Welton Taylor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Welton Ivan Taylor (November 12, 1919 – November 1, 2012) was an American
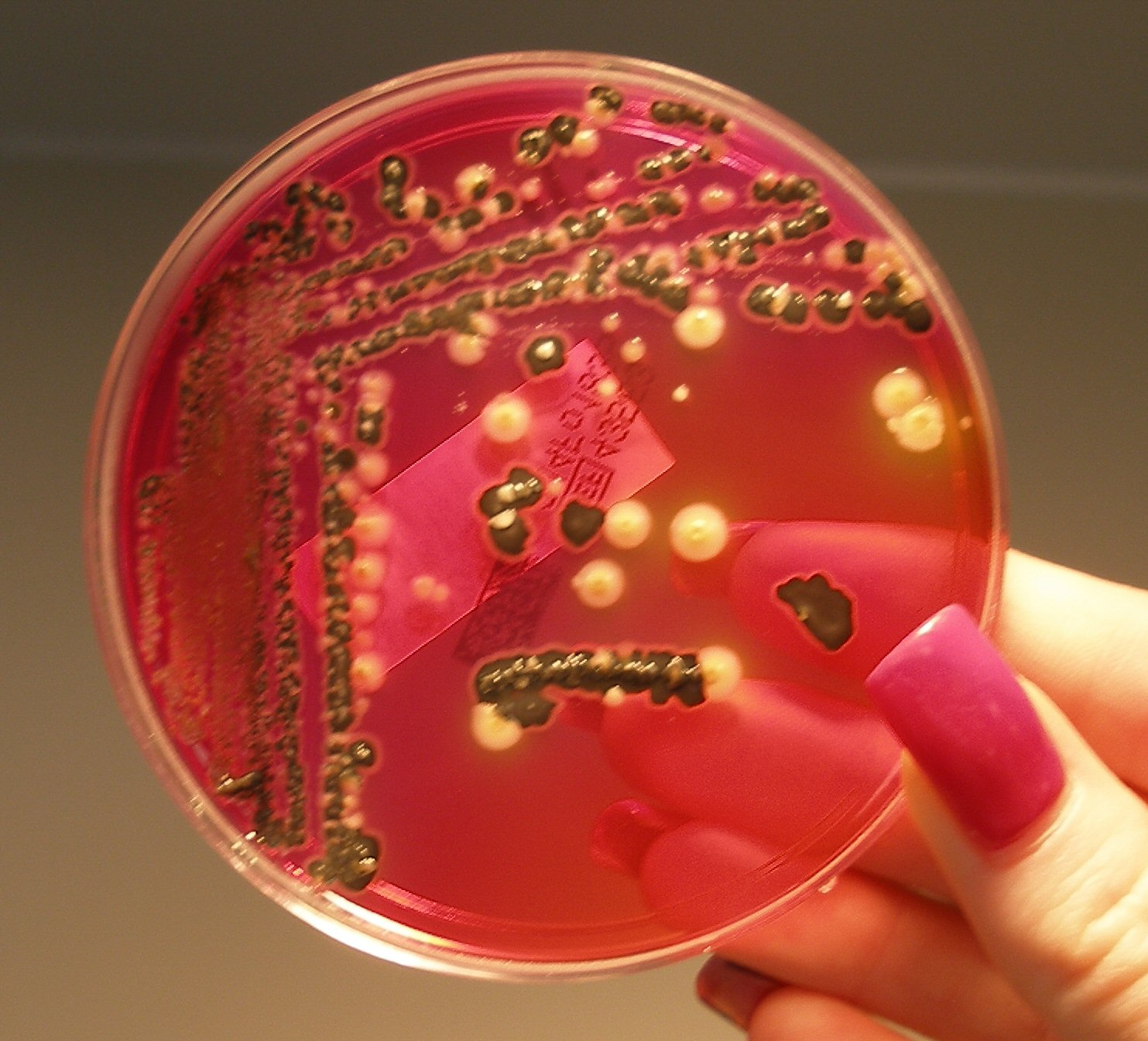 Between 1954 and 1959, Taylor worked at the food processing company
Between 1954 and 1959, Taylor worked at the food processing company
microbiologist
A microbiologist (from Ancient Greek, Greek ) is a scientist who studies microscopic life forms and processes. This includes study of the growth, interactions and characteristics of Microorganism, microscopic organisms such as bacteria, algae, f ...
, inventor
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an ...
and civil rights activist
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and political life o ...
. He is known for his work on food-borne pathogens, notably for developing tests for ''Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of rod-shaped (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' is the type species and is fur ...
'' and for inventing the XLD (Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate) agar, which can be used to isolate ''Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of rod-shaped (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' is the type species and is fur ...
