Walter Horn on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Walter William Horn (18 January 1908 - 26 December 1995) was a German-American medievalist scholar noted for his work on the
 Horn fled Germany in opposition to the Nazi regime. He continued his studies from 1934 to 1937 as a research associate at the German Institute for the History of Art in
Horn fled Germany in opposition to the Nazi regime. He continued his studies from 1934 to 1937 as a research associate at the German Institute for the History of Art in

 Horn's early position as research associate in Florence gave him firsthand knowledge of the city's medieval church architecture and produced two important studies, ''Das Florentiner Baptisterium'' (1938), an analysis of the fabric and ornamentation of the
Horn's early position as research associate in Florence gave him firsthand knowledge of the city's medieval church architecture and produced two important studies, ''Das Florentiner Baptisterium'' (1938), an analysis of the fabric and ornamentation of the
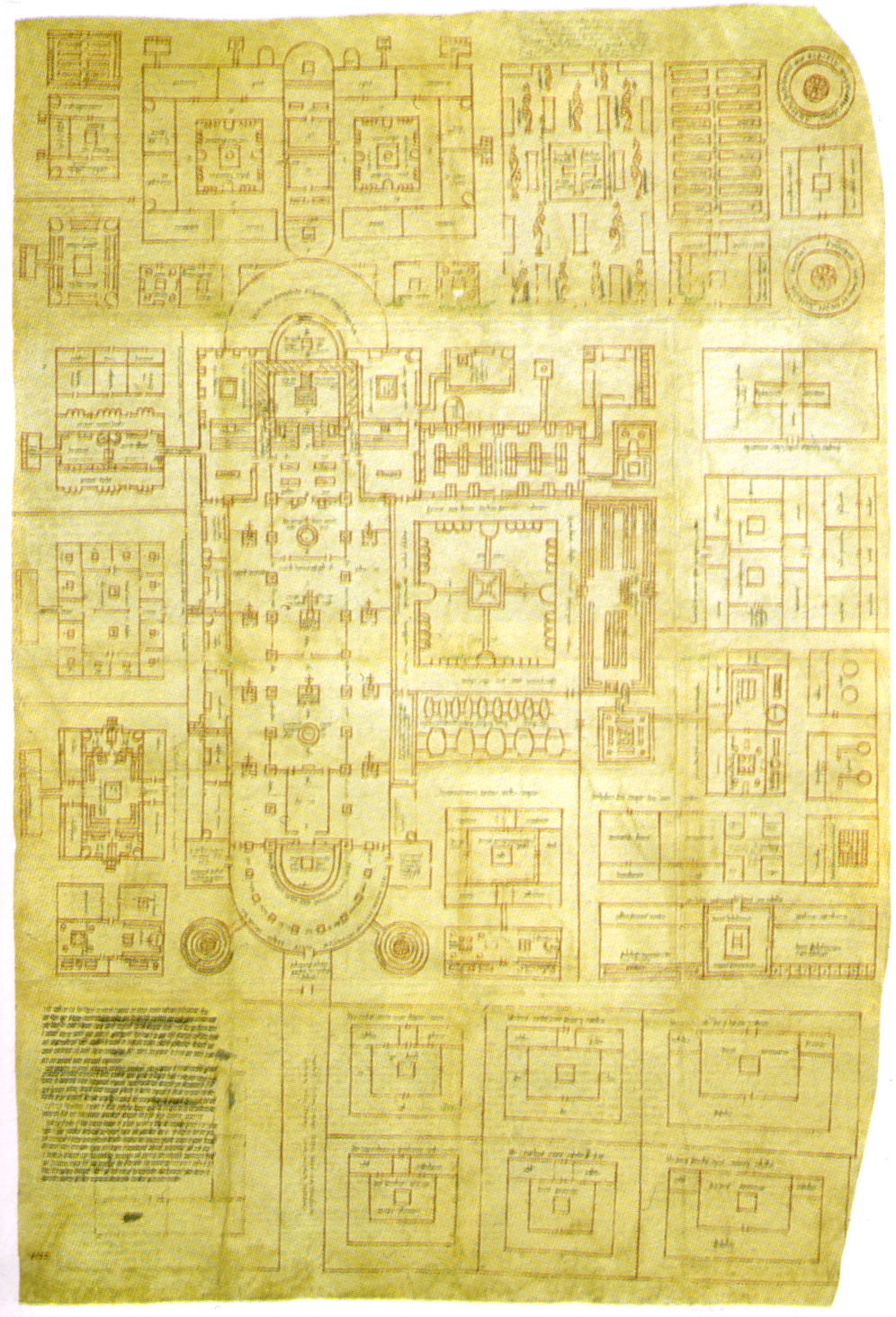 The
The
obituary
/ref> The first volume offers a reconstruction of the church and the living quarters for a community of monks numbering about a hundred. The second volume covered the guest and service buildings and the
"Walter Horn, History of Art: Berkeley"
* ''Dictionary of Art Historians: A Biographical Dictionary of Historic Scholars, Museum Professionals and Academic Historians of Art''
* William Grimes, "Walter Horn, 87, a Historian Of Medieval Cloisters and Barns," ''
obituary
* "Walter Horn," ''
obituary
* "Walter Horn; Specialist in Medieval Architecture," ''
obituary
* Rihoko Ueno
''A Finding Aid to the Walter Horn Papers, 1908-1992, bulk 1943-1950, in the Archives of American Art''
Washington, DC 2012. * Brown, Hillary, Finding Aid for the Walter Horn Papers, 1917-1989, at the
timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
architecture of the Middle Ages.
Horn was born in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, but fled Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
and spent most of his academic career at the University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant u ...
, where he became the university system's first art historian
Art history is the study of aesthetic objects and visual expression in historical and stylistic context. Traditionally, the discipline of art history emphasized painting, drawing, sculpture, architecture, ceramics and decorative arts; yet today ...
and co-founded the History of Art department. A naturalized citizen
