Women's Sports Competitions In Sweden on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female
 Although girls are born slightly less frequently than boys (the ratio is around 1:1.05), newborn girls are more likely to reach their first birthday than are boys, and women typically have a longer life expectancy by six to eight years, although in some areas discrimination against women has lowered female life expectancy to less than or equal to that of men. Out of the total human population in 2015, there were 1018 men for every 1000 women. The differences in life expectancy are partly due to inherent biological advantages, but also reflect behavioral differences between men and women. The gap is narrowing to some extent in some developed countries, possibly due to increased smoking among women and declining rates of cardiovascular disease among men. The World Health Organization (WHO) writes that it is "important to note that the extra years of life for women are not always lived in good health."
Although girls are born slightly less frequently than boys (the ratio is around 1:1.05), newborn girls are more likely to reach their first birthday than are boys, and women typically have a longer life expectancy by six to eight years, although in some areas discrimination against women has lowered female life expectancy to less than or equal to that of men. Out of the total human population in 2015, there were 1018 men for every 1000 women. The differences in life expectancy are partly due to inherent biological advantages, but also reflect behavioral differences between men and women. The gap is narrowing to some extent in some developed countries, possibly due to increased smoking among women and declining rates of cardiovascular disease among men. The World Health Organization (WHO) writes that it is "important to note that the extra years of life for women are not always lived in good health."
 Maternal mortality or maternal death is defined by WHO as "the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes." In 2008, noting that each year more than 500,000 women die of complications of pregnancy and childbirth and at least seven million experience serious health problems while 50 million more have adverse health consequences after childbirth, the World Health Organization urged midwife training to strengthen maternal and newborn health services. To support the upgrading of midwifery skills the WHO established a midwife training program, Action for Safe Motherhood.
In 2017, 94% of maternal deaths occur in low and lower middle-income countries. Approximately 86% of maternal deaths occur in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, with sub-Saharan Africa accounting for around 66% and Southern Asia accounting for around 20%. The main causes of maternal mortality include pre-eclampsia and eclampsia, unsafe abortion, pregnancy complications from malaria and HIV/AIDS, and severe bleeding and infections following childbirth. Most European countries, Australia, Japan, and Singapore are very safe in regard to childbirth.
In 1990, the US ranked 12th of the 14 developed countries that were analyzed and since that time the death rates of every country have steadily improved while the US rate has spiked dramatically. While the others that were analyzed in 1990 show a 2017 death rate of fewer than 10 deaths per every 100,000 live births, the U.S. rate rose to 26.4. Furthermore, for every one of the 700 to 900 women who die in the U.S. each year during pregnancy or childbirth, 70 experience significant complications, totaling more than one percent of all births.
Maternal mortality or maternal death is defined by WHO as "the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes." In 2008, noting that each year more than 500,000 women die of complications of pregnancy and childbirth and at least seven million experience serious health problems while 50 million more have adverse health consequences after childbirth, the World Health Organization urged midwife training to strengthen maternal and newborn health services. To support the upgrading of midwifery skills the WHO established a midwife training program, Action for Safe Motherhood.
In 2017, 94% of maternal deaths occur in low and lower middle-income countries. Approximately 86% of maternal deaths occur in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, with sub-Saharan Africa accounting for around 66% and Southern Asia accounting for around 20%. The main causes of maternal mortality include pre-eclampsia and eclampsia, unsafe abortion, pregnancy complications from malaria and HIV/AIDS, and severe bleeding and infections following childbirth. Most European countries, Australia, Japan, and Singapore are very safe in regard to childbirth.
In 1990, the US ranked 12th of the 14 developed countries that were analyzed and since that time the death rates of every country have steadily improved while the US rate has spiked dramatically. While the others that were analyzed in 1990 show a 2017 death rate of fewer than 10 deaths per every 100,000 live births, the U.S. rate rose to 26.4. Furthermore, for every one of the 700 to 900 women who die in the U.S. each year during pregnancy or childbirth, 70 experience significant complications, totaling more than one percent of all births.
 Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to human reproduction, reproduction and reproductive health. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics has stated that:
:... the human rights of women include their right to have control over and decide freely and responsibly on matters related to their sexuality, including sexual and reproductive health, free of coercion, discrimination and violence. Equal relationships between women and men in matters of sexual relations and reproduction, including full respect for the integrity of the person, require mutual respect, consent and shared responsibility for sexual behavior and its consequences.
The World Health Organization reports that based on data from 2010 to 2014, 56 million induced abortions occurred worldwide each year (25% of all pregnancies). Of those, about 25 million were considered as Unsafe abortions, unsafe. The WHO reports that in developed regions about 30 women die for every 100,000 unsafe abortions and that number rises to 220 deaths per 100,000 unsafe abortions in developing regions and 520 deaths per 100,000 unsafe abortions in sub-Saharan Africa. The WHO ascribes these deaths to:
*restrictive laws
*poor availability of services
*high cost
*stigma
*conscientious objection of health-care providers
*unnecessary requirements, such as mandatory waiting periods, mandatory counselling, provision of misleading information, third-party authorization, and medically unnecessary tests that delay care.
Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to human reproduction, reproduction and reproductive health. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics has stated that:
:... the human rights of women include their right to have control over and decide freely and responsibly on matters related to their sexuality, including sexual and reproductive health, free of coercion, discrimination and violence. Equal relationships between women and men in matters of sexual relations and reproduction, including full respect for the integrity of the person, require mutual respect, consent and shared responsibility for sexual behavior and its consequences.
The World Health Organization reports that based on data from 2010 to 2014, 56 million induced abortions occurred worldwide each year (25% of all pregnancies). Of those, about 25 million were considered as Unsafe abortions, unsafe. The WHO reports that in developed regions about 30 women die for every 100,000 unsafe abortions and that number rises to 220 deaths per 100,000 unsafe abortions in developing regions and 520 deaths per 100,000 unsafe abortions in sub-Saharan Africa. The WHO ascribes these deaths to:
*restrictive laws
*poor availability of services
*high cost
*stigma
*conscientious objection of health-care providers
*unnecessary requirements, such as mandatory waiting periods, mandatory counselling, provision of misleading information, third-party authorization, and medically unnecessary tests that delay care.
 The United Nations, UN Declaration on the Elimination of Violence against Women defines "violence against women" as:
It identifies three forms of such violence: that which occurs ''in the family'', that which occurs ''within the general community'', and that which is perpetrated or condoned ''by the State''. It also states that "violence against women is a manifestation of historically unequal power relations between men and women".
Violence against women remains a widespread problem, fueled, especially outside the West, by patriarchal social values, lack of adequate laws, and lack of enforcement of existing laws. Social norms that exist in many parts of the world hinder progress towards protecting women from violence. For example, according to surveys by UNICEF, the percentage of women aged 15–49 who think that a husband is justified in hitting or beating his wife under certain circumstances is as high as 90% in Afghanistan and Jordan, 87% in Mali, 86% in Guinea and Timor-Leste, 81% in Laos, and 80% in the Central African Republic. A 2010 survey conducted by the Pew Research Center found that stoning as a punishment for adultery was supported by 82% of respondents in Egypt and Pakistan, 70% in Jordan, 56% Nigeria, and 42% in Indonesia.
Specific forms of violence that affect women include female genital mutilation, sex trafficking, forced prostitution, forced marriage, rape, sexual harassment, honor killings, acid throwing, and dowry death, dowry related violence. Governments can be complicit in violence against women, such as when stoning is used as a legal punishment, mostly for women accused of adultery.
There have also been many forms of violence against women which have been prevalent historically, notably the Witch-hunt, burning of witches, the sacrifice of widows (such as Sati (practice), sati) and foot binding. The prosecution of women accused of witchcraft has a long tradition; for example, during the early modern period (between the 15th and 18th centuries), witch trials in the early modern period, witch trials were common in Europe and in the European colonies in North America. Today, there remain regions of the world (such as parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, rural North India, and Papua New Guinea) where belief in witchcraft is held by many people, and women accused of being witches are subjected to serious violence. In addition, there are also countries which have criminal legislation against the practice of witchcraft. In Saudi Arabia, witchcraft remains a crime punishable by death, and in 2011 the country beheaded a woman for 'witchcraft and sorcery'.
It is also the case that certain forms of violence against women have been recognized as criminal offenses only during recent decades, and are not universally prohibited, in that many countries continue to allow them. This is especially the case with marital rape. In the Western World, there has been a trend towards ensuring gender equality within marriage and prosecuting domestic violence, but in many parts of the world women still lose significant legal rights when entering a marriage.
Sexual violence against women greatly increases during times of war and armed conflict, during military occupation, or ethnic conflicts; most often in the form of war rape and sexual slavery. Contemporary examples of sexual violence during war include rape during the Armenian Genocide, rape during the Bangladesh Liberation War, rape in the Bosnian War, rape during the Rwandan genocide, and War rape#Democratic Republic of the Congo, rape during Second Congo War. In Colombia, the armed conflict has also resulted in increased sexual violence against women. The most recent case was the sexual jihad done by ISIL where 5000–7000 Yazidi and Christian girls and children were sold into sexual slavery during the Sexual violence in the Iraqi insurgency, genocide and rape of Yazidi and Christian women, some of whom jumped to their death from Mount Sinjar, as described in a witness statement.
