Waster on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In


 Arming sword wasters span the broad gap of thirty-two to forty-two inches in length and, like their historical counterparts, have a shorter hilt than a longsword, allowing only one full hand to hold the grip. These wasters also commonly feature defined edges, pommels, and other typical sword elements. Arming swords are featured heavily in the combat of Manuscript
Arming sword wasters span the broad gap of thirty-two to forty-two inches in length and, like their historical counterparts, have a shorter hilt than a longsword, allowing only one full hand to hold the grip. These wasters also commonly feature defined edges, pommels, and other typical sword elements. Arming swords are featured heavily in the combat of Manuscript  The ceremonial rudius, a wooden
The ceremonial rudius, a wooden
– Used within
martial arts
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defense; military and law enforcement applications; combat sport, competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; a ...
, a waster is a practice weapon, usually a sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
, and usually made out of wood, though nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers composed of polyamides ( repeating units linked by amide links).The polyamides may be aliphatic or semi-aromatic.
Nylon is a silk-like thermoplastic, generally made from petro ...
(plastic) wasters are also available. Nylon being much safer than wood, due to it having an adequate amount of flex for thrusts to be generally safe, unlike wooden wasters. Even a steel feder has more flex than most wooden wasters. The use of wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin th ...
or nylon instead of metal provides an economic option for initial weapons training and sparring, at some loss of genuine experience. A weighted waster may be used for a sort of strength training, theoretically making the movements of using an actual sword comparatively easier and quicker, though modern sports science shows that an athlete would most optimally train with an implement which is closest to the same weight, balance, and shape of the tool they will be using . Wasters as wooden practice weapons have been found in a variety of cultures over a number of centuries, including ancient China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
, Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
and renaissance Europe, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, and into the modern era in Europe and the United States. Over the course of time, wasters took a variety of forms not necessarily influenced by chronological succession, ranging from simple sticks to clip-point dowels with leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ...
basket hilts to careful replica
A 1:1 replica is an exact copy of an object, made out of the same raw materials, whether a molecule, a work of art, or a commercial product. The term is also used for copies that closely resemble the original, without claiming to be identical. Al ...
s of real swords.
Used commonly in the modern historical European martial arts
Historical European martial arts (HEMA) are martial arts of European origin, particularly using arts formerly practised, but having since died out or evolved into very different forms.
While there is limited surviving documentation of the martia ...
community, the term refers to wasters fashioned to resemble western European weapons like the longsword or arming sword. Historically, the term "waster" was used in English to refer to cudgels or clubs used as weapons, in addition to wooden swords. The increasingly popular historical martial arts reconstruction groups, as well as the live action role-playing and renaissance festival
A Renaissance fair, Renaissance faire or Renaissance festival is an outdoor gathering open to the public and typically commercial in nature, which purportedly recreates a historical setting for the amusement of its guests. Some are permanent the ...
groups, have provided an ample market for commercial waster retailers. As the martial art has grown and academic interest has risen in weapons other than the longsword and arming sword, other types of wasters have been produced commercially.
The concept of wooden practice weapons is not limited to the historical european martial arts
Historical European martial arts (HEMA) are martial arts of European origin, particularly using arts formerly practised, but having since died out or evolved into very different forms.
While there is limited surviving documentation of the martia ...
. Some Japanese martial arts
Japanese martial arts refers to the variety of martial arts native to the country of Japan. At least three Japanese terms (''budō'', ''bujutsu'', and ''bugei'') are used interchangeably with the English phrase Japanese martial arts.
The usage ...
involving swordsmanship, such as kenjutsu
is an umbrella term for all ('' ko-budō'') schools of Japanese swordsmanship, in particular those that predate the Meiji Restoration. Some modern styles of kendo and iaido that were established in the 20th century also included modern forms of ...
and iaido, use bokken or shinai
A is a Japanese sword typically made of bamboo used for practice and competition in ''kendo''. ''Shinai'' are also used in other martial arts, but may be styled differently from ''kendo shinai'', and represented with different characters. T ...
as practice weapons. Eskrima, a martial art from the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, also uses a type of rattan stick as a practice weapon in place of a blade. The martial art of singlestick
Singlestick is a martial art that uses a wooden stick as its weapon. It began as a way of training soldiers in the use of backswords (such as the sabre or the cutlass). Canne de combat, a French form of stick fighting, is similar to singlestick p ...
is more or less entirely derived from the use of wasters as practice weapons in place of broadsword
The basket-hilted sword is a sword type of the early modern era characterised by a basket-shaped guard that protects the hand. The basket hilt is a development of the quillons added to swords' crossguards since the Late Middle Ages.
