Wehrbauer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Wehrbauer'' (, ''defensive peasant''), plural ''Wehrbauern'', is a German term for settlers living on the marches of a realm, who were tasked with holding back foreign invaders until the arrival of proper military reinforcements. In turn, they were granted special liberties. Wehrbauern were mainly used on the eastern fringes of the
''The Myth of the Master Race: Alfred Rosenberg and Nazi Ideology''
p190 , 1972. A historical comparison was drawn to the '' Ordensburgen'' of the medieval German military orders, which Northern Crusaders established to fortify territory such as Terra Mariana against pagan Baltic natives. Beginning in 1938 the SS intensified the ideological indoctrination of the
(in Finnish language, Finnish). From a historical perspective, the SS Wehrbauer concept deliberately referenced the model of the
(in German)
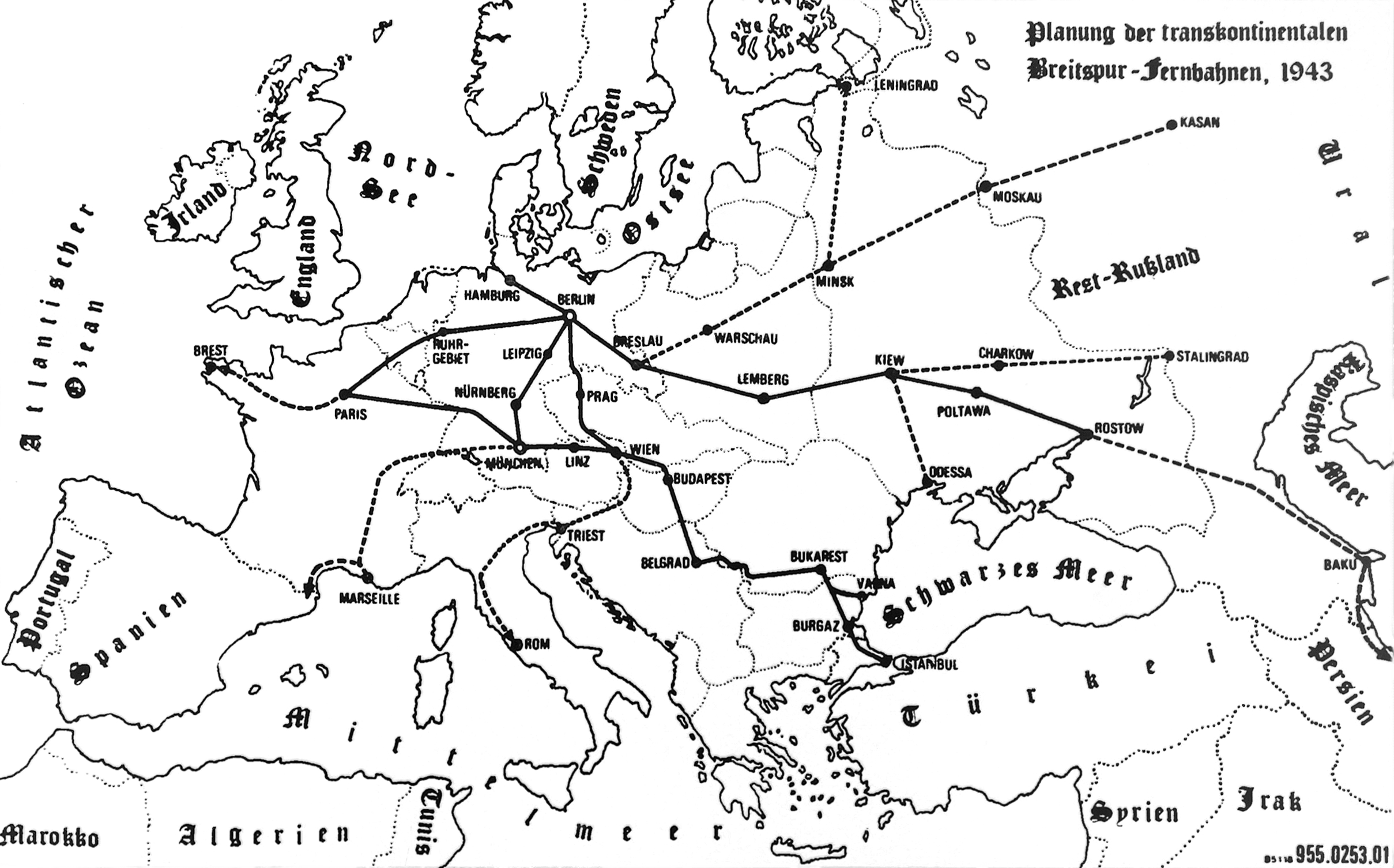 The settlement strings would follow the routes Cracow-
The settlement strings would follow the routes Cracow-
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
and later Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
to slow attacks by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. This historic term was resurrected and used by the Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
s in WWII
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
Etymology
The deployment of "Wehrbauern" is first recorded by theByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
which in the 7th century sought to defend itself with local settlers, then called Stratioti
The Stratioti or Stradioti ( gr, στρατιώτες ''stratiotes''; sq, Stratiotë, Stratiotët;, it, stradioti, stradiotti, stratioti, strathiotto, strathioti; french: estradiots; sh, stratioti, stradioti; es, estradiotes) were mercenary u ...
(''soldiers'') against eastern and southern attacks.
The Habsburg use of "Wehrbauern" was the Military Frontier
The Military Frontier (german: Militärgrenze, sh-Latn, Vojna krajina/Vojna granica, Војна крајина/Војна граница; hu, Katonai határőrvidék; ro, Graniță militară) was a borderland of the Habsburg monarchy and l ...
established by Ferdinand I in the 16th century which was placed under the jurisdiction of the Croatian Sabor and Croatian Ban
Ban of Croatia ( hr, Hrvatski ban) was the title of local rulers or office holders and after 1102, viceroys of Croatia. From the earliest periods of the Croatian state, some provinces were ruled by bans as a ruler's representative (viceroy) an ...