Laws and policies on violence against women vary by jurisdiction. In the European Union, sexual harassment and human trafficking are subject to Directive (European Union), directives.
The United Nations, UN Declaration on the Elimination of Violence against Women defines "violence against women" as:
It identifies three forms of such violence: that which occurs ''in the family'', that which occurs ''within the general community'', and that which is perpetrated or condoned ''by the State''. It also states that "violence against women is a manifestation of historically unequal power relations between men and women".
Violence against women remains a widespread problem, fueled, especially outside the West, by patriarchal social values, lack of adequate laws, and lack of enforcement of existing laws. Social norms that exist in many parts of the world hinder progress towards protecting women from violence. For example, according to surveys by UNICEF, the percentage of women aged 15–49 who think that a husband is justified in hitting or beating his wife under certain circumstances is as high as 90% in Afghanistan and Jordan, 87% in Mali, 86% in Guinea and Timor-Leste, 81% in Laos, and 80% in the Central African Republic. A 2010 survey conducted by the Pew Research Center found that stoning as a punishment for adultery was supported by 82% of respondents in Egypt and Pakistan, 70% in Jordan, 56% Nigeria, and 42% in Indonesia.
Specific forms of violence that affect women include female genital mutilation, sex trafficking, forced prostitution, forced marriage, rape, sexual harassment, honor killings, acid throwing, and dowry death, dowry related violence. Governments can be complicit in violence against women, such as when stoning is used as a legal punishment, mostly for women accused of adultery.
There have also been many forms of violence against women which have been prevalent historically, notably the Witch-hunt, burning of witches, the sacrifice of widows (such as Sati (practice), sati) and foot binding. The prosecution of women accused of witchcraft has a long tradition; for example, during the early modern period (between the 15th and 18th centuries), witch trials in the early modern period, witch trials were common in Europe and in the European colonies in North America. Today, there remain regions of the world (such as parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, rural North India, and Papua New Guinea) where belief in witchcraft is held by many people, and women accused of being witches are subjected to serious violence. In addition, there are also countries which have criminal legislation against the practice of witchcraft. In Saudi Arabia, witchcraft remains a crime punishable by death, and in 2011 the country beheaded a woman for 'witchcraft and sorcery'.
It is also the case that certain forms of violence against women have been recognized as criminal offenses only during recent decades, and are not universally prohibited, in that many countries continue to allow them. This is especially the case with marital rape. In the Western World, there has been a trend towards ensuring gender equality within marriage and prosecuting domestic violence, but in many parts of the world women still lose significant legal rights when entering a marriage.
Sexual violence against women greatly increases during times of war and armed conflict, during military occupation, or ethnic conflicts; most often in the form of war rape and sexual slavery. Contemporary examples of sexual violence during war include rape during the Armenian Genocide, rape during the Bangladesh Liberation War, rape in the Bosnian War, rape during the Rwandan genocide, and War rape#Democratic Republic of the Congo, rape during Second Congo War. In Colombia, the armed conflict has also resulted in increased sexual violence against women. The most recent case was the sexual jihad done by ISIL where 5000–7000 Yazidi and Christian girls and children were sold into sexual slavery during the Sexual violence in the Iraqi insurgency, genocide and rape of Yazidi and Christian women, some of whom jumped to their death from Mount Sinjar, as described in a witness statement.
Laws and policies on violence against women vary by jurisdiction. In the European Union, sexual harassment and human trafficking are subject to Directive (European Union), directives.


 The total fertility rate (TFR) – the average number of children born to a woman over her lifetime – differs significantly between different regions of the world. In 2016, the highest estimated TFR was in Niger (6.62 children born per woman) and the lowest in Singapore (0.82 children/woman). While most Sub-Saharan African countries have a high TFR, which creates problems due to lack of resources and contributes to overpopulation, most Western countries currently experience a sub replacement fertility rate which may lead to population ageing and population decline.
In many parts of the world, there has been a change in family structure over the past few decades. For instance, in the West, there has been a trend of moving away from living arrangements that include the extended family to those which only consist of the nuclear family. There has also been a trend to move from marital fertility to non-marital fertility. Children born outside marriage may be born to cohabitation, cohabiting couples or to single parent, single women. While births outside marriage are common and fully accepted in some parts of the world, in other places they are highly stigmatized, with unmarried mothers facing ostracism, including violence from family members, and in extreme cases even honor killings. In addition, sex outside marriage remains illegal in many countries (such as Saudi Arabia, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Iran, Kuwait, Maldives, Morocco, Oman, Mauritania, United Arab Emirates, Sudan, and Yemen).
The social role of the mother differs between cultures. In many parts of the world, women with dependent children are expected to stay at home and dedicate all their energy to child raising, while in other places mothers most often return to paid work (see Working parent, working mother and Housewife, stay-at-home mother).
The total fertility rate (TFR) – the average number of children born to a woman over her lifetime – differs significantly between different regions of the world. In 2016, the highest estimated TFR was in Niger (6.62 children born per woman) and the lowest in Singapore (0.82 children/woman). While most Sub-Saharan African countries have a high TFR, which creates problems due to lack of resources and contributes to overpopulation, most Western countries currently experience a sub replacement fertility rate which may lead to population ageing and population decline.
In many parts of the world, there has been a change in family structure over the past few decades. For instance, in the West, there has been a trend of moving away from living arrangements that include the extended family to those which only consist of the nuclear family. There has also been a trend to move from marital fertility to non-marital fertility. Children born outside marriage may be born to cohabitation, cohabiting couples or to single parent, single women. While births outside marriage are common and fully accepted in some parts of the world, in other places they are highly stigmatized, with unmarried mothers facing ostracism, including violence from family members, and in extreme cases even honor killings. In addition, sex outside marriage remains illegal in many countries (such as Saudi Arabia, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Iran, Kuwait, Maldives, Morocco, Oman, Mauritania, United Arab Emirates, Sudan, and Yemen).
The social role of the mother differs between cultures. In many parts of the world, women with dependent children are expected to stay at home and dedicate all their energy to child raising, while in other places mothers most often return to paid work (see Working parent, working mother and Housewife, stay-at-home mother).
 Single-sex education has traditionally been dominant and is still highly relevant. Universal education, meaning state-provided primary and secondary education independent of gender, is not yet a global norm, even if it is assumed in most developed countries. In some Western countries, women have surpassed men at many levels of education. For example, in the United States in 2005/2006, women earned 62% of associate degrees, 58% of bachelor's degrees, 60% of master's degrees, and 50% of doctorates.
The educational Sex ratio, gender gap in Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries has been reduced over the last 30 years. Younger women today are far more likely to have completed a tertiary qualification: in 19 of the 30 OECD countries, more than twice as many women aged 25 to 34 have completed tertiary education than have women aged 55 to 64. In 21 of 27 OECD countries with comparable data, the number of women graduating from university-level programmes is equal to or exceeds that of men. 15-year-old girls tend to show much higher expectations for their careers than boys of the same age.
While women account for more than half of university graduates in several OECD countries, they receive only 30% of tertiary degrees granted in science and engineering fields, and women account for only 25% to 35% of researchers in most OECD countries.
Research shows that while women are studying at prestigious universities at the same rate as men they are not being given the same chance to join the faculty. Sociologist Harriet Zuckerman has observed that the more prestigious an institute is, the more difficult and time-consuming it will be for women to obtain a faculty position there. In 1989, Harvard University tenured its first woman in chemistry, Cynthia Friend, and in 1992 its first woman in physics, Melissa Franklin. She also observed that women were more likely to hold their first professional positions as instructors and lecturers while men are more likely to work first in tenure positions. According to Smith and Tang, as of 1989, 65% of men and only 40% of women held tenured positions and only 29% of all scientists and engineers employed as assistant professors in four-year colleges and universities were women.
In 1992, women earned 9% of the PhDs awarded in engineering, but only one percent of those women became professors. In 1995, 11% of professors in science and engineering were women. In relation, only 311 deans of engineering schools were women, which is less than 1% of the total. Even in psychology, a degree in which women earn the majority of PhDs, they hold a significant amount of fewer tenured positions, roughly 19% in 1994.
Single-sex education has traditionally been dominant and is still highly relevant. Universal education, meaning state-provided primary and secondary education independent of gender, is not yet a global norm, even if it is assumed in most developed countries. In some Western countries, women have surpassed men at many levels of education. For example, in the United States in 2005/2006, women earned 62% of associate degrees, 58% of bachelor's degrees, 60% of master's degrees, and 50% of doctorates.
The educational Sex ratio, gender gap in Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries has been reduced over the last 30 years. Younger women today are far more likely to have completed a tertiary qualification: in 19 of the 30 OECD countries, more than twice as many women aged 25 to 34 have completed tertiary education than have women aged 55 to 64. In 21 of 27 OECD countries with comparable data, the number of women graduating from university-level programmes is equal to or exceeds that of men. 15-year-old girls tend to show much higher expectations for their careers than boys of the same age.
