Warren Hastings on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Warren Hastings (6 December 1732 – 22 August 1818) was a British colonial administrator, who served as the first Governor of the Presidency of Fort William (Bengal), the head of the Supreme Council of Bengal, and so the first Governor-General of Bengal in 1772–1785. He and Robert Clive are credited with laying the foundation of the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
in India. He was an energetic organizer and reformer. In 1779–1784 he led forces of the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
against a coalition of native states and the French. Finally, the well-organized British side held its own, while France lost influence in India. In 1787, he was accused of corruption and impeached, but after a long trial acquitted in 1795. He was made a Privy Councillor in 1814.
Early life
Hastings was born in Churchill, Oxfordshire, in 1732 to a poor gentleman father, Penystoe Hastings, and a mother, Hester Hastings, who died soon after he was born. Despite Penystone Hastings's lack of wealth, the family had been lords of the manor and patrons of the living of Daylesford in direct line from 1281 until 1715. It was relinquished after there had been a considerable loss of family wealth due to support given toCharles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
. Warren Hastings attended Westminster School
(God Gives the Increase)
, established = Earliest records date from the 14th century, refounded in 1560
, type = Public school Independent day and boarding school
, religion = Church of England
, head_label = Hea ...
, where he coincided with the future Prime Ministers Lord Shelburne
William Petty Fitzmaurice, 1st Marquess of Lansdowne, (2 May 17377 May 1805; known as the Earl of Shelburne between 1761 and 1784, by which title he is generally known to history), was an Irish-born British Whig statesman who was the first ...
and the Duke of Portland
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranke ...
and with the poet William Cowper
William Cowper ( ; 26 November 1731 – 25 April 1800) was an English poet and Anglican hymnwriter. One of the most popular poets of his time, Cowper changed the direction of 18th-century nature poetry by writing of everyday life and sce ...
. He joined the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
in 1750 as a clerk and sailed out to India, reaching Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
in August 1750. There he built up a reputation for diligence and spent his free time learning about India and mastering Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' For a while Hastings remained in Murshidabad and was even used by the Nawab as an intermediary, but fearing for his life, he escaped to the island of Fulta, where a number of refugees from Calcutta had taken shelter. While there, he met and married Mary Buchanan, the widow of one of the victims of the Black Hole. Shortly afterwards a British expedition from
For a while Hastings remained in Murshidabad and was even used by the Nawab as an intermediary, but fearing for his life, he escaped to the island of Fulta, where a number of refugees from Calcutta had taken shelter. While there, he met and married Mary Buchanan, the widow of one of the victims of the Black Hole. Shortly afterwards a British expedition from
 The
The
 In 1785, after 10 years of service, during which he helped extend and regularise the nascent Raj created by
In 1785, after 10 years of service, during which he helped extend and regularise the nascent Raj created by
/ref> Throughout the years of the trial, Hastings lived in considerable style at his leased town house,

 In the last quarter of the 18th century, many senior administrators realised that to govern Indian society it was essential to learn its various religious, social, and legal customs and precedents. The importance of such knowledge to the colonial government was in Hastings's mind when he remarked in 1784:
Under Hastings's term as governor-general, much administrative precedent set profoundly shaped later attitudes towards the government of British India. Hastings had great respect for the ancient scripture of
In the last quarter of the 18th century, many senior administrators realised that to govern Indian society it was essential to learn its various religious, social, and legal customs and precedents. The importance of such knowledge to the colonial government was in Hastings's mind when he remarked in 1784:
Under Hastings's term as governor-general, much administrative precedent set profoundly shaped later attitudes towards the government of British India. Hastings had great respect for the ancient scripture of
excerpt
*Alfred Mervyn Davies, ''Strange destiny: a biography of Warren Hastings'' (1935) *Suresh Chandra Ghosh, ''The Social Condition of the British Community in Bengal: 1757–1800'' (Brill, 1970) *
accessed 11 Nov 2014
* Penderel Moon, ''Warren Hastings and British India'' (Macmillan, 1949
online
*Patrick Turnbull, ''Warren Hastings''. (New English Library, 1975) *
"Warren Hastings" an essay by Thomas Babington Macaulay (October 1841)
* (within
''
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
. His work won him promotion in 1752 when he was sent to Kasimbazar
Cossimbazar is a sub-urban area of Berhampore City in the Berhampore CD block in the Berhampore subdivision in Murshidabad district in the Indian state of West Bengal."Cossimbazar" in ''Imperial Gazetteer of India'', Oxford, Clarendon Press, ...
, a major trading post in Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
, where he worked for William Watts. While there he gained further experience in the politics of East India.
British traders still relied on the whims of local rulers, so that the political turmoil in Bengal was unsettling. The elderly moderate Nawab
Nawab (Balochi language, Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب;
bn, নবাব/নওয়াব;
hi, नवाब;
Punjabi language, Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ;
Persian language, Persian,
Punjabi language, Punjabi ,
Sindhi language, Sindhi,
Urd ...
Alivardi Khan
Alivardi Khan (1671 – 9 April 1756) was the Nawab of Bengal from 1740 to 1756. He toppled the Nasiri dynasty of Nawabs by defeating Sarfaraz Khan in 1740 and assumed power himself.
