War of Spanish Succession on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European
 Unlike the crowns of France or Austria, that of Spain could be inherited through the female line. This allowed Charles' sisters Maria Theresa (1638–1683) and Margaret Theresa (1651–1673) to pass their rights onto the children of their respective marriages with Louis XIV and
Unlike the crowns of France or Austria, that of Spain could be inherited through the female line. This allowed Charles' sisters Maria Theresa (1638–1683) and Margaret Theresa (1651–1673) to pass their rights onto the children of their respective marriages with Louis XIV and
 With most of his objectives achieved by diplomacy, Louis now made a series of moves that combined to make war inevitable. The
With most of his objectives achieved by diplomacy, Louis now made a series of moves that combined to make war inevitable. The
 The importance of trade and economic interests to the participants is often underestimated; contemporaries viewed Dutch and English support for the Habsburg cause as primarily driven by a desire for access to Spanish markets in the Americas. Modern economists generally assume a constantly growing market, but the then dominant theory of Mercantilism viewed it as relatively static. Increasing one's share implied taking it from someone else, and the role of the state was to restrict foreign competition by attacking merchant ships and colonies.
This expanded the war to North America,
The importance of trade and economic interests to the participants is often underestimated; contemporaries viewed Dutch and English support for the Habsburg cause as primarily driven by a desire for access to Spanish markets in the Americas. Modern economists generally assume a constantly growing market, but the then dominant theory of Mercantilism viewed it as relatively static. Increasing one's share implied taking it from someone else, and the role of the state was to restrict foreign competition by attacking merchant ships and colonies.
This expanded the war to North America,
 British foreign policy was based on three general principles, which remained largely consistent from the 16th through the 20th centuries. The first, overriding all others, was to preserve a balance of power in Europe, an objective threatened by French expansion under Louis XIV. The second was to prevent the
British foreign policy was based on three general principles, which remained largely consistent from the 16th through the 20th centuries. The first, overriding all others, was to preserve a balance of power in Europe, an objective threatened by French expansion under Louis XIV. The second was to prevent the
 Despite being the dominant power within the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian and Imperial interests did not always coincide. The Habsburgs wanted to put Archduke Charles on the throne of an undivided Spanish Monarchy, while their Allies were fighting to prevent either the Bourbons or the Habsburgs from doing so. This divergence and Austria's financial collapse in 1703 meant the campaign in Spain was reliant on Anglo-Dutch naval support and after 1706, British funding. Particularly during the reign of Joseph I, the priority for the Habsburgs was to secure their southern borders from French intervention in northern Italy and suppress
Despite being the dominant power within the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian and Imperial interests did not always coincide. The Habsburgs wanted to put Archduke Charles on the throne of an undivided Spanish Monarchy, while their Allies were fighting to prevent either the Bourbons or the Habsburgs from doing so. This divergence and Austria's financial collapse in 1703 meant the campaign in Spain was reliant on Anglo-Dutch naval support and after 1706, British funding. Particularly during the reign of Joseph I, the priority for the Habsburgs was to secure their southern borders from French intervention in northern Italy and suppress
 In 1700, Spain remained a great power in terms of territory controlled, while recent research shows imports of bullion from the Americas actually reached their highest level between 1670 and 1700. However, this concealed major structural weaknesses; the vast majority of these imports were used to fund debt or pay foreign merchants. When the new Bourbon administration took over in 1701, they found the Empire bankrupt and effectively defenceless, with fewer than 15,000 troops in Spain itself and a navy consisting of 20 ships in total.
Almost constant warfare during the 17th century made the economy subject to long periods of low productivity and depression, and largely reliant upon others for its prosperity. In many ways, the continued existence of the Empire was not due to Spanish strength but to maintain a balance between the powers competing for a share of its markets. Despite fighting a series of wars against Spain from 1667 to 1697, France was also its most significant economic partner, supplying labour and controlling a large proportion of its foreign trade. This consideration was an important factor in the decision to name Philip heir. Its dependence on others was illustrated in 1703; despite the presence of an invading Allied army, the French ambassador urged Louis to allow Dutch and English merchants to purchase wool from Spanish farmers, "otherwise the flocks cannot be maintained".
Enacting political or economic reform was extremely complex since Habsburg Spain was a personal union between the Crowns of Castile and
In 1700, Spain remained a great power in terms of territory controlled, while recent research shows imports of bullion from the Americas actually reached their highest level between 1670 and 1700. However, this concealed major structural weaknesses; the vast majority of these imports were used to fund debt or pay foreign merchants. When the new Bourbon administration took over in 1701, they found the Empire bankrupt and effectively defenceless, with fewer than 15,000 troops in Spain itself and a navy consisting of 20 ships in total.
Almost constant warfare during the 17th century made the economy subject to long periods of low productivity and depression, and largely reliant upon others for its prosperity. In many ways, the continued existence of the Empire was not due to Spanish strength but to maintain a balance between the powers competing for a share of its markets. Despite fighting a series of wars against Spain from 1667 to 1697, France was also its most significant economic partner, supplying labour and controlling a large proportion of its foreign trade. This consideration was an important factor in the decision to name Philip heir. Its dependence on others was illustrated in 1703; despite the presence of an invading Allied army, the French ambassador urged Louis to allow Dutch and English merchants to purchase wool from Spanish farmers, "otherwise the flocks cannot be maintained".
Enacting political or economic reform was extremely complex since Habsburg Spain was a personal union between the Crowns of Castile and
 Over the course of the 17th century, the
Over the course of the 17th century, the
 The war in Italy primarily involved the Spanish-ruled Duchies of Milan and Mantua, considered essential to the security of Austria's southern borders. In 1701, French troops occupied both cities and
The war in Italy primarily involved the Spanish-ruled Duchies of Milan and Mantua, considered essential to the security of Austria's southern borders. In 1701, French troops occupied both cities and
 The first objective for the Grand Alliance in this theatre was to secure the Dutch frontiers, threatened by the alliance between France, Bavaria, and
The first objective for the Grand Alliance in this theatre was to secure the Dutch frontiers, threatened by the alliance between France, Bavaria, and
 British involvement was driven by safeguarding their trade routes in the Mediterranean. By putting Charles VI on the Spanish throne, they also hoped to gain commercial privileges within the Spanish Empire. The Habsburgs viewed Northern Italy, as well as suppressing the Hungarian revolt, as higher priorities, while, after 1704, the Dutch focused on Flanders. As a result, this theatre was largely dependent on British naval and military support; high casualties from disease made it a heavy drain on resources for little apparent benefit.
Spain was a union between the Crowns of Castile and
British involvement was driven by safeguarding their trade routes in the Mediterranean. By putting Charles VI on the Spanish throne, they also hoped to gain commercial privileges within the Spanish Empire. The Habsburgs viewed Northern Italy, as well as suppressing the Hungarian revolt, as higher priorities, while, after 1704, the Dutch focused on Flanders. As a result, this theatre was largely dependent on British naval and military support; high casualties from disease made it a heavy drain on resources for little apparent benefit.
Spain was a union between the Crowns of Castile and
 The close links between war and trade meant conflict extended beyond Europe, particularly in North America, where it is known as
The close links between war and trade meant conflict extended beyond Europe, particularly in North America, where it is known as
 Many Allied statesmen, including Marlborough, felt the terms seriously underestimated France's ability to continue the war and assumed Philip would abdicate on request. They also required the Spanish to accept Archduke Charles as king in his place, which they were clearly unwilling to do, as demonstrated by the failure of Allied campaigns to hold territory outside Catalonia. Although Louis was willing to abandon his ambitions in Spain, making war on his grandson was unacceptable, a stipulation so offensive that when made public the French resolved to fight on.
Marlborough's 1709 offensive in Northern France culminated in the
Many Allied statesmen, including Marlborough, felt the terms seriously underestimated France's ability to continue the war and assumed Philip would abdicate on request. They also required the Spanish to accept Archduke Charles as king in his place, which they were clearly unwilling to do, as demonstrated by the failure of Allied campaigns to hold territory outside Catalonia. Although Louis was willing to abandon his ambitions in Spain, making war on his grandson was unacceptable, a stipulation so offensive that when made public the French resolved to fight on.
