Wavefront Technology Solutions Inc on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In physics, the wavefront of a time-varying '' wave field'' is the set ( locus) of all 
 For a sinusoidal plane wave, the wavefronts are planes perpendicular to the direction of propagation, that move in that direction together with the wave. For a
For a sinusoidal plane wave, the wavefronts are planes perpendicular to the direction of propagation, that move in that direction together with the wave. For a
Wavefront tip/tilt estimation from defocused images
LightPipes
– Free Unix wavefront propagation software Optics Waves
points
Point or points may refer to:
Places
* Point, Lewis, a peninsula in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland
* Point, Texas, a city in Rains County, Texas, United States
* Point, the NE tip and a ferry terminal of Lismore, Inner Hebrides, Scotland
* Point ...
having the same '' phase''. The term is generally meaningful only for fields that, at each point, vary sinusoidally in time with a single temporal frequency (otherwise the phase is not well defined).
Wavefronts usually move with time. For waves propagating in a unidimensional
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coordina ...
medium, the wavefronts are usually single points; they are curve
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line (geometry), line, but that does not have to be Linearity, straight.
Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point (ge ...
s in a two dimensional medium, and surfaces in a three-dimensional one.
 For a sinusoidal plane wave, the wavefronts are planes perpendicular to the direction of propagation, that move in that direction together with the wave. For a
For a sinusoidal plane wave, the wavefronts are planes perpendicular to the direction of propagation, that move in that direction together with the wave. For a sinusoidal spherical wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a curve, mathematical curve defined in terms of the ''sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph of a function, graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a Smoothness, smooth p ...
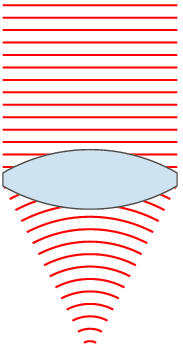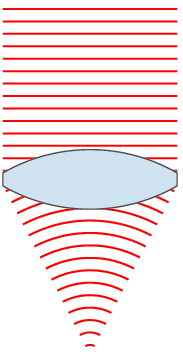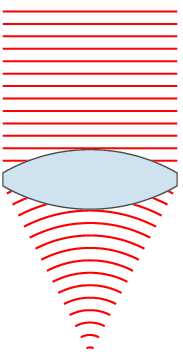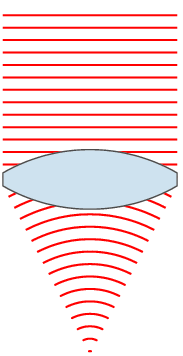
, the wavefronts are spherical surfaces that expand with it. If the speed of propagation is different at different points of a wavefront, the shape and/or orientation of the wavefronts may change by refraction. In particular, lenses
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
can change the shape of optical wavefronts from planar to spherical, or vice versa.
In classical physics
Classical physics is a group of physics theories that predate modern, more complete, or more widely applicable theories. If a currently accepted theory is considered to be modern, and its introduction represented a major paradigm shift, then the ...
, the diffraction phenomenon is described by the Huygens–Fresnel principle
The Huygens–Fresnel principle (named after Dutch physicist Christiaan Huygens and French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel) states that every point on a wavefront is itself the source of spherical wavelets, and the secondary wavelets emanating ...
that treats each point in a propagating wavefront as a collection of individual spherical wavelets. The characteristic bending pattern is most pronounced when a wave from a coherent source (such as a laser) encounters a slit/aperture that is comparable in size to its wavelength, as shown in the inserted image. This is due to the addition, or interference, of different points on the wavefront (or, equivalently, each wavelet) that travel by paths of different lengths to the registering surface. If there are multiple, closely spaced openings (e.g., a diffraction grating), a complex pattern of varying intensity can result.
