Victorian morality on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Victorian morality is a distillation of the
 Prostitution had been a factor in city life for centuries. The reformers started mobilizing in the late 1840s, major news organisations, clergymen, and single women became increasingly concerned about prostitution, which came to be known as "The Great Social Evil". Estimates of the number of prostitutes in London in the 1850s vary widely (in his landmark study, ''Prostitution'', William Acton reported that the police estimated there were 8,600 in London alone in 1857).
While the
Prostitution had been a factor in city life for centuries. The reformers started mobilizing in the late 1840s, major news organisations, clergymen, and single women became increasingly concerned about prostitution, which came to be known as "The Great Social Evil". Estimates of the number of prostitutes in London in the 1850s vary widely (in his landmark study, ''Prostitution'', William Acton reported that the police estimated there were 8,600 in London alone in 1857).
While the
 * Adams, James Eli, ed. ''Encyclopedia of the Victorian Era'' (4 vol. 2004). articles by scholars
* Bartley, Paula. ''Prostitution: Prevention and reform in England, 1860–1914'' (Routledge, 2012)
* Boddice, Rob. ''The Science of Sympathy: Morality, Evolution, and Victorian Civilization'' (2016)
* Briggs, Asa. ''The Age of Improvement, 1783–1867'' (1959).
* Churchill, David. ''Crime control and everyday life in the Victorian city: the police and the public'' (2017).
* Churchill, David C. "Rethinking the state monopolisation thesis: the historiography of policing and criminal justice in nineteenth-century England." ''Crime, Histoire & Sociétés/Crime, History & Societies'' 18.1 (2014): 131–152.
* Adams, James Eli, ed. ''Encyclopedia of the Victorian Era'' (4 vol. 2004). articles by scholars
* Bartley, Paula. ''Prostitution: Prevention and reform in England, 1860–1914'' (Routledge, 2012)
* Boddice, Rob. ''The Science of Sympathy: Morality, Evolution, and Victorian Civilization'' (2016)
* Briggs, Asa. ''The Age of Improvement, 1783–1867'' (1959).
* Churchill, David. ''Crime control and everyday life in the Victorian city: the police and the public'' (2017).
* Churchill, David C. "Rethinking the state monopolisation thesis: the historiography of policing and criminal justice in nineteenth-century England." ''Crime, Histoire & Sociétés/Crime, History & Societies'' 18.1 (2014): 131–152.
online
* Emsley, Clive.''Crime and Society in England, 1750–1900'' (5th ed. 2018) * Fraser, Derek. ''The evolution of the British welfare state: a history of social policy since the Industrial Revolution'' (Springer, 1973). * Gay, Peter. ''The Bourgeois Experience: Victoria to Freud'' * Harrison, Brian. "Philanthropy and the Victorians" ''Victorian Studies'' 9#4 (1955) 353-37
online
*Merriman, J (2004). ''A History of Modern Europe; From the French Revolution to the Present'' New York, London: W.W. Norton & Company. * Perkin, Harold.
The Origins of Modern English Society: 1780-1880
' (1969) * Searle, G. R. ''Morality and the Market in Victorian Britain'' (1998) * Woodward, E. L.
The Age of Reform, 1815–1870
' (1938); 692 pages; wide-ranging scholarly survey {{Queen Victoria, state=collapsed Morality Social philosophy Victorian culture
moral
A moral (from Latin ''morālis'') is a message that is conveyed or a lesson to be learned from a story or event. The moral may be left to the hearer, reader, or viewer to determine for themselves, or may be explicitly encapsulated in a maxim. ...
views of the middle class in 19th-century Britain, the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwa ...
.
Victorian values emerged in all classes and reached all facets of Victorian living. The values of the period—which can be classed as religion, morality, Evangelicalism
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual expe ...
, industrial work ethic, and personal improvement—took root in Victorian morality. Current plays and all literature—including old classics like Shakespeare—were cleansed of content considered to be inappropriate for children, or "bowdlerized
Expurgation, also known as bowdlerization, is a form of censorship that involves purging anything deemed noxious or offensive from an artistic work or other type of writing or media.
The term ''bowdlerization'' is a pejorative term for the practi ...
".
