Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (shortened as Roman or the Roman Space Telescope, and formerly the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Telescope or WFIRST) is a NASA
 The original design of Roman, called WFIRST Design Reference Mission 1, was studied in 2011–2012, featuring a diameter unobstructed
The original design of Roman, called WFIRST Design Reference Mission 1, was studied in 2011–2012, featuring a diameter unobstructed
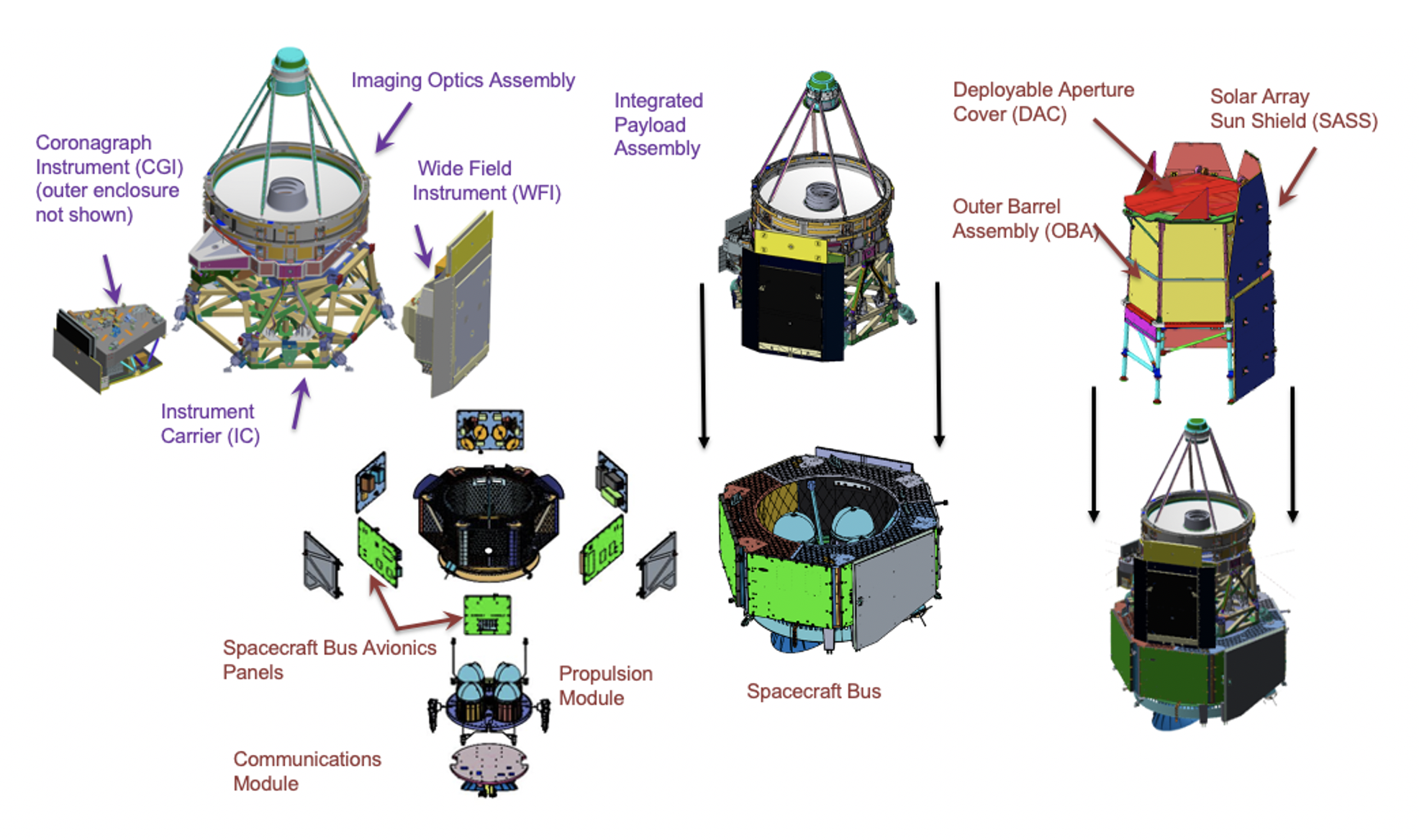 The science objectives of Roman aim to address cutting-edge questions in
The science objectives of Roman aim to address cutting-edge questions in
 The telescope is to carry two instruments.