Marlborough's 1709 offensive in Northern France culminated in the
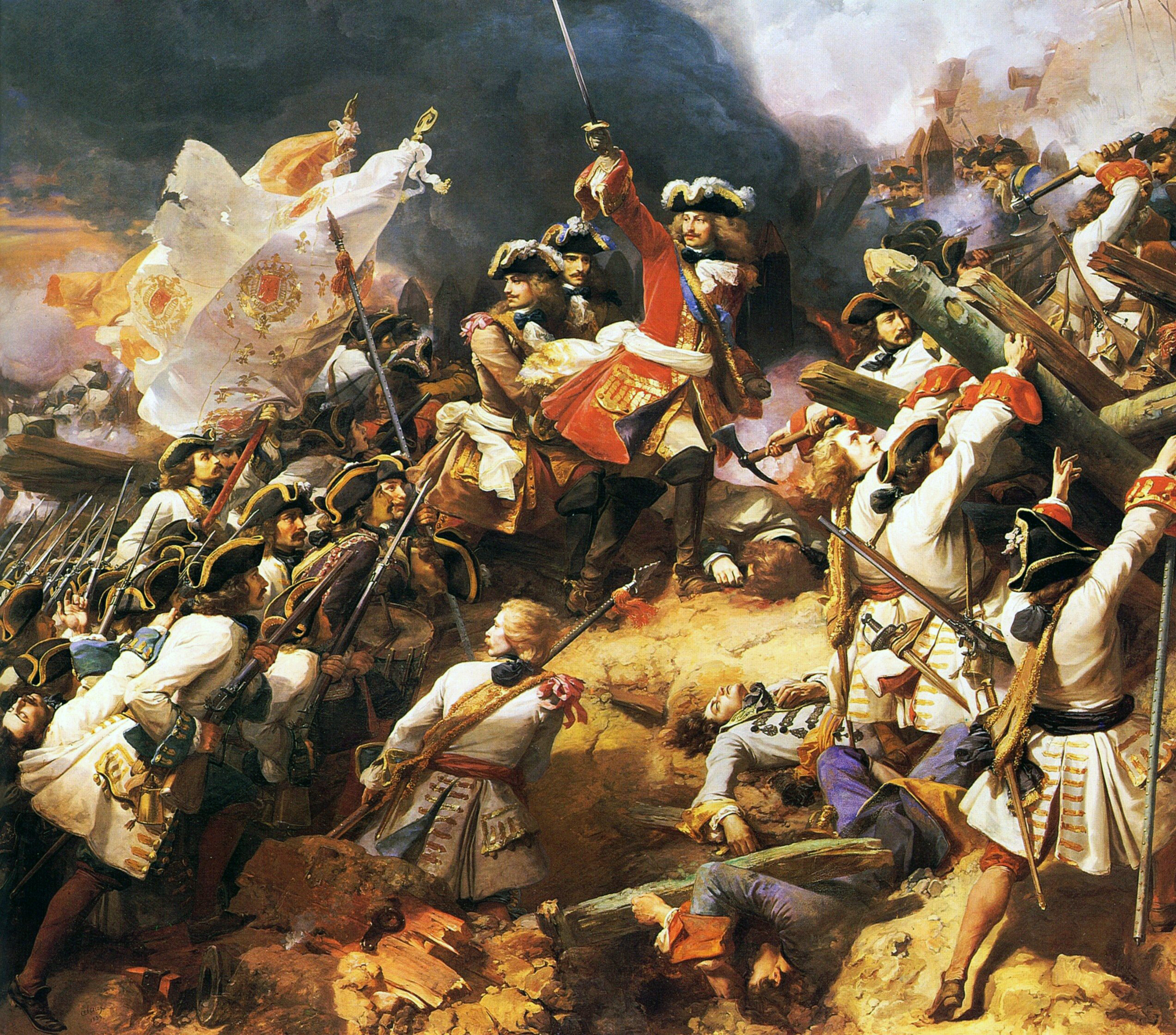 When negotiations resumed in March 1710 at
When negotiations resumed in March 1710 at
 Within weeks of the conference opening, events threatened the basis of the peace agreed between Britain and France. First, the French presented proposals awarding the Spanish Netherlands to Max Emmanuel of Bavaria and a minimal Barrier, leaving the Dutch with little to show for their huge investment of money and men. Second, a series of deaths left Louis XIV's two-year-old great-grandson, the future
Within weeks of the conference opening, events threatened the basis of the peace agreed between Britain and France. First, the French presented proposals awarding the Spanish Netherlands to Max Emmanuel of Bavaria and a minimal Barrier, leaving the Dutch with little to show for their huge investment of money and men. Second, a series of deaths left Louis XIV's two-year-old great-grandson, the future 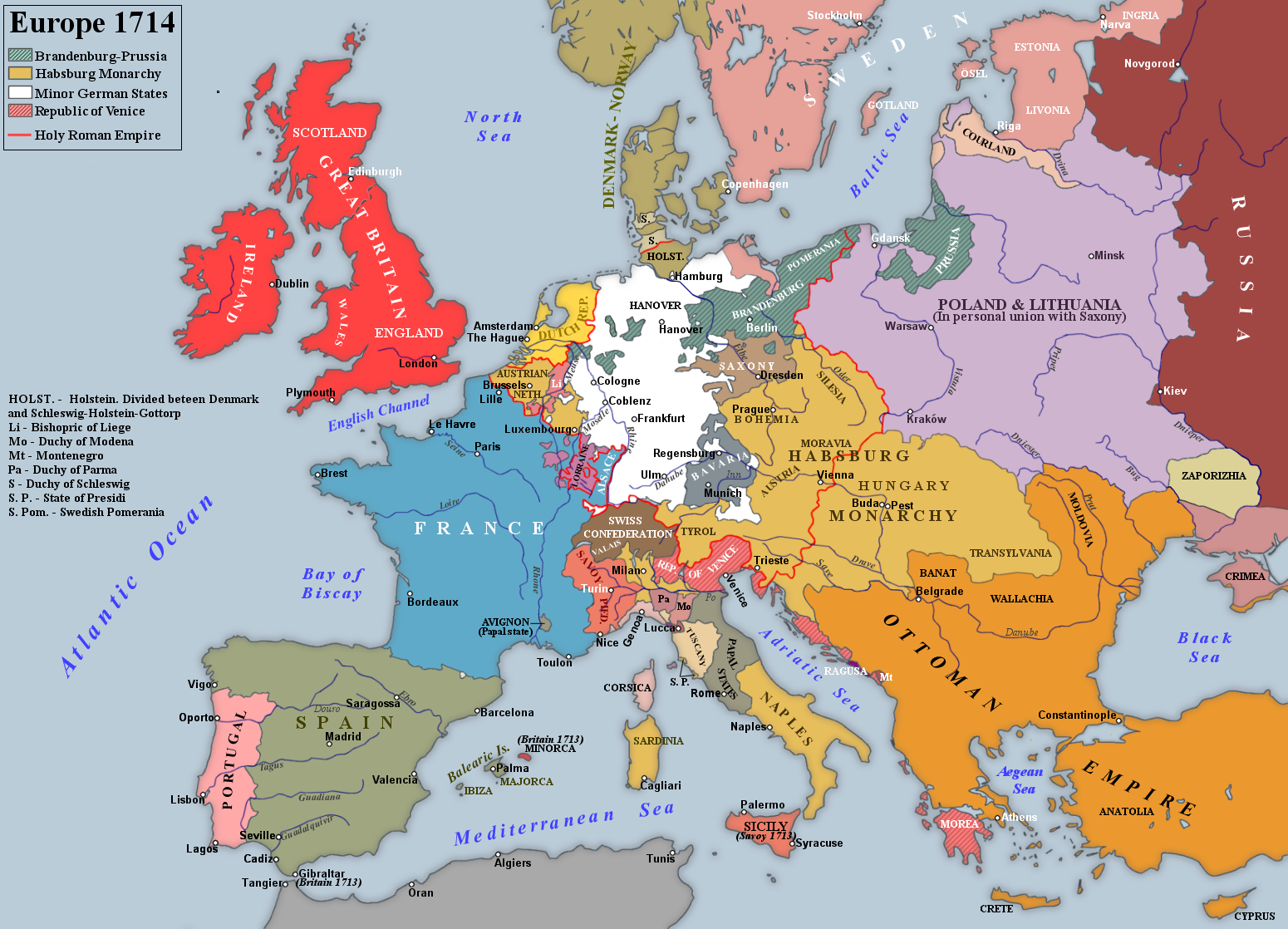 Charles withdrew from the Conference when France insisted he guarantee not to acquire Mantua or
Charles withdrew from the Conference when France insisted he guarantee not to acquire Mantua or
great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power inf ...
conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain
Charles II of Spain (''Spanish: Carlos II,'' 6 November 1661 – 1 November 1700), known as the Bewitched (''Spanish: El Hechizado''), was the last Habsburg ruler of the Spanish Empire. Best remembered for his physical disabilities and the War ...
in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
between his heirs, Philip of Anjou and Charles of Austria, and their respective supporters, among them Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
, Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
...
and Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
. Related conflicts include the 1700–1721 Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swed ...
, Rákóczi's War of Independence
Rákóczi's War of Independence (1703–11) was the first significant attempt to topple the rule of the Habsburgs over Hungary. The war was conducted by a group of noblemen, wealthy and high-ranking progressives and was led by Francis II Rák ...
in Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
, the Camisards revolt in southern France, Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In E ...
in North America and minor trade wars in India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
.
Although weakened by over a century of continuous conflict, Spain remained a global power whose territories included the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands ( Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the ...
, large parts of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, and much of the Americas, which meant its acquisition by either France or Austria potentially threatened the European balance of power
The European balance of power is the tenet in international relations that no single power should be allowed to achieve hegemony over a substantial part of Europe. During much of the Modern Age, the balance was achieved by having a small number of ...
. Attempts by Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of V ...
and William III of England
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from ...
to resolve the issue through diplomacy were rejected by the Spanish and Charles II named Louis' grandson, Philip of Anjou, as his heir. His proclamation as king of an undivided Spanish Empire on 16 November 1700 led to war, with France and Spain on one side and the Grand Alliance on the other.
