Waterfall model on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The waterfall model is a breakdown of developmental activities into linear sequential phases, meaning that each phase is passed down onto each other, where each phase depends on the deliverables of the previous one and corresponds to a specialization of tasks.
This approach is typical for certain areas of
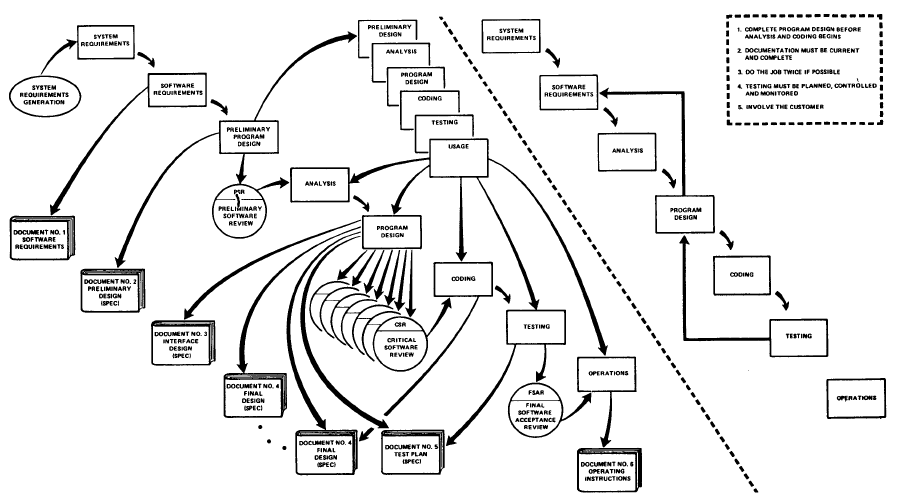 Winston W. Royce's final model, his intended improvement upon his initial "waterfall model", illustrated that feedback could (should, and often would) lead from code testing to design (as testing of code uncovered flaws in the design) and from design back to requirements specification (as design problems may necessitate the removal of conflicting or otherwise unsatisfiable/undesignable requirements). In the same paper Royce also advocated large quantities of documentation, doing the job "twice if possible" (a sentiment similar to that of
Winston W. Royce's final model, his intended improvement upon his initial "waterfall model", illustrated that feedback could (should, and often would) lead from code testing to design (as testing of code uncovered flaws in the design) and from design back to requirements specification (as design problems may necessitate the removal of conflicting or otherwise unsatisfiable/undesignable requirements). In the same paper Royce also advocated large quantities of documentation, doing the job "twice if possible" (a sentiment similar to that of
Understanding the pros and cons of the Waterfall Model of software development
* ttp://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/library/4626.html Going Over the Waterfall with the RUPby Philippe Kruchten
CSC and IBM Rational join to deliver C-RUP and support rapid business change
* c2:WaterFall
{{Software engineering Software development philosophies Project management Design
engineering design
The engineering design process, also known as the engineering method, is a common series of steps that engineers use in creating functional products and processes. The process is highly iterative – parts of the process often need to be repeat ...
. In software development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, wri ...
,
it tends to be among the less iterative and flexible approaches, as progress flows in largely one direction (downwards like a waterfall
A waterfall is any point in a river or stream where water flows over a vertical drop or a series of steep drops. Waterfalls also occur where meltwater drops over the edge
of a tabular iceberg or ice shelf.
Waterfalls can be formed in seve ...
) through the phases of conception, initiation, analysis
Analysis (: analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (38 ...
, design
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
, construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
, testing, deployment, and maintenance
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installa ...
.
The waterfall model is the earliest systems development life cycle ( SDLC) approach used in software development.
When it was first adopted, there were no recognized alternatives for knowledge-based creative work.
