White-noise on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In  In
In
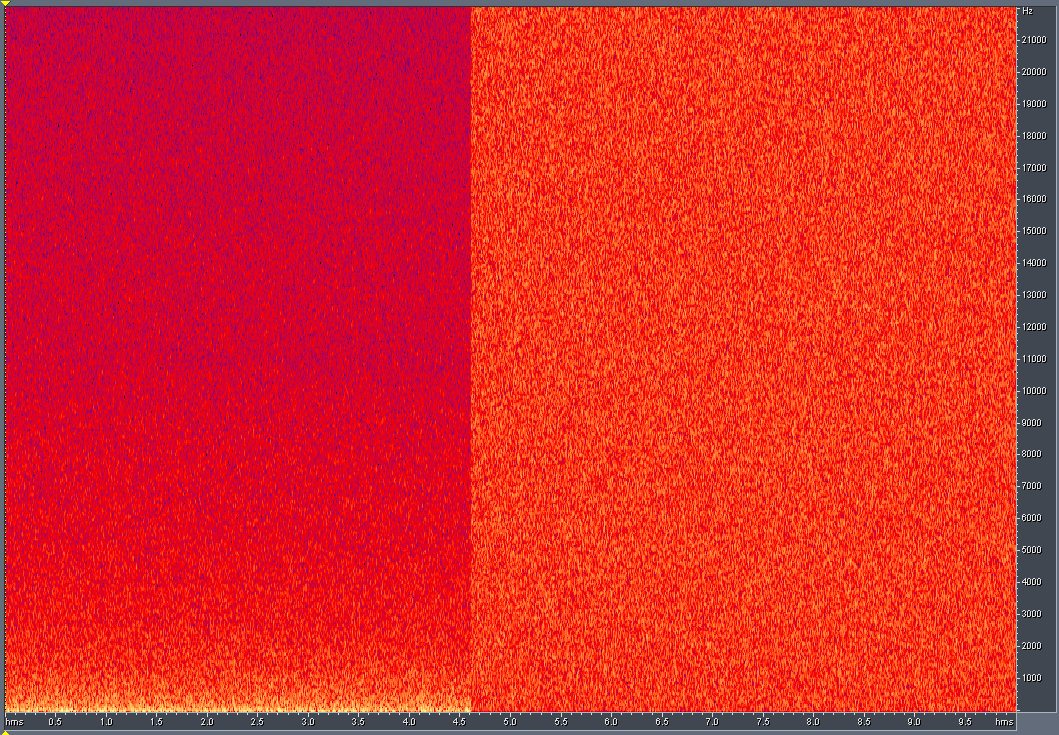 Any distribution of values is possible (although it must have zero
Any distribution of values is possible (although it must have zero
On Transformations of Random Vectors.
' Technical report 314, Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Univ. of Michigan. (
Modeling Financial Time Series with S-PLUS
Second Edition. (
Elements of Forecasting
'' 4th edition. (
signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniq ...
, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used, with this or similar meanings, in many scientific and technical disciplines, including physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
, acoustical engineering, telecommunications
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that fe ...
, and statistical forecasting. White noise refers to a statistical model for signals and signal sources, rather than to any specific signal. White noise draws its name from white light
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
, although light that appears white generally does not have a flat power spectral density over the visible band.
 In
In discrete time
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled.
Discrete time
Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "po ...
, white noise is a discrete signal whose samples are regarded as a sequence of serially uncorrelated random variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on random events. It is a mapping or a function from possible outcomes (e.g., the po ...
s with zero mean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude and sign) of a given data set.
For a data set, the ''arithme ...
and finite variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers ...
; a single realization of white noise is a random shock. Depending on the context, one may also require that the samples be independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independ ...
and have identical probability distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon i ...
