Water Turbine (en 2) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A water turbine is a rotary machine that converts
A water turbine is a rotary machine that converts
 Water wheels have been used for hundreds of years for industrial power. Their main shortcoming is size, which limits the flow rate and
Water wheels have been used for hundreds of years for industrial power. Their main shortcoming is size, which limits the flow rate and

 The earliest known water turbines date to the
The earliest known water turbines date to the
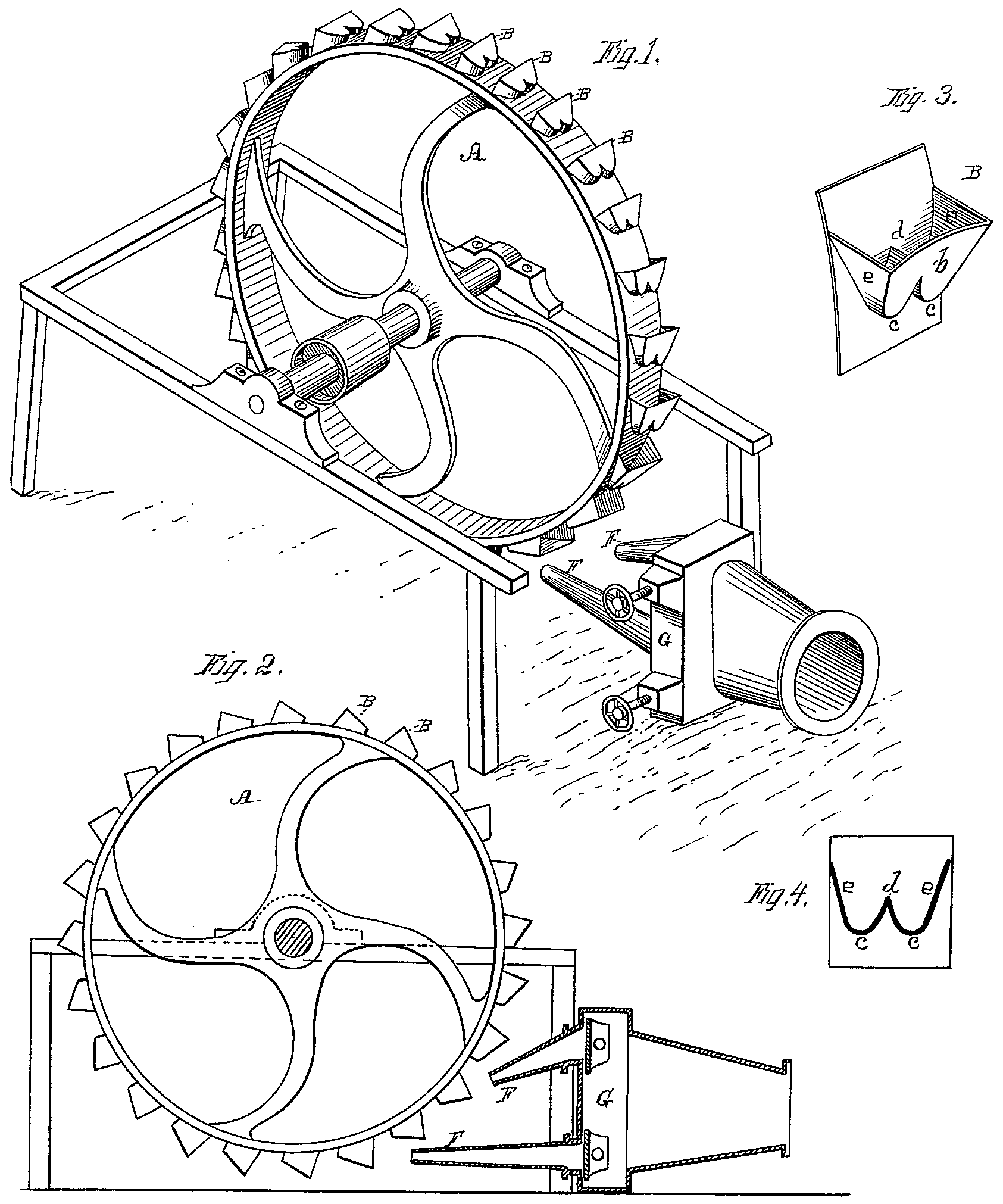 All common water machines until the late 19th century (including water wheels) were basically reaction machines; water ''pressure'' head acted on the machine and produced work. A reaction turbine needs to fully contain the water during energy transfer.
In 1866, California millwright Samuel Knight invented a machine that took the impulse system to a new level. Inspired by the high pressure jet systems used in hydraulic mining in the gold fields, Knight developed a bucketed wheel which captured the energy of a free jet, which had converted a high head (hundreds of vertical feet in a pipe or
All common water machines until the late 19th century (including water wheels) were basically reaction machines; water ''pressure'' head acted on the machine and produced work. A reaction turbine needs to fully contain the water during energy transfer.
In 1866, California millwright Samuel Knight invented a machine that took the impulse system to a new level. Inspired by the high pressure jet systems used in hydraulic mining in the gold fields, Knight developed a bucketed wheel which captured the energy of a free jet, which had converted a high head (hundreds of vertical feet in a pipe or


 Turbine selection is based on the available water head, and less so on the available flow rate. In general, impulse turbines are used for high head sites, and reaction turbines are used for
Turbine selection is based on the available water head, and less so on the available flow rate. In general, impulse turbines are used for high head sites, and reaction turbines are used for
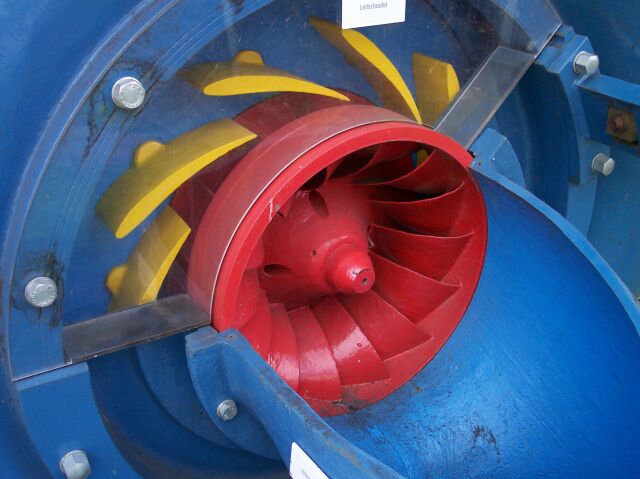 A wicket gate, or guide vane, is a component of water turbines to control the flow of water that enters the turbine. A series of small openings of the wicket gates surround the turbine. When the wicket gates are opened wider, more water will flow into the turbine runner which results in higher power output. The control of wicket gate opening and closing will allow the output energy generated by the turbines to be controlled to match the desired output energy levels.