While women account for more than half of university graduates in several OECD countries, they receive only 30% of tertiary degrees granted in science and engineering fields, and women account for only 25% to 35% of researchers in most OECD countries.
Research shows that while women are studying at prestigious universities at the same rate as men they are not being given the same chance to join the faculty. Sociologist Harriet Zuckerman has observed that the more prestigious an institute is, the more difficult and time-consuming it will be for women to obtain a faculty position there. In 1989, Harvard University tenured its first woman in chemistry, Cynthia Friend, and in 1992 its first woman in physics, Melissa Franklin. She also observed that women were more likely to hold their first professional positions as instructors and lecturers while men are more likely to work first in tenure positions. According to Smith and Tang, as of 1989, 65% of men and only 40% of women held tenured positions and only 29% of all scientists and engineers employed as assistant professors in four-year colleges and universities were women.
In 1992, women earned 9% of the PhDs awarded in engineering, but only one percent of those women became professors. In 1995, 11% of professors in science and engineering were women. In relation, only 311 deans of engineering schools were women, which is less than 1% of the total. Even in psychology, a degree in which women earn the majority of PhDs, they hold a significant amount of fewer tenured positions, roughly 19% in 1994.

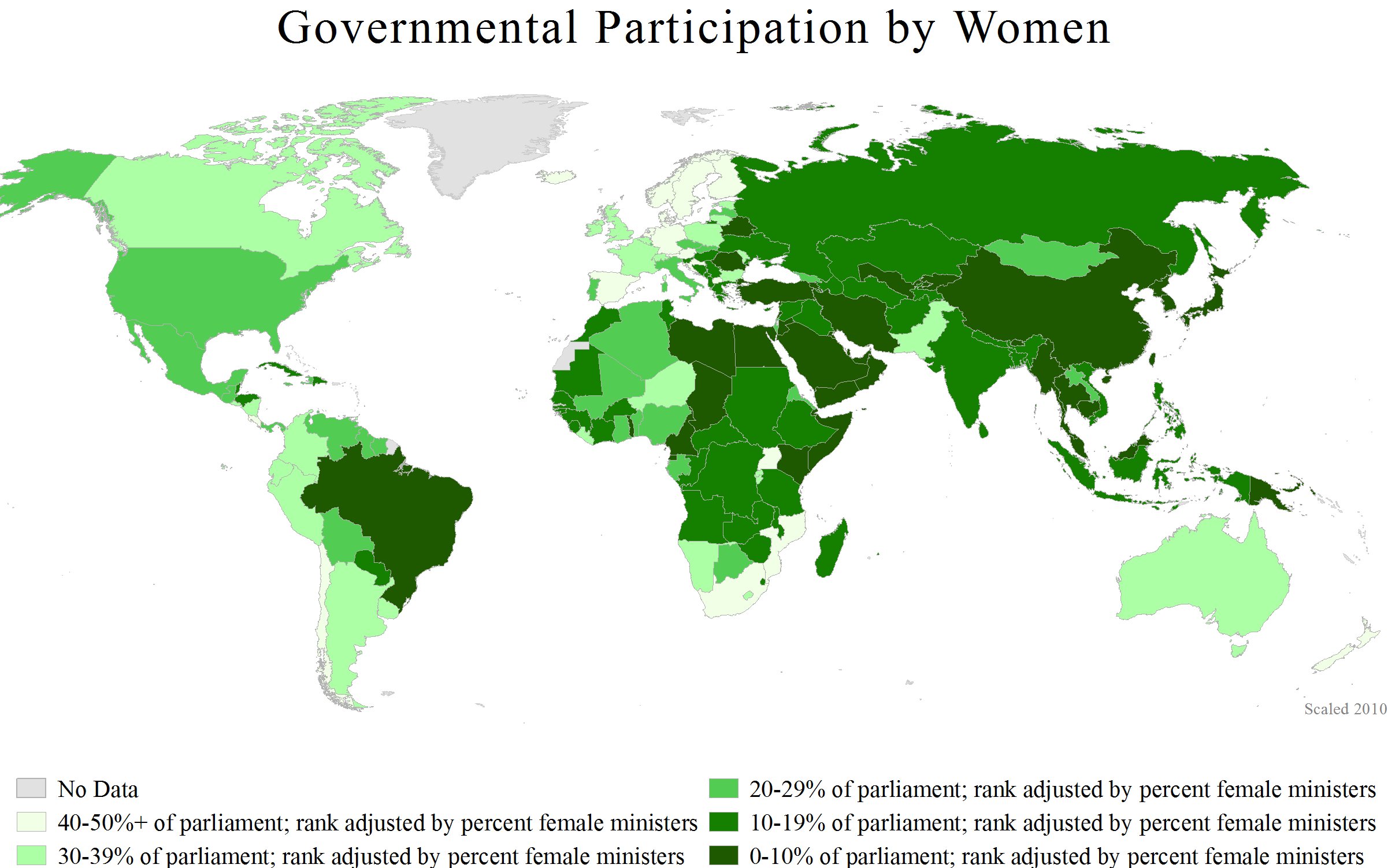 Women are underrepresented in government in most countries. In January 2019, the global average of women in national assemblies was 24.3%. Suffrage is the civil right to vote, and women's suffrage movements have a long Timeline of women's suffrage, historic timeline. For example, women's suffrage in the United States was achieved gradually, first at state and local levels in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, then in 1920 when women in the US received universal suffrage with the passage of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. Some Western countries were slow to allow women to vote, notably Switzerland, where women gained the right to vote in federal elections in 1971, and in the canton of Appenzell Innerrhoden women were granted the right to vote on local issues only in 1991, when the canton was forced to do so by the Federal Supreme Court of Switzerland; and Liechtenstein, in 1984, through Liechtenstein women's suffrage referendum, 1984, a women's suffrage referendum.
Women are underrepresented in government in most countries. In January 2019, the global average of women in national assemblies was 24.3%. Suffrage is the civil right to vote, and women's suffrage movements have a long Timeline of women's suffrage, historic timeline. For example, women's suffrage in the United States was achieved gradually, first at state and local levels in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, then in 1920 when women in the US received universal suffrage with the passage of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. Some Western countries were slow to allow women to vote, notably Switzerland, where women gained the right to vote in federal elections in 1971, and in the canton of Appenzell Innerrhoden women were granted the right to vote on local issues only in 1991, when the canton was forced to do so by the Federal Supreme Court of Switzerland; and Liechtenstein, in 1984, through Liechtenstein women's suffrage referendum, 1984, a women's suffrage referendum.
 Women have, throughout history, made contributions to science, literature and art. One area where women have been permitted most access historically was that of obstetrics and gynecology (prior to the 18th century, caring for pregnant women in Europe was undertaken by women; from the mid 18th century onwards, medical monitoring of pregnant women started to require rigorous formal education, to which women did not generally have access, and thus the practice was largely transferred to men).Gelis, Jacues. History of Childbirth. Boston: Northern University Press, 1991: 96–98
Writing was generally also considered acceptable for upper-class women, although achieving success as a female writer in a male-dominated world could be very difficult; as a result of several women writers adopted a male pen name (e.g. George Sand, George Eliot).
Women have been composers, songwriters, Musician, instrumental performers, singers, Conducting, conductors, musicology, music scholars, music teacher, music educators, music criticism, music critics/music journalists and other musical professions. There are music movements, events and genres related to women, women's rights, women's issues and feminism. In the 2010s, while women comprise a significant proportion of popular music and classical music singers, and a significant proportion of songwriters (many of them being singer-songwriters), there are few women record producers, music journalist, rock critics and rock instrumentalists. Although there have been a huge number of List of women composers, women composers in classical music, from the Medieval period to the present day, women composers are significantly underrepresented in the Western canon, commonly performed classical music repertoire, music history textbooks and music encyclopedias; for example, in the ''Concise Oxford History of Music'', Clara Schumann is one of the only female composers who is mentioned.
Women have, throughout history, made contributions to science, literature and art. One area where women have been permitted most access historically was that of obstetrics and gynecology (prior to the 18th century, caring for pregnant women in Europe was undertaken by women; from the mid 18th century onwards, medical monitoring of pregnant women started to require rigorous formal education, to which women did not generally have access, and thus the practice was largely transferred to men).Gelis, Jacues. History of Childbirth. Boston: Northern University Press, 1991: 96–98
Writing was generally also considered acceptable for upper-class women, although achieving success as a female writer in a male-dominated world could be very difficult; as a result of several women writers adopted a male pen name (e.g. George Sand, George Eliot).