Contemporary historians have generally come to regard the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwa ...
as a time of many conflicts, such as the widespread cultivation of an outward appearance of dignity and restraint, together with serious debates about exactly how the new morality should be implemented. The international slave trade was abolished, and this ban was enforced by the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
. Slavery was ended in all the British colonies, child labour was ended in British factories, and a long debate ensued regarding whether prostitution
Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in Sex work, sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, n ...
should be totally abolished or tightly regulated. Homosexuality
Homosexuality is Romance (love), romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or Human sexual activity, sexual behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romant ...
remained illegal.
Slavery
Opposition to slavery was the main evangelical cause from the late 18th century, led byWilliam Wilberforce
William Wilberforce (24 August 175929 July 1833) was a British politician, philanthropist and leader of the movement to abolish the slave trade. A native of Kingston upon Hull, Yorkshire, he began his political career in 1780, eventually becom ...
(1759–1833). The cause organized very thoroughly, and developed propaganda campaigns that made readers cringe at the horrors of slavery. The same moral fervor and organizational skills carried over into most of the other reform movements. Victoria ascended to the throne in 1837, only four years after the abolition of slavery
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
throughout the British Empire. The anti-slavery
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
movement had campaigned for years to achieve the ban, succeeding with a partial abolition in 1807 and the full ban on slave trading, but not slave ownership, which only happened in 1833. It took so long because the anti-slavery morality was pitted against powerful economic interests which claimed their businesses would be destroyed if they were not permitted to exploit slave labour. Eventually, plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
owners in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
received £20 million in cash compensation, which reflected the average market price of slaves. William E. Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and Liberal politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, spread over four non-conse ...
, later a famous reformer, handled the large payments to his father for their hundreds of slaves. The Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
patrolled the Atlantic Ocean, stopping any ships that it suspected of trading African slaves to the Americas and freeing any slaves found. The British had set up a Crown Colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Council ...
in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali ...
—Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ...
—and transported freed slaves there. Freed slaves from Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
founded and named the capital of Sierra Leone "Freetown
Freetown is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educ ...
".
Abolishing cruelty
Cruelty to animals
William Wilberforce
William Wilberforce (24 August 175929 July 1833) was a British politician, philanthropist and leader of the movement to abolish the slave trade. A native of Kingston upon Hull, Yorkshire, he began his political career in 1780, eventually becom ...
, Thomas Fowell Buxton
Sir Thomas Fowell Buxton, 1st Baronet (1 April 1786Olwyn Mary Blouet, "Buxton, Sir Thomas Fowell, first baronet (1786–1845)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online ed., May 201accessed 25 April 20 ...
and Richard Martin introduced the first legislation to prevent cruelty to animals, the Cruel Treatment of Cattle Act 1822
The Cruel Treatment of Cattle Act 1822 (3 Geo. IV c. 71) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom with the long title "An Act to prevent the cruel and improper Treatment of Cattle"; it is sometimes known as Martin's Act, after the MP an ...
; it pertained only to cattle and it passed easily in 1822.
In the Metropolitan Police Act 1839
The Metropolitan Police Act 1839 (2 & 3 Vict c 47) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The Act enlarged the district of, and gave greatly increased powers to the Metropolitan Police established by the Metropolitan Police Act 1829. ...
, "fighting or baiting Lions, Bears, Badgers, Cocks, Dogs, or other Animals" was made a criminal offence. The law laid numerous restrictions on how, when, and where animals could be used. It prohibited owners from letting mad dogs run loose and gave police the right to destroy any dog suspected of being rabid
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. Early symptoms can include fever and tingling at the site of exposure. These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, ...
. It prohibited the use of dogs for drawing carts. The law was extended to the rest of England and Wales in 1854. Dog-pulled carts were often used by very poor self-employed men as a cheap means to deliver milk, human foods, animal foods (the cat's-meat man), and for collecting refuse (the rag-and-bone man
A rag-and-bone man or ragpicker (UK English) or ragman, old-clothesman, junkman, or junk dealer (US English), also called a bone-grubber, bone-picker, chiffonnier, rag-gatherer, bag board, or totter, collects unwanted household items and sells t ...
). The dogs were susceptible to rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. Early symptoms can include fever and tingling at the site of exposure. These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, ...
; cases of the disease among humans had been on the rise. They also bothered the horses, which were economically much more vital to the city. Evangelicals and utilitarians in the Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals persuaded Parliament it was cruel and should be illegal; the Utilitarian element added government inspectors to provide enforcement. The owners had no more use for their dogs, and killed them.. Chapter: 'A Left-handed Blow: Writing the History of Animals' by Erica Fudge Cart dogs were replaced by people with handcarts.