A wicket gate, or guide vane, is a component of water turbines to control the flow of water that enters the turbine. A series of small openings of the wicket gates surround the turbine. When the wicket gates are opened wider, more water will flow into the turbine runner which results in higher power output. The control of wicket gate opening and closing will allow the output energy generated by the turbines to be controlled to match the desired output energy levels.
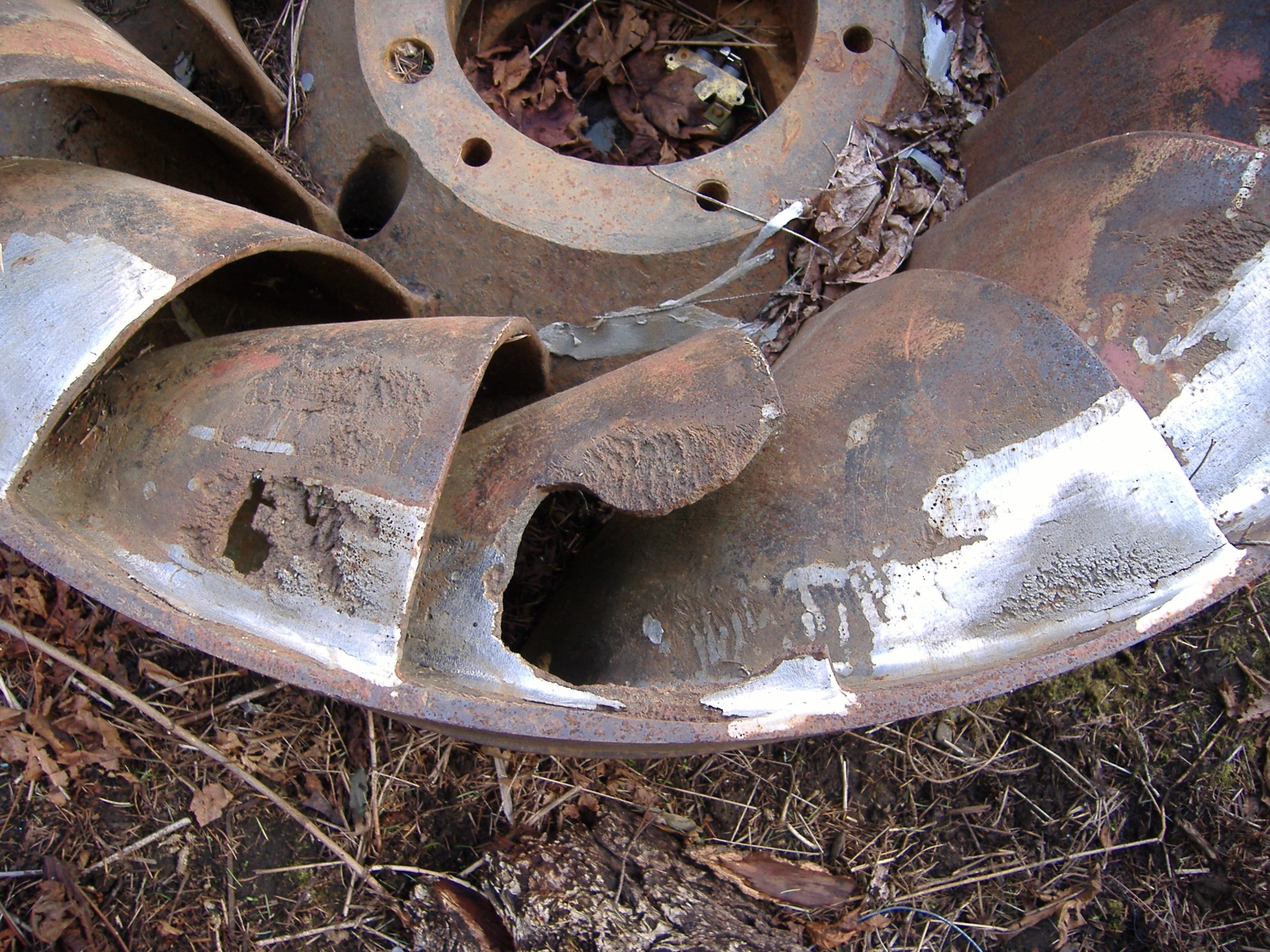 Turbines are designed to run for decades with very little maintenance of the main elements; overhaul intervals are on the order of several years. Maintenance of the runners and parts exposed to water include removal, inspection, and repair of worn parts.
Normal wear and tear includes
Turbines are designed to run for decades with very little maintenance of the main elements; overhaul intervals are on the order of several years. Maintenance of the runners and parts exposed to water include removal, inspection, and repair of worn parts.
Normal wear and tear includes
''Turbine Repair (Facilities Instructions, Standards & Techniques, Volume 2-5)''
(1.5 MB pdf).