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-citizen of a country may acquire citizenship or nationality of that country. It may be done automatically by a statute, i.e., without any effort on the part of the in ...
of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, Horn served in the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
and then in the special intelligence unit that tracked down art works plundered by the Nazis. His most celebrated exploit was the recovery of the crown jewels of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
, also known as Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
's Imperial Regalia
The Imperial Regalia, also called Imperial Insignia (in German ''Reichskleinodien'', ''Reichsinsignien'' or ''Reichsschatz''), are regalia of the Holy Roman Emperor. The most important parts are the Crown, the Imperial orb, the Imperial sce ...
. As a scholar, Horn is most noted for his work on the medieval architectural drawing known as the Plan of Saint Gall
The Plan of Saint Gall is a medieval architectural drawing of a monastic compound dating from 820–830 AD. It depicts an entire Benedictine monastic compound, including churches, houses, stables, kitchens, workshops, brewery, infirmary, and a ...
.
Additions: for recovery of Imperial Regalia, see Sidney Kirkpatrick, Hitler’s Holy Relics, Simon and Schuster, 2010. Horn was present as a guest of Austria at the reopening of the rooms dedicated to the Reglia at the Hofburg Museum in 1987.
Early life
Horn was born in the town of Waldangelloch in ruralBaden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden is ...
as Walther Wilhelm Adolf Horn. His mother was Matilde Peters; she married Karl Horn, a Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
minister. Walter attended a ''Gymnasium'' in nearby Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: ''Heidlberg'') is a city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914 ...
and went on to study art history
Art history is the study of aesthetic objects and visual expression in historical and stylistic context. Traditionally, the discipline of art history emphasized painting, drawing, sculpture, architecture, ceramics and decorative arts; yet today ...
at the University of Heidelberg
}
Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg, (german: Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg; la, Universitas Ruperto Carola Heidelbergensis) is a public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, ...
and the University of Berlin
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (german: Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a German public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin. It was established by Frederick William III on the initiative o ...