;WFI: The Wide-Field Instrument (WFI) is a 300.8-
The telescope is to carry two instruments.
;WFI: The Wide-Field Instrument (WFI) is a 300.8-
 In the fiscal year 2014, Congress provided US$56 million for Roman, and in 2015 Congress provided US$50 million. The fiscal year 2016 spending bill provided US$90 million for Roman, far above NASA's request of US$14 million, allowing the mission to enter the "formulation phase" in February 2016. On 18 February 2016, NASA announced that Roman had formally become a project (as opposed to a study), meaning that the agency intends to carry out the mission as baselined; at that time, the "AFTA" portion of the name was dropped as only that approach is being pursued. Roman is on a plan for a mid-2020s launch. The total cost of Roman at that point was expected at more than US$2 billion; NASA's 2015 budget estimate was around US$2.0 billion in 2010 dollars, which corresponds to around US$2.7 billion in real year (inflation-adjusted) dollars.
In April 2017, NASA commissioned an independent review of the project to ensure that the mission scope and cost were understood and aligned. The review acknowledged that Roman offers "groundbreaking and unprecedented survey capabilities for
In the fiscal year 2014, Congress provided US$56 million for Roman, and in 2015 Congress provided US$50 million. The fiscal year 2016 spending bill provided US$90 million for Roman, far above NASA's request of US$14 million, allowing the mission to enter the "formulation phase" in February 2016. On 18 February 2016, NASA announced that Roman had formally become a project (as opposed to a study), meaning that the agency intends to carry out the mission as baselined; at that time, the "AFTA" portion of the name was dropped as only that approach is being pursued. Roman is on a plan for a mid-2020s launch. The total cost of Roman at that point was expected at more than US$2 billion; NASA's 2015 budget estimate was around US$2.0 billion in 2010 dollars, which corresponds to around US$2.7 billion in real year (inflation-adjusted) dollars.
In April 2017, NASA commissioned an independent review of the project to ensure that the mission scope and cost were understood and aligned. The review acknowledged that Roman offers "groundbreaking and unprecedented survey capabilities for
Roman page at Goddard Space Flight Center site
Roman Science Data Center page at the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center (IPAC)
–
The WFIRST/AFTA astrophysics mission: bigger and better for exoplanets
, Tom Greene * * 30 May 2014 * 16 March 2015 * 18 February 2016 {{Future spaceflights Infrared telescopes Space telescopes Future spaceflights Proposed NASA space probes NASA programs Exoplanet search projects Goddard Space Flight Center 2026 in spaceflight Dark energy
infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
space telescope
A space telescope or space observatory is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launch ...
currently in development and scheduled to launch by May 2027. Roman was recommended in 2010 by the United States National Research Council
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (also known as NASEM or the National Academies) are the collective scientific national academy of the United States. The name is used interchangeably in two senses: (1) as an umbrel ...
Decadal Survey committee as the top priority for the next decade of astronomy. On 17 February 2016, WFIRST was approved for development and launch.
The Roman Space Telescope is based on an existing wide field of view
The field of view (FoV) is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation.
Human ...
primary mirror and will carry two scientific instruments. The Wide-Field Instrument (WFI) is a 300.8-megapixel multi-band visible and near-infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from ...
camera, providing a sharpness of images comparable to that achieved by the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
over a 0.28 square degree field of view, 100 times larger than imaging cameras on the Hubble. The Coronagraphic Instrument (CGI) is a high-contrast, small field of view camera and spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the ...
covering visible and near-infrared wavelengths using novel starlight-suppression technology.
Stated objectives include a search for extra-solar planets
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
using gravitational microlensing
Gravitational microlensing is an astronomical phenomenon due to the gravitational lens effect. It can be used to detect objects that range from the mass of a planet to the mass of a star, regardless of the light they emit. Typically, astronomers ...
, along with probing the chronology of the universe
The chronology of the universe describes the history and future of the universe according to Big Bang cosmology.
Research published in 2015 estimates the earliest stages of the universe's existence as taking place 13.8 billion years ago, wit ...
and growth of cosmic structure, with the end goal of measuring the effects of dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univ ...