During much of his reign Alivardi encountered frequent Mar ...
was likely to be succeeded by his grandson Siraj ud-Daulah
Mirza Muhammad Siraj-ud-Daulah ( fa, ; 1733 – 2 July 1757), commonly known as Siraj-ud-Daulah or Siraj ud-Daula, was the last independent Nawab of Bengal. The end of his reign marked the start of the rule of the East India Company over Beng ...
, but there were several other claimants. This made British trading posts throughout Bengal increasingly insecure, as Siraj ud-Daulah was known to harbour anti-European views and be likely to launch an attack once he took power. When Alivardi Khan died in April 1756, the British traders and a small garrison at Kasimbazar were left vulnerable. On 3 June, after being surrounded by a much larger force, the British were persuaded to surrender to prevent a massacre. Hastings was imprisoned with others in the Bengali capital, Murshidabad
Murshidabad fa, مرشد آباد (, or ) is a historical city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located on the eastern bank of the Bhagirathi River, a distributary of the Ganges. It forms part of the Murshidabad district.
Durin ...
, while the Nawab's forces marched on Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
and captured it. The garrison and civilians were then locked up under appalling conditions in the Black Hole of Calcutta
The Black Hole of Calcutta was a dungeon in Fort William, Calcutta, measuring , in which troops of Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, held British prisoners of war on the night of 20 June 1756. John Zephaniah Holwell, one of the Britis ...
.
 For a while Hastings remained in Murshidabad and was even used by the Nawab as an intermediary, but fearing for his life, he escaped to the island of Fulta, where a number of refugees from Calcutta had taken shelter. While there, he met and married Mary Buchanan, the widow of one of the victims of the Black Hole. Shortly afterwards a British expedition from
For a while Hastings remained in Murshidabad and was even used by the Nawab as an intermediary, but fearing for his life, he escaped to the island of Fulta, where a number of refugees from Calcutta had taken shelter. While there, he met and married Mary Buchanan, the widow of one of the victims of the Black Hole. Shortly afterwards a British expedition from Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
under Robert Clive arrived to rescue them. Hastings served as a volunteer in Clive's forces as they retook Calcutta in January 1757. After this swift defeat, the Nawab urgently sought peace and the war came to an end. Clive was impressed with Hastings when he met him, and arranged for his return to Kasimbazar to resume his pre-war activities. Later in 1757 fighting resumed, leading to the Battle of Plassey, where Clive won a decisive victory over the Nawab. Siraj ud-Daulah was overthrown and replaced by his commander-in-chief Mir Jafar, who initiated policies favourable to the East India Company traders, before falling out with them and being overthrown.
Rising status
In 1758 Hastings became the BritishResident
Resident may refer to:
People and functions
* Resident minister, a representative of a government in a foreign country
* Resident (medicine), a stage of postgraduate medical training
* Resident (pharmacy), a stage of postgraduate pharmaceuti ...
in the Bengali capital of Murshidabad
Murshidabad fa, مرشد آباد (, or ) is a historical city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located on the eastern bank of the Bhagirathi River, a distributary of the Ganges. It forms part of the Murshidabad district.
Durin ...
– a major step forward in his career – at the instigation of Clive. His role in the city was ostensibly that of an ambassador
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or sov ...
but as Bengal came increasingly under the dominance of the East India Company he was often given the task of issuing orders to the new Nawab on behalf of Clive and the Calcutta authorities. Hastings personally sympathised with Mir Jafar and regarded many of the demands placed on him by the company as excessive. Hastings had already developed a philosophy that was grounded in trying to establish a more understanding relationship with India's inhabitants and their rulers, and he often tried to mediate between the two sides.
During Mir Jafar's reign the East India Company exerted an increasingly large role in the running of the region, and effectively took over the defence of Bengal against external invaders when Bengal's troops proved insufficient for the task. As he grew older, Mir Jafar became gradually less effective in ruling the state, and in 1760 EIC troops ousted him from power and replaced him with Mir Qasim
Mir Qasim ( bn, মীর কাশিম; died 8 May 1777) was the Nawab of Bengal from 1760 to 1763. He was installed as Nawab with the support of the British East India Company, replacing Mir Jafar, his father-in-law, who had himself been su ...
. Hastings expressed his doubts to Calcutta over the move, believing they were honour-bound to support Mir Jafar, but his opinions were overruled. Hastings established a good relationship with the new Nawab and again had misgivings about the demands he relayed from his superiors. In 1761 he was recalled and appointed to the Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
council.
Conquest of Bengal
Hastings was personally angered when investigating trading abuses in Bengal. He alleged that some European and British-allied Indian merchants were taking advantage of the situation to enrich themselves personally. Persons travelling under the unauthorised protection of the British flag engaged in widespread fraud and illegal trading, knowing that local customs officials would be cowed into not interfering with them. Hastings felt this was bringing shame on Britain's reputation and urged the authorities in Calcutta to put an end to it. The Council considered his report but ultimately rejected Hastings' proposals. He was fiercely criticised by other members, many of whom had themselves profited from the trade. Ultimately, little was done to stem the abuses, and Hastings began to consider quitting his post and returning to Britain. His resignation was only delayed by the outbreak of fresh fighting in Bengal. Once on the throne Qasim proved increasingly independent in his actions, and he rebuilt Bengal's army by hiring European instructors andmercenaries
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any o ...
who greatly improved the standard of his forces. He felt gradually more confident and in 1764 when a dispute broke out in the settlement of Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
he captured its British garrison and threatened to execute them if the East India Company responded militarily. When Calcutta dispatched troops anyway, Mir Qasim executed the hostages. British forces then went on the attack and won a series of battles culminating in the decisive Battle of Buxar in October 1764. After this Mir Qasim fled into exile in Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
, where he died in 1777. The Treaty of Allahabad (1765) gave the East India Company the right to collect taxes
A tax collector (also called a taxman) is a person who collects unpaid taxes from other people or corporations. The term could also be applied to those who audit tax returns. Tax collectors are often portrayed as being evil, and in the modern wo ...
in Bengal on behalf of the Mughal Emperor.
