Wind Turbine Blade Transport I-35 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Wind is the natural movement of
Wind is the natural movement of
 Wind is caused by differences in atmospheric pressure, which are mainly due to temperature difference. When a difference in atmospheric pressure exists, air moves from the higher to the lower pressure area, resulting in winds of various speeds. On a rotating planet, air will also be deflected by the
Wind is caused by differences in atmospheric pressure, which are mainly due to temperature difference. When a difference in atmospheric pressure exists, air moves from the higher to the lower pressure area, resulting in winds of various speeds. On a rotating planet, air will also be deflected by the


Federal Meteorological Handbook No. 1 – Surface Weather Observations and Reports September 2005
Appendix A: Glossary. Retrieved 2008-04-06. India typically reports winds over a 3‑minute average. Knowing the wind sampling average is important, as the value of a one-minute sustained wind is typically 14% greater than a ten-minute sustained wind. A short burst of high speed wind is termed a
 The
The

 Easterly winds, on average, dominate the flow pattern across the poles, westerly winds blow across the
Easterly winds, on average, dominate the flow pattern across the poles, westerly winds blow across the
 The Westerlies or the Prevailing Westerlies are the
The Westerlies or the Prevailing Westerlies are the

 In coastal regions, sea breezes and land breezes can be important factors in a location's prevailing winds. The sea is warmed by the sun more slowly because of water's greater specific heat compared to land. As the temperature of the surface of the land rises, the land heats the air above it by conduction. The warm air is less dense than the surrounding environment and so it rises. The cooler air above the sea, now with higher sea level pressure, flows inland into the lower pressure, creating a cooler breeze near the coast. A background along-shore wind either strengthens or weakens the sea breeze, depending on its orientation with respect to the Coriolis force.
At night, the land cools off more quickly than the ocean because of differences in their specific heat values. This temperature change causes the daytime sea breeze to dissipate. When the temperature onshore cools below the temperature offshore, the pressure over the water will be lower than that of the land, establishing a land breeze, as long as an onshore wind is not strong enough to oppose it.
In coastal regions, sea breezes and land breezes can be important factors in a location's prevailing winds. The sea is warmed by the sun more slowly because of water's greater specific heat compared to land. As the temperature of the surface of the land rises, the land heats the air above it by conduction. The warm air is less dense than the surrounding environment and so it rises. The cooler air above the sea, now with higher sea level pressure, flows inland into the lower pressure, creating a cooler breeze near the coast. A background along-shore wind either strengthens or weakens the sea breeze, depending on its orientation with respect to the Coriolis force.
At night, the land cools off more quickly than the ocean because of differences in their specific heat values. This temperature change causes the daytime sea breeze to dissipate. When the temperature onshore cools below the temperature offshore, the pressure over the water will be lower than that of the land, establishing a land breeze, as long as an onshore wind is not strong enough to oppose it.
 Over elevated surfaces, heating of the ground exceeds the heating of the surrounding air at the same altitude above sea level, creating an associated thermal low over the terrain and enhancing any thermal lows that would have otherwise existed, and changing the wind circulation of the region. In areas where there is rugged topography that significantly interrupts the environmental wind flow, the wind circulation between mountains and valleys is the most important contributor to the prevailing winds. Hills and valleys substantially distort the airflow by increasing friction between the atmosphere and landmass by acting as a physical block to the flow, deflecting the wind parallel to the range just upstream of the topography, which is known as a barrier jet. This barrier jet can increase the low-level wind by 45%. Wind direction also changes because of the contour of the land.
If there is a mountain pass, pass in the mountain range, winds will rush through the pass with considerable speed because of the Bernoulli principle that describes an inverse relationship between speed and pressure. The airflow can remain turbulent and erratic for some distance downwind into the flatter countryside. These conditions are dangerous to ascending and descending airplanes. Cool winds accelerating through mountain gaps have been given regional names. In Central America, examples include the Papagayo wind, the Panama wind, and the Tehuano wind. In Europe, similar winds are known as the Bora (wind), Bora, Tramontane, and Mistral (wind), Mistral. When these winds blow over open waters, they increase mixing of the upper layers of the ocean that elevates cool, nutrient rich waters to the surface, which leads to increased marine life.
In mountainous areas, local distortion of the airflow becomes severe. Jagged terrain combines to produce unpredictable flow patterns and turbulence, such as lee waves, rotors, which can be topped by lenticular clouds. Strong updrafts, downdrafts, and eddies develop as the air flows over hills and down valleys. Orographic precipitation (meteorology), precipitation occurs on the windward side of mountains and is caused by the rising air motion of a large-scale flow of moist air across the mountain ridge, also known as upslope flow, resulting in adiabatic lapse rate, adiabatic cooling and condensation. In mountainous parts of the world subjected to relatively consistent winds (for example, the trade winds), a more moist climate usually prevails on the windward side of a mountain than on the leeward or downwind side. Moisture is removed by orographic lift, leaving drier air on the descending and generally warming, leeward side where a rain shadow is observed.
Winds that flow over mountains down into lower elevations are known as downslope winds. These winds are warm and dry. In Europe downwind of the Alps, they are known as foehn. In Poland, an example is the halny wiatr. In Argentina, the local name for down sloped winds is zonda (wind), zonda. In Java, the local name for such winds is koembang. In New Zealand, they are known as the Nor'west arch, and are accompanied by the cloud formation they are named after that has inspired artwork over the years. In the Great Plains of the United States, these winds are known as a chinook wind, chinook. Downslope winds also occur in the foothills of the Appalachian mountains of the United States, and they can be as strong as other downslope winds and unusual compared to other foehn winds in that the relative humidity typically changes little due to the increased moisture in the source air mass. In California, downslope winds are funneled through mountain passes, which intensify their effect, and examples include the Santa Ana wind, Santa Ana and sundowner (wind), sundowner winds. Wind speeds during downslope wind effect can exceed .
Over elevated surfaces, heating of the ground exceeds the heating of the surrounding air at the same altitude above sea level, creating an associated thermal low over the terrain and enhancing any thermal lows that would have otherwise existed, and changing the wind circulation of the region. In areas where there is rugged topography that significantly interrupts the environmental wind flow, the wind circulation between mountains and valleys is the most important contributor to the prevailing winds. Hills and valleys substantially distort the airflow by increasing friction between the atmosphere and landmass by acting as a physical block to the flow, deflecting the wind parallel to the range just upstream of the topography, which is known as a barrier jet. This barrier jet can increase the low-level wind by 45%. Wind direction also changes because of the contour of the land.
If there is a mountain pass, pass in the mountain range, winds will rush through the pass with considerable speed because of the Bernoulli principle that describes an inverse relationship between speed and pressure. The airflow can remain turbulent and erratic for some distance downwind into the flatter countryside. These conditions are dangerous to ascending and descending airplanes. Cool winds accelerating through mountain gaps have been given regional names. In Central America, examples include the Papagayo wind, the Panama wind, and the Tehuano wind. In Europe, similar winds are known as the Bora (wind), Bora, Tramontane, and Mistral (wind), Mistral. When these winds blow over open waters, they increase mixing of the upper layers of the ocean that elevates cool, nutrient rich waters to the surface, which leads to increased marine life.
In mountainous areas, local distortion of the airflow becomes severe. Jagged terrain combines to produce unpredictable flow patterns and turbulence, such as lee waves, rotors, which can be topped by lenticular clouds. Strong updrafts, downdrafts, and eddies develop as the air flows over hills and down valleys. Orographic precipitation (meteorology), precipitation occurs on the windward side of mountains and is caused by the rising air motion of a large-scale flow of moist air across the mountain ridge, also known as upslope flow, resulting in adiabatic lapse rate, adiabatic cooling and condensation. In mountainous parts of the world subjected to relatively consistent winds (for example, the trade winds), a more moist climate usually prevails on the windward side of a mountain than on the leeward or downwind side. Moisture is removed by orographic lift, leaving drier air on the descending and generally warming, leeward side where a rain shadow is observed.
Winds that flow over mountains down into lower elevations are known as downslope winds. These winds are warm and dry. In Europe downwind of the Alps, they are known as foehn. In Poland, an example is the halny wiatr. In Argentina, the local name for down sloped winds is zonda (wind), zonda. In Java, the local name for such winds is koembang. In New Zealand, they are known as the Nor'west arch, and are accompanied by the cloud formation they are named after that has inspired artwork over the years. In the Great Plains of the United States, these winds are known as a chinook wind, chinook. Downslope winds also occur in the foothills of the Appalachian mountains of the United States, and they can be as strong as other downslope winds and unusual compared to other foehn winds in that the relative humidity typically changes little due to the increased moisture in the source air mass. In California, downslope winds are funneled through mountain passes, which intensify their effect, and examples include the Santa Ana wind, Santa Ana and sundowner (wind), sundowner winds. Wind speeds during downslope wind effect can exceed .
 Wind shear, sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and direction over a relatively short distance in the Earth's atmosphere. Wind shear can be broken down into vertical and horizontal components, with horizontal wind shear seen across weather fronts and near the coast, and vertical shear typically near the surface, though also at higher levels in the atmosphere near upper level jets and frontal zones aloft.
Wind shear itself is a microscale meteorology, microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale meteorology, mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by
Wind shear, sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and direction over a relatively short distance in the Earth's atmosphere. Wind shear can be broken down into vertical and horizontal components, with horizontal wind shear seen across weather fronts and near the coast, and vertical shear typically near the surface, though also at higher levels in the atmosphere near upper level jets and frontal zones aloft.
Wind shear itself is a microscale meteorology, microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale meteorology, mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by
 There are many different forms of sailing ships, but they all have certain basic things in common. Except for rotor ships using the Magnus effect, every sailing ship has a hull (ship), hull, rigging and at least one mast (sailing), mast to hold up the sails that use the wind to power the ship. Ocean journeys by sailing ship can take many months, and a common hazard is becoming becalmed because of lack of wind, or being blown off course by severe storms or winds that do not allow progress in the desired direction. A severe storm could lead to shipwreck, and the loss of all hands. Sailing ships can only carry a certain quantity of supplies in their hold (ship), hold, so they have to plan long Maritime history, voyages carefully to include appropriate Provisioning of USS Constitution, provisions, including fresh water.
For aerodynamic aircraft which operate relative to the air, winds affect groundspeed, and in the case of lighter-than-air vehicles, wind may play a significant or solitary role in their movement and ground track. The
There are many different forms of sailing ships, but they all have certain basic things in common. Except for rotor ships using the Magnus effect, every sailing ship has a hull (ship), hull, rigging and at least one mast (sailing), mast to hold up the sails that use the wind to power the ship. Ocean journeys by sailing ship can take many months, and a common hazard is becoming becalmed because of lack of wind, or being blown off course by severe storms or winds that do not allow progress in the desired direction. A severe storm could lead to shipwreck, and the loss of all hands. Sailing ships can only carry a certain quantity of supplies in their hold (ship), hold, so they have to plan long Maritime history, voyages carefully to include appropriate Provisioning of USS Constitution, provisions, including fresh water.