, the consistency of general relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics ...
, and the curvature of spacetime.
On 20 May 2020, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine
James Frederick Bridenstine (born June 15, 1975) is an American military officer and politician who served as the 13th administrator of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Bridenstine was the United States representative f ...
announced that the mission would be named the Nancy Grace Roman
Nancy Grace Roman (May 16, 1925 – December 25, 2018) was an American astronomer who made important contributions to stellar classification and motions. The first female executive at NASA, Roman served as NASA's first Chief of Astronomy through ...
Space Telescope in recognition of the former NASA Chief of Astronomy's role in the field of astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
. On 29 September 2021, NASA announced that Roman had passed its Critical Design Review
In the United States military integrated acquisition lifecycle the Technical section has multiple acquisition "Technical Reviews". Technical reviews and audits assist the acquisition and the number and types are tailored to the acquisition. Over ...
(CDR), and that with predicted impacts from COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly ...
disruptions, the launch date would be no later than May 2027.
As of July 2022, Roman is scheduled to be launched on a Falcon Heavy
Falcon Heavy is a partially reusable heavy-lift launch vehicle that is produced by SpaceX, an American aerospace manufacturer. The rocket consists of two strap-on boosters made from Falcon 9 first stages, a center core also made from a Falc ...
launch vehicle under a contract specifying readiness by October 2026 in support of a NASA launch commitment of May 2027.
Development of mission
three-mirror anastigmat
A three-mirror anastigmat is an anastigmat telescope built with three curved mirrors, enabling it to minimize all three main optical aberrations – spherical aberration, coma, and astigmatism. This is primarily used to enable wide fields of view, ...
telescope. It contained a single instrument, a visible to near-infrared imager/slitless prism spectrometer.
In 2012, another possibility emerged: NASA could use a second-hand National Reconnaissance Office
The National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) is a member of the United States Intelligence Community and an agency of the United States Department of Defense which designs, builds, launches, and operates the reconnaissance satellites of the U.S. fe ...
(NRO) telescope made by Harris Corporation to accomplish a mission like the one planned for Roman. NRO offered to donate two telescopes, the same size as the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
but with a shorter focal length and hence a wider field of view
The field of view (FoV) is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation.
Human ...
. This provided important political momentum to the project, even though the telescope represents only a modest fraction of the cost of the mission and the boundary conditions from the NRO design may push the total cost over that of a fresh design. This mission concept, called WFIRST-AFTA (Astrophysics Focused Telescope Assets), was matured by a scientific and technical team; this mission is now the only present NASA plan for the use of the NRO telescopes. The Roman baseline design includes a coronagraph
A coronagraph is a telescopic attachment designed to block out the direct light from a star so that nearby objects – which otherwise would be hidden in the star's bright glare – can be resolved. Most coronagraphs are intended to view t ...
to enable the direct imaging
Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For example, a star like the Sun is about a billion times as bright as the reflected light from any of the planets orbiting it. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty ...
of exoplanets.
Several implementations of WFIRST/Roman were studied. These included the Joint Dark Energy Mission-Omega configuration, an Interim Design Reference Mission featuring a telescope, Design Reference Mission 1 with a 1.3 m telescope, Design Reference Mission 2, with a telescope, and several iterations of the AFTA configuration. In the 2015 "Final" report, Roman was considered for both geosynchronous
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbital ...
and L2 orbits. L2 has disadvantages versus geosynchronous orbit in available data rate and propellant required, but advantages for improved observing constraints, better thermal stability, and more benign radiation environment. Some science cases (such as exoplanet microlensing parallax) are improved at L2, but the possibility of robotic servicing at either of the locations is currently unknown. By Feb 2016 it had been decided to use a halo orbit around L2.
The project is led by a team at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland
Greenbelt is a city in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States, and a suburb of Washington, D.C. At the 2020 census, the population was 24,921.
Greenbelt is the first and the largest of the three experimental and controversial New D ...
. On 30 November 2018, NASA announced it had awarded a contract for the telescope. This was for a part called the Optical Telescope Assembly or OTA, and runs to 2025. This is in conjunction with the Goddard Space Flight Center for which the OTA is planned for delivery as part of this contract.