The French held the advantage in the early stages, but were forced onto the defensive after 1706; however, by 1710 the Allies had failed to make any significant progress, while Bourbon victories in Spain had secured Philip's position as king. When Emperor Joseph I
, father = Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor
, mother = Eleonore Magdalene of Neuburg
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Vienna, Austria
, death_date =
, death_place = Vienna, Austria
, burial_place = Imperial Crypt, Vienna
, ...
died in 1711, Archduke Charles succeeded his brother as emperor, and the new British government initiated peace talks. Since only British subsidies kept their allies in the war, this resulted in the 1713–15 Peace of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne of ...
treaties, followed by the 1714 Treaties of Rastatt and Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden ...
.
Philip was confirmed as King of Spain in return for renouncing the right of himself or his descendants to inherit the French throne; the Spanish Empire remained largely intact, but ceded territories in Italy and the Low Countries to Austria and Savoy. Britain retained Gibraltar and Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capi ...
which it captured during the war, acquired significant trade concessions in the Spanish Americas, and replaced the Dutch as the leading maritime and commercial European power. The Dutch gained a strengthened defence line
A defense line or fortification line is a geographically-recognizable line of troops and armament, fortified and set up to protect a high-value location or defend territory.
A defense line may be based on natural difficult terrain features, su ...
in what was now the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
; although they remained a major commercial power, the cost of the war permanently damaged their economy.
France withdrew backing for the exiled Jacobites and recognised the Hanoverians as heirs to the British throne; ensuring a friendly Spain was a major achievement, but left them financially exhausted. The decentralisation of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
continued, with Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
, Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
and Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
increasingly acting as independent states. Combined with victories over the Ottomans, this meant Austria increasingly switched focus to southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alba ...
.
Background
Charles II of Spain
Charles II of Spain (''Spanish: Carlos II,'' 6 November 1661 – 1 November 1700), known as the Bewitched (''Spanish: El Hechizado''), was the last Habsburg ruler of the Spanish Empire. Best remembered for his physical disabilities and the War ...
succeeded his father Philip IV at the age of four in 1665. Subject to extended periods of ill-health for much of his life, his death was anticipated almost from birth, and the issue of his successor a matter of diplomatic debate for decades, the two main contenders being Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of V ...
and Emperor Leopold I
Leopold I (Leopold Ignaz Joseph Balthasar Franz Felician; hu, I. Lipót; 9 June 1640 – 5 May 1705) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia. The second son of Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor, by his first wife, Maria ...
. In the 1670 Secret Treaty of Dover
The Treaty of Dover, also known as the Secret Treaty of Dover, was a treaty between England and France signed at Dover on 1 June 1670. It required that Charles II of England would convert to the Roman Catholic Church at some future date and t ...
, Charles II of England agreed to support the rights of Louis XIV, while the 1689 Grand Alliance committed England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
and the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
to back those of Leopold.
In 1700, the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
included possessions in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands ( Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and the Americas, and though no longer the dominant great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power inf ...
, it remained largely intact. Since the Spanish refused to allow their Empire to be divided and its acquisition by either the Austrian Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
or French Bourbons
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spanish ...
would change the balance of power, its inheritance led to a war that involved most of Europe. The 1700–1721 Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swed ...
is considered a connected conflict, since it affected the involvement of states such as Sweden, Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
, Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway ( Danish and Norwegian: ) was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (including the then Norwegian overseas possessions: the Faroe ...
and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
.
During the 1688–1697 Nine Years' War, armies grew from an average of 25,000 in 1648 to over 100,000 by 1697, which required a level of expenditure unsustainable for pre-industrial economies. The 1690s also marked the lowest point of the Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of regional cooling, particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. It was not a true ice age of global extent. The term was introduced into scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939. Ma ...
, a period of cold and wet weather that drastically reduced crop yields across Europe. The Great Famine of 1695–1697
The Great Famine of 1695–1697, or simply the Great Famine, was a catastrophic famine that affected the present Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Norway and Sweden, all of which belonged to the Swedish Empire with the exception of Norway. The areas worst ...
killed an estimated 15–25% of the population in present-day Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
, Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
and the Baltic states
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
, plus another two million in France and Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative Regions ...
. The 1697 Treaty of Ryswick
The Peace of Ryswick, or Rijswijk, was a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Rijswijk between 20 September and 30 October 1697. They ended the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War between France and the Grand Alliance, which included England ...
was the result of mutual exhaustion and the acceptance by Louis that France could no longer achieve its objectives without allies. Since the question of the succession was left unresolved, Leopold signed the treaty with extreme reluctance in October 1697, by which time it was clear Charles would die childless and a resumption of hostilities appeared inevitable.
Partition treaties
 Unlike the crowns of France or Austria, that of Spain could be inherited through the female line. This allowed Charles' sisters Maria Theresa (1638–1683) and Margaret Theresa (1651–1673) to pass their rights onto the children of their respective marriages with Louis XIV and
Unlike the crowns of France or Austria, that of Spain could be inherited through the female line. This allowed Charles' sisters Maria Theresa (1638–1683) and Margaret Theresa (1651–1673) to pass their rights onto the children of their respective marriages with Louis XIV and Emperor Leopold
Leopold I (Leopold Ignaz Joseph Balthasar Franz Felician; hu, I. Lipót; 9 June 1640 – 5 May 1705) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia. The second son of Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor, by his first wife, Maria An ...
. Louis sought to avoid conflict over the issue through direct negotiation with his main opponent William III of England
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from ...
, while excluding the Spanish.
Maria Antonia (1669–1692), daughter of Leopold and Margaret, married Maximillian Emanuel of Bavaria in 1685, and on 28 October 1692, they had a son, Joseph Ferdinand. Under the October 1698 Treaty of the Hague between France, Britain and the Dutch Republic, five-year old Joseph was designated heir to Charles II; in return, France and Austria would receive parts of Spain's European territories. Charles refused to accept this; on 14 November 1698, he published a will leaving an undivided Spanish monarchy to Joseph Ferdinand. However, the latter's death from smallpox in February 1699 undid these arrangements.
In 1685, Maria Antonia passed her claim to the Spanish throne onto Leopold's sons, Joseph
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the m ...
and Archduke Charles. Her right to do so was doubtful, but Louis and William used this to devise the 1700 Treaty of London The Treaty of London or London Convention or similar may refer to:
*Treaty of London (1358), established a truce between England and France following the Battle of Poitiers
*Treaty of London (1359), which ceded western France to England
*Treaty of ...
. Archduke Charles became the new heir, while France, Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
...
and Austria received territorial compensation; however, since neither Leopold or Charles agreed, the treaty was largely pointless. By early October 1700, Charles was clearly dying; his final will left the throne to Louis XIV's grandson Philip, Duke of Anjou; if he refused, the offer would pass to his younger brother the Duke of Berry
Duke of Berry (french: Duc de Berry) or Duchess of Berry (french: Duchesse de Berry) was a title in the Peerage of France. The Duchy of Berry, centred on Bourges, was originally created as an appanage for junior members of the French royal fami ...
, followed by Archduke Charles.
Charles died on 1 November 1700, and on the 9th, Spanish ambassadors formally offered the throne to Philip. Louis briefly considered refusing; although it meant the succession of Archduke Charles, insisting William help him enforce the Treaty of London meant he might achieve his territorial aims without fighting. However, his son the Dauphin rejected the idea; French diplomats also advised Austria would fight regardless, while neither the British or Dutch would go to war for a settlement intended to avoid war. Louis therefore accepted on behalf of his grandson, who was proclaimed Philip V of Spain on 16 November 1700.
Prelude to war
 With most of his objectives achieved by diplomacy, Louis now made a series of moves that combined to make war inevitable. The
With most of his objectives achieved by diplomacy, Louis now made a series of moves that combined to make war inevitable. The Tory
A Tory () is a person who holds a political philosophy known as Toryism, based on a British version of traditionalism and conservatism, which upholds the supremacy of social order as it has evolved in the English culture throughout history. The ...
majority in the English Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. ...
objected to the Partition Treaties, chiefly the French acquisition of Sicily, an important link in the lucrative Levant trade. However, a foreign diplomat observed their refusal to become involved in a European war was true "only so long as English commerce does not suffer". Louis either failed to appreciate this or decided to ignore it and his actions gradually eroded Tory opposition.
In early 1701, Louis registered Philip's claim to the French throne with the Paris Parlement
A ''parlement'' (), under the French Ancien Régime, was a provincial appellate court of the Kingdom of France. In 1789, France had 13 parlements, the oldest and most important of which was the Parlement of Paris. While both the modern Fr ...
, raising the possibility of union with Spain, contrary to Charles' will, though Philip was only third in the French succession. In February, the Spanish-controlled Duchies of Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard language, Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the List of cities in Italy, second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 ...
and Mantua
Mantua ( ; it, Mantova ; Lombard language, Lombard and la, Mantua) is a city and ''comune'' in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the Province of Mantua, province of the same name.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture ...
in Northern Italy announced their support for Philip and accepted French troops. Combined with efforts to build an alliance between France and Imperial German states in Swabia and Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper F ...
, these were challenges Leopold could not ignore.