For aerodynamic aircraft which operate relative to the air, winds affect groundspeed, and in the case of lighter-than-air vehicles, wind may play a significant or solitary role in their movement and ground track. The
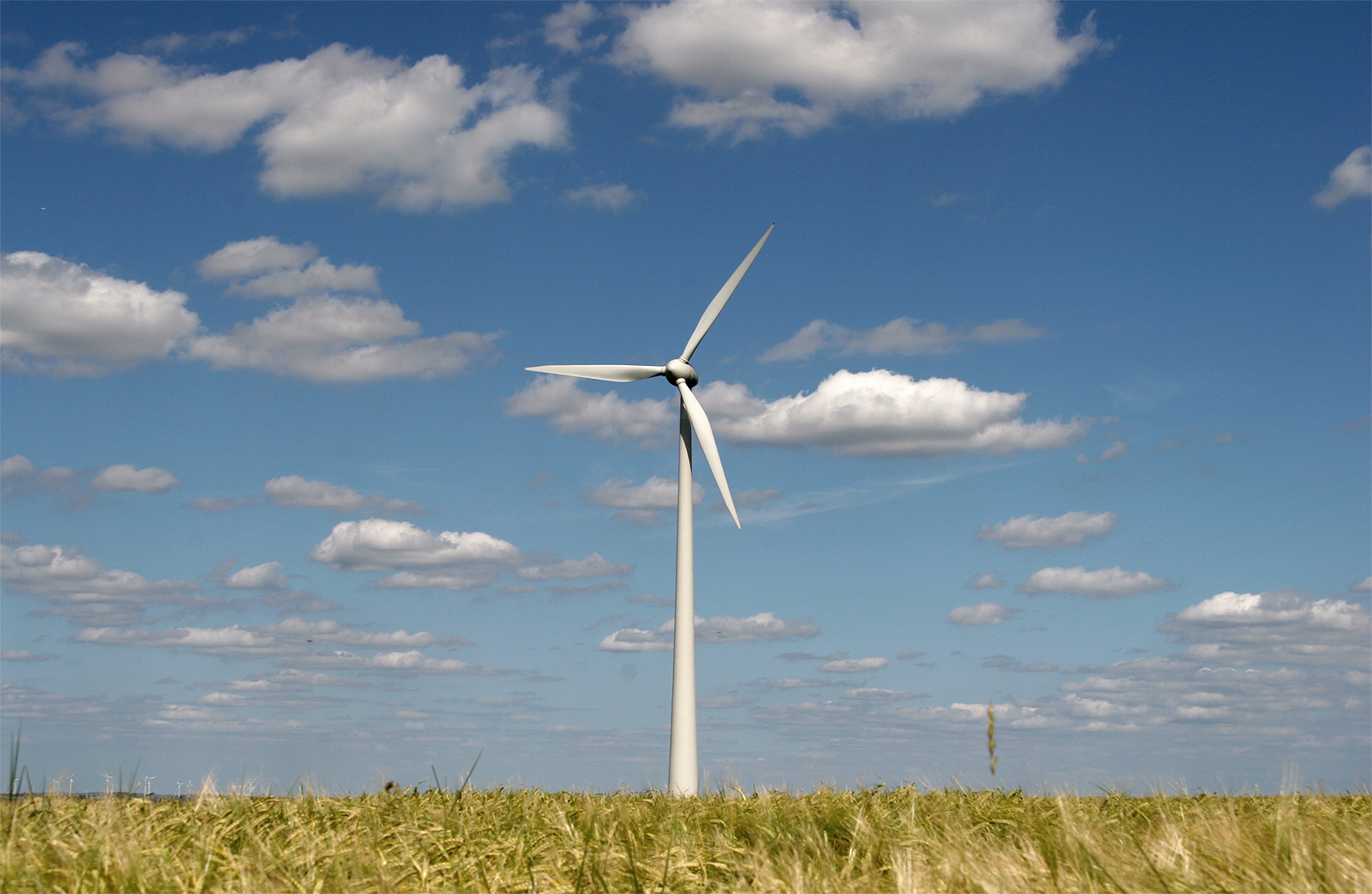 The ancient Sinhalese people, Sinhalese of Anuradhapura and in other cities around Sri Lanka used the monsoon winds to power furnaces as early as 300 Common Era, BCE. The furnaces were constructed on the path of the monsoon winds to bring the temperatures inside up to . A rudimentary windmill was used to power an organ (music), organ in the first century CE. Windmills were later built in Sistan, Afghanistan, from the 7th century CE. These were vertical-axle windmills, with Windmill sail, sails covered in reed mat (craft), reed matting or cloth material. These windmills were used to grind corn and draw up water, and were used in the gristmilling and sugarcane industries. Horizontal-axle windmills were later used extensively in Northwestern Europe to grind flour beginning in the 1180s, and many Dutch windmills still exist.
Wind power is now one of the main sources of renewable energy, and its use is growing rapidly, driven by innovation and falling prices. Most of the installed capacity in wind power is Wind farm, onshore, but offshore wind power offers a large potential as wind speeds are typically higher and more constant away from the coast. Wind energy the kinetic energy of the air, is proportional to the third power of wind velocity. Betz's law described the theoretical upper limit of what fraction of this energy wind turbines can extract, which is about 59%.
The ancient Sinhalese people, Sinhalese of Anuradhapura and in other cities around Sri Lanka used the monsoon winds to power furnaces as early as 300 Common Era, BCE. The furnaces were constructed on the path of the monsoon winds to bring the temperatures inside up to . A rudimentary windmill was used to power an organ (music), organ in the first century CE. Windmills were later built in Sistan, Afghanistan, from the 7th century CE. These were vertical-axle windmills, with Windmill sail, sails covered in reed mat (craft), reed matting or cloth material. These windmills were used to grind corn and draw up water, and were used in the gristmilling and sugarcane industries. Horizontal-axle windmills were later used extensively in Northwestern Europe to grind flour beginning in the 1180s, and many Dutch windmills still exist.
Wind power is now one of the main sources of renewable energy, and its use is growing rapidly, driven by innovation and falling prices. Most of the installed capacity in wind power is Wind farm, onshore, but offshore wind power offers a large potential as wind speeds are typically higher and more constant away from the coast. Wind energy the kinetic energy of the air, is proportional to the third power of wind velocity. Betz's law described the theoretical upper limit of what fraction of this energy wind turbines can extract, which is about 59%.
 Wind figures prominently in several popular sports, including recreational hang gliding, hot air ballooning, kite flying, snowkiting, kite landboarding, kite surfing, paragliding, sailing, and windsurfing. In gliding, wind gradients just above the surface affect the takeoff and landing phases of flight of a Glider aircraft, glider. Wind gradient can have a noticeable effect on ground launches, also known as winch launches or wire launches. If the wind gradient is significant or sudden, or both, and the pilot maintains the same pitch attitude, the indicated airspeed will increase, possibly exceeding the maximum ground launch tow speed. The pilot must adjust the airspeed to deal with the effect of the gradient. When landing, wind shear is also a hazard, particularly when the winds are strong. As the glider descends through the wind gradient on final approach to landing, airspeed decreases while sink rate increases, and there is insufficient time to accelerate prior to ground contact. The pilot must anticipate the wind gradient and use a higher approach speed to compensate for it.
Wind figures prominently in several popular sports, including recreational hang gliding, hot air ballooning, kite flying, snowkiting, kite landboarding, kite surfing, paragliding, sailing, and windsurfing. In gliding, wind gradients just above the surface affect the takeoff and landing phases of flight of a Glider aircraft, glider. Wind gradient can have a noticeable effect on ground launches, also known as winch launches or wire launches. If the wind gradient is significant or sudden, or both, and the pilot maintains the same pitch attitude, the indicated airspeed will increase, possibly exceeding the maximum ground launch tow speed. The pilot must adjust the airspeed to deal with the effect of the gradient. When landing, wind shear is also a hazard, particularly when the winds are strong. As the glider descends through the wind gradient on final approach to landing, airspeed decreases while sink rate increases, and there is insufficient time to accelerate prior to ground contact. The pilot must anticipate the wind gradient and use a higher approach speed to compensate for it.