Hastings resigned in December 1764 and sailed for Britain the following month. He left deeply saddened by the failure of the more moderate strategy that he had supported, but which had been rejected by the hawkish members of the Calcutta Council. Once he arrived in London Hastings began spending far beyond his means. He stayed in fashionable addresses and had his picture painted by Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter, specialising in portraits. John Russell said he was one of the major European painters of the 18th century. He promoted the "Grand Style" in painting which depend ...
in spite of the fact that, unlike many of his contemporaries, he had not amassed a fortune while in India. Eventually, having run up enormous debts, Hastings realised he needed to return to India to restore his finances, and applied to the East India Company for employment. His application was initially rejected as he had made many political enemies, including the powerful director Laurence Sulivan
Laurence Sulivan (1713–1786) was an Anglo-Irish politician, Member of Parliament first for Taunton in 1762 and then for Ashburton in 1768. He was also Chairman of the British East India Company.
Sulivan was born in Ireland and moved to wo ...
. Eventually an appeal to Sulivan's rival Robert Clive secured Hastings the position of deputy ruler at the city of Madras. He sailed from Dover in March 1769. On the voyage he met the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
Baroness Marian von Imhoff (1749–1837) and her husband. He fell in love with the Baroness and they began an affair, seemingly with her husband's consent. Hastings' first wife, Mary, had died in 1759, and he planned to marry the Baroness once she had obtained a divorce from her husband. The process took a long time and it was not until 1777 when news of divorce came from Germany that Hastings was finally able to marry her.
Madras and Calcutta
Hastings arrived in Madras shortly after theFirst Anglo-Mysore War
The First Anglo-Mysore War (1766–1769) was a conflict in India between the Sultanate of Mysore and the East India Company. The war was instigated in part by the machinations of Asaf Jah II, the Nizam of Hyderabad, who sought to divert the ...
of 1767–1769, when the forces of Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali ( حیدر علی, ''Haidarālī''; 1720 – 7 December 1782) was the Sultan and ''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the att ...
had threatened the capture of the city. The Treaty of Madras (4 April 1769) ended the war but failed to settle the dispute and three further Anglo-Mysore Wars
The Anglo-Mysore Wars were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company (represented chiefly by the neighbouring Madras Pres ...
followed (1780–1799). During his time at Madras Hastings initiated reforms of trading practices which cut out the use of middlemen and benefited both the Company and the Indian labourers, but otherwise the period was relatively uneventful for him.Turnbull p. 52.
By this stage Hastings shared Clive's view that the three major British Presidencies (settlements) – Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
, Bombay
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
and Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
– should be brought under single rule rather than being governed separately as they currently were. In 1771 he was appointed to be Governor of Calcutta, the most important of the Presidencies. In Britain moves were underway to reform the divided system of government and establish single rule across all of British-ruled India with its capital in Kolkata (Calcutta). Hastings became the first Governor General.
While Governor, Hastings launched a major crackdown on bandits operating in Bengal, which proved largely successful. He also faced the severe Bengal Famine, which resulted in between two and ten million deaths.
Governor-General
 The
The Regulating Act of 1773
The Regulating Act of 1773 (formally, the East India Company Act 1772) was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain intended to overhaul the management of the East India Company's rule in India. The Act did not prove to be a long-term soluti ...
brought the presidencies of Madras and Bombay under Bengal's control. It raised Hastings from Governor to the new post of Governor-General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
, but limited his power by making the Governor-General one member of a five-man Supreme Council. This was so confusingly structured that it was difficult to tell what constitutional position Hastings actually held.
According to William Dalrymple William Dalrymple may refer to:
* William Dalrymple (1678–1744), Scottish Member of Parliament
* William Dalrymple (moderator) (1723–1814), Scottish minister and religious writer
* William Dalrymple (British Army officer) (1736–1807), Scott ...
:
:He got quickly to work, beginning the process of turning the EIC into an administrative service. Hastings first major change was to move all of all the functions of government from Murshidabad to Calcutta.... Throughout 1773, Hastings worked with extraordinary energy. He unified currency systems, ordered the codification of Hindu laws and digests of Muslim law books, reformed the tax and customs system, fixed land revenue and stopped the worst oppression being carried out on behalf of private traders by the local agents. He created an efficient postal service, backed a proper cartographic survey of India by James Rennell
Major James Rennell, (3 December 1742 – 29 March 1830) was an English geographer, historian and a pioneer of oceanography. Rennell produced some of the first accurate maps of Bengal at one inch to five miles as well as accurate outlines of Ind ...
and built a series of public granaries, including the great Gola at Patna, to make sure the famine of 1770-71 was never repeated.... Underlying all Hastings' work was a deep respect for the land he had lived in since his teens.... Hastings genuinely liked India, and by the time he became Governor spoke not only good Bengali and Urdu but also fluent court and literary Persian.