Introductory turbine math
European Union publication, Layman's hydropower handbook,12 MB pdf
"Selecting Hydraulic Reaction Turbines", US Bureau of Reclamation publication, 48 MB pdf
"Laboratory for hydraulic machines", Lausanne (Switzerland)
{{Authority control Articles containing video clips
 A water turbine is a rotary machine that converts
A water turbine is a rotary machine that converts kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its accele ...
and potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects, stresses within itself, its electric charge, or other factors.
Common types of potential energy include the gravitational potentia ...
of water into mechanical work.
Water turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating e ...
s were developed in the 19th century and were widely used for industrial power prior to electrical grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
s. Now, they are mostly used for electric power generation.
Water turbines are mostly found in dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
s to generate electric power from water potential energy.
History
 Water wheels have been used for hundreds of years for industrial power. Their main shortcoming is size, which limits the flow rate and
Water wheels have been used for hundreds of years for industrial power. Their main shortcoming is size, which limits the flow rate and head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may ...
that can be harnessed.
The migration from water wheels to modern turbines took about one hundred years. Development occurred during the Industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, using scientific principles and methods. They also made extensive use of new materials and manufacturing methods developed at the time.
Swirl
The wordturbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating e ...
was introduced by the French engineer Claude Burdin
Claude Burdin (; 19 March 1788 – 12 November 1873) was a French engineer.
Born in Lépin-le-Lac, Savoie, when it was known as the Duchy of Savoy, he was professor at the school of mines, École nationale supérieure des mines de Saint-� ...
in the early 19th century and is derived from the Greek word "τύρβη" for "whirling" or a "vortex". The main difference between early water turbines and water wheels is a swirl component of the water which passes energy to a spinning rotor. This additional component of motion allowed the turbine to be smaller than a water wheel of the same power. They could process more water by spinning faster and could harness much greater heads. (Later, impulse turbines were developed which didn't use swirl.)
Timeline

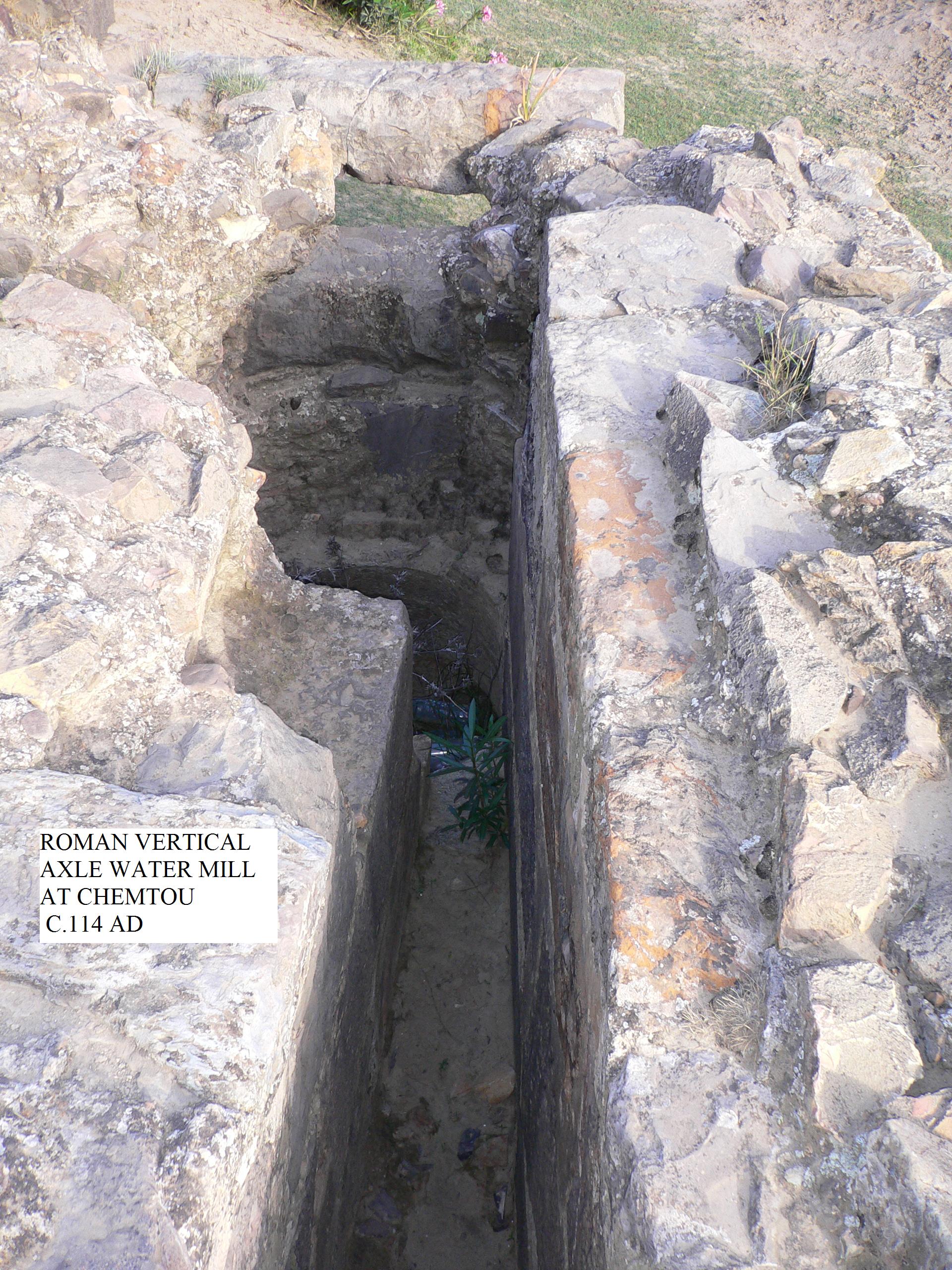
 The earliest known water turbines date to the
The earliest known water turbines date to the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
. Two helix-turbine mill sites of almost identical design were found at Chemtou
Chemtou or Chimtou was an ancient Roman-Berber town in northwestern Tunisia, located 20 km from the city of Jendouba near the Algerian frontier. It was known as Simitthu (or Simitthus in Roman period) in antiquity.