since it was carved out of Croatian territory. It acted as a Cordon sanitaire against Ottoman incursions. By the 19th century it was rendered obsolete by with the establishment of standing armies
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars or na ...
and was subsequently dissolved.
During the 30 Years War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
, battles and raids were common throughout its land, and the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
had to make greater use of Wehrbauern in other regions of the empire as well.
In the 20th century, the term re-emerged and was used by the Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
'' SS'' to refer to soldiers designated as settlers for the lands conquered during the German invasions of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
and the Soviet Union.
The SS Wehrbauern
Ideology
The concept of Wehrbauern predated the Nazis, with theArtaman League
The Artaman League (German language: Artamanen-Gesellschaft) was a German agrarian and völkisch movement committed to a '' Back-to-the-land ''–inspired ruralism. Active during the inter-war period, the League became closely linked to, and eve ...
(founded in 1923) sending urban German children to the countryside not only for the experience, but as a core of ''Wehrbauern''.
The Nazis intended to colonize
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
the conquered Eastern European lands in accordance with Hitler's ''Lebensraum
(, ''living space'') is a German concept of settler colonialism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, '' lso in:' became a geopolitical goal of Imperi ...
'' ideology through these soldier peasants. Plans envisaged them acting both as colonists and as soldiers, defending the new German colonies from the surrounding Slavic population in the event of insurgency. Wehrbauern would have the task, not of extending civilization, but of preventing it from arising outside Wehrbauer settlements. Any such civilization, as a non-German phenomenon, would pose a challenge to Germany.Robert Cecil Robert Cecil may refer to:
* Robert Cecil, 1st Earl of Salisbury (1563–1612), English administrator and politician, MP for Westminster, and for Hertfordshire
* Robert Cecil (1670–1716), Member of Parliament for Castle Rising, and for Wootton Ba ...