. He earned his doctorate
A doctorate (from Latin ''docere'', "to teach"), doctor's degree (from Latin ''doctor'', "teacher"), or doctoral degree is an academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism ''l ...
in 1934 at the University of Hamburg
The University of Hamburg (german: link=no, Universität Hamburg, also referred to as UHH) is a public research university in Hamburg, Germany. It was founded on 28 March 1919 by combining the previous General Lecture System ('' Allgemeines Vor ...
, studying under Erwin Panofsky
Erwin Panofsky (March 30, 1892 in Hannover – March 14, 1968 in Princeton, New Jersey) was a German-Jewish art historian, whose academic career was pursued mostly in the U.S. after the rise of the Nazi regime.
Panofsky's work represents a hig ...
. His dissertation, ''Die Fassade von Saint-Gilles'', on the façade
A façade () (also written facade) is generally the front part or exterior of a building. It is a Loanword, loan word from the French language, French (), which means 'frontage' or 'face'.
In architecture, the façade of a building is often t ...
of Saint-Gilles, Gard
Saint-Gilles (; Provençal: ''Sant Geli''; en, St. Giles) or Saint-Gilles-du-Gard is a commune in the Gard department in southern France.
It is the second most populous commune in the Nîmes metropolitan area.
History
The abbey of Saint-Gilles ...
, was published in 1937.
World War II era
 Horn fled Germany in opposition to the Nazi regime. He continued his studies from 1934 to 1937 as a research associate at the German Institute for the History of Art in
Horn fled Germany in opposition to the Nazi regime. He continued his studies from 1934 to 1937 as a research associate at the German Institute for the History of Art in Florence, Italy
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico an ...
. In 1938, Horn moved to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and began his long association with the University of California, Berkeley, as a lecturer
Lecturer is an List of academic ranks, academic rank within many universities, though the meaning of the term varies somewhat from country to country. It generally denotes an academic expert who is hired to teach on a full- or part-time basis. T ...
. A year later, he was given a permanent position as the first art historian in the University of California system. During this time, he married Ann Binkley Rand.
Horn became a naturalized citizen
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-citizen of a country may acquire citizenship or nationality of that country. It may be done automatically by a statute, i.e., without any effort on the part of the in ...
in 1943, dropping the forename Adolf because of its associations with the war. That same year, he volunteered for military duty
Military service is service by an individual or group in an army or other militia, air forces, and naval forces, whether as a chosen job (volunteer) or as a result of an involuntary draft (conscription).
Some nations (e.g., Mexico) require a ...
in the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
. By 1945, he was a lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations.
The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often sub ...
in the Third Army under General George S. Patton
George Smith Patton Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the Seventh United States Army in the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, and the Third United States Army in France ...
. Horn's skills as a native speaker of German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
were put to use in interrogating
Interrogation (also called questioning) is interviewing as commonly employed by law enforcement officers, military personnel, intelligence agencies, organized crime syndicates, and terrorist organizations with the goal of eliciting useful informa ...
prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
. After the war, he continued as a special investigator in the Monuments, Fine Arts, and Archives program, using his expertise as an art historian to track down art that had been stolen or concealed by the Nazis. Horn served until 1946, attaining the rank of captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
.
In 1945, Horn succeeded in recovering the Imperial Regalia
The Imperial Regalia, also called Imperial Insignia (in German ''Reichskleinodien'', ''Reichsinsignien'' or ''Reichsschatz''), are regalia of the Holy Roman Emperor. The most important parts are the Crown, the Imperial orb, the Imperial sce ...
of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
, the crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
, sceptre
A sceptre is a staff or wand held in the hand by a ruling monarch as an item of royal or imperial insignia. Figuratively, it means royal or imperial authority or sovereignty.
Antiquity
Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia
The ''Was'' and other ...
, and jewels
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semiprecious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, a ...
of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
. These had been kept hidden by Germans who hoped to return to power even after their defeat by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
.
The incident has been elaborated, sometimes with inaccuracies, by writers who take particular interest in the Holy Lance
The Holy Lance, also known as the Lance of Longinus (named after Saint Longinus), the Spear of Destiny, or the Holy Spear, is the lance that pierced the side of Jesus as he hung on the cross during his crucifixion.