History
The first known presentation describing the use of such phases in software engineering was held by Herbert D. Benington at the Symposium on Advanced Programming Methods for Digital Computers on 29 June 1956. This presentation was about the development of software for SAGE. In 1983, Benington republished his paper with a foreword explaining that the phases were on purpose organized according to the specialization of tasks, and pointing out that the process was not in fact performed in a strict top-down fashion, but depended on a prototype. Although the term "waterfall" is not used in the paper, the first formal detailed diagram of the process later known as the "waterfall model" is often cited as coming from a 1970 article by Winston W. Royce. However, he commented that it had major flaws stemming from how testing only happened at the end of the process, which he described as being "risky and nvitingfailure". The rest of his paper introduced five steps which he felt were necessary to "eliminate most of the development risks" associated with the unaltered waterfall approach. Royce's five additional steps (which included writing complete documentation at various stages of development) never took mainstream hold, but his diagram of what he considered a flawed process became the starting point when describing a "waterfall" approach. The earliest use of the term "waterfall" may have been in a 1976 paper by Bell and Thayer. In 1985, theUnited States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and superv ...
adopted the waterfall model in the DOD-STD-2167 standard for working with software development contractors. This standard referred for iterations of a software development to "''the sequential phases of a software development cycle''" and stated that "''the contractor shall implement a software development cycle that includes the following six phases: Software Requirement Analysis, Preliminary Design, Detailed Design, Coding and Unit Testing, Integration, and Testing''".
Model
Although Royce never recommended nor described a waterfall model, rigid adherence to the following phases are criticized by him: #System
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
and software requirements
Software requirements for a system are the description of what the system should do, the service or services that it provides and the constraints on its operation. The IEEE Standard Glossary of Software Engineering Terminology defines a requiremen ...
: captured in a product requirements document
A product requirements document (PRD) is a document containing all the requirements for a certain product.
It is written to allow people to understand ''what'' a product should do. A PRD should, however, generally avoid anticipating or defining ...
# Analysis
Analysis (: analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (38 ...
: resulting in models
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , .
Models can be divided int ...
, schema
Schema may refer to:
Science and technology
* SCHEMA (bioinformatics), an algorithm used in protein engineering
* Schema (genetic algorithms), a set of programs or bit strings that have some genotypic similarity
* Schema.org, a web markup vocab ...
, and business rule A business rule defines or constrains some aspect of a business. It may be expressed to specify an action to be taken when certain conditions are true or may be phrased so it can only resolve to either true or false. Business rules are intended to a ...
s
# Design
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
: resulting in the software architecture
Software architecture is the set of structures needed to reason about a software system and the discipline of creating such structures and systems. Each structure comprises software elements, relations among them, and properties of both elements a ...
# Coding: the development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development (music), the process by which thematic material is reshaped
* Photographic development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
* Development hell, when a proje ...
, proving, and integration of software
# Testing: the systematic discovery and debugging
In engineering, debugging is the process of finding the Root cause analysis, root cause, workarounds, and possible fixes for bug (engineering), bugs.
For software, debugging tactics can involve interactive debugging, control flow analysis, Logf ...
of defects
# Operations: the installation, migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
, support, and maintenance
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installa ...
of complete systems
Thus, the waterfall model maintains that one should move to a phase only when its preceding phase is reviewed and verified.
Various modified waterfall models (including Royce's final model), however, can include slight or major variations on this process. These variations include returning to the previous cycle after flaws are found downstream, or returning to the design phase if downstream phases are deemed insufficient.
Supporting arguments
Time spent early in the software production cycle can reduce costs at later stages. For example, a problem found in the early stages (such as requirements specification) is cheaper to fix than the same bug found later on in the process (by a factor of 50 to 200). In common practice, waterfall methodologies result in a project schedule with 20–40% of the time invested for the first two phases, 30–40% of the time to coding, and the rest dedicated to testing and implementation. With the project organization needing to be highly structured, most medium and large projects will include a detailed set of procedures and controls, which regulate every process on the project. A further argument supporting the waterfall model is that it places emphasis on documentation (such as requirements documents and design documents) as well assource code
In computing, source code, or simply code or source, is a plain text computer program written in a programming language. A programmer writes the human readable source code to control the behavior of a computer.