In mod ...
s.
Use
Historically, students and soldiers used wasters as inexpensive and expendable training tools. The cost of high quality steel weapons, especially swords, would have made them a poor choice for practice weapons. Constant training would fatigue the blade, rendering it far less effective and reliable as a weapon. To prevent the destruction of an expensive weapon and to permit the necessary training andsparring
Sparring is a form of training common to many combat sports. Although the precise form varies, it is essentially relatively ' free-form' fighting, with enough rules, customs, or agreements to minimize injuries. By extension, argumentative debate ...
intrinsic to any martial art, wooden practice weapons were created.
Today, especially in the reconstruction of historical European martial arts
Historical European martial arts (HEMA) are martial arts of European origin, particularly using arts formerly practised, but having since died out or evolved into very different forms.
While there is limited surviving documentation of the martia ...
and Historical reenactment, wasters have experienced renewed interest. Wasters provide a number of benefits to the modern practitioner, many of which would have applied to historic trainees as well. The wood construction coupled with unsharpened edges and blunted tip, crossguard, and pommel of wooden swords provides a safer alternative to practising with a sharpened or unsharpened steel weapon. Wasters do not cut flesh, but provide a decidedly blunt impact. The lower cost of ownership in comparison to a steel weapon of the same variety makes the waster a much more affordable and expendable tool. Many modern wasters are fashioned to replicate the original weapon with accuracy, including functional integral sword parts. This functionality allows the wooden weapon to be handled more like its steel counterpart.
Wasters are not without their faults. The all wooden construction usually makes wasters somewhat lighter and differently balanced than steel weapons. The difference of material properties between wood and steel creates a difference in performance when training and sparring. The wood wasters tend to recoil from strong contact with other wasters as may occur in a strong parry or ''absetzen'', a phenomenon colloquially referred to as "waster bounce". Steel weapons do not display this attribute to the same extent, usually binding and sliding with minimal rebound instead. The use of wooden wasters is somewhat safe as it lacks a cutting edge, but does not equate a safer alternative to steel training swords. The use of wood with rounded edges prevents any cutting injury when sparring but because wooden weapons typically are typically thicker bladed (compared to flat steel training swords like feders) while being of similar weight to steel weapons, they impact much harder than the thin blades of steel training swords (whose weight is concentrated at the hilt rather than the thin blade, compared to the evenly weighted waster). In addition, because of the waster's strong wooden construction, it does not bend at thrusts like feders or some steel training swords. It is for those reasons strong cuts or thrusts to unprotected body parts during sparring may lead to significant blunt force injuries (with the wooden weapon acting like a bludgeon).
Modern historical martial arts reconstruction
Historical European martial arts (HEMA) are martial arts of European origin, particularly using arts formerly practised, but having since died out or evolved into very different forms.
While there is limited surviving documentation of the martia ...
organizations, including the Association for Renaissance Martial Arts and the Chicago Swordplay Guild
The Chicago Swordplay Guild is a modern school of swordsmanship and Western martial arts, and non-profit organization based in Chicago, Illinois, United States. It provides organized instruction in the study and practice of historical European s ...
use wasters as the primary training tool of new practitioners. Wasters are used to learn, practice, and later spar with a variety of techniques including cuts, slices, thrusts and wards. During flourishes, a waster may be substituted for a blunt sword, especially if a lack of experience is a concern. Participants may also use wasters against a ''pell'', a training pole roughly simulating a human target. As the individual becomes more skilled, they will begin to use blunt steel weapons which offer a more realistic set of properties in comparison with a sharpened metal blade.
Construction
Modern commercial producers use primarilyHickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mexi ...