Biblical references
The l ...
, the spear supposed to have pierced the side of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
during his crucifixion. This artifact is sometimes called the Spear of Destiny and identified with the Vienna Lance, one of the components of the regalia. In speculative works of non-fiction
Nonfiction, or non-fiction, is any document or media content that attempts, in good faith, to provide information (and sometimes opinions) grounded only in facts and real life, rather than in imagination. Nonfiction is often associated with be ...
that endow the lance with occult powers or mystical significance in Nazism, Horn appears in narratives about its retrieval from the possession of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
. Usually identified as "Lt. Walter William Horn," he is said to have retrieved the lance at the behest of Patton on the very day of Hitler's death, that is, 30 April 1945.
The McCarthy era
Returning from the war, Horn married Alberta West Parker, aphysician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
, who became a Clinical Professor of Public Health at UC Berkeley. In 1949, Horn and his family became embroiled in the controversy at his university over a loyalty oath
A loyalty oath is a pledge of allegiance to an organization, institution, or state of which an individual is a member. In the United States, such an oath has often indicated that the affiant has not been a member of a particular organization or ...
requirement. During the era of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, the Red Scare
A Red Scare is the promotion of a widespread fear of a potential rise of communism, anarchism or other leftist ideologies by a society or state. The term is most often used to refer to two periods in the history of the United States which ar ...
, and McCarthyism
McCarthyism is the practice of making false or unfounded accusations of subversion and treason, especially when related to anarchism, communism and socialism, and especially when done in a public and attention-grabbing manner.
The term origin ...
, the Board of Regents
In the United States, a board often governs institutions of higher education, including private universities, state universities, and community colleges. In each US state, such boards may govern either the state university system, individual col ...
at the University of California began to require that all university employees sign an oath affirming their loyalty to the state constitution and denying their membership or belief in organizations advocating the overthrow of the U.S. government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a fede ...
. The requirement met with resistance, and in the summer of 1950 thirty-one professors
Professor (commonly abbreviated as Prof.) is an academic rank at universities and other post-secondary education and research institutions in most countries. Literally, ''professor'' derives from Latin as a "person who professes". Professors ...
who refused to sign were fired, despite their stature as "internationally distinguished scholars."
Horn's fellow medievalist
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often voc ...
Ernst Kantorowicz
Ernst Hartwig Kantorowicz (May 3, 1895 – September 9, 1963) was a German historian of medieval political and intellectual history and art, known for his 1927 book '' Kaiser Friedrich der Zweite'' on Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, and ''The Kin ...
resigned rather than sign the oath, stating his reasons in two letters to the university president
A chancellor is a leader of a college or university, usually either the executive or ceremonial head of the university or of a university campus within a university system.
In most Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth and former Commonwealth n ...
that were only published in English decades after the episode. Kantorowicz also presented a letter from Horn, who had signed the oath under protest. In the letter dated 23 August 1950, Horn, then acting chairman
The chairperson, also chairman, chairwoman or chair, is the presiding officer of an organized group such as a board, committee, or deliberative assembly. The person holding the office, who is typically elected or appointed by members of the grou ...
of the art department, pointed to his former military service and to his voluntary reactivation that same month as a reservist
A reservist is a person who is a member of a military reserve force. They are otherwise civilians, and in peacetime have careers outside the military. Reservists usually go for training on an annual basis to refresh their skills. This person is ...
in the Armed Services
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
.
Kantorowicz noted that Horn's letter "illustrates the grave conflict of conscience and savage economic coercion
Coercion () is compelling a party to act in an involuntary manner by the use of threats, including threats to use force against a party. It involves a set of forceful actions which violate the free will of an individual in order to induce a desi ...
to which, after fifteen months of pressure and struggle, he had finally to yield."