A February 2019 description of the mission's capabilities is available in a white paper issued by members of the Roman team.
Science objectives
 The science objectives of Roman aim to address cutting-edge questions in
The science objectives of Roman aim to address cutting-edge questions in cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosopher ...
and exoplanet research, including:
* Answering basic questions about dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univ ...
, complementary to the European Space Agency (ESA) Euclid
Euclid (; grc-gre, Εὐκλείδης; BC) was an ancient Greek mathematician active as a geometer and logician. Considered the "father of geometry", he is chiefly known for the '' Elements'' treatise, which established the foundations of ...
mission, and including: Is cosmic acceleration caused by a new energy component or by the breakdown of general relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics ...
on cosmological scales? If the cause is a new energy component, is its energy density constant in space and time, or has it evolved over the history of the universe
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
? Roman will use three independent techniques to probe dark energy: baryon acoustic oscillations
In cosmology, baryon acoustic oscillations (BAO) are fluctuations in the density of the visible baryonic matter (normal matter) of the universe, caused by acoustic density waves in the primordial plasma of the early universe. In the same way ...
, observations of distant supernovae, weak gravitational lensing
While the presence of any mass bends the path of light passing near it, this effect rarely produces the giant arcs and multiple images associated with strong gravitational lensing. Most lines of sight in the universe are thoroughly in the weak le ...
.
* Completing a census of exoplanets to help answer new questions about the potential for life in the universe: How common are solar systems like our own? What kinds of planets exist in the cold, outer regions of planetary systems? – What determines the habitability
Habitability refers to the adequacy of an environment for human living. Where housing is concerned, there are generally local ordinances which define habitability. If a residence complies with those laws it is said to be habitable. In extreme e ...
of Earth-like worlds? This census makes use of a technique that can find exoplanets down to a mass only a few times that of the Moon: gravitational microlensing
Gravitational microlensing is an astronomical phenomenon due to the gravitational lens effect. It can be used to detect objects that range from the mass of a planet to the mass of a star, regardless of the light they emit. Typically, astronomers ...
. The census would include also a sample of free-floating planets with masses likely down to the mass of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
.
* Establishing a guest investigator mode, enabling survey investigations to answer diverse questions about our galaxy and the universe.
* Providing a coronagraph
A coronagraph is a telescopic attachment designed to block out the direct light from a star so that nearby objects – which otherwise would be hidden in the star's bright glare – can be resolved. Most coronagraphs are intended to view t ...
for exoplanet direct imaging
Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For example, a star like the Sun is about a billion times as bright as the reflected light from any of the planets orbiting it. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty ...
that will provide the first direct images and spectra of planets around our nearest neighbors similar to our own giant planets.
Instruments
 The telescope is to carry two instruments.
;WFI: The Wide-Field Instrument (WFI) is a 300.8-
The telescope is to carry two instruments.
;WFI: The Wide-Field Instrument (WFI) is a 300.8-megapixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the sm ...
camera providing multi-band visible to near-infrared (0.48 to 2.30 µm) imaging using one wideband and six narrowband filters. A HgCdTe Hg1−xCdxTe or mercury cadmium telluride (also cadmium mercury telluride, MCT, MerCad Telluride, MerCadTel, MerCaT or CMT) is a chemical compound of cadmium telluride (CdTe) and mercury telluride (HgTe) with a tunable bandgap spanning the shortwav ...
-based focal-plane array captures a 0.28 square degree field of view
The field of view (FoV) is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation.
Human ...
with a pixel scale of 110 milliarcseconds. The detector array is composed of 18 H4RG-10 detectors provided by Teledyne
Teledyne Technologies Incorporated is an American industrial conglomerate. It was founded in 1960, as Teledyne, Inc., by Henry Singleton and George Kozmetsky.
From August 1996 to November 1999, Teledyne existed as part of the conglomerate All ...
. It also carries both high-dispersion grism and low-dispersion prism assemblies for wide-field slitless spectroscopy.