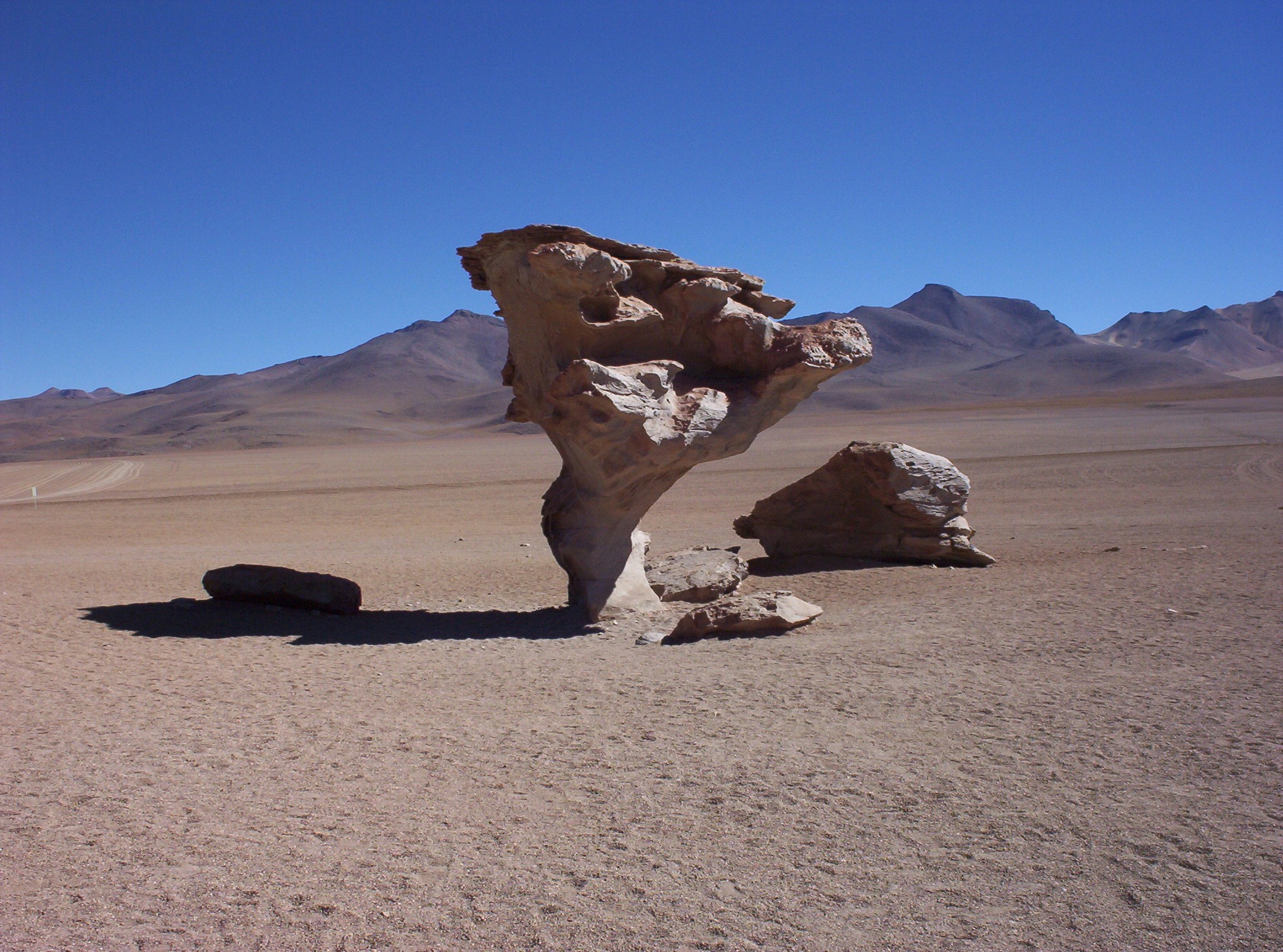 Erosion can be the result of material movement by the wind. There are two main effects. First, wind causes small particles to be lifted and therefore moved to another region. This is called deflation. Second, these suspended particles may impact on solid objects causing erosion by abrasion (ecological succession). Wind erosion generally occurs in areas with little or no vegetation, often in areas where there is insufficient rainfall to support vegetation. An example is the formation of sand dunes, on a beach or in a desert. Loess is a homogeneous, typically nonstratified, porous, friable, slightly coherent, often calcareous, fine-grained, silty, pale yellow or buff, windblown (Aeolian) sediment. It generally occurs as a widespread blanket deposit that covers areas of hundreds of square kilometers and tens of meters thick. Loess often stands in either steep or vertical faces. Loess tends to develop into highly rich soils. Under appropriate climatic conditions, areas with loess are among the most agriculturally productive in the world. Loess deposits are geologically unstable by nature, and will erode very readily. Therefore, windbreaks (such as big trees and bushes) are often planted by farmers to reduce the wind erosion of loess.
Erosion can be the result of material movement by the wind. There are two main effects. First, wind causes small particles to be lifted and therefore moved to another region. This is called deflation. Second, these suspended particles may impact on solid objects causing erosion by abrasion (ecological succession). Wind erosion generally occurs in areas with little or no vegetation, often in areas where there is insufficient rainfall to support vegetation. An example is the formation of sand dunes, on a beach or in a desert. Loess is a homogeneous, typically nonstratified, porous, friable, slightly coherent, often calcareous, fine-grained, silty, pale yellow or buff, windblown (Aeolian) sediment. It generally occurs as a widespread blanket deposit that covers areas of hundreds of square kilometers and tens of meters thick. Loess often stands in either steep or vertical faces. Loess tends to develop into highly rich soils. Under appropriate climatic conditions, areas with loess are among the most agriculturally productive in the world. Loess deposits are geologically unstable by nature, and will erode very readily. Therefore, windbreaks (such as big trees and bushes) are often planted by farmers to reduce the wind erosion of loess.

 Wind dispersal of seeds, or anemochory, is one of the more primitive means of dispersal. Wind dispersal can take on one of two primary forms: seeds can float on the breeze or alternatively, they can flutter to the ground. The classic examples of these dispersal mechanisms include dandelions (''Taraxacum'' spp., Asteraceae), which have a feathery pappus (flower structure), pappus attached to their seeds and can be dispersed long distances, and maples (''Acer (genus)'' spp., Sapindaceae), which have winged seeds and flutter to the ground. An important constraint on wind dispersal is the need for abundant seed production to maximize the likelihood of a seed landing in a site suitable for germination. There are also strong evolutionary constraints on this dispersal mechanism. For instance, species in the Asteraceae on islands tended to have reduced dispersal capabilities (i.e., larger seed mass and smaller pappus) relative to the same species on the mainland. Reliance upon wind dispersal is common among many weedy or ruderal species. Unusual mechanisms of wind dispersal include tumbleweeds. A related process to anemochory is anemophily, which is the process where pollen is distributed by wind. Large families of plants are pollinated in this manner, which is favored when individuals of the dominant plant species are spaced closely together.
Wind also limits tree growth. On coasts and isolated mountains, the tree line is often much lower than in corresponding altitudes inland and in larger, more complex mountain systems, because strong winds reduce tree growth. High winds scour away thin soils through erosion, as well as damage limbs and twigs. When high winds knock down or uproot trees, the process is known as windthrow. This is most likely on windward slopes of mountains, with severe cases generally occurring to tree stands that are 75 years or older. Plant varieties near the coast, such as the Sitka spruce and Coccoloba uvifera, sea grape, are pruning, pruned back by wind and salt spray near the coastline.
Wind can also cause plants damage through sand abrasion. Strong winds will pick up loose sand and topsoil and hurl it through the air at speeds ranging from to . Such windblown sand causes extensive damage to plant seedlings because it ruptures plant cells, making them vulnerable to evaporation and drought. Using a mechanical sandblaster in a laboratory setting, scientists affiliated with the Agricultural Research Service studied the effects of windblown sand abrasion on cotton seedlings. The study showed that the seedlings responded to the damage created by the windblown sand abrasion by shifting energy from stem and root growth to the growth and repair of the damaged stems. After a period of four weeks, the growth of the seedling once again became uniform throughout the plant, as it was before the windblown sand abrasion occurred.
Besides plant gametes (seeds) wind also helps plants' enemies: Spores and other propagules of plant pathogens are even lighter and able to travel long distances. A few plant diseases are known to have been known to travel over marginal seas and even entire oceans. Humans are unable to prevent or even slow down wind dispersal of plant pathogens, requiring prediction and amelioration instead.
Wind dispersal of seeds, or anemochory, is one of the more primitive means of dispersal. Wind dispersal can take on one of two primary forms: seeds can float on the breeze or alternatively, they can flutter to the ground. The classic examples of these dispersal mechanisms include dandelions (''Taraxacum'' spp., Asteraceae), which have a feathery pappus (flower structure), pappus attached to their seeds and can be dispersed long distances, and maples (''Acer (genus)'' spp., Sapindaceae), which have winged seeds and flutter to the ground. An important constraint on wind dispersal is the need for abundant seed production to maximize the likelihood of a seed landing in a site suitable for germination. There are also strong evolutionary constraints on this dispersal mechanism. For instance, species in the Asteraceae on islands tended to have reduced dispersal capabilities (i.e., larger seed mass and smaller pappus) relative to the same species on the mainland. Reliance upon wind dispersal is common among many weedy or ruderal species. Unusual mechanisms of wind dispersal include tumbleweeds. A related process to anemochory is anemophily, which is the process where pollen is distributed by wind. Large families of plants are pollinated in this manner, which is favored when individuals of the dominant plant species are spaced closely together.
Wind also limits tree growth. On coasts and isolated mountains, the tree line is often much lower than in corresponding altitudes inland and in larger, more complex mountain systems, because strong winds reduce tree growth. High winds scour away thin soils through erosion, as well as damage limbs and twigs. When high winds knock down or uproot trees, the process is known as windthrow. This is most likely on windward slopes of mountains, with severe cases generally occurring to tree stands that are 75 years or older. Plant varieties near the coast, such as the Sitka spruce and Coccoloba uvifera, sea grape, are pruning, pruned back by wind and salt spray near the coastline.
Wind can also cause plants damage through sand abrasion. Strong winds will pick up loose sand and topsoil and hurl it through the air at speeds ranging from to . Such windblown sand causes extensive damage to plant seedlings because it ruptures plant cells, making them vulnerable to evaporation and drought. Using a mechanical sandblaster in a laboratory setting, scientists affiliated with the Agricultural Research Service studied the effects of windblown sand abrasion on cotton seedlings. The study showed that the seedlings responded to the damage created by the windblown sand abrasion by shifting energy from stem and root growth to the growth and repair of the damaged stems. After a period of four weeks, the growth of the seedling once again became uniform throughout the plant, as it was before the windblown sand abrasion occurred.
Besides plant gametes (seeds) wind also helps plants' enemies: Spores and other propagules of plant pathogens are even lighter and able to travel long distances. A few plant diseases are known to have been known to travel over marginal seas and even entire oceans. Humans are unable to prevent or even slow down wind dispersal of plant pathogens, requiring prediction and amelioration instead.