Academic career and scholarship
 Horn's early position as research associate in Florence gave him firsthand knowledge of the city's medieval church architecture and produced two important studies, ''Das Florentiner Baptisterium'' (1938), an analysis of the fabric and ornamentation of the
Horn's early position as research associate in Florence gave him firsthand knowledge of the city's medieval church architecture and produced two important studies, ''Das Florentiner Baptisterium'' (1938), an analysis of the fabric and ornamentation of the Florence Baptistry
The Florence Baptistery, also known as the Baptistery of Saint John ( it, Battistero di San Giovanni), is a religious building in Florence, Italy, and has the status of a minor basilica. The octagonal baptistery stands in both the Piazza del D ...
that established new criteria for its dating, and '' Romanesque Churches in Florence: A Study of Their Chronology
Chronology (from Latin ''chronologia'', from Ancient Greek , ''chrónos'', "time"; and , '' -logia'') is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time. Consider, for example, the use of a timeline or sequence of events. I ...
and Stylistic Development'' (1943), which included an examination of the masonry
Masonry is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term ''masonry'' can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are bricks, building ...
construction of San Miniato al Monte
San Miniato al Monte (St. Minias on the Mountain) is a basilica in Florence, central Italy, standing atop one of the highest points in the city. It has been described as one of the finest Romanesque structures in Tuscany and one of the most scenic ...
. Throughout his career, he continued to explore the conceptual connections between classical and northern architecture. His specialty was three-aisled timber structures in medieval churches, market halls
A market house is a covered space historically used as a marketplace to exchange goods and services such as provisions or livestock, sometimes combined with spaces for public or civic functions on the upper floors and often with a jail or lockup ...
and manor halls. He was known for arriving at a precise dating of medieval buildings through studying their technologies and observing the physical evidence, drawing on scientific disciplines; he dated timber structures with reference to radiocarbon analysis and dendrochronological tables.
In 1958, Horn published what is considered his most important article, "On the Origins of the Medieval Bay System" in the ''Journal of the Society of Architectural Historians
The Society of Architectural Historians (SAH) is an international not-for-profit organization that promotes the study and preservation of the built environment worldwide. Based in Chicago in the United States, the Society's 3,500 members include ...
''. He argued that bay
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a Gulf (geography), gulf, sea, sound (geography), sound, or bight (geogra ...
-divided medieval churches derived from Germanic timber buildings and represented a continuous tradition of vernacular architecture
Vernacular architecture is building done outside any academic tradition, and without professional guidance. This category encompasses a wide range and variety of building types, with differing methods of construction, from around the world, bo ...
in transalpine
Gallia Narbonensis (Latin for "Gaul of Narbonne", from its chief settlement) was a Roman province located in what is now Languedoc and Provence, in Southern France. It was also known as Provincia Nostra ("Our Province"), because it was the ...
Europe. Horn was the first to assemble the known timber examples, which dated from as early as 1200 BC and extended into the medieval period. Because traces of early wooden structures were often scanty or oblique, Horn used scientific methods to uncover their architectural principles, and demonstrated that these were developed and applied to stone cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
s in the Romanesque and Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
periods.
The 1958 article was significant also in that it marked Horn's first collaboration with Ernest Born
Ernest Born (1898−1992) was an architect, designer, and artist based in California. He and his wife Esther Baum Born (1902−1987) collaborated on diverse projects in the San Francisco Bay Area from 1936 on. She was also a notable architect ...
, the San Franciscan architect and draftsman
A drafter (also draughtsman / draughtswoman in British and Commonwealth English, draftsman / draftswoman or drafting technician in American and Canadian English) is an engineering technician who makes detailed technical drawings or plans for m ...
with whom he was to author a series of books and articles over the next twenty years. Their first book was ''The Barns of the Abbey of Beaulieu at Its Granges of Great Coxwell
Great Coxwell is a village and civil parish southwest of Faringdon in the Vale of White Horse, England. It was in Berkshire until the 1974 boundary changes transferred it to Oxfordshire. The 2001 Census recorded the parish's population as 2 ...
and Beaulieu St. Leonard'' (1965), a study of the only two Cistercian
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint ...
tithe barn
A tithe barn was a type of barn used in much of northern Europe in the Middle Ages for storing rents and tithes. Farmers were required to give one-tenth of their produce to the established church. Tithe barns were usually associated with the vi ...
s, dating from the 13th century, that survive in England. But their major project was the three-volume work ''The Plan of St. Gall: A Study of the Architecture and Economy of, and Life in a Paradigmatic Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippin ...