War with France
In 1777 during theAmerican War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
(1775–1783), the Americans had captured a British field army at the Battle of Saratoga
The Battles of Saratoga (September 19 and October 7, 1777) marked the climax of the Saratoga campaign, giving a decisive victory to the Americans over the British in the American Revolutionary War. British General John Burgoyne led an invasion ...
during the Saratoga campaign. This emboldened the French to sign a military alliance with the new United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
, and declare war on Great Britain. The French concentrated in the Caribbean islands, and on India. Meanwhile, the presidencies of Madras and Bombay became involved in serious quarrels with the greatest of the native states. Madras with the formidable Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali ( حیدر علی, ''Haidarālī''; 1720 – 7 December 1782) was the Sultan and ''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the att ...
of Mysore and with the Nizam of Hyderabad, and Bombay with the Marathas
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
. France sent a fleet
Fleet may refer to:
Vehicles
*Fishing fleet
*Naval fleet
*Fleet vehicles, a pool of motor vehicles
*Fleet Aircraft, the aircraft manufacturing company
Places
Canada
* Fleet, Alberta, Canada, a hamlet
England
* The Fleet Lagoon, at Chesil Beach ...
under Admiral Pierre André de Suffren
Admiral comte Pierre André de Suffren de Saint Tropez, bailli de Suffren (17 July 1729 – Paris, 8 December 1788), Château de Saint-Cannat) was a French Navy officer and admiral. Beginning his career during the War of the Austrian Success ...
. The combination meant Hastings faced a formidable challenge, with only Oudh as an ally. In six years of intense and confused fighting, 1779–1784. Hastings sent one army marching across India to help Bombay, and another to Madras. His greatest achievement was in breaking up the hostile coalition. By 1782 he made peace with the Marathas. The French fleet had been repeatedly delayed. Suffren finally arrived in 1782 to discover that the Indian coalition had fallen apart, that Hastings had captured all the French ports, and Suffren could achieve nothing. When the wars ended in 1784, British rule in India had not changed, but the French position was now much weaker. The East India Company now had an efficient system in operation. However, Hastings's multiple wartime operations needed large sums of money and London sent nothing. His methods of using the local treasuries later became the main line of attack in the impeachment brought against him.
Bhutan and Tibet
In 1773, Hastings responded to an appeal for help from the Raja of the princely state ofCooch Behar
Cooch Behar (), or Koch Bihar, is a city and a municipality in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the headquarters of the Cooch Behar district. It is in the foothills of the Eastern Himalayas at . Cooch Behar is the only planned city in t ...
to the north of Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
, whose territory had been invaded by Zhidar, the Druk Desi
The Druk Desi (Dzongkha: འབྲུག་སྡེ་སྲིད་; Wylie:'' 'brug sde-srid''; also called " Deb Raja")The original title is Dzongkha: སྡེ་སྲིད་ཕྱག་མཛོད་; Wylie: ''sde-srid phyag-mdzod''. wa ...
of Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous ...
the previous year. Hastings agreed to help on the condition that Cooch Behar recognise British sovereignty. The Raja agreed and with the help of British troops they pushed the Bhutanese out of the Duars
The Dooars or Duars ( as, দুৱাৰ, duar, rkt, দুৱাৰ, duar, bn, দুয়ার, duyar) () are the alluvial floodplains in eastern-northeastern India that lie south of the outer foothills of the Himalayas and north of t ...
and into the foothills in 1773.
The Druk Desi returned to face civil war at home. His opponent Jigme Senge, the regent for the seven-year-old Shabdrung
Zhabdrung (also Shabdrung; ; "before the feet of ones submit") was a title used when referring to or addressing great lamas in Tibet, particularly those who held a hereditary lineage. In Bhutan the title almost always refers to Ngawang Namgyal (159 ...
(the Bhutanese equivalent of the Dalai Lama), had supported popular discontent. Zhidar was unpopular for his corvee tax (he sought unreasonably to rebuild a major dzong in one year), as well as for his overtures to the Manchu Emperors which threatened Bhutanese independence. Zhidar was soon overthrown and forced to flee to Tibet, where he was imprisoned and a new Druk Desi, Kunga Rinchen, installed in his place. Meanwhile, the Sixth Panchen Lama, who had imprisoned Zhidar, interceded on behalf of the Bhutanese with a letter to Hastings, imploring him to cease hostilities in return for friendship. Hastings saw the opportunity to establish relations with both the Tibetans and the Bhutanese and wrote a letter to the Panchen Lama proposing "a general treaty of amity and commerce between Tibet and Bengal".
In February 1782, news reached the headquarters of the EIC in Calcutta of the reincarnation of the Panchen Lama. Hastings proposed sending a mission to Tibet with a message of congratulation, designed to strengthen amicable relations established by Bogle on his earlier visit. With the assent of the EIC Court of Directors, Samuel Turner was appointed chief of the Tibet mission on 9 January 1783 with fellow EIC employee Samuel Davis as "Draftsman & Surveyor". Turner returned to the Governor-General's camp at Patna in 1784 where he reported he had been unable to visit the Tibetan capital at Lhasa, but received a promise that merchants sent there from India would be encouraged.
