Wagner DOWA 81 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Pfeil 5, more commonly referred to as the Wagner DOWA 81 (DOWA being a contraction of “Doctor Wagner” and "81" referring to the year of the intended escape) was an aircraft designed and built by Dr Gerhard Wagner in order to escape East Germany.
 East Germany, then part of the
East Germany, then part of the
File:Wagner DOWA 81 2024-02-21 Andre Gerwing Collection ID 017885.jpg, View from the front
File:MZ ES 250 2 2023 07 04 JM (2).jpg, MZ ES 250/2 motorcycle
File:Schnittmodell Antrieb MZ ES 250 2.JPG, MZ ES 250/2 engine
Background
 East Germany, then part of the
East Germany, then part of the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
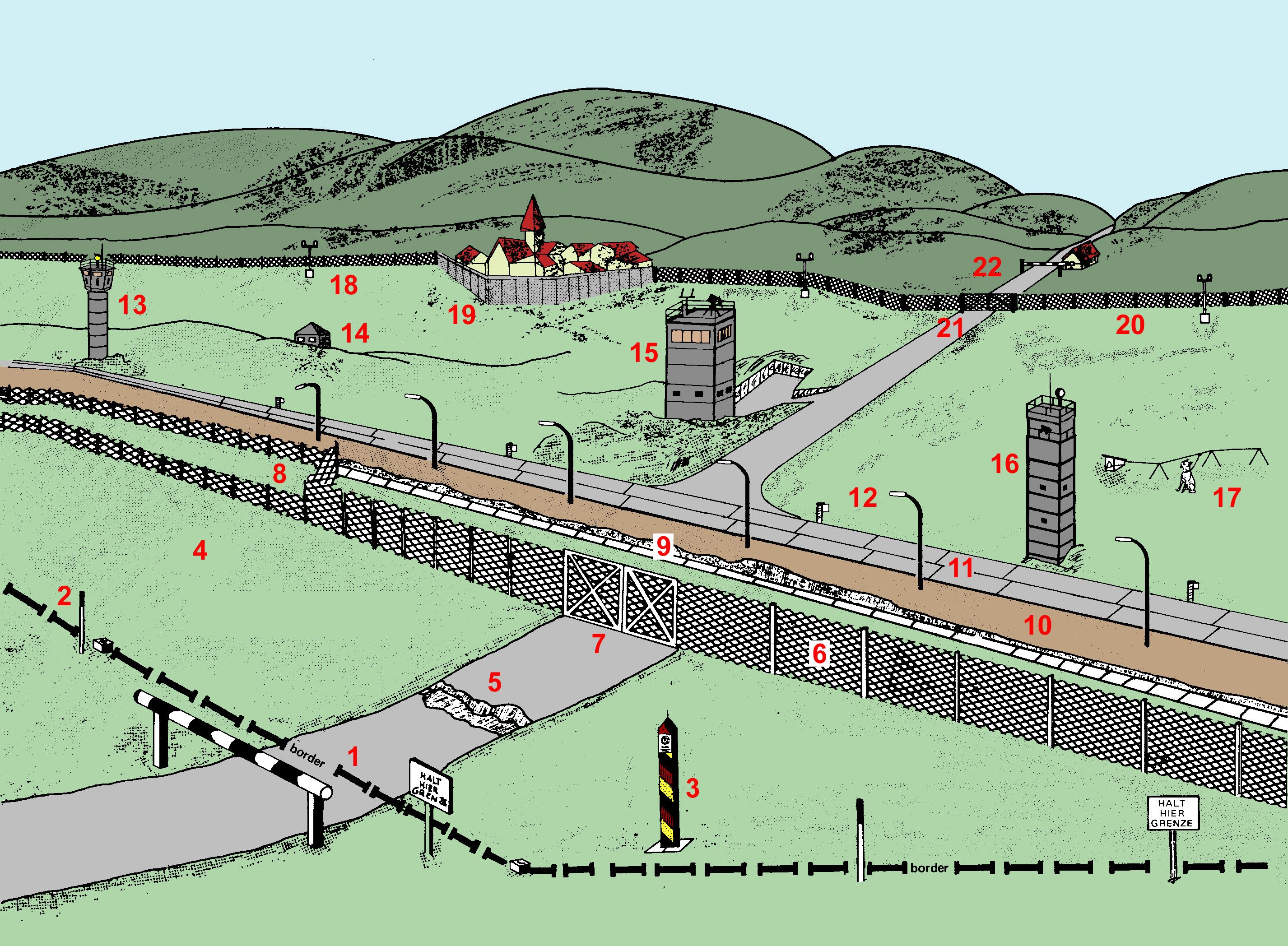
, was separated from West Germany in the Western Bloc by the inner German border
The inner German border (german: Innerdeutsche Grenze or ; initially also ) was the border between the German Democratic Republic (GDR, East Germany) and the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG, West Germany) from 1949 to 1990. Not including the ...
and the Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall (german: Berliner Mauer, ) was a guarded concrete barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and East Germany (GDR). Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the government ...
