West Texas Intermediate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 West Texas Intermediate (WTI) is a grade or mix of crude oil; the term is also used to refer to the spot price, the
West Texas Intermediate (WTI) is a grade or mix of crude oil; the term is also used to refer to the spot price, the
 Historically, WTI has generally traded at a premium to Brent before 2011, but since the shale oil boom in the 2010s it has been traded at a discount against Brent crude oil. Both the volatility of the WTI/Brent premium/discount, as well as its reversal from premium to discount in 2011, are studied and monitored by market participants as indicators for the functioning of WTI and Brent Crude as oil price benchmarks.
Historically, WTI has generally traded at a premium to Brent before 2011, but since the shale oil boom in the 2010s it has been traded at a discount against Brent crude oil. Both the volatility of the WTI/Brent premium/discount, as well as its reversal from premium to discount in 2011, are studied and monitored by market participants as indicators for the functioning of WTI and Brent Crude as oil price benchmarks.
U.S. Energy Information Administration
– Part of the U.S. Department of Energy, official source of price and other statistical information
West Texas Intermediate (WTI) (WTISPLC)
time series from 1946 at the St. Louis Fed {{Petroleum industry Benchmark crude oils Economy of Texas Petroleum in the United States
 West Texas Intermediate (WTI) is a grade or mix of crude oil; the term is also used to refer to the spot price, the
West Texas Intermediate (WTI) is a grade or mix of crude oil; the term is also used to refer to the spot price, the futures
Futures may mean:
Finance
*Futures contract, a tradable financial derivatives contract
*Futures exchange, a financial market where futures contracts are traded
* ''Futures'' (magazine), an American finance magazine
Music
* ''Futures'' (album), a ...
price, or assessed price for that oil. In colloquial usage, WTI usually refers to the WTI Crude Oil futures contract traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX). The WTI oil grade is also known as Texas light sweet, oil produced from any location can be considered WTI if the oil meets the required qualifications. Spot and futures prices of WTI are used as a benchmark in oil pricing. This grade is described as light crude oil because of its low density and sweet
Sweetness is a basic taste most commonly perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds are sweet, including aldehydes, keto ...
because of its low sulfur content.
The price of WTI is often included in news reports on oil prices, alongside the price of Brent crude
Brent Crude may refer to any or all of the components of the Brent Complex, a physically and financially traded oil market based around the North Sea of Northwest Europe; colloquially, Brent Crude usually refers to the price of the ICE (Intercon ...
from the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
. Other important oil markers include the Dubai crude, Oman crude, Urals oil
Urals oil is a reference oil brand used as a basis for pricing of the Russian export oil mixture. It is a mix of heavy sour oil of Urals and the Volga region with light oil of Western Siberia. Other reference oils are Brent, West Texas In ...
, and the OPEC reference basket. WTI is lighter and sweeter, containing less sulfur than Brent, and considerably lighter and sweeter than Dubai or Oman.
WTI crude oil as a trade grade
UnlikeBrent Crude
Brent Crude may refer to any or all of the components of the Brent Complex, a physically and financially traded oil market based around the North Sea of Northwest Europe; colloquially, Brent Crude usually refers to the price of the ICE (Intercon ...
, WTI crude oil is not from any specific oil fields. Rather, WTI can be described as "light sweet oil traded and delivered at Cushing, Oklahoma" (with WTI Midland and WTI Houston crude oil defined similarly for Midland, Texas, and Houston, Texas respectively). Historically, local trade between oilfield production and refineries around Midland, Texas, and Cushing, Oklahoma, could be said to define WTI oil, but as local production declined, pipelines into those areas began to deliver crude oil of other grades, produced and blended elsewhere, which were also accepted as WTI. The WTI futures contract formalized this relationship by specifying that the deliverable asset for the contract could be a blend of crude oil, as long as it was of acceptable lightness and sweetness. Crude oil lightness is characterized by oil gravity, and crude oil sweetness by sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
content. Measurements of lightness and sweetness of WTI changes depending on the particular light and sweet oil traded at Cushing at the time of the measurement, and even the particular measurement methodology.
The Platts and Argus API and sulfur measurements are descriptions of WTI as assessed, while the NYMEX WTI futures contract characterization is a requirement for WTI crude oil delivery to the contract. WTI crude oil will typically satisfy the WTI futures contract requirements and be close to the Platts and Argus assessed values at the time.
