War Of The Tyrolean Succession on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of Tyrol, a historical region in the middle alpine area of Central Europe, dates back to early human settlements at the end of the last glacier period, around 12,000 BC. Sedentary settlements of farmers and herders can be traced back to 5000 BC. Many of the main and side valleys were settled during the early Bronze Age, from 1800 to 1300 BC. From these settlements, two prominent cultures emerged: the Laugen-Melaun culture in the Bronze Age, and the Fritzens-Sanzeno culture in the Iron Age.
The region was conquered by the Romans in 15 BC. The northern and eastern areas were incorporated into the Roman Empire as the provinces of Raetia and Noricum, leaving deep impressions on the culture and language, with the Rhaeto-Romance languages. Following the conquest of Italy by the Goths, Tyrol became part of the Ostrogothic Kingdom in the fifth and sixth centuries. In 553, southern Tyrol was incorporated into the Lombards' Kingdom of Italy, northern Tyrol came under the influence of the
The history of Tyrol, a historical region in the middle alpine area of Central Europe, dates back to early human settlements at the end of the last glacier period, around 12,000 BC. Sedentary settlements of farmers and herders can be traced back to 5000 BC. Many of the main and side valleys were settled during the early Bronze Age, from 1800 to 1300 BC. From these settlements, two prominent cultures emerged: the Laugen-Melaun culture in the Bronze Age, and the Fritzens-Sanzeno culture in the Iron Age.
The region was conquered by the Romans in 15 BC. The northern and eastern areas were incorporated into the Roman Empire as the provinces of Raetia and Noricum, leaving deep impressions on the culture and language, with the Rhaeto-Romance languages. Following the conquest of Italy by the Goths, Tyrol became part of the Ostrogothic Kingdom in the fifth and sixth centuries. In 553, southern Tyrol was incorporated into the Lombards' Kingdom of Italy, northern Tyrol came under the influence of the
 In the Bronze and Iron Ages the region was home to a series of autochthonous cultures occupying roughly the area of the later county of Tyrol. The most prominent are the late Bronze Age Laugen-Melaun culture and Iron Age Fritzens-Sanzeno culture cultures.
The Laugen-Melaun culture, named after two important archaeological sites near the modern-day town of Brixen in South Tyrol, originated in the 14th century BC, in the area of today's South Tyrol and Trentino. It soon spread over the central area of the Southern Alps, encompassing South and East Tyrol, Trentino north of Rovereto and the Lower Engadine; the northern part of Tyrol came under the influence of the Urnfield culture. Distinguishing factors include its characteristic richly decorated pottery, while the metal-working is strongly influenced by adjacent cultures. As in the Urnfield culture, Laugen-Melaun-people cremated their dead, placing their ashes in urns, and worshipping their gods in sanctuaries sometimes situated in remote areas, on mountain-tops or close to water. Rich burial objects show that from the 13th to 11th century BC, the Laugen-Melaun culture (Laugen-Melaun A) flourished, due to the mining of copper, the source material for the alloy
In the Bronze and Iron Ages the region was home to a series of autochthonous cultures occupying roughly the area of the later county of Tyrol. The most prominent are the late Bronze Age Laugen-Melaun culture and Iron Age Fritzens-Sanzeno culture cultures.
The Laugen-Melaun culture, named after two important archaeological sites near the modern-day town of Brixen in South Tyrol, originated in the 14th century BC, in the area of today's South Tyrol and Trentino. It soon spread over the central area of the Southern Alps, encompassing South and East Tyrol, Trentino north of Rovereto and the Lower Engadine; the northern part of Tyrol came under the influence of the Urnfield culture. Distinguishing factors include its characteristic richly decorated pottery, while the metal-working is strongly influenced by adjacent cultures. As in the Urnfield culture, Laugen-Melaun-people cremated their dead, placing their ashes in urns, and worshipping their gods in sanctuaries sometimes situated in remote areas, on mountain-tops or close to water. Rich burial objects show that from the 13th to 11th century BC, the Laugen-Melaun culture (Laugen-Melaun A) flourished, due to the mining of copper, the source material for the alloy
 Over the centuries, the Counts residing in
Over the centuries, the Counts residing in
 Following defeat by
Following defeat by
/ref> In 1806, delegates from Tyrol travelled to Vienna to make plans for an insurrection of the Tyrolean people. Among them was the later leader of the insurgents, Andreas Hofer. The insurrection began on April 9, 1809 in
 On the eve of World War I, the southern part of the Austrian crown land of Tyrol was populated mainly by Italian speakers (the so-called ''Welschtirol'', or Trentino). Its border coincided with the present-day border between South Tyrol and Trentino, crossing the Adige valley at Salorno (''Chiusa di Salorno/Salurner Klause'').Alcock 1996, p. 67. The existence of areas largely populated by Italian-speaking populations under the rule of the Austrian Empire was a constant cause of friction between Austria and Italy, a national state set on the unification of all Italians. Being part of the
On the eve of World War I, the southern part of the Austrian crown land of Tyrol was populated mainly by Italian speakers (the so-called ''Welschtirol'', or Trentino). Its border coincided with the present-day border between South Tyrol and Trentino, crossing the Adige valley at Salorno (''Chiusa di Salorno/Salurner Klause'').Alcock 1996, p. 67. The existence of areas largely populated by Italian-speaking populations under the rule of the Austrian Empire was a constant cause of friction between Austria and Italy, a national state set on the unification of all Italians. Being part of the
South Tyrol in Figures 2008", Provincial Statistics Institute of the Autonomous Province of South Tyrol
Bozen/Bolzano 2007, p. 19, Table 11 The northern part of Tyrol was retained by the
Maps, charts, tables
Tyrolean History
(in German) {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Tyrol 1919 disestablishments States and territories established in 1140 Tyrol (region) History of the Alps History of South Tyrol Austrian Circle Historical regions in Austria
 The history of Tyrol, a historical region in the middle alpine area of Central Europe, dates back to early human settlements at the end of the last glacier period, around 12,000 BC. Sedentary settlements of farmers and herders can be traced back to 5000 BC. Many of the main and side valleys were settled during the early Bronze Age, from 1800 to 1300 BC. From these settlements, two prominent cultures emerged: the Laugen-Melaun culture in the Bronze Age, and the Fritzens-Sanzeno culture in the Iron Age.