''The Myth of the Master Race: Alfred Rosenberg and Nazi Ideology''
p190 , 1972. A historical comparison was drawn to the '' Ordensburgen'' of the medieval German military orders, which Northern Crusaders established to fortify territory such as Terra Mariana against pagan Baltic natives. Beginning in 1938 the SS intensified the ideological indoctrination of the
Hitler Youth
The Hitler Youth (german: Hitlerjugend , often abbreviated as HJ, ) was the youth organisation of the Nazi Party in Germany. Its origins date back to 1922 and it received the name ("Hitler Youth, League of German Worker Youth") in July 1926. ...
Land Service (HJ-Landdienst). It promulgated its ideal of the German Wehrbauer. Special high-schools were created under SS control to form a Nazi agrarian elite trained according to the principle of " blood and soil."
The SS plan for genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
and colonization of the territories of eastern Poland and of the Soviet Union was titled '' Generalplan Ost'' (English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
: General Plan East). This plan projected the settlement
Settlement may refer to:
*Human settlement, a community where people live
*Settlement (structural), the distortion or disruption of parts of a building
*Closing (real estate), the final step in executing a real estate transaction
*Settlement (fina ...
of 10 million racially valuable Germanics (Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, Dutch, Flemish, Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
ns and English) in these territories over a span of 30 years, displacing circa 30 million Slavs and Balts - either assimilated or forcefully transferred to Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
to make room for the newcomers. Volksdeutsche
In Nazi German terminology, ''Volksdeutsche'' () were "people whose language and culture had German origins but who did not hold German citizenship". The term is the nominalised plural of '' volksdeutsch'', with ''Volksdeutsche'' denoting a sin ...
, such as the Volga Germans, would also be transplanted. The German Foreign Ministry
, logo = DEgov-AA-Logo en.svg
, logo_width = 260 px
, image = Auswaertiges Amt Berlin Eingang.jpg
, picture_width = 300px
, image_caption = Entrance to the Foreign Office building
, headquarters = Werderscher Mark ...
, however, suggested the alternative of moving the racially unwanted population to Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
and Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, ...
as soon as Germany had recovered its colonies lost in the 1919 Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
.''Hitlerin Saksa ja sen vapaaehtoisliikkeet'', p. 35, Mauno Jokipii
Mauno Jokipii (21 August 1924 – 2 January 2007) was a Finnish professor at the University of Jyväskylä in history specializing in World War II. He was a thorough investigator and a prolific author. Among his works were studies of the local hist ...
, 2002, Suomalaisen Kirjallisuuden Seura(in Finnish language, Finnish). From a historical perspective, the SS Wehrbauer concept deliberately referenced the model of the
Military Frontier
The Military Frontier (german: Militärgrenze, sh-Latn, Vojna krajina/Vojna granica, Војна крајина/Војна граница; hu, Katonai határőrvidék; ro, Graniță militară) was a borderland of the Habsburg monarchy and l ...
held by the Habsburg Empire against the incursions of the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
. Also, Himmler believed that during the early migration period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
and the German eastward expansion
(, literally "East-settling") is the term for the Early Middle Ages, Early Medieval and High Middle Ages, High Medieval migration-period when ethnic Germans moved into the territories in the eastern part of Francia, East Francia, and the Hol ...
of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, the conquering Germanic peasant-farmer had, in addition to farming, defended his land with arms; the ''Wehrbauer'' model aimed to revive this custom.
Settlement division
In theGeneral Government
The General Government (german: Generalgouvernement, pl, Generalne Gubernatorstwo, uk, Генеральна губернія), also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (german: Generalgouvernement für die be ...
(composed entirely of pre-war Polish territory) plans envisaged setting up a number of "settlement areas" (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: ''Siedlungsgebiete''), centered on the six ''Teilräume'' ("spatial regions") of Cracow, Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
, Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of t ...