Turner was instructed to obtain a pair of yaks on his travels, which he duly did. They were transported to Hasting's menagerie in Calcutta and on the Governor-General's return to England, the yaks went too, although only the male survived the difficult sea voyage. Noted artist George Stubbs
George Stubbs (25 August 1724 – 10 July 1806) was an English painter, best known for his paintings of horses. Self-trained, Stubbs learnt his skills independently from other great artists of the 18th century such as Reynolds or Gainsborough ...
subsequently painted the animal's portrait as ''The Yak of Tartary
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bound ...
'' and in 1854 it went on to appear, albeit stuffed, at The Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary structure in which it was held), was an international exhibition which took pl ...
at Crystal Palace in London.
Hasting's return to England ended any further efforts to engage in diplomacy with Tibet.
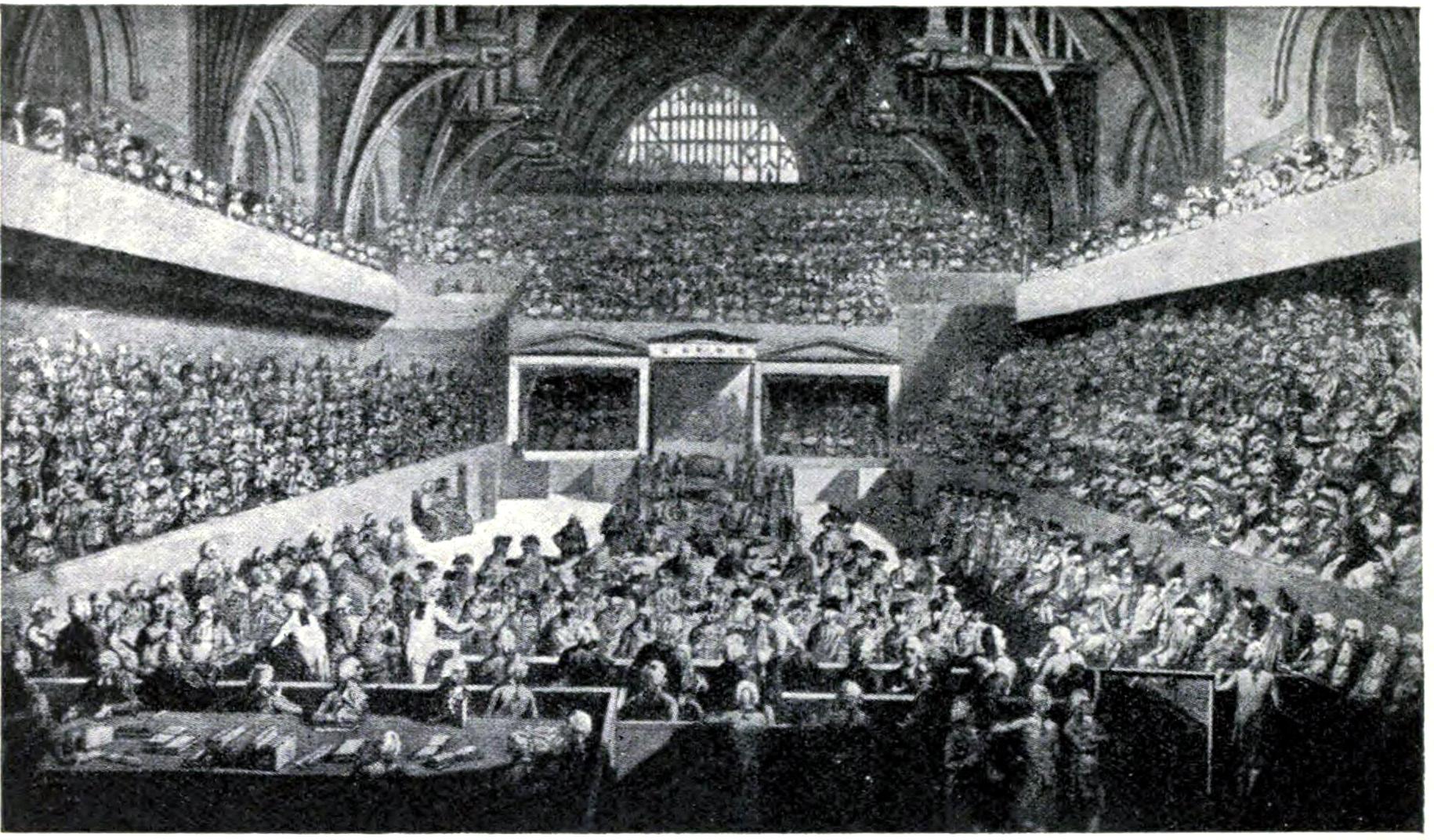
Impeachment
 In 1785, after 10 years of service, during which he helped extend and regularise the nascent Raj created by
In 1785, after 10 years of service, during which he helped extend and regularise the nascent Raj created by Clive of India
Robert Clive, 1st Baron Clive, (29 September 1725 – 22 November 1774), also known as Clive of India, was the first British Governor of the Bengal Presidency. Clive has been widely credited for laying the foundation of the British ...
, Hastings resigned. He was replaced by General Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis
Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis, (31 December 1738 – 5 October 1805), styled Viscount Brome between 1753 and 1762 and known as the Earl Cornwallis between 1762 and 1792, was a British Army general and official. In the United S ...
, the Earl Cornwallis; Cornwallis served as Commander-in-Chief of British India and Governor of the Presidency of Fort William, also known as the Bengal Presidency.