History
Chemtou was found ...
and Testour
Testour ( ar, تستور ') is a small town located in the north of Tunisia. The town is perched on the hills of Medjerda Valley, south-west of Medjez-el-Bab, the crossroads between Tunis, Béja, and the north of Tunisia. It was known during th ...
, modern-day Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, dating to the late 3rd or early 4th century AD. The horizontal water wheel with angled blades was installed at the bottom of a water-filled, circular shaft. The water from the mill-race entered the pit tangentially, creating a swirling water column which made the fully submerged wheel act like a true turbine.; ;
Fausto Veranzio
Fausto Veranzio ( la, Faustus Verantius; hr, Faust Vrančić; Hungarian and Vernacular Latin: ''Verancsics Faustus'';Andrew L. SimonMade in Hungary: Hungarian contributions to universal culture/ref>Francis turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency.
The proces ...
.
Johann Segner developed a reactive water turbine ( Segner wheel) in the mid-18th century in Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
. It had a horizontal axis and was a precursor to modern water turbines. It is a very simple machine that is still produced today for use in small hydro sites. Segner worked with Euler
Leonhard Euler ( , ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, astronomer, geographer, logician and engineer who founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made pioneering and influential discoveries in ma ...
on some of the early mathematical theories of turbine design. In the 18th century, a Dr. Robert Barker invented a similar reaction hydraulic turbine that became popular as a lecture-hall demonstration. The only known surviving example of this type of engine used in power production, dating from 1851, is found at Hacienda Buena Vista
Hacienda Buena Vista, also known as Hacienda Vives (or Buena Vista Plantation in English language, English), was a coffee plantation located in Barrio Magueyes, Ponce, Puerto Rico. The original plantation dates from the 19th century. The planta ...
in Ponce, Puerto Rico
Ponce (, , , ) is both a city and a municipality on the southern coast of Puerto Rico. The city is the seat of the municipal government.
Ponce, Puerto Rico's most populated city outside the San Juan metropolitan area, was founded on 12 August 1 ...
.R. Sackett, p. 16.
In 1820, Jean-Victor Poncelet
Jean-Victor Poncelet (; 1 July 1788 – 22 December 1867) was a French engineer and mathematician who served most notably as the Commanding General of the École Polytechnique. He is considered a reviver of projective geometry, and his work ''Tr ...
developed an inward-flow turbine.
In 1826, Benoît Fourneyron
Benoît Fourneyron (31 October 1802 – 31 July 1867) was a French engineer, born in Saint-Étienne, Loire. Fourneyron made significant contributions to the development of water turbines.
Benoît Fourneyron was educated at the École Nationa ...
developed an outward-flow turbine. This was an efficient machine (~80%) that sent water through a runner with blades curved in one dimension. The stationary outlet also had curved guides.
In 1844, Uriah A. Boyden
Uriah Atherton Boyden (February 17, 1804 – October 17, 1879) was an American civil and mechanical engineer and inventor from Foxborough, Massachusetts best known for the development of a water turbine, that later became known as the Boyden ...
developed an outward flow turbine that improved on the performance of the Fourneyron turbine. Its runner shape was similar to that of a Francis turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency.
The proces ...
.
In 1849, James B. Francis
James Bicheno Francis (May 18, 1815 – September 18, 1892) was a British-American civil engineer, who invented the Francis turbine.
Early years
James Francis was born in South Leigh, near Witney, Oxfordshire, in England, United Kingdom. ...
improved the inward flow reaction turbine to over 90% efficiency. He also conducted sophisticated tests and developed engineering methods for water turbine design. The Francis turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency.
The proces ...
, named for him, is the first modern water turbine. It is still the most widely used water turbine in the world today. The Francis turbine is also called a radial flow turbine, since water flows from the outer circumference towards the centre of runner.
Inward flow water turbines have a better mechanical arrangement and all modern reaction water turbines are of this design. As the water swirls inward, it accelerates, and transfers energy to the runner. Water pressure decreases to atmospheric, or in some cases subatmospheric, as the water passes through the turbine blades and loses energy.
In 1876, John B. McCormick
John Buchanan McCormick (November 4, 1834 – August 21, 1924) was an American mechanical engineer who invented the first modern mixed flow water turbine, the "Hercules", as well variants including the Holyoke-McCormick, and Achilles turbines. Mc ...
, building on Francis's designs, demonstrated the first modern mixed-flow turbine with the development of the Hercules turbine, initially manufactured by the Holyoke Machine Company
The Holyoke Machine Company was an American manufacturer of industrial machinery, best known for its work in paper manufacturing equipment and water turbines. The company, formed in 1863, was founded by Nathan H. Whitten, T.C. Page, T. B. Flande ...
and subsequently improved upon by engineers in Germany and the United States. The design effectively combined the inward flow principles of the Francis design with the downward discharge of the Jonval turbine
The Jonval turbine is a water turbine design invented in France in 1837 and introduced to the United States around 1850 and were widely used. The Jonval turbine is a "mixed-flow" turbine design. Mixed-flow designs were well suited for the low-head ...
, with flow inward at the inlet, axial through the wheel's body, and slightly outward at the outlet. Initially performing optimally at 90% efficiency at lower speeds, this design would see many improvements in the subsequent decades in derivatives under names like "Victor", "Risdon", "Samson" and "New American," ushering in a new era of American turbine engineering.
Water turbines, particularly in the Americas, would largely become standardized with the establishment of the Holyoke Testing Flume, described as the first modern hydraulic laboratory in the United States by Robert E. Horton
Robert Elmer Horton (May 18, 1875 – April 22, 1945) was an American hydrologist, geomorphologist, civil engineer, and soil scientist, considered by many to be the father of modern American hydrology. An eponymous medal is awarded by the Ameri ...
and Clemens Herschel
Clemens Herschel (March 23, 1842 – March 1, 1930) was an American hydraulic engineer. His career extended from about 1860 to 1930, and he is best known for inventing the Venturi meter, which was the first large-scale, accurate device for measur ...