Women have been composers, songwriters, Musician, instrumental performers, singers, Conducting, conductors, musicology, music scholars, music teacher, music educators, music criticism, music critics/music journalists and other musical professions. There are music movements, events and genres related to women, women's rights, women's issues and feminism. In the 2010s, while women comprise a significant proportion of popular music and classical music singers, and a significant proportion of songwriters (many of them being singer-songwriters), there are few women record producers, music journalist, rock critics and rock instrumentalists. Although there have been a huge number of List of women composers, women composers in classical music, from the Medieval period to the present day, women composers are significantly underrepresented in the Western canon, commonly performed classical music repertoire, music history textbooks and music encyclopedias; for example, in the ''Concise Oxford History of Music'', Clara Schumann is one of the only female composers who is mentioned. Women comprise a significant proportion of instrumental soloists in classical music and the percentage of women in orchestras is increasing. A 2015 article on concerto soloists in major Canadian orchestras, however, indicated that 84% of the soloists with the Orchestre Symphonique de Montreal were men. In 2012, women still made up just 6% of the top-ranked Vienna Philharmonic orchestra. Women are less common as instrumental players in popular music genres such as rock and Heavy metal music, heavy metal, although there have been a number of notable female instrumentalists and all-female bands. Women are particularly underrepresented in extreme metal genres. Women are also underrepresented in orchestral conducting, music criticism/music journalism, Music producer, music producing, and sound engineering. While women were discouraged from composing in the 19th century, and there are few women musicology, musicologists, women became involved in music education "... to such a degree that women dominated [this field] during the later half of the 19th century and well into the 20th century."
According to Jessica Duchen, a music writer for London's ''The Independent'', women musicians in classical music are "... too often judged for their appearances, rather than their talent" and they face pressure "... to look sexy onstage and in photos." Duchen states that while "[t]here are women musicians who refuse to play on their looks, ... the ones who do tend to be more materially successful."
According to the UK's Radio 3 editor, Edwina Wolstencroft, the classical music industry has long been open to having women in performance or entertainment roles, but women are much less likely to have positions of authority, such as being the Conducting, leader of an orchestra. In popular music, while there are many women singers recording songs, there are very few women behind the Audio mixer, audio console acting as music producers, the individuals who direct and manage the recording process.
Women comprise a significant proportion of instrumental soloists in classical music and the percentage of women in orchestras is increasing. A 2015 article on concerto soloists in major Canadian orchestras, however, indicated that 84% of the soloists with the Orchestre Symphonique de Montreal were men. In 2012, women still made up just 6% of the top-ranked Vienna Philharmonic orchestra. Women are less common as instrumental players in popular music genres such as rock and Heavy metal music, heavy metal, although there have been a number of notable female instrumentalists and all-female bands. Women are particularly underrepresented in extreme metal genres. Women are also underrepresented in orchestral conducting, music criticism/music journalism, Music producer, music producing, and sound engineering. While women were discouraged from composing in the 19th century, and there are few women musicology, musicologists, women became involved in music education "... to such a degree that women dominated [this field] during the later half of the 19th century and well into the 20th century."
According to Jessica Duchen, a music writer for London's ''The Independent'', women musicians in classical music are "... too often judged for their appearances, rather than their talent" and they face pressure "... to look sexy onstage and in photos." Duchen states that while "[t]here are women musicians who refuse to play on their looks, ... the ones who do tend to be more materially successful."
According to the UK's Radio 3 editor, Edwina Wolstencroft, the classical music industry has long been open to having women in performance or entertainment roles, but women are much less likely to have positions of authority, such as being the Conducting, leader of an orchestra. In popular music, while there are many women singers recording songs, there are very few women behind the Audio mixer, audio console acting as music producers, the individuals who direct and manage the recording process.

Chafe, William H.
, ''The American Woman: Her Changing Social, Economic, And Political Roles, 1920–1970'', Oxford University Press, 1972. * * ''Routledge International Encyclopedia of Women'', 4 vls., ed. by Cheris Kramarae and Dale Spender, Routledge 2000 * ''Women in World History, Women in World History : a biographical encyclopedia'', 17 vls., ed. by Anne Commire, Waterford, Conn. [etc.] : Yorkin Publ. [etc.], 1999–2002
''Woman In all ages and in all countries in 10 volumes''
Illustrated edition deluxe limited to 1,000 numbered copies with an index by Rénald Lévesque
 A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger ...
or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as " women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age.
Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular salpinx), are paired tubes in the human female that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In ot ...
s, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
, broader hip
In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or "coxa"Latin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.
The hip region is ...
s, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscular than men.
Throughout human history
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied throug ...
, traditional gender roles have often defined and limited women's activities and opportunities; many religious doctrines stipulate certain rules for women. With restrictions loosening during the 20th century in many societies, women have gained access to careers beyond the traditional homemaker, and the ability to pursue higher education. Violence against women, whether within families or in communities, has a long history and is primarily committed by men. Some women are denied reproductive rights. The movements and ideologies of feminism have a shared goal of achieving gender equality.
Trans women have a gender identity that does not align with their male sex assignment
Sex assignment (sometimes known as gender assignment) is the discernment of an infant's sex at or before birth. A relative, midwife, nurse or physician inspects the external genitalia when the baby is delivered and, in more than 99.95% of birt ...
at birth, while intersex women may have sex characteristics that do not fit typical notions of female biology.
Etymology
The spelling of "woman" in English has progressed over the past millennium from ''wīfmann'' to ''wīmmann'' to ''wumman'', and finally, the modern spelling ''woman''. InOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
, ''wīfmann'' meant "woman" (literally "woman-person"), whereas ''wer'' meant "man". ''Mann'' had a gender-neutral meaning of "human", corresponding to Modern English "person" or "someone"; however, subsequent to the Norman Conquest, ''man'' began to be used more in reference to "male human", and by the late 13th century it had begun to eclipse usage of the older term ''wer''. The medial labial consonants f and m in ''wīfmann'' coalesced into the modern form "woman", while the initial element ''wīf'', which had also meant "woman", underwent semantic narrowing to the sense of a married woman ("wife").
It is a popular misconception
Each entry on this list of common misconceptions is worded as a correction; the misconceptions themselves are implied rather than stated. These entries are concise summaries of the main subject articles, which can be consulted for more detail.
...
that the term "woman" is Etymology, etymologically connected to "womb". "Womb" derives from the Old English word ''wamb'' meaning "belly, uterus" (cognate to the modern German colloquial term ":wikt:Wamme, Wamme" from Old High German ''wamba'' for "belly, paunch, lap").
Terminology
Womanhood is the period in a human female's life after she has passed through childhood, puberty, and adolescence. Different countries have different laws, but age 18 is frequently considered the age of majority (the age at which a person is legally considered an adult). The word ''woman'' can be used generally, to mean any female human, or specifically, to mean an adult female human as contrasted with ''girl''. The word ''girl'' originally meant "young person of either sex" in English; it was only around the beginning of the 16th century that it came to mean specifically a ''female'' child. The term ''girl'' is sometimes used colloquially to refer to a young or unmarried woman; however, during the early 1970s, feminists challenged such use because the use of the word to refer to a fully grown woman may cause offence. In particular, previously common terms such as ''office girl'' are no longer widely used. Conversely, in certain cultures which link family honor with female virginity, the word ''girl'' (or its equivalent in other languages) is still used to refer to a never-married woman; in this sense it is used in a fashion roughly analogous to the more-or-less obsolete English ''maid'' or ''maiden''. There are various words used to refer to the quality of being a woman. The term "womanhood" merely means the state of being a woman; "femininity" is used to refer to a set of typical female qualities associated with a certain attitude to gender roles; "womanliness" is like "femininity", but is usually associated with a different view of gender roles. "Distaff" is an archaic adjective derived from women's conventional role as a spinner, now used only as a deliberate archaism. Menarche, the onset of menstruation, occurs on average at age 12–13. Many cultures have rites of passage to symbolize a girl's coming of age, such as confirmation in some branches of Christianity, bat mitzvah in Judaism, or a custom of a special celebration for a certain birthday (generally between 12 and 21), like the quinceañera of Latin America. Trans women had a malesex assignment
Sex assignment (sometimes known as gender assignment) is the discernment of an infant's sex at or before birth. A relative, midwife, nurse or physician inspects the external genitalia when the baby is delivered and, in more than 99.95% of birt ...
at birth that does not align with their gender identity, while intersex women may have sex characteristics that do not fit typical notions of female biology. In 2020, Merriam-Webster kept their definition of ''woman'' in terms of being "adult" and "female", but added a definition of ''female'', of having a gender identity opposite of male. In 2022, the Cambridge Dictionary updated its definition of ''woman'' to explictly include anyone whose gender identity is female.