, a hard and resilient wood, in the construction of their wasters. Some producers allow individuals to accent the waster with wood of other types including Jatobá and Purpleheart
''Peltogyne'', commonly known as purpleheart, violet wood, amaranth and other local names (often referencing the colour of the wood) is a genus of 23 species of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae; native to tropical rainforests of Central a ...
. Manufacturers usually apply a coating of linseed oil
Linseed oil, also known as flaxseed oil or flax oil (in its edible form), is a colourless to yellowish oil obtained from the dried, ripened seeds of the flax plant (''Linum usitatissimum''). The oil is obtained by pressing, sometimes followed by ...
or other protective liquid and instruct users to regularly apply it. This prevents splintering and works to create a stronger, more enduring tool. Different specimens of wood, even of the same variety, are not necessarily identical in performance, and may display different characteristics during use.
The form of modern wasters follows from their use as replica training swords. Blades on wasters have a lenticular (lens-shaped) or diamond cross-section and defined edges. This shape continues into the hilt, which features a grip with an oval-shaped cross section oriented in the same plane as the blade. An integral part of historical swords, this oval shape permits the wielder to know the sword's rotational blade alignment by feeling for the position of the oblong grip in their hand. The pommel acts as suitable counterweight for the blade and a stable gripping surface, providing the sword's intrinsic balance and allowing the user a weighted leverage point for more powerful manipulation of the weapon. A functional cross acts as it does on a steel sword, protecting the hands and assisting in a number of guards and parries. During half-sword
Half-sword, in 14th- to 16th-century fencing with longswords, refers to the technique of gripping the central part of the sword blade with the left hand in order to execute more forceful thrusts against armoured and unarmoured opponents. The term ...
ing, the cross and pommel may also function as a striking portions of the weapon, used directly to cause injury as in the mordhau.
History
Wooden practice swords have been in use since the LateBronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, with an original sword found on Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
's Mainland in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
still in existence at the National Museum of Edinburgh. A similar find in Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
adds historical backing to the Irish myth, the Táin Bó Cúailnge, in which the use of a wooden training sword is mentioned. Egyptian soldiers practiced a sort of sport fencing using blunt sticks as a sort of primitive waster. The Romans used a form of wooden sword, the ''rudis'', for combat training. Translations of Roman poets Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 – 27 November 8 BC), known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his ' ...
and Juvenal
Decimus Junius Juvenalis (), known in English as Juvenal ( ), was a Roman poet active in the late first and early second century CE. He is the author of the collection of satirical poems known as the ''Satires''. The details of Juvenal's life ...
provide evidence of this training weapon in use. One translation of Juvenal's poetry by Barten Holyday
Barten Holyday or Holiday (1593 – 2 October 1661) was an English clergyman, author and poet.F. D. A. Burns, ‘Holyday , Barten (1593–1661)’, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 2004
Career
He was educated ...
in 1661 makes note that the Roman trainees learned to fight with the wooden wasters before moving on to the use of sharpened steel, much in the way modern reconstruction groups progress. In fact, it is also found that Roman gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
s trained with a heavy wooden sword against a straw man or a wooden pole known as a ''palus'' (an early relative of the later wooden ''pell''). Wasters are mentioned in period works, including The Book of the Courtier. A number of Fechtbücher
Martial arts manuals are instructions, with or without illustrations, specifically designed to be learnt from a book. Many books detailing specific techniques of martial arts are often erroneously called manuals but were written as treatises.
Pros ...
also mention the use of wasters or depict them in use by models showing proper technique.
During the 16th century, the Dussack
A dusack (also ''dusägge'' and variants, from Czech ''tesák'' "cleaver; hunting sword", lit. "fang") is a single-edged sword of the cutlass or sabre type, in use as a side arm in Germany and the Habsburg monarchy during the 16th to 17th centur ...
came into use in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
fencing schools. A true waster, the dussack was made almost entirely of wood (in all but one known case) and acted as safe and cheap training weapon. The weapon's unique shape did not lend well to the replication of traditional cruciform-hilted swords like the arming sword or longsword
A longsword (also spelled as long sword or long-sword) is a type of European sword characterized as having a cruciform hilt with a grip for primarily two-handed use (around ), a straight double-edged blade of around , and weighing approximatel ...