The region was conquered by the Romans in 15 BC. The northern and eastern areas were incorporated into the Roman Empire as the provinces of Raetia and Noricum, leaving deep impressions on the culture and language, with the Rhaeto-Romance languages. Following the conquest of Italy by the Goths, Tyrol became part of the Ostrogothic Kingdom in the fifth and sixth centuries. In 553, southern Tyrol was incorporated into the Lombards' Kingdom of Italy, northern Tyrol came under the influence of the
The history of Tyrol, a historical region in the middle alpine area of Central Europe, dates back to early human settlements at the end of the last glacier period, around 12,000 BC. Sedentary settlements of farmers and herders can be traced back to 5000 BC. Many of the main and side valleys were settled during the early Bronze Age, from 1800 to 1300 BC. From these settlements, two prominent cultures emerged: the Laugen-Melaun culture in the Bronze Age, and the Fritzens-Sanzeno culture in the Iron Age.
The region was conquered by the Romans in 15 BC. The northern and eastern areas were incorporated into the Roman Empire as the provinces of Raetia and Noricum, leaving deep impressions on the culture and language, with the Rhaeto-Romance languages. Following the conquest of Italy by the Goths, Tyrol became part of the Ostrogothic Kingdom in the fifth and sixth centuries. In 553, southern Tyrol was incorporated into the Lombards' Kingdom of Italy, northern Tyrol came under the influence of the Bavarii
The Baiuvarii or Bavarians (german: Bajuwaren) were a Germanic people. The Baiuvarii had settled modern-day Bavaria (which is named after them), Austria, and South Tyrol by the 6th century AD, and are considered the ancestors of modern-day Bava ...
, and western Tyrol became part of Alamannia
Alamannia, or Alemannia, was the kingdom established and inhabited by the Alemanni, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribal confederation that had broken through the Roman ''Upper Germanic Limes, limes'' in 213.
The Alemanni expanded from the Main ...
—the three areas meeting at present-day Bolzano.
In 774, Charlemagne conquered the Lombards, and as a consequence, Tyrol became an important bridgehead to Italy. In the eleventh century, the Emperors of the Holy Roman Empire granted the counties of Trento, Bolzano, and Vinschgau to the Bishopric of Trent, and the county of Norital and Puster Valley to the Bishopric of Brixen—effectually placing the region under the control of the Emperors.
In the coming centuries, the counts residing in Tirol Castle
Tyrol Castle, less commonly Tirol Castle (german: Schloss Tirol, it, Castel Tirolo) is a castle in the ''comune'' (municipality) of Tirol near Merano, in the Burggrafenamt district of South Tyrol, Italy. It was the ancestral seat of the Counts o ...
near Merano extended their territory over the region. Later counts would hold much of their territory directly from the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
. The Meinhardinger family, originating in Gorizia, controlled the Tyrol, Gorizia, and the Duchy of Carinthia
The Duchy of Carinthia (german: Herzogtum Kärnten; sl, Vojvodina Koroška) was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, and was the first newly created Imperial Sta ...
. By 1295, the "county and reign of Tyrol" had established itself firmly in the "Land on the Adige and Inn", as the region was then called. When the Meinhardiner dynasty died out in 1369, the Tyrol was ceded to the House of Habsburg, who ruled over the region for the next five and a half centuries, with a brief period of control in the early nineteenth century by the Bavarians during the Napoleonic Wars.
At the conclusion of World War I, the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye of 1919 ceded the southern part of Tyrol to the Kingdom of Italy, including present-day South Tyrol, with its large German-speaking majority. The northern part of Tyrol was retained by the First Austrian Republic. The historical region is formed by the present-day Austrian State of Tyrol and the Italian provinces of South Tyrol and Trentino. The boundaries of this Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion correspond to the former Habsburg County of Tyrol, which gave this historical region its name.