, which were heavily fortified with watchtowers, land mines, armed soldiers, and various other measures to prevent illegal crossings. East German border troops
The Border Troops of the German Democratic Republic (german: Grenztruppen der DDR) was the border guard of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) from 1946 to 1990.
The were the primary force guarding the Berlin Wall and the Inner German border, ...
were instructed to prevent defection to West Germany by all means, including lethal force ( Schießbefehl; "order to fire").
Gerhard Wagner (b. 1939) was a qualified aircraft engineer. Whilst still a student, he had almost fled during construction of the Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall (german: Berliner Mauer, ) was a guarded concrete barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and East Germany (GDR). Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the government ...
. However, he later accepted the situation. He married Ingeburg Hallbauer, and had three sons - Udo, Jörg, and Gerd. In 1961, the GDR abolished the aviation industry, leaving Wagner without any demand for his skills. He was also unable to pursue his passion of flying gliders, as the law allowed only those joining the Air Force to fly.
Wagner initially considered building a submarine to escape via the Baltic Sea, but doubted his skill in this area, and so turned to his strength: aircraft design. In order to prevent informants discovering the plan, he partitioned off the back area of his apartment kitchen using cupboards and curtains.
Design
By mid-1979, Wagner, a qualified aircraft engineer, had completed the designs for his aeroplane. He designed it with an enclosed cockpit and contra-rotating twin propellers inpusher configuration
In an aircraft with a pusher configuration (as opposed to a tractor configuration), the propeller(s) are mounted behind their respective engine(s). Since a pusher propeller is mounted behind the engine, the drive shaft is in compression in nor ...
powered by two 19 hp engines taken from a pair of motorbikes. The motorbikes also provided the wheels for the undercarriage. He calculated the flight weight to be around 580 kilograms (himself, his wife, and his three sons), which necessitated adding landing flaps for the wings for better control. The aircraft, at just under six metres in length, was also designed to be easily disassembled into four parts, the largest of which did not exceed four metres in length, allowing it to be easily hidden and transported in a car trailer.
Construction
Wagner built the aeroplane in secret, using whatever materials he could acquire. Wagner's son Udo, who was seventeen at the time, was a motorbike enthusiast, playing for a Dresden Motoball club, and was able to secure the purchase of two heavily used MZ-ES-250/2 motorbikes for 4,500 Ostmarks. He then overhauled them, dismantled and removed the gearboxes in order to allow the crankshafts to turn the propellers, and reversed the polarity of one of the engines. The engine mufflers were rotated 90° due to the crankshaft being repositioned lengthways. Several steps were taken to reduce the amount of noise produced by the aircraft. The propellers, designed according to plans from the 1930s, already set to rotate at around 800 kmh, were prevented from going faster than the speed of sound, and the air inlets on the carburetors were also rotated 90°, and hidden in the chassis nacelles with the mufflers. The front wheels of the motorbikes, along with their brakes and suspension, were positioned here too. Air channels were created for cooling the cylinders. Before they attached the motorbike engines, Udo and Jörg mounted one on the car trailer and used a spring balance between the car and the trailer to determine whether the thrust would be enough to power the aircraft. Although the necessary materials (plywood
Plywood is a material manufactured from thin layers or "plies" of wood veneer that are glued together with adjacent layers having their wood grain rotated up to 90 degrees to one another. It is an engineered wood from the family of manufactured ...
, balsa wood, aluminium, plexiglass and polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
were in short supply in East Germany, the family was able to procure them from various hobby shops, which they visited in a wide area around Dresden to prevent drawing attention to themselves. Wagner's mother-in-law, who lived in the West, was brought in on the plan and smuggled in glass, silk, bearings, and saw blades for cutting the aluminium sheets. The instruments needed for flight and navigation ( altimeter, airspeed indicator and compass) were either built by Wagner, smuggled from the West, or purchased on the black market
A black market, underground economy, or shadow economy is a clandestine market or series of transactions that has some aspect of illegality or is characterized by noncompliance with an institutional set of rules. If the rule defines the se ...
.
Wagner tested all the various elements of the aircraft in order to ensure it would successfully fly, including stress-testing the wing-fuselage connection with the aid of jacks and springs, showing that it could carry at least 2.4 times the intended weight.