Simple wavefronts and propagation
Optical systems can be described with Maxwell's equations, and linear propagating waves such as sound or electron beams have similar wave equations. However, given the above simplifications, Huygens' principle provides a quick method to predict the propagation of a wavefront through, for example, free space. The construction is as follows: Let every point on the wavefront be considered a new point source. By calculating the total effect from every point source, the resulting field at new points can be computed. Computational algorithms are often based on this approach. Specific cases for simple wavefronts can be computed directly. For example, a spherical wavefront will remain spherical as the energy of the wave is carried away equally in all directions. Such directions of energy flow, which are always perpendicular to the wavefront, are called '' rays'' creating multiple wavefronts. The simplest form of a wavefront is the plane wave, where the rays are parallel to one another. The light from this type of wave is referred to as '' collimated'' light. The plane wavefront is a good model for a surface-section of a very large spherical wavefront; for instance, sunlight strikes the earth with a spherical wavefront that has a radius of about 150 million kilometers (1 AU). For many purposes, such a wavefront can be considered planar over distances of the diameter of Earth. Wavefronts travel with the speed of light in all directions in an isotropic medium.Wavefront aberrations
Methods utilizing wavefront measurements or predictions can be considered an advanced approach to lens optics, where a single focal distance may not exist due to lens thickness or imperfections. For manufacturing reasons, a perfect lens has a spherical (or toroidal) surface shape though, theoretically, the ideal surface would be ''aspheric''. Shortcomings such as these in an optical system cause what are called optical aberrations. The best-known aberrations includespherical aberration
In optics, spherical aberration (SA) is a type of optical aberration, aberration found in optical systems that have elements with spherical surfaces. Lens (optics), Lenses and curved mirrors are prime examples, because this shape is easier to man ...
and coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
.''Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd Edition)'', R.G. Lerner, G.L. Trigg, VHC publishers, 1991, ISBN (Verlagsgesellschaft) 3-527-26954-1, ISBN (VHC Inc.) 0-89573-752-3
However there may be more complex sources of aberrations such as in a large telescope due to spatial variations in the index of refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
of the atmosphere. The deviation of a wavefront in an optical system from a desired perfect planar wavefront is called the ''wavefront aberration''. Wavefront aberrations are usually described as either a sampled image or a collection of two-dimensional polynomial terms. Minimization of these aberrations is considered desirable for many applications in optical systems.
Wavefront sensor and reconstruction techniques
A wavefront sensor is a device which measures the wavefront aberration in a coherent signal to describe the optical quality or lack thereof in an optical system. A very common method is to use a Shack–Hartmann lenslet array. There are many applications that include adaptive optics, optical metrology and even the measurement of the aberrations in theeye
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and conv ...
itself. In this approach, a weak laser source is directed into the eye and the reflection off the retina is sampled and processed.
Alternative wavefront sensing techniques to the Shack–Hartmann system are emerging. Mathematical techniques like phase imaging or curvature sensing are also capable of providing wavefront estimations. These algorithms compute wavefront images from conventional brightfield images at different focal planes without the need for specialised wavefront optics. While Shack-Hartmann lenslet arrays are limited in lateral resolution to the size of the lenslet array, techniques such as these are only limited by the resolution of digital images used to compute the wavefront measurements. That said, those wavefront sensors are suffering from linearity issues and so are much less robust than the original SHWFS, in term of phase measurement.
Another application of software reconstruction of the phase is the control of telescopes through the use of adaptive optics. A common method is the Roddier test, also called wavefront curvature sensing. It yields good correction, but needs an already good system as a starting point. Indeed because of those linearity issues described above. That's why people are coupling different types of WFS in those next Gen adaptive optics systems.
See also
* Huygens-Fresnel principle * Wavefront sensor * Adaptive optics * Deformable mirror * Wave field synthesisReferences
Further reading
Textbooks and books
* ''Concepts of Modern Physics'' (4th Edition), A. Beiser, Physics, McGraw-Hill (International), 1987, * ''Physics with Modern Applications'', L. H. Greenberg, Holt-Saunders International W. B. Saunders and Co, 1978, * ''Principles of Physics'', J. B. Marion, W. F. Hornyak, Holt-Saunders International Saunders College, 1984, * ''Introduction to Electrodynamics'' (3rd Edition), D. J. Griffiths, Pearson Education, Dorling Kindersley, 2007, * ''Light and Matter: Electromagnetism, Optics, Spectroscopy and Lasers'', Y. B. Band, John Wiley & Sons, 2010, * ''The Light Fantastic – Introduction to Classic and Quantum Optics'', I. R. Kenyon, Oxford University Press, 2008, * ''McGraw Hill Encyclopaedia of Physics'' (2nd Edition), C. B. Parker, 1994, *Journals
* * * * {{Cite journal , last=Shcherbak , first=O. P. , year=1988 , title=Волновые фронты и группы отражений , via= Russian Mathematical Surveys, 43:3 (1988), 149–194 , trans-title=Wavefronts and reflection groups , url=http://www.mathnet.ru/links/100d8a1eb447dd5b7afb5374163c5c3d/rm1892.pdf , journal=Успехи математических наук , language=Russian , volume=43 , issue=3(261) , pages=125–160 , doi=10.1070/RM1988v043n03ABEH001741Wavefront tip/tilt estimation from defocused images
External links
LightPipes
– Free Unix wavefront propagation software Optics Waves