Prehistory
Archaeological findings show people settled in the middle alpine region, later to be called Tyrol, when the glaciers retreated and flora and fauna revived, after the last ice age ended around 12,000 BC. Artifacts found on the Seiser Alm date to the Upper Paleolithic era. In the valley bottoms near Bolzano, Brixen and Salorno,mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
hunters resting places were discovered. Stone artefacts recovered there were dated to the 8th millennia BC. Discovery of Ötzi on the Similaun glacier in 1991 proved man had already crossed the highest Alpine passes 5000 years ago. Sedentary settlements of farmers and herders can be traced back to 5000 BC. There is ample evidence of settlements in the main and side valleys during the early and middle Bronze Age (1800-1300 BC). Preferred settlement sites were sunny terraces on the valleys slopes, and hill tops in the middle heights. In the Bronze and Iron Ages the region was home to a series of autochthonous cultures occupying roughly the area of the later county of Tyrol. The most prominent are the late Bronze Age Laugen-Melaun culture and Iron Age Fritzens-Sanzeno culture cultures.
The Laugen-Melaun culture, named after two important archaeological sites near the modern-day town of Brixen in South Tyrol, originated in the 14th century BC, in the area of today's South Tyrol and Trentino. It soon spread over the central area of the Southern Alps, encompassing South and East Tyrol, Trentino north of Rovereto and the Lower Engadine; the northern part of Tyrol came under the influence of the Urnfield culture. Distinguishing factors include its characteristic richly decorated pottery, while the metal-working is strongly influenced by adjacent cultures. As in the Urnfield culture, Laugen-Melaun-people cremated their dead, placing their ashes in urns, and worshipping their gods in sanctuaries sometimes situated in remote areas, on mountain-tops or close to water. Rich burial objects show that from the 13th to 11th century BC, the Laugen-Melaun culture (Laugen-Melaun A) flourished, due to the mining of copper, the source material for the alloy
In the Bronze and Iron Ages the region was home to a series of autochthonous cultures occupying roughly the area of the later county of Tyrol. The most prominent are the late Bronze Age Laugen-Melaun culture and Iron Age Fritzens-Sanzeno culture cultures.
The Laugen-Melaun culture, named after two important archaeological sites near the modern-day town of Brixen in South Tyrol, originated in the 14th century BC, in the area of today's South Tyrol and Trentino. It soon spread over the central area of the Southern Alps, encompassing South and East Tyrol, Trentino north of Rovereto and the Lower Engadine; the northern part of Tyrol came under the influence of the Urnfield culture. Distinguishing factors include its characteristic richly decorated pottery, while the metal-working is strongly influenced by adjacent cultures. As in the Urnfield culture, Laugen-Melaun-people cremated their dead, placing their ashes in urns, and worshipping their gods in sanctuaries sometimes situated in remote areas, on mountain-tops or close to water. Rich burial objects show that from the 13th to 11th century BC, the Laugen-Melaun culture (Laugen-Melaun A) flourished, due to the mining of copper, the source material for the alloy bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
.
Around 500 BC, the Fritzens-Sanzeno culture, also known as culture of the Raeti, after the goddess Raetia who according to Roman authors was the main deity of the people inhabiting the region, succeeded both the Laugen-Melaun culture of the southern and the Urnfield culture of the northern part of Tyrol. As in the preceding culture, the richly ornamented pottery is very characteristic, while many aspects such as the metal-working, burial customs and religion are strongly influenced by its neighbours, primarily the Etruscans and Celts. Nonetheless, the Fritzens-Sanzeno-people possessed important distinct cultural traits distinguishing them from adjacent groups, such as the typical mountain-sanctuaries already in use during the time of the Laugen-Melaun culture, certain types of fibulae
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is ...
, bronze armor, and their own alphabet derived from one of North Etruscan alphabets (but not from the Etruscan alphabet). The language of the Raeti was kin to Etruscan, but different enough to suggest a very ancient divergence between them.
Antiquity
In 15 BC, the region was conquered by the Romans, and its northern and eastern part incorporated into the Roman Empire as the provinces of Raetia and Noricum respectively. The part south of and including the area around the modern day cities of Bolzano and Merano became part of Italia's ''Regio X''. As in the rest of Europe, the Roman era left deep impressions on the culture and language, with the Rhaeto-Romance languages.Middle Ages
After the conquest of Italy by the Goths, Tyrol became part of the Ostrogothic Kingdom from the 5th to the 6th century. After the fall of the Ostrogothic Kingdom in 553, the Germanic tribe of the Lombards invaded Italy and founded the Lombard Kingdom of Italy, which no longer included all of Tyrol, only its southern part. The northern part of Tyrol came under the influence of theBavarii
The Baiuvarii or Bavarians (german: Bajuwaren) were a Germanic people. The Baiuvarii had settled modern-day Bavaria (which is named after them), Austria, and South Tyrol by the 6th century AD, and are considered the ancestors of modern-day Bava ...
, while the west probably was part of Alamannia
Alamannia, or Alemannia, was the kingdom established and inhabited by the Alemanni, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribal confederation that had broken through the Roman ''Upper Germanic Limes, limes'' in 213.
The Alemanni expanded from the Main ...
. Thus, Tyrol was divided among three spheres of influence that met in the approximate area of today's Bolzano. During the 6th century Bavaria and Alamannia became stem duchies
A stem duchy (german: Stammesherzogtum, from '' Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Bavarians and Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the German Empire at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dynasty (death of ...
of the Frankish Kingdom
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
. On conquering the Lombard Kingdom of Italy in 774, Charlemagne had himself crowned King of the Lombards. Consequently, Tyrol came to be of great importance as a bridgehead to Italy, which was re-affirmed during the Italian Campaign of Otto I. In the years 1007 and 1027 the Emperors of the Holy Roman Empire granted the counties of Trento, Bolzano and Vinschgau to the Bishopric of Trent. In 1027 the County of Norital was granted to the Bishopric of Brixen, followed in 1091 by the County of Puster Valley. Since the Bishops were nominated directly by the Emperor and their office was not hereditary, putting the area under their control was intended to secure it to the Emperors.