, the latter of which would serve as its chief engineer for a time. Initially created in 1872 by James B. Emerson from the testing flumes of Lowell, after 1880 the Holyoke, Massachusetts
Holyoke is a city in Hampden County, Massachusetts, United States, that lies between the western bank of the Connecticut River and the Mount Tom Range. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 38,238. Located north of Springfield ...
hydraulic laboratory was standardized by Herschel, who used it to develop the Venturi meter
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section (or choke) of a pipe. The Venturi effect is named after its discoverer, the 18th century Italian physicist, Giovanni Battista ...
, the first accurate means of measuring large flows, to properly measure water power efficiency by different turbine models. While skepticism of certain weir calculations were held by European hydrologists, the facility allowed for standard efficiency testing among major manufacturers through 1932, by which time more modern facilities and methods had proliferated.
Around 1890, the modern fluid bearing
Fluid bearings are bearings in which the load is supported by a thin layer of rapidly moving pressurized liquid or gas between the bearing surfaces. Since there is no contact between the moving parts, there is no sliding friction, allowing flui ...
was invented, now universally used to support heavy water turbine spindles. As of 2002, fluid bearings appear to have a mean time between failures
Mean time between failures (MTBF) is the predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a mechanical or electronic system during normal system operation. MTBF can be calculated as the arithmetic mean (average) time between failures of a system ...
of more than 1300 years.
Around 1913, Viktor Kaplan
Viktor Kaplan (27 November 1876 – 23 August 1934) was an Austrian engineer and the inventor of the Kaplan turbine.
Life
Kaplan was born in Mürzzuschlag, Austria into a railroad worker's family. He graduated from high school in Vienna in 1895 ...
created the Kaplan turbine
The Kaplan turbine is a propeller-type water turbine which has adjustable blades. It was developed in 1913 by Austrian professor Viktor Kaplan, who combined automatically adjusted propeller blades with automatically adjusted wicket gates to ach ...
, a propeller-type machine. It was an evolution of the Francis turbine and revolutionized the ability to develop low-head hydro sites.
New concept
 All common water machines until the late 19th century (including water wheels) were basically reaction machines; water ''pressure'' head acted on the machine and produced work. A reaction turbine needs to fully contain the water during energy transfer.
In 1866, California millwright Samuel Knight invented a machine that took the impulse system to a new level. Inspired by the high pressure jet systems used in hydraulic mining in the gold fields, Knight developed a bucketed wheel which captured the energy of a free jet, which had converted a high head (hundreds of vertical feet in a pipe or
All common water machines until the late 19th century (including water wheels) were basically reaction machines; water ''pressure'' head acted on the machine and produced work. A reaction turbine needs to fully contain the water during energy transfer.
In 1866, California millwright Samuel Knight invented a machine that took the impulse system to a new level. Inspired by the high pressure jet systems used in hydraulic mining in the gold fields, Knight developed a bucketed wheel which captured the energy of a free jet, which had converted a high head (hundreds of vertical feet in a pipe or penstock
A penstock is a sluice or gate or intake structure that controls water flow, or an enclosed pipe that delivers water to hydro turbines and sewerage systems. The term is inherited from the earlier technology of mill ponds and watermills.
H ...
) of water to kinetic energy. This is called an impulse or tangential turbine. The water's velocity, roughly twice the velocity of the bucket periphery, does a U-turn in the bucket and drops out of the runner at low velocity.
In 1879, Lester Pelton, experimenting with a Knight Wheel, developed a Pelton wheel
The Pelton wheel or Pelton Turbine is an impulse-type water turbine invented by American inventor Lester Allan Pelton in the 1870s. The Pelton wheel extracts energy from the impulse of moving water, as opposed to water's dead weight like the trad ...
(double bucket design), which exhausted the water to the side, eliminating some energy loss of the Knight wheel which exhausted some water back against the center of the wheel. In about 1895, William Doble improved on Pelton's half-cylindrical bucket form with an elliptical bucket that included a cut in it to allow the jet a cleaner bucket entry. This is the modern form of the Pelton turbine which today achieves up to 92% efficiency. Pelton had been quite an effective promoter of his design and although Doble took over the Pelton company he did not change the name to Doble because it had brand name recognition.
Turgo
Turgo is a small basaltic hill on the southern slopes of Mount Merapi, Indonesia, and is also known as Gunung Turgo or Mount Turgo. It is administratively located in Purwobinangun, Pakem, Sleman Regency, Special Region of Yogyakarta. Recent work ...
and cross-flow turbine
A cross-flow turbine, Bánki-Michell turbine, or Ossberger turbine''E.F. Lindsley,'' Water power for your homePopular Science, May 1977, Vol. 210, No. 5 87-93. is a water turbine developed by the Australian Anthony Michell, the Hungarian Donát B ...
s were later impulse designs.
Theory of operation
Flowing water is directed on to the blades of a turbine runner, creating a force on the blades. Since the runner is spinning, the force acts through a distance (force acting through a distance is the definition ofwork
Work may refer to:
* Work (human activity), intentional activity people perform to support themselves, others, or the community
** Manual labour, physical work done by humans
** House work, housework, or homemaking
** Working animal, an animal tr ...
). In this way, energy is transferred from the water flow to the turbine.
Water turbines are divided into two groups: reaction
Reaction may refer to a process or to a response to an action, event, or exposure:
Physics and chemistry
*Chemical reaction
*Nuclear reaction
*Reaction (physics), as defined by Newton's third law
*Chain reaction (disambiguation).
Biology and me ...
turbines and impulse
Impulse or Impulsive may refer to:
Science
* Impulse (physics), in mechanics, the change of momentum of an object; the integral of a force with respect to time
* Impulse noise (disambiguation)
* Specific impulse, the change in momentum per uni ...
turbines.