Biology
Genetic characteristics
Typically, the cells of female humans contain two X chromosomes, while the cells of male humans have an X and a Y chromosome. During Human fertilization, early fetal development, all embryos have phenotypically female genitalia up until week 6 or 7, when a male embryo's gonads differentiate into testes due to the action of the SRY gene on the Y chromosome. Sex differentiation proceeds in female humans in a way that is independent of gonadal hormones. Because humans inherit mitochondrial DNA only from the mother's ovum, Genetic genealogy, genealogical researchers can trace Matrilineality, maternal lineage far back in time.Hormonal characteristics, menstruation and menopause
Female puberty triggers bodily changes that enable sexual reproduction via fertilisation, fertilization. In response to chemical signals from the pituitary gland, the ovaries secrete hormones that stimulate maturation of the body, including increased height and weight, body hair growth, breast development and menarche (the onset of menstruation). Most girls go through menarche between ages 12–13, and are then capable of becoming pregnant and childbirth, bearing children. Pregnancy generally requires Insemination, internal fertilization of the eggs with Spermatozoon, sperm, via either sexual intercourse or artificial insemination, though in vitro fertilization allows fertilization to occur outside the human body. Humans are similar to other large mammals in that they usually give birth to a single offspring per pregnancy, but are unusual in being Precociality and altriciality, altricial compared to most other large mammals, meaning young are Child development, undeveloped at time of birth and require the aid of their parents or guardians to fully mature. Sometimes humans have multiple births, most commonly twins. Usually between ages 49–52, a woman reaches menopause, the time when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Unlike most other mammals, the human lifespan usually extends many years after menopause. Many women become Grandparent, grandmothers and contribute to the care of grandchildren and other family members. Many biologists believe that the extended human lifespan is evolutionarily driven by kin selection, though other theories have also been proposed.Morphological and physiological characteristics
In terms of biology, the female sex organs are involved in the reproductive system, whereas the secondary sex characteristics are involved in breastfeeding children and attracting a mate. Humans are placental mammals, which means the mother carries the fetus in the uterus and the placenta facilitates the exchange of nutrients and waste between the mother and fetus. The ovaries, in addition to their regulatory function of producing hormones, produce female gametes called ovum, ova which, when fertilization, fertilized by male gametes (spermatozoon, sperm), form new genetic individuals. The uterus is an organ with tissue to protect and nurture the developing fetus and muscle to expel it when giving birth. The vagina is used in copulation and birthing, although the term ''vagina'' is often colloquially and incorrectly used in the English language for the vulva (or external female genitalia), which consists of (in addition to the vaginal opening) the labia (genitalia), labia, the clitoris, and the female urethra. The mammary glands are hypothesized to have evolved from apocrine-like glands to produce milk, a nutritious secretion that is the most distinctive characteristic of mammals, along with live birth. In mature women, the breast is generally more prominent than in most other mammals; this prominence, not necessary for milk production, is thought to be at least partially the result of sexual selection. Estrogens, which are primary female sex hormones, have a significant impact on a female's body shape. They are produced in both men and women, but their levels are significantly higher in women, especially in those of reproductive age. Besides other functions, estrogens promote the development of female secondary sexual characteristics, such as breasts andhip
In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or "coxa"Latin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.
The hip region is ...
s. As a result of estrogens, during puberty, girls develop breasts and their hips widen. Working against estrogen, the presence of testosterone in a pubescent female inhibits breast development and promotes muscle and facial hair development.

Gender distribution and life expectancy
 Although girls are born slightly less frequently than boys (the ratio is around 1:1.05), newborn girls are more likely to reach their first birthday than are boys, and women typically have a longer life expectancy by six to eight years, although in some areas discrimination against women has lowered female life expectancy to less than or equal to that of men. Out of the total human population in 2015, there were 1018 men for every 1000 women. The differences in life expectancy are partly due to inherent biological advantages, but also reflect behavioral differences between men and women. The gap is narrowing to some extent in some developed countries, possibly due to increased smoking among women and declining rates of cardiovascular disease among men. The World Health Organization (WHO) writes that it is "important to note that the extra years of life for women are not always lived in good health."
Although girls are born slightly less frequently than boys (the ratio is around 1:1.05), newborn girls are more likely to reach their first birthday than are boys, and women typically have a longer life expectancy by six to eight years, although in some areas discrimination against women has lowered female life expectancy to less than or equal to that of men. Out of the total human population in 2015, there were 1018 men for every 1000 women. The differences in life expectancy are partly due to inherent biological advantages, but also reflect behavioral differences between men and women. The gap is narrowing to some extent in some developed countries, possibly due to increased smoking among women and declining rates of cardiovascular disease among men. The World Health Organization (WHO) writes that it is "important to note that the extra years of life for women are not always lived in good health."
Health
Factors that specifically affect the health of women vs. men's health, men are most evident in those related to reproductive health, reproduction, but sex differences in medicine, sex differences have been identified from the molecular to the behavioral scale. Some of these differences are subtle and difficult to explain, partly due to the fact that it is difficult to separate the health effects of inherent biological factors from the effects of the surrounding environment they exist in. Sex chromosomes and hormones, as well as sex-specific lifestyles, metabolism, immune system function, and sensitivity to environmental factors are believed to contribute to sex differences in health at the levels of physiology, perception, and cognition. Women can have distinct responses to drugs and thresholds for diagnostic parameters. Some diseases primarily affect or are exclusively found in women, such as lupus erythematosus, lupus, breast cancer, cervical cancer, or ovarian cancer. The medical practice dealing with female reproduction and reproductive organs is called gynaecology ("science of women").Maternal mortality
 Maternal mortality or maternal death is defined by WHO as "the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes." In 2008, noting that each year more than 500,000 women die of complications of pregnancy and childbirth and at least seven million experience serious health problems while 50 million more have adverse health consequences after childbirth, the World Health Organization urged midwife training to strengthen maternal and newborn health services. To support the upgrading of midwifery skills the WHO established a midwife training program, Action for Safe Motherhood.
In 2017, 94% of maternal deaths occur in low and lower middle-income countries. Approximately 86% of maternal deaths occur in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, with sub-Saharan Africa accounting for around 66% and Southern Asia accounting for around 20%. The main causes of maternal mortality include pre-eclampsia and eclampsia, unsafe abortion, pregnancy complications from malaria and HIV/AIDS, and severe bleeding and infections following childbirth. Most European countries, Australia, Japan, and Singapore are very safe in regard to childbirth.
In 1990, the US ranked 12th of the 14 developed countries that were analyzed and since that time the death rates of every country have steadily improved while the US rate has spiked dramatically. While the others that were analyzed in 1990 show a 2017 death rate of fewer than 10 deaths per every 100,000 live births, the U.S. rate rose to 26.4. Furthermore, for every one of the 700 to 900 women who die in the U.S. each year during pregnancy or childbirth, 70 experience significant complications, totaling more than one percent of all births.
Maternal mortality or maternal death is defined by WHO as "the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes." In 2008, noting that each year more than 500,000 women die of complications of pregnancy and childbirth and at least seven million experience serious health problems while 50 million more have adverse health consequences after childbirth, the World Health Organization urged midwife training to strengthen maternal and newborn health services. To support the upgrading of midwifery skills the WHO established a midwife training program, Action for Safe Motherhood.
In 2017, 94% of maternal deaths occur in low and lower middle-income countries. Approximately 86% of maternal deaths occur in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, with sub-Saharan Africa accounting for around 66% and Southern Asia accounting for around 20%. The main causes of maternal mortality include pre-eclampsia and eclampsia, unsafe abortion, pregnancy complications from malaria and HIV/AIDS, and severe bleeding and infections following childbirth. Most European countries, Australia, Japan, and Singapore are very safe in regard to childbirth.
In 1990, the US ranked 12th of the 14 developed countries that were analyzed and since that time the death rates of every country have steadily improved while the US rate has spiked dramatically. While the others that were analyzed in 1990 show a 2017 death rate of fewer than 10 deaths per every 100,000 live births, the U.S. rate rose to 26.4. Furthermore, for every one of the 700 to 900 women who die in the U.S. each year during pregnancy or childbirth, 70 experience significant complications, totaling more than one percent of all births.
Reproductive rights and freedom
 Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to human reproduction, reproduction and reproductive health. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics has stated that:
:... the human rights of women include their right to have control over and decide freely and responsibly on matters related to their sexuality, including sexual and reproductive health, free of coercion, discrimination and violence. Equal relationships between women and men in matters of sexual relations and reproduction, including full respect for the integrity of the person, require mutual respect, consent and shared responsibility for sexual behavior and its consequences.
The World Health Organization reports that based on data from 2010 to 2014, 56 million induced abortions occurred worldwide each year (25% of all pregnancies). Of those, about 25 million were considered as Unsafe abortions, unsafe. The WHO reports that in developed regions about 30 women die for every 100,000 unsafe abortions and that number rises to 220 deaths per 100,000 unsafe abortions in developing regions and 520 deaths per 100,000 unsafe abortions in sub-Saharan Africa. The WHO ascribes these deaths to:
*restrictive laws
*poor availability of services
*high cost
*stigma
*conscientious objection of health-care providers
*unnecessary requirements, such as mandatory waiting periods, mandatory counselling, provision of misleading information, third-party authorization, and medically unnecessary tests that delay care.
Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to human reproduction, reproduction and reproductive health. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics has stated that:
:... the human rights of women include their right to have control over and decide freely and responsibly on matters related to their sexuality, including sexual and reproductive health, free of coercion, discrimination and violence. Equal relationships between women and men in matters of sexual relations and reproduction, including full respect for the integrity of the person, require mutual respect, consent and shared responsibility for sexual behavior and its consequences.
The World Health Organization reports that based on data from 2010 to 2014, 56 million induced abortions occurred worldwide each year (25% of all pregnancies). Of those, about 25 million were considered as Unsafe abortions, unsafe. The WHO reports that in developed regions about 30 women die for every 100,000 unsafe abortions and that number rises to 220 deaths per 100,000 unsafe abortions in developing regions and 520 deaths per 100,000 unsafe abortions in sub-Saharan Africa. The WHO ascribes these deaths to:
*restrictive laws
*poor availability of services
*high cost
*stigma
*conscientious objection of health-care providers
*unnecessary requirements, such as mandatory waiting periods, mandatory counselling, provision of misleading information, third-party authorization, and medically unnecessary tests that delay care.