Birth of the County of Tyrol

 Over the centuries, the Counts residing in
Over the centuries, the Counts residing in Tirol Castle
Tyrol Castle, less commonly Tirol Castle (german: Schloss Tirol, it, Castel Tirolo) is a castle in the ''comune'' (municipality) of Tirol near Merano, in the Burggrafenamt district of South Tyrol, Italy. It was the ancestral seat of the Counts o ...
, near Merano, extended their territory over the region. Later counts would hold much of their territory directly from the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
. The Meinhardinger family, originating in Gorizia, held not only Tyrol and Gorizia, but for a time the Duchy of Carinthia
The Duchy of Carinthia (german: Herzogtum Kärnten; sl, Vojvodina Koroška) was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, and was the first newly created Imperial Sta ...
. At the end of count Meinhard II
Meinhard II (c. 1238 – 1 November 1295), a member of the House of Gorizia (''Meinhardiner''), ruled the County of Gorizia (as Meinhard IV) and the County of Tyrol together with his younger brother Albert from 1258. In 1271 they divided their he ...
's rule (1259–1295) the "county and reign of Tyrol" had established itself firmly in the "Land on the Adige and Inn", as the region was then called. This happened on the expense of the power of the bishops, who were nominally the feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a wa ...
lords of the counts of Tyrol. Meinhard II also introduced more efficient systems for the administration of his territories.
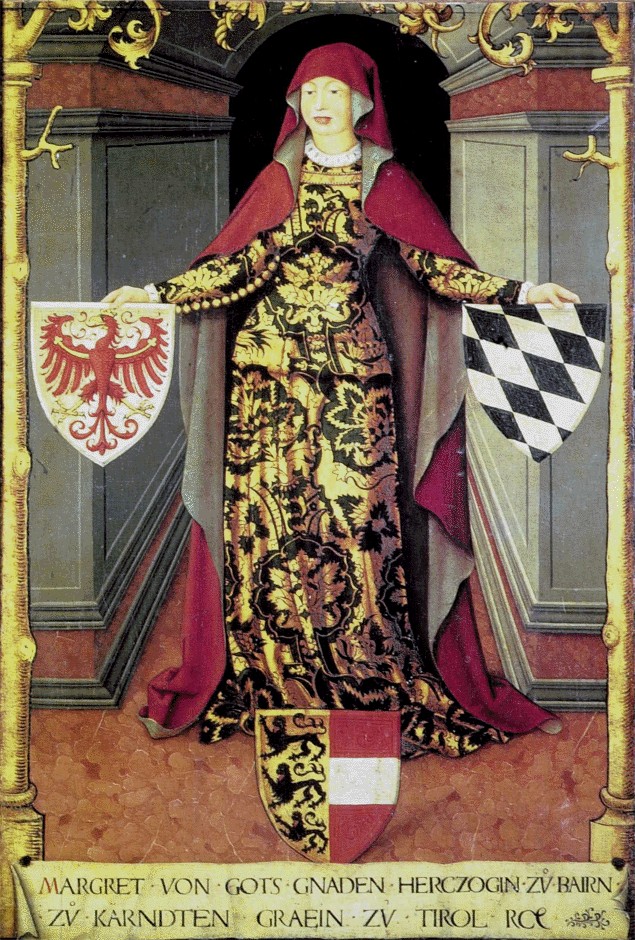
Margarete "Maultasch" was the last effective ruler of Tyrol from the Meinhardinger Dynasty. In 1330 she was married to John-Henry (who later became the margrave of Moravia), who she repudiated with the help of the Tyrolean aristocracy in order to marry Duke Ludwig V Ludwig V may refer to:
* Louis V, Duke of Bavaria (1315–1361)
* Louis V, Elector Palatine (1478–1544)
* Louis V, Landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this nam ...
of Bavaria, a member of the powerful Wittelsbach dynasty
The House of Wittelsbach () is a German dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including Bavaria, the Palatinate, Holland and Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland), Denmark, Norway, Hungary (with Romania), Bohemia, the Electorate ...
. This weakened the position of the countess and strengthened the local nobility. The only son of Margarete and Louis, Meinhard, died in 1363, two years after his father, leaving the countess without an heir.
Margarete Maultasch decided to bequeath Tyrol to Duke Rudolph IV
Rudolf IV (1 November 1339 – 27 July 1365), also called Rudolf the Founder (german: der Stifter), was a scion of the House of Habsburg who ruled as duke of Austria (self-proclaimed archduke), Styria and Carinthia from 1358, as well as cou ...
of the House of Habsburg, probably pressed by the aristocracy, an act which caused a conflict between Meinhard's uncle Stephen II, who forged an alliance with the powerful Lord of Milan Bernabò Visconti to invade Tyrol, and the House of Habsburg. Stephen finally renounced Tyrol to the Habsburgs with the Peace of Schärding for a huge financial compensation after the death of Margarete Maultasch in 1369. The red eagle in Tyrol's coat of arms derives from the red Brandenburg eagle, dating from the time when Louis V and Margarete Maultasch governed Brandenburg as well.
