WR 134 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
WR 134 is a 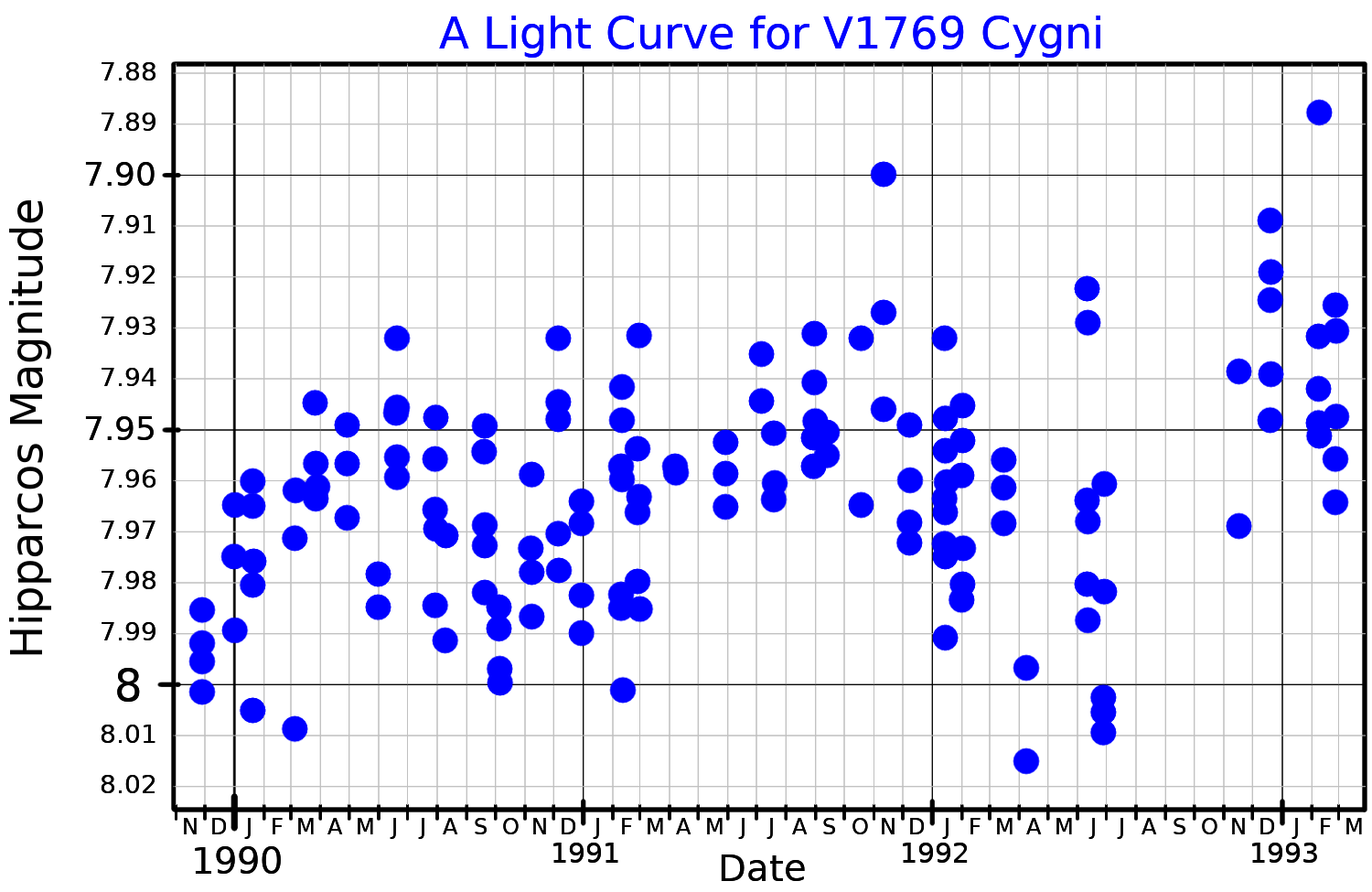 WR 134 is classified as an Algol type eclipsing variable and given the designation V1769 Cygni, but the variation is not strictly periodic and brightness changes occur on timescales of hours to days. It has been investigated several times to search for companions. Morel reported a 2.25 day primary period but considered the variations to be due to
WR 134 is classified as an Algol type eclipsing variable and given the designation V1769 Cygni, but the variation is not strictly periodic and brightness changes occur on timescales of hours to days. It has been investigated several times to search for companions. Morel reported a 2.25 day primary period but considered the variations to be due to
Wolf Rayet shells
WR134 and WR135
{{Stars of Cygnus Cygnus (constellation) Wolf–Rayet stars Cygni, V1769 Durchmusterung objects 191765 Algol variables 099377
variable
Variable may refer to:
* Variable (computer science), a symbolic name associated with a value and whose associated value may be changed
* Variable (mathematics), a symbol that represents a quantity in a mathematical expression, as used in many ...