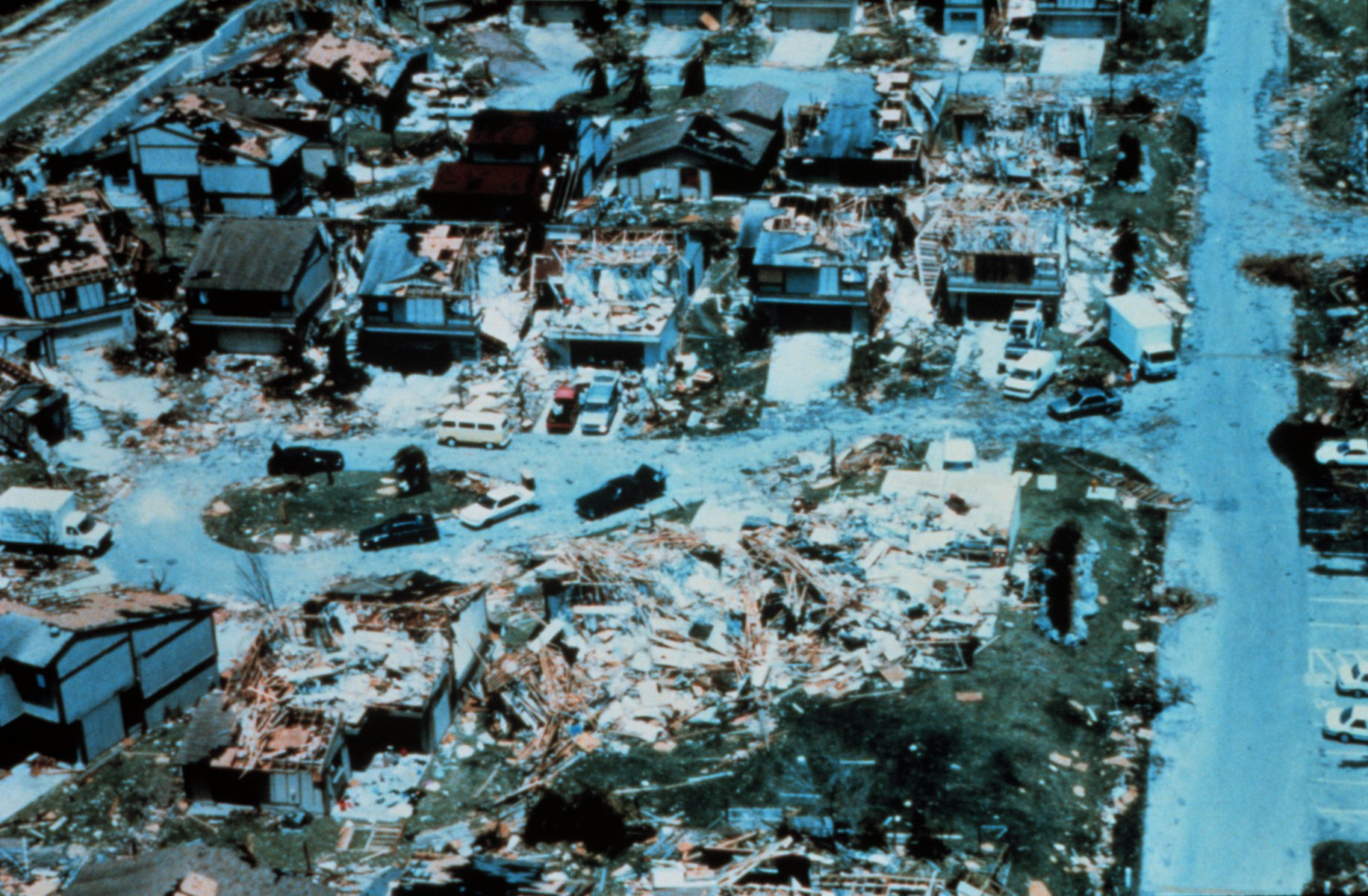 High winds are known to cause damage, depending upon the magnitude of their velocity and pressure differential. Wind pressures are positive on the windward side of a structure and negative on the leeward side. Infrequent wind gusts can cause poorly designed suspension bridges to sway. When wind gusts are at a similar frequency to the swaying of the bridge, the bridge can be destroyed more easily, such as what occurred with the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (1940), Tacoma Narrows Bridge in 1940. Wind speeds as low as can lead to power outages due to tree branches disrupting the flow of energy through power lines. While no species of tree is guaranteed to stand up to hurricane-force winds, those with shallow roots are more prone to uproot, and brittle trees such as eucalyptus, sea hibiscus, and avocado are more prone to damage. Hurricane-force winds cause substantial damage to mobile homes, and begin to structurally damage homes with foundations. Winds of this strength due to downsloped winds off terrain have been known to shatter windows and sandblast paint from cars. Once winds exceed , homes completely collapse, and significant damage is done to larger buildings. Total destruction to artificial structures occurs when winds reach . The Saffir–Simpson scale and Enhanced Fujita scale were designed to help estimate wind speed from the damage caused by high winds related to tropical cyclones and tornadoes, and vice versa.
Australia's Barrow Island (Western Australia), Barrow Island holds the record for the strongest wind gust, reaching 408 km/h (253 mph) during tropical cyclone Olivia on 10 April 1996, surpassing the previous record of 372 km/h (231 mph) set on Mount Washington (New Hampshire) on the afternoon of 12 April 1934.
Wildfire intensity increases during daytime hours. For example, burn rates of smoldering logs are up to five times greater during the day because of lower humidity, increased temperatures, and increased wind speeds. Sunlight warms the ground during the day and causes air currents to travel uphill, and downhill during the night as the land cools. Wildfires are fanned by these winds and often follow the air currents over hills and through valleys. United States wildfire operations revolve around a 24-hour ''fire day'' that begins at 10:00 a.m. because of the predictable increase in intensity resulting from the daytime warmth.
High winds are known to cause damage, depending upon the magnitude of their velocity and pressure differential. Wind pressures are positive on the windward side of a structure and negative on the leeward side. Infrequent wind gusts can cause poorly designed suspension bridges to sway. When wind gusts are at a similar frequency to the swaying of the bridge, the bridge can be destroyed more easily, such as what occurred with the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (1940), Tacoma Narrows Bridge in 1940. Wind speeds as low as can lead to power outages due to tree branches disrupting the flow of energy through power lines. While no species of tree is guaranteed to stand up to hurricane-force winds, those with shallow roots are more prone to uproot, and brittle trees such as eucalyptus, sea hibiscus, and avocado are more prone to damage. Hurricane-force winds cause substantial damage to mobile homes, and begin to structurally damage homes with foundations. Winds of this strength due to downsloped winds off terrain have been known to shatter windows and sandblast paint from cars. Once winds exceed , homes completely collapse, and significant damage is done to larger buildings. Total destruction to artificial structures occurs when winds reach . The Saffir–Simpson scale and Enhanced Fujita scale were designed to help estimate wind speed from the damage caused by high winds related to tropical cyclones and tornadoes, and vice versa.
Australia's Barrow Island (Western Australia), Barrow Island holds the record for the strongest wind gust, reaching 408 km/h (253 mph) during tropical cyclone Olivia on 10 April 1996, surpassing the previous record of 372 km/h (231 mph) set on Mount Washington (New Hampshire) on the afternoon of 12 April 1934.
Wildfire intensity increases during daytime hours. For example, burn rates of smoldering logs are up to five times greater during the day because of lower humidity, increased temperatures, and increased wind speeds. Sunlight warms the ground during the day and causes air currents to travel uphill, and downhill during the night as the land cools. Wildfires are fanned by these winds and often follow the air currents over hills and through valleys. United States wildfire operations revolve around a 24-hour ''fire day'' that begins at 10:00 a.m. because of the predictable increase in intensity resulting from the daytime warmth.
 The hydrodynamic wind within the upper portion of a planet's atmosphere allows light chemical elements such as hydrogen to move up to the exobase, the lower limit of the exosphere, where the gases can then reach escape velocity, entering outer space without impacting other particles of gas. This type of gas loss from a planet into space is known as planetary wind. Such a process over geologic time causes water-rich planets such as the Earth to evolve into planets like Venus. Additionally, planets with hotter lower atmospheres could accelerate the loss rate of hydrogen.
The hydrodynamic wind within the upper portion of a planet's atmosphere allows light chemical elements such as hydrogen to move up to the exobase, the lower limit of the exosphere, where the gases can then reach escape velocity, entering outer space without impacting other particles of gas. This type of gas loss from a planet into space is known as planetary wind. Such a process over geologic time causes water-rich planets such as the Earth to evolve into planets like Venus. Additionally, planets with hotter lower atmospheres could accelerate the loss rate of hydrogen.
Current map of global surface winds
{{Authority control Wind, Atmospheric dynamics Meteorological phenomena
 Wind is the natural movement of
Wind is the natural movement of air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
or other gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
es relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are some ...
flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various isla ...
surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zone
Climate classifications are systems that categorize the world's climates. A climate classification may correlate closely with a biome classification, as climate is a major influence on life in a region. One of the most used is the Köppen climate ...
s on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, bu ...
are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low
Thermal lows, or heat lows, are non-frontal low-pressure areas that occur over the continents in the subtropics during the warm season, as the result of intense heating when compared to their surrounding environments.Glossary of Meteorology (200 ...
circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze
A sea breeze or onshore breeze is any wind that blows from a large body of water toward or onto a landmass; it develops due to differences in air pressure created by the differing heat capacities of water and dry land. As such, sea breezes ar ...
/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail.
Winds are commonly classified by their spatial scale
Spatial scale is a specific application of the term scale for describing or categorizing (e.g. into orders of magnitude) the size of a space (hence ''spatial''), or the extent of it at which a phenomenon or process occurs.
For instance, in phy ...
, their speed
In everyday use and in kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (ma ...
and direction, the forces that cause them, the regions in which they occur, and their effect. Winds have various aspects: velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity i ...
(wind speed
In meteorology, wind speed, or wind flow speed, is a fundamental atmospheric quantity caused by air moving from high to low pressure, usually due to changes in temperature. Wind speed is now commonly measured with an anemometer.
Wind speed ...
); the density of the gas involved; energy content, or wind energy
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically, w ...
. In meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did no ...
, winds are often referred to according to their strength, and the direction from which the wind is blowing. The convention for directions refer to where the wind comes from; therefore, a 'western' or 'westerly' wind blows from the west to the east, a 'northern' wind blows south, and so on. This is sometimes counter-intuitive.
Short bursts of high speed wind are termed gusts. Strong winds of intermediate duration (around one minute) are termed squall
A squall is a sudden, sharp increase in wind speed lasting minutes, as opposed to a wind gust, which lasts for only seconds. They are usually associated with active weather, such as rain showers, thunderstorms, or heavy snow. Squalls refer to the ...
s. Long-duration winds have various names associated with their average strength, such as breeze, gale
A gale is a strong wind; the word is typically used as a descriptor in nautical contexts. The U.S. National Weather Service defines a gale as sustained surface winds moving at a speed of between 34 and 47 knots (, or ).storm
A storm is any disturbed state of the natural environment or the atmosphere of an astronomical body. It may be marked by significant disruptions to normal conditions such as strong wind, tornadoes, hail, thunder and lightning (a thunderstorm), ...
, and hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
.
In outer space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, pred ...
, solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
is the movement of gases or charged particles from the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
through space, while planetary wind
Atmospheric escape is the loss of planetary atmospheric gases to outer space. A number of different mechanisms can be responsible for atmospheric escape; these processes can be divided into thermal escape, non-thermal (or suprathermal) escape, and ...
is the outgassing
Outgassing (sometimes called offgassing, particularly when in reference to indoor air quality) is the release of a gas that was dissolved, trapped, frozen, or absorbed in some material. Outgassing can include sublimation and evaporation (which ...
of light chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
s from a planet's atmosphere into space. The strongest observed winds on a planet in the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
occur on Neptune and Saturn.
In human civilization, the concept of wind has been explored in mythology
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narra ...
, influenced the events of history, expanded the range of transport and warfare, and provided a power source for mechanical work, electricity, and recreation. Wind powers the voyages of sailing ship
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships ...
s across Earth's oceans. Hot air balloon
A hot air balloon is a lighter-than-air aircraft consisting of a bag, called an envelope, which contains heated air. Suspended beneath is a gondola or wicker basket (in some long-distance or high-altitude balloons, a capsule), which carries ...
s use the wind to take short trips, and powered flight uses it to increase lift and reduce fuel consumption. Areas of wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizont ...
caused by various weather phenomena can lead to dangerous situations for aircraft. When winds become strong, trees and human-made structures can be damaged or destroyed.