Monastery'', which has been called "one of the greatest monograph
A monograph is a specialist work of writing (in contrast to reference works) or exhibition on a single subject or an aspect of a subject, often by a single author or artist, and usually on a scholarly subject.
In library cataloging, ''monograph ...
s on medieval architecture that has ever appeared."Kleinhauer ''et al.'', "Memoir," p. 801.
Plan of St. Gall
 The
The plan of Saint Gall
The Plan of Saint Gall is a medieval architectural drawing of a monastic compound dating from 820–830 AD. It depicts an entire Benedictine monastic compound, including churches, houses, stables, kitchens, workshops, brewery, infirmary, and a ...
had engaged Horn's imagination and curiosity since he was introduced to it by his mentor Erwin Panofsky
Erwin Panofsky (March 30, 1892 in Hannover – March 14, 1968 in Princeton, New Jersey) was a German-Jewish art historian, whose academic career was pursued mostly in the U.S. after the rise of the Nazi regime.
Panofsky's work represents a hig ...
. In 1957, Horn had participated in an international congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
on the plan, and his interest in its guest and service buildings led to his survey of medieval structures in France and England. In 1965, Horn and Born contributed to the creation of a scale model
A scale model is a physical model which is geometrically similar to an object (known as the prototype). Scale models are generally smaller than large prototypes such as vehicles, buildings, or people; but may be larger than small prototypes ...
of the 40 buildings rendered on the plan. The model was displayed at the international exhibit '' Karl der Grosse'' held at Aachen
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th- ...
. Their two decades of collaboration culminated in a work of 1,056 pages with an estimated 1,200 illustrations.
''The Plan of St. Gall'' was praised by French historian Emmanuel LeRoy Ladurie for its "prodigious scholarship," and for its wide-ranging elucidation of Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippin ...
daily life.William Grimes, "Walter Horn, 87, a Historian Of Medieval Cloisters and Barns," ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' 29 December 1995,obituary
/ref> The first volume offers a reconstruction of the church and the living quarters for a community of monks numbering about a hundred. The second volume covered the guest and service buildings and the
horticultural
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
spaces for growing vegetables, medicinal herbs, and fruit and nut trees. The third volume contains supplemental material such as Horn's 88-page catalogue of the plan's explanatory ''tituli'', or captions, and Charles W. Jones
Charles William Jones (December 24, 1834October 11, 1897) was a United States Senator from Florida. He abandoned the seat after an apparent onset of mental illness.
Early life, travel and career
Jones was born in Balbriggan, Ireland. His father ...
' English translation of the ''Consuetudines Corbienses'' by Adalhard of the abbey of Corbie
Corbie Abbey is a former Benedictine monastery in Corbie, Picardy, France, dedicated to Saint Peter. It was founded by Balthild, the widow of Clovis II, who had monks sent from Luxeuil. The Abbey of Corbie became celebrated both for its library ...
. Through meticulous reimagining of the activities that the architecture was meant to facilitate, Horn presents a rich picture of Carolingian life and thought.
The most controversial aspect of the work was Horn's major thesis: that the plan was a copy of a lost master plan dating to 816 or 817 that would have been part of documents pertaining to the official monastic reform movement under Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqui ...
at Aachen. The dominant strand of criticism to the contrary holds that the plan was intended to represent an ideal and was never meant to be carried out at a particular site. Horn's last article on the plan, "The Medieval Monastery as a Setting for the Production of Manuscripts," was a response to this criticism.
''The Plan of St. Gall'' earned twelve major awards for its scholarship, bookmaking
A bookmaker, bookie, or turf accountant is an organization or a person that accepts and pays off bets on sporting and other events at agreed-upon odds.