Habsburg rule
The acquisition of Tyrol was strategically important to the Habsburg dynasty, since it allowed it to connect their Austrian territories with their territorial possessions in the area of today's Switzerland. From that time, Tyrol was ruled by various lines of the Habsburg family, who bore the title Count. Tyrol repeatedly became involved in the political and military conflicts of the Habsburgs with Milan,Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, Switzerland and the County of Gorizia, as well as Bavaria and Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
.
The Battle of Sempach
The Battle of Sempach was fought on 9 July 1386, between Leopold III, Duke of Austria and the Old Swiss Confederacy. The battle was a decisive Swiss victory in which Duke Leopold and numerous Austrian nobles died. The victory helped turn the lo ...
in 1386, in which Duke Leopold III of Austria was defeated by the Old Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy or Swiss Confederacy (German language, Modern German: ; historically , after the Swiss Reformation, Reformation also , "Confederation of the Swiss") was a loose confederation of independent small states (, German or ...
had important repercussions on Tyrol, and was the first of a series of military conflicts between the county and its neighbours. The 1405-1408 war against the Swiss Appenzell
Appenzell is a historic canton in the northeast of Switzerland, and entirely surrounded by the canton of St. Gallen.
Appenzell became independent of the Abbey of Saint Gall in 1403 and entered a league with the Old Swiss Confederacy in 1411, ...
er, 1413 the conflict with Venice and 1410 the invasion of the lower Inn valley by the Bavarians. In 1423, during the rule of Frederick IV "Empty Pockets", the first meeting that could be called a Tyrolean Parliament met. It consisted of aristocrats, bourgeois and even peasant representatives. During Frederick IV's tenure internal conflicts between the powerful local aristocracy and the duke arose, which eventually led to the decline of the nobles and of their traditional system of values, and strengthened the duke's rule over the country. This enabled Sigismund "Rich in Coin" to continue his father's rule to the end of the 15th century and lead the county into the modern era.
Sigismund's opulent lifestyle and the misfortunes of war with Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
bled the treasury, leading to his decision to mortgage the Tyrolean silver mines. By 1490, Sigismund became so unpopular that he was forced to abdicate in favor of his more prosperous cousin, Maximilian
Maximilian, Maximillian or Maximiliaan (Maximilien in French) is a male given name.
The name " Max" is considered a shortening of "Maximilian" as well as of several other names.
List of people
Monarchs
*Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor (1459� ...
, King of the Germans. Three years after the succession, Maximilian became Holy Roman Emperor, making his preferred residence, Innsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol (state), Tyrol and the List of cities and towns in Austria, fifth-largest city in Austria. On the Inn (river), River Inn, at its junction with the ...
, the imperial capitol. Maximilian added Kufstein, Rattenberg and Kitzbühel
Kitzbühel (, also: ; ) is a medieval town situated in the Kitzbühel Alps along the river Kitzbüheler Ache in Tyrol, Austria, about east of the state capital Innsbruck and is the administrative centre of the Kitzbühel district (). Kitzbühel ...
to Tyrol, and when he inherited the Puster Valley and East Tyrol the borders of Tyrol were set, with the exception of the 1817 addition of the Ziller Valley
Napoleonic Wars
 Following defeat by
Following defeat by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
in 1805, Austria was forced to cede Tyrol to the Kingdom of Bavaria in the Peace of Pressburg. Tyrol, as a part of Bavaria, became a member of the Confederation of the Rhine in 1806. Consequently, King Maximilian I of Bavaria introduced far reaching economic, religious and administrative reforms. When in 1808 a new constitution for the Kingdom of Bavaria was introduced, Tyrol was integrated into South Bavaria, and divided into three districts, losing its special status in the kingdom. Furthermore, Tyroleans were now subjected to the Bavarian conscription levies, and faced the prospect of having to fight against Austrian troops. This, together with the economic decline under Bavarian rule, and the kingdom's religious reforms which were opposed by the Catholic population, led to a growing conflict between the Tyrolean population and the Bavarian authorities.DAVEY WRIGHT Hamish, Andreas Hofer and the insurrection in the Tyrol, 1809/ref> In 1806, delegates from Tyrol travelled to Vienna to make plans for an insurrection of the Tyrolean people. Among them was the later leader of the insurgents, Andreas Hofer. The insurrection began on April 9, 1809 in
Innsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol (state), Tyrol and the List of cities and towns in Austria, fifth-largest city in Austria. On the Inn (river), River Inn, at its junction with the ...
. On April 12, 1809 Innsbruck was freed by the Tyrolean "Landsturm" commanded by captain Martin Teimer in the battle later known as the First battle of the Bergisel. One day later a military unit of 8000 men consisting of Bavarian and French Troops approached Innsbruck from the Brenner Pass
The Brenner Pass (german: link=no, Brennerpass , shortly ; it, Passo del Brennero ) is a mountain pass through the Alps which forms the border between Italy and Austria. It is one of the principal passes of the Eastern Alpine range and has ...
, but was convinced to surrender by captain Teimer, who dressed up as a Major of the regular Austrian army and made the Bavarian officers believe that the Austrian army was approaching Innsbruck, when in fact it was still about 40 miles away. In order to convalidate the capitulation agreement, Teimer was subsequently appointed Major of the Austrian army.