Helped by the Viceroy, Max Emanuel of Bavaria, French troops replaced Dutch garrisons in the 'Barrier' fortresses in the Spanish Netherlands, granted at Ryswick. It also threatened the Dutch monopoly over the Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to ...
granted by the 1648 Peace of Münster
The Peace of Münster was a treaty between the Lords States General of the Seven United Netherlands and the Spanish Crown, the terms of which were agreed on 30 January 1648. The treaty, parallelly negotiated to but not part of the Peace of We ...
, while French control of Antwerp and Ostend
Ostend ( nl, Oostende, ; french: link=no, Ostende ; german: link=no, Ostende ; vls, Ostende) is a coastal city and municipality, located in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariake ...
would allow them to blockade the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or (Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kan ...
at will. Combined with other French actions that threatened English trade, this produced a clear majority for war and in May 1701, Parliament urged William to negotiate an anti-French alliance.
On 7 September, Leopold, the Dutch Republic and Britain signed the Treaty of The Hague renewing the 1689 Grand Alliance. Its provisions included securing the Dutch Barrier in the Spanish Netherlands, the Protestant succession in England and Scotland and an independent Spain but did not refer to placing Archduke Charles on the Spanish throne. When the exiled James II of England
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Re ...
died on 16 September 1701, Louis reneged on his recognition of the Protestant William III as king of England and Scotland and supported the claim of James' son, James Francis Edward Stuart
James Francis Edward Stuart (10 June 16881 January 1766), nicknamed the Old Pretender by Whigs, was the son of King James II and VII of England, Scotland and Ireland, and his second wife, Mary of Modena. He was Prince of Wales fr ...
. War became inevitable and when William himself died in March 1702, his successor Queen Anne confirmed her support for the Treaty of the Hague. The Dutch now led by Grand Pensionary Anthonie Heinsius
Anthonie (or Antonius) Heinsius (23 November 1641, Delft – 3 August 1720, The Hague) was a Dutch statesman who served as Grand Pensionary of Holland from 1689 to his death in 1720.
Life
Heinsius was born at Delft on 23 November 1641, son of ...
did the same, despite French hopes that without a Stadtholder
In the Low Countries, ''stadtholder'' ( nl, stadhouder ) was an office of steward, designated a medieval official and then a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and ...
the Republic would be torn apart internally. On 15 May the Grand Alliance declared war on France, followed by the Imperial Diet on 30 September.
General strategic drivers
 The importance of trade and economic interests to the participants is often underestimated; contemporaries viewed Dutch and English support for the Habsburg cause as primarily driven by a desire for access to Spanish markets in the Americas. Modern economists generally assume a constantly growing market, but the then dominant theory of Mercantilism viewed it as relatively static. Increasing one's share implied taking it from someone else, and the role of the state was to restrict foreign competition by attacking merchant ships and colonies.
This expanded the war to North America,
The importance of trade and economic interests to the participants is often underestimated; contemporaries viewed Dutch and English support for the Habsburg cause as primarily driven by a desire for access to Spanish markets in the Americas. Modern economists generally assume a constantly growing market, but the then dominant theory of Mercantilism viewed it as relatively static. Increasing one's share implied taking it from someone else, and the role of the state was to restrict foreign competition by attacking merchant ships and colonies.
This expanded the war to North America, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, and other parts of Asia, with tariffs used as a policy weapon. From 1690 to 1704, English import duties on foreign goods increased by 400%, and the 1651–1663 Navigation Acts
The Navigation Acts, or more broadly the Acts of Trade and Navigation, were a long series of English laws that developed, promoted, and regulated English ships, shipping, trade, and commerce between other countries and with its own colonies. The ...
were a major factor in the Anglo-Dutch Wars
The Anglo–Dutch Wars ( nl, Engels–Nederlandse Oorlogen) were a series of conflicts mainly fought between the Dutch Republic and England (later Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain) from mid-17th to late 18th century. The first three w ...
. On 6 September 1700, France banned the import of English manufactured goods such as cloth, and imposed prohibitive duties on a wide range of others.
Armies of the Nine Years' War often exceeded 100,000 men, levels unsustainable for pre-industrial economies; those of 1701–1714 averaged around 35,000 to 50,000. Dependence on water-borne transport for supplying these numbers meant campaigns were focused on rivers like the Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
and Adda, which limited operations in poor areas like Northern Spain. Better logistics, unified command, and simpler internal lines of communication gave Bourbon armies an advantage over their opponents.
Strategic objectives by participant
Great Britain
 British foreign policy was based on three general principles, which remained largely consistent from the 16th through the 20th centuries. The first, overriding all others, was to preserve a balance of power in Europe, an objective threatened by French expansion under Louis XIV. The second was to prevent the
British foreign policy was based on three general principles, which remained largely consistent from the 16th through the 20th centuries. The first, overriding all others, was to preserve a balance of power in Europe, an objective threatened by French expansion under Louis XIV. The second was to prevent the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
being controlled by a hostile power or one stronger than Britain; this included both the Spanish Netherlands and the Dutch Republic, whose deep harbours and prevailing winds made her a natural embarkation point for an attack on England, as demonstrated in 1688. The third was to maintain a navy strong enough to protect British trade, control her waters and launch attacks on her enemies' commercial routes and coastal areas.
Alignment on reducing the power of France and securing the Protestant succession for the British throne masked differences on how to achieve them. In general, the Tories favoured a mercantilist strategy of using the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
to attack French and Spanish trade while protecting and expanding their own; land commitments were viewed as expensive and primarily of benefit to others. The Whigs argued France could not be defeated by seapower alone, making a Continental strategy essential, while Britain's financial strength made it the only member of the Alliance able to operate on all fronts against France.
Dutch Republic
Although the EnglishDuke of Marlborough
General John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, 1st Prince of Mindelheim, 1st Count of Nellenburg, Prince of the Holy Roman Empire, (26 May 1650 – 16 June 1722 O.S.) was an English soldier and statesman whose career spanned the reign ...
was Allied commander in the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, the Dutch provided much of the manpower, and strategy in this theatre was subject to their approval. The 1672 to 1678 Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-No ...
showed the Spanish could not defend the Southern Netherlands, and so the 1697 Treaty of Ryswick
The Peace of Ryswick, or Rijswijk, was a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Rijswijk between 20 September and 30 October 1697. They ended the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War between France and the Grand Alliance, which included England ...
allowed the Dutch to place garrisons in eight key cities. They hoped this barrier would provide the strategic depth needed to protect their commercial and demographic heartlands around Amsterdam against attack from the south. They were quickly over-run in 1701, but Dutch priorities were to re-establish and strengthen the Barrier fortresses, retain control of the economically vital Scheldt estuary, and gain access to trade in the Spanish Empire.
Austria and the Holy Roman Empire
 Despite being the dominant power within the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian and Imperial interests did not always coincide. The Habsburgs wanted to put Archduke Charles on the throne of an undivided Spanish Monarchy, while their Allies were fighting to prevent either the Bourbons or the Habsburgs from doing so. This divergence and Austria's financial collapse in 1703 meant the campaign in Spain was reliant on Anglo-Dutch naval support and after 1706, British funding. Particularly during the reign of Joseph I, the priority for the Habsburgs was to secure their southern borders from French intervention in northern Italy and suppress
Despite being the dominant power within the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian and Imperial interests did not always coincide. The Habsburgs wanted to put Archduke Charles on the throne of an undivided Spanish Monarchy, while their Allies were fighting to prevent either the Bourbons or the Habsburgs from doing so. This divergence and Austria's financial collapse in 1703 meant the campaign in Spain was reliant on Anglo-Dutch naval support and after 1706, British funding. Particularly during the reign of Joseph I, the priority for the Habsburgs was to secure their southern borders from French intervention in northern Italy and suppress Rákóczi's War of Independence
Rákóczi's War of Independence (1703–11) was the first significant attempt to topple the rule of the Habsburgs over Hungary. The war was conducted by a group of noblemen, wealthy and high-ranking progressives and was led by Francis II Rák ...
in Hungary.
Much of the Spanish nobility resented what they considered to be the arrogance of the Austrians, a key factor in the selection of Philip as their preferred candidate in 1700. In return for British support, Charles agreed to major commercial concessions within the Empire, as well as accepting British control of Gibraltar and Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capi ...
. These made him widely unpopular at all levels of Spanish society, and he was never able to sustain himself outside the coastal regions, which could be supplied by the Royal Navy.
The Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a German dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including Bavaria, the Palatinate, Holland and Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland), Denmark, Norway, Hungary (with Romania), Bohemia, the Electorate ...
-controlled states of Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
, Liège, and Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
allied with France, but the vast majority of the Empire remained neutral, or limited their involvement to the supply of mercenaries. Like Bavaria, the larger entities pursued their own policies; his claim to the Polish crown meant Augustus of Saxony
Augustus (31 July 152611 February 1586) was Elector of Saxony from 1553 to 1586.
First years
Augustus was born in Freiberg, the youngest child and third (but second surviving) son of Henry IV, Duke of Saxony, and Catherine of Mecklenburg. He ...
focused on the Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swed ...