Historian Harold Perkin
Harold James Perkin (11 November 1926 – 16 October 2004) was a distinguished English social historian who was the founder of the ''Social History Society'' in 1976.
Background
Perkin was born in Hanley, Staffordshire of humble origins. He a ...
writes:
Child labour
Evangelical religious forces took the lead in identifying the evils of child labour, and legislating against them. Their anger at the contradiction between the conditions on the ground for children of the poor and the middle-class notion of childhood as a time of innocence led to the first campaigns for the imposition of legal protection for children. Reformers attacked child labor from the 1830s onward. The campaign that led to theFactory Acts
The Factory Acts were a series of acts passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom to regulate the conditions of industrial employment.
The early Acts concentrated on regulating the hours of work and moral welfare of young children employed ...
was spearheaded by rich philanthropists of the era, especially Lord Shaftesbury
Earl of Shaftesbury is a title in the Peerage of England. It was created in 1672 for Anthony Ashley-Cooper, 1st Baron Ashley, a prominent politician in the Cabal then dominating the policies of King Charles II. He had already succeeded his fa ...
, who introduced bills in Parliament to mitigate the exploitation of children at the workplace. In 1833 he introduced the Ten Hours Act 1833, which provided that children working in the cotton and woollen mills must be aged nine or above; no person under the age of eighteen was to work more than ten hours a day or eight hours on a Saturday; and no one under twenty-five was to work nights. The Factory Act of 1844 said children 9–13 years could work for at most 9 hours a day with a lunch break. Additional legal interventions throughout the century increased the level of childhood protection, despite the resistance from the laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( ; from french: laissez faire , ) is an economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies) deriving from special interest groups ...
attitudes against government interference by factory owners. Parliament respected laissez-faire in the case of adult men, and there was minimal interference in the Victorian era.
Unemployed street children suffered too, as novelist Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian er ...
revealed to a large middle class audience the horrors of London street life.
Sexuality
HistoriansPeter Gay
Peter Joachim Gay (né Fröhlich; June 20, 1923 – May 12, 2015) was a German-American historian, educator, and author. He was a Sterling Professor of History at Yale University and former director of the New York Public Library's Center for Sc ...
and Michael Mason both point out that modern society often confuses Victorian etiquette for a lack of knowledge. For example, people going for a bath in the sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
or at the beach
A beach is a landform alongside a body of water which consists of loose particles. The particles composing a beach are typically made from rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles, etc., or biological sources, such as mollusc s ...
would use a bathing machine. Despite the use of the bathing machine, it was still possible to see people bathing nude. Contrary to popular conception, however, Victorian society recognised that both men and women enjoyed copulation.
Verbal or written communication of sexual feeling
"Sexual Feeling" is a 1990 single by American singer La Toya Jackson.
Song information
The song was recorded in Milan, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Eur ...
s was also often proscribed so people instead used the language of flowers
Floriography (language of flowers) is a means of cryptological communication through the use or arrangement of flowers. Meaning has been attributed to flowers for thousands of years, and some form of floriography has been practiced in tradition ...
. However, they also wrote explicit erotica
Erotica is literature or art that deals substantively with subject matter that is erotic, sexually stimulating or sexually arousing. Some critics regard pornography as a type of erotica, but many consider it to be different. Erotic art may use ...
, perhaps the most famous being the racy tell-all '' My Secret Life'' by the pseudonym Walter (allegedly Henry Spencer Ashbee
Henry Spencer Ashbee (21 April 1834 – 29 July 1900)(Walter) was a book collector, writer, and bibliographer. He is notable for his massive, clandestine three-volume bibliography of erotic literature published under the pseudonym of Pisanus Frax ...
), and the magazine '' The Pearl'', which was published for several years and reprinted as a paperback book in the 1960s. Victorian erotica
Victorian erotica is a genre of sexual art and literature which emerged in the Victorian era of 19th-century Britain. Victorian erotica emerged as a product of a Victorian sexual culture. The Victorian era was characterized by paradox of rigid mora ...
also survives in private letters archived in museums and even in a study of women's orgasms. Some current historians now believe that the myth of Victorian repression can be traced back to early twentieth-century views, such as those of Lytton Strachey
Giles Lytton Strachey (; 1 March 1880 – 21 January 1932) was an English writer and critic. A founding member of the Bloomsbury Group and author of '' Eminent Victorians'', he established a new form of biography in which psychological insight ...