Throughout Tyrol, the Bavarian troops were killed or driven out. The Tyroleans fought mainly as skirmishing sharpshooters, taking advantage of the mountainous nature of the land. They were highly mobile and made use of artificial avalanches to combat their enemies. Following the defeat of the Austrian Army on the Bavarian front, Napoleon dispatched Charles Lefebvre to Tyrol, and by May 19 Innsbruck had been seized again and the rebellion seemed quelled.
After Archduke Karl's Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
army was defeated by Napoleon at the Battle of Wagram, the Armistice of Znaim was signed. Point IV of the agreement stated that Austria was to withdraw its troops from the territories of Vorarlberg and Tyrol, returning them to Bavarian rule. But the Bavarians and the French found it difficult to gain control of the territory, with Tyrolean sharpshooters occupying high places along the roads, blocking roads and setting off avalanches to harm the occupying army. The Tyroleans managed to hold off and inflict heavy casualties on the French and Bavarian troops, and on August 13 the Tyrolean peasant army rallied at the Bergisel again for the decisive Battle. 15000 Bavarian, French and Saxon troops faced almost the same number of Tyrolean irregulars. Surrounded on all sides by the irregulars, and having sustained heavy casualties, Lefebvre was forced to withdraw. Andreas Hofer, who in the meantime had advanced to supreme commander of the insurgents, became regent of Tyrol in the name of the Emperor.
Following the Treaty of Schönbrunn Tyrol was again ceded to Bavaria by the Austrian Emperor. On October 21 Bavarian, French and Italian troops under the command of the Duke Drouet d’ Erlon poured into Tyrol, forcing the Tyroleans to retreat to the Bergisel again. As Winter approached, supplies began to dwindle, and many men left to return to their homes. On 28/29 October, news of the peace treaty that had been signed by Austria reached Tyrol. This had catastrophic effects on the morale of the Tyroleans, and Andreas Hofer, betrayed by his emperor, resorted to drinking. The Tyrolean morale had been broken. On November 1 Drouet d'Erlon had recaptured Innsbruck and the Bergisel, and by 11 November 1809, Tyrol was entirely occupied. Hofer fled into the mountains, and on 5 January 1810 he was betrayed and denounced to the authorities. On 28 January, he, his wife and his son were taken to Bolzano. Napoleon learnt of the capture at the start of February and ordered Hofer to be tried and executed. This order was acted upon soon and Hofer died at the dungeon of the fortress of Mantua on February 20, 1810.
The execution of Hofer, considered a Tyrolean hero until today, is the topic of the song ''Zu Mantua in Banden
''Zu Mantua in Banden'' (also known as the '' Andreas-Hofer-Lied'') is one of the most popular folk songs and, since 1948, the official anthem of the current Austrian State of Tyrol, i.e. the Northern and Eastern part of the former County of Tyrol. ...
'', since 1948 the Tyrol's official anthem.
Crownland of Tyrol
Tyrol remained divided under Bavarian and Italian authority for another four years, before its reunification and return to Austria following the decisions at the Congress of Vienna in 1814. Integrated into the Austrian Empire, from 1867 onwards, it was a ''Kronland'' (Crown Land
Crown land (sometimes spelled crownland), also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. ...
) of Cisleithania
Cisleithania, also ''Zisleithanien'' sl, Cislajtanija hu, Ciszlajtánia cs, Předlitavsko sk, Predlitavsko pl, Przedlitawia sh-Cyrl-Latn, Цислајтанија, Cislajtanija ro, Cisleithania uk, Цислейтанія, Tsysleitaniia it, Cislei ...
, the western half of Austria-Hungary.
World War I
 On the eve of World War I, the southern part of the Austrian crown land of Tyrol was populated mainly by Italian speakers (the so-called ''Welschtirol'', or Trentino). Its border coincided with the present-day border between South Tyrol and Trentino, crossing the Adige valley at Salorno (''Chiusa di Salorno/Salurner Klause'').Alcock 1996, p. 67. The existence of areas largely populated by Italian-speaking populations under the rule of the Austrian Empire was a constant cause of friction between Austria and Italy, a national state set on the unification of all Italians. Being part of the
On the eve of World War I, the southern part of the Austrian crown land of Tyrol was populated mainly by Italian speakers (the so-called ''Welschtirol'', or Trentino). Its border coincided with the present-day border between South Tyrol and Trentino, crossing the Adige valley at Salorno (''Chiusa di Salorno/Salurner Klause'').Alcock 1996, p. 67. The existence of areas largely populated by Italian-speaking populations under the rule of the Austrian Empire was a constant cause of friction between Austria and Italy, a national state set on the unification of all Italians. Being part of the Triple Alliance Triple Alliance may refer to:
* Aztec Triple Alliance (1428–1521), Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan and in central Mexico
* Triple Alliance (1596), England, France, and the Dutch Republic to counter Spain
* Triple Alliance (1668), England, the ...
with Germany and Austria was "an embarrassment, if not a contradiction" for Italy. Italy's fear that it would not get what it wanted in the event of a victorious Triple Alliance caused it to remain neutral during the first year of the war, and the preoccupation that it wouldn't get what it wanted from a victorious Entente
Entente, meaning a diplomatic "understanding", may refer to a number of agreements:
History
* Entente (alliance), a type of treaty or military alliance where the signatories promise to consult each other or to cooperate with each other in case o ...
either if it remained neutral led it to join the war on the side of the latter. Italy conducted intense negotiations with Austria, which was prepared to part with Trentino in exchange of Italy's neutrality, but Italy wanted (among other things) to reach the Alpine water divide
A drainage divide, water divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a singl ...