History
The first bookmaker, Ogden, stood at Newmarket in 1795.
Range of events
Bookm ...
, and typography
Typography is the art and technique of arranging type to make written language legible, readable and appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, point sizes, line lengths, line-spacing ( leading), and ...
, including a prize from France's Académie d'architecture
The Académie d'Architecture () is a French learned society whose purpose is the recognition of architectural quality. Founded in 1840 as the Société Centrale des Architectes (; en, "Central Society of Architects"), the society was renamed Ac ...
and a 1982 medal from the American Institute of Architects
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) is a professional organization for architects in the United States. Headquartered in Washington, D.C., the AIA offers education, government advocacy, community redevelopment, and public outreach to su ...
.
Later work
In 1974, Horn retired toemeritus
''Emeritus'' (; female: ''emerita'') is an adjective used to designate a retired chair, professor, pastor, bishop, pope, director, president, prime minister, rabbi, emperor, or other person who has been "permitted to retain as an honorary title ...
status after 36 years at the University of California. His last publication, ''The Forgotten Hermitage of Skellig Michael
Skellig Michael ( ga, Sceilg Mhichíl ), also called Great Skellig ( ga, link=no, Sceilig Mhór ), is a twin-pinnacled crag west of the Iveragh Peninsula in County Kerry, Ireland. The island is named after the archangel Michael, with "Skellig ...
'' (1990), co-authored with Jenny White Marshall and Grellan D. Rourke, resulted from fieldwork
Field research, field studies, or fieldwork is the collection of raw data outside a laboratory, library, or workplace setting. The approaches and methods used in field research vary across disciplines. For example, biologists who conduct fie ...
begun in 1978 on Ireland's Atlantic offshore islands. His interest in the Celtic roundhouse had been indicated earlier in "On the Origins of the Medieval Cloister
A cloister (from Latin ''claustrum'', "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cathedral or church, commonly against a ...
" (1973).
Honors and administrative achievements
Horn worked withclassical archaeologist
Classical archaeology is the archaeological investigation of the Mediterranean civilizations of Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome. Nineteenth-century archaeologists such as Heinrich Schliemann were drawn to study the societies they had read about i ...
Darrell A. Amyx to establish History of Art as a separate department at the University of California in 1971. He was a fellow
A fellow is a concept whose exact meaning depends on context.
In learned or professional societies, it refers to a privileged member who is specially elected in recognition of their work and achievements.
Within the context of higher education ...
of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and ...
(elected 1970) and of the Medieval Academy of America
The Medieval Academy of America (MAA; spelled Mediaeval until c. 1980) is the largest organization in the United States promoting the field of medieval studies. It was founded in 1925 and is based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The academy publishes ...
(1980). Horn was an active supporter of arts institutions outside academia, serving as trustee
Trustee (or the holding of a trusteeship) is a legal term which, in its broadest sense, is a synonym for anyone in a position of trust and so can refer to any individual who holds property, authority, or a position of trust or responsibility to t ...
of the Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco
The Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco (FAMSF), comprising the de Young Museum in Golden Gate Park and the Legion of Honor in Lincoln Park, is the largest public arts institution in the city of San Francisco. The permanent collection of the ...
and chairman of the museum's acquisitions committee. He was on the board of the College Art Association
The College Art Association of America (CAA) is the principal organization in the United States for professionals in the visual arts, from students to art historians to emeritus faculty. Founded in 1911, it "promotes these arts and their understa ...
1950–54 and 1964–68 and on the board of the Society of Architectural Historians
The Society of Architectural Historians (SAH) is an international not-for-profit organization that promotes the study and preservation of the built environment worldwide. Based in Chicago in the United States, the Society's 3,500 members include ...
1964–68.
Death
Horn died at home ofpneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
on Tuesday, 26 December 1995, at Point Richmond
Point Richmond, also sometimes referred to locally as The Point, is a neighborhood in Richmond, California, United States, near the eastern end of the Richmond-San Rafael Bridge, between Interstate 580 and the San Francisco Bay.
