W-53 warhead on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Mk/B53 was a high-yield
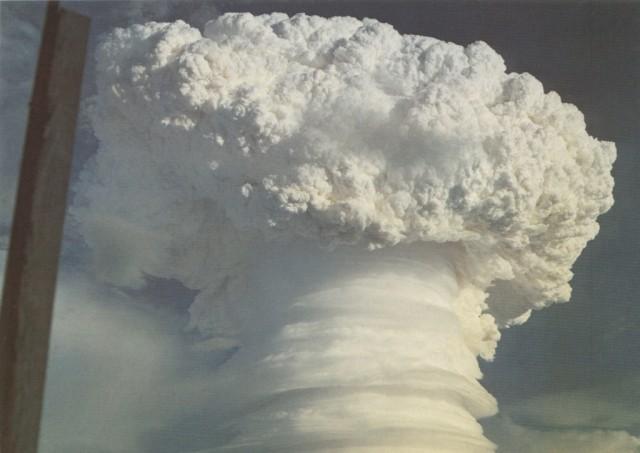 Development of the weapon began in 1955 by
Development of the weapon began in 1955 by
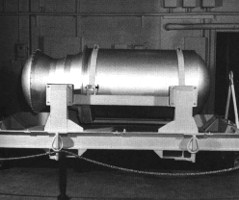
 The W-53 nuclear warhead of the
The W-53 nuclear warhead of the
 Assuming a detonation at optimum height, a 9 megaton blast would result in a fireball with an approximate diameter. The radiated heat would be sufficient to cause lethal burns to any unprotected person within a radius (). Blast effects would be sufficient to collapse most residential and industrial structures within a radius (); within () virtually all above-ground structures would be destroyed and blast effects would inflict near 100% fatalities. Within a 500 rem (5
Assuming a detonation at optimum height, a 9 megaton blast would result in a fireball with an approximate diameter. The radiated heat would be sufficient to cause lethal burns to any unprotected person within a radius (). Blast effects would be sufficient to collapse most residential and industrial structures within a radius (); within () virtually all above-ground structures would be destroyed and blast effects would inflict near 100% fatalities. Within a 500 rem (5
The B-53 (Mk-53) Bomb
{{United States nuclear devices Cold War aerial bombs of the United States Nuclear bombs of the United States Military equipment introduced in the 1960s 2011 disestablishments in the United States
bunker buster
A bunker buster is a type of munition that is designed to penetrate hardened targets or targets buried deep underground, such as military bunkers.
Armor piercing shells
Germany
Röchling shells were bunker-busting artillery shells, developed ...
thermonuclear weapon
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a low ...
developed by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
during the Cold War. Deployed on Strategic Air Command bombers, the B53, with a yield of 9 megatons, was the most powerful weapon in the U.S. nuclear arsenal after the last B41 nuclear bomb
The B-41 (also known as Mk-41) was a thermonuclear weapon deployed by the United States Strategic Air Command in the early 1960s. It was the most powerful nuclear bomb ever developed by the United States, with a maximum yield of . The B-41 was ...
s were retired in 1976.
The B53 was the basis of the W-53 warhead carried by the Titan II Missile
The Titan II was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company from the earlier Titan I missile. Titan II was originally designed and used as an ICBM, but was later adapted as a medium-lift space l ...
, which was decommissioned in 1987. Although not in active service for many years before 2010, fifty B53s were retained during that time as part of the "hedge" portion of the Enduring Stockpile until its complete dismantling in 2011. The last B53 was disassembled on 25 October 2011, a year ahead of schedule.
With its retirement, the largest bomb currently in service in the U.S. nuclear arsenal is the B83, with a maximum yield of 1.2 megatons. The B53 was replaced in the bunker-busting role by the B61 Mod 11.
History
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, ...
, based on the earlier Mk 21 and Mk 46 weapons. In March 1958 the Strategic Air Command issued a request for a new Class C (less than five tons, megaton-range) bomb to replace the earlier Mk 41. A revised version of the Mk 46 became the TX-53 in 1959. The development TX-53 warhead was apparently never tested, although an experimental TX-46 predecessor design was detonated 28 June 1958 as Hardtack
Hardtack (or hard tack) is a simple type of dense biscuit or cracker made from flour, water, and sometimes salt. Hardtack is inexpensive and long-lasting. It is used for sustenance in the absence of perishable foods, commonly during long sea voy ...
Oak, which detonated at a yield of 8.9 Megatons
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. The is a unit of energy defined by that convention to be , which is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a m ...
.
The Mk 53 entered production in 1962 and was built through June 1965. About 340 bombs were built. It entered service aboard B-47 Stratojet
The Boeing B-47 Stratojet (Boeing company designation Model 450) is a retired American long-range, six-engined, turbojet-powered strategic bomber designed to fly at high subsonic speed and at high altitude to avoid enemy interceptor aircraft. ...
, B-52G Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air ...
, and B-58 Hustler
The Convair B-58 Hustler, designed and produced by American aircraft manufacturer Convair, was the first operational bomber capable of Mach 2 flight.