On return to England, Hastings was impeached in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
for alleged crimes in India, notably embezzlement, extortion and coercion, and an alleged judicial killing of Maharaja Nandakumar Maharaja Nandakumar (also known as Nuncomar) (1705 – died 5 August 1775), was an Indian tax collector for various regions in what is modern-day West Bengal. Nanda Kumar was born at Bhadrapur, which is now in Birbhum. He was the first Indian to b ...
. At first thought unlikely to succeed, the prosecution was managed by MPs including Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS">New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS/nowiki>_1729_–_9_July_1797)_was_an_ NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style"> ...
, encouraged by Sir Philip Francis, whom Hastings had wounded during a duel in India, Charles James Fox
Charles James Fox (24 January 1749 – 13 September 1806), styled ''The Honourable'' from 1762, was a prominent British Whig statesman whose parliamentary career spanned 38 years of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. He was the arch-riv ...
and Richard Brinsley Sheridan
Richard Brinsley Butler Sheridan (30 October 17517 July 1816) was an Irish satirist, a politician, a playwright, poet, and long-term owner of the London Theatre Royal, Drury Lane. He is known for his plays such as ''The Rivals'', ''The Sc ...
. When the charges of the indictment were read, the 20 counts took Edmund Burke two full days to read. According to historian Mithi Mukherjee, the trial instituted debate between two radically opposed visions of empire – one based on ideas of power and conquest in pursuit of the exclusive national interests of the colonizer, and one represented by Burke, of sovereignty based on a recognition of the rights of the colonized.
The House sat for 148 days over a period of seven years during the investigation. The investigation was pursued at great cost to Hastings personally: he complained constantly that the cost of defending himself from the prosecution was bankrupting him. He is rumoured once to have said that the punishment would have been less extreme had he pleaded guilty. The House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
acquitted him of all charges on 24 April 1795. The Company subsequently compensated him with £4,000 annually, retroactive to the date he returned to England, but did not reimburse his legal fees, which he claimed to have been £70,000. He collected the stipend for nearly 29 years.'The captain-general of iniquity': The impeachment of Warren Hastings./ref> Throughout the years of the trial, Hastings lived in considerable style at his leased town house,
Somerset House, Park Lane
Somerset House, Park Lane (built 1769–70; demolished 1915), was an 18th-century town house on the east side of Park Lane, where it meets Oxford Street, in the Mayfair area of London. It was also known as 40 Park Lane, although a renumbering ...
. He subsequently sold the lease at auction for £9,450.
Among many who supported him in print was the pamphleteer Ralph Broome
Lieutenant colonel Ralph Howard Broome (5 July 1889 – 25 January 1985) was a British Army officer and bobsledder who competed during the early 1920s. He was born in Dalhousie, Himachal Pradesh, India, and died in Poole, Dorset, Engla ...
. Others disturbed by the perceived injustice of the proceedings included Frances Burney
Frances Burney (13 June 1752 – 6 January 1840), also known as Fanny Burney and later Madame d'Arblay, was an English satirical novelist, diarist and playwright. In 1786–1790 she held the post as "Keeper of the Robes" to Charlotte of Mecklen ...
.
Letters and journals of Jane Austen
Jane Austen (; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for her six major novels, which interpret, critique, and comment upon the British landed gentry at the end of the 18th century. Austen's plots of ...
and her family, who knew Hastings, show they followed the trial closely.
Later life
Hastings's supporters from theEdinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
East India Club and a number of other gentlemen from India, gave a reportedly "elegant entertainment" for Hastings when he visited Edinburgh. A toast on the occasion went to the "Prosperity to our settlements in India" and wished that "the virtue and talents which preserved them be ever remembered with gratitude."
In 1788 Hastings bought for £54,000 an estate at Daylesford, Gloucestershire
Daylesford is a small, privately owned village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Adlestrop, in the Cotswold district, in the county of Gloucestershire, England, on the border with Oxfordshire. It is situated just south of the A436 t ...
, including the site of the Hastings family's medieval seat. Thereafter he remodelled the house to designs by Samuel Pepys Cockerell
Samuel Pepys Cockerell (1753–1827) was an English architect.
He was a son of John Cockerell, of Bishop's Hull, Somerset, and the elder brother of Sir Charles Cockerell, 1st Baronet, for whom he designed the house he is best known for, Sezinc ...
with classical and Indian decoration and gardens landscaped by John Davenport. He rebuilt the Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
church in 1816, where he was buried two years later. In 1801 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural science, natural knowledge, incl ...
.
In spite of substantial compensation from the East India Company, Hastings was technically insolvent on his death.
Administrative ethos and legacy


 In the last quarter of the 18th century, many senior administrators realised that to govern Indian society it was essential to learn its various religious, social, and legal customs and precedents. The importance of such knowledge to the colonial government was in Hastings's mind when he remarked in 1784:
Under Hastings's term as governor-general, much administrative precedent set profoundly shaped later attitudes towards the government of British India. Hastings had great respect for the ancient scripture of
In the last quarter of the 18th century, many senior administrators realised that to govern Indian society it was essential to learn its various religious, social, and legal customs and precedents. The importance of such knowledge to the colonial government was in Hastings's mind when he remarked in 1784:
Under Hastings's term as governor-general, much administrative precedent set profoundly shaped later attitudes towards the government of British India. Hastings had great respect for the ancient scripture of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and set the British position on governance as one of looking back to the earliest precedents possible. This allowed Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru ...
advisors to mould the law, as no Briton thoroughly understood Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
until Sir William Jones
Sir William Jones (28 September 1746 – 27 April 1794) was a British philologist, a puisne judge on the Supreme Court of Judicature at Fort William in Bengal, and a scholar of ancient India. He is particularly known for his proposition of th ...