Winds can shape landforms, via a variety of aeolian processes
Aeolian processes, also spelled eolian, pertain to wind activity in the study of geology and weather and specifically to the wind's ability to shape the surface of the Earth (or other planets). Winds may erode, transport, and deposit mate ...
such as the formation of fertile soils, for example loess, and by erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
. Dust from large deserts can be moved great distances from its source region by the prevailing winds
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on ...
; winds that are accelerated by rough topography and associated with dust outbreaks have been assigned regional names in various parts of the world because of their significant effects on those regions. Wind also affects the spread of wildfires. Winds can disperse seeds from various plants, enabling the survival and dispersal of those plant species, as well as flying insect and bird populations. When combined with cold temperatures, the wind has a negative impact on livestock. Wind affects animals' food stores, as well as their hunting and defensive strategies.
Causes
 Wind is caused by differences in atmospheric pressure, which are mainly due to temperature difference. When a difference in atmospheric pressure exists, air moves from the higher to the lower pressure area, resulting in winds of various speeds. On a rotating planet, air will also be deflected by the
Wind is caused by differences in atmospheric pressure, which are mainly due to temperature difference. When a difference in atmospheric pressure exists, air moves from the higher to the lower pressure area, resulting in winds of various speeds. On a rotating planet, air will also be deflected by the Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
, except exactly on the equator. Globally, the two major driving factors of large-scale wind patterns (the atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, bu ...
) are the differential heating between the equator and the poles (difference in absorption of solar energy leading to buoyancy forces) and the rotation of the planet. Outside the tropics and aloft from frictional effects of the surface, the large-scale winds tend to approach geostrophic balance
In atmospheric science, balanced flow is an idealisation of atmospheric motion. The idealisation consists in considering the behaviour of one isolated parcel of air having constant density, its motion on a horizontal plane subject to selected for ...
. Near the Earth's surface, friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of ...
causes the wind to be slower than it would be otherwise. Surface friction also causes winds to blow more inward into low-pressure areas.
Winds defined by an equilibrium of physical forces are used in the decomposition and analysis of wind profiles. They are useful for simplifying the atmospheric equations of motion
In physics, equations of motion are equations that describe the behavior of a physical system in terms of its motion as a function of time.''Encyclopaedia of Physics'' (second Edition), R.G. Lerner, G.L. Trigg, VHC Publishers, 1991, ISBN (Ver ...
and for making qualitative arguments about the horizontal and vertical distribution of horizontal winds. The geostrophic wind component is the result of the balance between Coriolis force and pressure gradient force. It flows parallel to isobars and approximates the flow above the atmospheric boundary layer in the midlatitudes. The thermal wind
The thermal wind is the vector difference between the geostrophic wind at upper altitudes minus that at lower altitudes in the atmosphere. It is the hypothetical vertical wind shear that would exist if the winds obey geostrophic balance in the ...
is the ''difference'' in the geostrophic wind between two levels in the atmosphere. It exists only in an atmosphere with horizontal temperature gradients. The ageostrophic wind component is the difference between actual and geostrophic wind, which is responsible for air "filling up" cyclones over time. The gradient wind
In atmospheric science, balanced flow is an idealisation of atmospheric motion. The idealisation consists in considering the behaviour of one isolated parcel of air having constant density, its motion on a horizontal plane subject to selected for ...
is similar to the geostrophic wind but also includes centrifugal force
In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force (also called a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed away from an axis which is parall ...
(or centripetal acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by th ...
).
Measurement

Wind direction
Wind direction is generally reported by the direction from which it originates. For example, a ''north'' or ''northerly'' wind blows from the north to the south. The exceptions are onshore winds (blowing onto the shore from the water) and offsho ...
is usually expressed in terms of the direction from which it originates. For example, a ''northerly'' wind blows from the north to the south. Weather vane
A wind vane, weather vane, or weathercock is an instrument used for showing the direction of the wind. It is typically used as an architectural ornament to the highest point of a building. The word ''vane'' comes from the Old English word , m ...
s pivot to indicate the direction of the wind. At airports, windsock
A windsock (also called a wind cone) is a conical textile tube that resembles a giant sock. It can be used as a basic indicator of wind speed and direction, or as decoration. They are typically used at airports to show the direction and strength ...
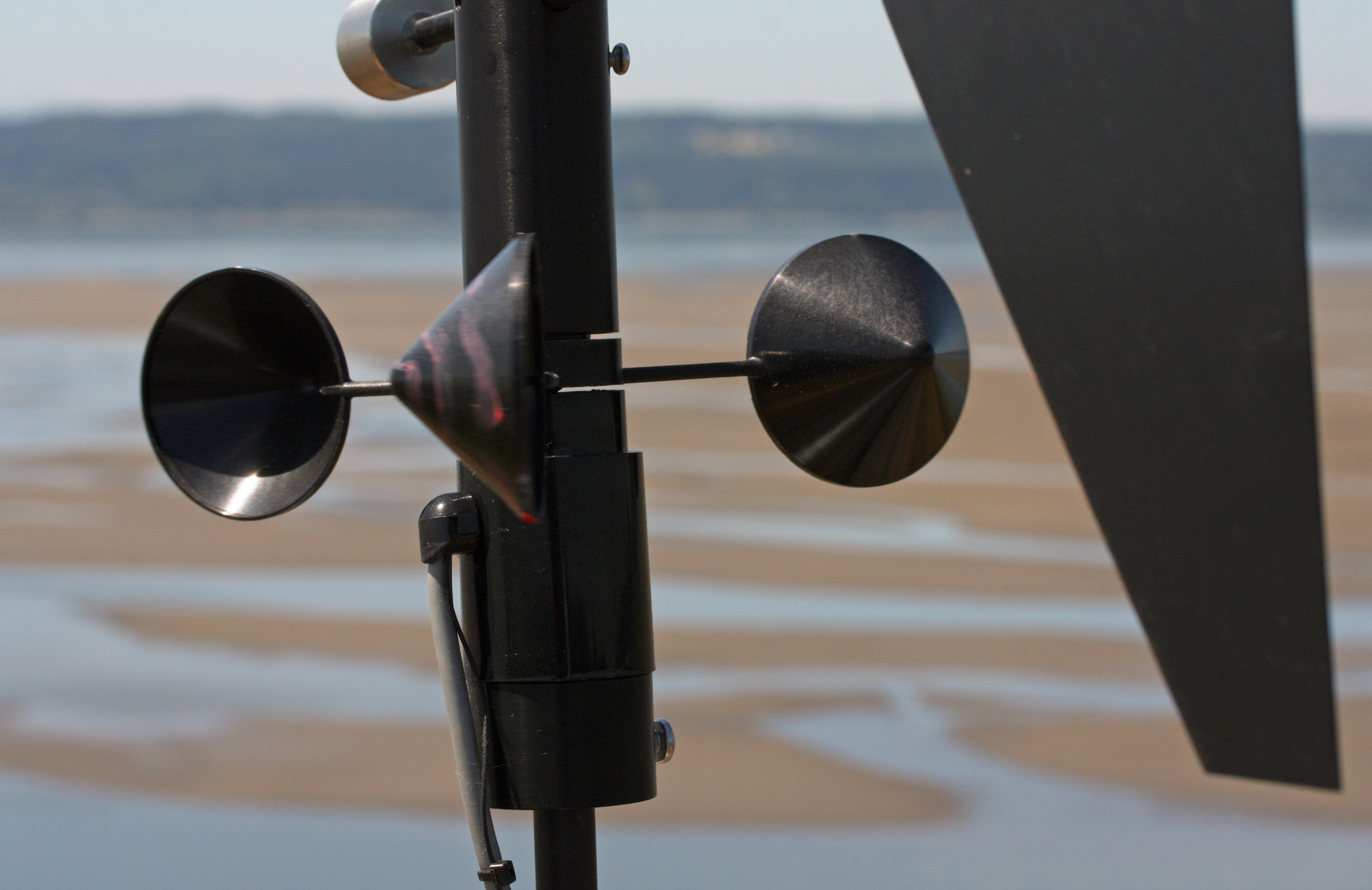
s indicate wind direction, and can also be used to estimate wind speed by the angle of hang. Wind speed is measured by anemometer
In meteorology, an anemometer () is a device that measures wind speed and direction. It is a common instrument used in weather stations. The earliest known description of an anemometer was by Italian architect and author Leon Battista Alberti ...
s, most commonly using rotating cups or propellers. When a high measurement frequency is needed (such as in research applications), wind can be measured by the propagation speed of ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
signals or by the effect of ventilation on the resistance of a heated wire. Another type of anemometer uses pitot tube
A pitot ( ) tube (pitot probe) measures fluid flow velocity. It was invented by a French engineer, Henri Pitot, in the early 18th century, and was modified to its modern form in the mid-19th century by a French scientist, Henry Darcy. It ...
s that take advantage of the pressure differential between an inner tube and an outer tube that is exposed to the wind to determine the dynamic pressure, which is then used to compute the wind speed.
Sustained wind speeds are reported globally at a height and are averaged over a 10‑minute time frame. The United States reports winds over a 1‑minute average for tropical cyclones, and a 2‑minute average within weather observations.Office of the Federal Coordinator for MeteorologyFederal Meteorological Handbook No. 1 – Surface Weather Observations and Reports September 2005
Appendix A: Glossary. Retrieved 2008-04-06. India typically reports winds over a 3‑minute average. Knowing the wind sampling average is important, as the value of a one-minute sustained wind is typically 14% greater than a ten-minute sustained wind. A short burst of high speed wind is termed a
wind gust
A gust or wind gust is a brief increase in the speed of the wind, usually less than 20 seconds. It is of a more transient character than a squall, which lasts minutes, and is followed by a lull or slackening in the wind speed. Generally, winds ar ...
, one technical definition of a wind gust is: the maxima that exceed the lowest wind speed measured during a ten-minute time interval by for periods of seconds. A squall
A squall is a sudden, sharp increase in wind speed lasting minutes, as opposed to a wind gust, which lasts for only seconds. They are usually associated with active weather, such as rain showers, thunderstorms, or heavy snow. Squalls refer to the ...
is an increase of the wind speed above a certain threshold, which lasts for a minute or more.
To determine winds aloft, rawinsondes determine wind speed by GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
, radio navigation
Radio navigation or radionavigation is the application of radio frequencies to determine a position of an object on the Earth, either the vessel or an obstruction. Like radiolocation, it is a type of radiodetermination.
The basic principles a ...