The B-58 was developed during the 1950s for the United States Air Force (USAF) Strategic Air ...
bomber aircraft
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an airc ...
in the mid-1960s. From 1968 it was redesignated B53.
Some early versions of the bomb were dismantled beginning in 1967. After the Titan II program ended, the remaining W-53s were retired in the late 1980s. The B53 was retired in 1986, but in 1988 50 units were brought back into service and received the B53 Mod 1 safety upgrade so the air force could cover certain targets previously covered by Titan II. These weapons remained in the active stockpile until the deployment of the B61-11 in 1997. At that point the obsolete B53s were slated for immediate disassembly; however, the process of disassembling the units was greatly hampered by safety concerns as well as a lack of resources. In 2010 authorization was given to disassemble the 50 bombs at the Pantex plant in Texas. The process of dismantling the last remaining B53 bomb in the stockpile was completed in 2011.
Specifications
The B53 was long with a diameter of . It weighed , including the W53 warhead, the parachute system and the honeycomb aluminumnose cone
A nose cone is the conically shaped forwardmost section of a rocket, guided missile or aircraft, designed to modulate oncoming airflow behaviors and minimize aerodynamic drag. Nose cones are also designed for submerged watercraft such as ...
to enable the bomb to survive laydown delivery Laydown delivery is a mode of delivery found in some nuclear gravity bombs: the bomb's descent to the target is slowed by parachute so that it lands on the ground without detonating. The bomb then detonates by timer some time later. Laydown deliver ...
. It had five parachutes: one pilot chute
A pilot chute is a small auxiliary parachute used to deploy the main or reserve parachute. The pilot chute is connected by a bridle to the deployment bag containing the parachute. Pilot chutes are a critical component of all modern skydiving and B ...
, one extractor chute, and three main chutes. Chute deployment depends on delivery mode, with the main chutes used only for laydown delivery. For free-fall delivery, the entire system was jettisoned.
The W53 warhead of the B53 used oralloy
Enriched uranium is a type of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 (written 235U) has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (238U ...
(highly enriched uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
) instead of plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibi ...
for fission, with a mix of lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
-6 deuteride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of ...
fuel for fusion. The explosive lens
An explosive lens—as used, for example, in nuclear weapons—is a highly specialized shaped charge. In general, it is a device composed of several explosive charges. These charges are arranged and formed with the intent to control the shape ...
comprised a mixture of RDX
RDX (abbreviation of "Research Department eXplosive") or hexogen, among other names, is an organic compound with the formula (O2N2CH2)3. It is a white solid without smell or taste, widely used as an explosive. Chemically, it is classified as a ...
and TNT
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagen ...
, which was not insensitive. Two variants were made: the B53-Y1, a "dirty" weapon using a U-238-encased secondary, and the B53-Y2 "clean" version with a non-fissile (lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
or tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
) secondary casing. The explosive yield for the Y1 version was declassified in 2014 as being 9 Mt.
In 1988, some B53s were upgraded to the B53 Mod 1 (B53-1) variant to improve weapon safety and to provide compatibility with the G/H variants of the B52 bomber. During this upgrade the weapon lost full-fuzing capability, Retaining only the laydown fuzing mode. The B53-1 had a selectable laydown time of 30 to 240 seconds in 30 second increments.
Role
It was intended as abunker buster
A bunker buster is a type of munition that is designed to penetrate hardened targets or targets buried deep underground, such as military bunkers.
Armor piercing shells
Germany
Röchling shells were bunker-busting artillery shells, developed ...
weapon, using a surface blast after laydown deployment to transmit a shock wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
through the earth to collapse its target. Attacks against the Soviet deep underground leadership shelters in the Chekhov
Anton Pavlovich Chekhov (; 29 January 1860 Old Style date 17 January. – 15 July 1904 Old Style date 2 July.) was a Russian playwright and short-story writer who is considered to be one of the greatest writers of all time. His career ...
/ Sharapovo area south of Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
envisaged multiple B53/W53 exploding at ground level. It has since been supplanted in such roles by the earth-penetrating B61 Mod 11, a bomb that penetrates the surface to deliver much more of its explosive energy into the ground, and therefore needs a much smaller yield to produce the same effects.
The B53 was intended to be retired in the 1980s, but 50 units remained in the active stockpile until the deployment of the B61-11 in 1997. At that point the obsolete B53s were slated for immediate disassembly; however, the process of disassembling the units was greatly hampered by safety concerns as well as a lack of resources. The last remaining B53 bomb began the disassembly processes on Tuesday, 25 October 2011 at the Energy Department's Pantex Plant.
An April 2014 GAO
Gao , or Gawgaw/Kawkaw, is a city in Mali and the capital of the Gao Region. The city is located on the River Niger, east-southeast of Timbuktu on the left bank at the junction with the Tilemsi valley.
For much of its history Gao was an impor ...
report notes that the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) is retaining canned sub-assemblies (CSAs) "associated with a certain warhead indicated as excess in the 2012 Production and Planning Directive are being retained in an indeterminate state pending a senior-level government evaluation of their use in planetary defense against earthbound asteroids." In its FY2015 budget request, the NNSA noted that the B53 component disassembly was "delayed", leading some observers to conclude they might be the warhead CSAs being retained for potential planetary defense purposes.