The precise shape of water turbine blades is a function of the supply pressure of water, and the type of impeller selected.
Reaction turbines
Reaction turbines are acted on by water, which changes pressure as it moves through the turbine and gives up its energy. They must be encased to contain the water pressure (or suction), or they must be fully submerged in the water flow.Newton's third law
Newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws can be paraphrased as follows:
# A body remains at rest, or in motion ...
describes the transfer of energy for reaction turbines.
Most water turbines in use are reaction turbines and are used in low (<) and medium () head applications.
In reaction turbine pressure drop occurs in both fixed and moving blades.
It is largely used in dam and large power plants
Impulse turbines
Impulse turbines change the velocity of a water jet. The jet pushes on the turbine's curved blades which changes the direction of the flow. The resulting change in momentum (impulse
Impulse or Impulsive may refer to:
Science
* Impulse (physics), in mechanics, the change of momentum of an object; the integral of a force with respect to time
* Impulse noise (disambiguation)
* Specific impulse, the change in momentum per uni ...
) causes a force on the turbine blades. Since the turbine is spinning, the force acts through a distance (work) and the diverted water flow is left with diminished energy. An impulse turbine is one in which the pressure of the fluid flowing over the rotor blades is constant and all the work output is due to the change in kinetic energy of the fluid.
Prior to hitting the turbine blades, the water's pressure (potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects, stresses within itself, its electric charge, or other factors.
Common types of potential energy include the gravitational potentia ...
) is converted to kinetic energy by a nozzle
A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow (specially to increase velocity) as it exits (or enters) an enclosed chamber or pipe.
A nozzle is often a pipe or tube of varying cross sectional area, a ...
and focused on the turbine. No pressure change occurs at the turbine blades, and the turbine doesn't require a housing for operation.
Newton's second law describes the transfer of energy for impulse turbines.
Impulse turbines are often used in very high (>300m/1000 ft) head applications.
Power
Thepower
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
available in a stream is;
where:
* power (J/s or watts)
* turbine efficiency
* density of fluid (kg/m3)
* acceleration of gravity (9.81 m/s2)
* head (m). For still water, this is the difference in height between the inlet and outlet surfaces. Moving water has an additional component added to account for the kinetic energy of the flow. The total head equals the ''pressure head'' plus ''velocity head''.
*= flow rate (m3/s)
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity
Some water turbines are designed for pumped-storage hydroelectricity. They can reverse flow and operate as apump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they u ...
to fill a high reservoir during off-peak electrical hours, and then revert to a water turbine for power generation during peak electrical demand. This type of turbine is usually a Deriaz or Francis turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency.
The proces ...
in design.
This type of system is used in El Hierro, one of the Canary Islands: "When wind production exceeds demand, excess energy will pump water from a lower reservoir at the bottom of a volcanic cone to an upper reservoir at the top of the volcano 700 meters above sea level. The lower reservoir stores 150,000 cubic meters of water. The stored water acts as a battery. The maximum storage capacity is 270 MWh. When demand rises and there is not enough wind power, the water will be released to four hydroelectric turbines with a total capacity of 11 MW."
Efficiency
Large modern water turbines operate at mechanical efficiencies greater than 90%.Types of water turbines


Reaction turbines
* VLH turbine *Francis turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency.
The proces ...
*Kaplan turbine
The Kaplan turbine is a propeller-type water turbine which has adjustable blades. It was developed in 1913 by Austrian professor Viktor Kaplan, who combined automatically adjusted propeller blades with automatically adjusted wicket gates to ach ...
*Tyson turbine
The Tyson turbine is a conical water turbine with helical blades emerging partway down from the apex gradually increasing in radial dimension and decreasing in pitch as they spiral towards the base of the cone. This design doesn't need a casement, ...
*Deriaz turbine
The Deriaz turbine, presented by engineer Paul Deriaz, was the first diagonal hydraulic pump-turbine to be designed. In contrast to most hydraulic machines, the flow in a Deriaz turbine does not follow a full axial nor radial direction but is a di ...
*Gorlov helical turbine
The Gorlov helical turbine (GHT) is a water turbine evolved from the Darrieus wind turbine, Darrieus turbine design by altering it to have Helix, helical blades/foils. It was patented in a series of patents from September 19, 1995''A. M. Gorlov' ...
Impulse turbine
*Water wheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets ...
*Pelton wheel
The Pelton wheel or Pelton Turbine is an impulse-type water turbine invented by American inventor Lester Allan Pelton in the 1870s. The Pelton wheel extracts energy from the impulse of moving water, as opposed to water's dead weight like the trad ...
*Turgo turbine
The Turgo turbine is an impulse water turbine designed for medium head applications. Operational Turgo turbines achieve efficiencies of about 87%. In factory and lab tests Turgo turbines perform with efficiencies of up to 90%. It works with net ...
*Cross-flow turbine
A cross-flow turbine, Bánki-Michell turbine, or Ossberger turbine''E.F. Lindsley,'' Water power for your homePopular Science, May 1977, Vol. 210, No. 5 87-93. is a water turbine developed by the Australian Anthony Michell, the Hungarian Donát B ...
(also known as the Bánki-Michell turbine, or Ossberger turbine)
*Jonval turbine
The Jonval turbine is a water turbine design invented in France in 1837 and introduced to the United States around 1850 and were widely used. The Jonval turbine is a "mixed-flow" turbine design. Mixed-flow designs were well suited for the low-head ...
*Reverse overshot water-wheel
Frequently used in mines and probably elsewhere (such as agricultural drainage), the reverse overshot water wheel was a Roman innovation to help remove water from the lowest levels of underground workings. It is described by Vitruvius in his work ' ...
*Screw turbine
A screw and a bolt (see '' Differentiation between bolt and screw'' below) are similar types of fastener typically made of metal and characterized by a helical ridge, called a ''male thread'' (external thread). Screws and bolts are used to f ...