, or radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
tracking of the probe. Alternatively, movement of the parent weather balloon position can be tracked from the ground visually using theodolite
A theodolite () is a precision optical instrument for measuring angles between designated visible points in the horizontal and vertical planes. The traditional use has been for land surveying, but it is also used extensively for building an ...
s. Remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Eart ...
techniques for wind include SODAR, Doppler lidars and radars, which can measure the Doppler shift of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) li ...
scattered or reflected off suspended aerosols or molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
s, and radiometers and radars can be used to measure the surface roughness of the ocean from space or airplanes. Ocean roughness can be used to estimate wind velocity close to the sea surface over oceans. Geostationary satellite imagery can be used to estimate the winds at cloud top based upon how far clouds move from one image to the next. Wind engineering
Wind engineering is a subset of mechanical engineering, structural engineering, meteorology, and applied physics that analyzes the effects of wind in the natural and the built environment and studies the possible damage, inconvenience or benefits ...
describes the study of the effects of the wind on the built environment, including buildings, bridges and other artificial objects.
Wind force scale
Historically, the Beaufort wind force scale (created by Beaufort) provides an empirical description of wind speed based on observed sea conditions. Originally it was a 13-level scale (0-12), but during the 1940s, the scale was expanded to 18 levels (0-17). There are general terms that differentiate winds of different average speeds such as a breeze, a gale, a storm, or a hurricane. Within the Beaufort scale, gale-force winds lie between and with preceding adjectives such as moderate, fresh, strong, and whole used to differentiate the wind's strength within the gale category. A storm has winds of to . The terminology for tropical cyclones differs from one region to another globally. Most ocean basins use the average wind speed to determine the tropical cyclone's category. Below is a summary of the classifications used by Regional Specialized Meteorological Centers worldwide:Enhanced Fujita scale
TheEnhanced Fujita Scale
The Enhanced Fujita scale (abbreviated as EF-Scale) rates tornado intensity based on the severity of the damage they cause. It is used in some countries, including the United States, Canada, China, and Mongolia.
The Enhanced Fujita scale repl ...
(EF Scale) rates the strength of tornadoes by using damage to estimate wind speed. It has six levels, from visible damage to complete destruction. It is used in the United States and some other countries with small modifications (among which include Canada and France).
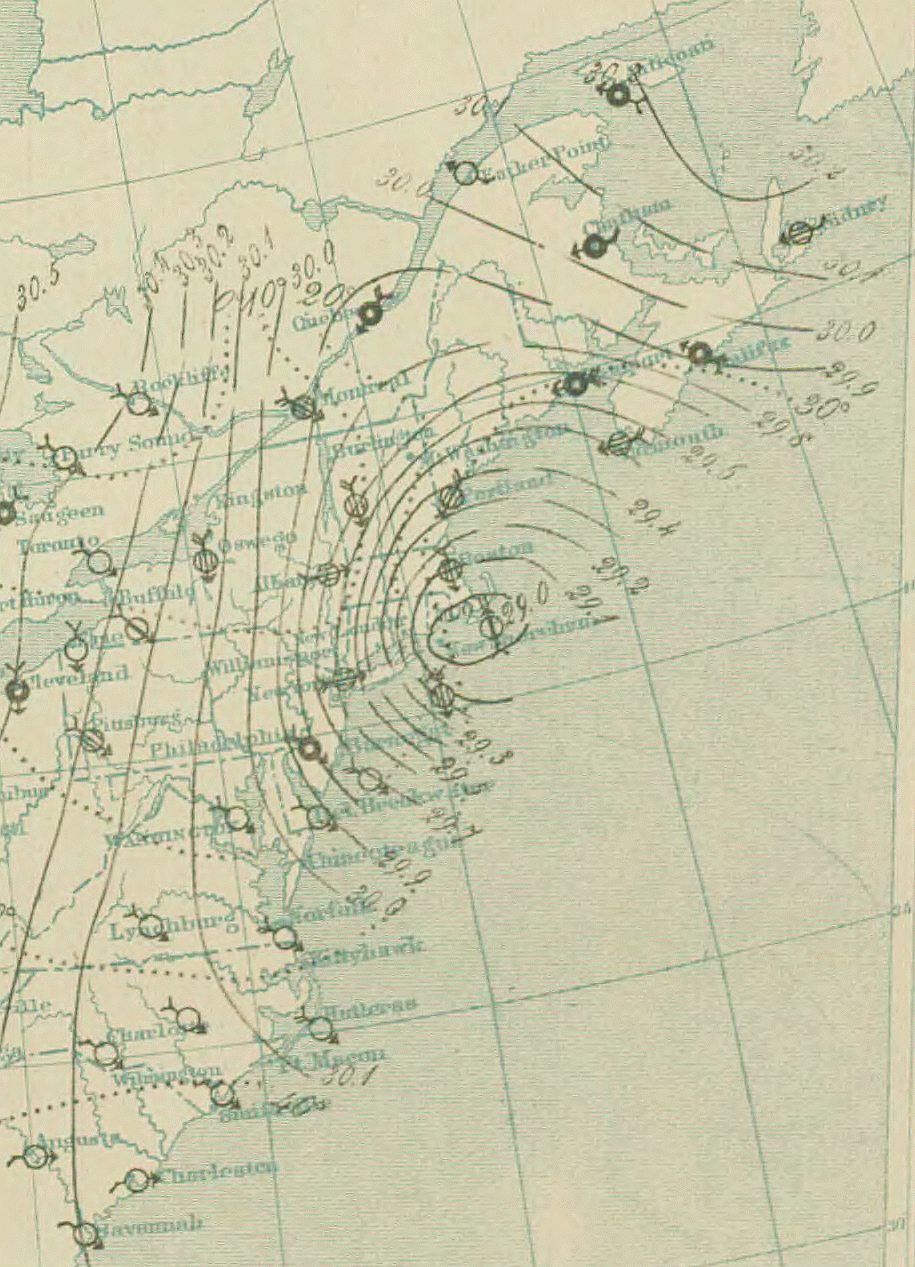
Station model
 The
The station model
In meteorology, station models are symbolic illustrations showing the weather occurring at a given reporting station. Meteorologists created the station model to fit a number of weather elements into a small space on weather maps. This allows map ...
plotted on surface weather map
A weather map, also known as synoptic weather chart, displays various meteorological features across a particular area at a particular point in time and has various symbols which all have specific meanings. Such maps have been in use since the m ...
s uses a wind barb to show both wind direction and speed. The wind barb shows the speed using "flags" on the end.
* Each half of a flag depicts of wind.
* Each full flag depicts of wind.
* Each pennant (filled triangle) depicts of wind.
Winds are depicted as blowing from the direction the barb is facing. Therefore, a northeast wind will be depicted with a line extending from the cloud circle to the northeast, with flags indicating wind speed on the northeast end of this line. Once plotted on a map, an analysis of isotach
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional grap ...
s (lines of equal wind speeds) can be accomplished. Isotachs are particularly useful in diagnosing the location of the jet stream on upper-level constant pressure charts, and are usually located at or above the 300 hPa level.
Global climatology

 Easterly winds, on average, dominate the flow pattern across the poles, westerly winds blow across the
Easterly winds, on average, dominate the flow pattern across the poles, westerly winds blow across the mid-latitudes
The middle latitudes (also called the mid-latitudes, sometimes midlatitudes, or moderate latitudes) are a spatial region on Earth located between the Tropic of Cancer (latitudes 23°26'22") to the Arctic Circle (66°33'39"), and Tropic of Caprico ...
of the earth, polewards of the subtropical ridge, while easterlies again dominate the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referr ...
.
Directly under the subtropical ridge are the doldrums, or horse latitudes, where winds are lighter. Many of the Earth's deserts lie near the average latitude of the subtropical ridge, where descent reduces the relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
of the air mass. The strongest winds are in the mid-latitudes where cold polar air meets warm air from the tropics.
Tropics
The trade winds (also called trades) are the prevailing pattern of easterly surface winds found in the tropics towards the Earth's equator. The trade winds blow predominantly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere. The trade winds act as the steering flow fortropical cyclones
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dependi ...
that form over the world's oceans. Trade winds also steer African dust westward across the Atlantic Ocean into the Caribbean, as well as portions of southeast North America.
A monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
is a seasonal prevailing wind that lasts for several months within tropical regions. The term was first used in English in India, Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
, Pakistan, and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
and Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Its poleward progression is accelerated by the development of a heat low over the Asian, African, and North American continents during May through July, and over Australia in December.
Westerlies and their impact
 The Westerlies or the Prevailing Westerlies are the
The Westerlies or the Prevailing Westerlies are the prevailing winds
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on ...
in the middle latitudes
The middle latitudes (also called the mid-latitudes, sometimes midlatitudes, or moderate latitudes) are a spatial region on Earth located between the Tropic of Cancer ( latitudes 23°26'22") to the Arctic Circle (66°33'39"), and Tropic of Cap ...
between 35 and 65 degrees latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
. These prevailing winds blow from the west to the east, and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere. They are strongest in the winter when the pressure is lower over the poles, and weakest during the summer and when pressures are higher over the poles.
Together with the trade wind
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisph ...
s, the westerlies enabled a round-trip trade route for sailing ships crossing the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, as the westerlies lead to the development of strong ocean currents on the western sides of oceans in both hemispheres through the process of western intensification. These western ocean currents transport warm, sub-tropical water polewards toward the polar regions. The westerlies can be particularly strong, especially in the southern hemisphere, where there is less land in the middle latitudes to cause the flow pattern to amplify, which slows the winds down. The strongest westerly winds in the middle latitudes are within a band known as the Roaring Forties, between 40th parallel south, 40 and 50th parallel south, 50 degrees latitude south of the equator. The Westerlies play an important role in carrying the warm, equatorial waters and winds to the western coasts of continents, especially in the southern hemisphere because of its vast oceanic expanse.
Polar easterlies
The polar easterlies, also known as Polar Hadley cells, are dry, cold prevailing winds that blow from the high-pressure areas of the polar highs at the north pole, north and south poles towards the low-pressure areas within the Westerlies at high latitudes. Unlike the Westerlies, these prevailing winds blow from the east to the west, and are often weak and irregular. Because of the low sun angle, cold air builds up and Subsidence (atmosphere), subsides at the pole creating surface high-pressure areas, forcing an equatorward outflow of air; that outflow is deflected westward by the Coriolis effect.Local considerations

Sea and land breezes
Near mountains
Shear
thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are some ...
s, weather fronts, areas of locally higher low level winds referred to as low level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur because of clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has a significant effect on the control of aircraft during take-off and landing, and was a significant cause of aircraft accidents involving large loss of life within the United States.
