership" in the traditional sense. In the UK, this system is known as