. Instead, the dussack resembled the '' großes Messer'' or "great knife", a weapon found more often amongst the common people than longswords, the cost of which allowed only relatively wealthy individuals to purchase them.
Swords


Longsword
A longsword (also spelled as long sword or long-sword) is a type of European sword characterized as having a cruciform hilt with a grip for primarily two-handed use (around ), a straight double-edged blade of around , and weighing approximatel ...
wasters are generally between forty-two and fifty inches long and are also known colloquially as Hand-and-a-Half swords, allowing the use of both hands on the hilt while using them. These weapons incorporate a ridge or fuller, defined edges, and other sword components commonly found on steel swords. Many of the fundamentals taught by Johannes Lichtenauer Johannes Liechtenauer (also ''Lichtnauer'', ''Hans Lichtenawer'') was a German fencing master who had a great level of influence on the German fencing tradition in the 14th century.
Biography
Liechtenauer seems to have been active during the mi ...
and his students Sigmund Ringeck
Sigmund Schining ein Ringeck (Sigmund ain Ringeck, Sigmund Amring, Sigmund Einring, Sigmund Schining) was a German Fencing master, fencing master. While the meaning of the surname "Schining" is uncertain, the suffix "ain Ringeck" may indicate that ...
and Hans Talhoffer frequently involve the longsword.
 Arming sword wasters span the broad gap of thirty-two to forty-two inches in length and, like their historical counterparts, have a shorter hilt than a longsword, allowing only one full hand to hold the grip. These wasters also commonly feature defined edges, pommels, and other typical sword elements. Arming swords are featured heavily in the combat of Manuscript
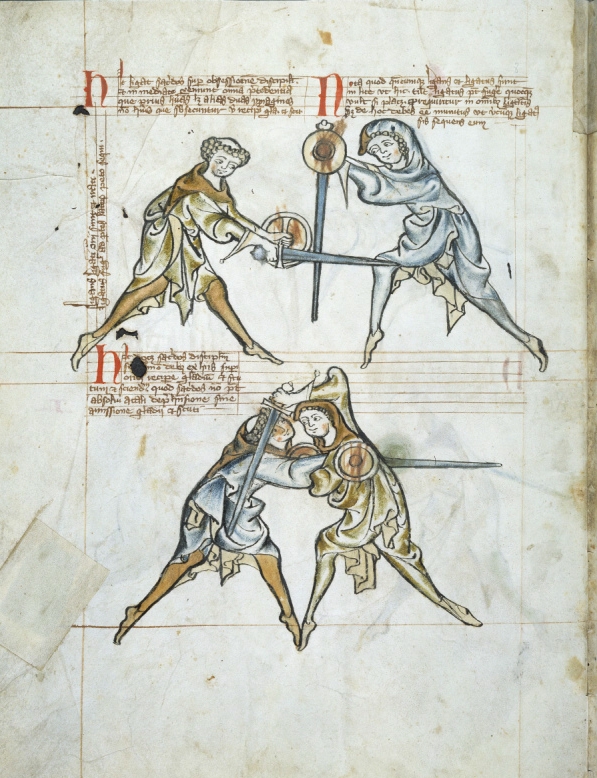
Arming sword wasters span the broad gap of thirty-two to forty-two inches in length and, like their historical counterparts, have a shorter hilt than a longsword, allowing only one full hand to hold the grip. These wasters also commonly feature defined edges, pommels, and other typical sword elements. Arming swords are featured heavily in the combat of Manuscript I.33
Royal Armouries Ms. I.33 is the earliest known surviving European ''fechtbuch'' (combat manual), and one of the oldest surviving martial arts manuals dealing with armed combat worldwide. I.33 is also known as the Walpurgis manuscript, after a fig ...
, the oldest manuscript on sword-and- buckler fighting, dating approximately to the turn of the 14th century.