Sound movement through the atmosphere is affected by wind shear, which can bend the wave front, causing sounds to be heard where they normally would not, or vice versa. Strong vertical wind shear within the troposphere also inhibits tropical cyclone development, but helps to organize individual thunderstorms into living longer life cycles that can then produce severe weather. The thermal wind
The thermal wind is the vector difference between the geostrophic wind at upper altitudes minus that at lower altitudes in the atmosphere. It is the hypothetical vertical wind shear that would exist if the winds obey geostrophic balance in the ...
concept explains how differences in wind speed with height are dependent on horizontal temperature differences, and explains the existence of the jet stream.
In civilization
Religion
As a natural force, the wind was often personified as one or more wind gods or as an expression of the supernatural in many cultures. Vayu is the Historical Vedic religion, Vedic and Hindu God of Wind. The Greek wind gods include Boreas (god), Boreas, Greek Goddess, Notus, Eurus, and Zephyrus. Aeolus, in varying interpretations the ruler or keeper of the four winds, has also been described as Astraeus, the god of dusk who fathered the four winds with Eos, goddess of dawn. The ancient Greeks also observed the seasonal change of the winds, as evidenced by the Tower of the Winds in Athens. Venti are the Roman gods of the winds. Fūjin is the Japanese wind god and is one of the eldest Shinto gods. According to legend, he was present at the creation of the world and first let the winds out of his bag to clear the world of mist. In Norse mythology, Njörðr is the god of the wind. There are also four dvärgar (Norse dwarves), named Norðri, Suðri, Austri and Vestri, and probably the four stags of Yggdrasil, personify the four winds, and parallel the four Greek wind gods. Stribog is the name of the Slavic Mythology, Slavic god of winds, sky and air. He is said to be the ancestor (grandfather) of the winds of the eight directions.History
Kamikaze (typhoon), Kamikaze is a Japanese word, usually translated as divine wind, believed to be a gift from the gods. The term is first known to have been used as the name of a pair or series of typhoons that are said to have saved Japan from two Mongol fleets under Kublai Khan that attacked Japan in 1274 and again in 1281. Protestant Wind is a name for the storm that deterred the Spanish Armada from an invasion of England in 1588 where the wind played a pivotal role, or the favorable winds that enabled William III of England, William of Orange to invade England in 1688. During Napoleon's French Invasion of Egypt (1798), Egyptian Campaign, the French soldiers had a hard time with the khamsin wind: when the storm appeared "as a blood-stint in the distant sky", the Ottomans went to take cover, while the French "did not react until it was too late, then choked and fainted in the blinding, suffocating walls of dust". During the North African Campaign of the World War II, "allied and German troops were several times forced to halt in mid-battle because of sandstorms caused by khamsin... Grains of sand whirled by the wind blinded the soldiers and created electrical disturbances that rendered compasses useless."Transportation
 There are many different forms of sailing ships, but they all have certain basic things in common. Except for rotor ships using the Magnus effect, every sailing ship has a hull (ship), hull, rigging and at least one mast (sailing), mast to hold up the sails that use the wind to power the ship. Ocean journeys by sailing ship can take many months, and a common hazard is becoming becalmed because of lack of wind, or being blown off course by severe storms or winds that do not allow progress in the desired direction. A severe storm could lead to shipwreck, and the loss of all hands. Sailing ships can only carry a certain quantity of supplies in their hold (ship), hold, so they have to plan long Maritime history, voyages carefully to include appropriate Provisioning of USS Constitution, provisions, including fresh water.
For aerodynamic aircraft which operate relative to the air, winds affect groundspeed, and in the case of lighter-than-air vehicles, wind may play a significant or solitary role in their movement and ground track. The
There are many different forms of sailing ships, but they all have certain basic things in common. Except for rotor ships using the Magnus effect, every sailing ship has a hull (ship), hull, rigging and at least one mast (sailing), mast to hold up the sails that use the wind to power the ship. Ocean journeys by sailing ship can take many months, and a common hazard is becoming becalmed because of lack of wind, or being blown off course by severe storms or winds that do not allow progress in the desired direction. A severe storm could lead to shipwreck, and the loss of all hands. Sailing ships can only carry a certain quantity of supplies in their hold (ship), hold, so they have to plan long Maritime history, voyages carefully to include appropriate Provisioning of USS Constitution, provisions, including fresh water.
For aerodynamic aircraft which operate relative to the air, winds affect groundspeed, and in the case of lighter-than-air vehicles, wind may play a significant or solitary role in their movement and ground track. The velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity i ...
of surface wind is generally the primary factor governing the direction of flight operations at an airport, and airfield runways are aligned to account for the common wind direction(s) of the local area. While taking off with a tailwind may be necessary under certain circumstances, a headwind is generally desirable. A tailwind increases takeoff distance required and decreases the climb gradient.
Power source
 The ancient Sinhalese people, Sinhalese of Anuradhapura and in other cities around Sri Lanka used the monsoon winds to power furnaces as early as 300 Common Era, BCE. The furnaces were constructed on the path of the monsoon winds to bring the temperatures inside up to . A rudimentary windmill was used to power an organ (music), organ in the first century CE. Windmills were later built in Sistan, Afghanistan, from the 7th century CE. These were vertical-axle windmills, with Windmill sail, sails covered in reed mat (craft), reed matting or cloth material. These windmills were used to grind corn and draw up water, and were used in the gristmilling and sugarcane industries. Horizontal-axle windmills were later used extensively in Northwestern Europe to grind flour beginning in the 1180s, and many Dutch windmills still exist.
Wind power is now one of the main sources of renewable energy, and its use is growing rapidly, driven by innovation and falling prices. Most of the installed capacity in wind power is Wind farm, onshore, but offshore wind power offers a large potential as wind speeds are typically higher and more constant away from the coast. Wind energy the kinetic energy of the air, is proportional to the third power of wind velocity. Betz's law described the theoretical upper limit of what fraction of this energy wind turbines can extract, which is about 59%.
The ancient Sinhalese people, Sinhalese of Anuradhapura and in other cities around Sri Lanka used the monsoon winds to power furnaces as early as 300 Common Era, BCE. The furnaces were constructed on the path of the monsoon winds to bring the temperatures inside up to . A rudimentary windmill was used to power an organ (music), organ in the first century CE. Windmills were later built in Sistan, Afghanistan, from the 7th century CE. These were vertical-axle windmills, with Windmill sail, sails covered in reed mat (craft), reed matting or cloth material. These windmills were used to grind corn and draw up water, and were used in the gristmilling and sugarcane industries. Horizontal-axle windmills were later used extensively in Northwestern Europe to grind flour beginning in the 1180s, and many Dutch windmills still exist.
Wind power is now one of the main sources of renewable energy, and its use is growing rapidly, driven by innovation and falling prices. Most of the installed capacity in wind power is Wind farm, onshore, but offshore wind power offers a large potential as wind speeds are typically higher and more constant away from the coast. Wind energy the kinetic energy of the air, is proportional to the third power of wind velocity. Betz's law described the theoretical upper limit of what fraction of this energy wind turbines can extract, which is about 59%.
Recreation
 Wind figures prominently in several popular sports, including recreational hang gliding, hot air ballooning, kite flying, snowkiting, kite landboarding, kite surfing, paragliding, sailing, and windsurfing. In gliding, wind gradients just above the surface affect the takeoff and landing phases of flight of a Glider aircraft, glider. Wind gradient can have a noticeable effect on ground launches, also known as winch launches or wire launches. If the wind gradient is significant or sudden, or both, and the pilot maintains the same pitch attitude, the indicated airspeed will increase, possibly exceeding the maximum ground launch tow speed. The pilot must adjust the airspeed to deal with the effect of the gradient. When landing, wind shear is also a hazard, particularly when the winds are strong. As the glider descends through the wind gradient on final approach to landing, airspeed decreases while sink rate increases, and there is insufficient time to accelerate prior to ground contact. The pilot must anticipate the wind gradient and use a higher approach speed to compensate for it.
Wind figures prominently in several popular sports, including recreational hang gliding, hot air ballooning, kite flying, snowkiting, kite landboarding, kite surfing, paragliding, sailing, and windsurfing. In gliding, wind gradients just above the surface affect the takeoff and landing phases of flight of a Glider aircraft, glider. Wind gradient can have a noticeable effect on ground launches, also known as winch launches or wire launches. If the wind gradient is significant or sudden, or both, and the pilot maintains the same pitch attitude, the indicated airspeed will increase, possibly exceeding the maximum ground launch tow speed. The pilot must adjust the airspeed to deal with the effect of the gradient. When landing, wind shear is also a hazard, particularly when the winds are strong. As the glider descends through the wind gradient on final approach to landing, airspeed decreases while sink rate increases, and there is insufficient time to accelerate prior to ground contact. The pilot must anticipate the wind gradient and use a higher approach speed to compensate for it.
In the natural world
In arid climates, the main source of erosion is wind. The general wind circulation moves small particulates such as dust across wide oceans thousands of kilometers downwind of their point of origin, which is known as deflation. Westerly winds in the mid-latitudes of the planet drive the movement of ocean currents from west to east across the world's oceans. Wind has a very important role in aiding plants and other immobile organisms in dispersal of seeds, spores, pollen, etc. Although wind is not the primary form of seed dispersal in plants, it provides dispersal for a large percentage of the biomass of land plants.Erosion
 Erosion can be the result of material movement by the wind. There are two main effects. First, wind causes small particles to be lifted and therefore moved to another region. This is called deflation. Second, these suspended particles may impact on solid objects causing erosion by abrasion (ecological succession). Wind erosion generally occurs in areas with little or no vegetation, often in areas where there is insufficient rainfall to support vegetation. An example is the formation of sand dunes, on a beach or in a desert. Loess is a homogeneous, typically nonstratified, porous, friable, slightly coherent, often calcareous, fine-grained, silty, pale yellow or buff, windblown (Aeolian) sediment. It generally occurs as a widespread blanket deposit that covers areas of hundreds of square kilometers and tens of meters thick. Loess often stands in either steep or vertical faces. Loess tends to develop into highly rich soils. Under appropriate climatic conditions, areas with loess are among the most agriculturally productive in the world. Loess deposits are geologically unstable by nature, and will erode very readily. Therefore, windbreaks (such as big trees and bushes) are often planted by farmers to reduce the wind erosion of loess.