(in other words independent and identically distributed random variables
In probability theory and statistics, a collection of random variables is independent and identically distributed if each random variable has the same probability distribution as the others and all are mutually independent. This property is us ...
are the simplest representation of white noise). In particular, if each sample has a normal distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
:
f(x) = \frac e^
The parameter \mu ...
with zero mean, the signal is said to be additive white Gaussian noise
Additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) is a basic noise model used in information theory to mimic the effect of many random processes that occur in nature. The modifiers denote specific characteristics:
* ''Additive'' because it is added to any nois ...
.
The samples of a white noise signal may be sequential in time, or arranged along one or more spatial dimensions. In digital image processing, the pixels of a ''white noise image'' are typically arranged in a rectangular grid, and are assumed to be independent random variables with uniform probability distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distribution or rectangular distribution is a family of symmetric probability distributions. The distribution describes an experiment where there is an arbitrary outcome that lies betw ...
over some interval. The concept can be defined also for signals spread over more complicated domains, such as a sphere or a torus.
An ''infinite-bandwidth white noise signal'' is a purely theoretical construction. The bandwidth of white noise is limited in practice by the mechanism of noise generation, by the transmission medium and by finite observation capabilities. Thus, random signals are considered "white noise" if they are observed to have a flat spectrum over the range of frequencies that are relevant to the context. For an audio signal
An audio signal is a representation of sound, typically using either a changing level of electrical voltage for analog signals, or a series of binary numbers for digital signals. Audio signals have frequencies in the audio frequency range of r ...
, the relevant range is the band of audible sound frequencies (between 20 and 20,000 Hz). Such a signal is heard by the human ear as a ''hissing sound'', resembling the /h/ sound in a sustained aspiration. On the other hand, the "sh" sound in "ash" is a colored noise because it has a formant structure. In music and acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician ...
, the term "white noise" may be used for any signal that has a similar hissing sound.
The term white noise is sometimes used in the context of phylogenetically based statistical methods to refer to a lack of phylogenetic pattern in comparative data. It is sometimes used analogously in nontechnical contexts to mean "random talk without meaningful contents".
Claire Shipman (2005), ''Good Morning America
''Good Morning America'' (often abbreviated as ''GMA'') is an American morning television program that is broadcast on ABC. It debuted on November 3, 1975, and first expanded to weekends with the debut of a Sunday edition on January 3, 1993. Th ...
'': "The political rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate parti ...
on Social Security is white noise." Said on ABC
ABC are the first three letters of the Latin script known as the alphabet.
ABC or abc may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Broadcasting
* American Broadcasting Company, a commercial U.S. TV broadcaster
** Disney–ABC Television ...
's ''Good Morning America
''Good Morning America'' (often abbreviated as ''GMA'') is an American morning television program that is broadcast on ABC. It debuted on November 3, 1975, and first expanded to weekends with the debut of a Sunday edition on January 3, 1993. Th ...
'' TV show, January 11, 2005.
Statistical properties
 Any distribution of values is possible (although it must have zero
Any distribution of values is possible (although it must have zero DC component
DC, D.C., D/C, Dc, or dc may refer to:
Places
* Washington, D.C. (District of Columbia), the capital and the federal territory of the United States
* Bogotá, Distrito Capital, the capital city of Colombia
* Dubai City, as distinct from the ...
). Even a binary signal which can only take on the values 1 or 0 will be white if the sequence is statistically uncorrelated. Noise having a continuous distribution, such as a normal distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
:
f(x) = \frac e^
The parameter \mu ...
, can of course be white.
It is often incorrectly assumed that Gaussian noise (i.e., noise with a Gaussian amplitude distributionsee normal distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
:
f(x) = \frac e^
The parameter \mu ...
) necessarily refers to white noise, yet neither property implies the other. Gaussianity refers to the probability distribution with respect to the value, in this context the probability of the signal falling within any particular range of amplitudes, while the term 'white' refers to the way the signal power is distributed (i.e., independently) over time or among frequencies.
White noise is the generalized mean-square derivative of the Wiener process or Brownian motion.