, Lviv/Lwów (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: ''Lemberg''), Bialystok, and Litzmannstadt ( pl , Lódz). The colonization of the former territories of the USSR would take place through forming three major "settlement marches" (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: ''Siedlungsmarken''), alternatively also called ''Reichsmarken'' ("marches of the Reich"). Smaller "settlement points" (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: ''Siedlungsstützpunkte'')., as well as a number of "settlement strings" (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: ''Siedlungsperlen'', literally meaning "settlement pearls
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle (mollusc), mantle) of a living animal shell, shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pea ...
") were also envisaged in the east.Heineman, Isabel (2003). ''"Rasse, Siedlung, deutsches Blut": Das Rasse- & Siedlungshauptamt der SS und die rassenpolitische Neuordnung Europas''. Wallstein, p. 418.(in German)
Siedlungsmarken
The settlement marches were to be separated from the civil administration of the Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories andReichskommissariat
''Reichskommissariat'' ( en, Imperial Commissariat) is a German word for a type of administrative entity headed by a government official known as a ''Reichskommissar'' ( en, Imperial Commissioner). Although many offices existed, primarily throug ...
s and given to the custody of the Reichsführer-SS, who was to name an SS and Police Leader (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: ''SS- und Polizeiführer'') for the region and also to distribute temporary and inheritable fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an Lord, overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a for ...
s and even permanent land-ownership for the settlers.
In a time-span of 25 years the populations of Ingria (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: ''Ingermanland''), the Memel-Narew
The Narew (; be, Нараў, translit=Naraŭ; or ; Sudovian: ''Naura''; Old German: ''Nare''; uk, Нарва, translit=Narva) is a 499-kilometre (310 mi) river primarily in north-eastern Poland, which is also a tributary of the river Vis ...
region (i.e. the district of Bialystok and Western Lithuania), and the southern Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and the Crimean peninsula (to be renamed ''Gotengau'' after the former Germanic tribe) were to become at least 50% German.
Siedlungsstützpunkte
In addition to the settlement marches, the SS planned to establish 36 settlement points. The population of these points was to be circa 20–30% German. Marking the center of each point, a planned German city of 20,000 inhabitants would be surrounded by closely-located German villages in a 5–10 km radius. The villages would secure the German control of all major road and railroad nodes.Siedlungsperlen
 The settlement strings would follow the routes Cracow-
The settlement strings would follow the routes Cracow-Lviv
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukraine ...
- Zhitomir-Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
, Leningrad
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
-Mogilev
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the bor ...
-Kiev, and Zhitomir- Vinnitsa-Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
(note however that Odessa came under the administration of Romania in the course of Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
in 1941). A major autobahn
The (; German plural ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official German term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track'. ...
system would connect the settlement strings, with new German cities planned for construction along the roadbeds of roughly every 100 kilometres. Further extensions run in the direction of the Don
Don, don or DON and variants may refer to:
Places
*County Donegal, Ireland, Chapman code DON
*Don (river), a river in European Russia
*Don River (disambiguation), several other rivers with the name
*Don, Benin, a town in Benin
*Don, Dang, a vill ...
and the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Cas ...
, and eventually towards the Ural mountains. Plans for the extreme broad-gauge ''Breitspurbahn
The Breitspurbahn (, translation: ''broad-gauge railway'') was a planned broad-gauge railway, proposed during the time of Nazi Germany, supposed to run with double-deck coaches between major cities of '' Grossdeutschland'', Hitler's expanded Ge ...
'' railway network proposed by the Nazis envisioned these railways having extensions running as far east as Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering a ...
, Stalingrad
Volgograd ( rus, Волгогра́д, a=ru-Volgograd.ogg, p=vəɫɡɐˈɡrat), geographical renaming, formerly Tsaritsyn (russian: Цари́цын, Tsarítsyn, label=none; ) (1589–1925), and Stalingrad (russian: Сталингра́д, Stal ...
and Baku
Baku (, ; az, Bakı ) is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. Baku is located below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world a ...
as possible railheads. Railways could provide another conceivable set of "strings" along which to place settlements.