* Barkh Turbine
Design and application
 Turbine selection is based on the available water head, and less so on the available flow rate. In general, impulse turbines are used for high head sites, and reaction turbines are used for
Turbine selection is based on the available water head, and less so on the available flow rate. In general, impulse turbines are used for high head sites, and reaction turbines are used for low head
Low Head is a rural residential locality in the local government area (LGA) of George Town Council, George Town in the Launceston LGA Region, Launceston LGA region of Tasmania. The locality is about north of the town of George Town, Tasmania, G ...
sites. Kaplan turbines with adjustable blade pitch are well-adapted to wide ranges of flow or head conditions, since their peak efficiency can be achieved over a wide range of flow conditions.
Small turbines (mostly under 10 MW) may have horizontal shafts, and even fairly large bulb-type turbines up to 100 MW or so may be horizontal. Very large Francis and Kaplan machines usually have vertical shafts because this makes best use of the available head, and makes installation of a generator more economical. Pelton wheels may be either vertical or horizontal shaft machines because the size of the machine is so much less than the available head. Some impulse turbines use multiple jets per runner to balance shaft thrust. This also allows for the use of a smaller turbine runner, which can decrease costs and mechanical losses.
Typical range of heads
•
•
• VLH turbine
•
•
•
•
0.2 < ''H'' < 4 (''H'' = head in m)
1 < ''H'' < 10
1.5 < ''H'' < 4.5
2 < ''H'' < 70
10 < ''H'' < 300
80 < ''H'' < 1600
50 < ''H'' < 250
Water wheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets ...
•
Screw turbine
A screw and a bolt (see '' Differentiation between bolt and screw'' below) are similar types of fastener typically made of metal and characterized by a helical ridge, called a ''male thread'' (external thread). Screws and bolts are used to f ...
• VLH turbine
•
Kaplan turbine
The Kaplan turbine is a propeller-type water turbine which has adjustable blades. It was developed in 1913 by Austrian professor Viktor Kaplan, who combined automatically adjusted propeller blades with automatically adjusted wicket gates to ach ...
•
Francis turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency.
The proces ...
•
Pelton wheel
The Pelton wheel or Pelton Turbine is an impulse-type water turbine invented by American inventor Lester Allan Pelton in the 1870s. The Pelton wheel extracts energy from the impulse of moving water, as opposed to water's dead weight like the trad ...
•
Turgo turbine
The Turgo turbine is an impulse water turbine designed for medium head applications. Operational Turgo turbines achieve efficiencies of about 87%. In factory and lab tests Turgo turbines perform with efficiencies of up to 90%. It works with net ...
0.2 < ''H'' < 4 (''H'' = head in m)
1 < ''H'' < 10
1.5 < ''H'' < 4.5
2 < ''H'' < 70
10 < ''H'' < 300
80 < ''H'' < 1600
50 < ''H'' < 250
Specific speed
The specific speed of a turbine characterizes the turbine's shape in a way that is not related to its size. This allows a new turbine design to be scaled from an existing design of known performance. The specific speed is also the main criteria for matching a specific hydro site with the correct turbine type. The specific speed is the speed with which the turbine turns for a particular discharge Q, with unit head and thereby is able to produce unit power.Affinity laws
Affinity laws
The affinity laws (also known as the "Fan Laws" or "Pump Laws") for pumps/fans are used in hydraulics, hydronics and/or HVAC to express the relationship between variables involved in pump or fan performance (such as head, volumetric flow rate, sha ...
allow the output of a turbine to be predicted based on model tests. A miniature replica of a proposed design, about one foot (0.3 m) in diameter, can be tested and the laboratory measurements applied to the final application with high confidence. Affinity laws are derived by requiring similitude
Similitude is a concept applicable to the testing of engineering models. A model is said to have similitude with the real application if the two share geometric similarity, kinematic similarity and dynamic similarity. ''Similarity'' and ''simili ...
between the test model and the application.
Flow through the turbine is controlled either by a large valve or by wicket gates arranged around the outside of the turbine runner. Differential head and flow can be plotted for a number of different values of gate opening, producing a hill diagram used to show the efficiency of the turbine at varying conditions.
Runaway speed
The runaway speed of a water turbine is its speed at full flow, and no shaft load. The turbine will be designed to survive the mechanical forces of this speed. The manufacturer will supply the runaway speed rating.Control systems
Different designs ofgovernors
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political_regions, political region, ranking under the Head of State, head of state and in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of ...
have been used since the mid-18th century to control the speeds of the water turbines. A variety of flyball
Flyball is a dog sport in which teams of dogs race against each other from the start to the finish line, over a line of hurdles, to a box that releases a tennis ball to be caught when the dog presses the spring-loaded pad, then back to their ha ...
systems, or first-generation governors, were used during the first 100 years of water turbine speed controls. In early flyball systems, the flyball component countered by a spring acted directly to the valve of the turbine or the wicket gate to control the amount of water that enters the turbines. Newer systems with mechanical governors started around 1880. An early mechanical governor is a servomechanism
In control engineering a servomechanism, usually shortened to servo, is an automatic device that uses error-sensing negative feedback to correct the action of a mechanism. On displacement-controlled applications, it usually includes a built-in ...
that comprises a series of gears that use the turbine's speed to drive the flyball and turbine's power to drive the control mechanism. The mechanical governors were continued to be enhanced in power amplification through the use of gears and the dynamic behavior. By 1930, the mechanical governors had many parameters that could be set on the feedback system for precise controls. In the later part of the twentieth century, electronic governors and digital systems started to replace the mechanical governors. In the electronic governors, also known as second-generation governors, the flyball was replaced by rotational speed sensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
but the controls were still done through analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analog ...
systems. In the modern systems, also known as third-generation governors, the controls are performed digitally by algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specificat ...
s that are programmed to the computer of the governor.