, a homosexual member of the Bloomsbury Group
The Bloomsbury Group—or Bloomsbury Set—was a group of associated English writers, intellectuals, philosophers and artists in the first half of the 20th century, including Virginia Woolf, John Maynard Keynes, E. M. Forster and Lytton St ...
, who wrote ''Eminent Victorians
''Eminent Victorians'' is a book by Lytton Strachey (one of the older members of the Bloomsbury Group), first published in 1918, and consisting of biographies of four leading figures from the Victorian era. Its fame rests on the irreverence and w ...
''.
Homosexuality
The enormous expansion of police forces, especially in London, produced a sharp rise in prosecutions for illegal sodomy at midcentury. Male sexuality became a favorite subject of study especially by medical researchers whose case studies explored the progression and symptoms of institutionalized subjects.Henry Maudsley
Henry Maudsley FRCP (5 February 183523 January 1918) was a pioneering English psychiatrist, commemorated in the Maudsley Hospital in London and in the annual Maudsley Lecture of the Royal College of Psychiatrists.
Life and career
Maudsley wa ...
shaped late Victorian views about aberrant sexuality. George Savage and Charles Arthur Mercier
Charles Arthur Mercier (21 June 1851 – 2 September 1919) was a British psychiatrist and leading expert on forensic psychiatry and insanity.Charles Arthur Mercier, M.D.Lond., F.R.C.P., F.R.C.S., Consulting Physician For Mental Diseases, Charin ...
wrote about homosexuals living in society. Daniel Hack Tuke's ''Dictionary of Psychological Medicine'' covered sexual perversion. All these works show awareness of continental insights, as well as moral disdain for the sexual practices described.
Simeon Solomon
Simeon Solomon (9 October 1840 – 14 August 1905) was a British painter associated with the Pre-Raphaelites who was noted for his depictions of Jewish life and same-sex desire. His career was cut short as a result of public scandal following hi ...
and poet Algernon Charles Swinburne
Algernon Charles Swinburne (5 April 1837 – 10 April 1909) was an English poet, playwright, novelist, and critic. He wrote several novels and collections of poetry such as '' Poems and Ballads'', and contributed to the famous Eleventh Edition ...
, as they contemplated their own sexual identities in the 1860s, fastened on the Greek lesbian poet Sappho
Sappho (; el, Σαπφώ ''Sapphō'' ; Aeolic Greek ''Psápphō''; c. 630 – c. 570 BC) was an Archaic Greek poet from Eresos or Mytilene on the island of Lesbos. Sappho is known for her Greek lyric, lyric poetry, written to be sung while ...
. They made Victorian intellectuals aware of Sappho, and their writings helped to shape the modern image of lesbianism.
The Labouchere Amendment
Section 11 of the Criminal Law Amendment Act 1885, commonly known as the Labouchere Amendment, made "gross indecency" a crime in the United Kingdom. In practice, the law was used broadly to prosecute male homosexuals where actual sodomy (meaning, ...
to the Criminal Law Amendment Act 1885
The Criminal Law Amendment Act 1885 ( 48 & 49 Vict. c.69), or "An Act to make further provision for the Protection of Women and Girls, the suppression of brothels, and other purposes," was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, the lat ...
, for the first time, made all male homosexual acts illegal. It provided for two years' imprisonment for males convicted of committing, or being a party to public or private acts of homosexuality. Lesbian acts—still scarcely known—were ignored. When Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish poet and playwright. After writing in different forms throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular playwrights in London in the early 1890s. He is ...
was convicted of violating the statute, and imprisoned for such violations, in 1895, he became the iconic victim of English puritanical repression.
Prostitution
 Prostitution had been a factor in city life for centuries. The reformers started mobilizing in the late 1840s, major news organisations, clergymen, and single women became increasingly concerned about prostitution, which came to be known as "The Great Social Evil". Estimates of the number of prostitutes in London in the 1850s vary widely (in his landmark study, ''Prostitution'', William Acton reported that the police estimated there were 8,600 in London alone in 1857).