;CGI: The Coronagraphic Instrument (CGI) is a high contrast coronagraph
A coronagraph is a telescopic attachment designed to block out the direct light from a star so that nearby objects – which otherwise would be hidden in the star's bright glare – can be resolved. Most coronagraphs are intended to view t ...
covering shorter wavelengths (0.5 to 0.8 µm) using dual deformable mirror starlight-suppression technology. It is intended to achieve a part-per-billion suppression of starlight to enable the detection and spectroscopy of planets with a visual separation of as little as 0.15 arcseconds from their host stars.
History
The design of the Roman Space Telescope has heritage to various proposed designs for the Joint Dark Energy Mission (JDEM) betweenNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
and the Department of Energy A Ministry of Energy or Department of Energy is a government department in some countries that typically oversees the production of fuel and electricity; in the United States, however, it manages nuclear weapons development and conducts energy-re ...
(DOE). Roman adds some extra capabilities to the original JDEM proposals, including a search for extra-solar planets
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
using gravitational microlensing
Gravitational microlensing is an astronomical phenomenon due to the gravitational lens effect. It can be used to detect objects that range from the mass of a planet to the mass of a star, regardless of the light they emit. Typically, astronomers ...
. In its present incarnation (2015), a large fraction of its primary mission will be focused on probing the expansion history of the Universe and the growth of cosmic structure with multiple methods in overlapping redshift ranges, with the goal of precisely measuring the effects of dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univ ...
, the consistency of general relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics ...
, and the curvature of spacetime.
On 2 March 2020, NASA announced that it had approved WFIRST to proceed to implementation, with an expected development cost of US$3.2 billion and a maximum total cost of US$3.934 billion, including the coronagraph and five years of mission science operations.
On 20 May 2020, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine
James Frederick Bridenstine (born June 15, 1975) is an American military officer and politician who served as the 13th administrator of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Bridenstine was the United States representative f ...
announced that the mission would be named the Nancy Grace Roman
Nancy Grace Roman (May 16, 1925 – December 25, 2018) was an American astronomer who made important contributions to stellar classification and motions. The first female executive at NASA, Roman served as NASA's first Chief of Astronomy through ...
Space Telescope in recognition of the former NASA Chief of Astronomy's role in the field of astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
.
On 31 March 2021, the NASA Office of Inspector General
The NASA Office of Inspector General (NASA OIG or OIG) is the inspector general office in the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the space agency of the United States. The OIG's stated mission is to "prevent and detect crime, fraud, wa ...
(OIG) released a report that stated that the development of the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope had been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
, which hit the US during a particularly important time in the telescope's development. NASA is expecting a total impact of US$400 million due to the pandemic and its effect on sub-contractors for the project. On 29 September 2021, NASA announced that Roman had passed its Critical Design Review
In the United States military integrated acquisition lifecycle the Technical section has multiple acquisition "Technical Reviews". Technical reviews and audits assist the acquisition and the number and types are tailored to the acquisition. Over ...
(CDR), and that with predicted impacts from COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly ...
disruptions the launch date would be no later than May 2027.
On 19 July 2022, NASA announced that Roman would be launched on a Falcon Heavy
Falcon Heavy is a partially reusable heavy-lift launch vehicle that is produced by SpaceX, an American aerospace manufacturer. The rocket consists of two strap-on boosters made from Falcon 9 first stages, a center core also made from a Falc ...
launch vehicle with a contract specifying readiness by October 2026 and a launch cost of approximately $255 million.
Funding history and status
 In the fiscal year 2014, Congress provided US$56 million for Roman, and in 2015 Congress provided US$50 million. The fiscal year 2016 spending bill provided US$90 million for Roman, far above NASA's request of US$14 million, allowing the mission to enter the "formulation phase" in February 2016. On 18 February 2016, NASA announced that Roman had formally become a project (as opposed to a study), meaning that the agency intends to carry out the mission as baselined; at that time, the "AFTA" portion of the name was dropped as only that approach is being pursued. Roman is on a plan for a mid-2020s launch. The total cost of Roman at that point was expected at more than US$2 billion; NASA's 2015 budget estimate was around US$2.0 billion in 2010 dollars, which corresponds to around US$2.7 billion in real year (inflation-adjusted) dollars.
