Wilkinson power divider on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In the field of
In the field of
 The
The  Then the design guideline isD.M. Pozar, ''Microwave Engineering'', Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons: New York, 2005:
Then the design guideline isD.M. Pozar, ''Microwave Engineering'', Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons: New York, 2005:
The equal-splitting Wilkinson Divider is obtained for .
Online Wilkinson Power Split CalculatorOnline Resistive Power Split CalculatorOnline Coaxial Power Split CalculatorWilkinson power divider tutorial
with other power divider / combiner pages {{DEFAULTSORT:Wilkinson Power Divider Microwave technology Radio electronics
microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ran ...
engineering and circuit design, the Wilkinson Power Divider is a specific class of power divider circuit that can achieve isolation between the output ports while maintaining a matched condition on all ports. The Wilkinson design can also be used as a power combiner because it is made up of passive components
Passivity is a property of engineering systems, most commonly encountered in analog electronics and control systems. Typically, analog designers use ''passivity'' to refer to incrementally passive components and systems, which are incapable of p ...
and hence reciprocal. First published by Ernest J. Wilkinson in 1960, this circuit finds wide use in radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upp ...
communication systems utilizing multiple channels since the high degree of isolation between the output ports prevents crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk is any phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, induc ...
between the individual channels.
It uses quarter wave transformers, which can be easily fabricated as quarter wave lines on printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
s. It is also possible to use other forms of transmission line (e.g. coaxial cable) or lumped circuit elements (inductors and capacitors).Theory

 The
The scattering parameters
Scattering parameters or S-parameters (the elements of a scattering matrix or S-matrix) describe the electrical behavior of linear electrical networks when undergoing various steady state stimuli by electrical signals.
The parameters are useful f ...
for the common case of a 2-way equal-split Wilkinson power divider at the design frequency is given by
:
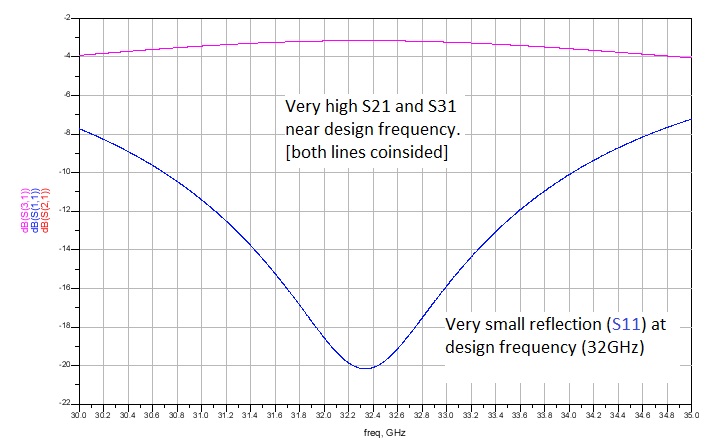
Inspection of the ''S'' matrix reveals that the network is reciprocal (), that the terminals are matched (), that the output terminals are isolated (=0), and that equal power division is achieved (). The non-unitary matrix
In linear algebra, a complex square matrix is unitary if its conjugate transpose is also its inverse, that is, if
U^* U = UU^* = UU^ = I,
where is the identity matrix.
In physics, especially in quantum mechanics, the conjugate transpose is ...
results from the fact that the network is lossy. An ideal Wilkinson divider would yield .
Network theorem governs that a divider cannot satisfy all three conditions (being matched, reciprocal and loss-less) at the same time. Wilkinson divider satisfies the first two (matched and reciprocal), and cannot satisfy the last one (being loss-less). Hence, there is some loss occurring in the network.
No loss occurs when the signals at ports 2 and 3 are in phase and have equal magnitude. In case of noise input to ports 2 and 3, the noise level at port 1 does not increase, half of the noise power is dissipated in the resistor.
By cascading, the input power might be divided to any -number of outputs.
Unequal/Asymmetric Division Through Wilkinson Divider
If the arms for port 2 and 3 are connected with un-equal impedances, then asymmetric division of power can be achieved.
When characteristic impedance is , and one wants to split power as and , and ≠ , then the design can be created following the equations:
A new constant is defined for ease of expression, where
 Then the design guideline isD.M. Pozar, ''Microwave Engineering'', Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons: New York, 2005:
Then the design guideline isD.M. Pozar, ''Microwave Engineering'', Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons: New York, 2005:The equal-splitting Wilkinson Divider is obtained for .
See also
*Power dividers and directional couplers
Power dividers (also power splitters and, when used in reverse, power combiners) and directional couplers are passive devices used mostly in the field of radio technology. They couple a defined amount of the electromagnetic power in a transmiss ...
References
External links
Online Wilkinson Power Split Calculator
with other power divider / combiner pages {{DEFAULTSORT:Wilkinson Power Divider Microwave technology Radio electronics