While the
Prostitution had been a factor in city life for centuries. The reformers started mobilizing in the late 1840s, major news organisations, clergymen, and single women became increasingly concerned about prostitution, which came to be known as "The Great Social Evil". Estimates of the number of prostitutes in London in the 1850s vary widely (in his landmark study, ''Prostitution'', William Acton reported that the police estimated there were 8,600 in London alone in 1857).
While the Magdalene asylum
Magdalene asylums, also known as Magdalene laundries, were initially Protestant but later mostly Roman Catholic institutions that operated from the 18th to the late 20th centuries, ostensibly to house "fallen women". The term referred to femal ...
s had been reforming prostitutes since the mid-18th century, the years between 1848 and 1870 saw a veritable explosion in the number of institutions working to "reclaim" these "fallen women" from the streets and retrain them for entry into respectable society—usually for work as domestic servants. The theme of prostitution and the "fallen woman" (any woman who has had sexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse (or coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion and thrusting of the penis into the vagina for sexual pleasure or reproduction.Sexual intercourse most commonly means penile–vaginal pene ...
out of marriage) became a staple feature of mid-Victorian literature
Victorian literature refers to English literature during the reign of Queen Victoria (1837–1901). The 19th century is considered by some to be the Golden Age of English Literature, especially for British novels. It was in the Victorian era tha ...
and politics. In the writings of Henry Mayhew
Henry Mayhew (25 November 1812 – 25 July 1887) was an English journalist, playwright, and advocate of reform. He was one of the co-founders of the satirical magazine ''Punch'' in 1841, and was the magazine's joint editor, with Mark Lemon, in ...
, Charles Booth, Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian er ...
and others, prostitution began to be seen as a social problem
A social issue is a problem that affects many people within a society. It is a group of common problems in present-day society and ones that many people strive to solve. It is often the consequence of factors extending beyond an individual's cont ...
.
When Parliament passed the first of the Contagious Diseases Acts
The Contagious Diseases Acts (CD Acts) were originally passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom in 1864 (27 & 28 Vict. c. 85), with alterations and additions made in 1866 (29 & 30 Vict. c. 35) and 1869 (32 & 33 Vict. c. 96). In 1862, a com ...
(CD) in 1864 (which allowed the local constabulary in certain defined areas to force any woman suspected of venereal disease
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and ora ...
to submit to its inspection), Josephine Butler
Josephine Elizabeth Butler (' Grey; 13 April 1828 – 30 December 1906) was an English feminist and social reformer in the Victorian era. She campaigned for women's suffrage, the right of women to better education, the end of coverture ...
's crusade to repeal the CD Acts yoked the anti-prostitution cause with the emergent feminist movement
The feminist movement (also known as the women's movement, or feminism) refers to a series of social movements and political campaigns for radical and liberal reforms on women's issues created by the inequality between men and women. Such ...
. Butler attacked the long-established double standard
A double standard is the application of different sets of principles for situations that are, in principle, the same. It is often used to describe treatment whereby one group is given more latitude than another. A double standard arises when two ...
of sexual morality
Sexual ethics (also known as sex ethics or sexual morality) is a branch of philosophy that considers the ethics or morality or otherwise in sexual behavior. Sexual ethics seeks to understand, evaluate and critique interpersonal relationships and ...
.
Prostitutes were often presented as victims in sentimental literature such as Thomas Hood
Thomas Hood (23 May 1799 – 3 May 1845) was an English poet, author and humorist, best known for poems such as " The Bridge of Sighs" and " The Song of the Shirt". Hood wrote regularly for ''The London Magazine'', '' Athenaeum'', and ''Punch' ...
's poem '' The Bridge of Sighs'', Elizabeth Gaskell
Elizabeth Cleghorn Gaskell (''née'' Stevenson; 29 September 1810 – 12 November 1865), often referred to as Mrs Gaskell, was an English novelist, biographer and short story writer. Her novels offer a detailed portrait of the lives of many st ...
's novel '' Mary Barton'', and Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian er ...
' novel ''Oliver Twist
''Oliver Twist; or, The Parish Boy's Progress'', Charles Dickens's second novel, was published as a serial from 1837 to 1839, and as a three-volume book in 1838. Born in a workhouse, the orphan Oliver Twist is bound into apprenticeship with ...
''. The emphasis on the purity of women found in such works as Coventry Patmore
Coventry Kersey Dighton Patmore (23 July 1823 – 26 November 1896) was an English poet and literary critic. He is best known for his book of poetry ''The Angel in the House'', a narrative poem about the Victorian ideal of a happy marriage.
