William Shanks on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
William Shanks (25 January 1812 – June 1882) was an
 To calculate , Shanks used Machin's formula:
:
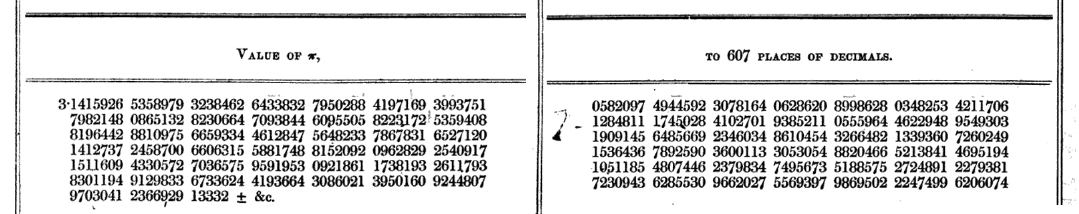
Shanks calculated to 530 decimal places in January 1853, of which the first 527 were correct (the last few likely being incorrect due to round-off errors). He subsequently expanded his calculation to 607 decimal places in April 1853, but an error introduced at the start of the new calculation, right at the 530th decimal place where his previous calculation ended, rendered the rest of his calculation erroneous. Due to the nature of Machin's formula, the error propagated back to the 528th decimal place, leaving only the first 527 digits correct once again. In April 1873, twenty years later, Shanks expanded his calculation to 707 decimal places. Due to this being an expansion of his previous calculation, all of the new digits were incorrect as well.
The approximation in the image reads as follows:
To calculate , Shanks used Machin's formula:
:
Shanks calculated to 530 decimal places in January 1853, of which the first 527 were correct (the last few likely being incorrect due to round-off errors). He subsequently expanded his calculation to 607 decimal places in April 1853, but an error introduced at the start of the new calculation, right at the 530th decimal place where his previous calculation ended, rendered the rest of his calculation erroneous. Due to the nature of Machin's formula, the error propagated back to the 528th decimal place, leaving only the first 527 digits correct once again. In April 1873, twenty years later, Shanks expanded his calculation to 707 decimal places. Due to this being an expansion of his previous calculation, all of the new digits were incorrect as well.
The approximation in the image reads as follows:
Shanks's biography at the University of St Andrews
Matt Parker explains the William Shanks method.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shanks, William 1812 births 1882 deaths 19th-century English mathematicians Pi-related people Amateur mathematicians People from Houghton-le-Spring
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
amateur mathematician. He is famous for his calculation of '' '' (pi) to 707 places in 1873, which was correct up to the first 527 places. The error was discovered in 1944 by D. F. Ferguson (using a mechanical desk calculator). Nevertheless, Shanks's approximation was the longest expansion of until the advent of the digital electronic computer in the 1940s.
Biography
Shanks was born in 1812 inCorsenside
Corsenside is one of the largest parishes in Northumberland, however the area is mainly a vast expanse of rolling hills and farmland, with three tiny villages: West Woodburn, East Woodburn and Ridsdale with about 600 inhabitants in total. The ar ...
. He may have been a student of William Rutherford as a young boy in the 1820s, and he dedicated a book on published in 1853 to Rutherford. After his marriage in 1846, Shanks earned his living by owning a boarding school at Houghton-le-Spring, which left him enough time to spend on his hobby of calculating mathematical constants.
In addition to calculating , Shanks also calculated '' e'' and the Euler–Mascheroni constant
Euler's constant (sometimes also called the Euler–Mascheroni constant) is a mathematical constant usually denoted by the lowercase Greek letter gamma ().
It is defined as the limiting difference between the harmonic series and the natural l ...
γ to many decimal places. He published a table of prime
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways ...
s (and the period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
s of their reciprocal
Reciprocal may refer to:
In mathematics
* Multiplicative inverse, in mathematics, the number 1/''x'', which multiplied by ''x'' gives the product 1, also known as a ''reciprocal''
* Reciprocal polynomial, a polynomial obtained from another pol ...
s) up to 110,000 and found the natural logarithms of 2, 3, 5 and 10 to 137 places. During his calculations, which took many tedious days of work, Shanks was said to have calculated new digits all morning and would then spend all afternoon checking his morning's work.
Shanks died in Houghton-le-Spring, County Durham, England in June 1882, aged 70, and was buried at the local Hillside Cemetery on 17 June 1882.
Calculations of pi
 To calculate , Shanks used Machin's formula:
:
Shanks calculated to 530 decimal places in January 1853, of which the first 527 were correct (the last few likely being incorrect due to round-off errors). He subsequently expanded his calculation to 607 decimal places in April 1853, but an error introduced at the start of the new calculation, right at the 530th decimal place where his previous calculation ended, rendered the rest of his calculation erroneous. Due to the nature of Machin's formula, the error propagated back to the 528th decimal place, leaving only the first 527 digits correct once again. In April 1873, twenty years later, Shanks expanded his calculation to 707 decimal places. Due to this being an expansion of his previous calculation, all of the new digits were incorrect as well.
The approximation in the image reads as follows:
To calculate , Shanks used Machin's formula:
:
Shanks calculated to 530 decimal places in January 1853, of which the first 527 were correct (the last few likely being incorrect due to round-off errors). He subsequently expanded his calculation to 607 decimal places in April 1853, but an error introduced at the start of the new calculation, right at the 530th decimal place where his previous calculation ended, rendered the rest of his calculation erroneous. Due to the nature of Machin's formula, the error propagated back to the 528th decimal place, leaving only the first 527 digits correct once again. In April 1873, twenty years later, Shanks expanded his calculation to 707 decimal places. Due to this being an expansion of his previous calculation, all of the new digits were incorrect as well.
The approximation in the image reads as follows:
See also
*Chronology of computation of π
The table below is a brief chronology of computed numerical values of, or bounds on, the mathematical constant pi (). For more detailed explanations for some of these calculations, see Approximations of π, Approximations of .
The last 100 dec ...
*History of π
The number (; spelled out as "pi") is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. The number appears in many formulas across mathematics and physics. It is an irrat ...
References
External links
Shanks's biography at the University of St Andrews
Matt Parker explains the William Shanks method.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shanks, William 1812 births 1882 deaths 19th-century English mathematicians Pi-related people Amateur mathematicians People from Houghton-le-Spring