Wicket gate
 A wicket gate, or guide vane, is a component of water turbines to control the flow of water that enters the turbine. A series of small openings of the wicket gates surround the turbine. When the wicket gates are opened wider, more water will flow into the turbine runner which results in higher power output. The control of wicket gate opening and closing will allow the output energy generated by the turbines to be controlled to match the desired output energy levels.
A wicket gate, or guide vane, is a component of water turbines to control the flow of water that enters the turbine. A series of small openings of the wicket gates surround the turbine. When the wicket gates are opened wider, more water will flow into the turbine runner which results in higher power output. The control of wicket gate opening and closing will allow the output energy generated by the turbines to be controlled to match the desired output energy levels.
Turbine blade materials
Given that the turbine blades in a water turbine are constantly exposed to water and dynamic forces, they need to have high corrosion resistance and strength. The most common material used in overlays on carbon steel runners in water turbines are austenitic steel alloys that have 17% to 20% chromium to increase stability of the film which improves aqueous corrosion resistance. The chromium content in these steel alloys exceed the minimum of 12% chromium required to exhibit some atmospheric corrosion resistance. Having a higher chromium concentration in the steel alloys allows for a much longer lifespan of the turbine blades. Currently, the blades are made ofmartensitic stainless steel
Martensitic stainless steel is a type of stainless steel alloy that has a martensite crystal structure. It can be hardened and tempered through aging and heat treatment. The other main types of stainless steel are ''austenitic'', ''ferritic'', '' ...
s which have high strength compared to austenitic stainless steels by a factor of 2. Besides corrosion resistance and strength as the criteria for material selection, weld-ability and density of the turbine blade. Greater weld-ability allows for easier repair of the turbine blades. This also allows for higher weld quality which results in a better repair. Selecting a material with low density is important to achieve higher efficiency because the lighter blades rotate more easily. The most common material used in Kaplan Turbine blades are stainless steel alloys (SS). The martensitic stainless steel alloys have high strength, thinner sections than standard carbon steel, and reduced mass that enhances the hydrodynamic flow conditions and efficiency of the water turbine. The SS(13Cr-4Ni) has been shown to have improved erosion resistance at all angles of attack through the process of laser peening
Laser peening (LP), or laser shock peening (LSP), is a surface engineering process used to impart beneficial residual stresses in materials. The deep, high-magnitude compressive residual stresses induced by laser peening increase the resistance o ...
. It is important to minimize erosion in order to maintain high efficiencies because erosion negatively impacts the hydraulic profile of the blades which reduces the relative ease to rotate.
Maintenance
pitting corrosion
Pitting corrosion, or pitting, is a form of extremely localized corrosion that leads to the random creation of small holes in metal. The driving power for pitting corrosion is the depassivation of a small area, which becomes anodic (oxidation re ...
from cavitation
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapour pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, cal ...
, fatigue cracking, and abrasion from suspended solids in the water. Steel elements are repaired by welding, usually with stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corros ...
rods. Damaged areas are cut or ground out, then welded back up to their original or an improved profile. Old turbine runners may have a significant amount of stainless steel added this way by the end of their lifetime. Elaborate welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Welding is distinct from lower ...
procedures may be used to achieve the highest quality repairs.
Other elements requiring inspection and repair during overhauls include bearings, packing box and shaft sleeves, servomotors, cooling systems for the bearings and generator coils, seal rings, wicket gate linkage elements and all surfaces.United States Department of the Interior Bureau of Reclamation; Duncan, William (revised April 1989)''Turbine Repair (Facilities Instructions, Standards & Techniques, Volume 2-5)''
(1.5 MB pdf).
Environmental impact
Water turbines are generally considered a clean power producer, as the turbine causes essentially no change to the water. They use a renewable energy source and are designed to operate for decades. They produce significant amounts of the world's electrical supply. Historically there have also been negative consequences, mostly associated with the dams normally required for power production. Dams alter the natural ecology of rivers, potentially killing fish, stopping migrations, and disrupting peoples' livelihoods. For example, Native American tribes in thePacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
had livelihoods built around salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
, but aggressive dam-building destroyed their way of life. Dams also cause less obvious, but potentially serious consequences, including increased evaporation of water (especially in arid regions), buildup of silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel when ...
behind the dam, and changes to water temperature and flow patterns. In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, it is now illegal to block the migration of fish, for example the white sturgeon
White sturgeon (''Acipenser transmontanus'') is a species of sturgeon in the family Acipenseridae of the order Acipenseriformes. They are an anadromous fish species ranging in the Eastern Pacific; from the Gulf of Alaska to Monterey, Californ ...
in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, so fish ladder
A fish ladder, also known as a fishway, fish pass, fish steps, or fish cannon is a structure on or around artificial and natural barriers (such as dams, locks and waterfalls) to facilitate diadromous fishes' natural migration as well as movemen ...
s must be provided by dam builders.
See also
*Archimedes' screw
The Archimedes screw, also known as the Archimedean screw, hydrodynamic screw, water screw or Egyptian screw, is one of the earliest hydraulic machines. Using Archimedes screws as water pumps (Archimedes screw pump (ASP) or screw pump) dates back ...
* Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other Renewabl ...
References
Notes
*Robert Sackett, Preservationist, PRSHPO (Original 1990 draft). Arleen Pabon, Certifying Official and State Historic Preservation Officer, State Historic Preservation Office, San Juan, Puerto Rico. September 9, 1994. In National Register of Historic Places Registration Form—Hacienda Buena Vista. United States Department of the Interior. National Park Service. (Washington, D.C.)Sources
* * *External links
Introductory turbine math
European Union publication, Layman's hydropower handbook,12 MB pdf
"Selecting Hydraulic Reaction Turbines", US Bureau of Reclamation publication, 48 MB pdf
"Laboratory for hydraulic machines", Lausanne (Switzerland)
{{Authority control Articles containing video clips