Western Park, Beijing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Taiye Lake or Taiye Pond was an
pp. 14 ff.
''Studies in the History of Gardens & Designed Landscapes: An International Quarterly''. Taylor & Francis, 2013. Accessed 16 November 2013.
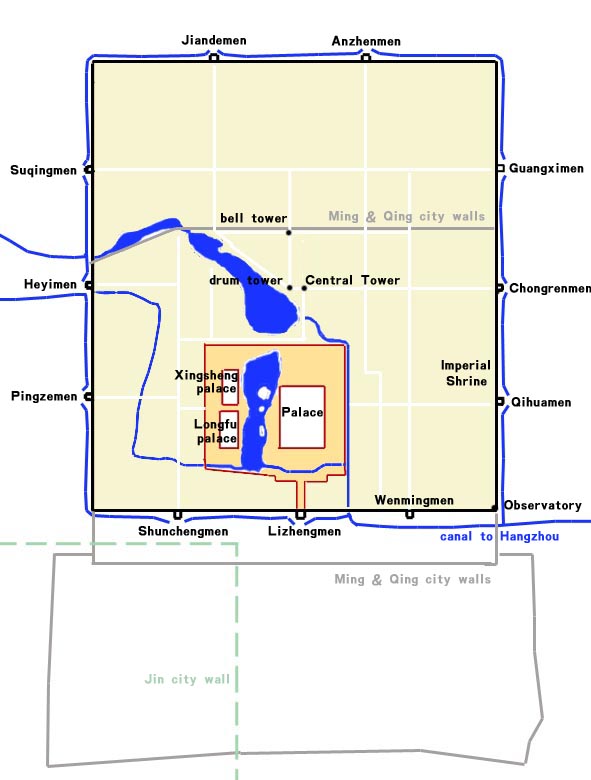 The lake was first constructed as part of the Jinshui River canal systemHou, Eve.
The lake was first constructed as part of the Jinshui River canal systemHou, Eve.
Nine Dragons, One River: The Role of Institutions in Developing Water Pricing Policy in Beijing, PRC
, p. 6. Univ. of British Columbia, 2001. under the
p. 137
Walter de Gruyter, 2011. Accessed 16 November 2013. During the
pp. 169 ff
Accessed 16 November 2013. The lake was expanded until it covered the area of the present northern and central "seas" and three palaces were built around it. The purity of the reservoir was protected by law: from its source at a spring on Yuquan Mountain to Lake Taiye, the Jinshui was given separate passes where it crossed other streams and commoners were forbidden to bathe, wash clothes, water livestock, or dump trash along its course.Du Pengfei. ''Zhōngguó Gǔdàide Chéngshì Jǐshuǐ''", "Water Supply of the Cities in Ancient China" ''China Historical Materials of Science and Technology'', Vol. 1, No. 19, pp. 3–10. Under the
Building an Immortal Land: The Ming Jiajing Emperor's West Park
. ''Asia Major'', 3rd Series, Vol. 22, No. 2 (2009), pp. 65-99. Accessed 15 November 2013. After the establishment of the
artificial lake
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including contro ...
in imperial City, Beijing
The Imperial City () is a section of the city of Beijing in the Ming dynasty, Ming and Qing dynasty, Qing dynasties, with the Forbidden City at its center. It refers to the collection of gardens, shrines, and other service areas between the Forbi ...
during the Jin, Yuan, Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
, and Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
dynasties
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A d ...
of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. The beauty and utility of the lake was responsible for the siting of Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of th ...
's palace and the position of modern Beijing. It continues to exist but it is now known separately as the "North", "Central", and "South Sea"s, the three interconnected lakes just west of the Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a Chinese palace, palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City, Beijing, Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples includ ...
in downtown Beijing. The northern lake makes up the public Beihai Park
Beihai Park () is a public park and former imperial garden located in the northwestern part of the Imperial City, Beijing. First built in the 11th century, it is among the largest of all Chinese gardens and contains numerous historicall ...
while the southern two are grouped together as Zhongnanhai
Zhongnanhai () is a former imperial garden in the Imperial City, Beijing, Imperial City, Beijing, adjacent to the Forbidden City; it serves as the central headquarters for the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the State Council of the People' ...
, the headquarters for the Communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
leadership of the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
.
Taiye Lake was immortalized in the early 1410s when the Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (; pronounced ; 2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), personal name Zhu Di (), was the third Emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 1424.
Zhu Di was the fourth son of the Hongwu Emperor, the founder of the Ming dyn ...
commissioned ''The Eight Views of Beijing'' (), recording the capital's chief sites in poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
and painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ...
in order to legitimize his removal of the imperial capital away from Nanking
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
. It is best remembered in China today from the scene of "Clear Waves at Taiye Lake" (, ''Taiye Qingbo'').Whiteman, Stephen. "From Upper Camp to Mountain Estate: Recovering Historical Narratives in Qing Imperial Landscapes"pp. 14 ff.