 The ceremonial rudius, a wooden
The ceremonial rudius, a wooden gladius
''Gladius'' () is a Latin word meaning "sword" (of any type), but in its narrow sense it refers to the sword of ancient Roman foot soldiers. Early ancient Roman swords were similar to those of the Greeks, called '' xiphe'' (plural; singular ''xi ...
given ceremonially to gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
s when they won enough battles to become free men, is produced by some current day vendors and is twenty-eight to thirty inches long. The producers warn that the rudii are for ceremonial purposes, however, and should not be used in mock combat. In this sense, the waster supersedes its place as a tool for combat and becomes primarily a work of art.
Dussack
A dusack (also ''dusägge'' and variants, from Czech ''tesák'' "cleaver; hunting sword", lit. "fang") is a single-edged sword of the cutlass or sabre type, in use as a side arm in Germany and the Habsburg monarchy during the 16th to 17th centur ...
s and falchion, two-handed sword
The English language terminology used in the classification of swords is imprecise and has varied widely over time. There is no historical dictionary for the universal names, classification or terminology of swords; a sword was simply a double ...
, cut and thrust sword
The ''spada da lato'' (Italian) or ''side-sword'' is a type of sword popular during the late 16th century.
It is a continuation of the medieval knightly sword, and the immediate predecessor (or early form) of the rapier
A rapier () or is a ...
, gladius
''Gladius'' () is a Latin word meaning "sword" (of any type), but in its narrow sense it refers to the sword of ancient Roman foot soldiers. Early ancient Roman swords were similar to those of the Greeks, called '' xiphe'' (plural; singular ''xi ...
, Viking sword and rapier wasters are not widely available from commercial vendors, but may be special ordered or hand-crafted.
Daggers
Rondel dagger wasters, like the daggers themselves, are generally about eighteen inches in length, with a twelve-inch blade and six inch hilt. These weapons may forgo defined edges altogether and take on a more cylindrical shape as the rondel dagger acted historically as a thrusting and stabbing weapon. Hilted dagger wasters are also available, featuring functional crosses and defined edges, often found in lengths of about 18 inches.See also
* Bokken a form of waster used in Budō *Dussack
A dusack (also ''dusägge'' and variants, from Czech ''tesák'' "cleaver; hunting sword", lit. "fang") is a single-edged sword of the cutlass or sabre type, in use as a side arm in Germany and the Habsburg monarchy during the 16th to 17th centur ...
a specific form of German waster
* Eskrima uses a rattan stick to represent the sword
*Federschwert
The ''Feder'' (plural ''Federn''; also ''Fechtfeder'', plural ''Fechtfedern''), is a type of training sword used in '' Fechtschulen'' (fencing schools) of the German Renaissance.
The type has existed since at least the 15th century, but it came ...
a steel practice sword
*Singlestick
Singlestick is a martial art that uses a wooden stick as its weapon. It began as a way of training soldiers in the use of backswords (such as the sabre or the cutlass). Canne de combat, a French form of stick fighting, is similar to singlestick p ...
a basket-hilted wooden practise-weapon for broadsword fencing
General references
*Clements, John. ''Get Thee a Waster!'' – Used withinUse
Use may refer to:
* Use (law), an obligation on a person to whom property has been conveyed
* Use (liturgy), a special form of Roman Catholic ritual adopted for use in a particular diocese
* Use–mention distinction, the distinction between using ...
& History
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
sections.
*Little Raven. ''Frequently Asked Questions'' – Used within Use
Use may refer to:
* Use (law), an obligation on a person to whom property has been conveyed
* Use (liturgy), a special form of Roman Catholic ritual adopted for use in a particular diocese
* Use–mention distinction, the distinction between using ...
, Construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and com ...
& Types sections.
*New Stirling Arms. ''About Our Wasters'' – Used within Use
Use may refer to:
* Use (law), an obligation on a person to whom property has been conveyed
* Use (liturgy), a special form of Roman Catholic ritual adopted for use in a particular diocese
* Use–mention distinction, the distinction between using ...
, Construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and com ...
& Types sections.
*Purpleheart Armoury. ''Frequently Asked Questions''– Used within
Use
Use may refer to:
* Use (law), an obligation on a person to whom property has been conveyed
* Use (liturgy), a special form of Roman Catholic ritual adopted for use in a particular diocese
* Use–mention distinction, the distinction between using ...
, Construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and com ...
& Types sections.
Notes
{{reflist Training weapons