'' and ''Shigella
''Shigella'' is a genus of bacteria that is Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, non-spore-forming, nonmotile, rod-shaped, and genetically closely related to ''E. coli''. The genus is named after Kiyoshi Shiga, who first discovered it in 1897. ...
'' bacteria.
After obtaining his PhD at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the Univ ...
, and research relevant to infections of soldiers' wounds at the university's College of Medicine, Taylor joined the food processing company Swift & Company
JBS USA Holdings, Inc. is an American food processing company and a wholly owned subsidiary of the multinational company JBS S.A. The subsidiary was created when JBS entered the U.S. market in 2007 with its purchase of Swift & Company. JBS speci ...
, developing for them an accurate test for the contamination of food with salmonella. This set the direction for his subsequent research, undertaken mostly at Microbiologist-in-Chief at Chicago's Children's Memorial Hospital
Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, formerly Children's Memorial Hospital and commonly known as Lurie Children's, is a nationally ranked pediatric acute care children's hospital located in Chicago, Illinois. The hospital has 3 ...
, on different ways of detecting specific pathogens accurately and quickly, in a clinical setting.
Taylor was a life-long civil-rights activist, promoting racial equality and working towards de-segregation.
In 2016, Taylor was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame
The National Inventors Hall of Fame (NIHF) is an American not-for-profit organization, founded in 1973, which recognizes individual engineers and inventors who hold a U.S. patent of significant technology. Besides the Hall of Fame, it also opera ...
. In 1985, a species of bacteria was named jointly after Taylor and an eponymous colleague.
Life
Taylor was born inBirmingham, Alabama
Birmingham ( ) is a city in the north central region of the U.S. state of Alabama. Birmingham is the seat of Jefferson County, Alabama's most populous county. As of the 2021 census estimates, Birmingham had a population of 197,575, down 1% fr ...
on November 12, 1919. A few weeks after his birth, his family was forced to move because Taylor's mother had inadvertently discovered the identity of a local Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to the KKK or the Klan, is an American white supremacist, right-wing terrorist, and hate group whose primary targets are African Americans, Jews, Latinos, Asian Americans, Native Americans, and ...
leader. The family moved first to Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, then to Peoria, and eventually back to the Bronzeville neighborhood of Chicago, where Taylor attended DuSable High School
Jean Baptiste Point DuSable High School is a public four-year high school campus located in the Bronzeville neighborhood on the South Side of Chicago, Illinois, United States. DuSable is owned by the Chicago Public Schools district. The school ...
. He graduated from high school in 1937 as valedictorian
Valedictorian is an academic title for the highest-performing student of a graduating class of an academic institution.
The valedictorian is commonly determined by a numerical formula, generally an academic institution's grade point average (GPA ...
of his class.
With the help of local African-American businessmen active in the Kappa Alpha Psi
Kappa Alpha Psi Fraternity, Inc. () is a historically African American fraternity. Since the fraternity's founding on January 5, 1911 at Indiana University Bloomington, the fraternity has never restricted membership on the basis of color, creed ...
fraternity, who had been impressed with his academic performance in high school, Taylor was able to attend the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the Univ ...
, earning a bachelor's degree in bacteriology Bacteriology is the branch and specialty of biology that studies the morphology, ecology, genetics and biochemistry of bacteria as well as many other aspects related to them. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classificat ...
in 1941. At the university, Taylor was a Reserve Officers' Training Corps
The Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC ( or )) is a group of college- and university-based officer-training programs for training commissioned officers of the United States Armed Forces.
Overview
While ROTC graduate officers serve in all ...
cadet.
When World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
broke out, Taylor enlisted in the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
, serving in the South Pacific theater of operations as a liaison pilot for the Army Field Artillery, that is, using air surveillance to help direct field artillery fire. His unit was the 93rd Infantry Division, a segregated unit that had already fought in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
After the war, Taylor returned to his alma mater on the G.I. Bill
The Servicemen's Readjustment Act of 1944, commonly known as the G.I. Bill, was a law that provided a range of benefits for some of the returning World War II veterans (commonly referred to as G.I.s). The original G.I. Bill expired in 1956, bu ...
to complete his M.S. degree in the same subject in 1947, and a PhD degree in 1948. For his PhD, Taylor studied "The growth and toxin production of Clostridium botulinum
''Clostridium botulinum'' is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, anaerobic, spore-forming, motile bacterium with the ability to produce the neurotoxin botulinum.