Development of the physical WTI market
The US governmental decontrol of oil prices on January 28, 1981, marked the beginning of the physical WTI Crude Oil spot market. Under the previous US Emergency Petroleum Allocation Act of 1973, WTI crude oil traded under a variety of spot prices split into various categories set by the price controls. After the price decontrol, WTI graded crude oil traded under spot prices centered around spot prices at Cushing, Oklahoma, Midland, Texas, and Houston, Texas (specifically at the Magellan East Houston "MEH" Terminal). Oil price collapses during 1985-1986 significantly reduced local oil production around Cushing, and linked Gulf Coast imported crude oil supplies into the Cushing region and the WTI market. The growth of the WTI spot market came in tandem with the growth of the WTI futures market. The volatility of WTI spot prices lead to the development of WTI futures contracts, while the adoption of the WTI futures contracts as hedging tools by producers and refiners worldwide lead to the worldwide adoption of assessed physical WTI spot prices as benchmark prices for crude.Global adoption of WTI assessed prices as oil benchmark prices
Price Reporting Agencies (PRAs), such as Platts and Argus Media, compiled assessment prices of WTI based on prices of spot transactions starting in 1981. Eligible spot transaction prices at Cushing, Oklahoma, is typically reported as WTI, while eligible spot transactions at Midland, Texas, and Houston, Texas (at the MEH Terminal) are reported as WTI Midland, and WTI Houston respectively. The development of WTI spot and futures markets led crude oil producers around the world to use assessed WTI prices as a benchmark in oil pricing. For example, in 2008, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iraq, Colombia, and Ecuador based their crude oil selling prices on either the Platts WTI Mnth 1 index or the Platts WTI Mnth 2 index (the assessed prices of transactions with delivery in the next deliverable month or the second deliverable month). Subsequently, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and Iraq started using the Argus Sour Crude Index (ASCI) as their price index in 2009, but the ASCI index itself is priced in relation to WTI futures with a differential, which imply those countries still effectively benchmark their crude oil selling prices to WTI.NYMEX WTI Crude Oil futures contract
The volatility of crude oil prices after the US oil price decontrol led to the development of the NYMEX WTI Light Sweet Crude Oil futures contract in 1983. The NYMEX Crude Oil contract trades under the symbol CL on the New York Mercantile Exchange, now part ofChicago Mercantile Exchange
The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) (often called "the Chicago Merc", or "the Merc") is a global derivatives marketplace based in Chicago and located at 20 S. Wacker Drive. The CME was founded in 1898 as the Chicago Butter and Egg Board, a ...
. The contract is for 1,000 US barrels, or 42,000 US gallons, of WTI crude oil, the minimum tick size of the contract is $0.01 per barrel ($10 for contract), and the contract price is quoted in US dollars. Monthly contracts are available for the current year, the following 10 calendar years, and 2 additional months. For example, from the perspective of any day in June before the last trade date for the June 2020 contracts, contracts for June 2020, July 2020, August 2020, ... December 2030, January 2031, and February 2031 are available for trading. The maximum number of contracts would be 134 contracts, which occurs at the expiry of a December contract when contracts for a new calendar year and two months are made available for trading.
Futures contract delivery
Cushing, Oklahoma
Cushing ( sac, Koshineki, iow, Amína P^óp^oye Chína, ''meaning: "Soft-seat town"'') is a city in Payne County, Oklahoma, United States. The population was 7,826 at the time of the 2010 census, a decline of 6.5% since 8,371 in 2000. Cushing ...
is a major trading hub for crude oil and has been the delivery point for crude contracts and therefore the price settlement point for West Texas Intermediate on the New York Mercantile Exchange for over three decades. The town of Cushing, Oklahoma is a small, remote place with only 7,826 inhabitants (according to the 2010 Census). However, it is the site of the Cushing Oil Field, which was discovered in 1912, and dominated U.S. oil production for several years. The area became a "vital transhipment point with many intersecting pipelines, storage facilities, and easy access to refiners and suppliers," infrastructure which remained after the Cushing field had declined in importance. Crude oil flows "inbound to Cushing from all directions and outbound through dozens of pipelines". It is in Payne County, Oklahoma, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
.