History
O ...
, California. He was 87. He was survived by his wife, Alberta; his son, Michael; two daughters, Rebecca and Robin; and grandchildren, Matthew and Dulce. His obituary
An obituary ( obit for short) is an article about a recently deceased person. Newspapers often publish obituaries as news articles. Although obituaries tend to focus on positive aspects of the subject's life, this is not always the case. Ac ...
in the ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' labeled him "historian of medieval cloister
A cloister (from Latin ''claustrum'', "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cathedral or church, commonly against a ...
s and barn
A barn is an agricultural building usually on farms and used for various purposes. In North America, a barn refers to structures that house livestock, including cattle and horses, as well as equipment and fodder, and often grain.Allen G. ...
s." Horn was remembered by colleagues as one of the university's "best-loved and most influential teachers and ... most effective leaders." He was eulogized for "his oratorical skills and uncanny ability to bring the medieval building or pile of ruins
Ruins () are the remains of a civilization's architecture. The term refers to formerly intact structures that have fallen into a state of partial or total disrepair over time due to a variety of factors, such as lack of maintenance, deliberate ...
vividly to life. His eloquence and grace matched his endless curiosity about prehistoric and medieval buildings in northern Europe and how people utilized them."Kleinhauer ''et al.'', "Memoir," pp. 801–802.
Selected bibliography
Standard biographical and publishing data on Horn not otherwise cited comes from two or more of the following sources. * W. Eugene Kleinbauer, James Marrow and Ruth Mellinkoff. "Memoirs of Fellows and Corresponding Fellows of theMedieval Academy of America
The Medieval Academy of America (MAA; spelled Mediaeval until c. 1980) is the largest organization in the United States promoting the field of medieval studies. It was founded in 1925 and is based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The academy publishes ...
: Walter W. Horn," ''Speculum'' 71 (1996) 800-802.
* University of California (System) Academic Senate, "1996, University of California: In Memoriam,"Walter Horn, History of Art: Berkeley"
* ''Dictionary of Art Historians: A Biographical Dictionary of Historic Scholars, Museum Professionals and Academic Historians of Art''
* William Grimes, "Walter Horn, 87, a Historian Of Medieval Cloisters and Barns," ''
New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' 29 December 1995,obituary
* "Walter Horn," ''
San Francisco Chronicle
The ''San Francisco Chronicle'' is a newspaper serving primarily the San Francisco Bay Area of Northern California. It was founded in 1865 as ''The Daily Dramatic Chronicle'' by teenage brothers Charles de Young and M. H. de Young, Michael H. de ...
'', 30 December 1995obituary
* "Walter Horn; Specialist in Medieval Architecture," ''
Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' (abbreviated as ''LA Times'') is a daily newspaper that started publishing in Los Angeles in 1881. Based in the LA-adjacent suburb of El Segundo since 2018, it is the sixth-largest newspaper by circulation in the Un ...
'', 31 December 1995obituary
* Rihoko Ueno
''A Finding Aid to the Walter Horn Papers, 1908-1992, bulk 1943-1950, in the Archives of American Art''
Washington, DC 2012. * Brown, Hillary, Finding Aid for the Walter Horn Papers, 1917-1989, at the
Getty Research Institute
The Getty Research Institute (GRI), located at the Getty Center in Los Angeles, California, is "dedicated to furthering knowledge and advancing understanding of the visual arts".
, Los Angeles.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Horn, Walter American art historians German art historians German medievalists Medieval architecture University of California, Berkeley College of Letters and Science faculty Imperial Regalia of the Holy Roman Empire United States Army officers 1908 births 1995 deaths Emigrants from Nazi Germany to the United States People from Sinsheim United States Army personnel of World War II University of Hamburg alumni Humboldt University of Berlin alumni Heidelberg University alumni American medievalists Monuments men 20th-century American historians German male non-fiction writers 20th-century American male writers Fellows of the Medieval Academy of America American male non-fiction writers Writers from Baden-Württemberg Historians from California