Culture and gender roles
In recent history, gender roles have changed greatly. At some earlier points in history, children's occupational aspirations starting at a young age differed according to gender. Traditionally, middle class women were involved in domestic tasks emphasizing child care. For poorer women, especially working class women, although this often remained an ideal, economic necessity compelled them to seek employment outside the home. Many of the occupations that were available to them were lower in pay than those available to men. As changes in the labor market for women came about, availability of employment changed from only "dirty", long hour factory jobs to "cleaner", more respectable office jobs where more education was demanded. Women's participation in the U.S. labor force rose from 6% in 1900 to 23% in 1923. These shifts in the labor force led to changes in the attitudes towards women at work, allowing for the revolution which resulted in women becoming career and education oriented. In the 1970s, many female academics, including scientists, avoided having children. Throughout the 1980s, institutions tried to equalize conditions for men and women in the workplace. Even so, the inequalities at home hampered women's opportunities: professional women were still generally considered responsible for domestic labor and child care, which limited the time and energy they could devote to their careers. Until the early 20th century, U.S. women's colleges required their women faculty members to remain single, on the grounds that a woman could not carry on two full-time professions at once. According to Schiebinger, "Being a scientist and a wife and a mother is a burden in society that expects women more often than men to put family ahead of career." (p. 93). Movements advocate equality of opportunity for both sexes and civil rights, equal rights irrespective of gender. Through a combination of economics, economic changes and the efforts of the feminist movement, in recent decades women in many societies have gained access to careers beyond the traditional homemaker. Despite these advances, modern women in Western society still face challenges in the workplace as well as with the topics of education, violence, health care, politics, and motherhood, and others. Sexism can be a main concern and barrier for women almost anywhere, though its forms, perception, and gravity vary between societies and social classes. There has been an increase in the endorsement of egalitarian gender roles in the home by both women and men. Although a greater number of women are seeking higher education, their salaries are often less than those of men. CBS News said in 2005 that in the United States women who are ages 30 to 44 and hold a university degree make 62% of what similarly qualified men do, a lower rate than in all but three of the 19 countries for which numbers are available. Some Western nations with greater inequality in pay are Germany, New Zealand and Switzerland.Violence against women
 The United Nations, UN Declaration on the Elimination of Violence against Women defines "violence against women" as:
It identifies three forms of such violence: that which occurs ''in the family'', that which occurs ''within the general community'', and that which is perpetrated or condoned ''by the State''. It also states that "violence against women is a manifestation of historically unequal power relations between men and women".
Violence against women remains a widespread problem, fueled, especially outside the West, by patriarchal social values, lack of adequate laws, and lack of enforcement of existing laws. Social norms that exist in many parts of the world hinder progress towards protecting women from violence. For example, according to surveys by UNICEF, the percentage of women aged 15–49 who think that a husband is justified in hitting or beating his wife under certain circumstances is as high as 90% in Afghanistan and Jordan, 87% in Mali, 86% in Guinea and Timor-Leste, 81% in Laos, and 80% in the Central African Republic. A 2010 survey conducted by the Pew Research Center found that stoning as a punishment for adultery was supported by 82% of respondents in Egypt and Pakistan, 70% in Jordan, 56% Nigeria, and 42% in Indonesia.
Specific forms of violence that affect women include female genital mutilation, sex trafficking, forced prostitution, forced marriage, rape, sexual harassment, honor killings, acid throwing, and dowry death, dowry related violence. Governments can be complicit in violence against women, such as when stoning is used as a legal punishment, mostly for women accused of adultery.
There have also been many forms of violence against women which have been prevalent historically, notably the Witch-hunt, burning of witches, the sacrifice of widows (such as Sati (practice), sati) and foot binding. The prosecution of women accused of witchcraft has a long tradition; for example, during the early modern period (between the 15th and 18th centuries), witch trials in the early modern period, witch trials were common in Europe and in the European colonies in North America. Today, there remain regions of the world (such as parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, rural North India, and Papua New Guinea) where belief in witchcraft is held by many people, and women accused of being witches are subjected to serious violence. In addition, there are also countries which have criminal legislation against the practice of witchcraft. In Saudi Arabia, witchcraft remains a crime punishable by death, and in 2011 the country beheaded a woman for 'witchcraft and sorcery'.
It is also the case that certain forms of violence against women have been recognized as criminal offenses only during recent decades, and are not universally prohibited, in that many countries continue to allow them. This is especially the case with marital rape. In the Western World, there has been a trend towards ensuring gender equality within marriage and prosecuting domestic violence, but in many parts of the world women still lose significant legal rights when entering a marriage.
Sexual violence against women greatly increases during times of war and armed conflict, during military occupation, or ethnic conflicts; most often in the form of war rape and sexual slavery. Contemporary examples of sexual violence during war include rape during the Armenian Genocide, rape during the Bangladesh Liberation War, rape in the Bosnian War, rape during the Rwandan genocide, and War rape#Democratic Republic of the Congo, rape during Second Congo War. In Colombia, the armed conflict has also resulted in increased sexual violence against women. The most recent case was the sexual jihad done by ISIL where 5000–7000 Yazidi and Christian girls and children were sold into sexual slavery during the Sexual violence in the Iraqi insurgency, genocide and rape of Yazidi and Christian women, some of whom jumped to their death from Mount Sinjar, as described in a witness statement.
Laws and policies on violence against women vary by jurisdiction. In the European Union, sexual harassment and human trafficking are subject to Directive (European Union), directives.
The United Nations, UN Declaration on the Elimination of Violence against Women defines "violence against women" as:
It identifies three forms of such violence: that which occurs ''in the family'', that which occurs ''within the general community'', and that which is perpetrated or condoned ''by the State''. It also states that "violence against women is a manifestation of historically unequal power relations between men and women".
Violence against women remains a widespread problem, fueled, especially outside the West, by patriarchal social values, lack of adequate laws, and lack of enforcement of existing laws. Social norms that exist in many parts of the world hinder progress towards protecting women from violence. For example, according to surveys by UNICEF, the percentage of women aged 15–49 who think that a husband is justified in hitting or beating his wife under certain circumstances is as high as 90% in Afghanistan and Jordan, 87% in Mali, 86% in Guinea and Timor-Leste, 81% in Laos, and 80% in the Central African Republic. A 2010 survey conducted by the Pew Research Center found that stoning as a punishment for adultery was supported by 82% of respondents in Egypt and Pakistan, 70% in Jordan, 56% Nigeria, and 42% in Indonesia.
Specific forms of violence that affect women include female genital mutilation, sex trafficking, forced prostitution, forced marriage, rape, sexual harassment, honor killings, acid throwing, and dowry death, dowry related violence. Governments can be complicit in violence against women, such as when stoning is used as a legal punishment, mostly for women accused of adultery.
There have also been many forms of violence against women which have been prevalent historically, notably the Witch-hunt, burning of witches, the sacrifice of widows (such as Sati (practice), sati) and foot binding. The prosecution of women accused of witchcraft has a long tradition; for example, during the early modern period (between the 15th and 18th centuries), witch trials in the early modern period, witch trials were common in Europe and in the European colonies in North America. Today, there remain regions of the world (such as parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, rural North India, and Papua New Guinea) where belief in witchcraft is held by many people, and women accused of being witches are subjected to serious violence. In addition, there are also countries which have criminal legislation against the practice of witchcraft. In Saudi Arabia, witchcraft remains a crime punishable by death, and in 2011 the country beheaded a woman for 'witchcraft and sorcery'.
It is also the case that certain forms of violence against women have been recognized as criminal offenses only during recent decades, and are not universally prohibited, in that many countries continue to allow them. This is especially the case with marital rape. In the Western World, there has been a trend towards ensuring gender equality within marriage and prosecuting domestic violence, but in many parts of the world women still lose significant legal rights when entering a marriage.
Sexual violence against women greatly increases during times of war and armed conflict, during military occupation, or ethnic conflicts; most often in the form of war rape and sexual slavery. Contemporary examples of sexual violence during war include rape during the Armenian Genocide, rape during the Bangladesh Liberation War, rape in the Bosnian War, rape during the Rwandan genocide, and War rape#Democratic Republic of the Congo, rape during Second Congo War. In Colombia, the armed conflict has also resulted in increased sexual violence against women. The most recent case was the sexual jihad done by ISIL where 5000–7000 Yazidi and Christian girls and children were sold into sexual slavery during the Sexual violence in the Iraqi insurgency, genocide and rape of Yazidi and Christian women, some of whom jumped to their death from Mount Sinjar, as described in a witness statement.
Laws and policies on violence against women vary by jurisdiction. In the European Union, sexual harassment and human trafficking are subject to Directive (European Union), directives.