The planned peasant-soldier community
The soldier-peasants would mainly be front-lineveteran
A veteran () is a person who has significant experience (and is usually adept and esteemed) and expertise in a particular occupation or field. A military veteran is a person who is no longer serving in a military.
A military veteran that has ...
s of the SS and members of the Allgemeine-SS, who were to be supplied with weaponry for the armed defense of their respective communities. In October 1939 Himmler stated that the German settlements in Poland would be divided between different German cultural and linguistic sub-groups such as Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
ns, Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper Fr ...
ns, Westphalians and Lower Saxons.
The compulsory savings of the individual SS men would fund the foundation of the settlements.Longerich, P. (2008), Heinrich Himmler, p, 443–445, Each settlement was to be planned in advance (Soviet villages emptied of their previous inhabitants were to be destroyed) and would comprise 30 to 40 farms, each of 121.5 hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is a ...
s (300 acres); a NSDAP
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that crea ...
party headquarters; a manor house
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals w ...
for the SS or party leader
Leadership, both as a research area and as a practical skill, encompasses the ability of an individual, group or organization to "lead", influence or guide other individuals, teams, or entire organizations. The word "leadership" often gets vi ...
; an agricultural instruction center; a house for a community nurse; and a cinema. The houses of the settlement were to be built "as in the old days" - two or three stone courses
Course may refer to:
Directions or navigation
* Course (navigation), the path of travel
* Course (orienteering), a series of control points visited by orienteers during a competition, marked with red/white flags in the terrain, and corresponding ...
thick. Baths and showers were to be available in every house.
The SS calculated the exact amount of weaponry for delivery to each individual soldier-peasant. An SS or NSDAP leader of merit, chosen for his qualities as a man and a soldier, would occupy the manor. This individual would become the Leader (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: ''Leiter'') of the settlement, acting on the administrative side as a Burgomeister
Burgomaster (alternatively spelled burgermeister, literally "master of the town, master of the borough, master of the fortress, master of the citizens") is the English form of various terms in or derived from Germanic languages for the chief ...
and on the Party side as the political leader of the local group, effectively combining the jurisdictions of the Party and the State.Kersten (1957), p. 134-135. He would also act as the military commander of a company-sized force consisting of the community's peasants, their sons and laborers.
The plans for the ''Wehrbauer'' communities did not include provision for any churches - unlike Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
farming villages.Kersten (1957), p. 136 Himmler stated that if the clergy were to acquire money to construct churches on their own in these settlements, the SS would later take the buildings over and transform them into "Germanic holy places".
During one of his many private-dinner monologues, Hitler presented his vision of the soldier-peasant.Hitler (2000), p. 16 After twelve years of military service, soldiers from peasant families would receive completely-equipped farms located in the conquered East. The last two years of their military service would focus on agricultural education. The soldier was not to be allowed to marry a townswoman, but only a peasant woman who, if possible, had not begun to live in a town with him. This would enable the settlers to live out the blood and soil principles of Nazi Germany. Also, it would encourage large families.Gerhard L. Weinberg
Gerhard Ludwig Weinberg (born 1 January 1928) is a German-born American diplomatic and military historian noted for his studies in the history of Nazi Germany and World War II. Weinberg is the William Rand Kenan, Jr. Professor Emeritus of History ...
