Wairarapa Fault on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
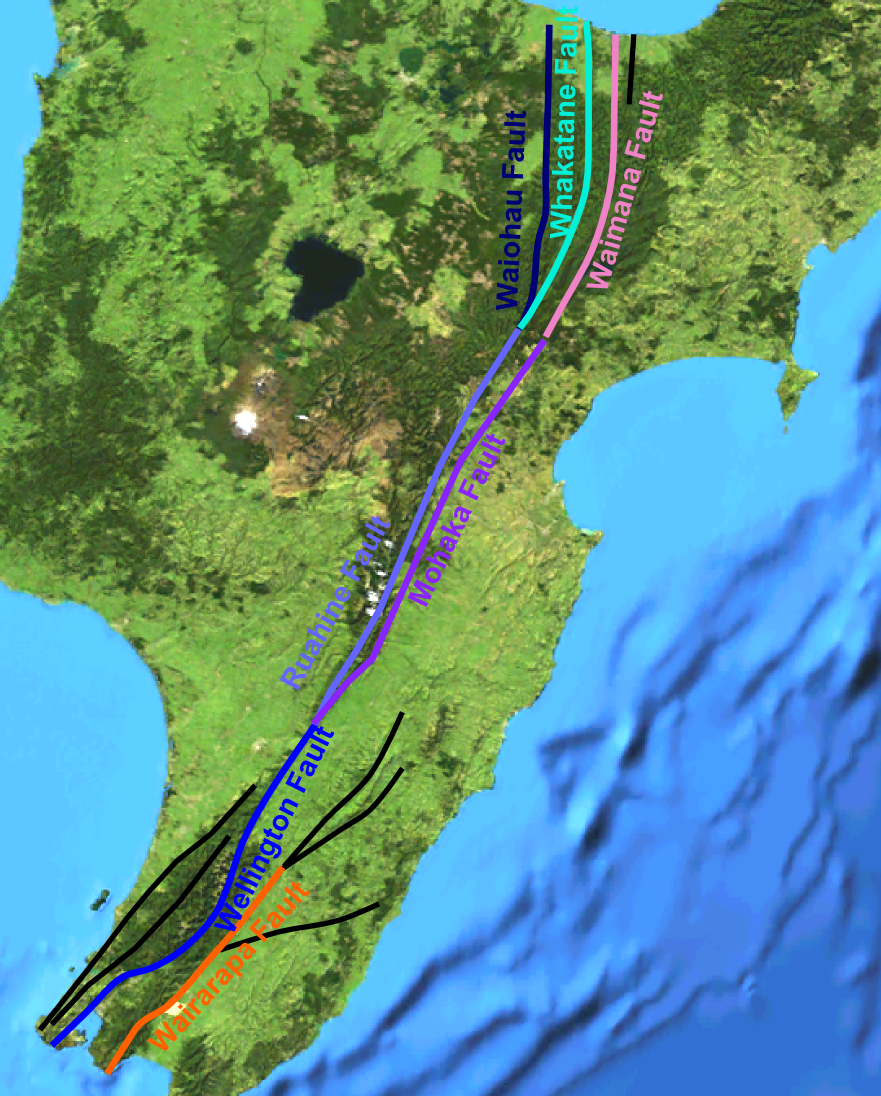 The Wairarapa Fault is an active seismic fault in the southern part of the
The Wairarapa Fault is an active seismic fault in the southern part of the
Proceedings of the 1855 Wairarapa Earthquake Symposium, 2005
{{Seismic faults of New Zealand Seismic faults of New Zealand Strike-slip faults
 The Wairarapa Fault is an active seismic fault in the southern part of the
The Wairarapa Fault is an active seismic fault in the southern part of the North Island
The North Island, also officially named Te Ika-a-Māui, is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but much less populous South Island by the Cook Strait. The island's area is , making it the world's 14th-largest ...
of New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
. It is a dextral (right lateral) strike-slip fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
with a component of uplift to the northwest as expressed by the Rimutaka Range
The Remutaka Range (spelled Rimutaka Range before 2017) is the southernmost range of a mountain chain in the lower North Island of New Zealand. The chain continues north into the Tararua, then Ruahine Ranges, running parallel with the east co ...
. It forms part of the North Island Fault System
The North Island Fault System (also known as North Island Dextral Fault Belt or NIFS) is a set of southwest–northeast trending seismically-active faults in the North Island of New Zealand that carry most of the dextral (right lateral) strike- ...
, which accommodates the transfer of displacement along the oblique convergent boundary between the Indo-Australian Plate
The Indo-Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes the continent of Australia and the surrounding ocean and extends northwest to include the Indian subcontinent and the adjacent waters. It was formed by the fusion of the Indian an ...
and Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Iza ...
.
Geometry
The Wairarapa Fault continues south of Lake Wairarapa as the Wharekauhau thrust, which can be traced on the seabed in theCook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A H, ...
for about 30 km with a possible further continuation on a fault strand lying to the northwest. These faults segments are considered likely to be the active traces of the southern Wairarapa Fault. At its northeastern end the fault terminates near Mauriceville, with the displacement apparently continued on the Pa Valley and Alfredton Faults.
Seismicity
Rupture along the Wairarapa Fault and Wharekauhau thrust was responsible for the 1855 Wairarapa earthquake, there is also evidence from trenching that the rupture continued onto the Alfredton Fault. The uplifted beach ridges ofTurakirae Head
Turakirae Head is a promontory on the southern coast of New Zealand's North Island. It is located at the western end of Palliser Bay, 20 kilometres southeast of Wellington, at the southern end of the Remutaka Range. The head is an excellent ex ...
provide a proxy record of prehistoric earthquakes. This record has been checked by trenching across parts of the Wairarapa Fault. The trenching recorded five surface rupturing events since about 5,500 years BP, the last of which is the 1855 earthquake and two of which are not recorded by beach ridges. Together the observations give a mean recurrence interval of about 1,200 years.
See also
*Geology of New Zealand
The geology of New Zealand is noted for its volcanic activity, earthquakes and geothermal areas because of its position on the boundary of the Australian Plate and Pacific Plates. New Zealand is part of Zealandia, a microcontinent nearly half t ...
*Geology of the Wellington Region The Wellington Region of New Zealand has a foundation of Torlesse Greywacke rocks, that make up the Tararua and Rimutaka Ranges, that go from Wellington in the south to the Manawatū Gorge, where they are renamed as the Ruahine Ranges, and contin ...
*North Island Fault System
The North Island Fault System (also known as North Island Dextral Fault Belt or NIFS) is a set of southwest–northeast trending seismically-active faults in the North Island of New Zealand that carry most of the dextral (right lateral) strike- ...
* Wellington Fault
References
External links
Proceedings of the 1855 Wairarapa Earthquake Symposium, 2005
{{Seismic faults of New Zealand Seismic faults of New Zealand Strike-slip faults