As ...
's ''The Angel in the House
''The Angel in the House'' is a narrative poem by Coventry Patmore, first published in 1854 and expanded until 1862. Although largely ignored upon publication, it became enormously popular in the United States during the later 19th century and ...
'' led to the portrayal of the prostitute and fallen woman as soiled, corrupted, and in need of cleansing.
This emphasis on female purity was allied to the stress on the homemaking role of women, who helped to create a space free from the pollution and corruption of the city. In this respect, the prostitute came to have symbolic significance as the embodiment of the violation of that divide. The double standard remained in force. The Matrimonial Causes Act 1857
The Matrimonial Causes Act 1857 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The Act reformed the law on divorce, moving litigation from the jurisdiction of the ecclesiastical courts to the civil courts, establishing a model of marriage ...
allowed for a man to divorce his wife for adultery, but a woman could only divorce for adultery combined with other offences such as incest, cruelty, bigamy
In cultures where monogamy is mandated, bigamy is the act of entering into a marriage with one person while still legally married to another. A legal or de facto separation of the couple does not alter their marital status as married persons. ...
, desertion, etc., or based on cruelty alone.
The anonymity of the city led to a large increase in prostitution and unsanctioned sexual relationships. Dickens and other writers associated prostitution with the mechanisation and industrialisation of modern life, portraying prostitutes as human commodities consumed and thrown away like refuse when they were used up. Moral reform movements attempted to close down brothels, something that has sometimes been argued to have been a factor in the concentration of street-prostitution.
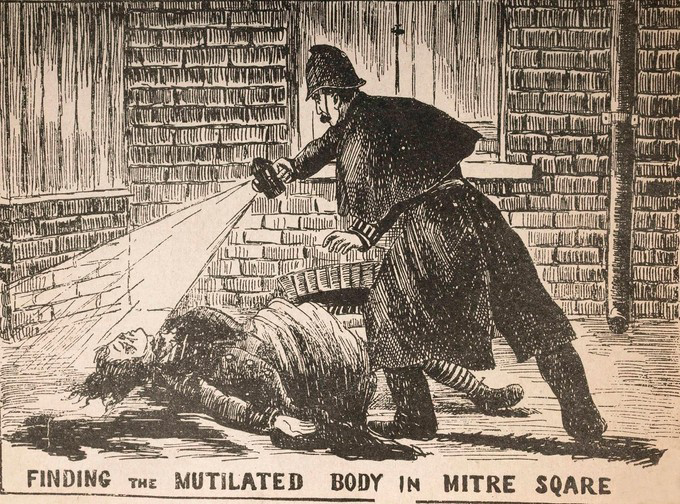
The extent of prostitution in London in the 1880s gained national and global prominence through the highly publicised murders attributed to Whitechapel-based serial killer Jack the Ripper
Jack the Ripper was an unidentified serial killer active in and around the impoverished Whitechapel district of London, England, in the autumn of 1888. In both criminal case files and the contemporaneous journalistic accounts, the killer w ...
, whose victims were exclusively prostitutes living destitute in the East End
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have uni ...
. Given that many prostitutes were living in poverty as late as the 1880s and 1890s, offering sex services was a source of desperate necessity to fund their meals and temporary lodging accommodation from the cold, and as a result prostitutes represented easy prey for criminals as they could do little to personally protect themselves from harm.
Crime and police
After 1815, there was widespread fear of growing crimes, burglaries, mob action, and threats of large-scale disorder. Crime had been handled on an ad-hoc basis by poorly organized local parish constables and private watchmen, supported by very stiff penalties, including hundreds of causes for execution or deportation to Australia. London, with 1.5 million people—more than the next 15 cities combined—over the decades had worked out informal arrangements to develop a uniform policing system in its many boroughs. The Metropolitan Police Act 1829, championed by Home SecretaryRobert Peel
Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet, (5 February 1788 – 2 July 1850) was a British Conservative statesman who served twice as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (1834–1835 and 1841–1846) simultaneously serving as Chancellor of the Excheque ...
, was not so much a startling innovation, as a systemization with expanded funding of established informal practices. It created the Metropolitan Police Service
The Metropolitan Police Service (MPS), formerly and still commonly known as the Metropolitan Police (and informally as the Met Police, the Met, Scotland Yard, or the Yard), is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement and ...