, which it claimed as its 'natural border', a demand which Austria refused, since it would have meant giving up a territory regarded as personal fief by the Habsburg Emperors. On 26 April 1915, Italy signed the Treaty of London The Treaty of London or London Convention or similar may refer to:
*Treaty of London (1358), established a truce between England and France following the Battle of Poitiers
*Treaty of London (1359), which ceded western France to England
*Treaty of ...
, agreeing to declare war against the Central Powers in exchange for the unredeemed territories of Trentino, Gorizia, Trieste and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
, as well as the part of German Tyrol south of the main Alpine divide. Apart from these territorial gains the alliance change enabled Italy to realise its aspiration: Italian military dominance in the Mediterranean. The ideals of irredentism were used to convince the population of the necessity of the war, but the true motive of the political leadership to join the war was their idea that Italy should become a great European power.
War against the Austro-Hungarian Empire was declared May 24, 1915. This put Tyrol on the front line, which passed through some of the highest mountains in the Alps. The ensuing front became known as the "War in ice and snow", as troops occupied the highest mountains and glaciers all year long. Twelve metres (40 feet) of snow were common during the winter of 1915–16, and tens of thousands of soldiers disappeared in avalanches. The remains of these soldiers are still being uncovered today. The Italian Alpini
The Alpini are the Italian Army's specialist mountain infantry. Part of the army's infantry corps, the speciality distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. Currently the active Alpini units are organized in two operatio ...
, their Austrian counterparts (''Kaiserjäger
The ''Kaiserjäger'' (officially designated by the Imperial and Royal (''k.u.k.'') military administration as the ''Tiroler Jäger-Regimenter'' or "Tyrolean Rifle Regiments"), were formed in 1895 as four normal infantry regiments within the Commo ...
'', '' Standschützen'' and '' Landesschützen''), and the German Alpenkorps occupied every hill and mountain top. They began carving extensive fortifications and military quarters, even drilling tunnels inside the mountains and deep into glaciers, like at Marmolada
Marmolada (Ladin: ''Marmolèda''; German: ''Marmolata'', ) is a mountain in northeastern Italy and the highest mountain of the Dolomites (a section of the Alps). It lies between the borders of Trentino and Veneto. The Marmolada is an ultra-pr ...
. Hundreds of troops would drag guns over mountains up to 3,890 m (12,760 ft). Streets, cable cars, mountain railways and walkways through the steepest of walls were built. The first to occupy higher ground became almost impossible to dislodge, so both sides turned to drilling tunnels under mountain peaks, filling them up with explosives, then detonating the entire mountain, including its defenders, such as Col di Lana
The Col di Lana is a mountain of the Fanes Group in the Italian Dolomites. The actual peak is called ''Cima Lana'' and situated in the municipality of Livinallongo del Col di Lana (German: ''Buchenstein'') in the Province of Belluno, Veneto r ...
, Monte Pasubio, Lagazuoi, etc. Climbing and skiing became essential skills for the troops of both sides and soon Ski Battalions and Special Climbing units were formed.
On May 15, 1916, the Austrian army staged an attack from the Trentino, unaided by the German army, whose command had advised against such a move. Several divisions were withdrawn from the Russian front to achieve necessary troop strength. The offensive was of limited tactical success. Austrians penetrated twelve miles into Italian territory, inflicting heavy casualties on the Italians, but fell short of their strategic and political goals. This inconclusive attack weakened the eastern front, which enabled the Russian Army to overrun Austrian positions in Galicia and threaten the heart of the Habsburg Empire
The armistice
After the Battle of Asiago in 1916, which ended in a stalemate and brought only minor territorial gains to Austria, the Tyrolean frontline remained largely static. The main battles were fought elsewhere. This changed in October, 1918, with Austro-Hungarian defeat in the Battle of Vittorio Veneto, the Imperial army collapsed and started to withdraw and, on 29 October, the Austro-Hungarians asked for an armistice. On 30 October 1918, the Austro-Hungarian army was split in two. The armistice was signed at 3.20 p.m., November 3, to become effective 24 hours later, at 3.00 p.m., November 4. Following the signing of the armistice, Austrian General Weber informed his Italian counterparts that the Imperial army had already laid down its weapons, due to a previous order and requested combat and Italian advancement to cease. The Italian General Pietro Badoglio sharply rejected the proposal, and threatened to stop all negotiations and continue the war. General Weber repeated the request, with no results. Even before the order to cease hostilities, the Imperial Army had already started to collapse, ceasing to exist as a combat force. Italian troops continued their advance until 3.00 p.m. on November 4. The occupation of all Tyrol, includingInnsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol (state), Tyrol and the List of cities and towns in Austria, fifth-largest city in Austria. On the Inn (river), River Inn, at its junction with the ...
, was completed in the days that followed.
Under the terms of the Austrian-Italian Armistice of Villa Giusti, as well as being required to evacuate all territory occupied since August, Austria-Hungary's forces were required to withdraw from South Tyrol, Tarvisio, the Isonzo valley, Gorizia, Trieste, Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the larges ...