, while Frederick I Frederick I may refer to:
* Frederick of Utrecht or Frederick I (815/16–834/38), Bishop of Utrecht.
* Frederick I, Duke of Upper Lorraine (942–978)
* Frederick I, Duke of Swabia (1050–1105)
* Frederick I, Count of Zol ...
made his support dependent on Leopold recognising Prussia as a kingdom and making it an equal member of the Grand Alliance. Since George, Elector Hanover, was also heir to the British throne, his support was more reliable, but the suspicion remained the interests of Hanover came first.
France
Under Louis XIV, France was the most powerful state in Europe, with revenue-generating capacities that far exceeded those of its rivals. Its geographical position provided enormous tactical flexibility; unlike Austria, it had a navy, and as the campaigns of 1708–1710 proved, even under severe pressure it could defend its borders. The Nine Years' War had shown France could not impose its objectives without support but the alliance with Spain and Bavaria made a successful outcome far more likely. Apart from denying an undivided Spanish Monarchy to others, Louis's objectives were to secure his borders with the Holy Roman Empire, weaken his rival Austria, and increase French commercial strength through access to trade with the Americas.Spain
 In 1700, Spain remained a great power in terms of territory controlled, while recent research shows imports of bullion from the Americas actually reached their highest level between 1670 and 1700. However, this concealed major structural weaknesses; the vast majority of these imports were used to fund debt or pay foreign merchants. When the new Bourbon administration took over in 1701, they found the Empire bankrupt and effectively defenceless, with fewer than 15,000 troops in Spain itself and a navy consisting of 20 ships in total.
Almost constant warfare during the 17th century made the economy subject to long periods of low productivity and depression, and largely reliant upon others for its prosperity. In many ways, the continued existence of the Empire was not due to Spanish strength but to maintain a balance between the powers competing for a share of its markets. Despite fighting a series of wars against Spain from 1667 to 1697, France was also its most significant economic partner, supplying labour and controlling a large proportion of its foreign trade. This consideration was an important factor in the decision to name Philip heir. Its dependence on others was illustrated in 1703; despite the presence of an invading Allied army, the French ambassador urged Louis to allow Dutch and English merchants to purchase wool from Spanish farmers, "otherwise the flocks cannot be maintained".
Enacting political or economic reform was extremely complex since Habsburg Spain was a personal union between the Crowns of Castile and
In 1700, Spain remained a great power in terms of territory controlled, while recent research shows imports of bullion from the Americas actually reached their highest level between 1670 and 1700. However, this concealed major structural weaknesses; the vast majority of these imports were used to fund debt or pay foreign merchants. When the new Bourbon administration took over in 1701, they found the Empire bankrupt and effectively defenceless, with fewer than 15,000 troops in Spain itself and a navy consisting of 20 ships in total.
Almost constant warfare during the 17th century made the economy subject to long periods of low productivity and depression, and largely reliant upon others for its prosperity. In many ways, the continued existence of the Empire was not due to Spanish strength but to maintain a balance between the powers competing for a share of its markets. Despite fighting a series of wars against Spain from 1667 to 1697, France was also its most significant economic partner, supplying labour and controlling a large proportion of its foreign trade. This consideration was an important factor in the decision to name Philip heir. Its dependence on others was illustrated in 1703; despite the presence of an invading Allied army, the French ambassador urged Louis to allow Dutch and English merchants to purchase wool from Spanish farmers, "otherwise the flocks cannot be maintained".
Enacting political or economic reform was extremely complex since Habsburg Spain was a personal union between the Crowns of Castile and Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to so ...
, each with very different political cultures. Most of Philip's support came from the Castilian elite. The Spanish Netherlands had been governed by Bavaria since 1690, while links with Italy, traditionally the major source of Spanish recruits and funding, had been weakened by decades of neglect and heavy taxation. It was widely, if reluctantly, accepted in Madrid that preserving an independent Spanish empire required comprehensive reforms, including elimination of the privileges or ''Fuero
(), (), () or () is a Spanish legal term and concept. The word comes from Latin , an open space used as a market, tribunal and meeting place. The same Latin root is the origin of the French terms and , and the Portuguese terms and ; all ...
s'' held by the Aragonese states. It was no coincidence Archduke Charles had strong support in areas which were part of the Crown of Aragon, including Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
and Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the autonomous community of Valencia and the third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. The wider urban area al ...
.
Savoy
 Over the course of the 17th century, the
Over the course of the 17th century, the Savoyard state
The Savoyard state is a term of art used by historians to denote collectively all of the states ruled by the counts and dukes of Savoy from the Middle Ages to the formation of the Kingdom of Italy. At the end of the 17th century, its population ...
, generally known as Savoy, sought to replace Spain as the dominant power in Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative Regions ...
. Savoy consisted of two main geographic segments; Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, which contained the capital Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. Th ...
, and the Duchy of Aosta
__NOTOC__
The Duchy of Aosta, originally the County of Aosta, was a realm ruled by the House of Savoy from the early 11th century until the late 18th, when its independent institutions were aligned with those of the Principality of Piedmont. The t ...
on the Italian side of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, ...
, with the Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy ( it, Ducato di Savoia; french: Duché de Savoie) was a country in Western Europe that existed from 1416.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy for Amadeus VIII. The du ...
and County of Nice
The County of Nice (french: Comté de Nice / Pays Niçois, it, Contea di Nizza/Paese Nizzardo, Niçard oc, Contèa de Niça/País Niçard) is a historical region of France located around the southeastern city of Nice and roughly equivalent t ...
in Transalpine France. The latter were almost impossible to defend and combined with the anti-Habsburg policy pursued by Louis XIV and his predecessors, this meant Savoy generally sided with France. However, Piedmont provided foreign powers access to the restive southern French provinces of the Dauphiné
The Dauphiné (, ) is a former province in Southeastern France, whose area roughly corresponded to that of the present departments of Isère, Drôme and Hautes-Alpes. The Dauphiné was originally the Dauphiné of Viennois.
In the 12th centu ...
and Vaunage, former Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bez ...
strongholds with a long history of rebellion. This provided Victor Amadeus II
Victor Amadeus II (Vittorio Amedeo Francesco; 14 May 166631 October 1732) was Duke of Savoy from 1675 to 1730. He also held the titles of Prince of Piedmont, Duke of Montferrat, Marquis of Saluzzo and Count of Aosta, Moriana and Nice.
Louis XIV ...
with a degree of leverage, allowing him to manoeuvre between opposing parties in order to expand his territories.
During the Nine Years' War in 1690, Savoy joined the Grand Alliance before agreeing a separate peace with France in 1696. The accession of Philip V in 1701 led to a reversal of long-standing strategic policy, with France now supporting the Spanish position in Lombardy, rather than seeking to weaken it, and Austria doing the opposite. While Victor Amadeus initially allied Savoy with France, his long-term goal was the acquisition of Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan ( it, Ducato di Milano; lmo, Ducaa de Milan) was a state in northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city sinc ...
, which neither the Bourbons or Habsburgs would relinquish voluntarily. In fact, as discussed elsewhere in this article, securing his borders in Italy was of greater concern to Emperor Leopold than Spain itself. This meant Britain was the only power inclined to help Victor Amadeus achieve this objective and he changed sides in 1703 after the Royal Navy won control of the Western Mediterranean.
Military campaigns 1701–1708
Italy
 The war in Italy primarily involved the Spanish-ruled Duchies of Milan and Mantua, considered essential to the security of Austria's southern borders. In 1701, French troops occupied both cities and
The war in Italy primarily involved the Spanish-ruled Duchies of Milan and Mantua, considered essential to the security of Austria's southern borders. In 1701, French troops occupied both cities and Victor Amadeus II
Victor Amadeus II (Vittorio Amedeo Francesco; 14 May 166631 October 1732) was Duke of Savoy from 1675 to 1730. He also held the titles of Prince of Piedmont, Duke of Montferrat, Marquis of Saluzzo and Count of Aosta, Moriana and Nice.
Louis XIV ...
, Duke of Savoy, allied with France, his daughter Maria Luisa Maria Luisa may refer to:
People
* Anna Maria Luisa de' Medici (1667–1743), last lineal descent of the House of Medici
* Maria Luisa Ambrosini (20th century), non-fiction author
* Maria Luisa, Duchess of Lucca (1782–1824), Queen of Etruria ...
marrying Philip V. In May 1701, an Imperial army under Prince Eugene of Savoy
Prince Eugene Francis of Savoy–Carignano, (18 October 1663 – 21 April 1736) better known as Prince Eugene, was a Generalfeldmarschall, field marshal in the army of the Holy Roman Empire and of the Austrian Habsburg dynasty during the 17th a ...
moved into Northern Italy; by February 1702, victories at Carpi, Chiari and Cremona
Cremona (, also ; ; lmo, label= Cremunés, Cremùna; egl, Carmona) is a city and ''comune'' in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po river in the middle of the ''Pianura Padana'' (Po Valley). It is the capital of the ...
forced the French behind the Adda river.
Vendôme
Vendôme (, ) is a subprefecture of the department of Loir-et-Cher, France. It is also the department's third-biggest commune with 15,856 inhabitants (2019).
It is one of the main towns along the river Loir. The river divides itself at the ent ...