, headquartered at Scotland Yard
Scotland Yard (officially New Scotland Yard) is the headquarters of the Metropolitan Police, the territorial police force responsible for policing Greater London's 32 boroughs, but not the City of London, the square mile that forms London's ...
. London now had the world's first modern police force. The 3000 policemen were called "bobbies" (after Peel's first name). They were well-organized, centrally directed, and wore standard blue uniforms. Legally they had the historic status of constable, with authority to make arrests of suspicious persons and book offenders before a magistrate court. They were assigned in teams to specified beats, especially at night. Gas lighting was installed on major streets, making their task of surveillance much easier. Crime rates went down. An 1835 law required all incorporated boroughs in England and Wales to establish police forces. Scotland, with its separate legal system, was soon added. By 1857 every jurisdiction in Great Britain had an organized police force, for which the Treasury paid a subsidy. The police had steady pay, were selected by merit rather than by political influence, and were rarely used for partisan purposes. The pay scale was not high (one guinea a week in 1833), but the prestige was especially high for Irish Catholics, who were disproportionately represented in every city where they had a large presence.
Causation
Intellectual historians searching for causes of the new morality often point to the ideas byHannah More
Hannah More (2 February 1745 – 7 September 1833) was an English religious writer, philanthropist, poet and playwright in the circle of Johnson, Reynolds and Garrick, who wrote on moral and religious subjects. Born in Bristol, she taught at a ...
, William Wilberforce
William Wilberforce (24 August 175929 July 1833) was a British politician, philanthropist and leader of the movement to abolish the slave trade. A native of Kingston upon Hull, Yorkshire, he began his political career in 1780, eventually becom ...
, and the Clapham Sect
The Clapham Sect, or Clapham Saints, were a group of social reformers associated with Clapham in the period from the 1780s to the 1840s. Despite the label "sect", most members remained in the established (and dominant) Church of England, which ...
. Perkin argues this exaggerates the influence of a small group of individuals, who were "as much an effect of the revolution as a cause." It also has a timing problem, for many predecessors had failed. The intellectual approach tends to minimize the importance of Nonconformists and Evangelicals—the Methodists, for example, played a powerful role among the upper tier of the working class. Finally, it misses a key ingredient: instead of trying to improve an old society, the reformers were trying to lead Britain into a new society of the future.
Victorian era movements for justice, freedom, and other strong moral values made greed, and exploitation into public evils. The writings of Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian er ...
, in particular, observed and recorded these conditions.
Peter Shapely examined 100 charity leaders in Victorian Manchester. They brought significant cultural capital, such as wealth, education and social standing. Besides the actual reforms for the city they achieved for themselves a form of symbolic capital, a legitimate form of social domination and civic leadership. The utility of charity as a means of boosting one's social leadership was socially determined and would take a person only so far.
The Marxist
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialecti ...
intellectual Walter Benjamin
Walter Bendix Schönflies Benjamin (; ; 15 July 1892 – 26 September 1940) was a German Jewish philosopher, cultural critic and essayist.
An eclectic thinker, combining elements of German idealism, Romanticism, Western Marxism, and Jewish ...
connected Victorian morality to the rise of the bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. Th ...
. Benjamin alleged that the shopping culture of the petite bourgeoisie
''Petite bourgeoisie'' (, literally 'small bourgeoisie'; also anglicised as petty bourgeoisie) is a French term that refers to a social class composed of semi-autonomous peasants and small-scale merchants whose politico-economic ideological st ...
established the sitting room as the centre of personal and family life; as such, the English bourgeois culture is a ''sitting-room culture'' of prestige
Prestige refers to a good reputation or high esteem; in earlier usage, ''prestige'' meant "showiness". (19th c.)
Prestige may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Films
* ''Prestige'' (film), a 1932 American film directed by Tay Garnet ...
through conspicuous consumption
In sociology and in economics, the term conspicuous consumption describes and explains the consumer practice of buying and using goods of a higher quality, price, or in greater quantity than practical. In 1899, the sociologist Thorstein Veblen c ...