Wolf-Rayet star located around 6,000 light years away from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
in the constellation of Cygnus, surrounded by a faint bubble nebula blown by the intense radiation and fast wind from the star. It is five times the radius of the sun, but due to a temperature over it is 400,000 times as luminous as the Sun.
WR 134 was one of three stars in Cygnus observed in 1867 to have unusual spectra consisting of intense emission line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identi ...
s rather than the more normal continuum and absorption lines. These were the first members of the class of stars that came to be called Wolf-Rayet stars (WR stars) after Charles Wolf and Georges Rayet
Georges-Antoine-Pons Rayet (12 December 1839 – 14 June 1906) was a French astronomer.
He was born in Bordeaux, France. He began working at the Paris Observatory in 1863. He worked on meteorology in addition to astronomy. He specialized ...
who discovered their unusual appearance. It is a member of the nitrogen sequence of WR stars, while the other two (WR 135
WR 135 is a variable Wolf-Rayet star located around 6,000 light years away from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus, surrounded by a faint bubble nebula blown by the intense radiation and fast wind from the star. It is just over four ti ...
and WR 137
WR 137 is a variable Wolf-Rayet star located around 6,000 light years away from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus.
WR 137, together with WR 134 and WR 135, was one of three stars in Cygnus observed in 1867 to have unusual spectra ...
) are both members of the carbon sequence that also have OB companions. WR 134 has a spectrum with NIII and NIV emission between two and five times stronger than NV, leading to the assignment of a WN6 spectral type. The spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors i ...
also shows strong HeII emission and weaker lines of HeI and CIV.
 WR 134 is classified as an Algol type eclipsing variable and given the designation V1769 Cygni, but the variation is not strictly periodic and brightness changes occur on timescales of hours to days. It has been investigated several times to search for companions. Morel reported a 2.25 day primary period but considered the variations to be due to
WR 134 is classified as an Algol type eclipsing variable and given the designation V1769 Cygni, but the variation is not strictly periodic and brightness changes occur on timescales of hours to days. It has been investigated several times to search for companions. Morel reported a 2.25 day primary period but considered the variations to be due to rotational modulation
This glossary of astronomy is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to astronomy and cosmology, their sub-disciplines, and related fields. Astronomy is concerned with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outsi ...
rather than the effects of a companion. Rustamov suggests a 1.887 day orbital period with a K-M dwarf companion, but with additional optical variations.
Both hard and soft X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s have been detected from WR 134 but the sources are not fully explained. The emissions do not match a single star of the expected temperature, are not sufficient for colliding winds between two hot stars, and any compact source such as a neutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. w ...
or cool dwarf would be in an unlikely orbit.
WR 134 is less than a degree away from WR 135 and the two are believed to lie at approximately the same distance from Earth within the Cygnus OB3 association. Both stars lie within a shell of hydrogen thought to have been swept up from the interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
when one or both stars were on the main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Her ...
. The shell is over forty parsecs wide and contains about of hydrogen. It is unclear which of the two stars is primarily responsible for creating the shell.
References
External links
*Wolf Rayet shells
WR134 and WR135
{{Stars of Cygnus Cygnus (constellation) Wolf–Rayet stars Cygni, V1769 Durchmusterung objects 191765 Algol variables 099377