, and even then, a literal translation was of little use – it needed to be elucidated by religious commentators well-versed in the lore and its application. This approach accentuated the Hindu caste system
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic example of classification of castes. It has its origins in ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, especially the Mug ...
and to an extent the frameworks of other religions, which had at least in recent centuries been somewhat more flexibly applied. So British influence on the fluid social structure of India can largely be seen as a solidification of the privileges of the Hindu caste system through the influence of exclusively high-caste Hindu scholars advising the British on their laws. In short, under Hastings there was a codification of Hindu laws, and a digest of Muslim law books. Where British translators or interpreters read in the Artha Shastra a ''caste system'' in India, the actual wording speaks of ''varna'' and ''jati'': skin-colour and birth, i. e. clan, and it speaks of the four societal classes, not castes: from upper-class Brahmin to lower-class Shudra.
In 1781, Hastings founded Madrasa 'Aliya
Aliah University (AU; ur, جامعہ عالیہ) is a state government controlled autonomous university in New Town, West Bengal, India. Previously known as Mohammedan College of Calcutta, it was elevated to university in 2008. It offers und ...
at Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
(transformed in 2007 into Aliah University by the Government of West Bengal). In 1784, he supported the foundation of the Bengal Asiatic Society, now the Asiatic Society of Bengal, by the oriental scholar Sir William Jones. This became a storehouse for information on the subcontinent and has remained in various institutional guises to the present day. Hastings's legacy as an administrator has been somewhat dualistic: he was able to institute reforms during the time he spent as governor that would change the path India followed in subsequent years, but he retained the distinction of being also the "architect of British India and the one ruler of British India to whom the creation of such an entity was anathema."
Legacy
The city ofHastings
Hastings () is a large seaside town and borough in East Sussex on the south coast of England,
east to the county town of Lewes and south east of London. The town gives its name to the Battle of Hastings, which took place to the north-west ...
, and the Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
outer suburb of Hastings, Victoria, Australia were named after him. There is also a road and the neighbourhood of Hastings, Kolkata
Hastings is a neighbourhood of Central Kolkata in Kolkata district in the Indian state of West Bengal.
History
Hastings is an area in Central Kolkata between the Maidan and the Hooghly River. The area named after Warren Hastings, who was the ...
in India named after him.
"Hastings" is the name of one of the four school houses in La Martiniere Calcutta
''La Martiniere ''(informally known as LMC) is an elite, independent private day school located in Kolkata (Calcutta), West Bengal. It comprises two single-gender boys and girls schools. It was established in 1836 in accordance with the will of ...
(Kolkata). It is represented by the colour red. "Hastings" is also the name of one of the four school houses in Bishop Westcott Girls' School, Ranchi, again represented by the colour red. "Hastings" is a senior wing house at St Paul's School, Darjeeling, India, where all the senior wing houses are named after Anglo-Indian colonial figures.
RIMS ''Warren Hastings'' was a Royal Indian Marine troopship built by the Barrow Shipbuilding Co. and launched on 18 April 1893. The ship struck a rock and was wrecked off the coast of Réunion
Réunion (; french: La Réunion, ; previously ''Île Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La Rényon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island ...
on the night of 14 January 1897.
Literature
Warren Hastings took an interest in seeing the ''Bhagavad Gita
The Bhagavad Gita (; sa, श्रीमद्भगवद्गीता, lit=The Song by God, translit=śrīmadbhagavadgītā;), often referred to as the Gita (), is a 700- verse Hindu scripture that is part of the epic ''Mahabharata'' (c ...
'' turned into English. His efforts led to a first translation by Charles Wilkins
Sir Charles Wilkins (1749 – 13 May 1836) was an English typographer and Orientalist, and founding member of The Asiatic Society. He is notable as the first translator of ''Bhagavad Gita'' into English, He supervised Panchanan Karmakar to c ...
appearing in 1785. He wrote the introduction to it which appeared on 4 October 1784 in Benares
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tra ...
.
"Warren Hastings and His Bull", a short story by the Indian writer Uday Prakash
Uday Prakash (born 1 January 1952) is a Hindi poet, scholar, journalist, translator and short story writer from India.
He has worked as administrator, editor, researcher, and TV director. He writes for major dailies and periodicals as a freelance ...
, was adapted for stage under the same title by the director Arvind Gaur
Arvind Gaur is an Indian theatre director known for innovative, socially and politically relevant plays in India. Gaur's plays are contemporary and thought-provoking, connecting intimate personal spheres of existence to larger social politica ...
. It presents Hastings's interaction with traditional India in a work of socio-economic political satire.
A short story by the Hindi author Shivprasad Singh 'Rudra' Kashikeya called ''Bahti Ganga'' features Chait Singh
Rafa'at wa Awal-i-Martabat Maharaja Sri Chait Singh Sahib Bahadur (died 29 March 1810), commonly known as Chait Singh, was a ruler of Kingdom of Benares in northern India.