A generalization to random elements on infinite dimensional spaces, such as random fields, is the white noise measure
In mathematics, nuclear spaces are topological vector spaces that can be viewed as a generalization of finite dimensional Euclidean spaces and share many of their desirable properties. Nuclear spaces are however quite different from Hilbert space ...
.
Practical applications
Music
White noise is commonly used in the production of electronic music, usually either directly or as an input for a filter to create other types of noise signal. It is used extensively inaudio synthesis
A synthesizer (also spelled synthesiser) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating Waveform, waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synth ...
, typically to recreate percussive instruments such as cymbal
A cymbal is a common percussion instrument. Often used in pairs, cymbals consist of thin, normally round plates of various alloys. The majority of cymbals are of indefinite pitch, although small disc-shaped cymbals based on ancient designs soun ...
s or snare drum
The snare (or side drum) is a percussion instrument that produces a sharp staccato sound when the head is struck with a drum stick, due to the use of a series of stiff wires held under tension against the lower skin. Snare drums are often used ...
s which have high noise content in their frequency domain. A simple example of white noise is a nonexistent radio station (static).
Electronics engineering
White noise is also used to obtain theimpulse response
In signal processing and control theory, the impulse response, or impulse response function (IRF), of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an Dirac delta function, impulse (). More generally, an impulse ...
of an electrical circuit, in particular of amplifiers and other audio equipment. It is not used for testing loudspeakers as its spectrum contains too great an amount of high-frequency content. Pink noise, which differs from white noise in that it has equal energy in each octave, is used for testing transducers such as loudspeakers and microphones.
Computing
White noise is used as the basis of some random number generators. For example,Random.org
Random.org (stylized as RANDOM.ORG) is a website that produces random numbers based on atmospheric noise.
In addition to generating random numbers in a specified range and subject to a specified probability distribution, which is the most commo ...
uses a system of atmospheric antennae to generate random digit patterns from white noise.
Tinnitus treatment
White noise is a common synthetic noise source used for sound masking by a tinnitus masker.White noise machine
A white noise machine is a device that produces a noise that calms the listener, which in many cases sounds like a rushing waterfall or wind blowing through trees, and other serene or nature-like sounds. Often such devices do not produce actual wh ...
s and other white noise sources are sold as privacy enhancers and sleep aids (see music and sleep
Music and sleep involves the listening of music in order to improve sleep quality or improve sleep onset insomnia in adults (for infant use of music and sleep, see lullaby). This process can be either self-prescribed or under the guidance of a musi ...
) and to mask tinnitus. The Marpac Sleep-Mate was the first domestic use white noise machine built in 1962 by traveling salesman Jim Buckwalter. Alternatively, the use of an FM radio tuned to unused frequencies ("static") is a simpler and more cost-effective source of white noise. However, white noise generated from a common commercial radio receiver tuned to an unused frequency is extremely vulnerable to being contaminated with spurious signals, such as adjacent radio stations, harmonics from non-adjacent radio stations, electrical equipment in the vicinity of the receiving antenna causing interference, or even atmospheric events such as solar flares and especially lightning.
There is evidence that white noise exposure therapies may induce maladaptive changes in the brain that degrade neurological health and compromise cognition.
Work environment
The effects of white noise upon cognitive function are mixed. Recently, a small study found that white noise background stimulation improves cognitive functioning among secondary students with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), while decreasing performance of non-ADHD students. Other work indicates it is effective in improving the mood and performance of workers by masking background office noise, but decreases cognitive performance in complex card sorting tasks. Similarly, an experiment was carried out on sixty-six healthy participants to observe the benefits of using white noise in a learning environment. The experiment involved the participants identifying different images whilst having different sounds in the background. Overall the experiment showed that white noise does in fact have benefits in relation to learning. The experiments showed that white noise improved the participants' learning abilities and their recognition memory slightly.Mathematical definitions
White noise vector
A random vector (that is, a partially indeterminate process that produces vectors of real numbers) is said to be a white noise vector or white random vector if its components each have aprobability distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon i ...
with zero mean and finite variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers ...