. This acquisition of prestige is then reinforced by the repression of emotion and of sexual desire, and by the construction of a regulated social-space where propriety
Etiquette () is the set of norms of personal behaviour in polite society, usually occurring in the form of an ethical code of the expected and accepted social behaviours that accord with the conventions and norms observed and practised by a ...
is the key personality trait desired in men and women.Walter Benjamin
Walter Bendix Schönflies Benjamin (; ; 15 July 1892 – 26 September 1940) was a German Jewish philosopher, cultural critic and essayist.
An eclectic thinker, combining elements of German idealism, Romanticism, Western Marxism, and Jewish ...
, ''The Halles Project''.
Demystifying
It seems necessary to clarify that the sense of moral exceptionality shared by Victorians did not come into being the moment that Queen Victoria took to the throne. Before the Victorian Era, there had already been some foundation — built upon decades and centuries of evolving ideologies and discourses — for a Victorian culture of dignity, restraint, and moral goodness to emerge. Moreover, just as the Victorians were not the sole originators of the social rules that governed their society and political climate, they were also not beholden to them to the same rigid degree as the modern-day person may think. That is to say, practices on the ground associated with the Victorian Era morality — a gendered public and private binary, for example — did not always align with abstract ideals found in contemporary documents and literature. In '' The History of Sexuality'' philosopher Michel Foucault rejects the notion that power relationships emanate from a single source or have any solid foundation capable of imparting legitimacy. He writes that the viewpoint from which one understands power “must not be sought in the primary existence of a central point, in a unique source of sovereignty from which secondary and descendent forms would emanate” that, rather, power is “the moving substrate of force relations…hat is
A hat is a head covering which is worn for various reasons, including protection against weather conditions, ceremonial reasons such as university graduation, religious reasons, safety, or as a fashion accessory. Hats which incorporate mecha ...
always local and unstable.” Foucault forces a reimagining of power that requires a rejection of normative narratives and blanket analyses of historical eras and entreats us to destabilize entrenched understandings. The established concept of “Victorian morality” seems vulnerable to such a treatment.
References
Further reading
 * Adams, James Eli, ed. ''Encyclopedia of the Victorian Era'' (4 vol. 2004). articles by scholars
* Bartley, Paula. ''Prostitution: Prevention and reform in England, 1860–1914'' (Routledge, 2012)
* Boddice, Rob. ''The Science of Sympathy: Morality, Evolution, and Victorian Civilization'' (2016)
* Briggs, Asa. ''The Age of Improvement, 1783–1867'' (1959).
* Churchill, David. ''Crime control and everyday life in the Victorian city: the police and the public'' (2017).
* Churchill, David C. "Rethinking the state monopolisation thesis: the historiography of policing and criminal justice in nineteenth-century England." ''Crime, Histoire & Sociétés/Crime, History & Societies'' 18.1 (2014): 131–152.
* Adams, James Eli, ed. ''Encyclopedia of the Victorian Era'' (4 vol. 2004). articles by scholars
* Bartley, Paula. ''Prostitution: Prevention and reform in England, 1860–1914'' (Routledge, 2012)
* Boddice, Rob. ''The Science of Sympathy: Morality, Evolution, and Victorian Civilization'' (2016)
* Briggs, Asa. ''The Age of Improvement, 1783–1867'' (1959).
* Churchill, David. ''Crime control and everyday life in the Victorian city: the police and the public'' (2017).
* Churchill, David C. "Rethinking the state monopolisation thesis: the historiography of policing and criminal justice in nineteenth-century England." ''Crime, Histoire & Sociétés/Crime, History & Societies'' 18.1 (2014): 131–152.online
* Emsley, Clive.''Crime and Society in England, 1750–1900'' (5th ed. 2018) * Fraser, Derek. ''The evolution of the British welfare state: a history of social policy since the Industrial Revolution'' (Springer, 1973). * Gay, Peter. ''The Bourgeois Experience: Victoria to Freud'' * Harrison, Brian. "Philanthropy and the Victorians" ''Victorian Studies'' 9#4 (1955) 353-37
online
*Merriman, J (2004). ''A History of Modern Europe; From the French Revolution to the Present'' New York, London: W.W. Norton & Company. * Perkin, Harold.
The Origins of Modern English Society: 1780-1880
' (1969) * Searle, G. R. ''Morality and the Market in Victorian Britain'' (1998) * Woodward, E. L.
The Age of Reform, 1815–1870
' (1938); 692 pages; wide-ranging scholarly survey {{Queen Victoria, state=collapsed Morality Social philosophy Victorian culture