, one of the best French generals, took command and was substantially reinforced; Prince Eugene managed a draw at the Battle of Luzzara but the French recovered most of the territory lost the year before. In October 1703, Victor Amadeus declared war on France; by May 1706, the French held most of Savoy except Turin while victories at Cassano and Calcinato forced the Imperialists into the Trentino valley.
However, in July 1706 Vendôme and any available forces were sent to reinforce France's northern frontier after the defeat at Ramillies. Reinforced by German auxiliaries led by Leopold of Anhalt-Dessau, Prince Eugene broke the Siege of Turin in September; despite a minor French victory at Castiglione, the war in Italy was over. To the fury of his allies, in the March 1707 Convention of Milan Emperor Joseph gave French troops in Lombardy free passage to Southern France.
A combined Savoyard-Imperial attack on the French base of Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label=Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is the ...
planned for April was postponed when Imperial troops were diverted to seize the Spanish Bourbon Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
. By the time they besieged Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label=Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is the ...
in August, the French were too strong, and they were forced to withdraw. By the end of 1707, fighting in Italy ceased, apart from small-scale attempts by Victor Amadeus to recover Nice and Savoy.
Low Countries, Rhine and Danube
 The first objective for the Grand Alliance in this theatre was to secure the Dutch frontiers, threatened by the alliance between France, Bavaria, and
The first objective for the Grand Alliance in this theatre was to secure the Dutch frontiers, threatened by the alliance between France, Bavaria, and Joseph Clemens of Bavaria
Joseph Clemens of Bavaria (german: Joseph Clemens von Bayern) (5 December 1671 – 12 November 1723) was a member of the Wittelsbach dynasty of Bavaria and Archbishop-Elector of Cologne from 1688 to 1723.
Biography
The third son of Ferdina ...
, ruler of Liège and Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
. During 1702, the Barrier fortresses were retaken along with Kaiserswerth
Kaiserswerth is one of the oldest quarters of the City of Düsseldorf, part of Borough 5. It is in the north of the city and next to the river Rhine. It houses the where Florence Nightingale worked.
Kaiserswerth has an area of , and 7,923 inh ...
, Venlo
Venlo () is a city and municipality in the southeastern Netherlands, close to the border with Germany. It is situated in the province of Limburg, about 50 km east of the city of Eindhoven, 65 km north east of the provincial capital Maastricht, a ...
, Roermond
Roermond (; li, Remunj or ) is a city, municipality, and diocese in the Limburg province of the Netherlands. Roermond is a historically important town on the lower Roer on the east bank of the river Meuse. It received town rights in 1231. Ro ...
and Liège. The 1703 campaign was marred by Allied conflicts over strategy; they failed to take Antwerp, and the Dutch narrowly escaped defeat at Ekeren
Ekeren () is a northern district of the municipality of Antwerp in the Flemish Region of Belgium. The suburb celebrated its 850th birthday in 2005; the name of the town was first mentioned in 1155, as "Hecerna".
The name possibly originates from ...
in June, which led to bitter recriminations.
On the Upper Rhine
The Upper Rhine (german: Oberrhein ; french: Rhin Supérieur) is the section of the Rhine between Basel in Switzerland and Bingen in Germany, surrounded by the Upper Rhine Plain. The river is marked by Rhine-kilometres 170 to 529 (the ...
, Imperial forces under Louis of Baden remained on the defensive, although they took Landau
Landau ( pfl, Landach), officially Landau in der Pfalz, is an autonomous (''kreisfrei'') town surrounded by the Südliche Weinstraße ("Southern Wine Route") district of southern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a university town (since 1990 ...
in 1702. Throughout 1703, French victories at Friedlingen
The Battle of Friedlingen was fought in 1702 between France and the Holy Roman Empire. The Imperial forces were led by Louis William, Margrave of Baden-Baden, while the French were led by Claude Louis Hector de Villars. The French were victorio ...
, Höchstädt and Speyerbach with the capture of Kehl
Kehl (; gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Kaal) is a town in southwestern Germany in the Ortenaukreis, Baden-Württemberg. It is on the river Rhine, directly opposite the French city of Strasbourg, with which it shares some municipal servicesfor exa ...
, Breisach
Breisach (formerly Altbreisach; Low Alemannic: ''Alt-Brisach'') is a town with approximately 16,500 inhabitants, situated along the Rhine in the Rhine Valley, in the district Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald, Baden-Württemberg, Germany, about halfway b ...
and Landau directly threatened Vienna.
In 1704, Franco-Bavarian forces continued their advance with the Austrians struggling to suppress Rákóczi's revolt in Hungary. To relieve the pressure, Marlborough marched up the Rhine, joined forces with Louis of Baden and Prince Eugene, and crossed the Danube on 2 July. Allied victory at Blenheim on 13 August forced Bavaria out of the war and the Treaty of Ilbersheim placed it under Austrian rule.
Allied efforts to exploit their victory in 1705 foundered on poor co-ordination, tactical disputes and command rivalries, while the ruthless rule of Leopold's successor Joseph in Bavaria caused a brief but vicious peasant revolt
This is a chronological list of conflicts in which peasants played a significant role.
Background
The history of peasant wars spans over two thousand years. A variety of factors fueled the emergence of the peasant revolt phenomenon, including:
...
. In May 1706, an Allied force under Marlborough shattered a French army at the Battle of Ramillies
The Battle of Ramillies (), fought on 23 May 1706, was a battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. For the Grand Alliance – Austria, England, and the Dutch Republic – the battle had followed an indecisive campaign against the Bourbon a ...
and the Spanish Netherlands fell to the Allies in under two weeks. France assumed a defensive posture for the rest of the war; despite the loss of strongpoints like Lille
Lille ( , ; nl, Rijsel ; pcd, Lile; vls, Rysel) is a city in the northern part of France, in French Flanders. On the river Deûle, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France region, the prefecture of the Nord ...
, they prevented the Allies from making a decisive breach in their frontiers. By 1712, the overall position remained largely unchanged from 1706.
Spain and Portugal
 British involvement was driven by safeguarding their trade routes in the Mediterranean. By putting Charles VI on the Spanish throne, they also hoped to gain commercial privileges within the Spanish Empire. The Habsburgs viewed Northern Italy, as well as suppressing the Hungarian revolt, as higher priorities, while, after 1704, the Dutch focused on Flanders. As a result, this theatre was largely dependent on British naval and military support; high casualties from disease made it a heavy drain on resources for little apparent benefit.
Spain was a union between the Crowns of Castile and
British involvement was driven by safeguarding their trade routes in the Mediterranean. By putting Charles VI on the Spanish throne, they also hoped to gain commercial privileges within the Spanish Empire. The Habsburgs viewed Northern Italy, as well as suppressing the Hungarian revolt, as higher priorities, while, after 1704, the Dutch focused on Flanders. As a result, this theatre was largely dependent on British naval and military support; high casualties from disease made it a heavy drain on resources for little apparent benefit.
Spain was a union between the Crowns of Castile and Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to so ...
, which was divided into the Principality of Catalonia
The Principality of Catalonia ( ca, Principat de Catalunya, la, Principatus Cathaloniæ, oc, Principat de Catalonha, es, Principado de Cataluña) was a Middle Ages, medieval and early modern state (polity), state in the northeastern Iberian P ...
, plus the Kingdoms of Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to so ...
, Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the autonomous community of Valencia and the third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. The wider urban area al ...
, Majorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest island in the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain and located in the Mediterranean.
The capital of the island, Palma, is also the capital of the autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. The Bale ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
and Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label= Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, af ...
. In 1701, Majorca, Naples, Sicily, and Sardinia declared for Philip, while a mixture of anti-Castilian and anti-French sentiment meant the others supported Archduke Charles, the most important being Catalonia. Allied victory at Vigo Bay
Vigo ( , , , ) is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, th ...
in October 1702 persuaded Peter II of Portugal
'' Dom'' Pedro II (Peter II; 26 April 1648 – 9 December 1706), nicknamed "the Pacific", was King of Portugal from 1683 until his death, previously serving as regent for his brother Afonso VI from 1668 until his own accession. He was the fifth ...
to switch sides, giving them an operational base in this area.
Archduke Charles landed at Lisbon in March 1704 to begin a land campaign, while the British-Dutch capture of Gibraltar
The Capture of Gibraltar by Anglo-Dutch forces of the Grand Alliance occurred between 1 and 4 August 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession. Since the beginning of the war the Alliance had been looking for a harbour in the Iberian Penins ...
was a significant blow to Bourbon prestige. An attempt to retake it was defeated in August, with a land siege being abandoned in April 1705. The 1705 Pact of Genoa
The Pact of Genoa was a military and political alliance formed in 1705 between the Kingdom of England and landowning Austracists (known as Vigatans) on behalf of the Principality of Catalonia within the framework set by the War of Spanish Succe ...
between Catalan representatives and Britain opened a second front in the north-east; the loss of Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ...
and Valencia left Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label=Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is the ...
as the only major port available to the Bourbons in the Western Mediterranean. Philip tried to retake Barcelona in May 1706 but was repulsed, while his absence allowed an Allied force from Portugal to enter Madrid and Saragossa
Zaragoza, also known in English as Saragossa,''Encyclopædia Britannica'"Zaragoza (conventional Saragossa)" is the capital city of the Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. It lies by the Ebro river and its tributari ...