, and are statistically independent: that is, their joint probability distribution
Given two random variables that are defined on the same probability space, the joint probability distribution is the corresponding probability distribution on all possible pairs of outputs. The joint distribution can just as well be considered ...
must be the product of the distributions of the individual components.
Jeffrey A. Fessler (1998), On Transformations of Random Vectors.
' Technical report 314, Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Univ. of Michigan. (
PDF
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
)
A necessary (but, in general, not sufficient) condition for statistical independence of two variables is that they be statistically uncorrelated; that is, their covariance is zero. Therefore, the covariance matrix
In probability theory and statistics, a covariance matrix (also known as auto-covariance matrix, dispersion matrix, variance matrix, or variance–covariance matrix) is a square matrix giving the covariance between each pair of elements of ...
''R'' of the components of a white noise vector ''w'' with ''n'' elements must be an ''n'' by ''n'' diagonal matrix, where each diagonal element ''Rii'' is the variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers ...
of component ''wi''; and the correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics ...
matrix must be the ''n'' by ''n'' identity matrix.
If, in addition to being independent, every variable in ''w'' also has a normal distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
:
f(x) = \frac e^
The parameter \mu ...
with zero mean and the same variance , ''w'' is said to be a Gaussian white noise vector. In that case, the joint distribution of ''w'' is a multivariate normal distribution; the independence between the variables then implies that the distribution has spherical symmetry in ''n''-dimensional space. Therefore, any orthogonal transformation of the vector will result in a Gaussian white random vector. In particular, under most types of discrete Fourier transform, such as FFT and Hartley
Hartley may refer to:
Places Australia
*Hartley, New South Wales
*Hartley, South Australia
**Electoral district of Hartley, a state electoral district
Canada
*Hartley Bay, British Columbia
United Kingdom
*Hartley, Cumbria
*Hartley, Plymou ...
, the transform ''W'' of ''w'' will be a Gaussian white noise vector, too; that is, the ''n'' Fourier coefficients of ''w'' will be independent Gaussian variables with zero mean and the same variance .
The power spectrum ''P'' of a random vector ''w'' can be defined as the expected value of the squared modulus
In mathematics, a square is the result of multiplication, multiplying a number by itself. The verb "to square" is used to denote this operation. Squaring is the same as exponentiation, raising to the power 2 (number), 2, and is denoted by a ...
of each coefficient of its Fourier transform ''W'', that is, ''Pi'' = E(, ''Wi'', 2). Under that definition, a Gaussian white noise vector will have a perfectly flat power spectrum, with ''Pi'' = ''σ''2 for all ''i''.
If ''w'' is a white random vector, but not a Gaussian one, its Fourier coefficients ''Wi'' will not be completely independent of each other; although for large ''n'' and common probability distributions the dependencies are very subtle, and their pairwise correlations can be assumed to be zero.
Often the weaker condition "statistically uncorrelated" is used in the definition of white noise, instead of "statistically independent". However, some of the commonly expected properties of white noise (such as flat power spectrum) may not hold for this weaker version. Under this assumption, the stricter version can be referred to explicitly as independent white noise vector.Eric Zivot and Jiahui Wang (2006)Modeling Financial Time Series with S-PLUS
Second Edition. (
PDF
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
) Other authors use strongly white and weakly white instead.Francis X. Diebold
Francis X. Diebold (born November 12, 1959) is an American economist known for his work in predictive econometric modeling, financial econometrics, and macroeconometrics. He earned both his B.S. and Ph.D. degrees at the University of Pennsylvani ...
(2007), Elements of Forecasting
'' 4th edition. (
PDF
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
)
An example of a random vector that is "Gaussian white noise" in the weak but not in the strong sense is