Maharaja Balwant Singh's elder son, Rafa'at wa Awal-i-Martabat Raja Sri ...
, then Raja of Banaras, in conflict with Hastings, who is imprisoned by the Raja, but escapes, though ordinary people of the city make fun of him.
The Hastings career is much discussed in the historical mystery novel, ''Secrets in the Stones'', by Tessa Harris.
Hastings is named in Book 5 of George Eliot
Mary Ann Evans (22 November 1819 – 22 December 1880; alternatively Mary Anne or Marian), known by her pen name George Eliot, was an English novelist, poet, journalist, translator, and one of the leading writers of the Victorian era. She wrot ...
's novel Middlemarch
''Middlemarch, A Study of Provincial Life'' is a novel by the English author Mary Anne Evans, who wrote as George Eliot. It first appeared in eight installments (volumes) in 1871 and 1872. Set in Middlemarch, a fictional English Midland town, ...
, where his greed for Daylesford is compared to the character Joshua Rigg's greed for money.
Hastings was rumoured to be the biological father of Eliza de Feuillide
Eliza Capot, Comtesse de Feuillide (née Hancock; 22 December 1761 – 25 April 1813) was the cousin, and later sister-in-law, of novelist Jane Austen. She is believed to have been the inspiration for a number of Austen's works, such as ''L ...
, the daughter of Philadelphia Austen Hancock
Philadelphia Austen Hancock (15 May 1730 – 26 February 1792) was an English socialite and the aunt of Jane Austen. Throughout her life, rumours circulated in India and England that she was the mistress of Warren Hastings, who was the godfather ...
and a cousin of Jane Austen
Jane Austen (; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for her six major novels, which interpret, critique, and comment upon the British landed gentry at the end of the 18th century. Austen's plots of ...
. Some scholars have seen parallels between Hastings and Colonel Brandon in Austen's ''Sense and Sensibility
''Sense and Sensibility'' is a novel by Jane Austen, published in 1811. It was published anonymously; ''By A Lady'' appears on the title page where the author's name might have been. It tells the story of the Dashwood sisters, Elinor (age 19) a ...
'': both left for India at age 17; both may have had illegitimate daughters named Eliza; both participated in a duel. Linda Robinson Walker argues that Hastings "haunts ''Sense and Sensibility'' in the character of Colonel Brandon."
See also
*Company rule in India
Company rule in India (sometimes, Company ''Raj'', from hi, rāj, lit=rule) refers to the rule of the British East India Company on the Indian subcontinent. This is variously taken to have commenced in 1757, after the Battle of Plassey, when ...
*Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
*Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II (; 25 June 1728 – 19 November 1806), also known by his birth name Ali Gohar (or Ali Gauhar), was the seventeenth Mughal Emperor and the son of Alamgir II. Shah Alam II became the emperor of a crumbling Mughal empire. His powe ...
References
Bibliography
*William Dalrymple, ''The Anarchy: The East India Company, Corporate Violence, and the Pillage of an Empire'' (2019excerpt
*Alfred Mervyn Davies, ''Strange destiny: a biography of Warren Hastings'' (1935) *Suresh Chandra Ghosh, ''The Social Condition of the British Community in Bengal: 1757–1800'' (Brill, 1970) *
Keith Feiling
Sir Keith Grahame Feiling (7 September 1884 – 16 September 1977) was a British historian, biographer and academic. He was Chichele Professor of Modern History at the University of Oxford, 1946–1950. He was noted for his conservative interpre ...
, ''Warren Hastings'' (1954)
*Philip Lawson, ''The East India Company: A History'' (Routledge, 2014)
*P. J. Marshall
Peter James Marshall (born 1933 in Calcutta) is a British historian known for his work on the British Empire, particularly the activities of British East India Company servants in 18th-century Bengal, and also the history of British involvemen ...
, ''The impeachment of Warren Hastings'' (1965)
*P. J. Marshall, "Hastings, Warren (1732–1818)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (Oxford University Press, 2004); online edn, Oct 200accessed 11 Nov 2014
* Penderel Moon, ''Warren Hastings and British India'' (Macmillan, 1949
online
*Patrick Turnbull, ''Warren Hastings''. (New English Library, 1975) *
Primary sources
*G. W. Forrest, ed., ''Selections from the State Papers of the Governors-General of India: Warren Hastings'' (2 vols.),Blackwell's
Blackwell UK, also known as Blackwell's and Blackwell Group, is a British academic book retailer and library supply service owned by Waterstones. It was founded in 1879 by Benjamin Henry Blackwell, after whom the chain is named, on Broad Street, ...
, Oxford (1910)
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
"Warren Hastings" an essay by Thomas Babington Macaulay (October 1841)
* (within
Critical and Historical Essays (Macaulay)
''Critical and Historical Essays: Contributed to the Edinburgh Review'' (1843) is a collection of articles by Thomas Babington Macaulay, 1st Baron Macaulay, Thomas Babington Macaulay, later Lord Macaulay. They have been acclaimed for their reada ...
)
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hastings, Warren
1732 births
1818 deaths
Governors-General of India
British East India Company people
Founders of Indian schools and colleges
Members of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom
Impeached British officials
Fellows of the Royal Society
English duellists
People educated at Westminster School, London
People from Cotswold District
People from West Oxfordshire District