.
However, lack of popular support and logistical issues meant the Allies could not hold territory away from the coastline, and by November, Philip controlled Castile, Murcia
Murcia (, , ) is a city in south-eastern Spain, the Capital (political), capital and most populous city of the autonomous community of the Region of Murcia, and the List of municipalities of Spain, seventh largest city in the country. It has a ...
, and parts of Valencia. Allied efforts to regain the initiative ended with defeat at Almansa in April 1707, followed by failure to take Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label=Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is the ...
in August. The capture of Menorca in 1708, combined with possession of Gibraltar, gave the British control of the Western Mediterranean, which many considered their primary objective.
War beyond Europe and related conflicts
 The close links between war and trade meant conflict extended beyond Europe, particularly in North America, where it is known as
The close links between war and trade meant conflict extended beyond Europe, particularly in North America, where it is known as Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In E ...
, and the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Great ...
, which produced sugar, then a hugely profitable commodity. Also, there were minor trade conflicts in South America, India, and Asia; the financial strains of war particularly affected the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock c ...
, as it was a huge drain on scarce naval resources.
Related conflicts include Rákóczi's War of Independence
Rákóczi's War of Independence (1703–11) was the first significant attempt to topple the rule of the Habsburgs over Hungary. The war was conducted by a group of noblemen, wealthy and high-ranking progressives and was led by Francis II Rák ...
in Hungary, which was funded by France and a serious concern for the Habsburgs throughout the war. In South-Eastern France, Britain funded the Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bez ...
1704–1710 Camisard rebellion; one objective of the 1707 campaign in Northern Italy and Southern France was to support this revolt, one of a series that began in the 1620s.
Towards peace; 1709–1715
By the end of 1708, the French had withdrawn from Northern Italy, while the Maritime Powers controlled the Spanish Netherlands, and secured the borders of the Dutch Republic; in the Mediterranean, the Maritime Powers had achieved naval supremacy, and Britain acquired permanent bases in Gibraltar and Menorca. However, as Marlborough himself pointed out, the French frontiers remained largely intact, their army showed no signs of being defeated, while Philip proved far more popular with the Spanish than his rival. Many of the objectives set out by the Grand Alliance in 1701 had been achieved, but success in 1708 made them overconfident.Diplomacy
French diplomats focused on the Dutch, whom they considered were more likely to favour peace than their allies since victory at Ramillies removed any direct military threat to the Republic, while highlighting differences with Britain on the Spanish Netherlands. Peace talks broke down in late 1708 because the Allies had agreed not to negotiate a separate peace but could not agree on the terms. TheGreat Frost of 1709
The Great Frost, as it was known in England, or ' ("The Great Winter"), as it was known in France, was an extraordinarily cold winter in Europe in 1708–1709,. and was the coldest European winter during the past 500 years.
Notability
William ...
caused widespread famine in France and Spain, forcing Louis to re-open negotiations and in May 1709 the Allies presented him with the Preliminaries of the Hague. Philip was given two months to cede his throne to Archduke Charles, while France was required to remove him by force if he did not comply.
 Many Allied statesmen, including Marlborough, felt the terms seriously underestimated France's ability to continue the war and assumed Philip would abdicate on request. They also required the Spanish to accept Archduke Charles as king in his place, which they were clearly unwilling to do, as demonstrated by the failure of Allied campaigns to hold territory outside Catalonia. Although Louis was willing to abandon his ambitions in Spain, making war on his grandson was unacceptable, a stipulation so offensive that when made public the French resolved to fight on.
Marlborough's 1709 offensive in Northern France culminated in the
Many Allied statesmen, including Marlborough, felt the terms seriously underestimated France's ability to continue the war and assumed Philip would abdicate on request. They also required the Spanish to accept Archduke Charles as king in his place, which they were clearly unwilling to do, as demonstrated by the failure of Allied campaigns to hold territory outside Catalonia. Although Louis was willing to abandon his ambitions in Spain, making war on his grandson was unacceptable, a stipulation so offensive that when made public the French resolved to fight on.
Marlborough's 1709 offensive in Northern France culminated in the Battle of Malplaquet
The Battle of Malplaquet took place on 11 September 1709 during the War of the Spanish Succession and was fought between a French army commanded by the Duke of Villars and a Grand Alliance force under the Duke of Marlborough. In one of the bl ...
on 11 September; a narrow Allied victory, total casualties were around 24,500 out of 86,000, the Dutch losing 8,500 out of 18,000. Although the French strategic position continued to deteriorate, it showed their fighting abilities remained intact and increased war-weariness in both Britain and the Dutch Republic. More significant were Franco-Spanish victories at Alicante
Alicante ( ca-valencia, Alacant) is a city and municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city was 337,482 , the second-largest in th ...
in April, and La Gudina in May 1709, which meant a successful military solution now appeared remote.
Shortly after, the Dutch discovered they had been excluded from a commercial agreement signed by Archduke Charles which granted Britain exclusive trading rights in Spanish America. This deepened divisions between the Allies, while increasing Spanish opposition to having the Archduke as their king. When the Whig government in London tried to compensate the Dutch by agreeing concessions in the Spanish Netherlands, they were opposed by their Tory opponents as detrimental to British commerce.
The Whigs had won the 1708 British general election
The 1708 British general election was the first general election to be held after the Acts of Union had united the Parliaments of England and Scotland.
The election saw the Whigs finally gain a majority in the House of Commons, and by November ...
by arguing military victory was the quickest road to peace, but failure in France was mirrored in Spain. Archduke Charles re-entered Madrid in 1710 after victories in the Battle of Almenar
The Battle of Almenar also referred to as Almenara was a battle in the Iberian theatre of the War of the Spanish Succession.
In June 1710, the Bourbon-Spanish army of Phillip V crossed into Catalonia in an attempt to capture Balaguer; an Al ...
and Battle of Saragossa, but the Allies could not hold the interior and were forced to retreat. 3,500 British troops surrendered at Brihuega
Brihuega is a municipality located in the province of Guadalajara, Spain. According to the 2007 census (INE), the municipality had a population of 2,835 inhabitants.
In 1710 a hard-fought battle took place in the township between Lord Stanhope ...
on 8 December, and the Battle of Villaviciosa
The Battle of Villaviciosa (11 December 1710) was a battle between a Franco-Spanish army led by Louis Joseph, Duke of Vendôme and Philip V of Spain and a Habsburg-allied army commanded by Austrian Guido Starhemberg. The battle took place duri ...
on 10 December confirmed Bourbon control of Spain. At the same time, costs continued to spiral; the Dutch were close to bankruptcy while Austrian troops were almost entirely funded by Britain. In 1709, Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. ...
approved expenditures of £6.4 million, up from £5.0 million in 1706; by the end of 1710, these had nearly doubled to £12.9 million, despite minimal gains.
Negotiations
 When negotiations resumed in March 1710 at
When negotiations resumed in March 1710 at Geertruidenberg
Geertruidenberg () is a city and municipality in the province North Brabant in the south of the Netherlands. The city, named after Saint Gertrude of Nivelles, received city rights in 1213 from the count of Holland. The fortified city prospered un ...
, it was clear to the French the mood in Britain had changed. This was confirmed when the pro-peace Tories won a landslide victory in the October 1710 British general election, although they confirmed their commitment to the war to prevent a credit crisis. Despite the capture of Bouchain
Bouchain (; vls, Boesem) is a commune in the Nord department in northern France.
It lies halfway between Cambrai and Valenciennes. Bouchain, seat of the early medieval County of Ostrevent, was taken by Arnulf I, Count of Flanders, in the 10th ...
in September, a decisive victory in Northern France continued to elude the Allies, and an expedition against Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
in French North America ended in disaster.
When Emperor Joseph died in April 1711, Archduke Charles was elected Emperor; continuing the war now seemed pointless since the union of Spain with Austria was as unwelcome as one with France. The British secretly negotiated peace terms directly with France, leading to the signing of the Preliminary Articles of London on 8 October 1711. They included French acceptance of the Act of Settlement and a guarantee the French and Spanish crowns would remain separate; France undertook to ensure Spain ceded Gibraltar and Menorca, while giving Britain a thirty-year monopoly on the , the right to import slaves into their American colonies. Despite their resentment at being excluded from these negotiations, the Dutch were financially exhausted by the enormous cost of the war, and could not continue without British support. Charles VI initially rejected the idea of a peace conference; he reluctantly agreed once the Dutch decided to support it, but Habsburg opposition to the treaty continued.
Peace of Utrecht
 Within weeks of the conference opening, events threatened the basis of the peace agreed between Britain and France. First, the French presented proposals awarding the Spanish Netherlands to Max Emmanuel of Bavaria and a minimal Barrier, leaving the Dutch with little to show for their huge investment of money and men. Second, a series of deaths left Louis XIV's two-year-old great-grandson, the future
Within weeks of the conference opening, events threatened the basis of the peace agreed between Britain and France. First, the French presented proposals awarding the Spanish Netherlands to Max Emmanuel of Bavaria and a minimal Barrier, leaving the Dutch with little to show for their huge investment of money and men. Second, a series of deaths left Louis XIV's two-year-old great-grandson, the future Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached ...
as heir, making Philip next in line and his immediate renunciation imperative.