Since a computer, at base, only ...
. In less thoroughly designed and documented methodologies, knowledge is lost if team members leave before the project is completed, and it may be difficult for a project to recover from the loss. If a fully working design document is present (as is the intent of big design up front and the waterfall model), new team members and new teams should be able to familiarise themselves to the project by reading the documents.
The waterfall model provides a structured approach; the model itself progresses linearly through discrete, easily understandable and explainable phases and thus is easy to understand. It also provides easily identifiable milestones in the development process, often being used as a beginning example of a development model in many software engineering texts and courses.
Similarly, simulation can play a valuable role within the waterfall model. By creating computerized or mathematical simulations of the system being developed, teams can gain insights into how the system will perform before proceeding to the next phase. Simulations allow for testing and refining the design, identifying potential issues or bottlenecks, and making informed decisions about the system's functionality and performance.
Criticism
Clients may not know the exact requirements before they see working software and thus change their requirements further on, leading to redesign, redevelopment, and retesting, and increased costs. Designers may not be aware of future difficulties when designing a new software product or feature, in which case revising the design initially can increase efficiency in comparison to a design not built to account for newly discovered constraints, requirements, or problems. Organisations may attempt to deal with a lack of concrete requirements from clients by employing systems analysts to examine existing manual systems and analyse what they do and how they might be replaced. However, in practice, it is difficult to sustain a strict separation betweensystems analysis
Systems analysis is "the process of studying a procedure or business to identify its goal and purposes and create systems and procedures that will efficiently achieve them". Another view sees systems analysis as a problem-solving technique that ...
and programming, as implementing any non-trivial system will often expose issues and edge cases that the systems analyst did not consider.
Some organisations, such as the United States Department of Defense, now have a stated preference against waterfall-type methodologies, starting with MIL-STD-498 released in 1994, which encourages ''evolutionary acquisition'' and ''iterative and incremental development
Iterative and incremental development is any combination of both iterative design (or iterative method) and incremental build model for New product development, development.
Usage of the term began in software development, with a long-standing com ...
''.
Modified waterfall models
In response to the perceived problems with the "pure" waterfall model, many 'modified waterfall models' have been introduced. These models may address some or all of the criticisms of the "pure" waterfall model. These include the rapid development models thatSteve McConnell
Steven C. McConnell is an author of software engineering textbooks such as '' Code Complete'', ''Rapid Development'', and ''Software Estimation''. He is cited as an expert in software engineering and project management.
Career
McConnell gradua ...
calls "modified waterfalls": Peter DeGrace's "sashimi model" (waterfall with overlapping phases), waterfall with subprojects, and waterfall with risk reduction. Other software development model combinations such as "incremental waterfall model" also exist.
Royce's final model
Fred Brooks
Frederick Phillips Brooks Jr. (April 19, 1931 – November 17, 2022) was an American computer architect, software engineer, and computer scientist, best known for managing development of IBM's System/360 family of mainframe computers and the ...
, famous for writing the Mythical Man Month — an influential book in software project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
— who advocated planning to "throw one away"), and involving the customer as much as possible (a sentiment similar to that of extreme programming
Extreme programming (XP) is a software development methodology intended to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements. As a type of agile software development,"Human Centred Technology Workshop 2006 ", 2006, ...
).
Royce notes on the final model are the following:
# Complete program design before analysis and coding begins
# Documentation must be current and complete
# Do the job twice if possible
# Testing must be planned, controlled, and monitored
# Involve the customer
See also
References
External links
Understanding the pros and cons of the Waterfall Model of software development
* ttp://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/library/4626.html Going Over the Waterfall with the RUPby Philippe Kruchten
CSC and IBM Rational join to deliver C-RUP and support rapid business change
* c2:WaterFall
{{Software engineering Software development philosophies Project management Design