W-53

 The W-53 nuclear warhead of the
The W-53 nuclear warhead of the Titan II
The Titan II was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company from the earlier Titan I missile. Titan II was originally designed and used as an ICBM, but was later adapted as a medium-lift space l ...
ICBM used the same physics package
Nuclear weapon designs are physical, chemical, and engineering arrangements that cause the physics package of a nuclear weapon to detonate. There are three existing basic design types:
* pure fission weapons, the simplest and least technically ...
as the B53, without the air drop-specific components like the parachute system and crushable structures in the nose and sides needed for lay-down delivery, reducing its mass to about . The Mark-6 re-entry vehicle containing the W53 warhead was about long, in diameter and was mounted atop a spacer which was in diameter at the missile interface (compared to the missile's core diameter of ). With a yield of 9 megatons
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. The is a unit of energy defined by that convention to be , which is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a m ...
, it was the highest yield warhead ever deployed on a US missile. About 65 W53 warheads were constructed between December 1962 and December 1963.
On 19 September 1980 a fuel leak caused a Titan II to explode
An explosion is a rapid expansion in volume associated with an extreme outward release of energy, usually with the generation of high temperatures and release of high-pressure gases. Supersonic explosions created by high explosives are known ...
within its silo in Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
, throwing the W53 warhead some distance away. Due to the safety measures built into the weapon, it did not explode or release any radioactive material
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transfe ...
. Fifty-two active missiles were deployed in silos prior to the beginning of the retirement program in October 1982.
Effects
 Assuming a detonation at optimum height, a 9 megaton blast would result in a fireball with an approximate diameter. The radiated heat would be sufficient to cause lethal burns to any unprotected person within a radius (). Blast effects would be sufficient to collapse most residential and industrial structures within a radius (); within () virtually all above-ground structures would be destroyed and blast effects would inflict near 100% fatalities. Within a 500 rem (5
Assuming a detonation at optimum height, a 9 megaton blast would result in a fireball with an approximate diameter. The radiated heat would be sufficient to cause lethal burns to any unprotected person within a radius (). Blast effects would be sufficient to collapse most residential and industrial structures within a radius (); within () virtually all above-ground structures would be destroyed and blast effects would inflict near 100% fatalities. Within a 500 rem (5 Sievert
The sievert (symbol: SvNot be confused with the sverdrup or the svedberg, two non-SI units that sometimes use the same symbol.) is a unit in the International System of Units (SI) intended to represent the stochastic health risk of ionizing rad ...
) dose of ionizing radiation would be received by the average person, sufficient to cause a 50% to 90% casualty rate independent of thermal or blast effects at this distance.
Artifacts
*B53 on display in the free introduction exhibit room at theAtomic Testing Museum
The National Atomic Testing Museum in Las Vegas, Nevada, documents the history of nuclear testing at the Nevada Test Site (NTS) in the Mojave Desert about 65 miles (105 km) northwest of Las Vegas. The museum operates as an affiliate of the Smithso ...
, Las Vegas, Nevada
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vega ...
*B53 on display at the Wings Over the Rockies Air and Space Museum at the former Lowry AFB
Lowry Air Force Base (Lowry Field in 1938–1948) is a former United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) training base during World War II and a United States Air Force (USAF) training base during the Cold War, serving as the initial 1955–1958 si ...
, Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
, Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
*B53 on display at the Grissom Air Museum at Grissom Air Reserve Base
Grissom Air Reserve Base is a United States Air Force base, located about north of Kokomo in Cass and Miami counties in Indiana. The facility was established as a U.S. Navy installation, Naval Air Station Bunker Hill, in 1942 and was an active ...
, the former Grissom AFB, in Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
*Mark 53 casing is on display in the Cold War Gallery at the National Museum of the United States Air Force
The National Museum of the United States Air Force (formerly the United States Air Force Museum) is the official museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, northeast of Dayton, Ohio. The NMUSAF is the ...
at Wright-Patterson AFB in Dayton, Ohio
Dayton () is the sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County. The 2020 U.S. census estimate put the city population at 137,644, while Greater D ...
*B53 casing in display yard of The National Museum of Nuclear Science & History, adjacent to Kirtland AFB
Kirtland Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in the southeast quadrant of the Albuquerque, New Mexico urban area, adjacent to the Albuquerque International Sunport. The base was named for the early Army aviator Col. Ro ...
in Albuquerque, New Mexico
*W-53 on display in the visitors center of the Titan Missile Museum
The Titan Missile Museum, also known as Air Force Facility Missile Site 8 or as Titan II ICBM Site 571-7, is a former ICBM ( intercontinental ballistic missile) site located about south of Tucson, Arizona in the United States. It was constructed ...
near Tucson, Arizona
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* *External links
The B-53 (Mk-53) Bomb
{{United States nuclear devices Cold War aerial bombs of the United States Nuclear bombs of the United States Military equipment introduced in the 1960s 2011 disestablishments in the United States