, ''Visions of Victory: The Hopes of Eight World War II Leaders'' p 23 Thus, Hitler stated, "we shall again find in the countryside the blessing of numerous families. Whereas the present law of rural inheritance dispossesses the younger sons, in future every peasant's son will be sure of having his patch of ground." Hitler also believed that former non-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enli ...
s would make ideal teachers for the primary school
A primary school (in Ireland, the United Kingdom, Australia, Trinidad and Tobago, Jamaica, and South Africa), junior school (in Australia), elementary school or grade school (in North America and the Philippines) is a school for primary e ...
s of these Utopia
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imaginary community or society that possesses highly desirable or nearly perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia (book), Utopia'', describing a fictional ...
n communities. Although Himmler wanted the settlements to be totally agrarian, Hitler planned to introduce certain types of small-scale industry to them. At the time of his 54th birthday in April 1943, the ''Führer
( ; , spelled or ''Fuhrer'' when the Umlaut (diacritic), umlaut is not available) is a German word meaning "leader" or "guide". As a political title, it is strongly associated with the Nazi Germany, Nazi dictator Adolf Hitler.
Nazi Germany ...
'' had a discussion with Albert Speer
Berthold Konrad Hermann Albert Speer (; ; 19 March 1905 – 1 September 1981) was a German architect who served as the Minister of Armaments and War Production in Nazi Germany during most of World War II. A close ally of Adolf Hitler, he ...
and Karl-Otto Saur on a design he had personally drawn up for a six-person bunker that was to be used in the Atlantic Wall
The Atlantic Wall (german: link=no, Atlantikwall) was an extensive system of coastal defences and fortifications built by Nazi Germany between 1942 and 1944 along the coast of continental Europe and Scandinavia as a defence against an anticip ...
, featuring machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) a ...
s, an anti-tank gun
An anti-tank gun is a form of artillery designed to destroy tanks and other armored fighting vehicles, normally from a static defensive position. The development of specialized anti-tank munitions and anti-tank guns was prompted by the appearance ...
, and flame thrower
A flamethrower is a ranged weapon, ranged incendiary device designed to project a controllable jet (fluid), jet of fire. Greek fire, First deployed by the Byzantine Empire in the 7th century AD, flamethrowers saw use in modern times during Wo ...
s
Speer, Albert (1976). '' Spandau: The Secret Diaries'' Macmillan Company, p. 58.
— this design was also to be used for defense purposes on Germany's "ultimate eastern border deep within Russia" where the easternmost ''Wehrbauer'' "settlement-pearl" villages would likely have grown up — if the Axis had completely defeated the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
s, there might have existed the possibility either of remnant Soviet forces, or of troops of the northwestern Siberian extremities of Imperial Japan's Co-Prosperity Sphere territories on the eastern side of such a frontier.
Implementation
See also
*Greater Germanic Reich
The Greater Germanic Reich (german: Großgermanisches Reich), fully styled the Greater Germanic Reich of the German Nation (german: Großgermanisches Reich deutscher Nation), was the official state name of the political entity that Nazi Germany ...
* New Order
* Blood and soil
*Reichskommissariat Ostland
The Reichskommissariat Ostland (RKO) was established by Nazi Germany in 1941 during World War II. It became the civilian occupation regime in Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and the western part of Byelorussian SSR. German planning documents initia ...
*Reichskommissariat Ukraine
During World War II, (abbreviated as RKU) was the civilian occupation regime () of much of Nazi German-occupied Ukraine (which included adjacent areas of modern-day Belarus and pre-war Second Polish Republic). It was governed by the Reich Min ...
* Hegewald
*Tondenhei
The were military settler colonists recruited after the Meiji Restoration to develop and defend Japan's northern frontier in Hokkaidō and Karafuto against foreign nations, particularly Imperial Russia. (The term tonden comes from ancient China, ...
*Zamość Uprising
The Zamość uprising comprised World War II partisan operations, 1942–1944, by the Polish resistance (primarily the Home Army and Peasant Battalions) against Germany's '' Generalplan-Ost'' forced expulsion of Poles from the Zamość region ...
*Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
References
{{reflist, 2 Nazi terminology Ethnic cleansing in Europe German words and phrases Nazi SS German colonial empire Germany–Soviet Union relations Axis powers Veterans' settlement schemes