In April 2017, NASA commissioned an independent review of the project to ensure that the mission scope and cost were understood and aligned. The review acknowledged that Roman offers "groundbreaking and unprecedented survey capabilities for
In the fiscal year 2014, Congress provided US$56 million for Roman, and in 2015 Congress provided US$50 million. The fiscal year 2016 spending bill provided US$90 million for Roman, far above NASA's request of US$14 million, allowing the mission to enter the "formulation phase" in February 2016. On 18 February 2016, NASA announced that Roman had formally become a project (as opposed to a study), meaning that the agency intends to carry out the mission as baselined; at that time, the "AFTA" portion of the name was dropped as only that approach is being pursued. Roman is on a plan for a mid-2020s launch. The total cost of Roman at that point was expected at more than US$2 billion; NASA's 2015 budget estimate was around US$2.0 billion in 2010 dollars, which corresponds to around US$2.7 billion in real year (inflation-adjusted) dollars.
In April 2017, NASA commissioned an independent review of the project to ensure that the mission scope and cost were understood and aligned. The review acknowledged that Roman offers "groundbreaking and unprecedented survey capabilities for dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univ ...
, exoplanet, and general astrophysics", but directed the mission to "reduce cost and complexity sufficient to have a cost estimate consistent with the US$3.2 billion cost target set at the beginning of Phase B". NASA announced (Jan 2018) the reductions taken in response to this recommendation, and that Roman would proceed to its mission design review in February 2018 and begin Phase B by April 2018. NASA confirmed (March 2018) that the changes made to the project had reduced its estimated life cycle cost to US$3.2 billion and that the Phase B decision was on track to begin on 11 April 2018.
In Feb 2018, the Trump administration's proposed a FY2019 budget that would have delayed the funding of the Roman (then called WFIRST), citing higher priorities within NASA and the increasing cost of this telescope. The proposed defunding of the project was met with criticism by professional astronomers, who noted that the American astronomical community had rated Roman the highest-priority space mission for the 2020s in the 2010 Decadal Survey. The American Astronomical Society expressed "grave concern" about the proposed defunding, and noted that the estimated lifecycle cost for Roman had not changed over the previous two years. However, on 22-23 March 2018, Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
approved a FY18 Roman budget in excess of the administration's budget request for that year and stated that Congress "rejects the cancellation of scientific priorities recommended by the National Academy of Sciences decadal survey process", and further directed NASA to develop new estimates of Roman's total and annual development costs. Later, the President announced he had signed the bill on 23 March 2018. NASA was funded via a FY2019 appropriations bill on February 15, 2019, with US$312 million for Roman, rejecting the President's reduced Budget Request and reasserting the desire for completion of Roman with a planning budget of US$3.2 billion.
In March 2019, again the Trump administration proposed to defund the Roman (then called WFIRST) in its FY2020 budget proposal to Congress. In testimony on 27 March 2019, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine
James Frederick Bridenstine (born June 15, 1975) is an American military officer and politician who served as the 13th administrator of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Bridenstine was the United States representative f ...
hinted that NASA would continue Roman after the James Webb Space Telescope, stating "WFIRST will be a critical mission when James Webb is on orbit". In a 26 March 2019, presentation to the National Academies' Committee on Astronomy and Astrophysics, NASA Astrophysics Division Director Paul L. Hertz
Paul Louis Hertz is an American astrophysicist, and is best known for being the longest-serving Director of the Astrophysics Division at NASA, with a tenure from 2012 to 2022.
Early life and education
Hertz studied both physics and mathemat ...
stated that Roman "is maintaining its US$3.2 billion cost for now... We need US$542 million in FY2020 to stay on track". At that time, it was stated that Roman would hold its Preliminary Design Review (PDR) for the overall mission in October 2019 followed by a formal mission confirmation in early 2020.
NASA announced the completion of the Preliminary Design Review
In the United States military integrated acquisition lifecycle the Technical section has multiple acquisition "Technical Reviews". Technical reviews and audits assist the acquisition and the number and types are tailored to the acquisition. Over ...
(PDR) on 1 November 2019, but warned that though the mission remained on track for a 2025 launch date, shortfalls in the Senate's FY2020 budget proposal for Roman threatened to delay it further.