Discovery
Gerhard Wagner intended to take off from an abandoned coal mine in Nonnewitz near Leipzig, as it was a good distance away from any public roads and buildings. He planned to assemble the aircraft in a nearby warehouse and use the track bed of the mine railway as the runway. At 600 metres long, it would be adequate for the aircraft, which required a runway of at least 450 metres. Following assembly of the aircraft, he would flight-test it before landing. His family would then board, and he would fly south, following the highway (keeping low so as to stay below the radar), and after a journey of around 90 kilometres (an estimated half hour flight), land in a field near Hof, West Germany. Unknown to Wagner, theStasi
The Ministry for State Security, commonly known as the (),An abbreviation of . was the Intelligence agency, state security service of the East Germany from 1950 to 1990.
The Stasi's function was similar to the KGB, serving as a means of maint ...
was spying on him. They carried out extensive checks and created a file about him, in addition to secretly searching and bugging his apartment and checking his mail. At least four unofficial Stasi employees were also assigned to him.
On July 25, 1981, at 7.00 in the morning, the day before the intended escape, the Stasi arrested Wagner and his family at their apartment. The family was sentenced to a total of twelve years in prison for preparing to cross the border illegally. Wagner was sent to Brandenburg Prison, his wife to Hoheneck Women's Prison
Hoheneck Women's Prison (German: ''Frauengefängnis Hoheneck'') was a women's correctional facility in operation between 1862 and 2001 in Stollberg, Germany. It became most notable as a detention facility for female political prisoners in East Ger ...
, and their three children to the Halle Juvenile Detention Centre. A year later, in July 1982, they were considered 'unwanted', and ransomed by the West. They moved to West Germany and settled in Kaiserslautern
Kaiserslautern (; Palatinate German: ''Lautre'') is a city in southwest Germany, located in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate at the edge of the Palatinate Forest. The historic centre dates to the 9th century. It is from Paris, from Frankfur ...
. Dr Wagner established himself as an expert for packaging, whilst continuing to design gliders. In 2011, he was awarded the Oskar Ursinus Prize.
The aircraft was examined by the State Aviation Authority of the GDR, who determined that it determined that it was probably the smallest five-person aircraft in the world, and would have able to fly for the required half hour the trip would have taken. It was kept in the evidence chamber of the Stasi in East Berlin
East Berlin was the ''de facto'' capital city of East Germany from 1949 to 1990. Formally, it was the Allied occupation zones in Germany, Soviet sector of Berlin, established in 1945. The American, British, and French sectors were known as ...
until the Peaceful Revolution
The Peaceful Revolution (german: Friedliche Revolution), as a part of the Revolutions of 1989, was the process of sociopolitical change that led to the opening of East Germany's borders with the West, the end of the ruling of the Socialist Unity ...
in 1989.
Initially, the aircraft was preserved at the Stasi Museum
The Stasi Museum (also known in German as the ''Forschungs- und Gedenkstätte Normannenstraße'') is a research and memorial centre concerning the political system of the former East Germany. It is located in the Lichtenberg locality of Berli ...
, before being transferred to Flugwerft Schleissheim in Munich in 1991. In 2023, Dr Gerhard Wagner permanently loaned the aircraft to Deutsch-Deutsches Museum Mödlareuth in Mödlareuth
Mödlareuth () is a German village situated partly in Bavaria and partly in Thuringia. Between 1949 and 1990, the northern part was in East Germany and the southern part in West Germany.
The Thuringian part of the village belongs to Gefell while ...
.
Similar attempts
Wagner's aeroplane was not the only attempt at escaping the Eastern bloc using a homemade aircraft. In 1973, an Armenian named Henrik Arakelyan attempted to flee Armenia in a homemade aircraft, only for it to crash. Three years after Wagner's arrest, in 1984, Ivo Zdarsky, future founder of Ivoprop, successfully escaped communistCzechslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
to Austria in a homemade powered hang glider, which used an engine from a Trabant.
Specifications
General Characteristics * Crew: 5 * Wingspan: 9.0 metres * Length: 5.85 metres * Wing area: 8.61 square metres * Empty mass: 240 kilograms * Take-off mass: 580 kilograms * Wing load: 67 kilograms/square metre Performance * Drive: Two 19 hp motorcycle engines * Flight speed: max. 210 km/h, min. 90 km/h * Take-off distance: 450 metres * Climb speed: 1.8 metres/secondGallery
See also
* East Germany balloon escape, a successful escape from East Germany using a homemade aircraft * Colditz Cock, built by Allied POWs for the purpose of escaping Oflag IV-CReferences
{{reflist 1980s German aircraft German special-purpose aircraft High-wing aircraft Homebuilt aircraft Twin-engined pusher aircraft Unflown aircraft