History
The earliest women whose names are known include: * Neithhotep (c. 3200 BCE), the wife of Narmer and the first queen of ancient Egypt. * Merneith (c. 3000 BCE), Queen consort, consort and regent of ancient Egypt during the First Dynasty of Egypt, first dynasty. She may have been ruler of Egypt in her own right. * Peseshet (c. 2600 BCE), a physician in Ancient Egypt. * Puabi (c. 2600 BCE), or Shubad – queen of Ur whose tomb was discovered with many expensive artifacts. Other known pre-Sargonic queens of Ur (royal wives) include Ashusikildigir, Ninbanda, and Gansamannu. * Kubaba, Kugbau (''circa'' 2,500 BCE), a taverness from Kish (Sumer), Kish chosen by the Nippur priesthood to become hegemonic ruler of Sumer, and in later ages deified as "Kubaba". * Tashlultum (c. 2400 BCE), Akkadian Empire, Akkadian queen, wife of Sargon of Akkad and mother of Enheduanna. * Baranamtarra (c. 2384 BCE), prominent and influential queen of Lugalanda of Lagash. Other known pre-Sargonic queens of the first Lagash dynasty include Menbara-abzu, Ashume'eren, Ninkhilisug, Dimtur, and Shagshag, and the names of several princesses are also known. * Enheduanna (c. 2285 BCE), the Ordination of women#Sumer and Akkad, high priestess of the temple of the Sin (mythology), Moon God in the Sumerian city-state of Ur and possibly the first known poet and first named author of either gender. * Shibtu (c. 1775 BCE), king Zimrilim's consort and queen of the Syrian city-state of Mari, Syria, Mari. During her husband's absence, she ruled as regent of Mari and enjoyed extensive administrative powers as queen.Clothing, fashion and dress codes
Women in different parts of the world dress in different ways, with their choices of clothing being influenced by local culture, religious tenets, traditions, social norms, and fashion trends, amongst other factors. Different societies have different ideas about modesty. However, in many jurisdictions, women's choices in regard to dress are not always free, with laws limiting what they may or may not wear. This is especially the case in regard to Islam and clothing, Islamic dress. While certain jurisdictions legally mandate such clothing (the wearing of the headscarf), other countries forbid or restrict the wearing of certain hijab attire (such as burqa/covering the face) in public places (one such country is France – see French ban on face covering). These laws – both those mandating and those prohibiting certain articles of dress – are highly controversial.Fertility and family life

 The total fertility rate (TFR) – the average number of children born to a woman over her lifetime – differs significantly between different regions of the world. In 2016, the highest estimated TFR was in Niger (6.62 children born per woman) and the lowest in Singapore (0.82 children/woman). While most Sub-Saharan African countries have a high TFR, which creates problems due to lack of resources and contributes to overpopulation, most Western countries currently experience a sub replacement fertility rate which may lead to population ageing and population decline.
In many parts of the world, there has been a change in family structure over the past few decades. For instance, in the West, there has been a trend of moving away from living arrangements that include the extended family to those which only consist of the nuclear family. There has also been a trend to move from marital fertility to non-marital fertility. Children born outside marriage may be born to cohabitation, cohabiting couples or to single parent, single women. While births outside marriage are common and fully accepted in some parts of the world, in other places they are highly stigmatized, with unmarried mothers facing ostracism, including violence from family members, and in extreme cases even honor killings. In addition, sex outside marriage remains illegal in many countries (such as Saudi Arabia, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Iran, Kuwait, Maldives, Morocco, Oman, Mauritania, United Arab Emirates, Sudan, and Yemen).
The social role of the mother differs between cultures. In many parts of the world, women with dependent children are expected to stay at home and dedicate all their energy to child raising, while in other places mothers most often return to paid work (see Working parent, working mother and Housewife, stay-at-home mother).
The total fertility rate (TFR) – the average number of children born to a woman over her lifetime – differs significantly between different regions of the world. In 2016, the highest estimated TFR was in Niger (6.62 children born per woman) and the lowest in Singapore (0.82 children/woman). While most Sub-Saharan African countries have a high TFR, which creates problems due to lack of resources and contributes to overpopulation, most Western countries currently experience a sub replacement fertility rate which may lead to population ageing and population decline.
In many parts of the world, there has been a change in family structure over the past few decades. For instance, in the West, there has been a trend of moving away from living arrangements that include the extended family to those which only consist of the nuclear family. There has also been a trend to move from marital fertility to non-marital fertility. Children born outside marriage may be born to cohabitation, cohabiting couples or to single parent, single women. While births outside marriage are common and fully accepted in some parts of the world, in other places they are highly stigmatized, with unmarried mothers facing ostracism, including violence from family members, and in extreme cases even honor killings. In addition, sex outside marriage remains illegal in many countries (such as Saudi Arabia, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Iran, Kuwait, Maldives, Morocco, Oman, Mauritania, United Arab Emirates, Sudan, and Yemen).
The social role of the mother differs between cultures. In many parts of the world, women with dependent children are expected to stay at home and dedicate all their energy to child raising, while in other places mothers most often return to paid work (see Working parent, working mother and Housewife, stay-at-home mother).
Religion
Particular religious doctrines have specific stipulations relating to gender roles, social and private interaction between the sexes, appropriate dressing attire for women, and various other issues affecting women and their position in society. In many countries, these religious teachings influence the criminal law, or the family law of those jurisdictions (see Sharia law, for example). The relation between religion, law and gender equality has been discussed by international organizations.Education
 Single-sex education has traditionally been dominant and is still highly relevant. Universal education, meaning state-provided primary and secondary education independent of gender, is not yet a global norm, even if it is assumed in most developed countries. In some Western countries, women have surpassed men at many levels of education. For example, in the United States in 2005/2006, women earned 62% of associate degrees, 58% of bachelor's degrees, 60% of master's degrees, and 50% of doctorates.
The educational Sex ratio, gender gap in Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries has been reduced over the last 30 years. Younger women today are far more likely to have completed a tertiary qualification: in 19 of the 30 OECD countries, more than twice as many women aged 25 to 34 have completed tertiary education than have women aged 55 to 64. In 21 of 27 OECD countries with comparable data, the number of women graduating from university-level programmes is equal to or exceeds that of men. 15-year-old girls tend to show much higher expectations for their careers than boys of the same age.
While women account for more than half of university graduates in several OECD countries, they receive only 30% of tertiary degrees granted in science and engineering fields, and women account for only 25% to 35% of researchers in most OECD countries.
Research shows that while women are studying at prestigious universities at the same rate as men they are not being given the same chance to join the faculty. Sociologist Harriet Zuckerman has observed that the more prestigious an institute is, the more difficult and time-consuming it will be for women to obtain a faculty position there. In 1989, Harvard University tenured its first woman in chemistry, Cynthia Friend, and in 1992 its first woman in physics, Melissa Franklin. She also observed that women were more likely to hold their first professional positions as instructors and lecturers while men are more likely to work first in tenure positions. According to Smith and Tang, as of 1989, 65% of men and only 40% of women held tenured positions and only 29% of all scientists and engineers employed as assistant professors in four-year colleges and universities were women.
In 1992, women earned 9% of the PhDs awarded in engineering, but only one percent of those women became professors. In 1995, 11% of professors in science and engineering were women. In relation, only 311 deans of engineering schools were women, which is less than 1% of the total. Even in psychology, a degree in which women earn the majority of PhDs, they hold a significant amount of fewer tenured positions, roughly 19% in 1994.
Single-sex education has traditionally been dominant and is still highly relevant. Universal education, meaning state-provided primary and secondary education independent of gender, is not yet a global norm, even if it is assumed in most developed countries. In some Western countries, women have surpassed men at many levels of education. For example, in the United States in 2005/2006, women earned 62% of associate degrees, 58% of bachelor's degrees, 60% of master's degrees, and 50% of doctorates.
The educational Sex ratio, gender gap in Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries has been reduced over the last 30 years. Younger women today are far more likely to have completed a tertiary qualification: in 19 of the 30 OECD countries, more than twice as many women aged 25 to 34 have completed tertiary education than have women aged 55 to 64. In 21 of 27 OECD countries with comparable data, the number of women graduating from university-level programmes is equal to or exceeds that of men. 15-year-old girls tend to show much higher expectations for their careers than boys of the same age.
While women account for more than half of university graduates in several OECD countries, they receive only 30% of tertiary degrees granted in science and engineering fields, and women account for only 25% to 35% of researchers in most OECD countries.
Research shows that while women are studying at prestigious universities at the same rate as men they are not being given the same chance to join the faculty. Sociologist Harriet Zuckerman has observed that the more prestigious an institute is, the more difficult and time-consuming it will be for women to obtain a faculty position there. In 1989, Harvard University tenured its first woman in chemistry, Cynthia Friend, and in 1992 its first woman in physics, Melissa Franklin. She also observed that women were more likely to hold their first professional positions as instructors and lecturers while men are more likely to work first in tenure positions. According to Smith and Tang, as of 1989, 65% of men and only 40% of women held tenured positions and only 29% of all scientists and engineers employed as assistant professors in four-year colleges and universities were women.