, western Carniola
Carniola ( sl, Kranjska; , german: Krain; it, Carniola; hu, Krajna) is a historical region that comprised parts of present-day Slovenia. Although as a whole it does not exist anymore, Slovenes living within the former borders of the region sti ...
, and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
. Terms mandated German forces expulsion from Austria-Hungary within 15 days or their internment, and the Allies were to have free use of Austria-Hungary's internal communications. They were also obliged to allow Entente armies' transit, to reach Germany from the South.
The Italian General Rodolfo Graziani's 11th Italian army continued to advance, supported on the right by the 9th army. The result was that Austria-Hungary lost about 30,000 casualties and between 300,000 and 500,000 prisoners (50,000 by 31 October, 100,000 by 1 November and 428,000 by 4 November). Italian losses numbered about 38,000, including 145 French and 374 Britons.
It appears that the large quantity of prisoners stemmed from the Austrian command decision that captivity in Italy was preferable to starvation at home. After the armistice, hundreds of thousands of Austrian soldiers without weapons, food and discipline made their way home through the alpine valleys. The alpine villages were caught between the retreating, half-starved soldiers who repeatedly resorted to theft and robbery to survive, and the advancing Italian army. At the same time, great numbers of Italian war prisoners were making their way south towards their homeland. Austria did not have the means to guarantee the orderly retreat of its own army or the organized return of Italian war prisoners.Pasquali 2007, p. 113. In the meantime, Italian occupation of Tyrol was going as planned. On 11 November, Italian troops occupied the Brenner Pass and the Pass at Toblach. To secure access to the Inn valley, crucial for an advance into southern Germany, Innsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol (state), Tyrol and the List of cities and towns in Austria, fifth-largest city in Austria. On the Inn (river), River Inn, at its junction with the ...
, capital of Tyrol, and the village Landeck
Landeck () is a city in the Austrian state of Tyrol, the capital of the district of Landeck.
Geography
Landeck is located in the Tyrolean Oberland in the west of the state at an elevation of about . The town is situated in the valley of the Inn Ri ...
were occupied as well. On 10 January 1919, the commander of the 3rd army corps, Gen. Ugo Sani, was appointed military governor of northern Tyrol with residence in Innsbruck.
After World War I
The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye of 1919 ruled that, according to theTreaty of London The Treaty of London or London Convention or similar may refer to:
*Treaty of London (1358), established a truce between England and France following the Battle of Poitiers
*Treaty of London (1359), which ceded western France to England
*Treaty of ...
, the southern part of Tyrol had to be ceded to the Kingdom of Italy. Italy's border was pushed northward to the strategically important Alpine water divide
A drainage divide, water divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a singl ...
, including present day-South Tyrol with its large German-speaking majority.Oscar Benvenuto (ed.):South Tyrol in Figures 2008", Provincial Statistics Institute of the Autonomous Province of South Tyrol
Bozen/Bolzano 2007, p. 19, Table 11 The northern part of Tyrol was retained by the
First Austrian Republic
The First Austrian Republic (german: Erste Österreichische Republik), officially the Republic of Austria, was created after the signing of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye on 10 September 1919—the settlement after the end of World War I w ...
. In 1923, towns of Buchenstein, Hayden Hayden may refer to:
Places Inhabited places in the United States
*Hayden, Alabama
*Hayden, Arizona
*Hayden's Ferry, former name of Tempe, Arizona
*Hayden, California, former name of Hayden Hill, California
*Hayden, Colorado
*Hayden, Idaho
*Hayden ...
and Verseil were transferred from Province of Bolzano to Province of Belluno
The Province of Belluno ( it, Provincia di Belluno; de-AT, Provinz Belluno; lld, Provinzia de Belum) is a province in the Veneto region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Belluno.
It has an area of and a total population of about 205,000.
...
. Also, Hastachtal (includes former municipality of Casotto) was transferred from Province of Trento
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous region ...
to Province of Vicenza in 1929, and towns of Magasa Magasa may refer to places in:
;Greece
* Magasa, Crete
Magasa ( el, Μαγκασά) is a Neolithic settlement on the eastern part of the island of Crete in present-day Greece. Magasa is notable as a Neolithic Cretan settlement for some use of lar ...
and Valvestino
Valvestino (Brescian: ) is a ''comune'' in the province of Brescia, in Lombardy in northern Italy.
Historical and cultural profile
The Stoni and the Gallic Cenomani, then the Romans and the Lombards lived here. The Lodrone family established ...
were transferred from Province of Trento
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous region ...
to Province of Brescia in 1934.
See also
* Tyrol * Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion * Tyrol (state) * History of South Tyrol * Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol *Haymon
image:Wilten-riese-haymon.jpg, Figure of the giant Haymon in the chapel in Wilten
image:Cl. Wilthan und Bildnuß Heimonii (Merian).jpg, Haymon and the dragon with its tongue torn; below the monastery of Wilten. Copperplate engraving from Topograph ...
References
Further reading
* * Cole, John W. and Wolf, Eric R., '' The Hidden Frontier: Ecology and Ethnicity in an Alpine Valley'', New York: Academic Press, 1974; University of California Press 1999. * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Maps, charts, tables
Tyrolean History
(in German) {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Tyrol 1919 disestablishments States and territories established in 1140 Tyrol (region) History of the Alps History of South Tyrol Austrian Circle Historical regions in Austria