The Dutch and Austrians fought on, hoping to improve their negotiating position but Bolingbroke issued 'Restraining Orders' to Marlborough's replacement, the Duke of Ormonde, instructing him not to participate in offensive operations against the French. These orders caused fury then and later, with Whigs urging Hanoverian military intervention; those George considered responsible, including Ormonde and Bolingbroke were driven into exile after his succession, and became prominent Jacobites.
Prince Eugene captured Le Quesnoy
Le Quesnoy (; pcd, L' Kénoé) is a Communes of France, commune and small town in the east of the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department of northern France. It was part of the historical province of French Hainaut. It ...
in June and besieged Landrecies but was defeated at Denain
Denain (; pcd, Dnain) is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. Denain had a population of 19,877, on a land area of 11.52 km² (4.448 sq mi).
It is the largest of 47 communes which comprise the Communauté d'agglomératio ...
on 24 July; the French went on to recapture Le Quesnoy and many towns lost in previous years, including Marchines, Douai, and Bouchain. This showed the French retained their fighting ability, while the Dutch finally reached the end of their willingness and ability to continue the war.
On 6 June, Philip confirmed his renunciation of the French throne, and the British offered the Dutch a revised Barrier Treaty
The "Barrier Treaties" (, ) were a series of agreements signed and ratified between 1709 and 1715 that created a buffer zone between the Dutch Republic and France by allowing the Dutch to occupy a number of fortresses in the Southern Netherlands, ...
, replacing that of 1709 which they rejected as overly generous. A significant improvement on the 1697 Barrier, it was subject to Austrian approval; although the final terms were less beneficial, it was sufficient for the Dutch to agree peace terms.
 Charles withdrew from the Conference when France insisted he guarantee not to acquire Mantua or
Charles withdrew from the Conference when France insisted he guarantee not to acquire Mantua or Mirandola
Mirandola ( Mirandolese: ) is a city and ''comune'' of Emilia-Romagna, Italy, in the Province of Modena, northeast of the provincial capital by railway.
History
Mirandola originated as a Renaissance city-fortress. For four centuries it w ...
; he was supported in this by George, Elector of Hanover, who wanted France to withdraw support for the Stuart heir James Francis. As a result, neither Austria nor the Empire signed the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne of ...
of 11 April 1713 between France and the other Allies; Spain made peace with the Dutch in June, then Savoy and Britain on 13 July 1713.
Treaties of Rastatt and Baden
Fighting continued on the Rhine, but Austria was financially exhausted, and after the loss of Landau and Freiburg in November 1713, Charles finally made peace on 7 March 1714. In theTreaty of Rastatt
The Treaty of Rastatt was a peace treaty between France and Austria that was concluded on 7 March 1714 in the Baden city of Rastatt to end the War of the Spanish Succession between both countries. The treaty followed the Treaty of Utrecht of 11 ...
, the Habsburg monarchy acceded to the terms of Utrecht, which confirmed their gains in Southern Italy, returned Breisach, Kehl
Kehl (; gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Kaal) is a town in southwestern Germany in the Ortenaukreis, Baden-Württemberg. It is on the river Rhine, directly opposite the French city of Strasbourg, with which it shares some municipal servicesfor exa ...
, and Freiburg, ended French support for the Hungarian revolt and agreed on terms for the Dutch Barrier fortresses. Charles abandoned his claim to Strasbourg and Alsace and agreed to the restoration of the Wittelsbach Electors of Bavaria and Cologne, Max Emmanuel, and Joseph Clemens. Article XIX of the treaty transferred sovereignty over the Spanish Netherlands to Austria. On 7 September, the Holy Roman Empire joined the agreement by the Treaty of Baden; although Catalonia and Majorca were not finally subdued by the Bourbons until June 1715, the war was over.
Aftermath
Article II of thePeace of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne of ...
included the stipulation "because of the great danger which threatened the liberty and safety of all Europe, from the too-close conjunction of the kingdoms of Spain and France, ... the same person should never become King of both kingdoms." Some historians view this as a key point in the evolution of the modern nation-state; Randall Lesaffer argues it marks a significant milestone in the concept of collective security.
Britain is usually seen as the main beneficiary of Utrecht, which marked its rise to becoming the dominant European commercial power. It established naval superiority over its competitors, acquired the strategic Mediterranean ports of Gibraltar and Menorca and trading rights in Spanish America. France accepted the Protestant succession, ensuring a smooth inheritance by George I in August 1714, while agreeing to end support for the Stuarts in the 1716 Anglo-French Treaty. Although the war left all participants with unprecedented levels of government debt, only Britain was able to finance it efficiently, providing a relative advantage over its competitors.
Philip was confirmed as King of Spain, which retained its independence and the majority of its empire, in return for ceding the Spanish Netherlands, most of their Italian possessions, as well as Gibraltar and Menorca. These losses were deeply felt; Naples and Sicily were regained in 1735 and Menorca in 1782, although Gibraltar is still held by Britain, despite numerous attempts to regain it. The 1707 decrees centralised power in Madrid, and abolished regional political structures, although Catalonia and Majorca remained outside the system until 1767. Their economy recovered remarkably quickly, while the House of Bourbon still holds the Spanish throne.
Despite failure in Spain, Austria secured its position in Italy and Hungary and acquired the bulk of the Spanish Netherlands; even after reimbursing the Dutch for the cost of their Barrier garrisons, the increased revenues funded a significant expansion of the Austrian army. The shift of Habsburg focus away from Germany and into Southern Europe continued with victory in the Austro-Turkish War of 1716–1718. Their position as the dominant power within the Holy Roman Empire was challenged by Bavaria, Hanover, Prussia, and Saxony, who increasingly acted as independent powers; in 1742, Charles of Bavaria became the first non-Habsburg Emperor in over 300 years.
The Dutch had successfully defended their positions in the Southern Netherlands, and their troops were central to the alliance which halted French territorial expansion in Europe until a new cycle began in 1792
Events
January–March
* January 9 – The Treaty of Jassy ends the Russian Empire's war with the Ottoman Empire over Crimea.
* February 18 – Thomas Holcroft produces the comedy '' The Road to Ruin'' in London.
* Februar ...
. However, the war left them effectively bankrupt, and inflicted permanent damage on the Dutch merchant navy; while they remained the dominant economic power in the Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The te ...
, Britain took over as the pre-eminent global commercial and maritime power. The Barrier Treaty
The "Barrier Treaties" (, ) were a series of agreements signed and ratified between 1709 and 1715 that created a buffer zone between the Dutch Republic and France by allowing the Dutch to occupy a number of fortresses in the Southern Netherlands, ...
fortresses became the central driver of Dutch foreign policy in the decades after 1713, but although judged favourably by contemporaries, more recent historians suggest their protection was largely illusory. The forts were quickly over-run during the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George' ...
, with British military support proving far more effective as a defensive weapon.
Louis XIV died on 1 September 1715, and was succeeded by his five-year-old great-grandson Louis XV; on his deathbed, he is alleged to have admitted, "I have loved war too well". True or not, while the final settlement was far more favourable than the Allied terms of 1709, it is hard to see what Louis gained he had not already achieved through diplomacy by February 1701. Since 1666, French policies assumed military and economic superiority over their rivals, but this was no longer the case by 1714 when Britain appeared to have overtaken France on both fronts. The continued widening of this gap as British trade expanded post-Utrecht was viewed by Louis' successors as a permanent threat to the European balance of power. Seeking to reduce this was a major factor in France entering the 1740 to 1748 War of the Austrian Succession.
Wider implications include the rise of Prussia and Savoy while many of the participants were involved in the 1700–1721 Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swed ...
, with Russia becoming a major European power for the first time as a result. Finally, while colonial conflicts were relatively minor and largely confined to the North American theatre, the so-called Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In E ...
, they were to become a key element in future wars. Meanwhile, maritime unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refer ...
brought on by the war's end led to the third stage of the Golden Age of Piracy
The Golden Age of Piracy is a common designation for the period between the 1650s and the 1730s, when maritime piracy was a significant factor in the histories of the Caribbean, the United Kingdom, the Indian Ocean, North America, and West Afric ...
, as many sailors formerly employed in the navies of the warring powers turned to piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
for survival.
Claims to the Spanish throne
Explanatory notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Navarro i Soriano, Ferran (2019). ''Harca, harca, harca! Músiques per a la recreació històrica de la Guerra de Successió (1794–1715)''. Editorial DENES. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Spanish Succession 1700s conflicts 1700s in Austria 1700s in France 1700s in Italy 1700s in Spain 1700s in the Caribbean 1710s conflicts 1710s in Austria 1710s in France 1710s in Italy 1710s in Spain 1710s in the Caribbean Anglo-French wars Global conflicts History of the Royal Marines Pretenders to the Spanish throne Wars of succession involving the states and peoples of Africa Wars of succession involving the states and peoples of Asia Wars of succession involving the states and peoples of Europe Wars of succession involving the states and peoples of North America