In 1992, women earned 9% of the PhDs awarded in engineering, but only one percent of those women became professors. In 1995, 11% of professors in science and engineering were women. In relation, only 311 deans of engineering schools were women, which is less than 1% of the total. Even in psychology, a degree in which women earn the majority of PhDs, they hold a significant amount of fewer tenured positions, roughly 19% in 1994.
Literacy
World literacy is lower for women than for men. The CIA World Factbook presents an estimate from 2010 which shows that 80% of women are literate, compared to 88.6% of men (aged 15 and over). Literacy rates are lowest in South and West Asia, and in parts of Sub-Saharan Africa.Women in politics
 Women are underrepresented in government in most countries. In January 2019, the global average of women in national assemblies was 24.3%. Suffrage is the civil right to vote, and women's suffrage movements have a long Timeline of women's suffrage, historic timeline. For example, women's suffrage in the United States was achieved gradually, first at state and local levels in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, then in 1920 when women in the US received universal suffrage with the passage of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. Some Western countries were slow to allow women to vote, notably Switzerland, where women gained the right to vote in federal elections in 1971, and in the canton of Appenzell Innerrhoden women were granted the right to vote on local issues only in 1991, when the canton was forced to do so by the Federal Supreme Court of Switzerland; and Liechtenstein, in 1984, through Liechtenstein women's suffrage referendum, 1984, a women's suffrage referendum.
Women are underrepresented in government in most countries. In January 2019, the global average of women in national assemblies was 24.3%. Suffrage is the civil right to vote, and women's suffrage movements have a long Timeline of women's suffrage, historic timeline. For example, women's suffrage in the United States was achieved gradually, first at state and local levels in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, then in 1920 when women in the US received universal suffrage with the passage of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. Some Western countries were slow to allow women to vote, notably Switzerland, where women gained the right to vote in federal elections in 1971, and in the canton of Appenzell Innerrhoden women were granted the right to vote on local issues only in 1991, when the canton was forced to do so by the Federal Supreme Court of Switzerland; and Liechtenstein, in 1984, through Liechtenstein women's suffrage referendum, 1984, a women's suffrage referendum.
Science, literature and art
 Women have, throughout history, made contributions to science, literature and art. One area where women have been permitted most access historically was that of obstetrics and gynecology (prior to the 18th century, caring for pregnant women in Europe was undertaken by women; from the mid 18th century onwards, medical monitoring of pregnant women started to require rigorous formal education, to which women did not generally have access, and thus the practice was largely transferred to men).Gelis, Jacues. History of Childbirth. Boston: Northern University Press, 1991: 96–98
Writing was generally also considered acceptable for upper-class women, although achieving success as a female writer in a male-dominated world could be very difficult; as a result of several women writers adopted a male pen name (e.g. George Sand, George Eliot).
Women have been composers, songwriters, Musician, instrumental performers, singers, Conducting, conductors, musicology, music scholars, music teacher, music educators, music criticism, music critics/music journalists and other musical professions. There are music movements, events and genres related to women, women's rights, women's issues and feminism. In the 2010s, while women comprise a significant proportion of popular music and classical music singers, and a significant proportion of songwriters (many of them being singer-songwriters), there are few women record producers, music journalist, rock critics and rock instrumentalists. Although there have been a huge number of List of women composers, women composers in classical music, from the Medieval period to the present day, women composers are significantly underrepresented in the Western canon, commonly performed classical music repertoire, music history textbooks and music encyclopedias; for example, in the ''Concise Oxford History of Music'', Clara Schumann is one of the only female composers who is mentioned.
Women have, throughout history, made contributions to science, literature and art. One area where women have been permitted most access historically was that of obstetrics and gynecology (prior to the 18th century, caring for pregnant women in Europe was undertaken by women; from the mid 18th century onwards, medical monitoring of pregnant women started to require rigorous formal education, to which women did not generally have access, and thus the practice was largely transferred to men).Gelis, Jacues. History of Childbirth. Boston: Northern University Press, 1991: 96–98
Writing was generally also considered acceptable for upper-class women, although achieving success as a female writer in a male-dominated world could be very difficult; as a result of several women writers adopted a male pen name (e.g. George Sand, George Eliot).
Women have been composers, songwriters, Musician, instrumental performers, singers, Conducting, conductors, musicology, music scholars, music teacher, music educators, music criticism, music critics/music journalists and other musical professions. There are music movements, events and genres related to women, women's rights, women's issues and feminism. In the 2010s, while women comprise a significant proportion of popular music and classical music singers, and a significant proportion of songwriters (many of them being singer-songwriters), there are few women record producers, music journalist, rock critics and rock instrumentalists. Although there have been a huge number of List of women composers, women composers in classical music, from the Medieval period to the present day, women composers are significantly underrepresented in the Western canon, commonly performed classical music repertoire, music history textbooks and music encyclopedias; for example, in the ''Concise Oxford History of Music'', Clara Schumann is one of the only female composers who is mentioned. Women comprise a significant proportion of instrumental soloists in classical music and the percentage of women in orchestras is increasing. A 2015 article on concerto soloists in major Canadian orchestras, however, indicated that 84% of the soloists with the Orchestre Symphonique de Montreal were men. In 2012, women still made up just 6% of the top-ranked Vienna Philharmonic orchestra. Women are less common as instrumental players in popular music genres such as rock and Heavy metal music, heavy metal, although there have been a number of notable female instrumentalists and all-female bands. Women are particularly underrepresented in extreme metal genres. Women are also underrepresented in orchestral conducting, music criticism/music journalism, Music producer, music producing, and sound engineering. While women were discouraged from composing in the 19th century, and there are few women musicology, musicologists, women became involved in music education "... to such a degree that women dominated [this field] during the later half of the 19th century and well into the 20th century."
According to Jessica Duchen, a music writer for London's ''The Independent'', women musicians in classical music are "... too often judged for their appearances, rather than their talent" and they face pressure "... to look sexy onstage and in photos." Duchen states that while "[t]here are women musicians who refuse to play on their looks, ... the ones who do tend to be more materially successful."
According to the UK's Radio 3 editor, Edwina Wolstencroft, the classical music industry has long been open to having women in performance or entertainment roles, but women are much less likely to have positions of authority, such as being the Conducting, leader of an orchestra. In popular music, while there are many women singers recording songs, there are very few women behind the Audio mixer, audio console acting as music producers, the individuals who direct and manage the recording process.
Women comprise a significant proportion of instrumental soloists in classical music and the percentage of women in orchestras is increasing. A 2015 article on concerto soloists in major Canadian orchestras, however, indicated that 84% of the soloists with the Orchestre Symphonique de Montreal were men. In 2012, women still made up just 6% of the top-ranked Vienna Philharmonic orchestra. Women are less common as instrumental players in popular music genres such as rock and Heavy metal music, heavy metal, although there have been a number of notable female instrumentalists and all-female bands. Women are particularly underrepresented in extreme metal genres. Women are also underrepresented in orchestral conducting, music criticism/music journalism, Music producer, music producing, and sound engineering. While women were discouraged from composing in the 19th century, and there are few women musicology, musicologists, women became involved in music education "... to such a degree that women dominated [this field] during the later half of the 19th century and well into the 20th century."
According to Jessica Duchen, a music writer for London's ''The Independent'', women musicians in classical music are "... too often judged for their appearances, rather than their talent" and they face pressure "... to look sexy onstage and in photos." Duchen states that while "[t]here are women musicians who refuse to play on their looks, ... the ones who do tend to be more materially successful."
According to the UK's Radio 3 editor, Edwina Wolstencroft, the classical music industry has long been open to having women in performance or entertainment roles, but women are much less likely to have positions of authority, such as being the Conducting, leader of an orchestra. In popular music, while there are many women singers recording songs, there are very few women behind the Audio mixer, audio console acting as music producers, the individuals who direct and manage the recording process.

Gender symbol
The glyph (♀) for the Venus, planet and Roman goddess Venus (mythology), Venus, or Aphrodite in Greek, is the Gender symbol, symbol used in biology for the female sex. In ancient alchemy, the Venus symbol stood for copper and was associated with femininity.Femininity
''Femininity'' (also called ''womanliness'' or ''girlishness'') is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with women and girls. Although femininity is socially constructed, some behaviors considered feminine are biologically influenced. The extent to which femininity is biologically or socially influenced is subject to debate. It is distinct from the definition of the biological female sex,Ferrante, Joan (January 2010). Sociology: A Global Perspective (7th ed.). Belmont, CA: Thomson Wadsworth. pp. 269–272. ISBN 978-0-8400-3204-1. as both men and women can exhibit feminine traits.See also
References
Further reading
Chafe, William H.
, ''The American Woman: Her Changing Social, Economic, And Political Roles, 1920–1970'', Oxford University Press, 1972. * * ''Routledge International Encyclopedia of Women'', 4 vls., ed. by Cheris Kramarae and Dale Spender, Routledge 2000 * ''Women in World History, Women in World History : a biographical encyclopedia'', 17 vls., ed. by Anne Commire, Waterford, Conn. [etc.] : Yorkin Publ. [etc.], 1999–2002
''Woman In all ages and in all countries in 10 volumes''
Illustrated edition deluxe limited to 1,000 numbered copies with an index by Rénald Lévesque
External links
* * {{Authority control Female Women,