Adoption of WTI futures for investment purposes
Starting in 2003, an influx of traders from outside of the oil industry begun to participate in oil futures and other commodities futures markets. These market participants, which includes hedge funds, pension funds, insurance companies, and retail investors, were motivated by the increasing acceptance of oil futures contracts and related derivatives as financial assets. Demand from these investors and general financial innovation created inexpensive access to financial instruments related to oil futures contracts, such as options, index funds, and exchange-traded funds. As part of wave of investor interest, WTI crude oil futures prices (as well as Brent Crude oil prices) are included in both the Bloomberg Commodity Index and the S&P GSCI commodity index, which are benchmark indices widely followed infinancial markets
A financial market is a market in which people trade financial securities and derivatives at low transaction costs. Some of the securities include stocks and bonds, raw materials and precious metals, which are known in the financial markets ...
by traders and institutional investors. Its weighting in these commodity indices give LME Nickel prices non-trivial influence on returns on a wide range of investment fund
An investment fund is a way of investing money alongside other investors in order to benefit from the inherent advantages of working as part of a group such as reducing the risks of the investment by a significant percentage. These advantages in ...
s and portfolios.
Effect of futures contract trading on physical WTI market
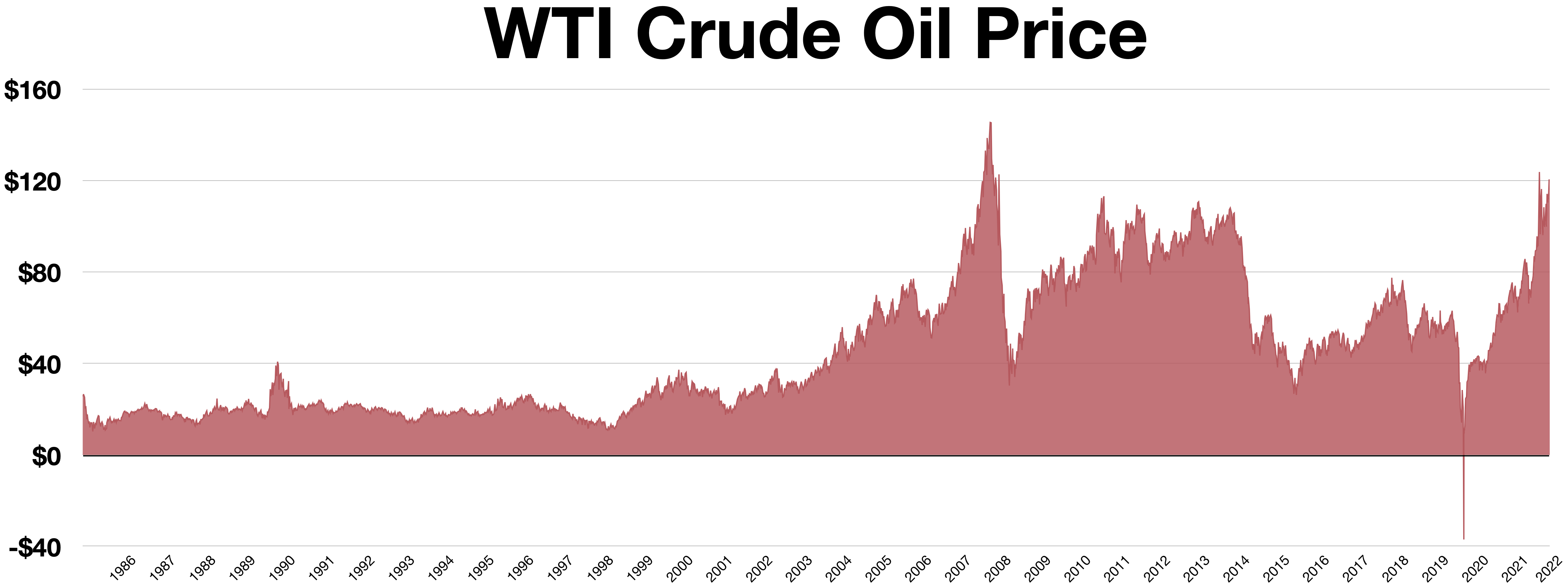
For financial investors without oil storage, purchasing the shortest maturity futures contract and then rolling to the next contract priory to expiry offered the closest approximation to investing in physical oil prices. However, financial markets are much larger than oil markets, and investor flows began to dominate oil producers' hedging needs and moved the oil futures market into contango, where futures prices are greater than spot prices. Contango imposes a roll cost on investors who must roll futures contracts, as they must pay a relatively higher price for those contracts to get the same underlying spot price exposure as their previous expiring contract. These roll costs could be viewed as compensation, purchased virtual storage, or an indirect subsidy for storage owners to provide the service of storing crude on behalf of financial investors. In the WTI context, storage owners would include most participants in the physical WTI market. Beyond the need by financial investors in oil, oil storage is also valuable because it provides insurance against supply disruptions or unexpected increases in demand. Refiners who wish to avoid carrying real physical oil inventories can purchase futures contracts as virtual storage as an alternative. Oil producers wishing to maintain real physical oil inventories similarly could lower the cost of those inventories through selling futures contracts. Index fund participation in the crude oil market is also associated with lower price volatility. WTI futures contracts are tied to physical deliveries into the physical spot WTI market, so