''Studies in the History of Gardens & Designed Landscapes: An International Quarterly''. Taylor & Francis, 2013. Accessed 16 November 2013.
Name
The literal meaning of the Chinese characters is "Great Liquid Pool" or "Pond". Prior to the Taiye Lake watershed system in Beijing that still exists today known as North, Central and South Seas, the name "Taiye" had honored several lakes in imperial gardens or palaces in various locations that once served as capital cities of imperial China. An early example of Taiye Lake is located in the city ofXi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by #Name, other names, is the list of capitals in China, capital of Shaanxi, Shaanxi Province. A Sub-provincial division#Sub-provincial municipalities, sub-provincial city o ...
. There were two lakes named Taiye existed in Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by #Name, other names, is the list of capitals in China, capital of Shaanxi, Shaanxi Province. A Sub-provincial division#Sub-provincial municipalities, sub-provincial city o ...
(known as Chang'an). The earlier Taiye Lake was excavated in the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
by the Emperor Wu in the 1st century BC as part of his Jianzhang Palace (, ''Jiànzhānggōng''). This lake, along with the Kunming Lake
Kunming Lake (Chinese: , p ''Kūnmíng Hú'') is the central lake on the grounds of the Summer Palace in Beijing, China. Together with the Longevity Hill, Kunming Lake forms the key landscape features of the Summer Palace gardens.
Wit ...
, was a necessary addition to the city's water supply after the expansion of the capital city under Emperor Wu's reign.
The second Taiye Lake in Xi'an was excavated in the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
by the Emperor Taizong next to his father
His or HIS may refer to:
Computing
* Hightech Information System, a Hong Kong graphics card company
* Honeywell Information Systems
* Hybrid intelligent system
* Microsoft Host Integration Server
Education
* Hangzhou International School, in ...
's Daming Palace
The Daming Palace was the imperial palace complex of the Tang dynasty, located in its capital Chang'an. It served as the imperial residence of the Tang emperors for more than 220 years. Today, it is designated as a national heritage site of China ...
, after the capital had been relocated several miles northward due to the growing salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
of the water source at the original site.
There are older Taiye Lakes in Beijing, too. In 1151, Beijing (known as Zhongdu) became the capital city of the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty. The emperor Wanyan Liang
Digunai (24 February 1122 – 15 December 1161), also known by his sinicised name Wanyan Liang (完顏亮) and his formal title Prince of Hailing (海陵王, ''Hǎilíng Wáng''), was the fourth emperor of the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty of China. H ...
ordered to rebuild Beijing in style of Kaifeng
Kaifeng () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Henan province, China. It is one of the Eight Ancient Capitals of China, having been the capital eight times in history, and is best known for having been the Chinese capital during the Nort ...
, the former capital city of Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
in the south. During the reconstruction of Beijing, a Taiye Lake was built near the palace of Jurchens. The relic of this Taiye Lake is in today's Xicheng district outside of the southwestern second ring road
The 2nd Ring Road () is the innermost ring road highway which encircles the city center of Beijing, People's Republic of China. (The first ring road had been a circular tram route.)
The ring road can be divided into two parts: the original rin ...
and roughly near the Guang'an Gate of Beijing in later dynasties.
The still-existing Taiye Lakes in Beijing were first created in the Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
-led Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fifth ...
when Beijing was reconstructed as Khanbaliq (Dadu) after the previous Beijing city had been seriously damaged during the Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty
The Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty, also known as the Mongol–Jin War, was fought between the Mongol Empire and the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in Manchuria and North China. The war, which started in 1211, lasted over 23 years and ended w ...
.
History
 The lake was first constructed as part of the Jinshui River canal systemHou, Eve.
The lake was first constructed as part of the Jinshui River canal systemHou, Eve.Nine Dragons, One River: The Role of Institutions in Developing Water Pricing Policy in Beijing, PRC
, p. 6. Univ. of British Columbia, 2001. under the
Emperor Zhangzong of Jin
Emperor Zhangzong of Jin (31 August 1168 – 29 December 1208), personal name Madage, sinicized name Wanyan Jing, was the sixth emperor of the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty of China. He reigned from 20 January 1189 to 29 December 1208.Tao, p. 85-86
...
. Although still within the limits of modern Beijing, the Jin capital of Zhongdu
Zhongdu (, lit. "Central Capital") was the capital of the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in medieval China. It was located in the southwestern part of Beijing's Xicheng District. It had a population of nearly one million by the late 12th century, and ...
was located well south of the site, in a separate watershed. Zhangzong constructed the Daning Palace ( t , s , ''Dànínggōng'', lit. "Palace of Great Peace") beside the new lake in 1179.Rinaldi, Bianca. ''The Chinese Garden: Garden Types for Contemporary Landscape Architecture''p. 137
Walter de Gruyter, 2011. Accessed 16 November 2013. During the
Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fifth ...