Erosion can be the result of material movement by the wind. There are two main effects. First, wind causes small particles to be lifted and therefore moved to another region. This is called deflation. Second, these suspended particles may impact on solid objects causing erosion by abrasion (ecological succession). Wind erosion generally occurs in areas with little or no vegetation, often in areas where there is insufficient rainfall to support vegetation. An example is the formation of sand dunes, on a beach or in a desert. Loess is a homogeneous, typically nonstratified, porous, friable, slightly coherent, often calcareous, fine-grained, silty, pale yellow or buff, windblown (Aeolian) sediment. It generally occurs as a widespread blanket deposit that covers areas of hundreds of square kilometers and tens of meters thick. Loess often stands in either steep or vertical faces. Loess tends to develop into highly rich soils. Under appropriate climatic conditions, areas with loess are among the most agriculturally productive in the world. Loess deposits are geologically unstable by nature, and will erode very readily. Therefore, windbreaks (such as big trees and bushes) are often planted by farmers to reduce the wind erosion of loess.
Desert dust migration
During mid-summer (July in the northern hemisphere), the westward-moving trade winds south of the northward-moving subtropical ridge expand northwestward from the Caribbean into southeastern North America. When dust from the Sahara moving around the southern periphery of the ridge within the belt of trade winds moves over land, rainfall is suppressed and the sky changes from a blue to a white appearance, which leads to an increase in red sunsets. Its presence negatively impacts air quality by adding to the count of airborne particulates. Over 50% of the African dust that reaches the United States affects Florida. Since 1970, dust outbreaks have worsened because of periods of drought in Africa. There is a large variability in the dust transport to the Caribbean and Florida from year to year. Dust events have been linked to a decline in the health of coral reefs across the Caribbean and Florida, primarily since the 1970s. Similar dust plumes originate in the Gobi Desert, which combined with pollutants, spread large distances downwind, or eastward, into North America. There are local names for winds associated with sand and dust storms. The Calima carries dust on southeast winds into the Canary islands. The Harmattan carries dust during the winter into the Gulf of Guinea. The Sirocco brings dust from north Africa into southern Europe because of the movement of extratropical cyclones through the Mediterranean. Spring storm systems moving across the eastern Mediterranean Sea cause dust to carry across Egypt and the Arabian peninsula, which are locally known as Khamsin. The Shamal (wind), Shamal is caused by cold fronts lifting dust into the atmosphere for days at a time across the Persian Gulf states.Effect on plants

Effect on animals
Cattle and sheep are prone to wind chill caused by a combination of wind and cold temperatures, when winds exceed , rendering their hair and wool coverings ineffective. Although penguins use both a layer of fat and feathers to help guard against coldness in both water and air, their flipper (anatomy), flippers and feet are less immune to the cold. In the coldest climates such as Antarctica, emperor penguins use kleptothermy, huddling behavior to survive the wind and cold, continuously alternating the members on the outside of the assembled group, which reduces heat loss by 50%. Flying insects, a subset of arthropods, are swept along by the prevailing winds, while birds follow their own course taking advantage of wind conditions, in order to either fly or glide. As such, fine line patterns within weather radar imagery, associated with converging winds, are dominated by insect returns. Bird migration, which tends to occur overnight within the lowest of the Earth's atmosphere, contaminates wind profiles gathered by weather radar, particularly the WSR-88D, by increasing the environmental wind returns by to . Pikas use a wall of pebbles to store dry plants and grasses for the winter in order to protect the food from being blown away. Cockroaches use slight winds that precede the attacks of potential predators, such as toads, to survive their encounters. Their cercus, cerci are very sensitive to the wind, and help them survive half of their attacks. Elk have a keen sense of smell that can detect potential upwind predators at a distance of . Increases in wind above signals glaucous gulls to increase their foraging and aerial attacks on thick-billed murres.Related damage
 High winds are known to cause damage, depending upon the magnitude of their velocity and pressure differential. Wind pressures are positive on the windward side of a structure and negative on the leeward side. Infrequent wind gusts can cause poorly designed suspension bridges to sway. When wind gusts are at a similar frequency to the swaying of the bridge, the bridge can be destroyed more easily, such as what occurred with the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (1940), Tacoma Narrows Bridge in 1940. Wind speeds as low as can lead to power outages due to tree branches disrupting the flow of energy through power lines. While no species of tree is guaranteed to stand up to hurricane-force winds, those with shallow roots are more prone to uproot, and brittle trees such as eucalyptus, sea hibiscus, and avocado are more prone to damage. Hurricane-force winds cause substantial damage to mobile homes, and begin to structurally damage homes with foundations. Winds of this strength due to downsloped winds off terrain have been known to shatter windows and sandblast paint from cars. Once winds exceed , homes completely collapse, and significant damage is done to larger buildings. Total destruction to artificial structures occurs when winds reach . The Saffir–Simpson scale and Enhanced Fujita scale were designed to help estimate wind speed from the damage caused by high winds related to tropical cyclones and tornadoes, and vice versa.
Australia's Barrow Island (Western Australia), Barrow Island holds the record for the strongest wind gust, reaching 408 km/h (253 mph) during tropical cyclone Olivia on 10 April 1996, surpassing the previous record of 372 km/h (231 mph) set on Mount Washington (New Hampshire) on the afternoon of 12 April 1934.
Wildfire intensity increases during daytime hours. For example, burn rates of smoldering logs are up to five times greater during the day because of lower humidity, increased temperatures, and increased wind speeds. Sunlight warms the ground during the day and causes air currents to travel uphill, and downhill during the night as the land cools. Wildfires are fanned by these winds and often follow the air currents over hills and through valleys. United States wildfire operations revolve around a 24-hour ''fire day'' that begins at 10:00 a.m. because of the predictable increase in intensity resulting from the daytime warmth.
High winds are known to cause damage, depending upon the magnitude of their velocity and pressure differential. Wind pressures are positive on the windward side of a structure and negative on the leeward side. Infrequent wind gusts can cause poorly designed suspension bridges to sway. When wind gusts are at a similar frequency to the swaying of the bridge, the bridge can be destroyed more easily, such as what occurred with the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (1940), Tacoma Narrows Bridge in 1940. Wind speeds as low as can lead to power outages due to tree branches disrupting the flow of energy through power lines. While no species of tree is guaranteed to stand up to hurricane-force winds, those with shallow roots are more prone to uproot, and brittle trees such as eucalyptus, sea hibiscus, and avocado are more prone to damage. Hurricane-force winds cause substantial damage to mobile homes, and begin to structurally damage homes with foundations. Winds of this strength due to downsloped winds off terrain have been known to shatter windows and sandblast paint from cars. Once winds exceed , homes completely collapse, and significant damage is done to larger buildings. Total destruction to artificial structures occurs when winds reach . The Saffir–Simpson scale and Enhanced Fujita scale were designed to help estimate wind speed from the damage caused by high winds related to tropical cyclones and tornadoes, and vice versa.
Australia's Barrow Island (Western Australia), Barrow Island holds the record for the strongest wind gust, reaching 408 km/h (253 mph) during tropical cyclone Olivia on 10 April 1996, surpassing the previous record of 372 km/h (231 mph) set on Mount Washington (New Hampshire) on the afternoon of 12 April 1934.
Wildfire intensity increases during daytime hours. For example, burn rates of smoldering logs are up to five times greater during the day because of lower humidity, increased temperatures, and increased wind speeds. Sunlight warms the ground during the day and causes air currents to travel uphill, and downhill during the night as the land cools. Wildfires are fanned by these winds and often follow the air currents over hills and through valleys. United States wildfire operations revolve around a 24-hour ''fire day'' that begins at 10:00 a.m. because of the predictable increase in intensity resulting from the daytime warmth.
In outer space
The solar wind is quite different from a terrestrial wind, in that its origin is the Sun, and it is composed of charged particles that have escaped the Sun's atmosphere. Similar to the solar wind, theplanetary wind
Atmospheric escape is the loss of planetary atmospheric gases to outer space. A number of different mechanisms can be responsible for atmospheric escape; these processes can be divided into thermal escape, non-thermal (or suprathermal) escape, and ...
is composed of light gases that escape planetary atmospheres. Over long periods of time, the planetary wind can radically change the composition of planetary atmospheres.
The fastest wind ever recorded came from the accretion disc of the IGR J17091-3624 black hole. Its speed is , which is 3% of the speed of light.
Planetary wind
 The hydrodynamic wind within the upper portion of a planet's atmosphere allows light chemical elements such as hydrogen to move up to the exobase, the lower limit of the exosphere, where the gases can then reach escape velocity, entering outer space without impacting other particles of gas. This type of gas loss from a planet into space is known as planetary wind. Such a process over geologic time causes water-rich planets such as the Earth to evolve into planets like Venus. Additionally, planets with hotter lower atmospheres could accelerate the loss rate of hydrogen.
The hydrodynamic wind within the upper portion of a planet's atmosphere allows light chemical elements such as hydrogen to move up to the exobase, the lower limit of the exosphere, where the gases can then reach escape velocity, entering outer space without impacting other particles of gas. This type of gas loss from a planet into space is known as planetary wind. Such a process over geologic time causes water-rich planets such as the Earth to evolve into planets like Venus. Additionally, planets with hotter lower atmospheres could accelerate the loss rate of hydrogen.
Solar wind
Rather than air, the solar wind is a Electric current, stream of charged particles—a plasma (physics), plasma—ejected from the stellar atmosphere, upper atmosphere of the sun at a rate of . It consists mostly of electrons and protons with energies of about 1 electron volt, keV. The stream of particles varies in temperature and speed with the passage of time. These particles are able to escape the Sun's gravity, in part because of the high temperature of the solar corona, corona, but also because of high kinetic energy that particles gain through a process that is not well understood. The solar wind creates the Heliosphere, a vast bubble in the interstellar medium surrounding the Solar System. Planets require large magnetic fields in order to reduce the ionization of their upper atmosphere by the solar wind. Other phenomena caused by the solar wind include geomagnetic storms that can knock out power grids on Earth, the aurora (phenomenon), aurorae such as the Aurora (astronomy), Northern Lights, and the plasma tails of comets that always point away from the Sun.On other planets
Strong winds at Venus's cloud tops circle the planet every four to five earth days. When the poles of Mars are exposed to sunlight after their winter, the frozen CO2 Sublimation (physics), sublimates, creating significant winds that sweep off the poles as fast as , which subsequently transports large amounts of dust and water vapor over its landscape. Other Martian winds have resulted in cleaning events and Spirit rover#Dust devils, dust devils. On Jupiter, wind speeds of are common in zonal jet streams. Saturn's winds are among the Solar System's fastest. Cassini–Huygens data indicated peak easterly winds of . On Uranus, northern hemisphere wind speeds reach as high as near 50 degrees north latitude. At the cloud tops of Neptune, prevailing winds range in speed from along the equator to at the poles. At 70° S latitude on Neptune, a high-speed jet stream travels at a speed of . The fastest wind on any known planet is on HD 80606 b located 190 light years away, where it blows at more than 11,000 mph or 5 km/s.See also
References
External links
Current map of global surface winds
{{Authority control Wind, Atmospheric dynamics Meteorological phenomena