WTI futures contract prices should converge to physical spot WTI market conditions and prices. But since deliveries made to settle an expiring WTI futures contract are also physical spot WTI transactions that can be included into PRA assessed prices, abnormal futures contract transactions could drive WTI spot prices and assessed prices. This was the case on April 20, 2020, when WTI futures contract trading drove both assessed WTI and ASCI prices to negative territories.WTI Negative Pricing April 20, 2020
On April 20, 2020, WTI's May contract closed at -$37.63/barrel while the June contract closed at positive $20.43/barrel. Prices mainly dropped due to theCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified ...
, which reduced demand, with storage issues and the expiration of the May contract on the following day resulting in reduced trading. For the first time ever, the reduction in trading shut down the Trade at Settlement (TAS) mechanism of the May 2020 WTI contract 30 minutes before the end of trading due to a lack of buyers. The TAS shutdown signaled to market participants that all remaining open May 2020 WTI contracts that have to be sold, either outright or for the purposes of rolling to the June 2020 contract, have to be sold in the open market in the next twenty minutes. The speed at which the contracts had to be sold, and the closeness of that time to contract expiry meant that large physical oil traders, who could have transported and stored oil elsewhere given a low enough price, could not buy contracts due to operational, risk management, and position limit constraints. Any remaining traders who were willing to buy contracts gained enormous market power
In economics, market power refers to the ability of a firm to influence the price at which it sells a product or service by manipulating either the supply or demand of the product or service to increase economic profit. In other words, market pow ...
and pushed prices downwards into negative territory. This situation is an extreme case of contango. Assess WTI prices were affected, and the WTI spot price dropped to -$36.98 on April 20. At the same time, Mars crude oil produced in the US Gulf Coast (USGC) settled at -$26.63, and Middle East exporters who uses ASCI (of which Mars is a component) as the selling price benchmark had to settle for negative prices that day.
Pricing premium/discount in relation to Brent
 Historically, WTI has generally traded at a premium to Brent before 2011, but since the shale oil boom in the 2010s it has been traded at a discount against Brent crude oil. Both the volatility of the WTI/Brent premium/discount, as well as its reversal from premium to discount in 2011, are studied and monitored by market participants as indicators for the functioning of WTI and Brent Crude as oil price benchmarks.
Historically, WTI has generally traded at a premium to Brent before 2011, but since the shale oil boom in the 2010s it has been traded at a discount against Brent crude oil. Both the volatility of the WTI/Brent premium/discount, as well as its reversal from premium to discount in 2011, are studied and monitored by market participants as indicators for the functioning of WTI and Brent Crude as oil price benchmarks.