, the ruined site of Zhongdu and its more meager water sources were abandoned in favor of the Gaoliang watershed. The imperial engineers Liu Bingzhong
Liu Bingzhong (; 1216–1274), or Liu Kan () was a Yuan dynasty court adviser and architect. He was born in Ruizhou (Rui prefecture), during the Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin dynasty. In 1233, he entered the Jin's bureaucracy. He still was an of ...
and Guo Shoujing
Guo Shoujing (, 1231–1316), courtesy name Ruosi (), was a Chinese astronomer, hydraulic engineer, mathematician, and politician of the Yuan dynasty. The later Johann Adam Schall von Bell (1591–1666) was so impressed with the preserved astron ...
directed the construction of the new Imperial City
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
of Khanbaliq
Khanbaliq or Dadu of Yuan () was the winter capital of the Yuan dynasty of China in what is now Beijing, also the capital of the People's Republic of China today. It was located at the center of modern Beijing. The Secretariat directly administ ...
(Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
's Cambaluc & the Chinese Dadu) around Zhangzong's former palace and Lake Taiye, which was an important part of the capital's water supply.Du Pengfei & al. "History of Water Supply in Pre-Modern China" from ''Evolution of Water Supply through the Millennia''pp. 169 ff
Accessed 16 November 2013. The lake was expanded until it covered the area of the present northern and central "seas" and three palaces were built around it. The purity of the reservoir was protected by law: from its source at a spring on Yuquan Mountain to Lake Taiye, the Jinshui was given separate passes where it crossed other streams and commoners were forbidden to bathe, wash clothes, water livestock, or dump trash along its course.Du Pengfei. ''Zhōngguó Gǔdàide Chéngshì Jǐshuǐ''", "Water Supply of the Cities in Ancient China" ''China Historical Materials of Science and Technology'', Vol. 1, No. 19, pp. 3–10. Under the
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
, construction on the present-day Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a Chinese palace, palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City, Beijing, Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples includ ...
began in AD 1406 as part of the Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (; pronounced ; 2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), personal name Zhu Di (), was the third Emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 1424.
Zhu Di was the fourth son of the Hongwu Emperor, the founder of the Ming dyn ...
's relocation of the capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
away from Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
. The new palace was south of the former Yuan one and the Taiye was expanded south along with it. The soil excavated from the lake and the fortress's moat were piled up to the palace's north to form the Mountain of Long Life (now known as Jingshan), burying the former Yuan site and improving the '' fengshui'' of the new one. The lake now comprised the three present-day "seas", which were divided by bridges, but continued to be known collectively as Taiye. The grounds were known as the West or (, ''Xīyuàn'') and the Jiajing Emperor
The Jiajing Emperor (; 16September 150723January 1567) was the 12th List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, Emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1521 to 1567. Born Zhu Houcong, he was the former Zhengde Emperor's cousin. His father, Zhu You ...
and others retreated to it to escape life at court.Wan, Maggie C.K.Building an Immortal Land: The Ming Jiajing Emperor's West Park
. ''Asia Major'', 3rd Series, Vol. 22, No. 2 (2009), pp. 65-99. Accessed 15 November 2013. After the establishment of the
Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
-led Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
in the 17th century, the new government reduced the extensive Ming-era parks around the lake, enclosed the smaller present-day area within walls attached to the imperial palace, and began calling the separate sections by their modern names. Successive emperors built pavilions and houses along the lake shore, where they held court during the summer.
See also
*Beihai Park
Beihai Park () is a public park and former imperial garden located in the northwestern part of the Imperial City, Beijing. First built in the 11th century, it is among the largest of all Chinese gardens and contains numerous historicall ...
* Zhongnanhai
Zhongnanhai () is a former imperial garden in the Imperial City, Beijing, Imperial City, Beijing, adjacent to the Forbidden City; it serves as the central headquarters for the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the State Council of the People' ...
* History of Beijing
The city of Beijing has a long and rich history that dates back over 3,000 years. Prior to the unification of China by the Qin Shi Huang, First Emperor in 221 BC, Beijing had been for centuries the capital of the ancient states of Ji (state), Ji ...
* Chinese garden
The Chinese garden is a landscape garden style which has evolved over three thousand years. It includes both the vast gardens of the Chinese emperors and members of the imperial family, built for pleasure and to impress, and the more intimate ...
ing
References
{{coord missing, Beijing Chinese architectural history Parks in Beijing Lakes of China Bodies of water of Beijing