On 2 March 2020, NASA announced that it had approved WFIRST to proceed to implementation, with an expected development cost of US$3.2 billion and a maximum total cost of US$3.934 billion, including the coronagraph and five years of mission science operations.
On 29 September 2021, NASA announced that Roman had successfully passed its Critical Design Review
In the United States military integrated acquisition lifecycle the Technical section has multiple acquisition "Technical Reviews". Technical reviews and audits assist the acquisition and the number and types are tailored to the acquisition. Over ...
(CDR), and that with flight hardware fabrication completed by 2024 followed by mission integration, the launch date would be no later than May 2027.
Institutions, partnerships, and contracts
The Roman project office is located at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center inGreenbelt, Maryland
Greenbelt is a city in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States, and a suburb of Washington, D.C. At the 2020 census, the population was 24,921.
Greenbelt is the first and the largest of the three experimental and controversial New D ...
, and holds responsibility for overall project management. GSFC also leads the development of the Wide-Field Instrument, the spacecraft, and the telescope. The Coronagraphic Instrument is being developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States.
Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA an ...
in Pasadena, California. Science support activities for Roman are shared among Space Telescope Science Institute
The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) is the science operations center for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), science operations and mission operations center for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), and science operations center for the ...
(Baltimore, Maryland
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by popula ...
), which is the Science Operations Center; the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center
The Infrared Processing and Analysis Center (IPAC) provides science operations, data management, data archives and community support for astronomy and planetary science missions. IPAC has a historical emphasis on infrared-submillimeter astronomy a ...
, Pasadena, California; and GSFC
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC empl ...
.
Partners
Four international space agencies, namely the French space agencyCNES
The (CNES; French: ''Centre national d'études spatiales'') is the French government space agency (administratively, a "public administration with industrial and commercial purpose"). Its headquarters are located in central Paris and it is und ...
, German Aerospace Center
The German Aerospace Center (german: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany ...
(DLR), European Space Agency (ESA), and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are (in 2019) in discussion with NASA to provide various components and science support for Roman. In 2016 NASA expressed interest in ESA contributions to the spacecraft, coronagraph and ground station support. For the coronagraph instrument, contributions from Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
and Japan are being discussed.
In 2018 a contribution from Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
's Max Planck Institute for Astronomy
The Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie (Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, MPIA) is a research institute of the Max Planck Society (MPG). It is located in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany near the top of the Königstuhl, adjacent to the ...
was under consideration, namely the filter wheels for the star-blocking mask inside the coronagraph. In 2016 the Japanese space agency JAXA proposed to add a polarization module for the coronagraph, plus a polarization compensator. An accurate polarimetry capability on Roman may strengthen the science case for exoplanets and planetary disks, which shows polarization.
In addition to these potential partnerships, Australia offered ground station contributions for the mission.
Construction contracts
In May 2018, NASA awarded a multi-year contract toBall Aerospace
Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. is an American manufacturer of spacecraft, components and instruments for national defense, civil space and commercial space applications. The company is a wholly owned subsidiary of Ball Corporation (NYSE: BAL ...
to provide key components (the WFI Opto-Mechanical Assembly) for the Wide-Field Instrument on Roman. In June 2018, NASA awarded a contract to Teledyne Scientific and Imaging to provide the infrared detectors for the Wide-Field Instrument. On 30 November 2018, NASA announced it had awarded the contract for Optical Telescope Assembly to the Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York
Rochester () is a city in the U.S. state of New York, the seat of Monroe County, and the fourth-most populous in the state after New York City, Buffalo, and Yonkers, with a population of 211,328 at the 2020 United States census. Located in W ...
.
See also
* * * * *References
External links
Roman page at Goddard Space Flight Center site
Roman Science Data Center page at the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center (IPAC)
–
Space.com
Space.com is an online publication focused on space exploration, astronomy, skywatching and entertainment, with editorial teams based in the United States and United Kingdom. The website offers live coverage of space missions, astronomical discov ...
The WFIRST/AFTA astrophysics mission: bigger and better for exoplanets
, Tom Greene * * 30 May 2014 * 16 March 2015 * 18 February 2016 {{Future spaceflights Infrared telescopes Space telescopes Future spaceflights Proposed NASA space probes NASA programs Exoplanet search projects Goddard Space Flight Center 2026 in spaceflight Dark energy