US supply factors
In February 2011, WTI was trading around $85/barrel while Brent was at $103/barrel. The reason most cited for this difference was that Cushing had reached capacity due to a surplus of oil in the interior of North America. At the same time, Brent moved up in reaction to civil unrest in Egypt and across the Middle East. Since WTI-priced stockpiles at Cushing could not easily be transported to the Gulf Coast, WTI crude was unable to bearbitrage
In economics and finance, arbitrage (, ) is the practice of taking advantage of a difference in prices in two or more markets; striking a combination of matching deals to capitalise on the difference, the profit being the difference between t ...
d in bringing the two prices back to parity. Oil prices at coastal areas of the United States were closer to Brent than to WTI. In June 2012, the Seaway Pipeline, which had been transporting oil from the Gulf Coast to Cushing, reversed its flow direction, to transport WTI-priced crude to the Gulf Coast, where it received Brent prices. The price difference persisted, however, and was large enough that some oil producers in North Dakota put their oil on tanker cars, and shipped it by rail to the Gulf and East Coast, where it received Brent prices. Brent continued to trade $10–20 higher than WTI for two years, until June 2013.
Freight rate factors
To the extent that price difference between WTI and Brent crude entice traders to ship WTI to North Sea refineries or ship Brent to US Gulf Cost refineries, the premium/discount between WTI and Brent crude must reflectoil tanker
An oil tanker, also known as a petroleum tanker, is a ship designed for the bulk transport of oil or its products. There are two basic types of oil tankers: crude tankers and product tankers. Crude tankers move large quantities of unrefined c ...
freight costs. Oil tanker
An oil tanker, also known as a petroleum tanker, is a ship designed for the bulk transport of oil or its products. There are two basic types of oil tankers: crude tankers and product tankers. Crude tankers move large quantities of unrefined c ...
freight cost rates could be highly volatile, due to circular dependence on fuel oil prices and ultimately crude prices, to demand for oil tankers to serve non-USGC non-North-Sea trade routes (especially to China), and to demand for using oil tankers as floating storage for crude oil. From 2000 to 2009, oil tanker freight rates represented a substantial contributor to the WTI premium over Brent crude.
Brent crude production and trading factors
Premiums/discounts between WTI and Brent crude also reflects declining crude oil production priced under Brent crude prices. As crude production declines from depletion in Brent crude associated North Sea oilfields ( Brent,Forties Forties can mean:
*1940s, the years 1940–1949
*40s, the years 40-49 AD
*The years 40-49 of any century - see List of decades
*Long Forties, area in the North Sea
*The Forties shipping forecast area (roughly corresponding to the Long Forties)
*Fo ...
, Oseberg, Ekofisk, and Troll
A troll is a being in Nordic folklore, including Norse mythology. In Old Norse sources, beings described as trolls dwell in isolated areas of rocks, mountains, or caves, live together in small family units, and are rarely helpful to human be ...
; also referred to as BFOET), a higher proportion of that oil production is consumed by local European refiners, and both a lesser proportion and a lesser absolute amount of that oil production can be exported to the US. During periods when WTI trades at a premium to Brent crude, declining Brent crude production pushes up that premium as traders cannot source supplies to sell into the US for a profit.
As well, participants in the Brent crude market compensates for declining North Sea production by associating additional oilfields and different quality crude production into the definition of Brent crude, which affects the quality differential between Brent and WTI crude oils. Forties and Oseberg crude oil was added in 2002, Ekofisk crude oil was added in 2007, and Troll crude oil was added in 2018 to Brent crude oil pricing basket. Moreover, the different grades in the "Brent basket" are priced different. For example, Ekofisk, Oseberg, and Troll crude oil grades have a quality premium over Brent crude oil grades, while Forties have a price discount for high sulphur content. Brent prices usually reflect the cheapest or the most competitive physical crude oil in the above basket, which means that Brent prices usually reflect prices for Forties crude oil. These quality changes to Brent Crude oil directly affect the premium or discount between what refiners would pay for WTI and Brent crude oil.
See also
* Dubai Mercantile Exchange * List of crude oil products *Petrobourse
The Iranian Oil Bourse ( fa, بورس نفت ایران), International Oil Bourse, Iran Petroleum Exchange Kish Exchange or Oil Bourse in Kish (IOB; the official English language name is unclear) also known as Iran Crude Oil Exchange, is a commod ...
* Petroeuro
* Petroleum classification
References
External links
U.S. Energy Information Administration
– Part of the U.S. Department of Energy, official source of price and other statistical information
West Texas Intermediate (WTI) (WTISPLC)
time series from 1946 at the St. Louis Fed {{Petroleum industry Benchmark crude oils Economy of Texas Petroleum in the United States