The botulinum toxin can cause botulism, a severe flaccid paralytic disease in humans an ...
in cottage cheese
Cottage cheese is a curdled milk product with a mild flavor and a creamy, non-homogeneous, soupy texture. It is made from skimmed milk by draining the cheese, as opposed to pressing it to make cheese curd—retaining some of the whey and keeping ...
".
Throughout his career, including his service in an army that was, at the time, still subject to Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the Sout ...
rules, Taylor was confronted with anti-black racism. He recounts a number of such confrontations in the memoirs he wrote on his time in the army, published in 2012. As a civil rights activist, Taylor promoted racial equality, including work with white veterans in Urbana-Champaign with the aim of de-segregating restaurants, movie theaters and public swimming pools. Taylor was one of the first African Americans to integrate Chicago's Chatham
Chatham may refer to:
Places and jurisdictions Canada
* Chatham Islands (British Columbia)
* Chatham Sound, British Columbia
* Chatham, New Brunswick, a former town, now a neighbourhood of Miramichi
* Chatham (electoral district), New Brunswic ...
neighborhood, serving as president of the Chatham Avalon Park Community Council.
Taylor married Jayne Rowena Kemp in 1945, and had two daughters, whose names are Karyn and Shelley. Taylor and Jayne were married for many years until Jayne passed away in 2005.
Scientific career
In 1948, Taylor joined the faculty at theUniversity of Illinois College of Medicine
The University of Illinois College of Medicine offers a four-year program leading to the MD degree at four different sites in Illinois: Chicago, Peoria, Illinois, Peoria, Rockford, Illinois, Rockford, and formerly Champaign–Urbana metropolitan a ...
. As research subjects, he chose gas gangrene
Gas gangrene (also known as clostridial myonecrosis and myonecrosis) is a bacterial infection that produces tissue gas in gangrene. This deadly form of gangrene usually is caused by ''Clostridium perfringens'' bacteria. About 1,000 cases of gas g ...
and tetanus
Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a bacterial infection caused by ''Clostridium tetani'', and is characterized by muscle spasms. In the most common type, the spasms begin in the jaw and then progress to the rest of the body. Each spasm usually ...
, both of which were infections relevant to the military as complications of soldiers' wounds. Taylor and his colleague Milan Novak found that penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
could be used as prophylaxis for both diseases.
Swift & Company
JBS USA Holdings, Inc. is an American food processing company and a wholly owned subsidiary of the multinational company JBS S.A. The subsidiary was created when JBS entered the U.S. market in 2007 with its purchase of Swift & Company. JBS speci ...
. When there was an outbreak of salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of rod-shaped (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' is the type species and is fur ...
at the company, Taylor, with his colleague John Silliker, developed an accurate test that could be used to test egg yolks for salmonella. The testing method is still in use today. Taylor and Silliker jointly took out a patent on a new method of destroying food-borne bacteria using bacteriophages
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacterio ...
in 1959.
In 1959, Taylor left the company to take up a post as Microbiologist-in-Chief at Chicago's Children's Memorial Hospital
Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, formerly Children's Memorial Hospital and commonly known as Lurie Children's, is a nationally ranked pediatric acute care children's hospital located in Chicago, Illinois. The hospital has 3 ...
.
With a Special Research Fellowship from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID, ) is one of the 27 institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health (NIH), an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). NIAID's ...
, Taylor spent 1961 at Britain's Central Public Health Laboratory
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
in Colindale
Colindale is a district in the London Borough of Barnet; its main shopping street on the A5 forming the borough boundary with neighbouring Brent. Colindale is a suburban area, and in recent years has had many new apartments built. It's also th ...
and France's Pasteur Institute
The Pasteur Institute (french: Institut Pasteur) is a French non-profit private foundation dedicated to the study of biology, micro-organisms, diseases, and vaccines. It is named after Louis Pasteur, who invented pasteurization and vaccines f ...
in Lille
Lille ( , ; nl, Rijsel ; pcd, Lile; vls, Rysel) is a city in the northern part of France, in French Flanders. On the river Deûle, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region, the Pref ...
, helping to develop procedures aimed at preventing salmonella poisoning caused by meat imports.
Upon his return to Children's Memorial Hospital
Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, formerly Children's Memorial Hospital and commonly known as Lurie Children's, is a nationally ranked pediatric acute care children's hospital located in Chicago, Illinois. The hospital has 3 ...
in 1962, Taylor went on to develop rapid testing methods for two more classes of bacteria known to cause food poisoning
Foodborne illness (also foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food,
as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disease) ...
, notably Shigella
''Shigella'' is a genus of bacteria that is Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, non-spore-forming, nonmotile, rod-shaped, and genetically closely related to ''E. coli''. The genus is named after Kiyoshi Shiga, who first discovered it in 1897. ...
e – one of the leading bacterial causes of diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin wi ...
worldwide – and Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae is a large family (biology), family of Gram-negative bacteria. It was first proposed by Rahn in 1936, and now includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of family is still a subject ...
, obtaining several patents. The methods he developed were adopted internationally as part of the ongoing effort to keep processed food safe. Taylor acted as a consultant for eleven Chicago-area hospitals, seven corporations, three government agencies, as well as for the Center for Disease Control
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
on subjects ranging from toxic shock syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a condition caused by bacterial toxins. Symptoms may include fever, rash, skin peeling, and low blood pressure. There may also be symptoms related to the specific underlying infection such as mastitis, osteomyeliti ...
and Legionnaire's disease
Legionnaires' disease is a form of atypical pneumonia caused by any species of ''Legionella'' bacteria, quite often '' Legionella pneumophila''. Signs and symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, high fever, muscle pains, and headaches. Naus ...
to sexually transmitted diseases
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and oral sex ...
and AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
.
In 1965, Taylor developed the XLD agar
Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate agar (XLD agar) is a selective growth medium used in the isolation of '' Salmonella'' and ''Shigella'' species from clinical samples and from food. The agar was developed by Welton Taylor in 1965.
It has a pH of approx ...
, which can be used to isolate ''Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of rod-shaped (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' is the type species and is fur ...
'' and ''Shigella
''Shigella'' is a genus of bacteria that is Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, non-spore-forming, nonmotile, rod-shaped, and genetically closely related to ''E. coli''. The genus is named after Kiyoshi Shiga, who first discovered it in 1897. ...
'' bacterial species both from clinical samples and from food. This agar
Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from ogonori (''Gracilaria'') and "tengusa" (''Gelidiaceae''). As found in nature, agar is ...
remains a standard diagnostic tool of clinical microbiology, and is particularly well-suited for routine diagnostic work on Salmonella enterica
''Salmonella enterica'' (formerly ''Salmonella choleraesuis'') is a rod-headed, flagellate, facultative anaerobic, Gram-negative bacterium and a species of the genus ''Salmonella''. A number of its serovars are serious human pathogens.
Epidemi ...
.
In 1975, Taylor was one of the founders of the Journal of Clinical Microbiology
The ''Journal of Clinical Microbiology'' is a monthly medical journal published by the American Society for Microbiology. The journal was established in 1975. The editor-in-chief is Alexander J. McAdam (Boston Children's Hospital). It is a delayed ...
, which is published by the American Society for Microbiology
The American Society for Microbiology (ASM), originally the Society of American Bacteriologists, is a professional organization for scientists who study viruses, bacteria, fungi, algae, and protozoa as well as other aspects of microbiology. It ...
; he also served as one of the journal's editors from 1975 to 1983.
In pursuit of his research, Taylor set about combining different culture media in a form that would allow for easy identification of different bacteria in a clinical setting. For the resulting "Device for Use in the Identification of Microorganisms", which includes different compartments with specific culture media allowing for accurate and fast identification, a patent was issued to Taylor on March 1, 1977. The device was approved by the FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food s ...
as well as by food-safety regulatory agencies in Canada and in Europe as a means of certifying food as bacteria free. Taylor founded ''Micro-Palettes Inc.'' in order to commercialize devices of this type, but the company was dissolved in 1988.
Honors and awards
Taylor's inventions in the area of food testing eventually led to his induction into theNational Inventors Hall of Fame
The National Inventors Hall of Fame (NIHF) is an American not-for-profit organization, founded in 1973, which recognizes individual engineers and inventors who hold a U.S. patent of significant technology. Besides the Hall of Fame, it also opera ...
in 2016.
In 1985, a group of researchers from the Center for Disease Control
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
named a newly identified Enterobacter
''Enterobacter'' is a genus of common Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. It is the type genus of the order Enterobacterales. Several strains of these bacteria are pat ...
bacterium ''Enterobacter taylorae'' in honor of both the British bacteriologist Joan Taylor and Welton Taylor. The citation reads "The name also honors Welton Taylor, an American clinical microbiologist who has also made many contributions to our knowledge of the family ''Enterobacteriaceae'', particularly the development of the XLD agar and the isolation of ''Shigella'' and other bacterial pathogens from feces.''
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Taylor, Welton 1919 births 2012 deaths 20th-century American inventors American patent holders American microbiologists Academic journal editors Academics from Chicago Activists for African-American civil rights American anti-racism activists University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign alumni People from Birmingham, Alabama United States Army Air Forces pilots of World War II 21st-century African-American people Military personnel from Birmingham, Alabama United States Army personnel of World War II United States Army soldiers